Submitted:
10 November 2023
Posted:
13 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Computational lithography model with subdomain division
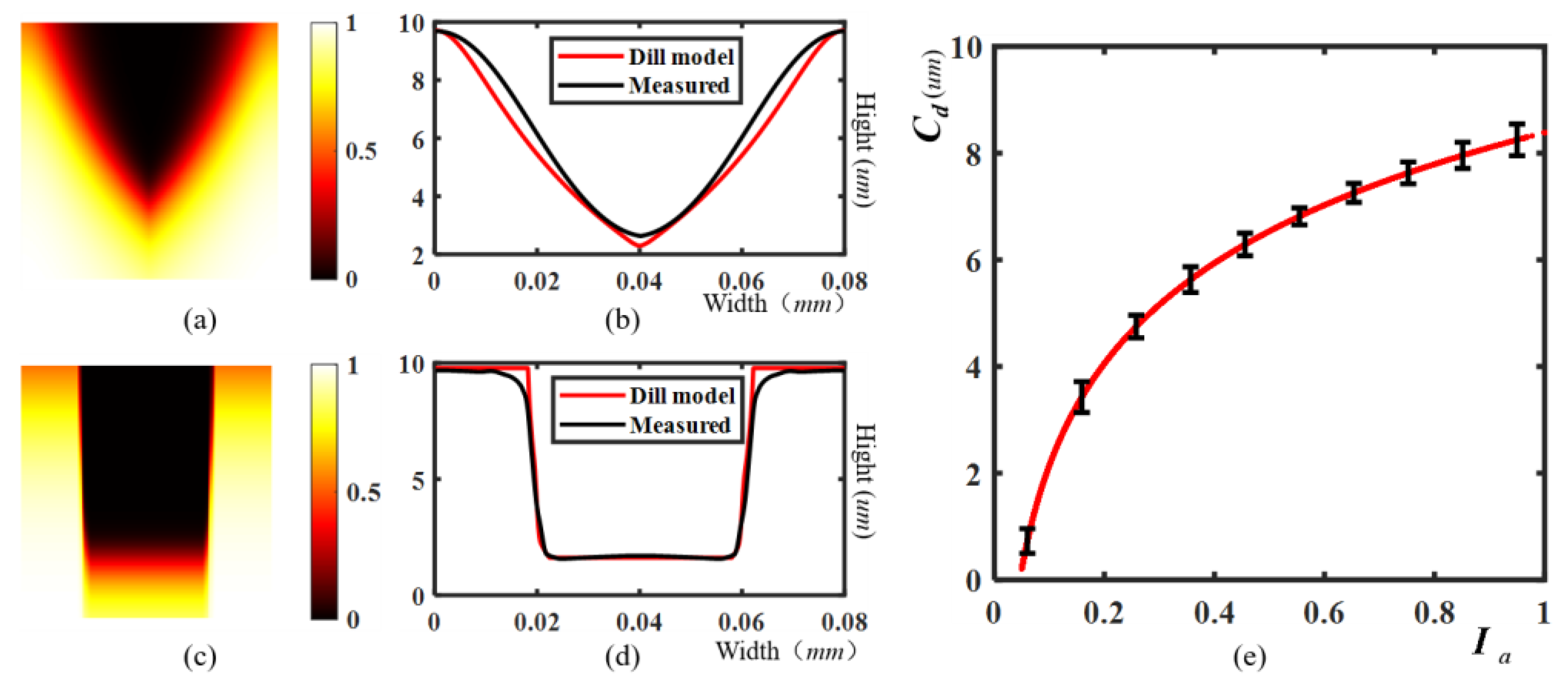
2.1. Forward imaging model
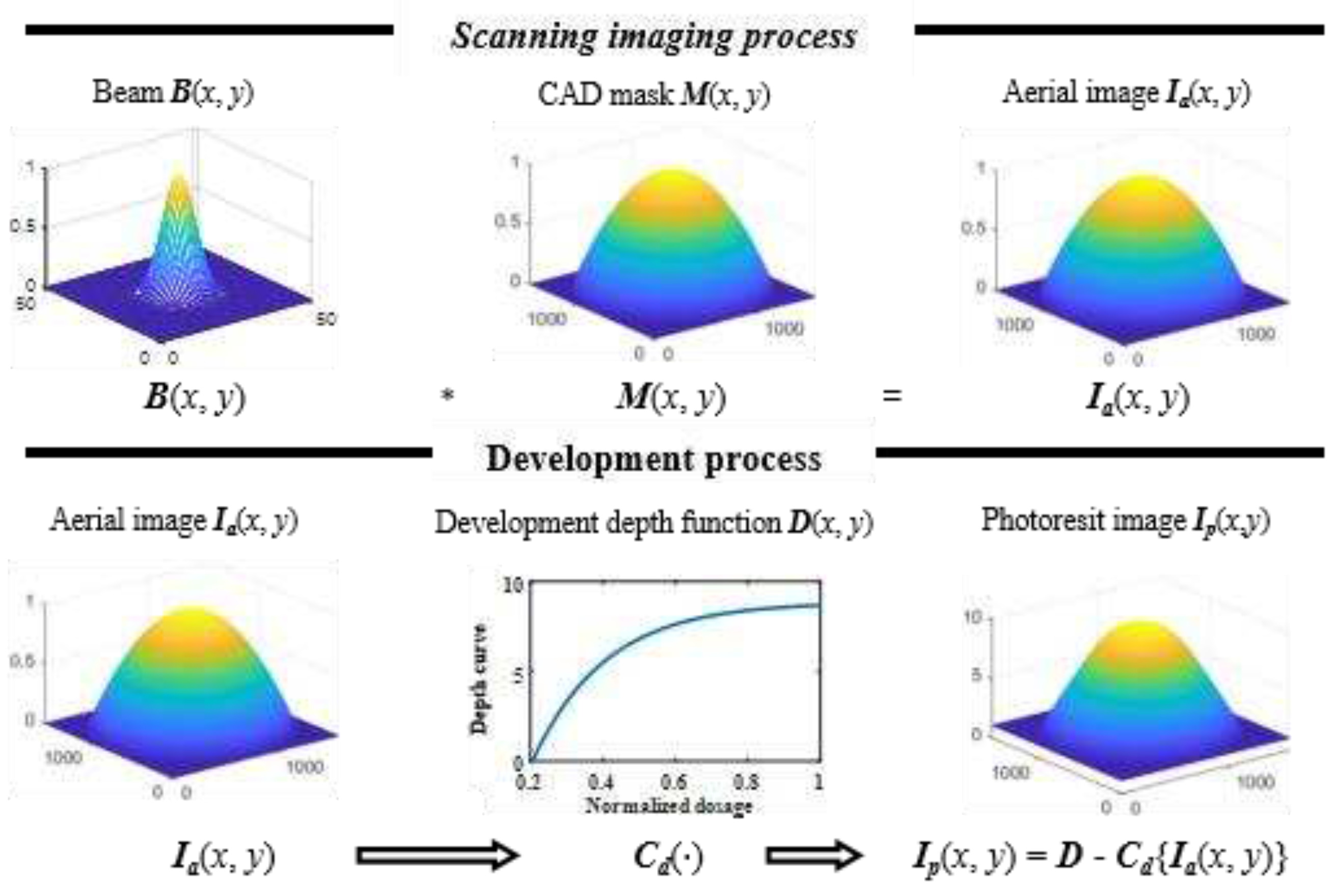
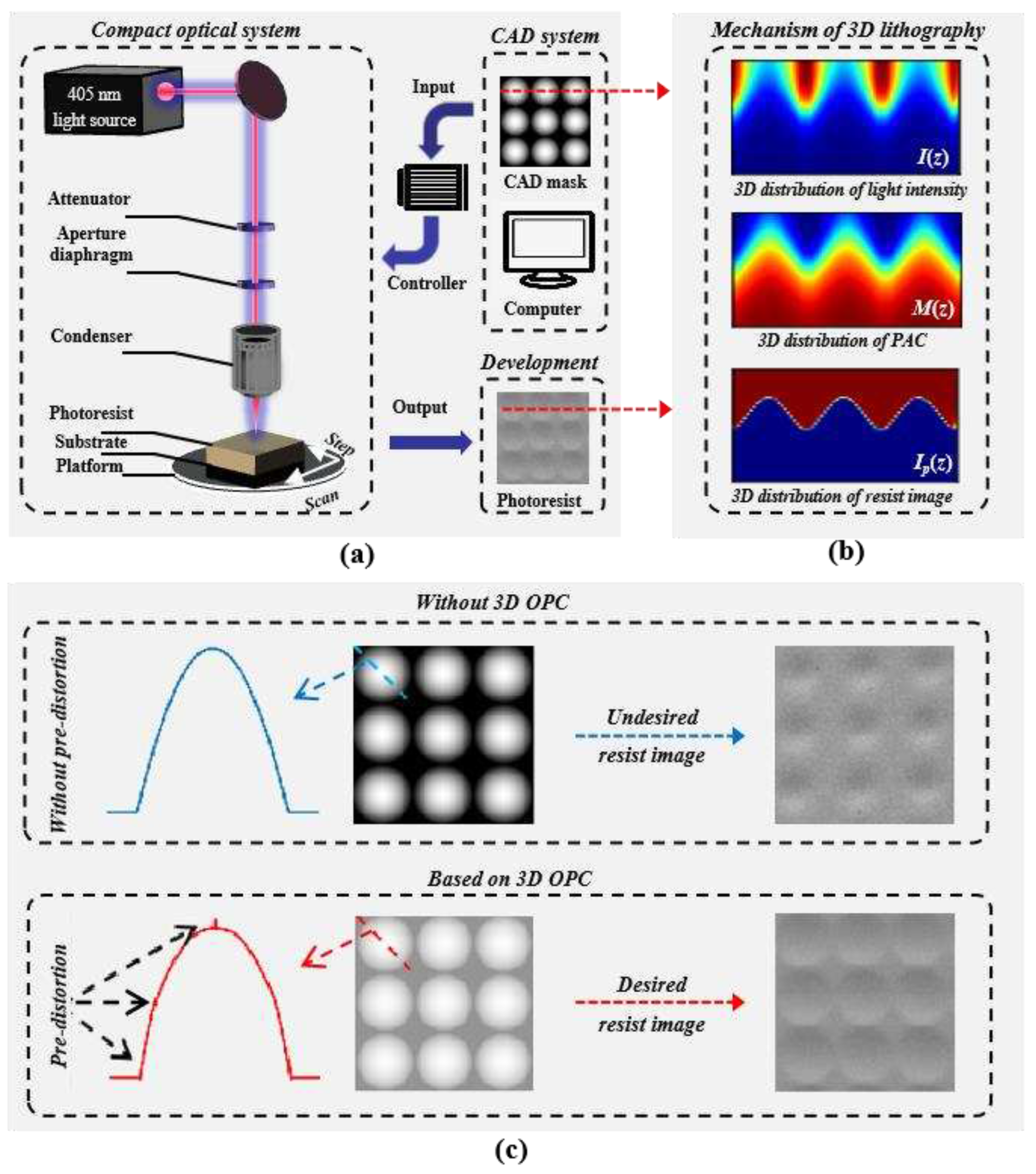
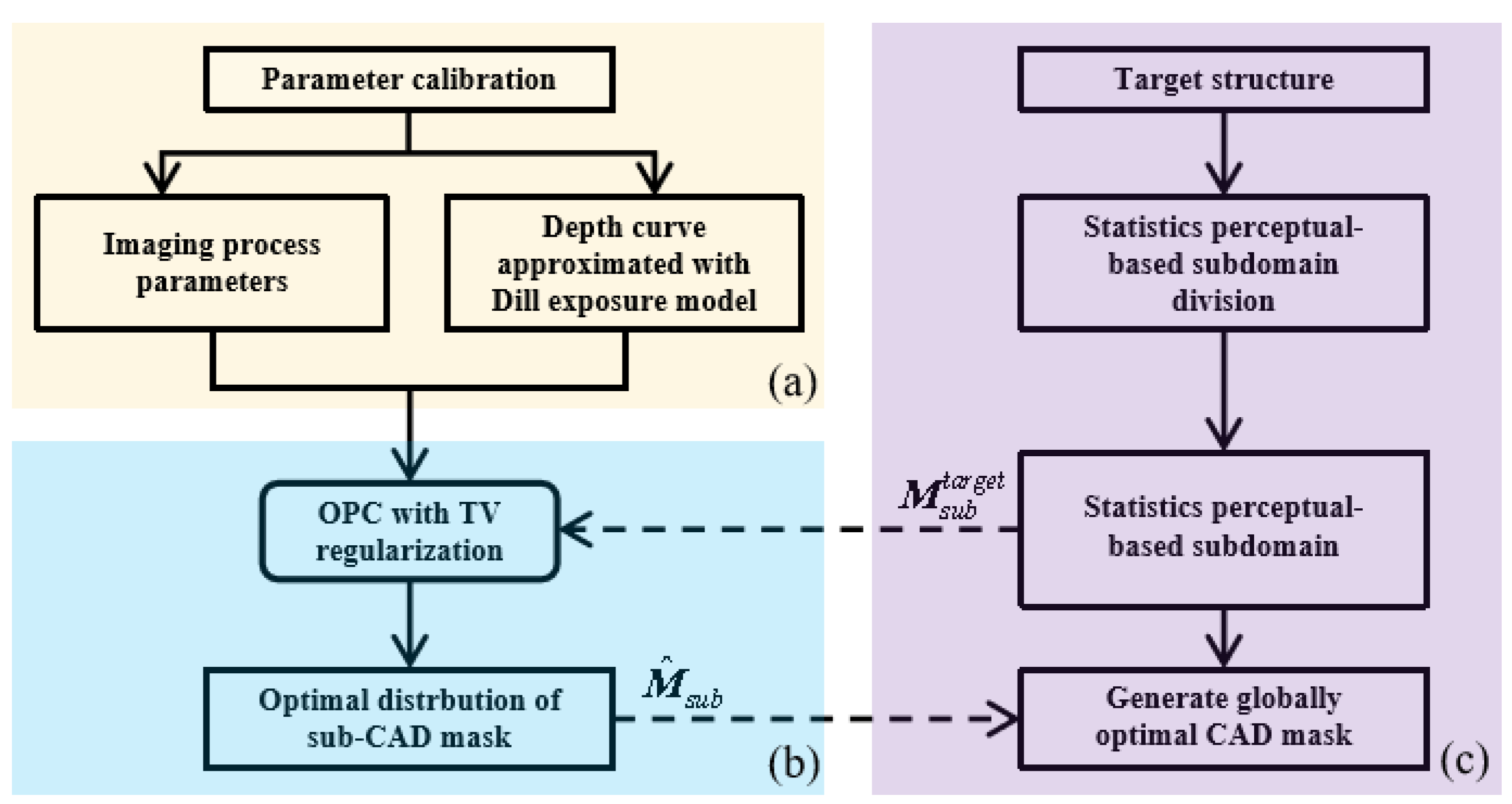
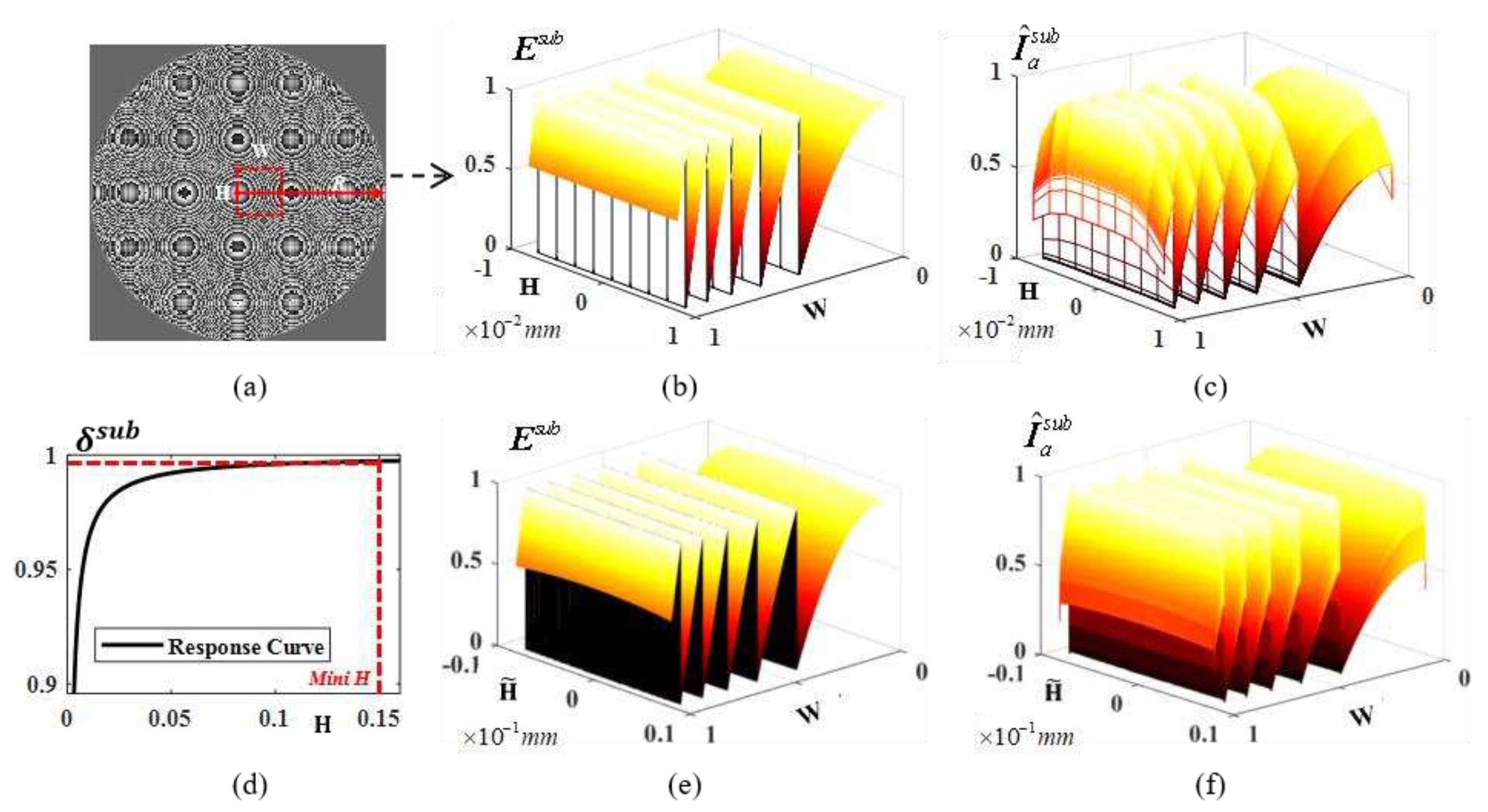
2.2. Inverse optimization method with statistics subdomain division
2.3. Accelerated algorithms
3. Fabrication of the Fresnel lens
3.1. Design of the Fresnel lens
3.2. Equipment and process parameters
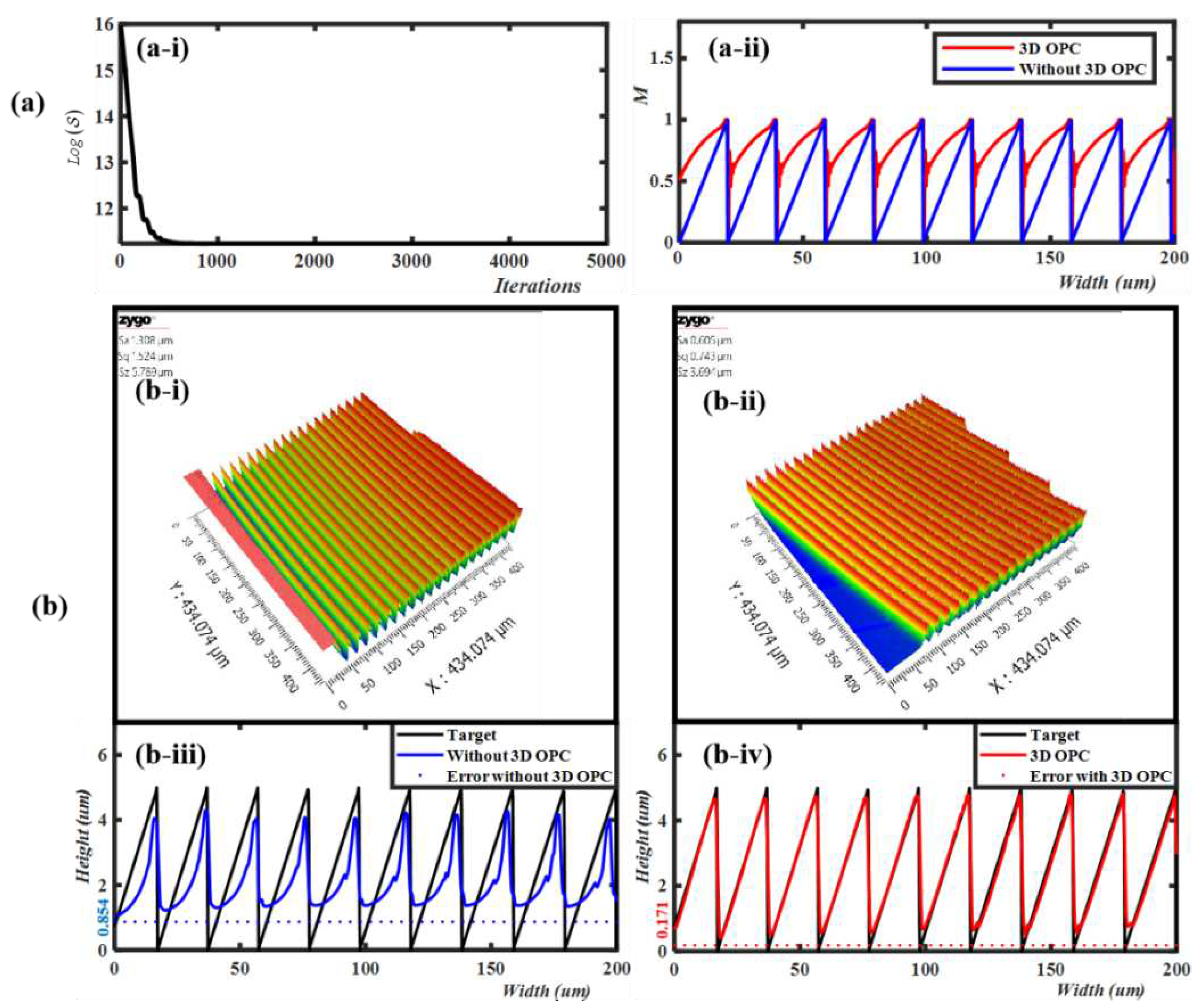
3.3. Simulation parameters of 3D OPC
3.4. Results and Discussion
4. Application of the Fresnel lens
4.1. Fabrication of the transferred Fresnel lens
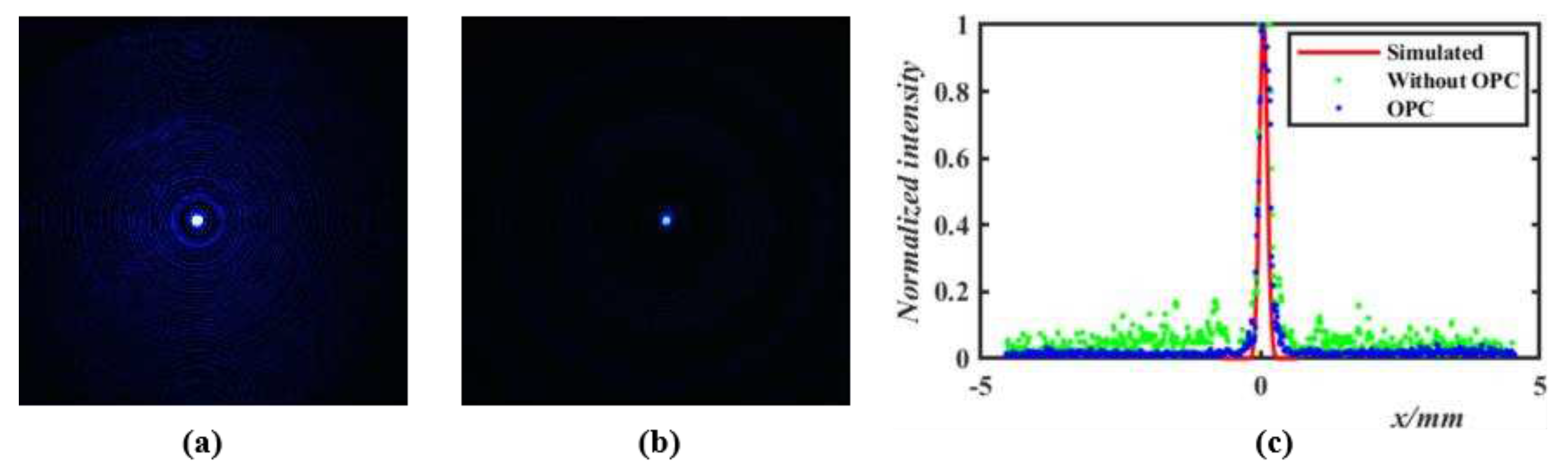
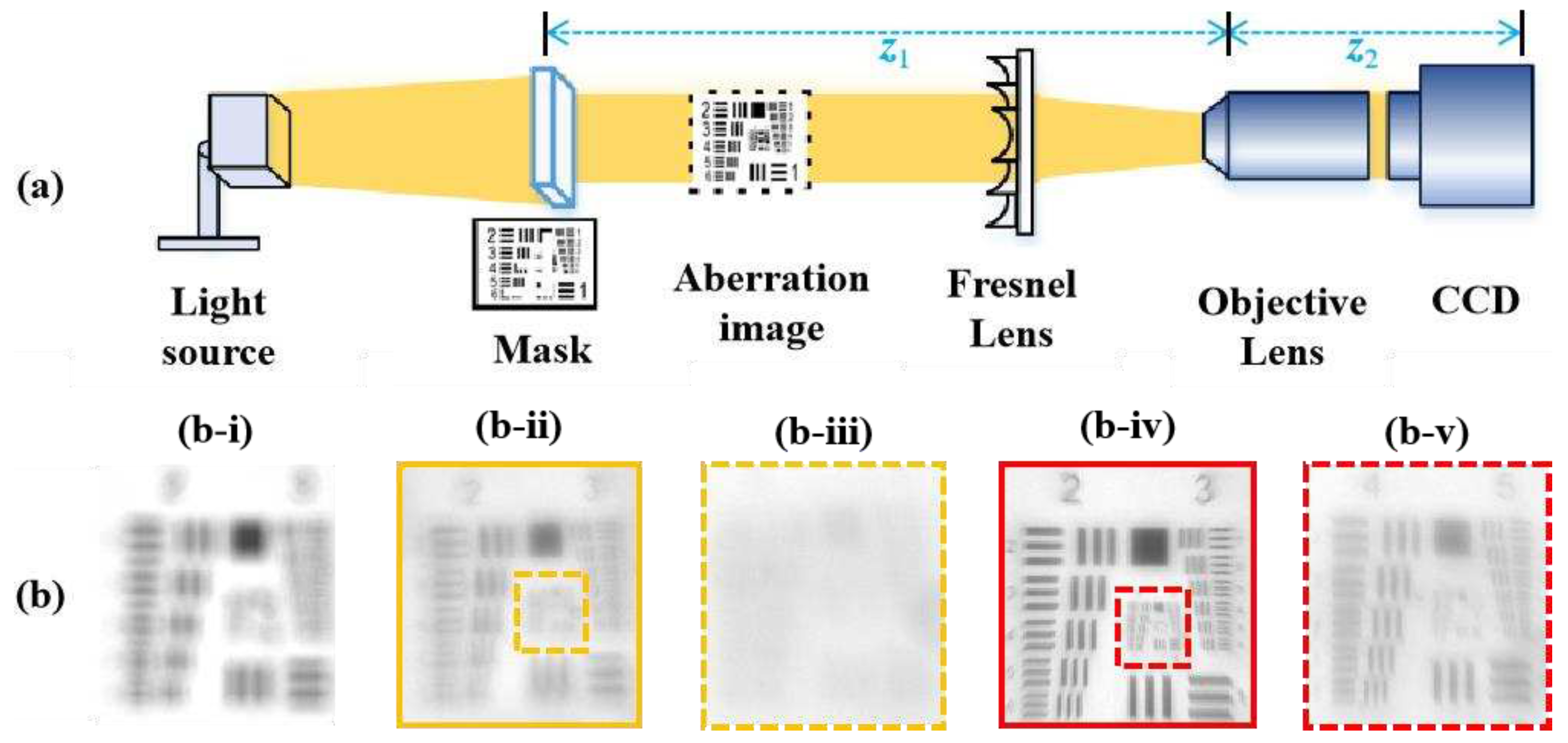
4.2. Vision-correcting System
4.3. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- T. Trantidou, M. S. Friddin, K. B. Gan, L. Han, G. Bolognesi, N. J. Brooks, and O. Ces. Mask-free laser lithography for rapid and low-cost microfluidic device fabrication. Analytical Chemistry 2018, 90, 13915-13921. [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, S. Köble, S. Schweiger, Y. K. Chiang, S. Marburg, and D. A. Powell. Microacoustic metagratings at ultra-high frequencies fabricated by two-photon lithography. Advanced Science 2022, 9, 2198-3844. [CrossRef]
- M. Guizar-Sicairos, I. Johnson, A. Diaz, M. Holler, P. Karvinen, H.-C. Stadler, R. Dinapoli, O. Bunk, and A. Menzel. High-throughput ptychography using Eiger: scanning X-ray nano-imaging of extended regions. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 14859–14870. [CrossRef]
- S. Achenbach, S. Hengsbach, J. Schulz, and J. Mohr. Optimization of laser writer-based UV lithography with high magnification optics to pattern X-ray lithography mask templates. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 2975–2983. [CrossRef]
- Lin, V., Liu, X., Huo, T., and Zheng, G. Design and fabrication of long-focal-length microlens arrays for Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensors. Micro & Nano Letters 2011, 6 (7), 523-526. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang, W. Zhou, Neil J. Naples, and Allen Y. Yi. Fabrication of an infrared Shack–Hartmann sensor by combining high-speed single-point diamond milling and precision compression molding processes. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3598-3605. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X. T. et al. Fabrication of large-Scale microlens arrays based on screen printing for integral imaging 3D display. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2016, 8, 24248-24255. [CrossRef]
- J. Hong, Y. Kim, S. Park, J. Hong, S. Min, S. Lee, and B. Lee, 3D/2D convertible projection-type integral imaging using concave half mirror array. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 20628-20637. [CrossRef]
- S. Luan, P. Xu, Y. Zhang, L. Xue, Y. Song, and C. Gui. Flexible Superhydrophobic Microlens Arrays for Humid Outdoor Environment Applications. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2022, 14, 53433-53441. [CrossRef]
- S. Luan, H. Cao, H. Deng, G. Zheng, Y. Song, and C. Gui. Artificial Hyper Compound Eyes Enable Variable-Focus Imaging on both Curved and Flat Surfaces. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2022, 14, 46112-46121. [CrossRef]
- S. Su, J. Liang, X. Li, W. Xin, X. Ye, J. Xiao, J. Xu, L. Chen, and P. Yin. Hierarchical Artificial Compound Eyes with Wide Field-of-View and Antireflection Properties Prepared by Nanotip-Focused Electrohydrodynamic Jet Printing. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, 13, 60625-60635. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, W. et al. Single-shot lensless imaging with fresnel zone aperture and incoherent illumination. Light: Science and Applications 2020, 9, 53. [CrossRef]
- Y. Ma, J. Wu, S. Chen, and L. Cao. Explicit-restriction convolutional framework for lensless imaging. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 15266-15278. [CrossRef]
- V. Vu, S. Hasan, H. Youn, Y. Park, and H. Lee. Imaging performance of an ultra-precision machining-based Fresnel lens in ophthalmic devices. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 32068-32080. [CrossRef]
- V. Vu, H. Yeon, H. Youn, J. Lee, and H. Lee. High diopter spectacle using a flexible Fresnel lens with a combination of grooves. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 38371-38382. [CrossRef]
- X. Dun, H. Ikoma, G. Wetzstein, Z. Wang, X. Cheng, and Y. Peng. Learned rotationally symmetric diffractive achromat for full-spectrum computational imaging. Optica 2020, 7, 913-922. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X., Zhao, Y., Ye, X. et al. Large-scale achromatic flat lens by light frequency-domain coherence optimization. Light: Science and Applications 2022, 11, 323. [CrossRef]
- H. Arguello, S. Pinilla, Y. Peng, H. Ikoma, J. Bacca, and G.Wetzstein. Shift-variant color-coded diffractive spectral imaging system. Optica 2021, 8, 1424-1434. [CrossRef]
- V. Sitzmann, S. Diamond, Y. Peng, X. Dun, S. Boyd, W. Heidrich, F. Heide, and G. Wetzstein. End-to-end optimization of optics and image processing for achromatic extended depth of field and super-resolution imaging. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2018, 37, pp. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- S. Luan, F. Peng, G. Zheng, C. Gui, Y. Song, S. Liu. High-speed, large-area and high-precision fabrication of aspheric micro-lens array based on 12-bit direct laser writing lithography. Light: Advanced Manufacturing 2022, 3, 47. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, F. Peng, S. Luan, H. Wan, Y. Song, and C. Gui. 3D OPC method for controlling the morphology of micro structures in laser direct writing. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 3212-3226. [CrossRef]
- A. J. Fleming, A. G. Wills, and B. S. Routley. Exposure optimization in scanning laser lithography. IEEE Potentials 2016, 35, pp. 33–39. [CrossRef]
- O. T. Ghalehbeygi, J. O'Connor, B. S. Routley and A. J. Fleming. Iterative Deconvolution for Exposure Planning in Scanning Laser Lithography. In Proceedings of 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC), Milwaukee, WI, 27-29 June, 2018 pp. 6684-6689.
- O. T. Ghalehbeygi, A. G. Wills, B. S. Routley, and A. J. Fleming. Gradient-based optimization for efficient exposure planning in maskless lithography. J. Micro/Nanolithogr., MEMS, MOEMS 2017, 16. [CrossRef]
- A. J. Fleming, O. T. Ghalehbeygi, B. S. Routley, and A. G. Wills. Scanning laser lithography with constrainedquadratic exposure optimization. IEEE Trans. Contr. Syst. Technol. 2019, 27, 2221–2228. [CrossRef]
- X. Sun, S. Yin, H. Jiang, W. Zhang, M. Gao, J. Du, and C. Du. U-Net convolutional neural network-based modification method for precise fabrication of three-dimensional microstructures using laser direct writing lithography. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 6236. [CrossRef]
- W. Lv, S. Liu, Q. Xia, X. Wu, Y. Shen and E. Y. Lam. Level-set-based inverse lithography for mask synthesis using the conjugate gradient and an optimal time step. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B. 2013, 31, 041605–041605–13. [CrossRef]
- J. Li and E. Y. Lam. Robust source and mask optimization compensating for mask topography effects in computational lithography. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 9471-9485. [CrossRef]
- J. Li, S. Liu and E. Y. Lam. Efficient source and mask optimization with augmented lagrangian methods in optical lithography. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8076–8090. [CrossRef]
- X. Ma, D. Shi, Z. Wang, Y. Li, and G. R. Arce. Lithographic source optimization based on adaptive projection compressive sensing. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 7131–7149. [CrossRef]
- X. Ma, Z. Wang, Y. Li, G. R. Arce, L. Dong, and J. Garcia-Frias. Fast optical proximity correction method based on nonlinear compressive sensing. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 14479–14498. [CrossRef]
- Y. Shen, F. Peng, and Z. Zhang. Efficient optical proximity correction based on semi-implicit additive operator splitting. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 1520-1528. [CrossRef]
- Y. Shen, F. Peng, and Z. Zhang. Semi-implicit level set formulation for lithographic source and mask optimization. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 29659-29668. [CrossRef]
- Xu Ma, Qile Zhao, Hao Zhang, Zhiqiang Wang, and Gonzalo R. Arce. Model-driven convolution neural network for inverse lithography. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 32565-32584. [CrossRef]
- Xu Ma, Xianqiang Zheng, and Gonzalo R. Arce. Fast inverse lithography based on dual-channel model-driven deep learning. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 20404-20421. [CrossRef]
- F. Peng, Z. Yang, and Y. Song. 3D grayscale lithography based on exposure optimization. In International Workshop on Advanced Patterning Solutions (IWAPS), (IEEE, 2021), pp. 1-3. [CrossRef]
- C. Jidling, A. J. Fleming, A. G. Wills, and T. B. Schön. Memory efficient constrained optimization of scanning-beam lithography. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 20564-20579. [CrossRef]
- K. Yuan, B. Yu, and D. Z. Pan. E-beam lithography stencil planning and optimization with overlapped characters. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2012, 31, 167–179. [CrossRef]
- F. Yesilkoy, K. Choi, M. Dagenais, and M. Peckerar. Implementation of e-beam proximity effect correction using linear programming techniques for the fabrication of asymmetric bow-tie antennas. Solid-State Electron. 2010, 54, 1211–1215. [CrossRef]
- J. Bolten, T. Wahlbrink, M. Schmidt, H. D. Gottlob, and H. Kurz. Implementation of electron beam grey scale lithography and proximity effect correction for silicon nanowire device fabrication. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 1910–1912. [CrossRef]
- F. H. Dill, W. P. Hornberger, P. S. Hauge, J. M. Shaw. Characterization of positive photoresist. IEEE Trans. On Electron Devices 1975, 22, 445-452. [CrossRef]
- F. L, Y. Xie, Q. Sun. Analyzing of line profile for laser direct writing lithograph. ACTA PHOTONICA SINICA 2004, 33, 136-139.
- C. Du, X. Dong, C. Qiu, Q. Deng, C. Zhou. Profile control technology for high-performance microlens array. Opt. Eng. 2004, 43, 2595-2602. [CrossRef]
- C. A. Mack, Fundamental Principles of Optical Lithography: The Science of Microfabrication (John Wiley & Sons,Ltd., 2007). [CrossRef]
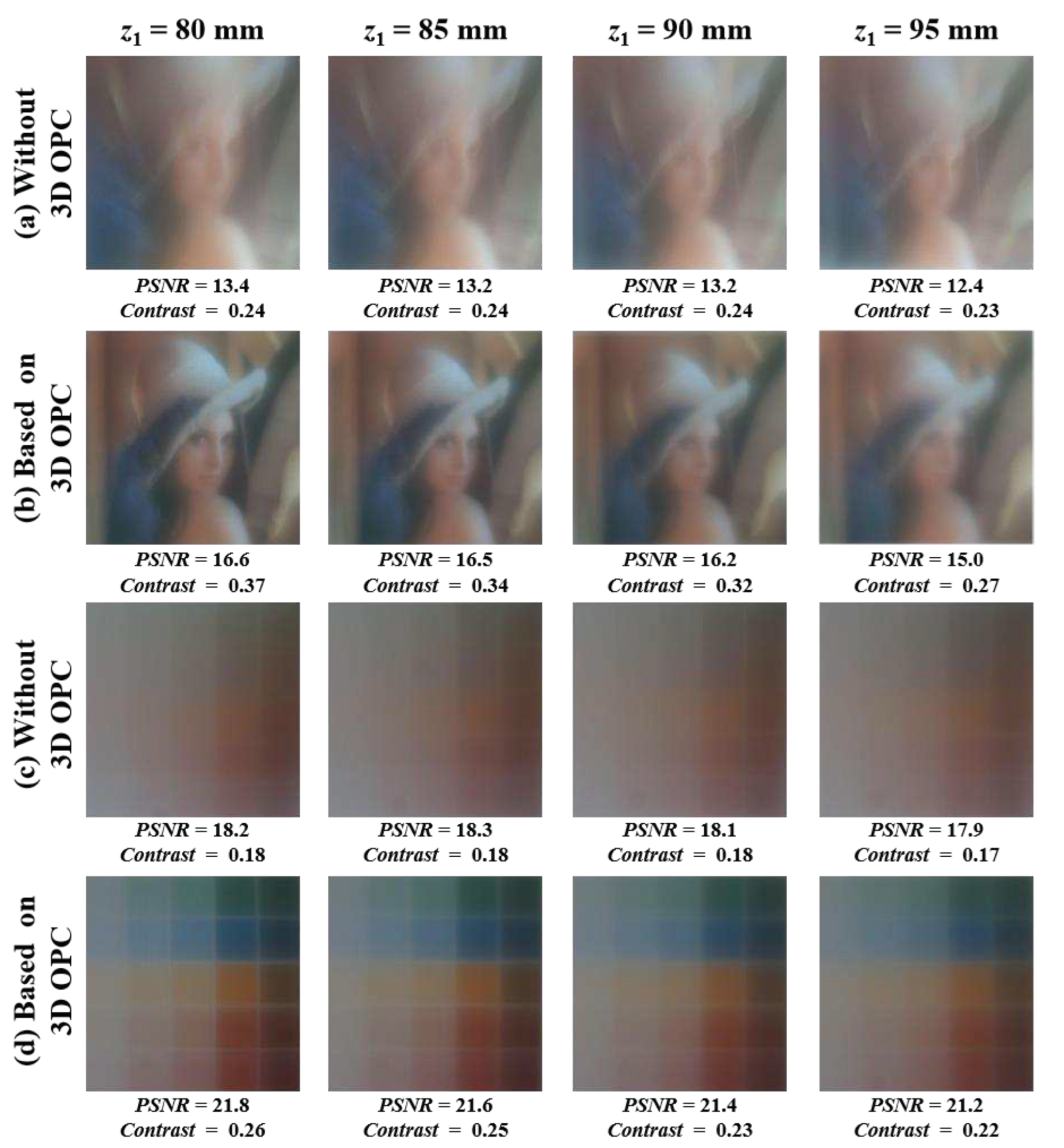
| Mask | Vision correction lens without 3D OPC | Vision correction lens with 3D OPC | Improvement | |||
| PSNR (dB) | Contrast | PSNR (dB) | Contrast | PSNR | Contrast | |
| Portrait | 13.0 | 0.24 | 16.1 | 0.32 | 23.3 % | 37.29 % |
| Color Blocks | 18.1 | 0.18 | 21.5 | 0.24 | 18.92 % | 36 % |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





