Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
14 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental design
2.2. Soil sampling and physicochemical properties analysis
2.3. Soil DNA extraction and amplicon sequencing
2.4. Plant sampling and assaying
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results and Discussion
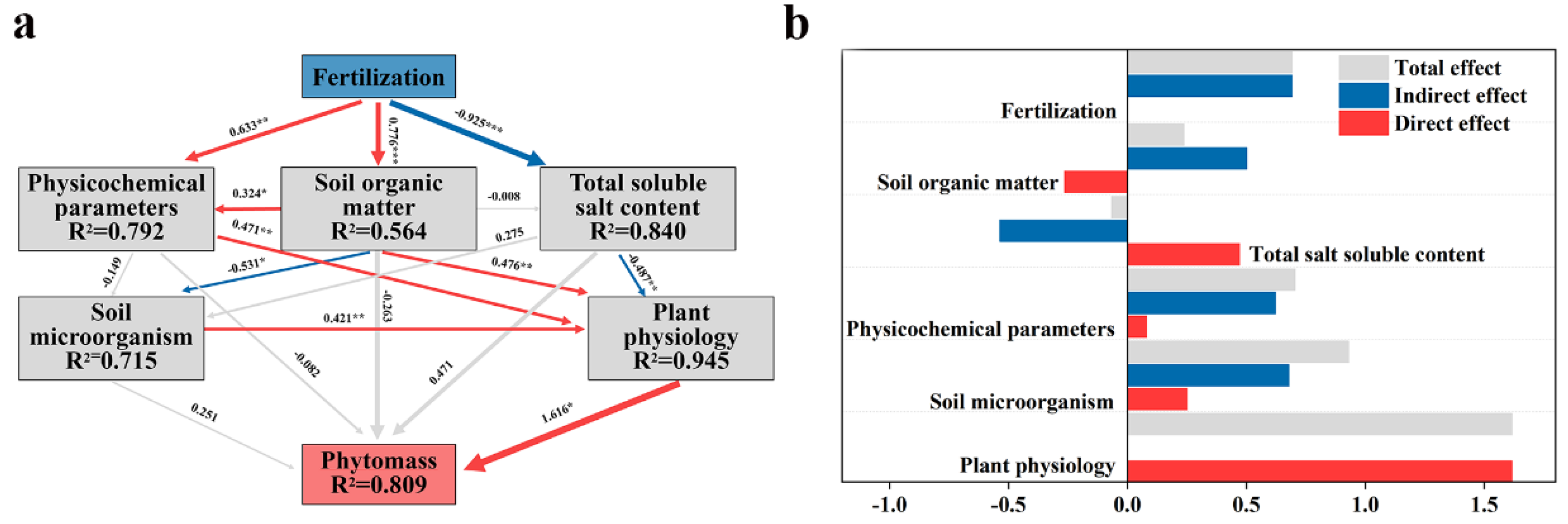
3.1. Amendments of saline soil by biofertilizer
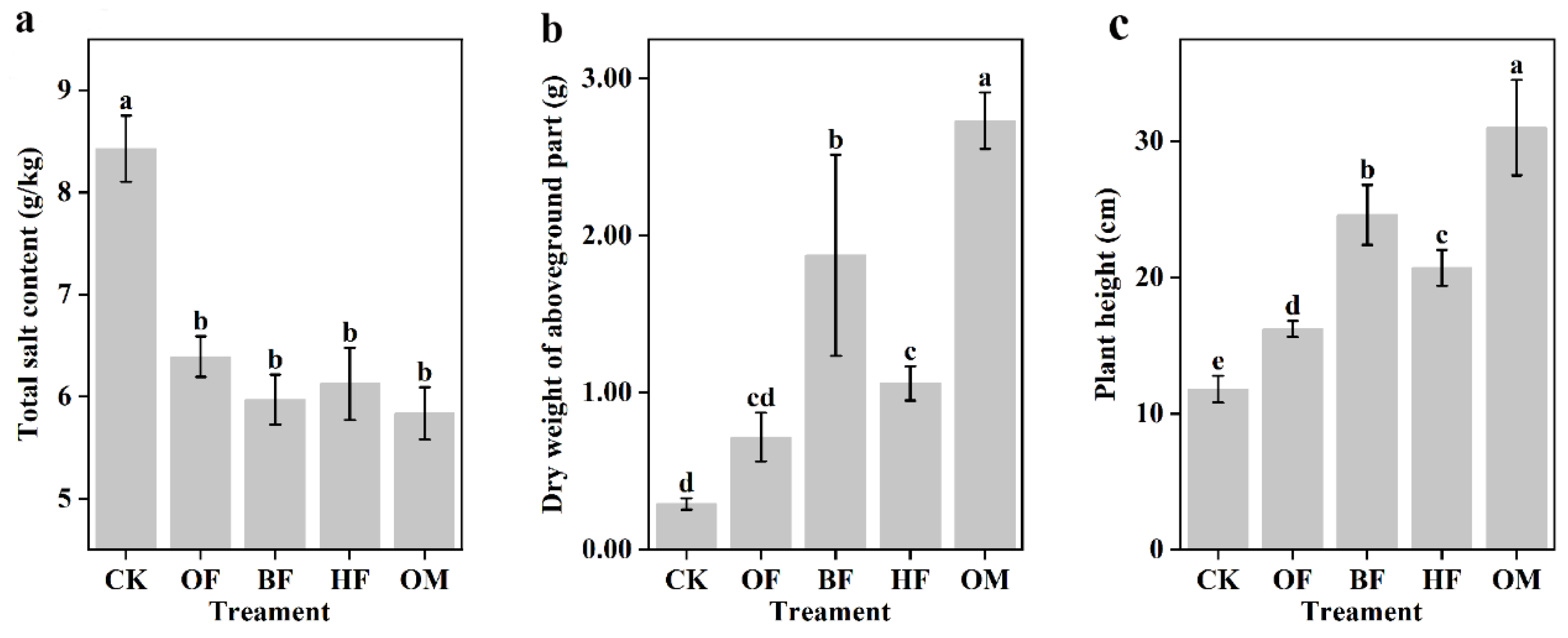
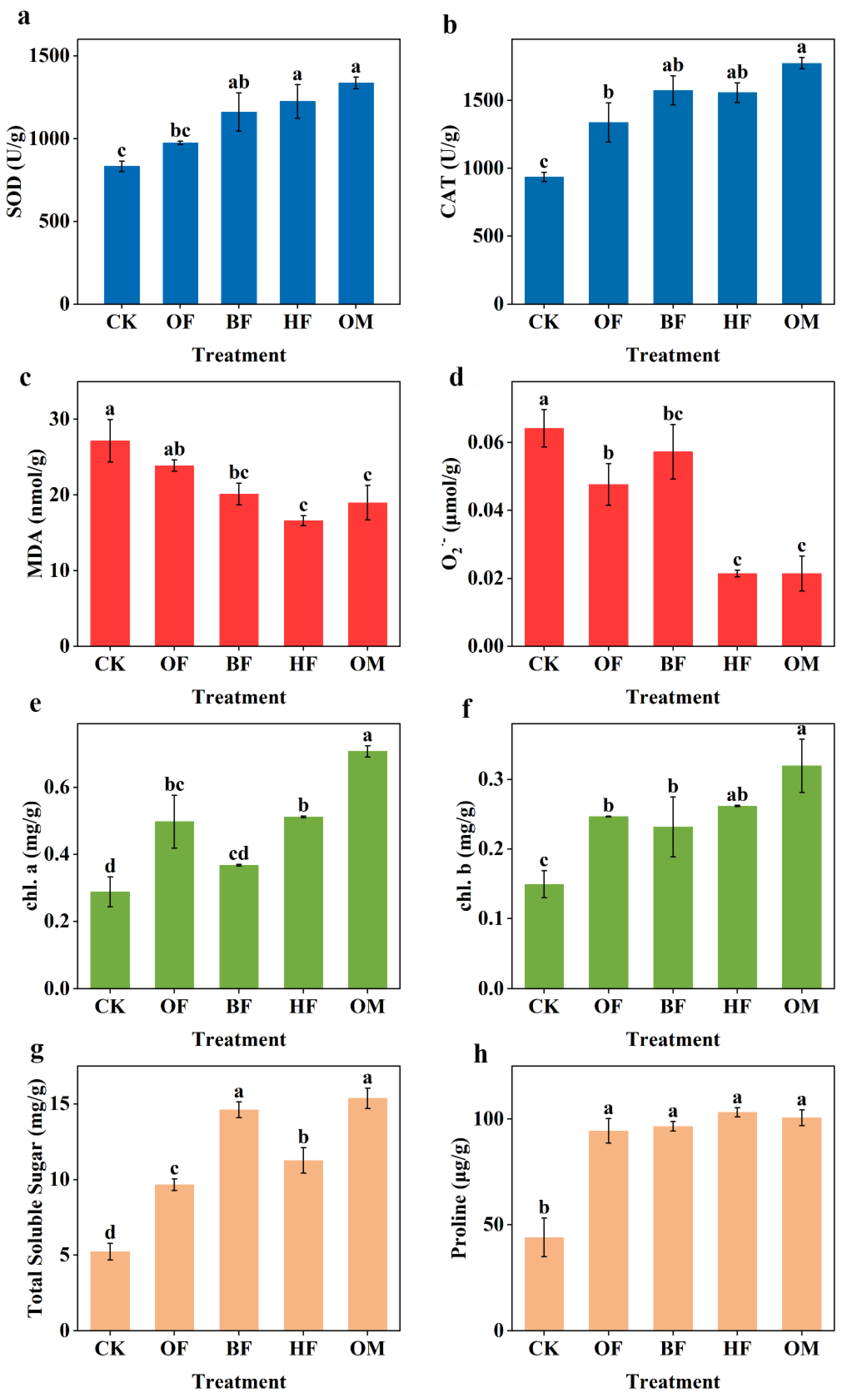
3.2. Response of plant physiological characteristics to fertilization under salt stress
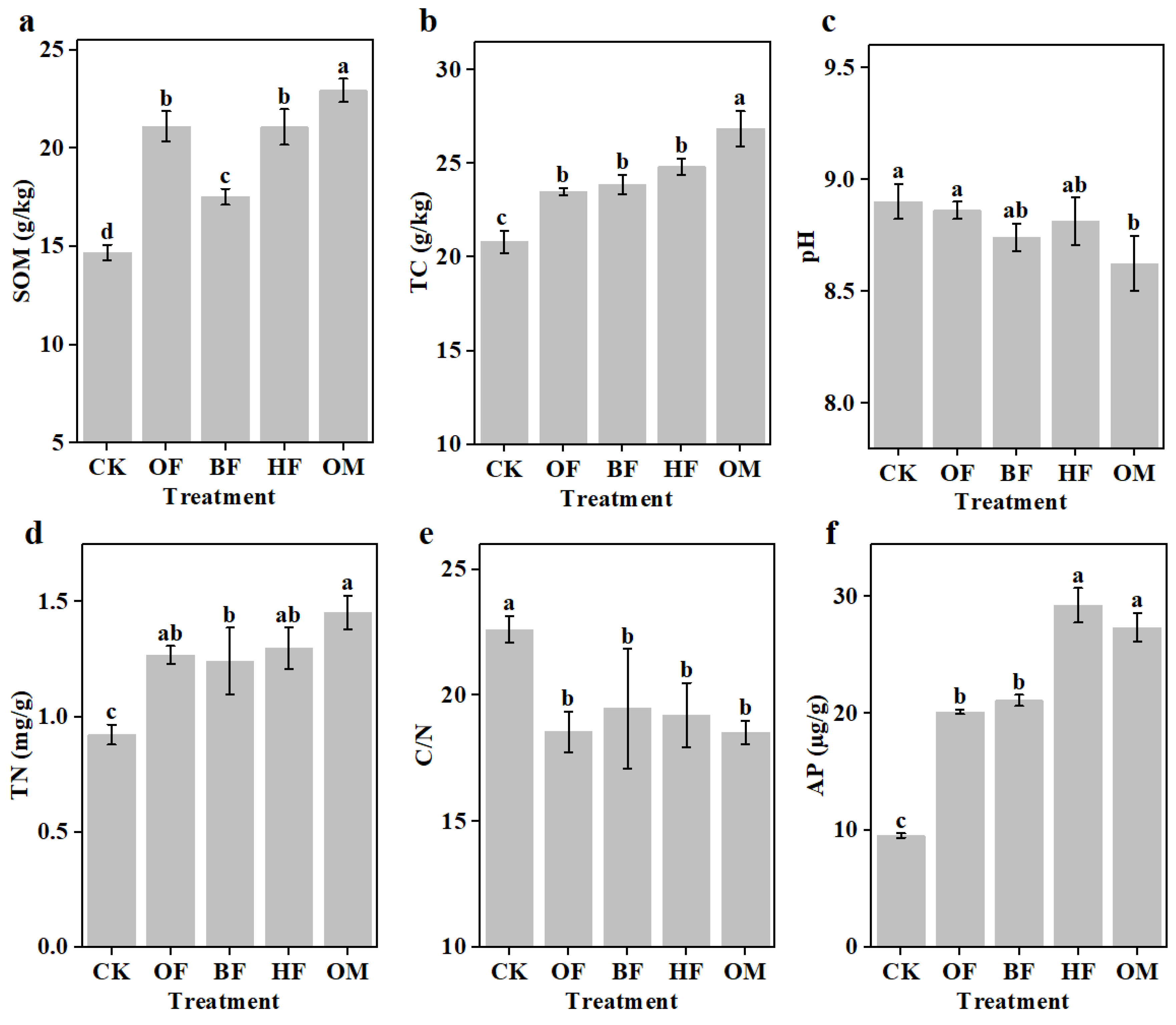
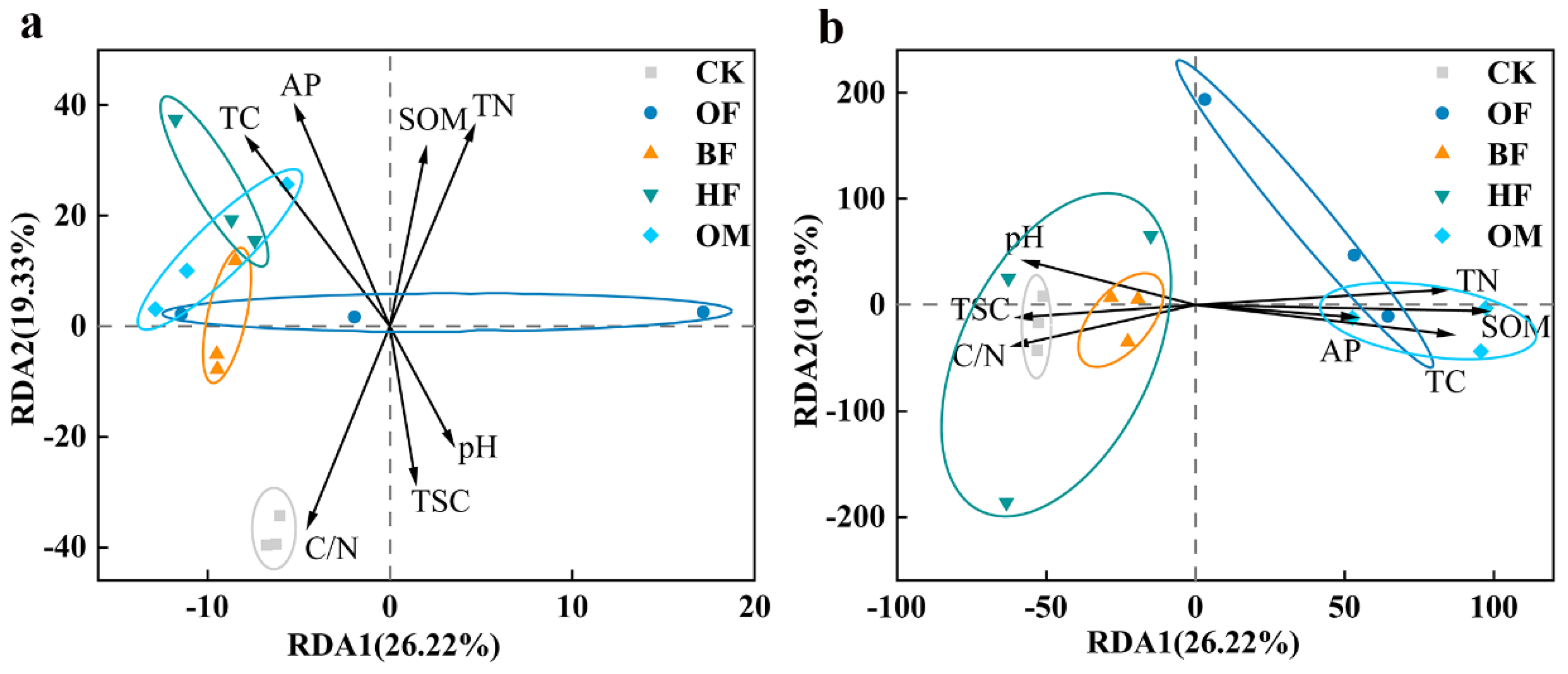
3.3. Improvement of saline soil properties by biofertilizer
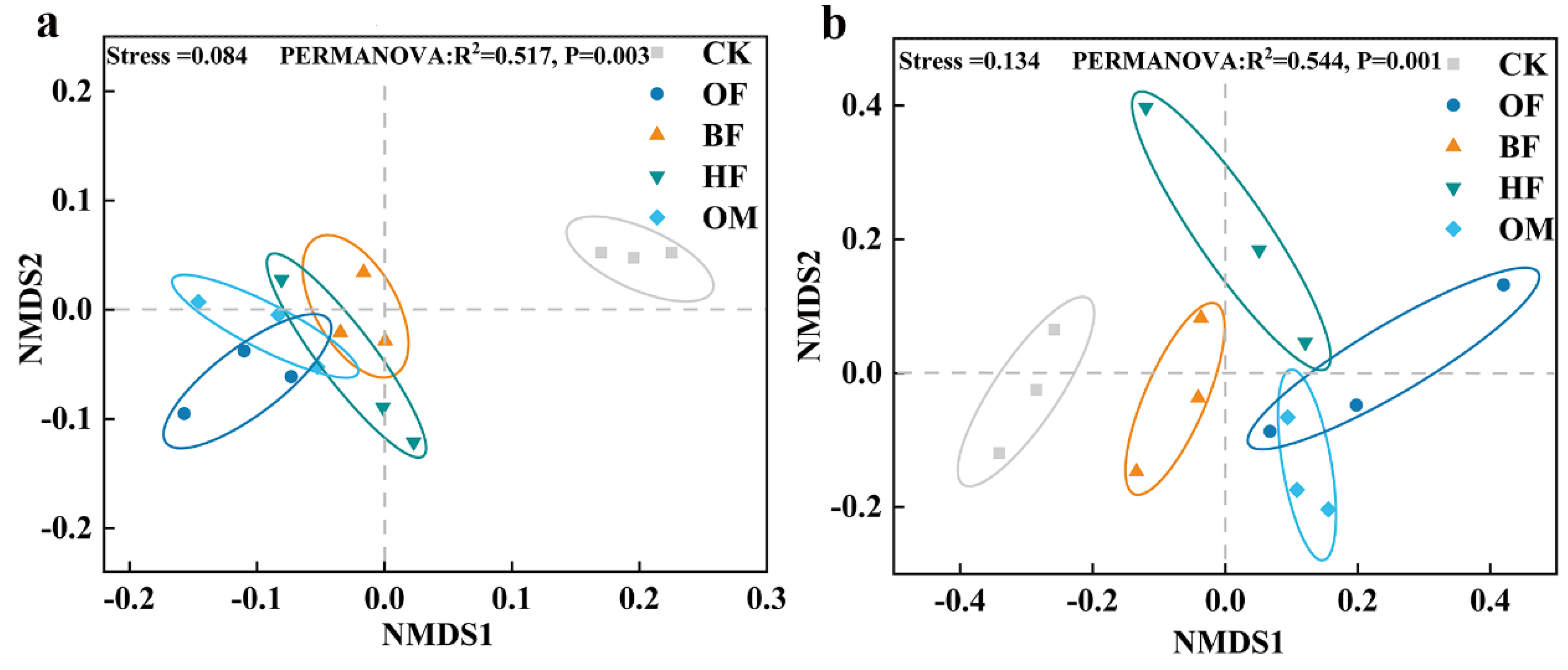
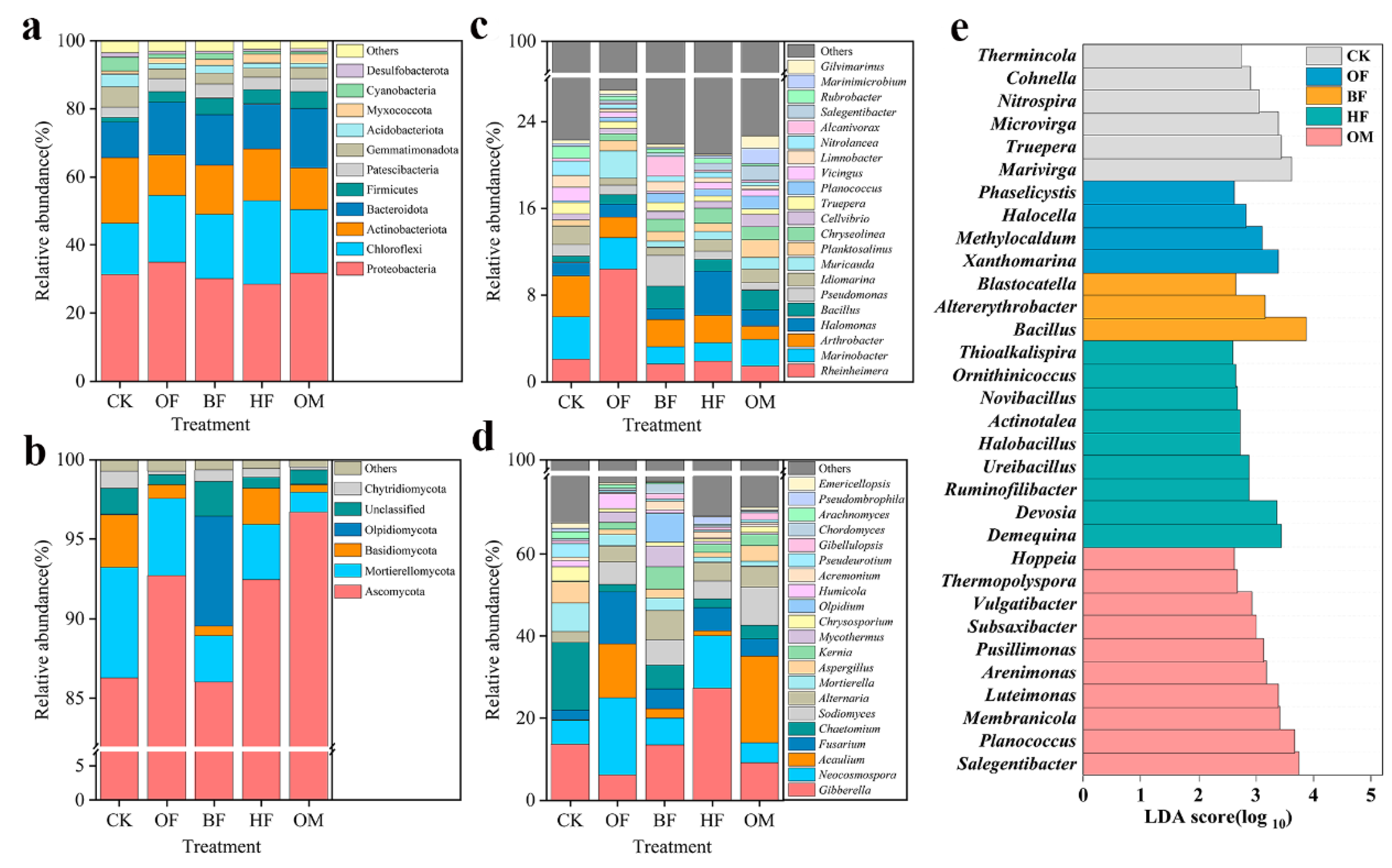
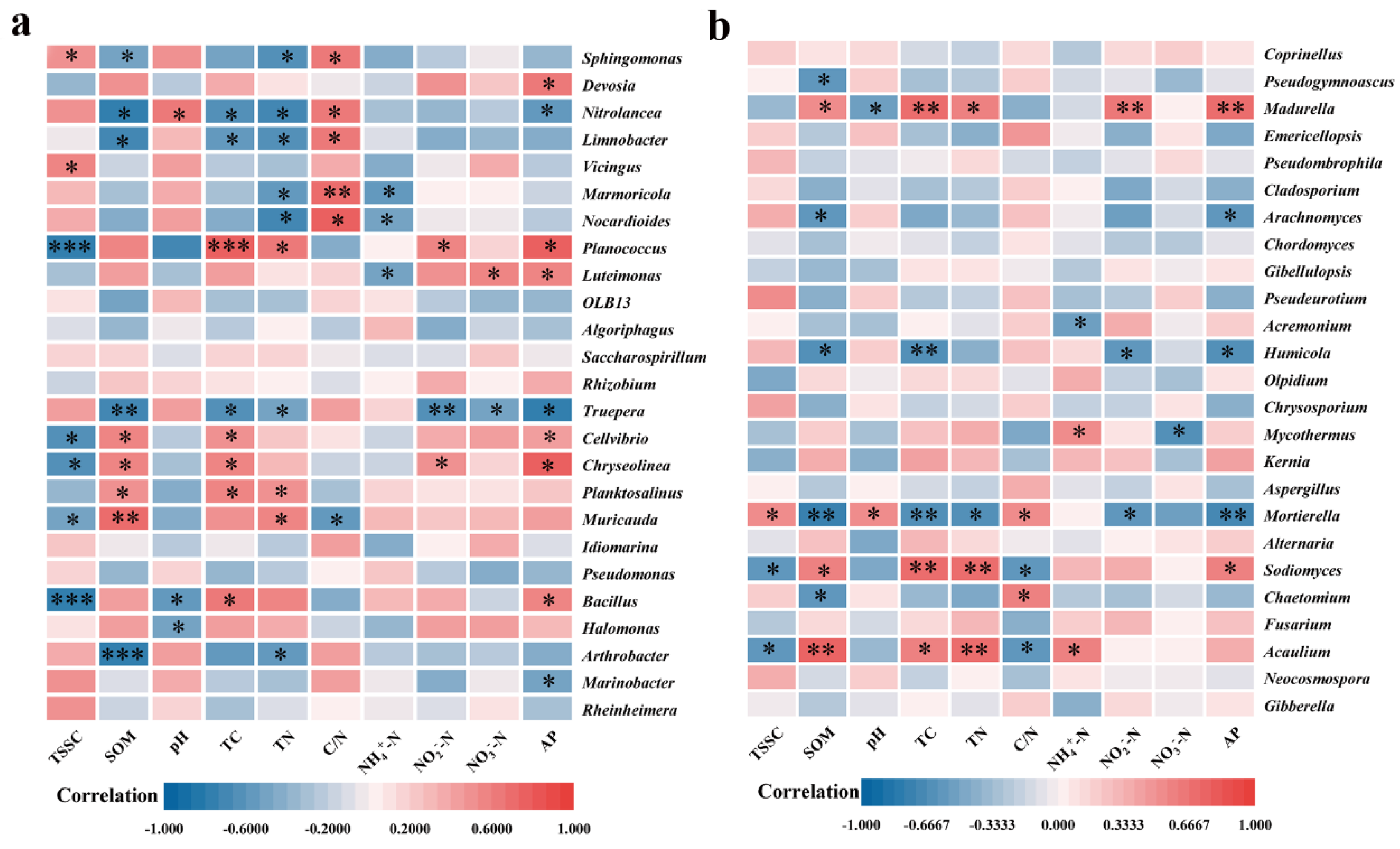
3.4. Alteration of microbial communities in saline soils by biofertilizer
3.5. Response of plant physiological characteristics to fertilization under salt stress
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amirnia, R., Ghiyasi, M., Moghaddam, S.S., Rahimi, A., Damalas, C.A., Heydarzadeh, S., 2019. Nitrogen-Fixing soil bacteria plus mycorrhizal fungi improve seed yield and quality traits of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 19, 592–602. [CrossRef]
- Backer, R., Rokem, J.S., Ilangumaran, G., Lamont, J., Praslickova, D., Ricci, E., Subramanian, S., Smith, D.L., 2018. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria: Context, Mechanisms of Action, and Roadmap to Commercialization of Biostimulants for Sustainable Agriculture. Front. Plant Sci. 9. [CrossRef]
- Barrón, C., Duarte, C.M., Frankignoulle, M., Borges, A.V., 2006. Organic carbon metabolism and carbonate dynamics in a Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica), meadow. Estuaries Coasts 29, 417–426. [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E., Rideout, J.R., Dillon, M.R., Bokulich, N.A., Abnet, C.C., Al-Ghalith, G.A., Alexander, H., Alm, E.J., Arumugam, M., Asnicar, F., Bai, Y., Bisanz, J.E., Bittinger, K., Brejnrod, A., Brislawn, C.J., Brown, C.T., Callahan, B.J., Caraballo-Rodríguez, A.M., Chase, J., Cope, E.K., Da Silva, R., Diener, C., Dorrestein, P.C., Douglas, G.M., Durall, D.M., Duvallet, C., Edwardson, C.F., Ernst, M., Estaki, M., Fouquier, J., Gauglitz, J.M., Gibbons, S.M., Gibson, D.L., Gonzalez, A., Gorlick, K., Guo, J., Hillmann, B., Holmes, S., Holste, H., Huttenhower, C., Huttley, G.A., Janssen, S., Jarmusch, A.K., Jiang, L., Kaehler, B.D., Kang, K.B., Keefe, C.R., Keim, P., Kelley, S.T., Knights, D., Koester, I., Kosciolek, T., Kreps, J., Langille, M.G.I., Lee, J., Ley, R., Liu, Y.-X., Loftfield, E., Lozupone, C., Maher, M., Marotz, C., Martin, B.D., McDonald, D., McIver, L.J., Melnik, A.V., Metcalf, J.L., Morgan, S.C., Morton, J.T., Naimey, A.T., Navas-Molina, J.A., Nothias, L.F., Orchanian, S.B., Pearson, T., Peoples, S.L., Petras, D., Preuss, M.L., Pruesse, E., Rasmussen, L.B., Rivers, A., Robeson, M.S., Rosenthal, P., Segata, N., Shaffer, M., Shiffer, A., Sinha, R., Song, S.J., Spear, J.R., Swafford, A.D., Thompson, L.R., Torres, P.J., Trinh, P., Tripathi, A., Turnbaugh, P.J., Ul-Hasan, S., van der Hooft, J.J.J., Vargas, F., Vázquez-Baeza, Y., Vogtmann, E., von Hippel, M., Walters, W., Wan, Y., Wang, M., Warren, J., Weber, K.C., Williamson, C.H.D., Willis, A.D., Xu, Z.Z., Zaneveld, J.R., Zhang, Y., Zhu, Q., Knight, R., Caporaso, J.G., 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 37, 852–857. [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, S.A., Ianutsevich, E.A., Danilova, O.A., Grum-Grzhimaylo, A.A., Kotlova, E.R., Kamzolkina, O.V., Bilanenko, E.N., Tereshina, V.M., 2017. Membrane lipids and soluble sugars dynamics of the alkaliphilic fungus Sodiomyces tronii in response to ambient pH. Extremophiles 21, 743–754. [CrossRef]
- Chavoushi, M., Najafi, F., Salimi, A., Angaji, S.A., 2020. Effect of salicylic acid and sodium nitroprusside on growth parameters, photosynthetic pigments and secondary metabolites of safflower under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 259, 108823. [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo Neto, A.D., Prisco, J.T., Enéas-Filho, J., Abreu, C.E.B. de, Gomes-Filho, E., 2006. Effect of salt stress on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive maize genotypes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 56, 87–94. [CrossRef]
- Desale, P., Patel, B., Singh, S., Malhotra, A., Nawani, N., 2014. Plant growth promoting properties of Halobacillus sp. and Halomonas sp. in presence of salinity and heavy metals. J. Basic Microbiol. 54, 781–791. [CrossRef]
- Devkota, K.P., Devkota, M., Rezaei, M., Oosterbaan, R., 2022. Managing salinity for sustainable agricultural production in salt-affected soils of irrigated drylands. Agric. Syst. 198, 103390. [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z., Kheir, A.M.S., Ali, O.A.M., Hafez, E.M., ElShamey, E.A., Zhou, Z., Wang, B., Lin, X., Ge, Y., Fahmy, A.E., Seleiman, M.F., 2021. A vermicompost and deep tillage system to improve saline-sodic soil quality and wheat productivity. J. Environ. Manage. 277, 111388. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C., 2018. Accuracy of taxonomy prediction for 16S rRNA and fungal ITS sequences. PeerJ 6, e4652. [CrossRef]
- FAO, 2021a. Global Map of Salt Affected Soils.
- FAO, 2021b. Economical losses due to soil salinization.
- Gadallah, M. a. A., 1999. Effects of proline and glycinebetaine on Vicia faba responses to salt stress. Biol. Plant. 42, 249–257. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y., Dong, K., Geisen, S., Yang, W., Yan, Y., Gu, D., Liu, N., Borisjuk, N., Luo, Y., Friman, V.-P., 2020. The effect of microbial inoculant origin on the rhizosphere bacterial community composition and plant growth-promotion. Plant Soil 452, 105–117. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z., Lu, Y., Xu, J., Li, M., Shan, G., Li, Q., 2019. Exploring the characteristics of dissolved organic matter and succession of bacterial community during composting. Bioresour. Technol. 292, 121942. [CrossRef]
- Kean, T., Thanou, M., 2010. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 62, 3–11. [CrossRef]
- Kolton, M., Harel, Y.M., Pasternak, Z., Graber, E.R., Elad, Y., Cytryn, E., 2011. Impact of biochar application to soil on the root-associated bacterial community structure of fully developed greenhouse pepper plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 4924–4930. [CrossRef]
- Larsbrink, J., McKee, L.S., 2020. Chapter Two - Bacteroidetes bacteria in the soil: Glycan acquisition, enzyme secretion, and gliding motility, in: Gadd, G.M., Sariaslani, S. (Eds.), Advances in Applied Microbiology. Academic Press, pp. 63–98. [CrossRef]
- Leogrande, R., Vitti, C., 2019. Use of organic amendments to reclaim saline and sodic soils: a review. Arid Land Res. Manag. 33, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Li, F., Chen, L., Zhang, J., Yin, J., Huang, S., 2017. Bacterial community structure after long-term organic and inorganic fertilization reveals important associations between soil nutrients and specific taxa involved in nutrient transformations. Front. Microbiol. 8. [CrossRef]
- Li, N., Shao, T., Zhou, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Sun, Q., Long, X., Yue, Y., Gao, X., Rengel, Z., 2021. Effects of planting Melia azedarach L. on soil properties and microbial community in saline-alkali soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 32, 2951–2961. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Zhang, Jiejie, Zhang, Jianqiang, Xu, W., Mou, Z., 2019. Characteristics of inorganic phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from the sediments of a eutrophic Lake. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 16, 2141. [CrossRef]
- Liao, H., Zhao, Q., Cui, P., Chen, Z., Yu, Z., Geisen, S., Friman, V.-P., Zhou, S., 2019. Efficient reduction of antibiotic residues and associated resistance genes in tylosin antibiotic fermentation waste using hyperthermophilic composting. Environ. Int. 133, 105203.
- Lima, D.L.D., Santos, S.M., Scherer, H.W., Schneider, R.J., Duarte, A.C., Santos, E.B.H., Esteves, V.I., 2009. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on soil organic matter properties. Geoderma 150, 38–45. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q., Tang, J., Liu, X., Song, B., Zhen, M., Ashbolt, N.J., 2019. Vertical response of microbial community and degrading genes to petroleum hydrocarbon contamination in saline alkaline soil. J. Environ. Sci. 81, 80–92. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., Shang, H., Han, F., Zhang, M., Li, Q., Zhou, W., 2021. Improvement of nitrogen and phosphorus availability by Pseudoalteromonas sp. during salt-washing in saline-alkali soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 168, 104117. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, K., Heidari, G., Khalesro, S., Sohrabi, Y., 2011. Soil management, microorganisms and organic matter interactions: A review. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10, 19840–19849. [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, A., Naganna, S.R., Al-Ansari, N., 2021. Irrigation induced salinity and sodicity hazards on soil and groundwater: an overview of its causes, Impacts and mitigation strategies. Agriculture 11, 983. [CrossRef]
- Munchan, C., Kurata, O., Hatai, K., Hashiba, N., Nakaoka, N., Kawakami, H., 2006. Mass mortality of young striped jack pseudocaranx dentex caused by a fungus Ochroconis humicola. Fish Pathol. 41, 179–182. [CrossRef]
- Munns, R., Tester, M., 2008. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59, 651–681. [CrossRef]
- Orhan, F., 2021. Potential of Halophilic/Halotolerant bacteria in enhancing plant growth under salt stress. Curr. Microbiol. 78, 3708–3719. [CrossRef]
- Qi, R., Lin, W., Gong, K., Han, Z., Ma, H., Zhang, M., Zhang, Q., Gao, Y., Li, J., Zhang, X., 2021. Bacillus co-inoculation alleviated salt stress in seedlings cucumber. Agron.-Basel 11, 966. [CrossRef]
- Qurashi, A.W., Sabri, A.N., 2012. Bacterial exopolysaccharide and biofilm formation stimulate chickpea growth and soil aggregation under salt stress. Braz. J. Microbiol. 43, 1183–1191. [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, R., Hashem, A., Abd_Allah, E.F., 2017. Bacillus: A biological tool for crop improvement through bio-molecular changes in adverse environments. Front. Physiol. 8. [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M., Elrys, A.S., Selem, E., Mohsen, A.A.A., Arnaout, S.M.A.I., El-Sappah, A.H., El-Tarabily, K.A., Desoky, E.-S.M., 2022. Spirulina platensis extract improves the production and defenses of the common bean grown in a heavy metals-contaminated saline soil. J. Environ. Sci. [CrossRef]
- Rajput, L., Imran, A., Mubeen, F., Hafeez, F.Y., 2013. Salt-tolerant pgpr strain Planococcus Rifietoensis promotes the growth and yield of wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) cultivated in saline soil. Pak. J. Bot. 45, 1955–1962. [CrossRef]
- Ribes, J.A., Vanover-Sams, C.L., Baker, D.J., 2000. Zygomycetes in human disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 13, 236–301. [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T., Flouri, T., Nichols, B., Quince, C., Mahé, F., 2016. VSEARCH: a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4, e2584. [CrossRef]
- Seyed Sharifi, R., Khalilzadeh, R., Jalilian, J., 2017. Effects of biofertilizers and cycocel on some physiological and biochemical traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under salinity stress. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 63, 308–318. [CrossRef]
- Shabala, S., Wu, H., Bose, J., 2015. Salt stress sensing and early signalling events in plant roots: Current knowledge and hypothesis. Plant Sci. 241, 109–119. [CrossRef]
- Shi, S., Tian, L., Nasir, F., Bahadur, A., Batool, A., Luo, S., Yang, F., Wang, Z., Tian, C., 2019. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 135, 16–24. [CrossRef]
- Siddikee, Md.A., Chauhan, Puneet.S., Anandham, R., Han, G.-H., Sa, T., 2010. Isolation, characterization, and use for plant growth promotion under salt stress, of ACC deaminase-producing halotolerant bacteria derived from coastal soil. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 1577–1584. [CrossRef]
- Singh, M., Awasthi, A., Soni, S.K., Singh, R., Verma, R.K., Kalra, A., 2015. Complementarity among plant growth promoting traits in rhizospheric bacterial communities promotes plant growth. Sci. Rep. 5, 15500. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S., Singh, M., 2000. Genotypic basis of response to saliniity stress in some crosses of spring wheat Triticum aestivum L. Euphytica 115, 209–214. [CrossRef]
- Sudhir, P., Murthy, S.D.S., 2004. Effects of salt stress on basic processes of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 42, 481–486. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B., Bai, Z., Bao, L., Xue, L., Zhang, S., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhuang, G., Zhuang, X., 2020a. Bacillus subtilis biofertilizer mitigating agricultural ammonia emission and shifting soil nitrogen cycling microbiomes. Environ. Int. 144, 105989. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B., Bai, Z., Li, Y., Li, R., Song, M., Xu, S., Zhang, H., Zhuang, X., 2022a. Emission mitigation of CH4 and N2O during semi-permeable membrane covered hyperthermophilic aerobic composting of livestock manure. J. Clean. Prod. 379, 134850. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B., Gu, L., Bao, L., Zhang, S., Wei, Y., Bai, Z., Zhuang, G., Zhuang, X., 2020b. Application of biofertilizer containing Bacillus subtilis reduced the nitrogen loss in agricultural soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 148, 107911. [CrossRef]
- Sun, B., Li, Y., Song, M., Li, R., Li, Z., Zhuang, G., Bai, Z., Zhuang, X., 2022b. Molecular characterization of the composition and transformation of dissolved organic matter during the semi-permeable membrane covered hyperthermophilic composting. J. Hazard. Mater. 425, 127496. [CrossRef]
- Szabados, L., Savouré, A., 2010. Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci. 15, 89–97. [CrossRef]
- Tejada, M., Garcia, C., Gonzalez, J.L., Hernandez, M.T., 2006. Use of organic amendment as a strategy for saline soil remediation: Influence on the physical, chemical and biological properties of soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 38, 1413–1421. [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P., Singh, K., Pankaj, U., Verma, S.K., Verma, R.K., Patra, D.D., 2017. Effect of organic amendments and microbial application on sodic soil properties and growth of an aromatic crop. Ecol. Eng. 102, 127–136. [CrossRef]
- Tseng, M.J., Liu, C.-W., Yiu, J.-C., 2007. Enhanced tolerance to sulfur dioxide and salt stress of transgenic Chinese cabbage plants expressing both superoxide dismutase and catalase in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 45, 822–833. [CrossRef]
- Velez, M.L., Marfetan, J.A., Salgado Salomon, M.E., Taccari, L.E., 2020. Mortierella species from declining Araucaria araucanatrees in Patagonia, Argentina. For. Pathol. 50, e12591. [CrossRef]
- Visioli, G., Sanangelantoni, A.M., Vamerali, T., Dal Cortivo, C., Blandino, M., 2018. 16S rDNA profiling to reveal the influence of seed-applied biostimulants on the rhizosphere of young maize plants. Molecules 23, 1461. [CrossRef]
- Volk, T.J., 2013. Fungi, in: Levin, S.A. (Ed.), Encyclopedia of Biodiversity (Second Edition). Academic Press, Waltham, pp. 624–640. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T., Chen, Y., Zhang, M., Chen, J., Liu, J., Han, H., Hua, X., 2017. Arabidopsis AMINO ACID PERMEASE1 contributes to salt stress-induced proline uptake from exogenous sources. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 2182. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Bian, Q., Jiang, Y., Zhu, L., Chen, Y., Liang, Y., Sun, B., 2021. Organic amendments drive shifts in microbial community structure and keystone taxa which increase C mineralization across aggregate size classes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 153, 108062. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Hu, M., Xia, Y., Wen, X., Ding, K., 2012. Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in 14 wastewater treatment systems in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78, 7042–7047. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X., Xu, S., Wu, S., Feng, S., Bai, Z., Zhuang, G., Zhuang, X., 2018. Effect of Trichoderma viride biofertilizer on ammonia volatilization from an alkaline soil in Northern China. J. Environ. Sci. 66, 199–207. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S., Zhuang, G., Bai, Z., Cen, Y., Xu, S., Sun, H., Han, X., Zhuang, X., 2018. Mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from acidic soils by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, a plant growth-promoting bacterium. Glob. Change Biol. 24, 2352–2365. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W., Gong, T., Wang, J., Li, G., Liu, Y., Zhen, J., Ning, M., Yue, D., Du, Z., Chen, G., 2020. Effects of compound microbial fertilizer on soil characteristics and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 20, 2740–2748. [CrossRef]
- You, X., Yin, S., Suo, F., Xu, Z., Chu, D., Kong, Q., Zhang, C., Li, Y., Liu, L., 2021. Biochar and fertilizer improved the growth and quality of the ice plant (Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L.) shoots in a coastal soil of Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 775, 144893. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F., Xu, X., Wang, G., Wu, B., Xiao, Y., 2020. Medicago sativa and soil microbiome responses to Trichoderma as a biofertilizer in alkaline-saline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 153, 103573. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Xu, S., Li, C., Zhao, L., Feng, H., Yue, G., Ren, Z., Cheng, G., 2014. The soil carbon/nitrogen ratio and moisture affect microbial community structures in alkaline permafrost-affected soils with different vegetation types on the Tibetan plateau. Res. Microbiol. 165, 128–139. [CrossRef]
- Zou, P., Tian, X., Dong, B., Zhang, C., 2017. Size effects of chitooligomers with certain degrees of polymerization on the chilling tolerance of wheat seedlings. Carbohydr. Polym. 160, 194–202. [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Chao index | Shannon index | Shannoneven index | |||
| Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | |
| CK | 2378±100 c | 415±7 a | 6.23±0.04 a | 4.09±0.14 a | 0.83±0.01 a | 0.06±0.01 a |
| OF | 2729±13 a | 394±25 a | 6.11±0.07 a | 3.07±0.48 a | 0.76±0.02 a | 0.03±0.01 a |
| BF | 2609±131 a | 458±24 a | 6.13±0.27 a | 3.65±0.10 a | 0.81±0.03 a | 0.04±0.01 a |
| HF | 2563±56 b | 410±75 a | 5.89±0.62 a | 2.90±0.73 a | 0.78±0.01 a | 0.02±0.01 a |
| OM | 2555±68 b | 407±23 a | 6.01±0.64 a | 3.23±0.13 a | 0.79±0.02 a | 0.03±0.01 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





