Submitted:
09 November 2023
Posted:
09 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
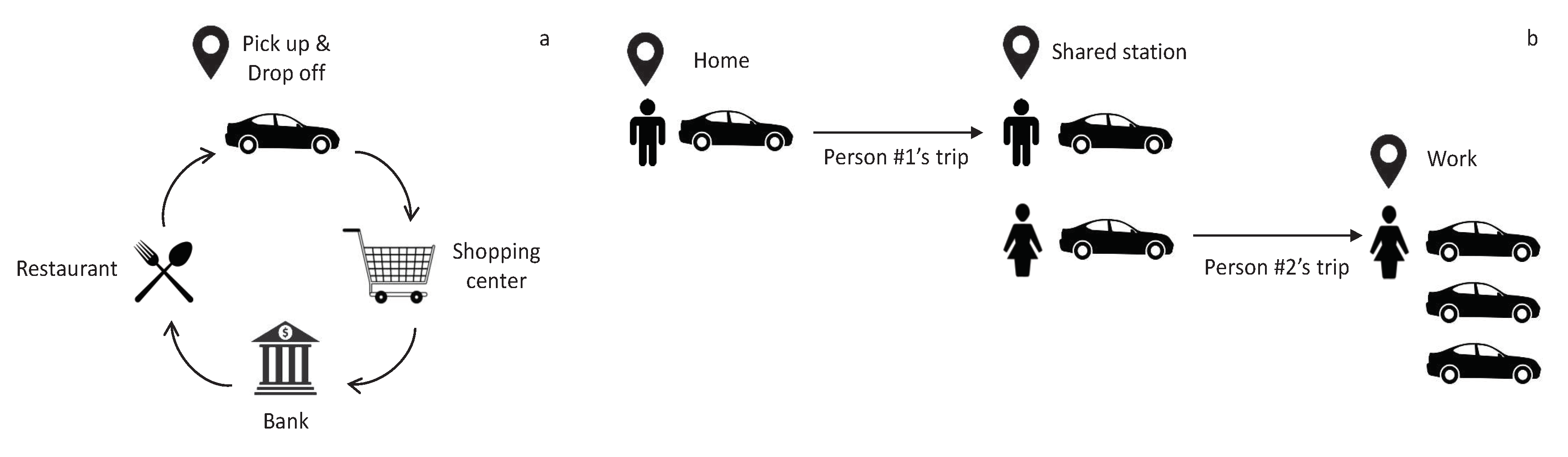
1. Introduction
2. Vehicle rebalancing
- -
- : donates customer request on arc , each time a commuter request is transversed by this arc, there is a negative variation of vehicle energy, i.e. , and a positive profit, i.e. .
- -
- : waiting arc for either vehicles or relocation staff at a station i, . Each waiting arc is associated with a positive energy variation, , and a zero profit, i.e.
- -
- : vehicle relocation arc by at least one relocator, . Each relocation arc is associated with a negative energy variation, i.e. , and a negative profit, i.e. .
- -
- : transfer arc , represents the relocator’s movement when they don’t move by vehicle or wait at a station. Each transfer arc is correlated with a zero energy consumption, , and a zero generated profit, .
3. Resource dimensioning and allocation
4. Trip pricing
5. Carsharing stations related decisions
6. Operators decisions and commuters demand
- Budget constraints in (39).
- Parking slots availability only on opened stations in Constraints (40)
- Number of vehicles assigned to a station doesn’t exceed its capacity in Constraints (41)
- Limiting the number of opened stations in Constraints (42)
- Flow conservation for each node in Constraints (46).
- Relating the travel and waiting times for frequency-based links in Constraints (47).
- Flows are only between opened stations in Constraints (48) and (49)
- Capacity constrains for the shared stations in Constraints (50) and (51)
7. Future research direction
8. Conclusion and future work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shams Esfandabadi, Z.; Diana, M.; Zanetti, M. Carsharing services in sustainable urban transport: An inclusive science map of the field. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2022, 357, 131981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Ye, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, F. Locating Station of One-Way Carsharing Based on Spatial Demand Characteristics. Journal Of Advanced Transportation. 2018, 2018, 5493632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatuni, L.; Ottelin, J.; Steubing, B.; Mogollón, J. Does car sharing reduce greenhouse gas emissions? Assessing the modal shift and lifetime shift rebound effects from a life cycle perspective. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2020, 266, 121869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S. Community detection in graphs. Phys. Rep.-Rev. Sec. Phys. Lett.. 2010, 486, 75–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.; Girvan, M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks. Phys. Rev. E. 2004, 69, 026113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehlow, C.; Reinhardt, T.; Weiskopf, D. Visualizing Fuzzy Overlapping Communities in Networks. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph.. 2013, 19, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šubelj, L.; Bajec, M. Robust network community detection using balanced propagation. Eur. Phys. J. B.. 2011, 81, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauset, A. , Newman, M. & Moore, C. Finding community structure in very large networks. Phys. Rev. E. 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.; Guillaume, J.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech.-Theory Exp.. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šubelj, L.; Bajec, M. Unfolding communities in large complex networks: Combining defensive and offensive label propagation for core extraction. Phys. Rev. E.. 2011, 83, 036103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Eustace, J. Detecting overlapping communities by seed community in weighted complex networks. Physica A. 2013, 392, 6125–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, D.; Fabio, D.; Carlo, P. Profiling core-periphery network structure by random walkers. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1467. [Google Scholar]
- Nepusz, T.; Petróczi, A.; Négyessy, L.; Bazsó, F. Fuzzy communities and the concept of bridgeness in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E.. 2008, 77, 016107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricio, B.; Liang, Z. Fuzzy community structure detection by particle competition and cooperation. Soft Comput. 2013, 17, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, D.; Liu, X.; Pan, L. Fuzzy overlapping community detection based on local random walk and multidimensional scaling. Physica A. 2013, 392, 6578–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yeung, D. Overlapping Community Detection via Bounded Nonnegative Matrix Tri-Factorization. In Proc. ACM SIGKDD Conf. 2012, 606–614. [Google Scholar]
- Havens, T.; Bezdek, J.; Leckie, Palaniswami, M. A Soft Modularity Function For Detecting Fuzzy Communities in Social Networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst.. 2013, 21, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Network data. (http://www-personal.umich.edu/ mejn/netdata/,2013).
- Šubelj, L.; Bajec, M. Ubiquitousness of link-density and link-pattern communities in real-world networks. Eur. Phys. J. B.. 2012, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancichinetti, A.; Fortunato, S.; Radicchi, F. Benchmark graphs for testing community detection algorithms. Phys. Rev. E.. 2008, 78, 046110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Pellegrini, M.; Wang, X. Detecting Communities Based on Network Topology. Sci. Rep.. 2014, 4, 5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danon, L.; Diaz-Guilera, A.; Duch, J.; Arenas, A. Comparing community structure identification. J. Stat. Mech.-Theory Exp. 2005; P09008. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, S. Fuzzy overlapping communities in networks. J. Stat. Mech.-Theory Exp. 2011; P02017. [Google Scholar]
- Lancichinetti, A.; Fortunato, S. Benchmarks for testing community detection algorithms on directed and weighted graphs with overlapping communities. Phys. Rev. E.. 2009, 80, 016118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hullermeier, E.; Rifqi, M. A Fuzzy Variant of the Rand Index for Comparing Clustering Structures. In Proc. IFSA/EUSFLAT Conf. 2009; 1294–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Takiddin, A. An Artificial Intelligence Tool to Detect and Classify Skin Cancer. (College of Science,2020).
- Linares, M.; Zakaria, A.; Nizran, P. Skin Cancer. Primary Care: Clinics In Office Practice. 2015, 42, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu-Smith, F.; Jia, J.; Zheng, Y. UV-Induced Molecular Signaling Differences in Melanoma and Non-melanoma Skin Cancer. Ultraviolet Light In Human Health, Diseases And Environment. 2017, 27–40.
- Raghavan, U.; Albert, R.; Kumara, S. Near linear time algorithm to detect community structures in large-scale networks. Phys. Rev E.. 2007, 76, 036106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y. Detecting community structure using label propagation with weighted coherent neighborhood propinquity. Physica A.. 2013, 392, 3095–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolevsky, S.; Campari, R. General optimization technique for high-quality community detection in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E.. 2014, 90, 012811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Barthelemy, M. Resolution limit in community detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.. 2007, 104, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, M. & Todd, M. Simulation model performance analysis of a multiple station shared vehicle system. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 1999, 7, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J. Detecting communities by the core-vertex and intimate degree in complex networks. Physica A.. 2013, 392, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wu, T.; Fang, M. Detecting local community structure in complex networks based on local degree central nodes. Physica A.. 2013, 392, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Identification of overlapping community structure in complex networks using fuzzy c-means clustering. Physica A.. 2007, 374, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Gao, L.; Han, S. Identification of overlapping and non-overlapping community structure by fuzzy clustering in complex networks. Inf. Sci.. 2011, 181, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psorakis, I.; Roberts, S.; Ebden, M.; Sheldon, B. Overlapping community detection using Bayesian non-negative matrix factorization. Phys. Rev. E.. 2011, 83, 066114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Fuzzy modularity and fuzzy community structure in networks. Eur. Phys. J. B.. 2010, 77, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglic, M.; Agatz, N.; Savelsbergh, M.; Gradisar, M. Enhancing urban mobility: Integrating ride-sharing and public transit. Computers & Operations Research. 2018, 90, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Somenahalli, S.; Berry, S. Policy implementation of multi-modal (shared) mobility: review of a supply-demand value proposition canvas. Transport Reviews. 2020, 40, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaga, N.; Rotstein, N.; Oren, N.; Nelson, J.; Norman, T.; Wright, S. Development of an integrated flexible transport systems platform for rural areas using argumentation theory. Research In Transportation Business & ManagementResearch In Transportation Business 2012, 3, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.; Chan, N. Mobility and the Sharing Economy: Potential to Facilitate the First- and Last-Mile Public Transit Connections. Built Environment. 2016, 42, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Nie, Y. Analysis of an idealized system of demand adaptive paired-line hybrid transit. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2017, 102, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Quadrifoglio, L. Evaluation of Zoning Design with Transfers for Paratransit Services. Transportation Research Record Journal Of The Transportation Research Board. 2012, 2277, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Savelsbergh, M. An extended demand responsive connector. EURO Journal On Transportation And Logistics. 2014, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelsbergh, M. & Sol, M. The General Pickup and Delivery Problem. Transportation Science. 1995, 29, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Sun, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, X. Optimizing fleet size and scheduling of feeder transit services considering the influence of bike-sharing systems. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2019, 236, 117550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Savelsbergh, M. An extended demand responsive connector. EURO Journal On Transportation And Logistics. 2017, 6, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basciftci, B.; Hentenryck, P. Capturing Travel Mode Adoption in Designing On-demand Multimodal Transit Systems. (2021).
- Dalmeijer, K.; Hentenryck, P. Transfer-Expanded Graphs for On-Demand Multimodal Transit Systems. (2019).
- Li, X.; Quadrifoglio, L. Feeder transit services: Choosing between fixed and demand responsive policy. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2010, 18, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, J.; Cats, O.; Van Oort, N.; Hoogendoorn, S. Integrated route choice and assignment model for fixed and flexible public transport systems. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2020, 115, 102631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, M.; Andersson, H.; Häll, C. The integrated dial-a-ride problem with timetabled fixed route service. Public Transport. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrifoglio, L.; Li, X. A methodology to derive the critical demand density for designing and operating feeder transit services. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2009, 43, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Q.; Ma, W. Optimization of dynamic relocation operations for one-way electric carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2019, 101, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Hentenryck, P.; Dillahunt, T. Mobility-on-demand versus fixed-route transit systems: An evaluation of traveler preferences in low-income communities. Transportation Research Part A: Policy And Practice. 2021, 148, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Almeida, Correia, G. ; Van Arem, B. Optimizing the service area and trip selection of an electric automated taxi system used for the last mile of train trips. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2016, 93, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, H.; Hyl,; M. ; Mahmassani, H.; Verbas, I. Joint design of multimodal transit networks and shared autonomous mobility fleets. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2020, 113, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. Integrating shared autonomous vehicle in public transportation system: A supply-side simulation of the first-mile service in Singapore. Transportation Research Part A: Policy And Practice. 2018, 113, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Ma, X. Joint optimization of scheduling and capacity for mixed traffic with autonomous and human-driven buses: A dynamic programming approach. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2020, 114, 598–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, R. Preferences of urban rail users for first- and last-mile autonomous vehicles: Price and service elasticities of demand in a multimodal environment. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2021, 126, 103105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafoutellis, P.; Mantouka, E. Major Limitations and Concerns Regarding the Integration of Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Transportation Systems: Proceedings of 4th Conference on Sustainable Urban Mobility (CSUM2018), 24 - 25 May, Skiathos Island, Greece. (2019,1).
- Pakusch, C.; Stevens, G.; Boden, A.; Bossauer, P. Unintended Effects of Autonomous Driving: A Study on Mobility Preferences in the Future. Sustainability. 2018, 10, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamini, G.; Pires, Ferreira, D. An informal transportation as a feeder of the rapid transit system. Spatial analysis of the e-bike taxi service in Shenzhen, China. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives. 2019, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, H.; Shi, B. Exploring Bike-Sharing Behavior Affected by Public Transportation Disruption: Case of Washington, DC, Metro Shutdown. Journal Of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems. 2021, 147, 04020163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Uz, V. A review on bike-sharing: The factors affecting bike-sharing demand. Sustainable Cities And Society. 2020, 54, 101882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zheng, Z.; Whitehead, J.; Perrons, R.; Washington, S.; Page, L. Examining the impact of car-sharing on private vehicle ownership. Transportation Research Part A: Policy And Practice. 2020, 138, 322–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Br, stätter, G. ; Kahr, M.; Leitner, M. Determining optimal locations for charging stations of electric car-sharing systems under stochastic demand. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2017, 104, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida Correia, G.; Antunes, A. Optimization approach to depot location and trip selection in one-way carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2012, 48, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassi, A.; Awasthi, A.; Viviani, M. Evaluation of carsharing network’s growth strategies through discrete event simulation. Expert Systems With Applications. 2012, 39, 6692–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Almeida Correia, G.; An, K. Solving the station-based one-way carsharing network planning problem with relocations and non-linear demand. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2018, 90, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bierlaire, M. Optimizing Locations for a Vehicle Sharing System. (2012). 2012.
- Lin, M.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z. MULTIMOORA based MCDM model for site selection of car sharing station under picture fuzzy environment. Sustainable Cities And Society. 2020, 53, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Miller-Hooks, E. Equilibrium network design of shared-vehicle systems. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2014, 235, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seign, R.; Schüßler, M.; Bogenberger, K. Enabling sustainable transportation: The model-based determination of business/operating areas of free-floating carsharing systems. Research In Transportation Economics. 2015, 51, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepolina, E.; Farina, A. A new shared vehicle system for urban areas. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2012, 21, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Xia, C. Fleet-sizing and service availability for a vehicle rental system via closed queueing networks. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2011, 211, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhandwala, M.; Cai, H. Siting charging stations for electric vehicle adoption in shared autonomous fleets. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment. 2020, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. Optimal investment strategy of a free-floating sharing platform. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2020, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z. Electric vehicle fleet size and trip pricing for one-way carsharing services considering vehicle relocation and personnel assignment. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2018, 111, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Meng, Q. Fleet sizing for one-way electric carsharing services considering dynamic vehicle relocation and nonlinear charging profile. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 128, 23–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruglieri, M.; Colorni, A.; Luè, A. The Vehicle Relocation Problem for the One-way Electric Vehicle Sharing: An Application to the Milan Case. Procedia - Social And Behavioral Sciences. 2014, 111, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huwer, U. Public transport and car-sharing - benefits and effectsof combined services. Transport Policy. 2004, 11, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Mathew, T. Integrated Multimodal Transit Route Network Design with Feeder Systems. Transportation Research Procedia. 2020, 48, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, S.; Chan, N. Mobility and the Sharing Economy: Potential to Overcome First-and Last-Mile Public Transit Connections. (UC Berkeley: Transportation Sustainability Research Center. 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tabassum, S.; Tanaka, S.; Nakamura, F.; Ryo, A. Feeder Network Design for Mass Transit System in Developing Countries (Case study of Lahore, Pakistan). Transportation Research Procedia. 2017, 25, 3129–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheu, R.; Lee, D. Dynamic relocating vehicle resources using a microscopic traffic simulation model for carsharing services. 3rd International Joint Conference On Computational Sciences And Optimization, CSO 2010: Theoretical Development And Engineering Practice. 2010, 1, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Mahéo, A.; Kilby, P.; Hentenryck, P. Benders Decomposition for the Design of a Hub and Shuttle Public Transit System. Transp. Sci.. 2019, 53, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacı, B.; Zografos, K.; Geroliminis, N. An optimization framework for the development of efficient one-way car-sharing systems. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2015, 240, 718–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; An, K.; Rich, J.; Ma, W. Vehicle relocation in one-way station-based electric carsharing systems: A comparative study of operator-based and user-based methods. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2020, 142, 102081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; An, K.; Almeida Correia, G. Planning station capacity and fleet size of one-way electric carsharing systems with continuous state of charge functions. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2020, 287, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalık, H.; Fortz, B. A Benders decomposition method for locating stations in a one-way electric car sharing system under demand uncertainty. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 125, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, A.; Cheu, R.; Meng, Q.; Fung, C. A decision support system for vehicle relocation operations in carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2009, 45, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Heterogeneous fleet management for one-way electric carsharing system with optional orders, vehicle relocation and on-demand recharging. Computers & Operations Research. 2022, 145, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illgen, S.; Höck, M. Literature review of the vehicle relocation problem in one-way car sharing networks. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 120, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfian, G.; Rhee, J.; Yoon, B. A simulation tool for prioritizing product-service system (PSS) models in a carsharing service. Computers & Industrial Engineering. 2014, 70, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Y. Joint design of parking capacities and fleet size for one-way station-based carsharing systems with road congestion constraints. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2016, 93, 268–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantuso, G. Exact solutions to a carsharing pricing and relocation problem under uncertainty. Computers And Operations Research. 2022, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Y. Dynamic pricing, vehicle relocation and staff rebalancing for station-based one-way electric carsharing systems considering nonlinear charging profile. Transportation Letters. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; An, K.; Almeida, Correia, G. ; Rich, J.; Ma, W. An innovative approach to solve the carsharing demand-supply imbalance problem under demand uncertainty. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2021, 132, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Almeida, Correia, G. ; Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Lv, Y. Performance of one-way carsharing systems under combined strategy of pricing and relocations. Transportmetrica B: Transport Dynamics. 2021, 9, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocca, M.; Giordano, D.; Mellia, M.; Vassio, L. Free floating electric car sharing design: Data driven optimisation. Pervasive And Mobile Computing. 2019, 55, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roni, M.; Yi, Z.; Smart, J. Optimal charging management and infrastructure planning for free-floating shared electric vehicles. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment. 2019, 76, 155–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkestad, C.; Hansen, N.; Fagerholt, K.; Andersson, H.; Pantuso, G. Optimal charging and repositioning of electric vehicles in a free-floating carsharing system. Computers & Operations Research. 2020, 113, 104771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, T.; Tan, Z. Electric vehicle fleet size for carsharing services considering on-demand charging strategy and battery degradation. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2021, 127, 103146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, X. Incentivized self-rebalancing fleet in electric vehicle sharing. IISE Transactions. 2022, 54, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prencipe, L.; Theresia, van Essen, J. ; Caggiani, L.; Ottomanelli, M.; Homem de Almeida Correia, G. A mathematical programming model for optimal fleet management of electric car-sharing systems with Vehicle-to-Grid operations. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2022, 368, 133147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambella, C.; Malaguti, E.; Masini, F.; Vigo, D. Optimizing relocation operations in electric car-sharing. Omega. 2018, 81, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, Z.; Liang, Y. A hybrid adaptive large neighborhood search and tabu search algorithm for the electric vehicle relocation problem. Computers & Industrial Engineering. 2022, 167, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wu, J.; Almeida, Correia, G. ; Sun, H.; Feng, Z. A cooperative strategy for optimizing vehicle relocations and staff movements in cities where several carsharing companies operate simultaneously. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2022, 161, 102711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lang, Z. A rolling-horizon decision framework for integrating relocation and user flexibility in one-way electric carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2022, 144, 103867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Qu, Y.; Wang, D. Integrated optimization of pricing and relocation in the competitive carsharing market: A multi-leader-follower game model. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2022, 138, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, M.; Hiermann, G.; Rüdel, F.; Walther, G. A polynomial-time algorithm for user-based relocation in free-floating car sharing systems. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2021, 143, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, D.; Molnar, G.; De Almeida, Correia, G. Trip pricing of one-way station-based carsharing networks with zone and time of day price variations. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2015, 81, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, A.; Hoang, N.; An, K.; Vu, H. A framework for railway transit network design with first-mile shared autonomous vehicles. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2021, 130, 103223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.; Susilawati, S. Shared autonomous vehicles implementation for the first and last-mile services. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives. 2021, 11, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokkink, P.; Geroliminis, N. Predictive user-based relocation through incentives in one-way car-sharing systems. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2021, 149, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Ko, J.; Kim, J. Carsharing travel distance and its associated factors: A case study of Seoul, South Korea. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2022, 362, 132380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, M.; Jamal, A.; Al-Ahmadi, H.; Rahman, M.; Almoshaogeh, M. Analysis of the Influential Factors towards Adoption of Car-Sharing: A Case Study of a Megacity in a Developing Country. Sustainability. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mi, X. A Comparative Study on Demand Forecast of Car Sharing Users Based on ARIMA and LSTM. 2020 5th International Conference On Electromechanical Control Technology And Transportation (ICECTT). pp. 565-574 (2020).
- Cocca, M.; Teixeira, D.; Vassio, L.; Mellia, M.; Almeida, J.; Silva, A. On Car-Sharing Usage Prediction with Open Socio-Demographic Data. Electronics. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahimi, N.; Zhang, H.; Dai, L.; Zhang, J. Modelling on Car-Sharing Serial Prediction Based on Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Complexity. 2022, 2022, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rožanec, J.; Kažič, B.; Škrjanc, M.; Fortuna, B.; Mladenić, D. Automotive OEM Demand Forecasting: A Comparative Study of Forecasting Algorithms and Strategies. Applied Sciences. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Z.; Zhong, Q.; Yi, A.; Chen, W. Demand Management of Station-Based Car Sharing System Based on Deep Learning Forecasting. Journal Of Advanced Transportation. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, T.; Cherry, C.; Ryerson, M.; Bell, J. Carsharing demand estimation and fleet simulation with EV adoption. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2019, 206, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maybury, L.; Corcoran, P.; Cipcigan, L. Mathematical modelling of electric vehicle adoption: A systematic literature review. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment 2022, 107, 103278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weikl, S.; Bogenberger, K. A practice-ready relocation model for free-floating carsharing systems with electric vehicles – Mesoscopic approach and field trial results. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2015, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Su, E.; Wang, Y.; Li, J. Branch-and-price-and-cut for the electric vehicle relocation problem in one-way carsharing systems. Omega. 2022, 109, 102609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogyrbayeva, A.; Jang, S.; Shah, A.; Jang, Y.; Kwon, C. A Reinforcement Learning Approach for Rebalancing Electric Vehicle Sharing Systems. IEEE Transactions On Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzella, F.; Pisacane, O. A two-phase optimization method for a multiobjective vehicle relocation problem in electric carsharing systems. Journal Of Combinatorial Optimization. 2018, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Chen, N. Stochastic one-way carsharing systems with dynamic relocation incentives through preference learning. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2022, 166, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, L.; Dias, B.; Soares, T.; Borba, B.; Quirós-Tortós, J. e-Carsharing siting and sizing DLMP-based under demand uncertainty. Applied Energy. 2023, 330, 120347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Sakurama, K. Communication-aware distributed rebalancing for cooperative car-sharing service. IET Control Theory & Applications 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kuo, J. The vehicle deployment and relocation problem for electric vehicle sharing systems considering demand and parking space stochasticity. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2021, 156, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liao, F. Incentivized user-based relocation strategies for moderating supply–demand dynamics in one-way car-sharing services. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2023, 171, 103017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Ouahmed, A.; Josselin, D.; Zhou, F. Relocation optimization of electric cars in one-way car-sharing systems: modeling, exact solving and heuristics algorithms. International Journal Of Geographical Information Science. 2018, 32, 367–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, D.; Correia, G.; Barnhart, C. Comparing Optimal Relocation Operations With Simulated Relocation Policies in One-Way Carsharing Systems. IEEE Transactions On Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2014, 15, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Jia, S.; Liu, Q. A user-based relocation model for one-way electric carsharing system based on micro demand prediction and multi-objective optimization. Journal Of Cleaner Production. 2021, 296, 126485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourinejad, M.; Zhu, S.; Bahrami, S.; Roorda, M. Vehicle relocation and staff rebalancing in one-way carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2015, 81, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, G. Planning of Relocation Staff Operations in Electric Vehicle Sharing Systems. Intelligent Information And Database Systems. 2013, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacı, B.; Zografos, K.; Geroliminis, N. An integrated optimization-simulation framework for vehicle and personnel relocations of electric carsharing systems with reservations. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2017, 95, 214–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Y. An overnight relocation problem for one-way carsharing systems considering employment planning, return restrictions, and ride sharing of temporary workers. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2022, 168, 102950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekli, S.; Boyacı, B.; Zografos, K. Enhancing the performance of one-way electric carsharing systems through the optimum deployment of fast chargers. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2021, 152, 118–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; Wu, X.; Li, M.; Zheng, N.; Yu, G. The allocation problem of electric car-sharing system: A data-driven approach. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment. 2020, 78, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balac, M.; Becker, H.; Ciari, F.; Axhausen, K. Modeling competing free-floating carsharing operators – A case study for Zurich, Switzerland. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2019, 98, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Cui, J.; Yang, L.; An, S. An integrated framework for electric vehicle rebalancing and staff relocation in one-way carsharing systems: Model formulation and Lagrangian relaxation-based solution approach. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2018, 117, 542–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruglieri, M.; Pezzella, F.; Pisacane, O. An Adaptive Large Neighborhood Search for relocating vehicles in electric carsharing services. Discrete Applied Mathematics. 2019, 253, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulos, A.; Gavalas, D.; Konstantopoulos, C.; Kypriadis, D.; Pantziou, G. Incentivized vehicle relocation in vehicle sharing systems. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2018, 97, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruglieri, M.; Pezzella, F.; Pisacane, O. Heuristic algorithms for the operator-based relocation problem in one-way electric carsharing systems. Discrete Optimization. 2017, 23, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, G.; Almeida, Correia, G. Long-term vehicle reservations in one-way free-floating carsharing systems: A variable quality of service model. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2019, 98, 298–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, F.; Albiński, S.; Boysen, N. Matching supply and demand for free-floating car sharing: On the value of optimization. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2023, 308, 1380–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatz, N.; Erera, A.; Savelsbergh, M.; Wang, X. Optimization for dynamic ride-sharing: A review. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2012, 223, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielbaum, A.; Bai, X.; Alonso-Mora, J. On-demand ridesharing with optimized pick-up and drop-off walking locations. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies 2021, 126, 103061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppert, M.; Steinhardt, C.; Müller, C.; Gönsch, J.; Bhogale, P. Matching functions for free-floating shared mobility system optimization to capture maximum walking distances. European Journal Of Operational Research. 2023, 305, 1194–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, L.; Jiang, Y. Collaborative strategic and tactical planning for one-way station-based carsharing systems with trip selection and vehicle relocation. Transportation Letters. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourinejad, M.; Roorda, M. A dynamic carsharing decision support system. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2014, 66, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayez, Eliyan, A. ; Kerbache, L.; Elomri, A. Shared clean mobility operations for first-mile and last-mile public transit connections: A case study of doha, Qatar. Journal Of Advanced Transportation. 2022, 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, X.; Broaddus, A.; Johnson, J.; Srinivasan, S. Evaluating shared e-scooters’ potential to enhance public transit and reduce driving. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment. 2023, 117, 103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzouras, P.; Mitropoulos, L.; Koliou, K.; Stavropoulou, E.; Karolemeas, C.; Antoniou, E.; Karaloulis, A.; Mitropoulos, K.; Vlahogianni, E.; Kepaptsoglou, K. Describing Micro-Mobility First/Last-Mile Routing Behavior in Urban Road Networks through a Novel Modeling Approach. Sustainability. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, K.; Kapatsila, B.; Grisé, E. Integrating Public Transit and Shared Micromobility Payments to Improve Transportation Equity in Seattle, WA. Transportation Research Record. 2023, 2677, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeschger, G.; Carroll, P.; Caulfield, B. Micromobility and public transport integration: The current state of knowledge. Transportation Research Part D: Transport And Environment. 2020, 89, 102628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romm, D.; Verma, P.; Karpinski, E.; S. ; ers, T.; McKenzie, G. Differences in first-mile and last-mile behaviour in candidate multi-modal Boston bike-share micromobility trips. Journal Of Transport Geography. 2022, 102, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Joint infrastructure planning and fleet management for one-way electric car sharing under time-varying uncertain demand. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 128, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Cardin, M. Integrating operational decisions into the planning of one-way vehicle-sharing systems under uncertainty. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. 2018, 86, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Gupta, A.; Shroff, N. Fleet sizing and charger allocation in electric vehicle sharing systems. IFAC Journal Of Systems And Control. 2022, 22, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporte, G.; Meunier, F.; Wolfler, Calvo, R. Shared mobility systems: an updated survey. Annals Of Operations Research. 2018, 271, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.; Miller-Hooks, E. Fleet Management for Vehicle Sharing Operations. Transportation Science. 2011, 45, 524–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daganzo, C.; Newell, G. Configuration of physical distribution networks. Networks. 1986, 16, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Febbraro, A.; Sacco, N.; Saeednia, M. One-Way Car-Sharing Profit Maximization by Means of User-Based Vehicle Relocation. IEEE Transactions On Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2019, 20, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, J. P-D pair based EV-sharing vehicle relocation problem with route familiarity. Computers & Industrial Engineering. 2021, 159, 107529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repoux, M.; Kaspi, M.; Boyacı, B.; Geroliminis, N. Dynamic prediction-based relocation policies in one-way station-based carsharing systems with complete journey reservations. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 130, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y. Integrated Optimization of Planning and Operations for Shared Autonomous Electric Vehicle Systems. Transportation Science. 2023, 57, 106–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Cui, J.; Ghiasi, A.; Zhou, F. Design framework of large-scale one-way electric vehicle sharing systems: A continuum approximation model. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2016, 88, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Huang, W.; Jian, S. One-way carsharing service design under demand uncertainty: A service reliability-based two-stage stochastic program approach. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics And Transportation Review. 2022, 159, 102624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouza, Allende, G. ; Still, G. Solving bilevel programs with the KKT-approach. Mathematical Programming. 2012, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, G.; Jorge, D.; Antunes, D. The Added Value of Accounting For Users’ Flexibility and Information on the Potential of a Station-Based One-Way Car-Sharing System: An Application in Lisbon, Portugal. Journal Of Intelligent Transportation Systems. 2014, 18, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacı, B.; Zografos, K. Investigating the effect of temporal and spatial flexibility on the performance of one-way electric carsharing systems. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological. 2019, 129, 244–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vine, S.; Polak, J. The impact of free-floating carsharing on car ownership: Early-stage findings from London. Transport Policy. 2019, 75, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnovetckaia, R.; Mostofi, H. Impact of Car-Sharing and Ridesourcing on Public Transport Use: Attitudes, Preferences, and Future Intentions Regarding Sustainable Urban Mobility in the Post-Soviet City. Urban Science. 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Correia, G. Electric carsharing and micromobility: A literature review on their usage pattern, demand, and potential impacts. International Journal Of Sustainable Transportation. 2021, 16, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deza, A.; Huang, K.; Metel, M. Charging station optimization for balanced electric car sharing. Discrete Applied Mathematics. 2022, 308, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Br, statter, G. ; Leitner, M.; Ljubić, I. Location of Charging Stations in Electric Car Sharing Systems. Transportation Science. 2020, 54, 1408–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, B.; Hu, B.; Stubenschrott, M.; Ritzinger, U. ; Pr, tstetter, M. Optimizing Charging Station Locations for Electric Car-Sharing Systems. Evolutionary Computation In Combinatorial Optimization.
- Sonneberg, M.; Kuehne, K.; Breitner, M. A Decision Support System for the Optimization of Electric Car Sharing Stations. International Conference On Interaction Sciences. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jorge, D.; Correia, G.; Barnhart, C. Testing the Validity of the MIP Approach for Locating Carsharing Stations in One-way Systems. Procedia - Social And Behavioral Sciences. 2012, 54, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Tactical decisions | Operational decisions | Additional decisions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | ||
| [145] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | Fleet allocation |
| [109] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | Battery charge |
| [81] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | Staff assignment to vehicles Trip pricing |
| [100] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | Dynamic trip pricing |
| [143] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | Vehicle & staff initial allocation |
| [171] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - |
| [129] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | Staff routs & schedules |
| [112] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | State of charge of a vehicle at a specified time Vehicle and staff inventory at a specified time at a certain station Vehicle assignment to a trip |
| [172] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Vehicle and staff initial allocation |
| [168] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | Parking space inventory Vehicle inventory |
| [94] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | No. of rejected demand No. of rejected vehicle return |
| [157] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | Vehicle availability time |
| [140] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | - |
| [147] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | - | Fleet initial allocation Staff initial allocation Battery volume at time steps |
| [82] | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | Find a profitable trip chain |
| [142] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | No. of vehicles being charged |
| [178] | ✓ | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - |
| [102] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | Fleet initial allocation Trip pricing |
| [110] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | Staff routes & schedules for vehicle relocation |
| Reference | Strategic decisions | Tactical decisions | Objective function | Additional decisions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |||
| [186] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of parking spaces Vehicle inventory at each station at each time step |
| [138] | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of parking spaces Fleet allocation |
| [174] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Min costs | - |
| [69] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | Trip selection |
| [93] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | Trip selection |
| [182] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Max No. of EV trips Min No. of unserved commuters. |
Charging station allocation No. of parking spaces |
| [144] | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Max profits | No. of chargers to be installed Station upgrade with chargers of a certain type. No. of vehicles with a certain battery level to be charged with a charger of a certain type |
| [90] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Multi-objective: max operator profit and commuters’ benefit |
No. and location of shared stations No. of served and unserved orders |
| [175] | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Max profit | No. of parking spaces Vehicle movements Vehicle and staff allocation |
| [92] | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of parking spaces in a zone Fleet size in a zone No. of satisfied travel demand |
| [70] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | Fleet allocation Depot-size Vehicle inventory Trip selection |
| [72] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of stations No. of car parking spaces Vehicle allocation |
| [183] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | Number of chargers installed in a station Trip selection Trip assignment to vehicles |
| [184] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | First level: No. of stations Station capacity Fleet size. Second level: Trip selection |
| [185] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of vehicles being charged with a regular charger No. of vehicles being charged with fast chargers Trip assignment to a station |
| [165] | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Min costs | Vehicle allocation |
| [156] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | Max profit | No. of parking spaces Vehicle allocation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





