Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
14 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
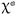 test. Statistical significance was established at p < 0.05.
test. Statistical significance was established at p < 0.05. 3. Results
3.1. Angiostrongylus cantonensis infected rats
3.2. Within-rat parasite community/coinfections
4. Discussion
4.1. Angiostrongylus cantonensis infected rats
4.2. Within-rat parasite community/coinfections
4.3. Host resistance or tolerance?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowie, R.H.; Ansdell, V.; Panosian Dunavan, C.; Rollins, R.L. Neuroangiostrongyliasis: Global Spread of an Emerging Disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., 2022, 107, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foronda, P.; López-González, M.; Miquel, J.; Torres, J.; Segovia, M.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Casanova, J.C.; Valladares, B.; Mas-Coma, S.; Bargues, M.D.; et al. Finding of Parastrongylus cantonensis (Chen, 1935) in Rattus rattus in Tenerife, Canary Islands (Spain). Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Esquivel, C; Sola, J; Delgado-Serra, S.; Puig Riera, M.; Negre, N.; Miranda, M.A.; Jurado-Rivera, J.A. Angiostrongylus cantonensis in North African hedgehogs as vertebrate hosts, Mallorca, Spain, October 2018. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1900489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Gómez-Samblás, M.; Osuna, A.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Fuentes, M.V. Autochthonous Angiostrongylus cantonensis Lungworms in Urban Rats, Valencia, Spain, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 2564–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Gómez-Samblás, M.; Osuna, A.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Fuentes, M.V. Update on the first finding of rat lungworm, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, in Rattus spp. in continental Europe, Valencia, Spain, 2022. Pathogens 2023, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Sanxis-Furió, J.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; Peracho, V.; Montalvo, T.; Fuentes, M.V. First survey on zoonotic helminthosis in urban brown rats (Rattus norvegicus) in Spain and associated public health considerations. Vet Parasitol. 2018, 259, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Trelis, M.; Sáez-Durán, S.; Cifre, S.; Gosálvez, C.; Sanxis-Furió, J.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; Peracho, V.; et al. One Health Approach to Zoonotic Parasites: Molecular Detection of Intestinal Protozoans in an Urban Population of Norway Rats, Rattus norvegicus, in Barcelona, Spain. Pathogens. 2021, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro, M.; Izquierdo, F.; Henriques-Gil, N.; Andrés, I.; Alonso, F.; Fenoy, S.; del Aguila, C. First detection and genotyping of human-associated microsporidia in pigeons from urban parks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 3153–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reischl, U.; Bretagne, S; Krüger, D. ; Ernault, P.; Costa, J.M. Comparison of two DNA targets for the diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis by real-time PCR using fluorescence resonance energy transfer hybridization probes. BMC Infect Dis. 2003, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Puchades, M.T.; Gómez-Samblás, M.; Suárez-Morán, J.M.; Osuna, A.; Sanxis-Furió, J.; Pascual, J.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Franco, S.; Peracho, V.; Montalvo, T.; et al. Leishmaniasis in Norway Rats in Sewers, Barcelona, Spain. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019, 2019 25, 1222–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosálbez, J. Insectivors i rosegadors de Catalunya. Metodologia d’estudi i cataleg faunistic; Ketres editora: Barcelona, Spain, 1987; p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.P.; Lai, D.H.; Zhu, X.Q.; Chen, X.G.; Lun, Z.R. Human angiostrongyliasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2008, 8, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prociv, P.; Spratt, D.M.; Carlisle, M.S. Neuroangistrongyliasis: unresolved issues. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Carrillo, N.; Feliu, C.; Abreu-Acosta, N.; Izquierdo-Rodriguez, E.; Dorta-Guerra, R.; Miquel, J.; Abreu-Yanes, E.; Martin-Alonso, A.; García-Livia, K.; Quispe-Ricalde, M.A.; et al. A Peculiar Distribution of the Emerging Nematode Angiostrongylus cantonensis in the Canary Islands (Spain): Recent Introduction or Isolation Effect? Animals 2021, 11, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherman, C.M.; Ionica, A.M.; Deak, G.; Chisamera, G.B.; Mihalca, A.D. Coinfection with Angiostrongylus chabaudi and Dirofilaria immitis in a wildcat, Felis silvestris from Romania—a case report. Acta Vet. Brno 2019, 88, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, S. Wormy world: comparative tests of theoretical hypotheses on parasite species richness. In Evolutionary Biology of Host-Parasite Relationships: Theory Meets Reality; Poulin, R., Morand, S., Skorping, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2000; pp. 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Rohr, J.R.; Raffel, T.R.; Hall, C.A. Developmental variation in resistance and tolerance in a multi-host–parasite system. Funct. Ecol. 2010, 24, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.S.; Dos Santos Bonfim, T.C.; Junior, A.M.; Tunholi, V.M.; Tunholi-Alves, V.M.; Mota, E.M.; Simoes, R.D.; Santana, A.C.; Hooper, C.; Pinheiro, J.; et al. Hematological and histopathological changes in Rattus norvegicus (Wistar) experimentally infected by Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Chen, 1935). Parasitol. Int. 2014, 63, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Yiyue, X.; Xujin, H.; Minghui, Z.; Mengying, Z.; Yue, H.; Yanqi, W.; Langui, S.; Xin, Z.; Datao, L.; et al. Study on the tolerance and adaptation of rats to Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection. Parasitol Res. 2017, 116, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaumourin, E.; Vourc’h, G.; Gasqui, P.; Vayssier-Taussat, M. The importance of multiparasitism: examining the consequences of co-infections for human and animal health. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protists/Microsporidia species |
Microhabitat | Cycle | n (host) |
P (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blastocystis | small intestine |
M | 8 (6 Rn, 2Rr) |
60 Rn 50 Rr |
| Giardia duodenalis | small intestine |
M | 9 (7 Rn, 2Rr) |
70 Rn 50 Rr |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | small intestine |
M | 1 (1 Rn) |
10 Rn |
| Enterocytoozoon bieneusi | small intestine |
M | 2 (1 Rn, 1 Rr) |
10 Rn 25 Rr |
| Encephalitozoon hellem | small intestine |
M | 1 (1 Rr) |
25 Rr |
| Toxoplasma gondii | brain | D | 6 (5 Rn, 1 Rr) |
50 Rn 25 Rr |
| Helminth species | ||||
|
Brachylaima spp. |
small intestine |
H | 1 (1 Rn) |
10 Rn |
|
Hydatigera taeniaeformis larvae |
liver | H | 5 (4 Rn,1 Rr) |
40 Rn 25 Rr |
|
Hymenolepis nana |
small intestine |
H/M | 3 (3 Rn) |
30 Rn |
|
Hymenolepis diminuta |
small intestine |
H | 4 (3 Rn,1 Rr) |
30 Rn 25 Rr |
| Angiostrongylus cantonensis | pulmonary arteries/brain | H | 14a (10 Rn, 4Rr) |
100 Rn 100 Rr |
|
Calodium hepaticumb |
liver | M | 11 (10 Rn,1 Rr) |
100 Rn 25 Rr |
|
Mastophorus muris |
stomach | H | 2 (1 Rn,1 Rr) |
10 Rn 25 Rr |
|
Eucoleus gastricus |
stomach | M | 3 (3 Rn) |
30 Rn |
|
Trichosomoides crassicauda |
urinary bladder | M | 3 (3 Rn) |
30 Rn |
|
Nippostrongylus brasiliensis |
small intestine/ lungs (larvae) |
M | 9 (8 Rn,1 Rr) |
80 Rn 25 Rr |
|
Heterakis spumosa |
large intestine |
M | 4 (3 Rn, 1Rr) |
30 Rn 25 Rr |
|
Gongylonema neoplasticum |
esophagus/ stomach |
H | 2 (2 Rn) |
20 Rn |
|
Moniliformis moniliformis |
small intestine |
H | 2 (2 Rn) |
20 Rn |
| Protists/Microsporidia species |
Rn Is |
Rn IIs |
Rn IIIo |
Rn IVo |
Rn Vo |
Rn VIo |
Rn VIIp |
Rn VIIIs |
Rn IXs |
Rn* Xs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blastocystis | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| G. duodenalis | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| Cryptosporidium spp. | + | |||||||||
| T. gondii | + | + | + | + | + | |||||
| E. bieneusi | + | |||||||||
| Helminth species | ||||||||||
| Brachylaima spp. | 4 | 4 | ||||||||
| H. taeniaeformis larvae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| H. nana | 1 | 65 | ||||||||
| H. diminuta | 2 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 43 | |||||
| A. cantonensis | 2 | 4 | 7 | 13 | 7 | 3 | 33 | 4 | 19 | 57 |
| C. hepaticum | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| M. muris | 10 | 2 | ||||||||
| E. gastricus | 5 | 9 | 21 | |||||||
| T. crassicauda | 4 | 4 | 14 | |||||||
| N. brasiliensis | 80 | 65 | 31 | 6 | 2 | 25 | HH | HH | ||
| H. spumosa | 9 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| G. neoplasticum | 1 | 3 | ||||||||
| M. moniliformis | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
| Total nº species | 8 | 6 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 3 |
| Protists/Microsporidia species |
Rr* Is 
|
Rr IIp |
Rr IIIo |
Rr* IVo 
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blastocystis | + | + | ||
| G. duodenalis | + | + | ||
| T. gondii | + | |||
| E. hellem | + | |||
| E. bieneusi | + | |||
| Helminth species | ||||
| H. taeniaeformis larvae | 1 | |||
| H. diminuta | 2 | |||
| A. cantonensis | 30 | 9 | 3 | 2 |
| C. hepaticum | + | |||
| M. muris | 2 | |||
| N. brasiliensis | 2 | |||
| H. spumosa | 7 | |||
| Total nº species | 4 | 3 | 6 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





