1. Introduction
The use of fuel sources including coal, oil and natural gas to generate electricity has given rise to many environmental problems, one of which appears to be global warming [
1,
2]. Consequently, global reliance has increased on finding clean, renewable (environmentally friendly) energy sources such as wind energy, solar energy, tidal energy, biofuels, fuel cells, hydrogen engines, and other technologies with a lower pollution rate, and these units are called distributed generation units. It is relevant to bring power sources as close as possible to electricity consumers using the principles of distributed generation [
3,
4]. However, the introduction of distributed generation units poses a number of technical problems associated with maintaining the required level of network voltage, power quality, and ensuring the correct functioning of automation systems and relay protection. The nature of the distribution system has changed in the era of distributed generation. Modern distribution systems are designed on the basis of receiving electrical power from network transformers and distributing it to consumers at the average distribution voltage and through the switching centers to consumers at the low voltage level. Thus, the flow of effective power P and reactive capacity Q is always from the highest level of tension to the lowest level. Distributed generation transforms the distribution system from a passive system, as is the case in traditional electric power systems, to an active distribution system. Since the power injected into the distribution network can affect its flow pattern, it must be ensured that it will not reduce the power supply specifications for other network users. With distributed generation in the distribution system, the flow and tension of the network are determined not only by the loads but also by the generators and the loads together. It is possible that the direction of the two-way power flow will be reversed in some branches of the network depending on the size and location of the distributed generation and the size of the loads. Thus, there is a need to expand research on the development of algorithms for protection systems in general and distance protection in particular [
5]. there are numerous proposed styles and bias to estimate the position of the faults on the lines. They can be grouped into styles grounded on the input impedance [
6] styles grounded on surge travelling goods [
7,
8,
9,
10]. Previous research has focused on improving the efficiency of distance protection by developing a set of mathematical laws to adjust the performance of these protection automation systems [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. Based on Thevenin’s laws, a set of algorithms was developed to obtain a more accurate value of damage resistance [
18,
19,
20]. Or depending on changes in the phase angle of power lines [
21,
22]. However, these studies did not focus on or examine the integration of distance protection mechanisms in a distribution network containing high-penetration distributed generation devices. Therefore, this study proposed a series of practical steps and applications to improve the sensitivity of distance protection in the presence of distributed generation, using neural network methods, multi-level deep learning and artificial intelligence to more accurately determine the location of the fault and thus accurately calculate the resistance of distance protection, and this in turn led to an improvement in the performance of the protection system.
2. Voltage Levels for the Distribution System
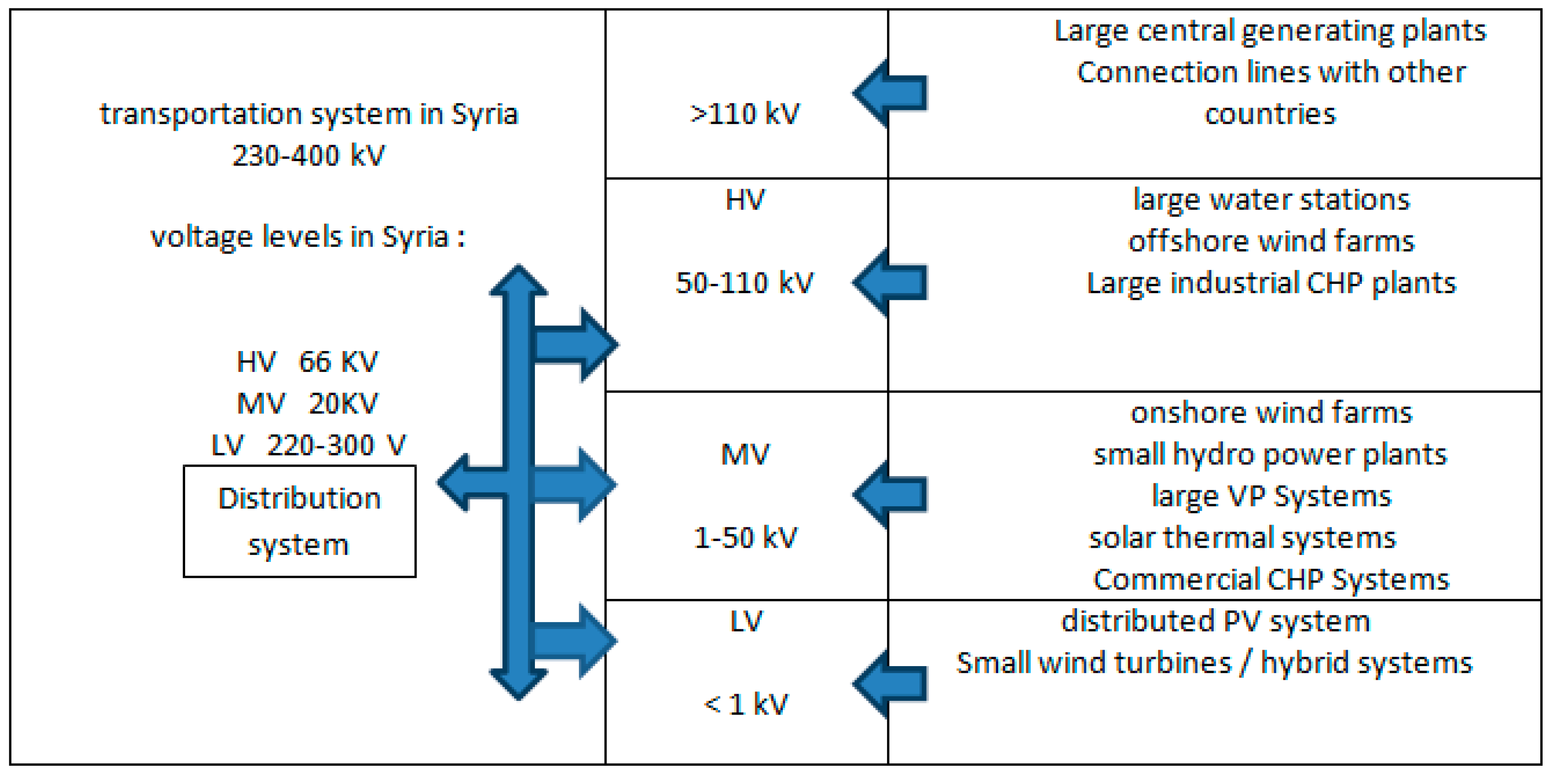
Most of the RDG units are related to the distribution system, which can be classified (
Figure 1) according to global systems in terms of the level of voltage into:
High voltage distribution network HV: Typical voltage levels are 50-110 kV (in the Syrian network 66 kV)
Medium voltage MV distribution network: Typical voltage levels are 10- 50 kV (in the Syrian network 20 kV)
Low voltage LV distribution network: levels less than 1000V (in the Syrian network 220/380V).
In fact, the names and limits of voltage levels change from one country to another. In Syria, labels such as secondary distribution voltage (220/380 V), main distribution voltage (20 kV), medium voltage (66 kV) and high voltage (230-400 kV) prevail.
3. An Overview of the Technical Impacts of Distributed Generation on the host Distribution Network
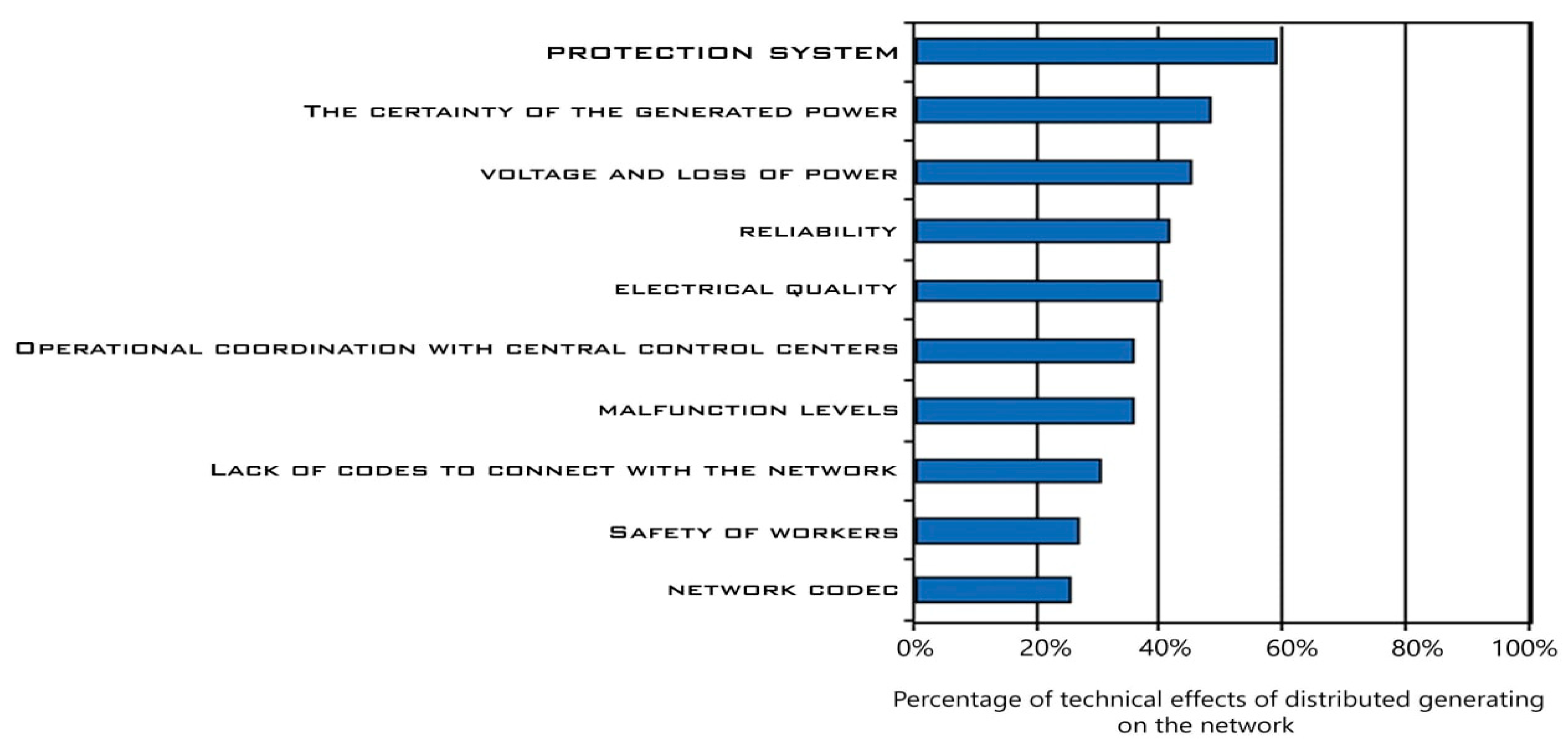
The inclusion of distributed generation in the distribution system generates technical effects in the network, which may be positive, negative or neutral depending on several factors. The main areas that are affected are tension and loss of power, fault levels, reliability, electrical quality, protection and stability, worker safety and network code.
Figure 2 shows a graphic representation of the relative sizes of these effects.
by analysis the percentages, notice that the greatest impact of distributed generation units lies in electrical protection systems in general. Therefore, this study will focus on developing the mechanism of operation of distance protections in distributed generation networks to increase sensitivity and improve performance. There are a few elements that could have an effect on the overall performance of any relay safety system. Economy is one of the maximum essential elements. Errors aren’t common. Therefore, one may also marvel why there’s a want to layout a protection system. However, unlucky occasions do happen, and if there’s no safety in place, sizeable economic losses can occur. In the occasion of a unmarried fault, if the designed circuit operates quick and accurately, it could lessen downtime and guard device from damage. In addition, it’s miles essential to lessen redundancy, i.e., Use most effective the minimal quantity of relays required for the specified safety zone. In a electricity system, it’s miles not possible to are expecting the location, kind and timing of any failure. Given the unsure possibilities, the safety engineer ought to broaden a safety scheme primarily based totally at the maximum in all likelihood occasions, beyond occasions, device producer hints and make the proper realistic decision.
4. Algorithm Using Neural Network Methods to Increase the Sensitivity of the Distance Protection System
4.1. The First Test: Correction of the Location of the Astronomical Error Using Neural Networks to the Distance Relay
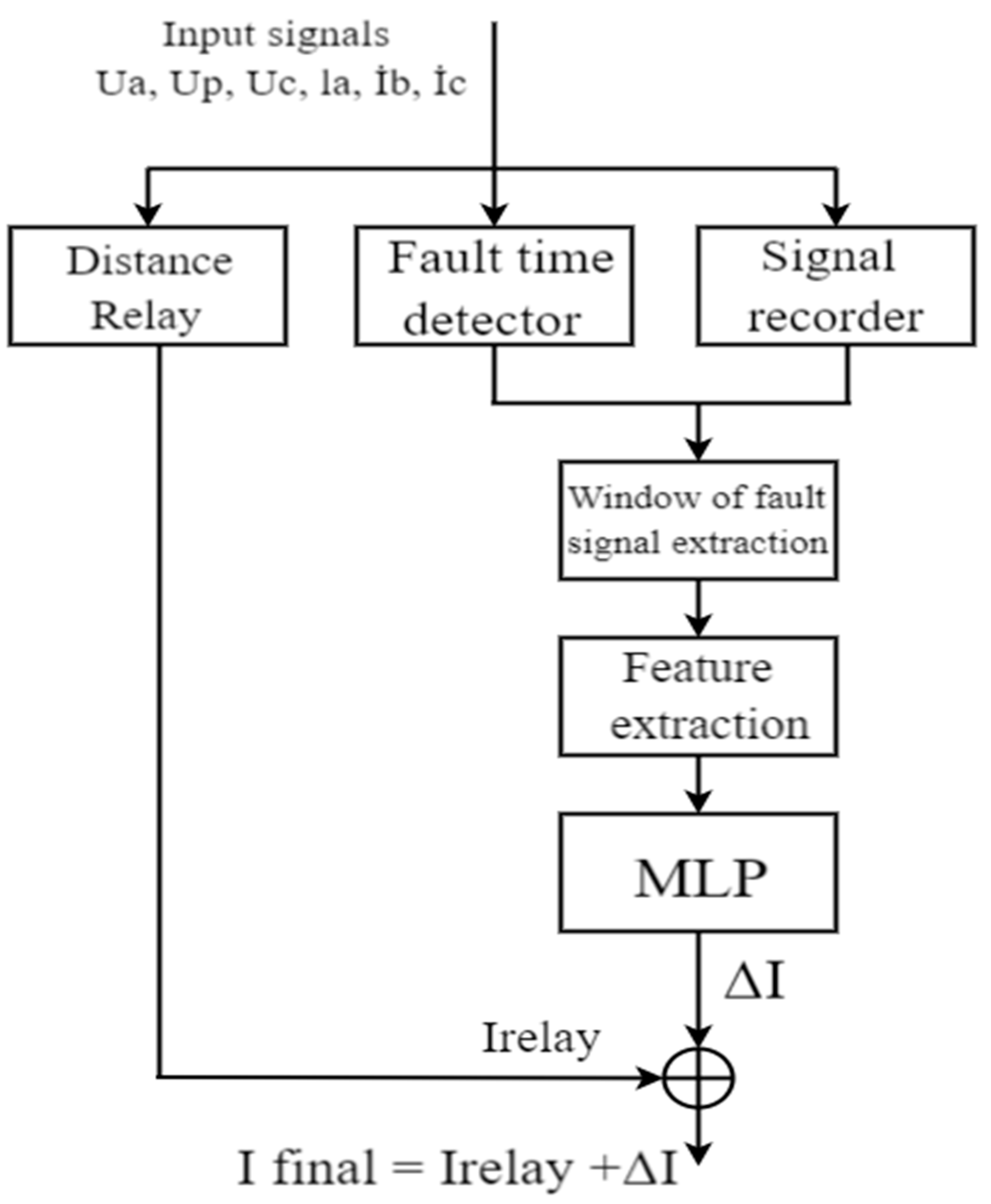
proposed in this test a method for improve relay fault location estimation by creating a correction point that is added to the set point setting to form a final result based on these steps and devices [
23].
Fault parameters➔EMTP (transmission line model)➔input (6 voltages and currents)➔CMC-356 Omicron (test universe device)➔ Distance relay (7SA522)➔Fault location l relay
Estimation edited value based on the voltage and current signals, and then added to the result from the relay [
23]. The block diagram of the proposed solution is presented in
Figure 3.
In the traditional case of the operation of distance protections, when electrical faults of various types occur on the electrical power supply lines, the distance protection is activated. Based on the distance between the fault site and the protection site, the resistance value of the distance protection is then estimated, and then the separation is made or not according to that value. In the presented proposal, it is done by: An algorithm that calculates a short time period before and after the protection is activated, to calculate the exact time of signal change. After that, the features are generated from the signal block [
23], and using these nonlinear functions, the correction amount is calculated as follows:
An MLP neural network was chosen as a nonlinear estimator and trained to ensure that the final result is more accurate than a relay. This approach was chosen to directly estimate the fault location. This model is designed for a 100 km AC transmission line with a voltage of 20 kV (voltage level of the Syrian distribution network) from Teshrin station to the industrial city of Adra (Syria).
4.1.1. Universal Relay Tester SMS-356
OMICRON’s CMC -356 universal relay tester and a real distance relay were used to bring the simulation and response closer to reality [
24].
Figure 4.
Relay devise CMC -356 from OMICRON [
25].
Figure 4.
Relay devise CMC -356 from OMICRON [
25].
Answers 7SA522 The remote relay will be read back to the computer via DIGSI 4.82 (Digital Information Group) compatible software [
25].
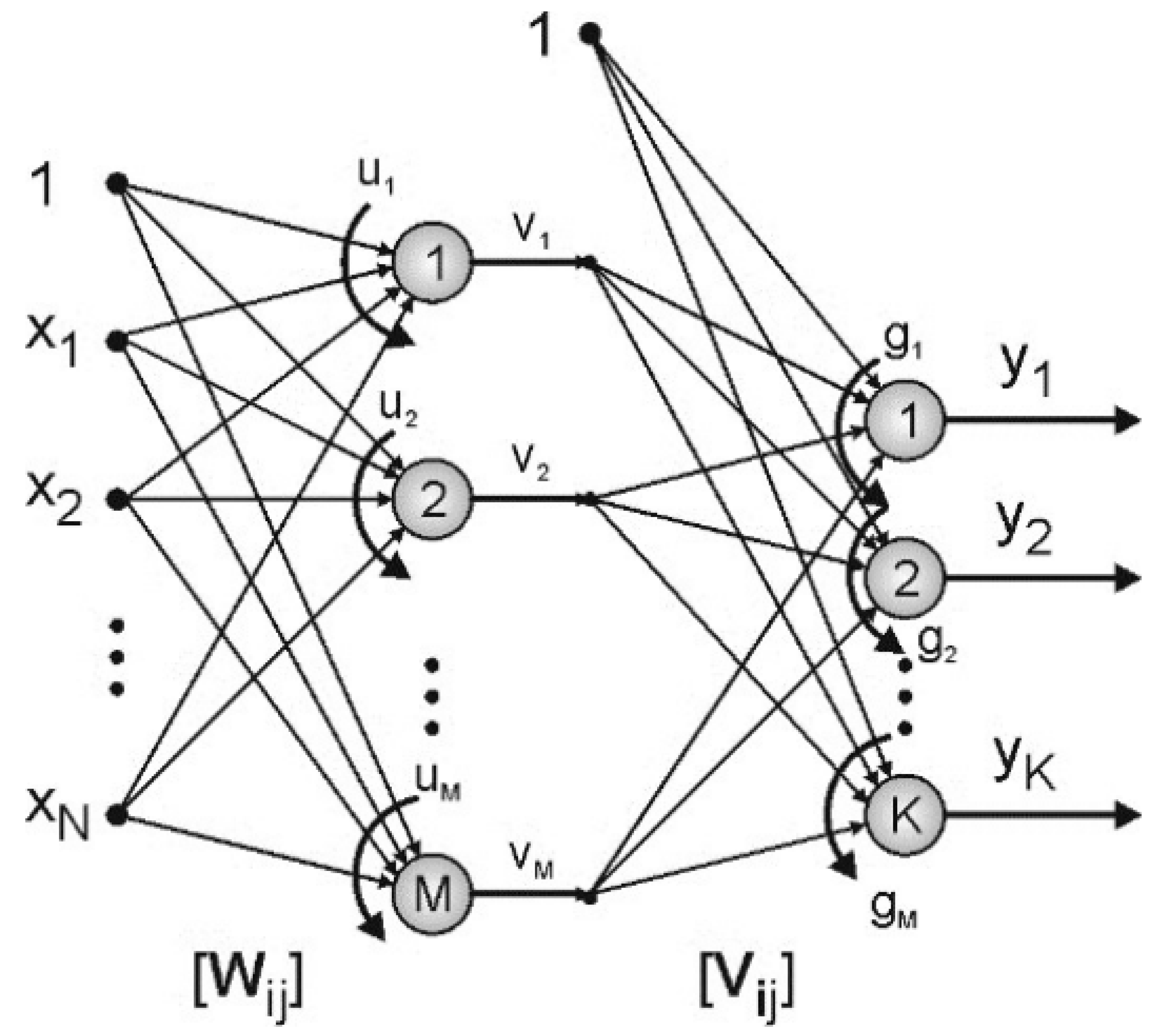
4.1.2. MLP (Multilayer Perceptron) network
A multilayer perceptron (MLP) is a modern feedforward artificial neural network, consisting of fully connected neurons with a nonlinear kind of activation function, organized in at least three layers, notable for being able to distinguish data that is not linearly separable. It is a misnomer because the original perceptron used a Heaviside step function, instead of a nonlinear kind of activation function (used by modern networks). is shown in
Figure 5.
4.1.3. Simulation and numerical results
ATP/EMTP software was used to simulate a real 100 km long, 20 kV power transmission line (Syria). Error scenarios when creating samples are given. Location of damage: one of N = 23 positions on the line (at a distance of 5, 10,..., 95 km
short circuit 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Ohm;
types of emergency situations: single-phase, two-phase, three-phase short circuit, two-phase short circuit to ground;
line load: 30%, 50% and 100% of the rated line load.
Additionally, to test the effect of fault time (relative phase) on the results, cases were created for short circuit resistance R - fault = 1 ohm at positions (10, 40, 80, 110 km) and M = 10 fault time in 2 ms steps (to cover the entire 20 ms period) of 50 Hz signals). This means:
Short circuit point location one of
N = 4 addresses (10- 40- 80-110 km),
Short circuit resistance R - fault : 1 Ohm,
Fault time: one of the values M = 10 (+00 ms, +02 ms,..., +18 ms).
This resulted in an additional
Total 1656+ 480 = 2136.
4.1.4. Fault Location Using Remote Relay
Using the simulated data from the ATP / EMTP, the data was first regenerated using a CMC -356 tester to feed the selected 7 SA 522- V 4.7 distance relay. Test suites allow the recorded data to be “replayed” and transferred to a similar data relay, which greatly simplifies the analysis of identified failures. [
26]. The statistics of these comparisons are presented in
Table 1,
Table 1.
Simulation results of distance protection without MLP.
Table 1.
Simulation results of distance protection without MLP.
| Type malfunctions |
Average position error (km) |
Average relative position error (%) |
| 1-ph short circuit |
0.19 |
0.151 |
| 2-ph short circuit |
0.157 |
1.31 |
| 2-ph fault in ground |
1.96 |
1.65 |
| 3-ph short circuit |
0.55 |
0.48 |
| Average |
1.08 |
0.91 |
Table 2.
Number of grouped by fault.
Table 2.
Number of grouped by fault.
| Type malfunctions |
Samples in the training set |
Samples in the test set |
| 1-ph -F |
372 |
164 |
| 2-ph- F |
352 |
182 |
| 2-ph –F to G |
386 |
178 |
| 3-ph-F |
340 |
192 |
| Average |
1450 |
716 |
Table 3.
Maximum errors DR 7SA-522 and after correction using Multilayer perceptron.
Table 3.
Maximum errors DR 7SA-522 and after correction using Multilayer perceptron.
| Method |
Maximum error (km) actual. |
maximum error (%) |
| 7SA522 |
9.2 |
8.32 |
| 7SA522 With Multilayer perceptron |
2.78 |
2.49 |
5. Determination of Fault Resistance (Distance Protection Resistance) Based on Neural Network Technology for Single-Phase Earth Fault for 20 kV Power Line—Southern Grid, Syria
To simulate the ANN-based method, a 20 kV power transmission line with a length of 100 km.The transmission line is modeled using the pi model. Model of the proposed transmission line using Matlab / Simulink. The ground resistance of the simulated system was 100 ohms, and the system frequency 50 Hz. Other values to the transmission line are given in
Table 4 [
28].
The most important step in using artificial neural networks is testing the trained network. Network testing is necessary to ensure that the network produces outputs that match new inputs and has good generalization ability to generate outputs [
29]. There are a number of methods used to test a trained ANN. In the first testing method, when training an ANN, a best-fit linear regression graph is plotted between the obtained results and the planned results. The slope of this plotted graph is determined by the coefficient R. The R ratio shows how closely the actual results can match the target results. This coefficient varies from 0 to 1. To achieve the best training results, ANN ( Artificial Neural Network ) should be equal to 1. The network is tested using a test dataset in which the input and target output are not present in the training set and the percentage error between outputs is calculated network data and target output data. If the average error rate is an acceptable value, it means that the ANN test has passed and the network can now be used [
30,
31]. The estimation error when determining the location of damage is found using equation 2.
5.1. Troubleshooting in the ANN
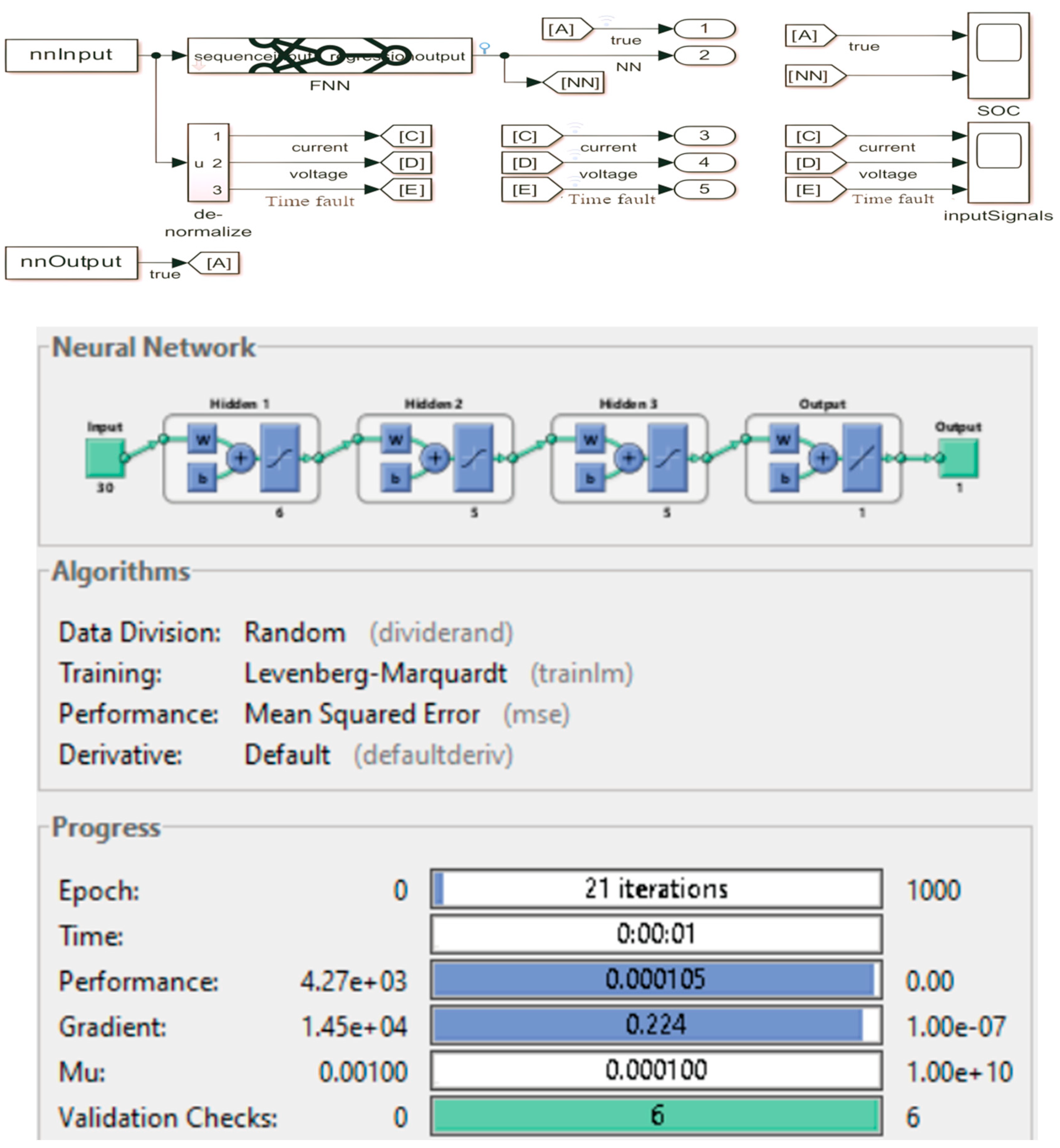
LM (Levenberg-Marquardt) learning function and the four-level ANN structure are defined as the ANN structure with the smallest estimation errors [
32,
33,
34]. A logarithmic sigmoid activation function was used in the first three layers of the defined network, and a linear activation function was used in the output layer[
35]. The number of neurons belonging to these layers was defined as 6, 5, 5 and 1, respectively. The general structure of the implemented network, created using Matlab / nntool, is shown in
Figure 6
According to the test results shown in Table 14, the largest prediction error is 0.236, the smallest prediction error is 0.0121, and the average absolute prediction error for the test cases is 0.12405. These results show that the accuracy of the algorithm is high. Therefore, this technology can be relied upon in practical applications for protection systems, especially in electrical networks with a high penetration rate[
38,
39,
40,
41,
42].
Table 5.
Incorrect location results.
Table 5.
Incorrect location results.
Actual fault
Location (km) |
Fault resistance Ω |
Suspected location of the fault |
Absolute error (%) |
| 10 |
2 |
10.2366 |
0.236 |
| 25 |
50 |
24.8931 |
0.106 |
| 35 |
5 |
35.0595 |
0.059 |
| 55 |
120 |
54.7784 |
0.221 |
| 80 |
3 |
80.1218 |
0.121 |
| 95 |
13 |
94.8768 |
0.123 |
6. Conclusions
As a result of changing electrical network parameters, especially electrical distribution networks that have high penetration rates from distributed generation units, such as changing network topology, load values, fault currents, and the level of electrical tension on distribution bars, it is necessary to develop new working algorithms for distance protections to integrate those protections and increase their sensitivity and accuracy.
Transmission lines are part of power systems, but system operators experience a large number of faults. In response, a number of attempts have been made to mitigate the effects of faults on power lines. The purpose of this thesis was to investigate the feasibility of using artificial neural networks as a fault detection mechanism on power lines. There are three methods for protecting power lines, namely fault detection, fault classification and fault location. The focus of this thesis was on the application of artificial neural networks (ANN) for fault detection. The goal of this study was to detect electrical faults and classify them in real time in a simulated environment. For this purpose, the Matlab/Simulink tool was used, which used artificial neural modeling tools.
Network Toolbox and SimPower Systems Toolbox. It has been shown in the literature and document content that ANN is a good method for detecting faults in power lines and can accurately identify faults. The present study also validated its application and that good performance results can be obtained with an ANN suitably trained using validated training data. Many of the goals were confirmed, re-examined and described in detail in the dissertation. One problem that has not been fully explored is fault location using ANN, primarily due to the time constraints of this project. cessation of damage location determination through ANN is reserved as a future study with its diversity. The research methodology used was to conduct a comprehensive literature review followed by an analysis of ANN and its application in fault detection of power lines. The literature review focused on understanding what fault detection is and its many applications. Analysis and Modeling showed that training an ANN requires extensive data preparation. This is by far the most time-consuming component of ANN design and application. It is noted that ANN has many applications and functions, but careful care is required while preparing and formulating the data. The INS fault detector measures faults efficiently and quickly, so the transmission line equipment is more likely to be protected. In addition, the ANN fault detection method has been tested and proven to be accurate for all types of faults.
References
- Lavrik, A.; Zhukovskiy, Y.; Tcvetkov, P. Optimizing the Size of Autonomous Hybrid Microgrids with Regard to Load Shifting. Energies 2021, 14, 5059. [CrossRef]
- Sychev Yu. A. , Kostin V. N., Serikov V. A., Aladin M. E. Nonsinusoidal modes in power-supply systems with nonlinear loads and capacitors in mining. MIAB. Mining Inf. Anal. Bull. 2023;(1):159-179. [In Russ]. [CrossRef]
- Pirog, S.; AGH Scientific and Technical University; Shklyarskiy, Y.; Skamyin, A. Saint Petersburg Mining University Non-linear Electrical Load Location Identification. J. Min. Inst. 2019, 237, 317–321.
- Shklyarskiy Y, Skamyin A, Vladimirov I, Gazizov F. Distortion Load Identification Based on the Application of Compensating Devices. Energies 2020, 13, 1430. [CrossRef]
- Sychev, Y.A., Aladin, M.E., Aleksandrovich, S.V. «Developing a hybrid filter structure and a control algorithm for hybrid power supply», International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive Systems, 2022, 13(3), pp. 1625–1634.
- Zimmerman K, David Costello. Impedance-based fault location experience. Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories,Inc. WA USA: Pullman, 2010.
- Aggarwal RK, Coury DV, Johns AT, Kalam A. A practical approach to accurate fault location on extra high voltage teed feeders. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 1993; 8: 874-883.
- Aurangzeb M, Crossley PA, Gale P. Fault location using high frequency travelling waves measured at a single location on transmission line. In: Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Developments in Power System Protection (DPSP 2001) 2001; 403-406.
- Bo ZQ, Weller G, Redfern MA. Accurate fault location technique for distribution system using fault-generated high-frequency transient voltage signals. IEE Proceedings - Generation, Transmission and Distribution 1999; 146 (1): 73-79.
- Bouthiba T. Fault location in EHV transmission lines using artificial neural networks. International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science 2004; 14 (1): 69-78.
- Ayyagari SB. Artificial neural network based fault location for transmission line. PhD, University of Kentucky, 2011.
- Chen Z and Maun JC. Artificial neural network approach to single-ended fault locator for transmission lines, IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2000; 15 (1): 370-375.
- Takagi K, Yamakoshi Y, Yamaura M, Kondow R, Matsushima T. Development of a new type fault locator using the one terminal voltage and current data. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems 1982; 101 (8): 2892-2898.
- Edmund OS. A Review of Impedance-Based Fault Locating experience. In: Fourteenth Annual Iowa-Nebraska System Protection Seminar 1990. pp. 1-31.
- Aggarwal RK, Blond SL, Beaumont P, Baber G, Kawano F et al. High frequency fault location method for transmission lines based on artificial neural network and genetic algorithm using current signals only. In: 11th International Conference on Developments in Power Systems Protection (DPSP 2012); 2012. pp. 1-6.
- Brahma SM. Iterative Fault Location Scheme for a Transmission Line Using Synchronized Phasor Measurements. International Journal of Emerging Electric Power Systems 2007; 8 (6); [CrossRef]
- Klyuev , R. V., Bosikov , I. I., & Gavrina , O. A. (2021). Improving the efficiency of relay protection at a mining and processing plant. Journal of Mining Institute, 248, 300-311. [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T. Electric Power Distribution Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; p. 768.
- Hariri, F.; Crow, M. New Infeed Correction Methods for Distance Protection in Distribution Systems. Energies 2021, 14, 4652. [CrossRef]
- Abo-Hamad, G.M.; Ibrahim, D.K.; Aboul Zahab, E.; Zobaa, A.F. Adaptive Mho Distance Protection for Interconnected Transmission Lines Compensated with Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor. Energies 2021, 14, 2477. [CrossRef]
- Brearley, B.J. and Prabu, R.R. (2017) A Review on Issues and Approaches for Microgrid Protection. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 67, 988-997. [CrossRef]
- TRAN, LINH. “Integration of neural network and distance relay to improve the fault localization on transmission lines.” Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences 31, no. 3 (2023): 566-580.
- Chaun, L. (2014) An Update on Power Quality. Intech-Open, Sydney.
- Wang Y, Orchard J. Fast Discrete Orthonormal Stockwell Transform. SIAM. J. Science Computation 2009;31(5):4000–12.
- Abramovich , B. N., & Bogdanov , I. A. (2021). Improving the efficiency of autonomous electrical complexes of oil and gas enterprises. Journal of Mining Institute, 249, 408-416. [CrossRef]
- Voronin V. A., Nepsha F. S. (2020). Simulation of the electric drive of the shearer to assess the energy efficiency indicators of the power supply system. Journal of Mining Institute, 246, 633-639. [CrossRef]
- Krishnanad KR, Dash PK. A new real-time discrete S-transform for cross-differential protection of shunt-compensated power systems. IEEE Trans Power Systems 2013; 28(1):402–10.
- Nguyen T, Liao Y. Power quality disturbance classification utilizing S-transform and binary feature matrix method. Electrical Power System Research 2009;79: 569–75.
- Coban, Melih, and S. S. Tezcan. “Artificial neural network based fault location on 230 kv transmission line using voltage and current signals.” In 2020 4th International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2020.
- Yuriy L. Zhukovskiy, Nikolay A. Korolev, Yana M. Malkova (2022) Monitoring of grinding condition in drum mills based on resulting shaft torque. Journal of Mining Institute. Vol 256. p. 686-700. [CrossRef]
- Chavez, Jose J., Marjan Popov, David López, Sadegh Azizi, and Vladimir Terzija. “S-Transform based fault detection algorithm for enhancing distance protection performance.” International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems 130 (2021): 106966. P 2-3. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Pradhan, A.K.; Bajpai, P. Adaptive Distance Relaying for Distribution Lines Connecting Inverter-Interfaced Solar PV Plant. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2300–2309.
- Jones, K.W.; Pourbeik, P.; Kobet, G.; Berner, A.; Fischer, N.; Huang, F.; Holbach, J.; Jensen, M.; O’Connor, J.; Patel, M.; et al. Impact of Inverter Based Generation on Bulk Power System Dynamics and Short-Circuit Performance; Technical Report PES-TR68; IEEE Power & Energy Society: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Dashtdar, Masoud, Milan Belik, Arvind Yadav, Seyed Mohammad Sadegh Hosseinimoghadam, Mohit Bajaj, and Olena Rubanenko. “Improving the Performance of Distance Relay-Based Artificial Neural Network.” In 2022 IEEE 3rd KhPI Week on Advanced Technology (KhPIWeek), pp. 1-6. IEEE, 2022.
- Ibrahim, M.A. Disturbance Analysis for Power Systems, 1st ed.;Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; p. 223.
- Amiri, E. Maali, and B. Vahidi. “Integrated protection scheme for both operation modes of microgrid using S-Transform.” International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems vol. 121, 2020): 106051.
- Suja, S., and Jovitha Jerome. “Pattern recognition of power signal disturbances using S transform and TT transform.” International journal of electrical power & energy systems 32, no. 1 (2010): 37-53.
- IEEE 519-2014: ’IEEE Recommended Practice and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems, PE/T&D - Transmission and Distribution’, 2014.
- Koteleva, N.I.; Korolev, N.A.; Zhukovskiy, Y.L. Identification of the Technical Condition of Induction Motor Groups by the Total Energy Flow. Energies 2021, 14, 6677. [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskiy, Y.L.; Batueva, D.E.; Buldysko, A.D.; Gil, B.; Starshaia, V.V. Fossil Energy in the Framework of Sustainable Development: Analysis of Prospects and Development of Forecast Scenarios. Energies 2021, 14, 5268. [CrossRef]
- Ustinov D.A., Aysar A.R. Analysis of the influence of distributed generation facilities on protection systems and voltage conditions: review// Occupational safety in industry. - 2023. - No. 2 - P. 15-20. [CrossRef]
- Nepsha , F. S., Varnavskiy , K. A., Voronin , V. A., Zaslavskiy , lya S., & Liven , A. S. (2023). Integration of renewable energy at coal mining enterprises: problems and prospects. Journal of Mining Institute, 261, 455-469. Retrieved from https://pmi.spmi.ru/pmi/article/view/16215.
- Skamyin , A. N., Dobush , V. S., & Jopri , M. H. (2023). Determination of the grid impedance in power consumption modes with harmonics. Journal of Mining Institute, 261, 443-454. [CrossRef]
- Sychev, Y.A., Nazarychev, A.N., Dyachenok, G.V. Improving the Labor Safety of Mining Dump Truck Drivers by Reducing the Risk of Failure of the Functional Units of the Traction Electric Drive under Operating Conditions // Bezopasnost’ Truda v Promyshlennosti— 2023. — № 9. — С. 52-58. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).