Submitted:
13 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
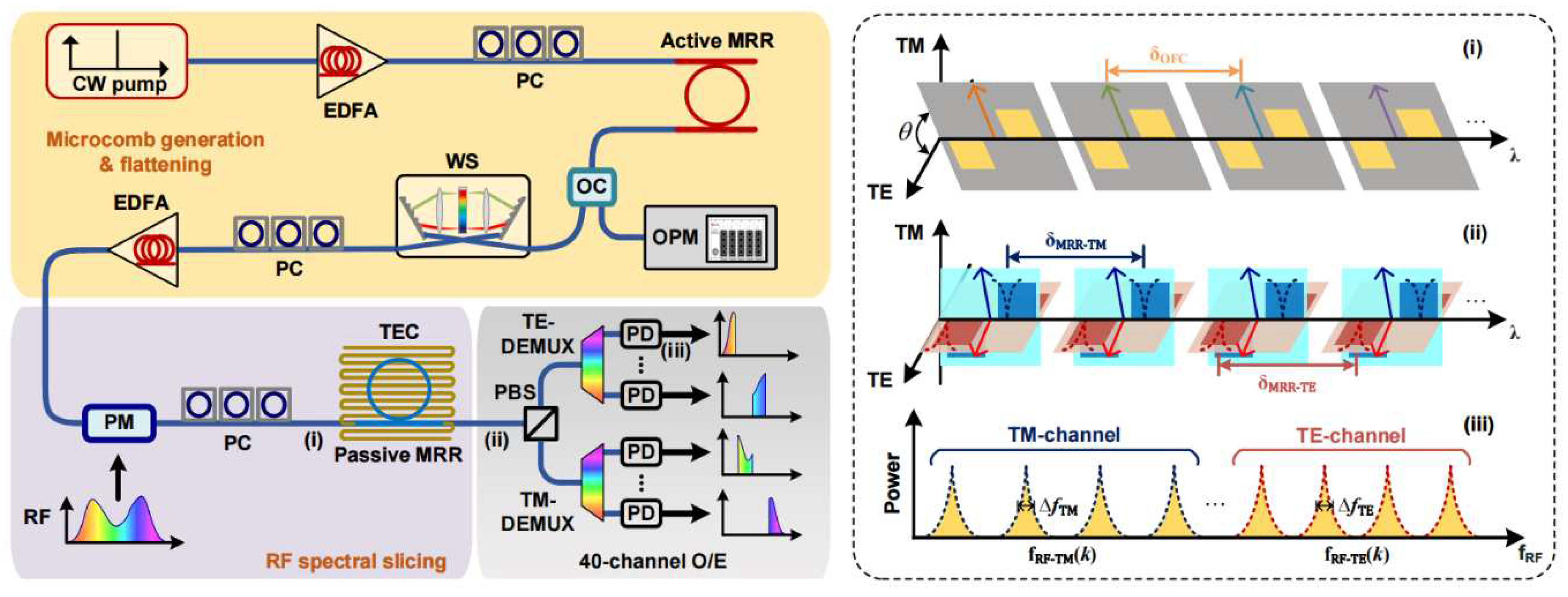
II. Principle
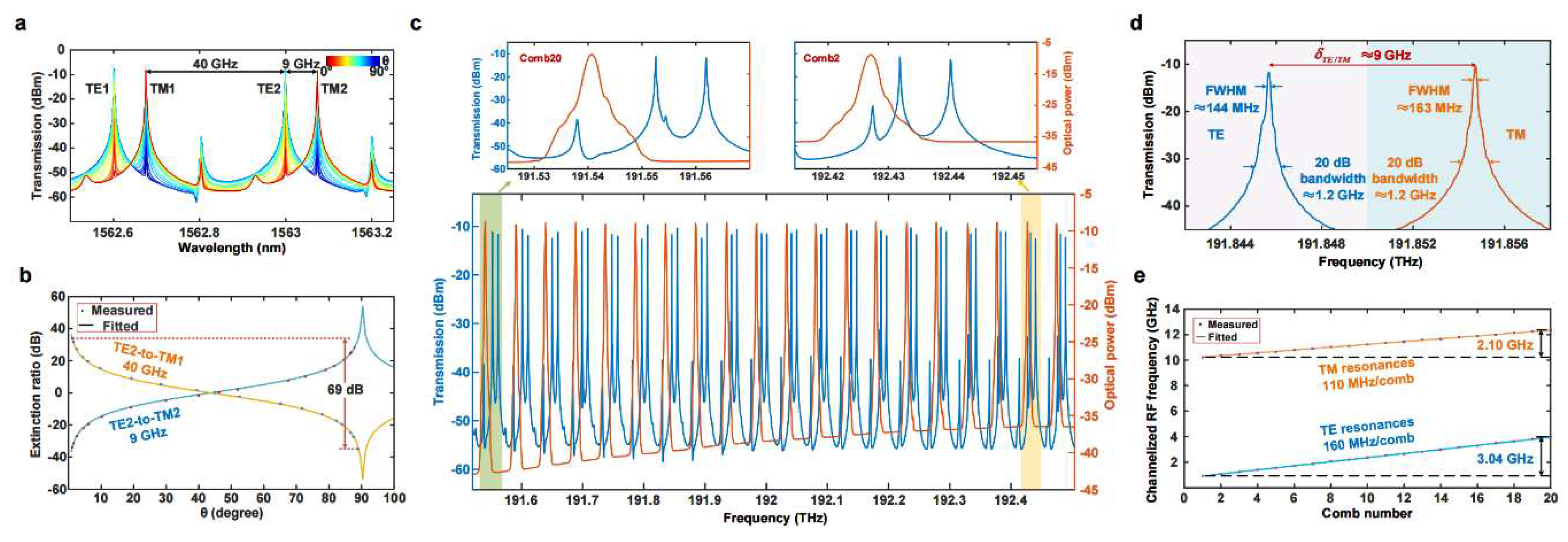
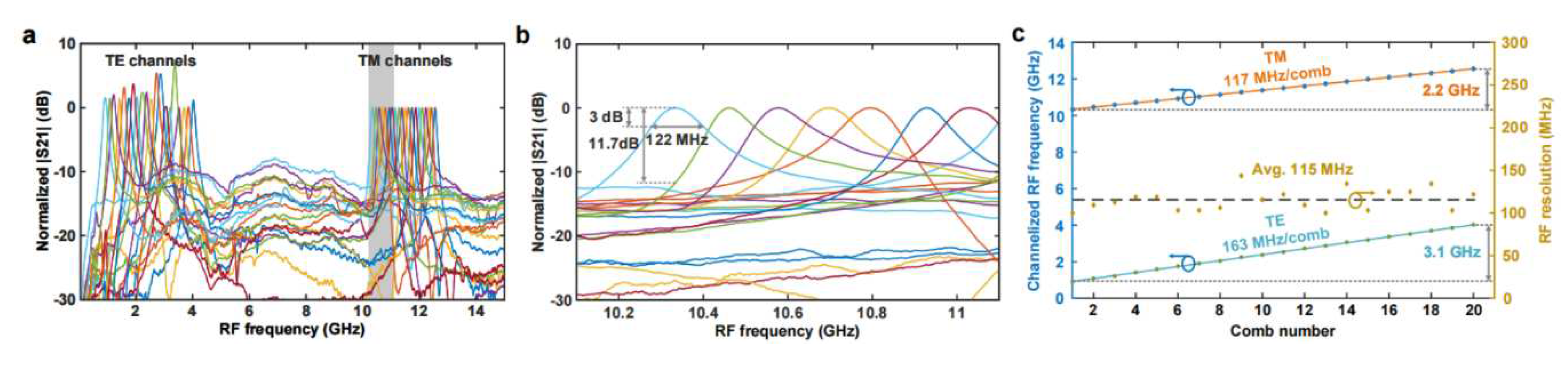
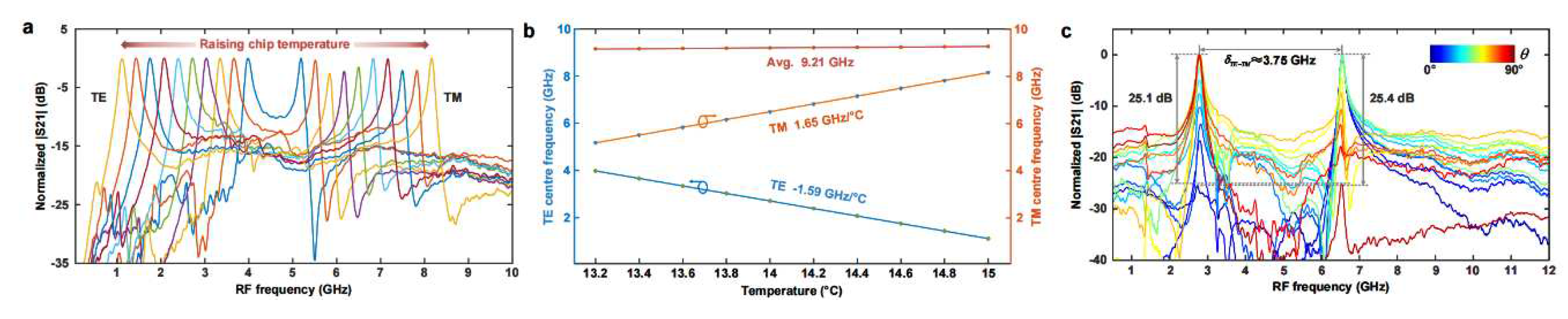
III. Experimental results
IV. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- G. W. Anderson, D. C. Webb, A. E. Spezio, and J. N. Lee, “Advanced channelization for RF, microwave, and millimeterwave applications,” Proc. IEEE, vol. 79, no. 3, pp. 355–388, Mar. 1991. [CrossRef]
- J. Capmany and D. Novak, “Microwave photonics combines two worlds,” Nature Photon, vol. 1, no. 6, pp. 319–330, Jun. 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Yao, “Microwave Photonics,” J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 314–335, Feb. 2009.
- X. Zou, B. Lu, W. Pan, L. Yan, A. Stöhr, and J. Yao, “Photonics for microwave measurements: Photonics for microwave measurements,” Laser & Photonics Reviews, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 711–734, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Wenshen Wang, R. L. Davis, T. J. Jung, R. Lodenkamper, L. J. Lembo, J. C. Brock, and M. C. Wu, “Characterization of a coherent optical RF channelizer based on a diffraction grating,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn., vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 1996–2001, Oct. 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. T. Winnall, A. C. Lindsay, M. W. Austin, J. Canning, and A. Mitchell, “A microwave channelizer and spectroscope based on an integrated optical Bragg-grating Fabry-Perot and integrated hybrid Fresnel lens system,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn., vol. 54, no. 2, pp. 868–872, Feb. 2006. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Strutz and K. J. Williams, “An 8-18-GHz all-optical microwave downconverter with channelization,” IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn., vol. 49, no. 10, pp. 1992–1995, Oct. 2001. [CrossRef]
- C.-S. Brès, S. Zlatanovic, A. O. J. Wiberg, and S. Radic, “Reconfigurable parametric channelized receiver for instantaneous spectral analysis,” Opt. Express, vol. 19, no. 4, p. 3531, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Xiaojun Xie, Yitang Dai, Kun Xu, Jian Niu, Ruixin Wang, Li Yan, and Jintong Lin, “Broadband Photonic RF Channelization Based on Coherent Optical Frequency Combs and I/Q Demodulators,” IEEE Photonics J., vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 1196–1202, Aug. 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. Li, H. Chen, Y. Yu, M. Chen, S. Yang, and S. Xie, “Multiple-frequency measurement based on serial photonic channelization using optical wavelength scanning,” Opt. Lett., vol. 38, no. 22, p. 4781, Nov. 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. Del’Haye, A. Schliesser, O. Arcizet, T. Wilken, R. Holzwarth, and T. J. Kippenberg, “Optical frequency comb generation from a monolithic microresonator,” Nature, vol. 450, no. 7173, pp. 1214–1217, Dec. 2007. [CrossRef]
- N. R. Newbury and W. C. Swann, “Low-noise fiber-laser frequency combs (Invited),” J. Opt. Soc. Am. B, vol. 24, no. 8, p. 1756, Aug. 2007. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, J. Wu, T. G. Nguyen, T. Moein, S. T. Chu, B. E. Little, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, “Photonic microwave true time delays for phased array antennas using a 49 GHz FSR integrated optical micro-comb source [Invited],” Photonics Research, vol. 6, no. 5, pp. B30-B36, May 1. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, J. Wu, T. G. Nguyen, S. T. Chu, B. E. Little, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, “Broadband RF Channelizer Based on an Integrated Optical Frequency Kerr Comb Source,” J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 36, no. 19, pp. 4519–4526, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, M. Tan, J. Wu, A. Boes, T. G. Nguyen, S. T. Chu, B. E. Little, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, “Broadband Photonic RF Channelizer With 92 Channels Based on a Soliton Crystal Microcomb,” J. Lightwave Technol., vol. 38, no. 18, pp. 5116–5121, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Bianucci, C. R. Fietz, J. W. Robertson, G. Shvets, and C.-K. Shih, “Whispering gallery mode microresonators as polarization converters,” Opt. Lett., vol. 32, no. 15, p. 2224, Aug. 2007. [CrossRef]
- D. J. Moss, R. Morandotti, A. L. Gaeta, and M. Lipson, “New CMOS-compatible platforms based on silicon nitride and Hydex for nonlinear optics,” Nature Photon, vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 597–607, Aug. 2013. [CrossRef]
- B. E. Little et al., “Very high-order microring resonator filters for WDM applications,” IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., vol. 16, no. 10, pp. 2263–2265, Oct. 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. S. Levy, A. Gondarenko, M. A. Foster, A. C. Turner-Foster, A. L. Gaeta, and M. Lipson, “CMOS-compatible multiple-wavelength oscillator for on-chip optical interconnects,” Nat. Photonics, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 37-40, Jan. 2010. [CrossRef]
- L. Razzari, et al., “CMOS-compatible integrated optical hyper-parametric oscillator,” Nature Photonics, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 41-45, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Yang Sun, Jiayang Wu, Mengxi Tan, Xingyuan Xu, Yang Li, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, and David Moss, “Applications of optical micro-combs”, Advances in Optics and Photonics 15 (1) 86-175 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Bao, C., et al., Direct soliton generation in microresonators, Opt. Lett, 42, 2519 (2017). [CrossRef]
- M.Ferrera et al., “CMOS compatible integrated all-optical RF spectrum analyzer”, Optics Express, vol. 22, no. 18, 21488 - 21498 (2014). [CrossRef]
- M. Kues, et al., “Passively modelocked laser with an ultra-narrow spectral width”, Nature Photonics, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 159, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Ferrera, et al., “Low-power continuous-wave nonlinear optics in doped silica glass integrated waveguide structures,” Nature Photonics, vol. 2, no. 12, pp. 737-740, 2008. [CrossRef]
- M.Ferrera et al.“On-Chip ultra-fast 1st and 2nd order CMOS compatible all-optical integration”, Opt. Express, vol. 19, (23)pp. 23153-23161 (2011). [CrossRef]
- D. Duchesne, M. Peccianti, M. R. E. Lamont, et al., “Supercontinuum generation in a high index doped silica glass spiral waveguide,” Optics Express, vol. 18, no, 2, pp. 923-930, 2010. [CrossRef]
- H Bao, L Olivieri, M Rowley, ST Chu, BE Little, R Morandotti, DJ Moss,... “Turing patterns in a fiber laser with a nested microresonator: Robust and controllable microcomb generation”, Physical Review Research 2 (2), 023395 (2020). [CrossRef]
- M. Ferrera, et al., “On-chip CMOS-compatible all-optical integrator”, Nature Communications, vol. 1, Article 29, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. Pasquazi, et al., “All-optical wavelength conversion in an integrated ring resonator,” Optics Express, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 3858-3863, 2010. [CrossRef]
- A. Pasquazi, Y. Park, J. Azana, et al., “Efficient wavelength conversion and net parametric gain via Four Wave Mixing in a high index doped silica waveguide,” Optics Express, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 7634-7641, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Peccianti, M. Ferrera, L. Razzari, et al., “Subpicosecond optical pulse compression via an integrated nonlinear chirper,” Optics Express, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 7625-7633, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Little, B. E. et al., “Very high-order microring resonator filters for WDM applications”, IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 16, 2263–2265 (2004). [CrossRef]
- M. Ferrera et al., “Low Power CW Parametric Mixing in a Low Dispersion High Index Doped Silica Glass Micro-Ring Resonator with Q-factor > 1 Million”, Optics Express, vol.17, no. 16, pp. 14098–14103 (2009). [CrossRef]
- M. Peccianti, et al., “Demonstration of an ultrafast nonlinear microcavity modelocked laser”, Nature Communications, vol. 3, pp. 765, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. Pasquazi, et al., “Self-locked optical parametric oscillation in a CMOS compatible microring resonator: a route to robust optical frequency comb generation on a chip,” Optics Express, vol. 21, no. 11, pp. 13333-13341, 2013. [CrossRef]
- A. Pasquazi, et al., “Stable, dual mode, high repetition rate mode-locked laser based on a microring resonator,” Optics Express, vol. 20, no. 24, pp. 27355-27362, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Pasquazi, A. et al. Micro-combs: a novel generation of optical sources. Physics Reports 729, 1-81 (2018). [CrossRef]
- H. Bao, et al., Laser cavity-soliton microcombs, Nature Photonics, vol. 13, no. 6, pp. 384-389, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Antonio Cutrona, Maxwell Rowley, Debayan Das, Luana Olivieri, Luke Peters, Sai T. Chu, Brent L. Little, Roberto Morandotti, David J. Moss, Juan Sebastian Totero Gongora, Marco Peccianti, Alessia Pasquazi, “High Conversion Efficiency in Laser Cavity-Soliton Microcombs”, Optics Express Vol. 30, Issue 22, pp. 39816-39825 (2022). [CrossRef]
- M.Rowley, P.Hanzard, A.Cutrona, H.Bao, S.Chu, B.Little, R.Morandotti, D. J. Moss, G. Oppo, J. Gongora, M. Peccianti and A. Pasquazi, “Self-emergence of robust solitons in a micro-cavity”, Nature 608 (7922) 303–309 (2022). [CrossRef]
- A. Cutrona, M. Rowley, A. Bendahmane, V. Cecconi,L. Peters, L. Olivieri, B. E. Little, S. T. Chu, S. Stivala, R. Morandotti, D. J. Moss, J. S. Totero-Gongora, M. Peccianti, A. Pasquazi, “Nonlocal bonding of a soliton and a blue-detuned state in a microcomb laser”, Nature Communications Physics 6 (2023). [CrossRef]
- A. Cutrona, M. Rowley, A. Bendahmane, V. Cecconi,L. Peters, L. Olivieri, B. E. Little, S. T. Chu, S. Stivala, R. Morandotti, D. J. Moss, J. S. Totero-Gongora, M. Peccianti, A. Pasquazi, “Stability Properties of Laser Cavity-Solitons for Metrological Applications”, Applied Physics Letters 122 (12) 121104 (2023). [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, M. Tan, J. Wu, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, “Microcomb-based photonic RF signal processing”, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 31 no. 23 1854-1857, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Xu, et al., “Advanced adaptive photonic RF filters with 80 taps based on an integrated optical micro-comb source,” Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 1288-1295 (2019). [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “Photonic RF and microwave integrator with soliton crystal microcombs”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 67, no. 12, pp. 3582-3586, 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “High performance RF filters via bandwidth scaling with Kerr micro-combs,” APL Photonics, vol. 4 (2) 026102. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, et al., “Microwave and RF photonic fractional Hilbert transformer based on a 50 GHz Kerr micro-comb”, Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 37, no. 24, pp. 6097 – 6104, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, et al., “RF and microwave fractional differentiator based on photonics”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems: Express Briefs, vol. 67, no.11, pp. 2767-2771, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, et al., “Photonic RF arbitrary waveform generator based on a soliton crystal micro-comb source”, Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 38, no. 22, pp. 6221-6226 (2020). [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, X. Xu, J. Wu, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, “RF and microwave high bandwidth signal processing based on Kerr Micro-combs”, Advances in Physics X, VOL. 6, NO. 1, 1838946 (2021). [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “Advanced RF and microwave functions based on an integrated optical frequency comb source,” Opt. Express, vol. 26 (3) 2569 (2018). [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, X. Xu, J. Wu, B. Corcoran, A. Boes, T. G. Nguyen, S. T. Chu, B. E. Little, R.Morandotti, A. Lowery, A. Mitchell, and D. J. Moss, ““Highly Versatile Broadband RF Photonic Fractional Hilbert Transformer Based on a Kerr Soliton Crystal Microcomb”, Journal of Lightwave Technology vol. 39 (24) 7581-7587 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. et al. RF Photonics: An Optical Microcombs’ Perspective. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics Vol. 24, 6101020, 1-20 (2018). [CrossRef]
- T. G. Nguyen et al., “Integrated frequency comb source-based Hilbert transformer for wideband microwave photonic phase analysis,” Opt. Express, vol. 23, no. 17, pp. 22087-22097, Aug. 2015. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “Continuously tunable orthogonally polarized RF optical single sideband generator based on micro-ring resonators,” Journal of Optics, vol. 20, no. 11, 115701. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “Orthogonally polarized RF optical single sideband generation and dual-channel equalization based on an integrated microring resonator,” Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 36, no. 20, pp. 4808-4818. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “Photonic RF phase-encoded signal generation with a microcomb source”, J. Lightwave Technology, vol. 38, no. 7, 1722-1727, 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., Broadband microwave frequency conversion based on an integrated optical micro-comb source”, Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 38 no. 2, pp. 332-338, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Tan, et al., “Photonic RF and microwave filters based on 49GHz and 200GHz Kerr microcombs”, Optics Comm. vol. 465,125563, Feb. 22. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Tan et al., “Orthogonally polarized Photonic Radio Frequency single sideband generation with integrated micro-ring resonators”, IOP Journal of Semiconductors, Vol. 42 (4), 041305 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Mengxi Tan, X. Xu, J. Wu, T. G. Nguyen, S. T. Chu, B. E. Little, R. Morandotti, A. Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Photonic Radio Frequency Channelizers based on Kerr Optical Micro-combs”, IOP Journal of Semiconductors Vol. 42 (4), 041302 (2021). [CrossRef]
- B. Corcoran, et al., “Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fiber with a single chip source”, Nature Communications, vol. 11, Article:2568, 2020. [CrossRef]
- X. Xu et al., “Photonic perceptron based on a Kerr microcomb for scalable high speed optical neural networks”, Laser and Photonics Reviews, vol. 14, no. 8, 2000070 (2020). [CrossRef]
- X. Xu, et al., “11 TOPs photonic convolutional accelerator for optical neural networks”, Nature 589, 44-51 (2021). [CrossRef]
- X. Xu et al., “Neuromorphic computing based on wavelength-division multiplexing”, 28 IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics Vol. 29 Issue: 2, Article 7400112 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Yunping Bai, Xingyuan Xu,1, Mengxi Tan, Yang Sun, Yang Li, Jiayang Wu, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, Kun Xu, and David J. Moss, “Photonic multiplexing techniques for neuromorphic computing”, Nanophotonics 12 (5): 795–817 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Chawaphon Prayoonyong, Andreas Boes, Xingyuan Xu, Mengxi Tan, Sai T. Chu, Brent E. Little, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, David J. Moss, and Bill Corcoran, “Frequency comb distillation for optical superchannel transmission”, Journal of Lightwave Technology 39 (23) 7383-7392 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Mengxi Tan, Xingyuan Xu, Jiayang Wu, Bill Corcoran, Andreas Boes, Thach G. Nguyen, Sai T. Chu, Brent E. Little, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Integral order photonic RF signal processors based on a soliton crystal micro-comb source”, IOP Journal of Optics 23 (11) 125701 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Yang Sun, Jiayang Wu, Yang Li, Xingyuan Xu, Guanghui Ren, Mengxi Tan, Sai Tak Chu, Brent E. Little, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Performance analysis of microcomb-based microwave photonic transversal signal processors with experimental errors”, Journal of Lightwave Technology Vol. 41 Special Issue on Microwave Photonics (2023). [CrossRef]
- Mengxi Tan, Xingyuan Xu, Andreas Boes, Bill Corcoran, Thach G. Nguyen, Sai T. Chu, Brent E. Little, Roberto Morandotti, Jiayang Wu, Arnan Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Photonic signal processor for real-time video image processing at 17 Tb/s”, Communications Engineering Vol. 2 (2023).
- Mengxi Tan, Xingyuan Xu, Jiayang Wu, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Photonic RF and microwave filters based on 49GHz and 200GHz Kerr microcombs”, Optics Communications, 465, Article: 125563 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Yang Sun, Jiayang Wu, Yang Li, Mengxi Tan, Xingyuan Xu, Sai Chu, Brent Little, Roberto Morandotti, Arnan Mitchell, and David J. Moss, “Quantifying the Accuracy of Microcomb-based Photonic RF Transversal Signal Processors”, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 29 no. 6, pp. 1-17, Art no. 7500317 (2023). [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



