1. Introduction
According to a broad definition, the artificial intelligence (AI) is a machine or computing platform that is capable of making intelligent decision in a similar way to the human mind [
1]. In healthcare, AI could improve prognosis, diagnosis, treatment and clinical workflow, particularly in the field of radiology, cardiovascular and pathology [
1,
2]. Many of these medical tasks have been widely adopted in everyday clinical practice [
1]. During the last pandemic, significant progress was made in the development of AI leading to more than 900 articles on COVID-19 and artificial intelligence [
3]. Although the presence of a physician is still essential, AI could assist the clinical team to provide the best possible care.
During 2020, up to 30% of radiologic screening were managed by AI and with almost 20% planned for the following year [
4]. A recent survey found that radiologists would like to see AI improve anatomical measurements, lesion detection and the quality of radiological imaging [
4]. In particular, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a rather heterogeneous syndrome characterized by an inflammatory lung edema leading to an increased lung weight, decreased lung aeration with the presence of alveolar collapse and interstitial opacities mainly in the dependent area [
5]. Lung imaging is an essential tool to assess not only the morphology but also the mechanical characteristics of ARDS patients. Chest computed tomography (CT) and lung ultrasound (LUS) have a higher sensitivity and specificity than conventional chest radiography.
2. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms and models that allow computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. These algorithms rely on manually engineered features. Developers write explicit instructions for the computer to follow. In ML, however, the computer learns patterns and relationships from data to make informed decisions or predictions. The primary goal of ML is to enable computers to improve their performance on a task over time by learning from examples rather than being explicitly programmed. ML algorithms are basically designed to classify objects, detect patterns, predict outcomes and make informed decisions [
6].
Differently, deep learning (DL) is a subfield of ML that focuses on training artificial neural networks with multiple layers (deep architectures) to learn complex patterns from data. In DL, models are based on deep artificial neural networks that can learn directly from data features without the need for manual extraction. These neural networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, where information is processed through interconnected neurons. The term "deep" in DL refers to the depth of the neural network, which consists of multiple hidden layers between the input and output layers. DL tends to work best with large datasets, as it requires a large amount of data to successfully train deep neural networks. Certain neural network architectures such as the so-called convolutional neural networks (CNN) are used specifically for image recognition. The possible applications of DL using CT lung and ultrasound may range from the early diagnosis, detection and segmentation of particular lung regions to the prediction of the short and long term clinical outcome [
7].
3. Search Strategy
In this narrative review, we focus on the role of AI in the field of lung imaging in ARDS.
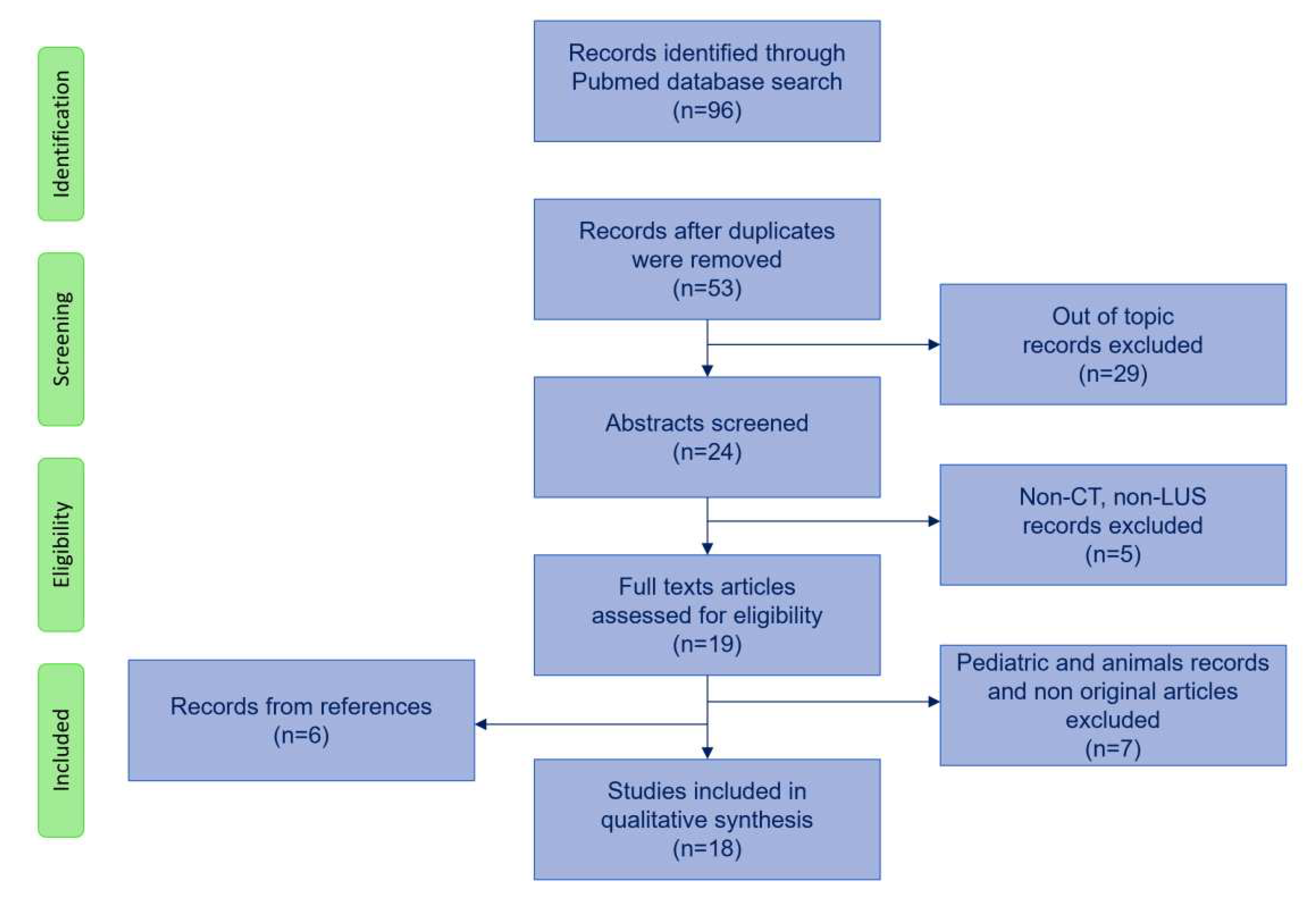
Search strategy flowchart is shown in
Figure 1. We used PubMed database with the following initial screening keywords: lung CT scan AND artificial intelligence/machine learning AND ARDS/acute respiratory failure and also lung ultrasound AND artificial intelligence/machine learning AND ARDS/acute respiratory failure. The search was augmented with lung imaging AND artificial intelligence/machine learning AND ARDS/acute respiratory failure resulting in 96 articles. After excluding duplicates, we screened abstracts and excluded articles that did not deal with artificial intelligence or with CT scan or LUS resulting in 19 articles. We excluded articles on pediatric patients and animals resulting in 12 papers. We included 6 articles from references. We included a total number of 18 studies in the review, which are summarized in Table 1.
4. CT Scan
The application of AI on CT scan lung images has been recently implemented in critically ill patients in order to automatically and efficiently analyze and segment acutely injured lungs over the full spectrum of ARDS severity. In particular, it has been demonstrated to be useful in the clinical practice to predict the development of ARDS, the alveolar recruitment and the relationship between the quantitative analysis of lung tissue and specific outcomes.
5. Prediction of ARDS
Blunt chest trauma is currently associated with parenchymal lung injury at various extents, which may increase the risk of developing ARDS. Usually, the presence of an injury severity score (ISI) higher than 25 significantly increases the risk of developing ARDS [
8]. In addition, it has previously been shown that trauma patients with pulmonary contusions involving at least 20% of the total lung volume had a significantly higher risk of developing ARDS [
9]. Thus, the ability to assess early information on lung CT that may be associated with risk of developing ARDS, could allow for timely supportive therapy. Röhrich et al developed a ML method for the early prediction of ARDS based on CT in trauma patients at hospital admission. One hundred twenty-three patients were enrolled. The model consisted in a fully automated ML and radiomics based approach, that had a higher accuracy compared to an established score (ISS and abbreviated injury score of the thorax) to identify ARDS in trauma patients [
8]. In this line, a rapid automated chest CT volumetry assessment of pulmonary contusion in trauma patients showed a good accuracy to assess the risk of ARDS, length of intensive care and time on mechanical ventilation [
10].
6. Alveolar Recruitment
The introduction of the lung CT quantitative analysis has allowed the assessment and quantification of the aerated and not aerated lung regions and the possible changes due to the mechanical ventilation and body position [
5]. In particular, the application of the lung CT quantitative analysis performed at two different levels of airway pressure, is considered the gold standard for the assessment of alveolar recruitment, because it can compute the difference of not aerated tissue [
11,
12].
However, since the med-1980, the application of the quantitative was rarely applied in clinical practice because it required the manual segmentation of the lung by the physicians [
12]. The assessment of lung recruitment can require up to 6-8 hours with a certain amount of error [
13]. In order to improve the possibility to evaluate lung recruitment, a visual anatomic assessment of recruitment was suggested [
12].
Moving from the successful application of DL to the segmentation process of CT lung images in ARDS [
14,
15], using two CNN architectures, the Seg-Net and U-Net, Herrmann et al decided to implement the U-net to develop a DL algorithm to automatically segment injured lungs affected with ARDS and to calculate the lung recruitment performing two CT scans at 5 and 45 cmH
2O of airways pressure [
16].
The training was performed on 15 healthy subjects (1302 slices), 100 ARDS patients (12279 slices), and 20 COVID-19 patients (1817 slices): 80% percent of patients was used for training, 20% for testing. The authors found that automatic lung segmentation performed by a properly trained neural network was reliable in close agreement with the ones obtained by manual segmentation. In fact, the total lung volume measured by AI and manual segmentation had a R2 of 0.99 and a bias -9.8 ml (CI +56.0/-75.7 ml). Although the model was not perfect, especially in the most damaged lung areas that are difficult to identify even for a trained radiologist, but not exceeded the 10% of the lung parenchyma, the AI segmentation showed the same degree of inaccuracy of the manual segmentation. In fact, the recruitability measured using manual and AI-segmentation, as change in not aerated tissue fraction had a bias of +0.3% (CI +6.2/-5.5%) and -0.5% (CI +2.3/-3.3%) expressed as change in well aerated tissue fraction.
Subsequently, Penarrubia et al in a single center study, assessed both intra- and inter-observer smallest real difference exceeding measurement error of recruitment using both human and ML lung segmentation on CT scan [
13]. Low-dose CT scans were acquired at 5 and 15 cmH
2O of positive end-expiratory pressure in 11 ARDS sedated and paralyzed patients and recruitment was computed as the weight change of the not aerated lung regions. The intra-observer small real difference of recruitment was 3.5% of lung weight, while the human–human inter-observer smallest real difference of recruitment was slightly higher amounting to 5.7% of lung weight, as also was the human–machine smallest real difference. Human–machine and human–human inter-observer measurement errors were similar, suggesting that ML segmentation algorithms are valid alternative to humans for quantifying alveolar recruitment on CT [
13].
Furthermore, to overcome the difficulty to perform two CT scans at two different airways pressures, Pennati et al developed a ML algorithm to predict lung recruitment in ARDS patients, starting from a single CT scan obtained at 5 cmH
2O at the admission in intensive care unit (ICU) [
2].
The authors demonstrated that in 221 ARDS patients retrospectively analyzed, the use of four ML algorithms (Logistic regression, Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, XGboost) based on a CT scan at 5 cmH
2O were able to classify lung recruiter patients with similar area under the curve (AUC) compared with a ML model based on the combination of lung mechanics, gas exchange and CT data [
2].
The application of this ML algorithm with an automatic lung segmentation and quantitative analysis could reduce the work load and the ionizing radiation load of the traditional method to assess lung recruitability.
7. Outcome
Concerning the outcome, the hospital mortality rate decreased through the decades, but it remained unchanged in the last years [
17].
A small retrospective study enrolling 42 patients with ARDS, evaluated the relationship between the volume of well aerated lung regions, automatically computed by a software and the outcome [
18]. The total lung volumes and well aerated lung regions were significantly higher in survivors. The estimation of the whole volumetry and the region of interest were obtained within three minutes with a very good reproducibility [
18].
Several data have shown that lung volume and the amount of not aerated lung areas in COVID-19 are related with respiratory severity and outcome [
19]. Typical lung CT findings in COVID-19 patients include bilateral pulmonary ground-glass opacities and opacities with rounded margins usually localized in the peripheral lung regions [
5].
Using a DL method to compute the description of the CT, two clusters typically associated with COVID-19 and two clusters associated with bacterial pneumonia were found [
20]. The clusters containing a diffuse ground-glass opacities in the central and peripheral lung showed up to 91% accuracy in correctly classifying COVID-19 and pneumonia.
Liu et al investigated the ability of quantitative lung CT analysis compared to traditional clinical biomarkers to predict progression to severe disease in the early stage of COVID-19 patients [
21]. A group of 134 patients with COVID-19 who underwent lung CT scan and laboratory testing on day 0 and 4 were enrolled. All patients were followed up for 28 days until to first onset of severe illness or otherwise. Three AI-derived CT features were computed according to Hounsfield units (-700/-500; -500/-200 and -200/-60 HU). The CT features showed the best discriminative ability at day 0, day 4 and their changes from day 0 to day 4 to predict patient progression to severe disease. In this line, a retrospective study of COVID-19 patients applied a DL segmentation to assess the volume and the density composition of the lung [
22]. The number of lung regions with a density between -549 and -450 of Hounsfield units was associated with an increased risk of ARDS. Although the results were not published, Lopes et al proposed a multicenter retrospective longitudinal study to correlate the possible findings on chest CT in patients with COVID-19 infection and the course of the disease [
23].
In COVID-19 patients, the use of the quantitative CT lung analysis at hospital admission which calculated the volume of the affected lung as the sum of the poorly aerated and not aerated lung regions, predicted the need for oxygenation support and intubation with good accuracy [
24].
Regarding hospital mortality in COVID-19 ARDS based on AI quantification of lung involvement on hospital admission, the AI did not predict the outcome [
25]. On the contrary, the sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) score resulted in an AUC for hospital mortality of 0.74 (95% CI 0.63-0.85) suggesting that other clinical parameters reflect the overall disease severity.
In severe COVID-19 ARDS patients with hypoxemia refractory to the conventional ventilation, veno-venous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be used to improve the outcome. However, the potential improvement in outcome is higher when ECMO support is applied in the early phase. Therefore, a possible early stratification should be considered. The use of an AI-based quantification of lung involvement was able to predict the need for ECMO with an acceptable AUC [0.83 (95% CI 0.73-0.94)] [
26]. In addition, combining SOFA score with lung involvement computed by CT at ICU admission, improved the AUC to 0.91 (95% CI 0.84-0.97) [
26].
8. Lung Ultrasound
LUS has demonstrated to be a useful tool in the assessment of numerous lung diseases and, in the last few years, has proven to be also effective in the emergency care setting to screen patients with suspected COVID-19 pneumonia [
27,
28,
29]. In fact, compared to traditional imaging, LUS has many advantages: it is free of radiations, low cost, rapid, viable at bedside, non-invasive and lacks the laborious workflow of a CT scan. Considering all these features and its good accuracy as compared with chest CT scan, LUS is commonly used in ICU to screen patients for ARDS [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. Indeed, LUS has the potential to predict mortality in ARDS patients with a high level of accuracy (AUC 0.85). These findings also exhibit a strong correlation with the prognostic value derived from invasively measured extravascular lung water index. Moreover, in this condition, LUS is capable of assessing the likelihood of post-extubation distress following a successful spontaneous breathing trial, with an AUC of 0.86 and is also able to assess regional and global lung aeration [
34,
35,
36,
37]. LUS images in ARDS are characterized by the presence of a non-homogeneously distributed alveolar sonographic interstitial syndrome characterized by the presence of vertical artifacts (which include the so called “B lines” and the “white lung”), along with pleural thickening and consolidations in dependent regions [
38,
39]. However, those features, in particular the vertical artifacts, are not specific for ARDS since they can be detected in many other pathological conditions (i.e., pulmonary edema, pneumonia and pulmonary fibrosis). Moreover, LUS interpretation can be limited by the operator’s confidence in images acquisition and interpretation, that can lead to intra-reader variability and a limited inter-reader agreement [
40,
41].
To overcome these limits and to curb operator-related variability, AI has been recently employed in different medical areas to aid LUS image analysis and interpretation [
21,
42], such as emergency and ICU settings [
3,
43].
DL has the capability to directly process and gather intermediate and advanced characteristics obtained from raw data, such as ultrasound (US) images, and subsequently reaching intelligent decisions based on learned features. Absence of cognitive bias or the need for spatial pixel connections allows DL to treat images as numerical sequences, enabling the assessment of quantitative patterns that could unveil insights beyond human interpretation and hence to empower human diagnostic ability. According to the type of the skill requested (i.e., classification, detection and segmentation), there are mainly three types of DL architecture: supervised deep networks or deep discriminative models, unsupervised deep networks or deep generative models, and hybrid deep networks. The supervised deep networks are the most used in US imaging, the major methodology of interest being the CNN [
21,
44,
45].
Regarding the application of DL in LUS for the evaluation of ARDS in non-COVID-19 patients, only few studies are currently available. During the recent COVID-19 pandemic, LUS disease specific patterns showed a higher sensitivity compared to chest-X ray in the identification of COVID-19 pneumonia [
46,
47], making this disease model the predominant focus of DL application. Indeed, the automated assessment enabled by DL ensures a prompt diagnosis in situations where resources and trained personal are scarce, ideally addressing such challenges.
9. Prediction of ARDS Diagnosis
Two studies investigated the possibility to introduce DL modalities to discriminate different stages of parenchymal alteration secondary to pneumonia [
48] by grade vertical artifacts [
49] of LUS.
Baloescu et al designed a new custom DL that operated on dynamic US data, for automated assessment of sonographic lung B lines. The DL consisted of a CNN developed using 2415 sub-clips of 12 frames each, from 400 emergency department patients. Each sub-clip was evaluated by two emergency physicians experts in LUS, based on predeterminate ordinal scale from 0 (none) to 4 (severe). Moreover, a binary classification was performed pooling together as “normal” the images with score 0 or 1, and as “abnormal” the images with score 2-4. The rating of the experts was used as ground truth and compared with the interpretations given by the new DL model using 100 sub-clips not used during the DL training. Considering the assessment of presence/absence of B lines, the new DL model showed an overall accuracy of 94% with kappa of 0.88; instead, for the severity assessment, the overall accuracy was only of 56% with kappa of 0.65, showing that the new algorithm is better at distinguishing B lines, but not their severity [
49].
Zhang et al investigated the feasibility of computer-assisted US diagnosis with three CNN-based DL models - VGG, ResNet and EfficientNet - for the detection and classification of pneumonia based on a self-made LUS image dataset built on a total of 10350 LUS images. Each image of the dataset was manually classified into 8 clinical features of pneumonia (0 = normal; 1 = B lines <3; 2 = B lines > 3; 3 = area of merging B line is less than half; 4 = area of merging B line is more than half; 5 = depth of pieces is less than 1 cm; 6 = air bronchogram and depth of parenchymal hepatization is less than 3 cm; 7 = pleural effusion and depth of parenchymal hepatization is more than 3 cm). Since for some of the evaluated features there were not enough images for training and testing sets, multiple clinical features were manually grouped together into different “classes” creating 3 different datasets: one including 3 classes (class 1: feature 0; class 2: features 1-4; class 3: features 5-7), one including 4 classes (class 1: feature 0; class 2: features 1-4; class 3: features 5-6; class 4: feature 7), and the last one encompassing 8 classes, i.e., a class for each of the 8 features. All the 3 datasets were compared across classification models and the EfficientNet showed to be the best model providing for 3 and 4 classes datasets an accuracy of 94.62% and 91.18%, respectively, whilst the best classification accuracy of the 8 classes dataset was only of 82.75% [
48].
10. Differential Diagnosis
AI has been applied to LUS imaging for its potential role in differentiating: healthy subjects from COVID-19 pneumonia and ARDS, hydrostatic pulmonary edema, bacterial pneumonia and ARDS.
Born et al proposed another DL LUS model able to distinguish COVID-19 from healthy subjects and bacterial pneumonia with a sensitivity of 0.90 ± 0.08 and a specificity of 0.96 ± 0.04. The model was developed using a dataset made by 261 recordings from a total of 216 patients affected by COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, non-COVID-19 viral pneumonia and healthy controls. Due to data availability, the three non-COVID-19 viral pneumonia videos were excluded. Five DL models were than compared in terms of recall, precision, specificity and F1-scores. Overall, both VGG and VGG-CAM showed encouraging results, achieving an accuracy of 88 ± 5% in detecting COVID-19 pneumonia, across a 5-fold cross-validation involving 3234 frames [
50]. Arntfield et al developed another CNN able to differentiate between similar appearing LUS images with pathological B lines of three different origins (COVID-19 ARDS, non-COVID ARDS and hydrostatic pulmonary edema) using a 612 LUS videos from 243 patients (84 COVID-19 ARDS, 78 non-COVID-19 ARDS and 81 hydrostatic pulmonary edema). To assess the CNN performance, a subset comprising 10% of the total data was used, not used during the training process. The evaluation made by CNN was then compared to the LUS interpretation given by proficient physicians, who complete an online interpretation exercise. The trained CNN performance on the independent dataset showed an ability to discriminate between COVID-19 (AUC 1.0), non-COVID-19 ARDS (AUC 0.934) and pulmonary edema (AUC 1.0) pathologies. This was significantly better than physician ability (AUCs 0.697, 0.704, 0.967 for the COVID-19 ARDS, non-COVID-19 ARDS and pulmonary edema classes, respectively; p<0.01), showing that a trained neural network is able to detect subvisible features within LUS images [
51].
Ebadi et al proposed a rapid and dependable DL model, specifically the Kinetics-I3D network, using LUS scans to explore the possibility to detect and differentiate ARDS from pneumonia. Compared with other DL, this trained model was capable of classifying an entire LUS scan obtained at the point-of-care, eliminating the need for preprocessing or analyzing frames individually, since the neural network could be retrained with new data to adapt the model to the needs of specific applications involving LUS. The results obtained with the new DL methods were benchmarked against ground truth assessed by expert radiologists showing an accuracy of 90% and a precision score of 95%. Moreover, the proposed model was very rapid since it was able to process the entire scan with a single forward pass into the network – avoiding time-consuming frame by frame analysis [
52].
11. Limitations of AI in LUS
To this moment, the application of DL in the echographic study of the thorax has been very limited as compared to other imaging techniques. One of the reasons is the restricted availability of organized LUS databases. In fact, to reach an optimal learning performance a wide number of labeled LUS images are needed. This requirement can present difficulties as LUS is a developing technique, and currently, there are only a limited number of experts capable of providing a suitable interpretation.
The prevalent issue deriving from a deep model using limited training samples is the over-fitting that can be addressed with two different approaches: the model optimization and the transfer learning. The model optimization focuses on making DL model itself to work better with available data using different types of strategies (e.g., well-designed initialization/momentum strategies, efficient activation functions, dropout, batch normalization, stack/denoising), whereas transfer learning utilizes knowledge from one domain to enhance the performance in another domain with limited data.
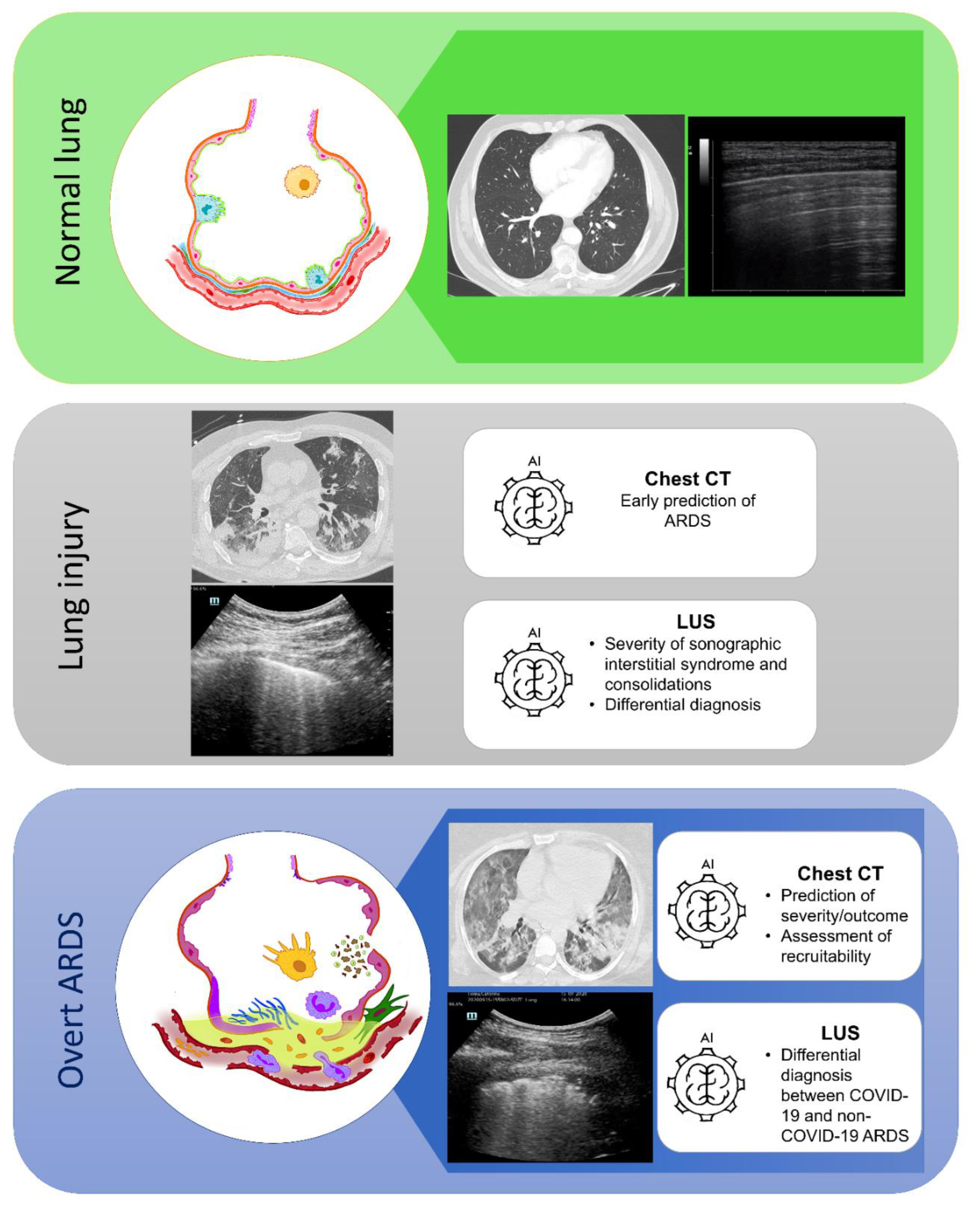
12. Conclusions
The application of ML technique to lung CT scan image processing can represent a valid tool to provide a broader adoption of CT scan quantitative analysis in the clinical practice of ARDS management, in particular the prediction of the alveolar recruitment and of the outcome. Similarly, the application of AI to LUS imaging may implement clinician performance in distinguish and interpreting similar LUS patterns deriving from different pathological etiologies with the potential to provide a prompt diagnosis (
Figure 2).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Haug, C.J.; Drazen, J.M. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Clinical Medicine, 2023. New England Journal of Medicine 2023, 388, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennati, F.; Aliverti, A.; Pozzi, T.; Gattarello, S.; Lombardo, F.; Coppola, S.; Chiumello, D. Machine Learning Predicts Lung Recruitment in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Using Single Lung CT Scan. Ann Intensive Care 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, J.S.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Puvvula, A.; Biswas, M.; Saba, L.; Bit, A.; Tandel, G.S.; Agarwal, M.; Patrick, A.; et al. A Narrative Review on Characterization of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in COVID-19-Infected Lungs Using Artificial Intelligence. Comput Biol Med 2021, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, B.; Agarwal, S.; Coombs, L.; Wald, C.; Dreyer, K. 2020 ACR Data Science Institute Artificial Intelligence Survey. Journal of the American College of Radiology 2021, 18, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Papa, G.F.S.; Artigas, A.; Bouhemad, B.; Grgic, A.; Heunks, L.; Markstaller, K.; Pellegrino, G.M.; Pisani, L.; Rigau, D.; et al. ERS Statement on Chest Imaging in Acute Respiratory Failure. European Respiratory Journal 2019, 54, 1900435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Badiei Khuzani, M.; Vasudevan, V.; Huang, C.; Ren, H.; Xiao, R.; Jia, X.; Xing, L. Machine Learning Techniques for Biomedical Image Segmentation: An Overview of Technical Aspects and Introduction to State-of-Art Applications. In Proceedings of the Medical Physics; John Wiley and Sons Ltd, June 1 2020; Vol. 47, pp. e148–e167.
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.-W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrich, S.; Hofmanninger, J.; Negrin, L.; Langs, G.; Prosch, H. Radiomics Score Predicts Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Based on the Initial CT Scan after Trauma. Eur Radiol 2021, 31, 5443–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, P.R.; Croce, M.A.; Bee, T.K.; Qaisi, W.G.; Smith, C.P.; Collins, G.L.; Fabian, T.C. ARDS after Pulmonary Contusion: Accurate Measurement of Contusion Volume Identifies High-Risk Patients; 2001, *!!! REPLACE !!!*.
- Sarkar, N.; Zhang, L.; Campbell, P.; Liang, Y.; Li, G.; Khedr, M.; Khetan, U.; Dreizin, D. Pulmonary Contusion: Automated Deep Learning-Based Quantitative Visualization. Emerg Radiol 2023, 30, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Caironi, P.; Cressoni, M.; Chiumello, D.; Ranieri, V.M.; Quintel, M.; Russo, S.; Patroniti, N.; Cornejo, R.; Bugedo, G. Lung Recruitment in Patients with the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2006, 354, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiumello, D.; Marino, A.; Brioni, M.; Menga, F.; Cigada, I.; Lazzerini, M.; Andrisani, M.C.; Biondetti, P.; Cesana, B.; Gattinoni, L. Visual Anatomical Lung CT Scan Assessment of Lung Recruitability. Intensive Care Med 2013, 39, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penarrubia, L.; Verstraete, A.; Orkisz, M.; Davila, E.; Boussel, L.; Yonis, H.; Mezidi, M.; Dhelft, F.; Danjou, W.; Bazzani, A.; et al. Precision of CT-Derived Alveolar Recruitment Assessed by Human Observers and a Machine Learning Algorithm in Moderate and Severe ARDS. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. InMedical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015. MICCAI 2015. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2015, 234–241.
- Herrmann, P.; Busana, M.; Cressoni, M.; Lotz, J.; Moerer, O.; Saager, L.; Meissner, K.; Quintel, M.; Gattinoni, L. Using Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Segmentation of CT Lung Images in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Front Physiol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellani, G.; Laffey, J.G.; Pham, T.; Fan, E.; Brochard, L.; Esteban, A.; Gattinoni, L.; Van Haren, F.M.P.; Larsson, A.; McAuley, D.F.; et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association 2016, 315, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Kawata, N.; Yokota, H.; Sugiura, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Higashide, T.; Horikoshi, T.; Oda, S.; Tatsumi, K.; Uno, T. A Predictive Factor for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: CT Lung Volumetry of the Well-Aerated Region as an Automated Method. Eur J Radiol 2020, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiumello, D.; Busana, M.; Coppola, S.; Romitti, F.; Formenti, P.; Bonifazi, M.; Pozzi, T.; Palumbo, M.M.; Cressoni, M.; Herrmann, P.; et al. Physiological and Quantitative CT-Scan Characterization of COVID-19 and Typical ARDS: A Matched Cohort Study. Intensive Care Med 2020, 46, 2187–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Hong, K.S.; Chikontwe, P.; Luna, M.; Jang, J.G.; Park, J.; Shin, K.C.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, J.H. Quantitative Assessment of Chest CT Patterns in COVID-19 and Bacterial Pneumonia Patients: A Deep Learning Perspective. J Korean Med Sci 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lei, B.; Liu, L.; Li, S.X.; Ni, D.; Wang, T. Deep Learning in Medical Ultrasound Analysis: A Review. Engineering 2019, 5, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, S.; Zeng, H.; Deng, W.; Huang, Z.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Chest CT Imaging Findings with the Risk of ARDS in COVID-19 Patients: A Preliminary Study. Ann Transl Med 2020, 8, 594–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva Proença Lobo Lopes, F.; Kitamura, F.C.; Prado, G.F.; de Aguiar Kuriki, P.E.; Taveira Garcia, M.R. Machine Learning Model for Predicting Severity Prognosis in Patients Infected with COVID-19: Study Protocol from COVID-AI Brasil. PLoS One 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, E.; Muglia, R.; Bolengo, I.; Santonocito, O.G.; Lisi, C.; Angelotti, G.; Morandini, P.; Savevski, V.; Letterio, &; Politi, S.; et al. Quantitative Chest CT Analysis in COVID-19 to Predict the Need for Oxygenation Support and Intubation. [CrossRef]
- Puhr-Westerheide, D.; Reich, J.; Sabel, B.O.; Kunz, W.G.; Fabritius, M.P.; Reidler, P.; Rübenthaler, J.; Ingrisch, M.; Wassilowsky, D.; Irlbeck, M.; et al. Article Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Outperforms Quantitative Chest Ct Imaging Parameters for Mortality Prediction in Covid-19 Ards. Diagnostics 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresser, E.; Reich, J.; Sabel, B.O.; Kunz, W.G.; Fabritius, M.P.; Rübenthaler, J.; Ingrisch, M.; Wassilowsky, D.; Irlbeck, M.; Ricke, J.; et al. Risk Stratification for Ecmo Requirement in Covid-19 Icu Patients Using Quantitative Imaging Features in Ct Scans on Admission. Diagnostics 2021, 11, NA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, G.; Smargiassi, A.; Inchingolo, R.; Buonsenso, D.; Perrone, T.; Briganti, D.F.; Perlini, S.; Torri, E.; Mariani, A.; Mossolani, E.E.; et al. Proposal for International Standardization of the Use of Lung Ultrasound for Patients With COVID-19. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 2020, 39, 1413–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.J.; Hayward, S.A.; Innes, S.M.; Miller, A.S.C. Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound in Patients with COVID-19 – a Narrative Review. Anaesthesia 2020, 75, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Down, B.; Jha, S. Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound in Intensive Care during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Clin Radiol 2020, 75, 710.e1–710e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li Lianhua; Yang Qian; Li Liming; Guan Jian; Liu Zhu; Han Jiaqi; Chao Yangong; Wang Zhong; Yu Xuezhong The Value of Lung Ultrasound Score on Evaluating Clinical Severity and Prognosis in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2015, 27, 79–84.
- Haddam, M.; Zieleskiewicz, L.; Perbet, S.; Baldovini, A.; Guervilly, C.; Arbelot, C.; Noel, A.; Vigne, C.; Hammad, E.; Antonini, F.; et al. Lung Ultrasonography for Assessment of Oxygenation Response to Prone Position Ventilation in ARDS. Intensive Care Med 2016, 42, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caltabeloti, F.P.; Monsel, A.; Arbelot, C.; Brisson, H.; Lu, Q.; Gu, W.J.; Zhou, G.J.; Auler, J.O.C.; Rouby, J.J. Early Fluid Loading in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with Septic Shock Deteriorates Lung Aeration without Impairing Arterial Oxygenation: A Lung Ultrasound Observational Study. Crit Care 2014, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhemad, B.; Brisson, H.; Le-Guen, M.; Arbelot, C.; Lu, Q.; Rouby, J.J. Bedside Ultrasound Assessment of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure-Induced Lung Recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011, 183, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitkopf, R.; Treml, B.; Rajsic, S. Lung Sonography in Critical Care Medicine. Diagnostics 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, L.; Xi, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wang, M.; Xing, J.; Zhang, D. Prognostic Value of Extravascular Lung Water Assessed with Lung Ultrasound Score by Chest Sonography in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. BMC Pulm Med 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soummer, A.; Perbet, S.; Brisson, H.; Arbelot, C.; Constantin, J.M.; Lu, Q.; Rouby, J.J. Ultrasound Assessment of Lung Aeration Loss during a Successful Weaning Trial Predicts Postextubation Distress. Crit Care Med 2012, 40, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiumello, D.; Umbrello, M.; Papa, G.F.S.; Angileri, A.; Gurgitano, M.; Formenti, P.; Coppola, S.; Froio, S.; Cammaroto, A.; Carrafiello, G. Global and Regional Diagnostic Accuracy of Lung Ultrasound Compared to CT in Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit Care Med 2019, 47, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, F.; Brusasco, C.; Pelosi, P. Chest Ultrasound in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care 2014, 20, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpicelli, G.; Mussa, A.; Garofalo, G.; Cardinale, L.; Casoli, G.; Perotto, F.; Fava, C.; Frascisco, M. Bedside Lung Ultrasound in the Assessment of Alveolar-Interstitial Syndrome. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2006, 24, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, F.; Via, G.; Forfori, F.; Brusasco, C.; Tavazzi, G. Lung Ultrasound and B-Lines Quantification Inaccuracy: B Sure to Have the Right Solution. Intensive Care Med 2020, 46, 1081–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, S.J.; Arntfield, R.T.; Guo, R.J.; Koenig, S.; Kory, P.; Noble, V.; Mallemat, H.; Schoenherr, J.R. Expert Agreement in the Interpretation of Lung Ultrasound Studies Performed on Mechanically Ventilated Patients. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 2018, 37, 2659–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muse, E.D.; Topol, E.J. Guiding Ultrasound Image Capture with Artificial Intelligence. The Lancet 2020, 396, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, J.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, S.; Puvvula, A.; Viskovic, K.; Suri, N.; Alizad, A.; El-Baz, A.; Saba, L.; Fatemi, M.; et al. Systematic Review of Artificial Intelligence in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome for COVID-19 Lung Patients: A Biomedical Imaging Perspective. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 2021, 25, 4128–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng Li; Dong Yu Deep Learning: Methods and Applications; Now Foundations and Trends, 2014.
- Gibbons, R.C.; Magee, M.; Goett, H.; Murrett, J.; Genninger, J.; Mendez, K.; Tripod, M.; Tyner, N.; Costantino, T.G. Lung Ultrasound vs. In Chest X-Ray Study for the Radiographic Diagnosis of COVID-19 Pneumonia in a High-Prevalence Population. In Proceedings of the Journal of Emergency Medicine; Elsevier Inc., May 1 2021; Vol. 60; pp. 615–625. [Google Scholar]
- Pare, J.R.; Camelo, I.; Mayo, K.C.; Leo, M.M.; Dugas, J.N.; Nelson, K.P.; Baker, W.E.; Shareef, F.; Mitchell, P.M.; Schechter-Perkins, E.M. Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound Is More Sensitive than Chest Radiograph for Evaluation of COVID-19. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine 2020, 21, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chng, C.-B.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, M.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chui, C.-K. Detection and Classification of Pneumonia from Lung Ultrasound Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Communication, Image and Signal Processing (CCISP); 2020; pp. 294–298.
- Baloescu, C.; Toporek, G.; Kim, S.; McNamara, K.; Liu, R.; Shaw, M.M.; McNamara, R.L.; Raju, B.I.; Moore, C.L. Automated Lung Ultrasound B-Line Assessment Using a Deep Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 2020, 67, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Born, J.; Wiedemann, N.; Cossio, M.; Buhre, C.; Brändle, G.; Leidermann, K.; Goulet, J.; Aujayeb, A.; Moor, M.; Rieck, B.; et al. Accelerating Detection of Lung Pathologies with Explainable Ultrasound Image Analysis. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arntfield, R.; Vanberlo, B.; Alaifan, T.; Phelps, N.; White, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Ho, J.; Wu, D. Development of a Convolutional Neural Network to Differentiate among the Etiology of Similar Appearing Pathological b Lines on Lung Ultrasound: A Deep Learning Study. BMJ Open 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfanian Ebadi, S.; Krishnaswamy, D.; Bolouri, S.E.S.; Zonoobi, D.; Greiner, R.; Meuser-Herr, N.; Jaremko, J.L.; Kapur, J.; Noga, M.; Punithakumar, K. Automated Detection of Pneumonia in Lung Ultrasound Using Deep Video Classification for COVID-19. Inform Med Unlocked 2021, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).