1. Introduction
As one of the monotypic genera in the family Lauraceae,
Eusideroxylon Teijsm. & Binn. includes the only tree species
Eusideroxylon zwageri Teijsm. & Binn. (
https://www.worldfloraonline.org/, accessed on: 10 Oct 2023), which is mainly distributed in the tropical rainforests of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines.
Eusideroxylon zwageri, known as "Belian" in Malaysia, "Ulin" in Indonesia, and "Tambulan" in the Philippines by local people, is recognized for its globally durable wood [1]. Belian is included in the list of threatened tree species [2]. Currently, Belian, under national protection in Indonesia, exhibits decreasing populations due to past over-exploitation [3]. Therefore, acquiring the genetic resources and population data of the tropical tree Belian is urgent.
Chloroplasts are vital organelles in the cells of green plants and certain algae, where photosynthesis occurs [4]. Higher plant chloroplast genomes are generally quadripartite, with one large single copy region (LSC), one small single copy region (SSC), and two reverse repeat regions (IRs) [5]. Terrestrial plant chloroplast genomes are typically 120 kb to 160 kb in size and comprise 110~130 genes [6-8]. Chloroplast genome size changes are frequently related to reverse repeat region expansion and contraction, gene deletion, intron deletion, gene spacer region differences, and short-segment repeat sequences [9,10]. Compared with the nuclear genome and mitochondrial genome, the chloroplast genome has moderate evolutionary speed, small molecular weight, relatively conservative structure, and primarily single-parent inheritance, rarely recombination. The success rate of obtaining complete genome by modern sequencing technology is high, and it is an ideal material for studying plant genetics and evolution [11,12].
The first molecular approach of Chanderbali et al. (2001) reported the chloroplast sequences including trnL-trnF, psbA-trnH, trnT-trnL, and rpl16 and nuclear ribosomal sequences 26S and ITS for Belian which grouped with the Aspidostemon, Beilschmiedia, Cryptocarya, Endiandra, Eusideroxylon, Hypodaphnis, Potameia, and Potoxylon species [13]. The second phylogenetic research, which used the chloroplast marker trnK intron to build a Bayesian tree of 49 species, revealed a well-supported Cryptocaryeae group that included Aspidostemon, Beilschmiedia, Cryptocarya, Endiandra, Eusideroxylon, and Potameia species [14]. Ten years later, Hiroyuki et al. (2015) identified 16 chloroplast polymorphic marker sequences, total 10,618 bp in length [15]. Then, Nurtjahjaningsih et al. (2017) developed 16 polymorphic markers using six chloroplast DNA regions (atpE, ccsA-ndhD, matK, trnL-trnF, rpl2, and ycf3) to investigate the genetic structure from 72 Belian trees from 9 populations [1]. Finally, Md-Isa et al. (2021) analysed Belian genetic variation using four microsatellite markers in 52 samples from three populations of Nirwana Rehabilitation Forest (NRF), and Tatau, Sarawak [16]. These genome fragments were significant for the genetic conservation and population management of Belian, yet they are not a substitute for the complete chloroplast genome.
Six years ago, we reported a complete chloroplast genome sequence of Belian (GenBank accession No. MF939351) and a monophyletic phylogenetic group of Belian and 45 other Lauraceae species [17]. Since then, the phylogenetic relationships of Lauraceae, or magnoliids, have been studied using this genome. Liu et al. (2021) constructed the largest plastid genome dataset of Lauraceae, combining Belian and 190 plastome genomes from 131 species of 25 genera, and generated a phylogenetic tree using ML and NJ methods [18]. Similarly, Yang et al. (2023) constructed two phylogenetic trees using the complete chloroplast sequence of Belian, along with other Lauraceae species by ML and BI methods [19]. In both studies, Belian was consistently placed within the Cryptocaryeae tribe, which comprises species from the genera Beilschmiedia, Cryptocarya, Endiandra, Eusideroxylon, Potameia, Sinopora, and Syndiclis. However, a recent study by Ariati et al. (2023) concluded that our sequenced Belian indivadual might be classified within the Myristicaceae clade instead of the Lauraceae [20]. We were particularly surprised by the result.
Here, we assembled two new complete chloroplast genomes of Belian and reanalyzed them alongside previously published one, including genome characterization, Codon usage, repeat sequences, IRs boundaries, mutational events, and nucleotide polymorphism (Pi) analysis. Forty-four plastomes from ten magnoliids families were used to reconstruct the phylogenetic trees to determine the location of Belian within the Lauraceae family. Our objectives were to look at the structural pattern of complete plastomes, and to establish the phylogenetic status of Belian species in the Lauraceae family using entire plastome sequencing. Our findings will pave the way for the molecular identification, safeguarding, and use of genetic resources while also assisting in our understanding of the genetic origins and evolutionary history of Belian.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials, extraction and sequencing of DNA
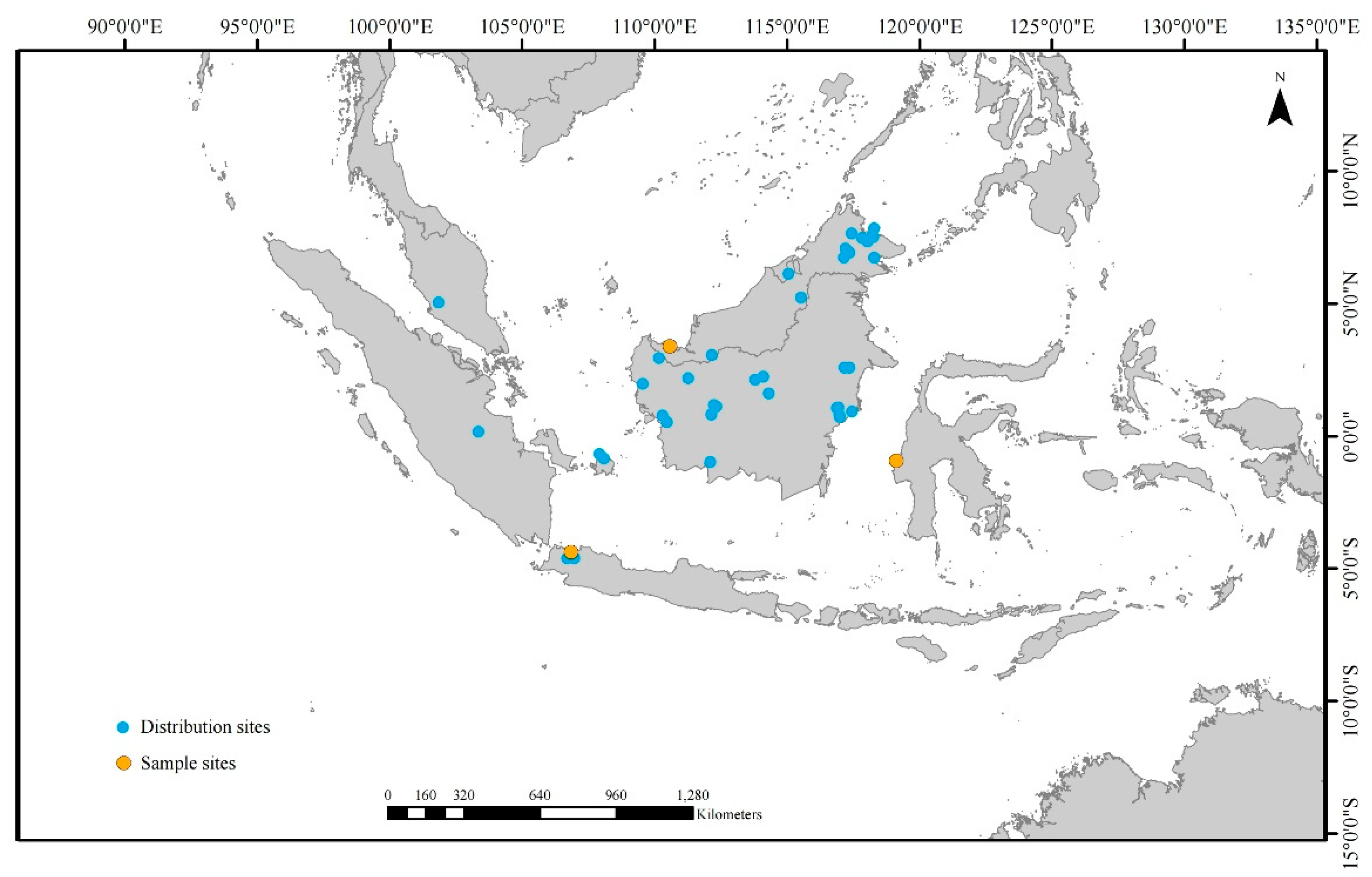
Two accessions of fresh Belian leaves were collected in Java, Indonesia, and Kalimantan, Malaysia (
Figure 1). The Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden's Herbarium, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, is home to the gathered plant specimens. Using a modified version CTAB approach, 2g of leaves were used to extract total DNA [21]. Before sequencing, 0.5 μg of pure DNA was fragmented to create short-insert (500 bp) libraries according to the manufacturer's specifications (Illumina). DNA samples were tagged, pooled together, and sequenced in one lane of a Genome Analyzer (Illumina HiSeq 2000) at BGI-Shenzhen, yielding >4.0 Gb of reads per sample.
2.2. Annotation and assembly of the chloroplast genome
Following the filtering of the sequencing data, the chloroplast genomes were automatically assembled using the GetOrganelle version 1.7.5 [22]. Bandage version 0.9.0 [23] was used to identify the circular maps to assess the assembly quality. The whole chloroplast genome sequence of
Cryptocarya chinensis (GenBank accession No. LC212965) was used as a reference, automatically annotated using CPGAVAS2 (
https://www.herbalgenomics.org/cpgavas2) [24]. Start and stop codons, as well as intron/exon borders of protein-coding genes, were manually verified. OGDRAW (
https://chlorobox.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/OGDraw.html) [25] was created a circular chloroplast genome map.
2.3. Chloroplast genome analysis
All protein-coding sequences from the three Belian chloroplast genomes were extracted using PhyloSuite version 1.2.3 [26]. Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of three chloroplast genomes was calculated using CodonW version 1.4.2 [27]. The repeat sequences were predicted using the online program REPuter (
https://bibiserv.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/reputer) [28]. The parameters were set as Maximum computed repeats=5,000, Minimal repeatsize=25, and Hamming distance=3. Simple repeat sequences (SSRs) were predicted using the online software MISA (
https://webblast.ipk-gatersleben.de/misa) [29], which included mono-nucleotide, di-nucleotide, tri-nucleotide, tetra-nucleotide, penta-nucleotide, and hexa-nucleotide, with repeat thresholds set at 10, 5, 4, 3, 3, and 3.
2.4. Comparative sequence analysis
CPJSdraw software [30] was used to analyze the boundary differences of IR regions of the chloroplast genome and draw a comparison map. The microstructural mutations of the sequences were detected in the Genenious Prime version 2023.2.1, and manually examined in the BioEdit version 7.0.9, especially for the inversion sites. We performed a sliding window analysis to evaluate the variability (Pi) over the plastomes in DnaSP version 6.12 [31]. The window length was set to 600 bp and the step size was set as 200 bp.
2.5. Phylogenetic analysis
A total of 48 chloroplast genomes from 10 families of the Magnoliids and 5 species of Chloranthaceae were aligned using MAFFT version 7 (
https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/) [32], of which 39 sequences were downloaded from NCBI and nine were from LCGDB (Supplementary Table S1). The complete chloroplast genome matrix was obtained and manually adjusted by BioEdit version 7.0.9. Phylogenetic relationships were reconstructed based on the maximum-likelihood (ML) method in IQ tree version 2.2.2 [33] and the Bayesian inference (BI) method in MrBayes version 3.2.7 [34]. 1000 bootstrap replicates were run for ML analysis to provide confidence support. Using the jModelTest version 2.1.10 software, the whole chloroplast genome dataset was examined for BI analysis, and the best TVM+I+G model was chosen [35]. The combined data were run for one million generations, sampling every 1000 generations. The first 25% of the tree was discarded as burn-in, and the remaining trees were used to generate a majority-rule consensus tree. In all phylogenetic analyses,
Chloranthus erectus (GenBank accession No. MH394412),
Chloranthus spicatus (GenBank accession No. EF380352),
Chloranthus henryi (GenBank accession No. MK922064), and
Chloranthus japonicus (GenBank accession No. KP256024) were used as outgroup. All phylogenetic trees were visualized or further edited in Fig Tree version 1.4.4 (
http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/publications/).
3. Results and discussion
3.1. General features of the Belian chloroplast genomes
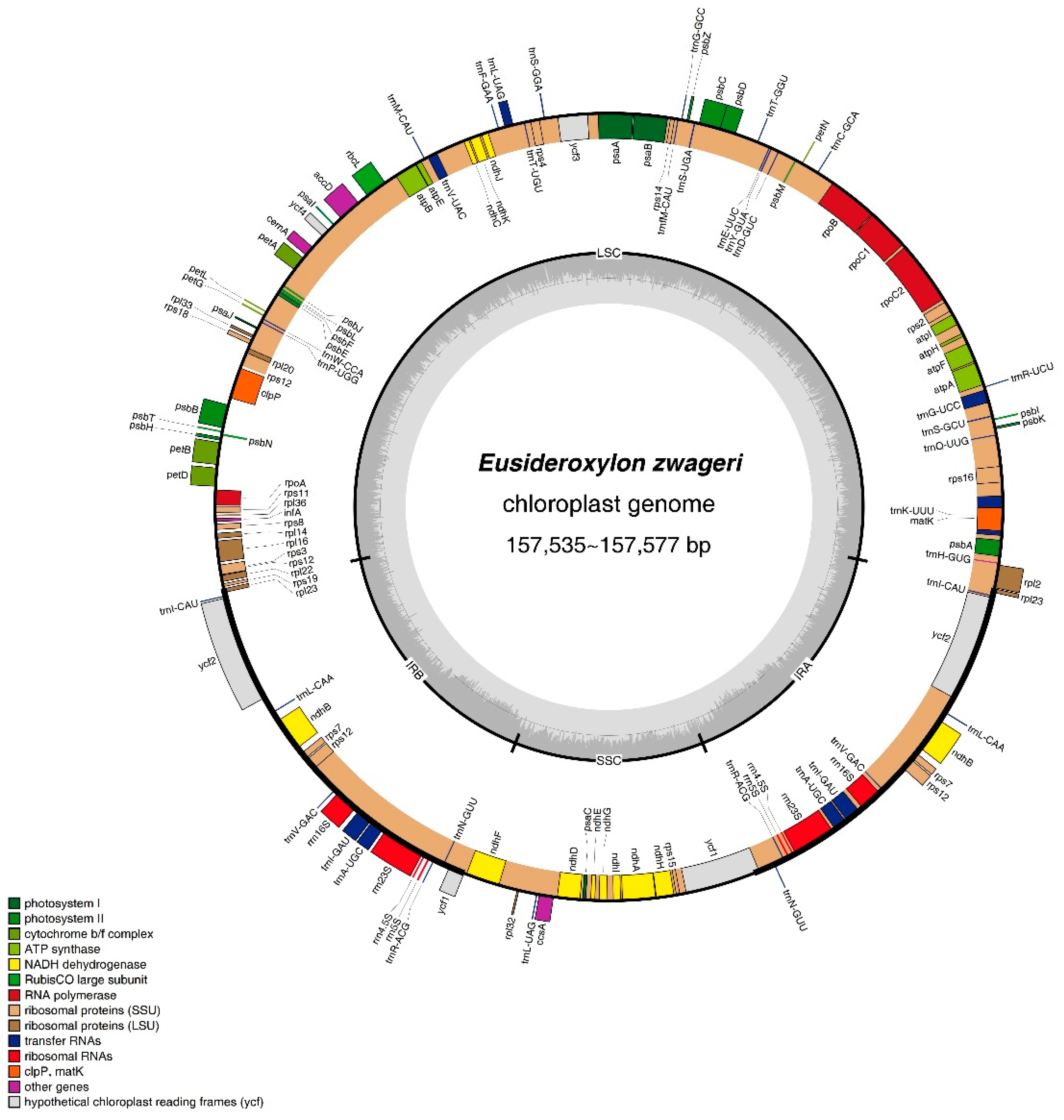
The newly assembled two plastomes had quadripartite structures forming circular molecules, and the size of both genomes was 157,535 bp of Belian Ⅰ and 157,536 bp of Belian Ⅲ (
Figure 2), respectively. They were 41 bp and 42 bp more minor than that of Belian Ⅱ. Both genomes included a pair of inverted repeats (IRs) of 24,717 bp in Belian Ⅰ and 24,706 bp in Belian Ⅲ, separated by a small single copy (SSC) region of 18,912 bp in Belian Ⅰ and 18,916 bp in Belian Ⅲ, and a large single copy (LSC) region of 89,189 bp in Belian Ⅰ and 89,208 bp in Belian Ⅲ (
Table 1). Their GC content, similar to that of Belian Ⅱ, was 39%. As predicted, we annotated 130 genes each in two plastids, including 113 unique genes and 17 duplicate in the IR regions (Supplementary Table S2). Among these genes, there were 85 PCGs, 37 tRNA genes, and eight rRNA genes (
Figure 2). Introns were also found in twelve protein-coding genes and eight tRNA genes (Supplementary Table S2).
3.2. Codon usage
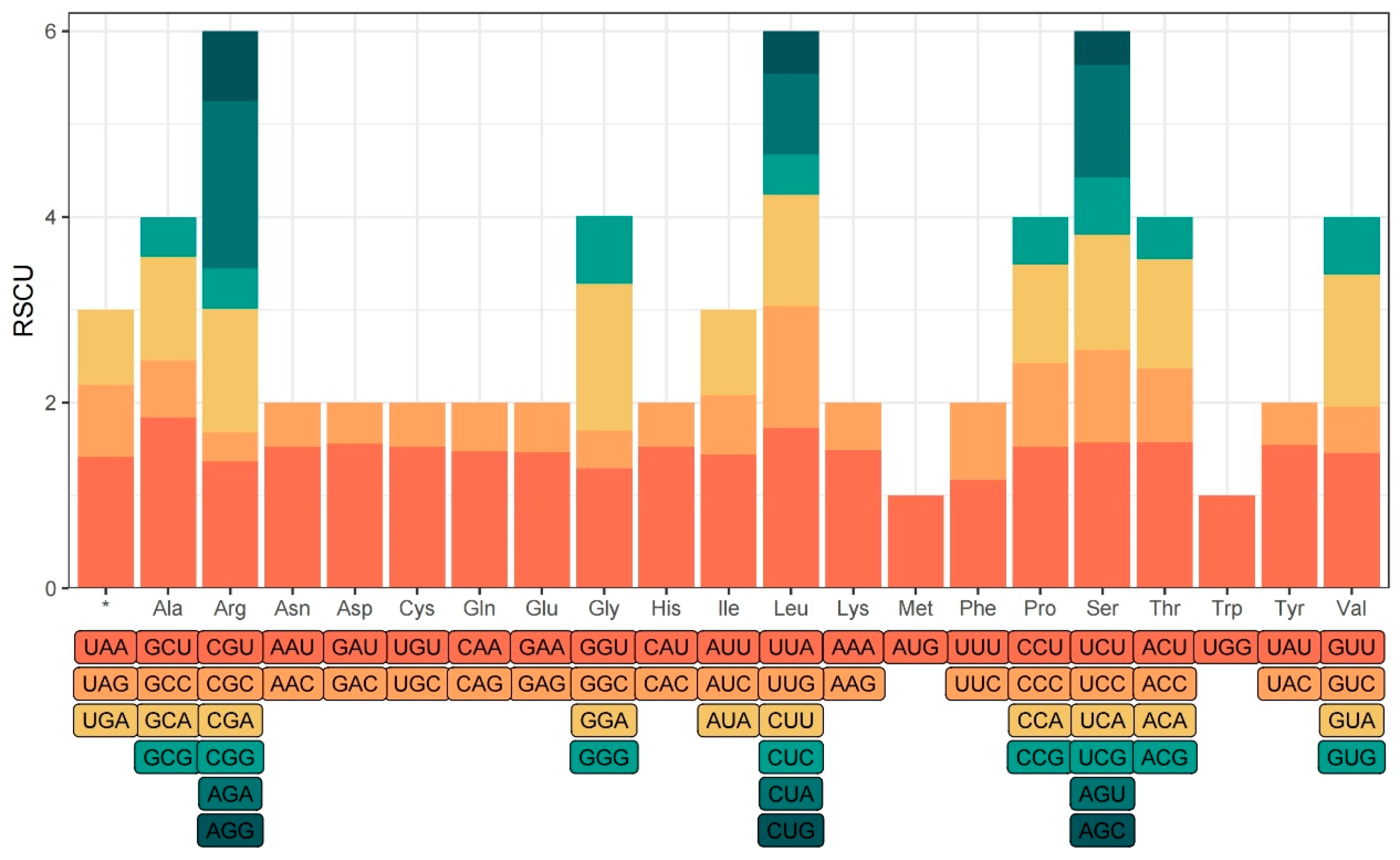
The relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) of the three Belian chloroplast genomes was calculated using CodonW 1.4.2, and a total of 78,289 codons were detected, averaging 26,096 codons per individual. All the codons are divided into 64 types, coding for 20 amino acids. There were 31 high-frequency codons with RSCU>1, comprising 13 codons ending in A and 16 ending in U, accounting for 93.55% (
Figure 3). The codons AGU and UGG had an RSCU value of 1, indicating an unbiased usage. RSCU>1.6 was found in the codons GCU, CCA, UUA, and AGA, suggesting that they appeared more frequently and were overused. Leucine, Arginine, and Serine were encoded by six codons, while methionine and tryptophan were encoded by only one codon each. The rest of the amino acids were encoded by two to four codons.
3.3. Repeat sequences and simple sequence repeats analysis
We identified 95 to 101 long repeat sequences (>25 bp) in three Belian chloroplast genomes using REPuter, including 43~45 palindromic repeats, 37~41 forward repeats, 10~12 reverse repeats, and 4~5 complement repeats (
Figure 4A). Palindromic repeats were the most common in the genomes of the three individuals, followed by forward repeats and complement repeats. Most of the repeats ranged from 25 to 29 bp in length and with nine repeats being 40 to 49 bp in length. In addition, the reverse repeats and complement repeats were only detected in the range of 25~29 bp, but not in the range of 30~39 bp and 40~49 bp (
Figure 4B).
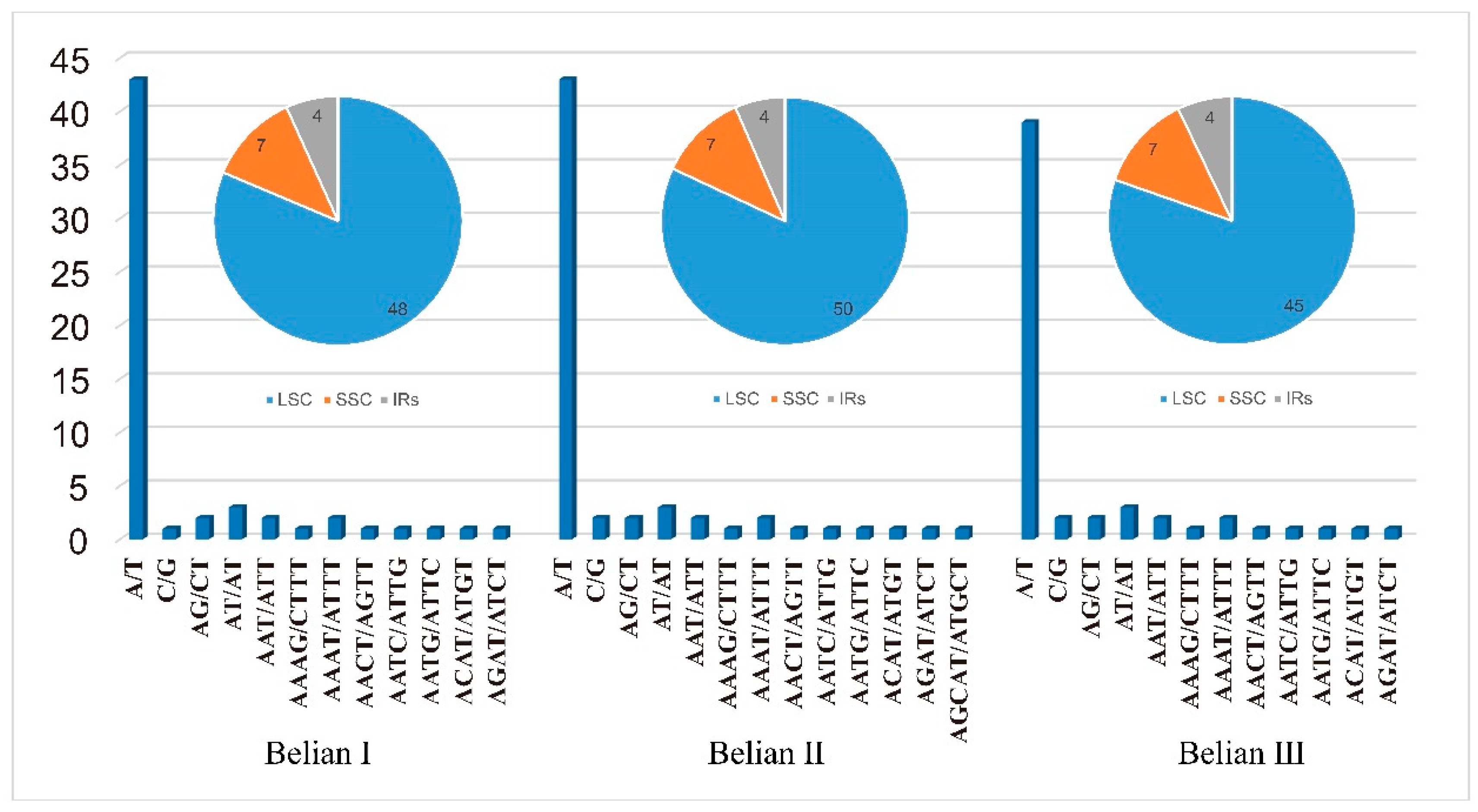
Simple repeat sequences (SSRs) are widely distributed in chloroplast genome. In all, 176 SSRs were found in the three Belian chloroplast genomes, with an average of 59 per individual. Mono-nucleotides were the most numerous, accounting for 73.1% to 74.58% of the total, followed by five di-nucleotides, two tri-nucleotides, eight tetra-nucleotides, and one penta-nucleotide, and no hex-nucleotides were detected (
Figure 5). More than 90% of mono-nucleotides belong to A or T base repeats. SSRs are not distributed equally across the genome. There were 48/50/45, 7, and four SSR repeats distributed in LSC, SSC, and IRs of the three Belian genomes, respectively. The variability in SSR numbers among the three individuals was primarily observed in the LSC region, while the counts in the SSC and IR regions remained consistent.
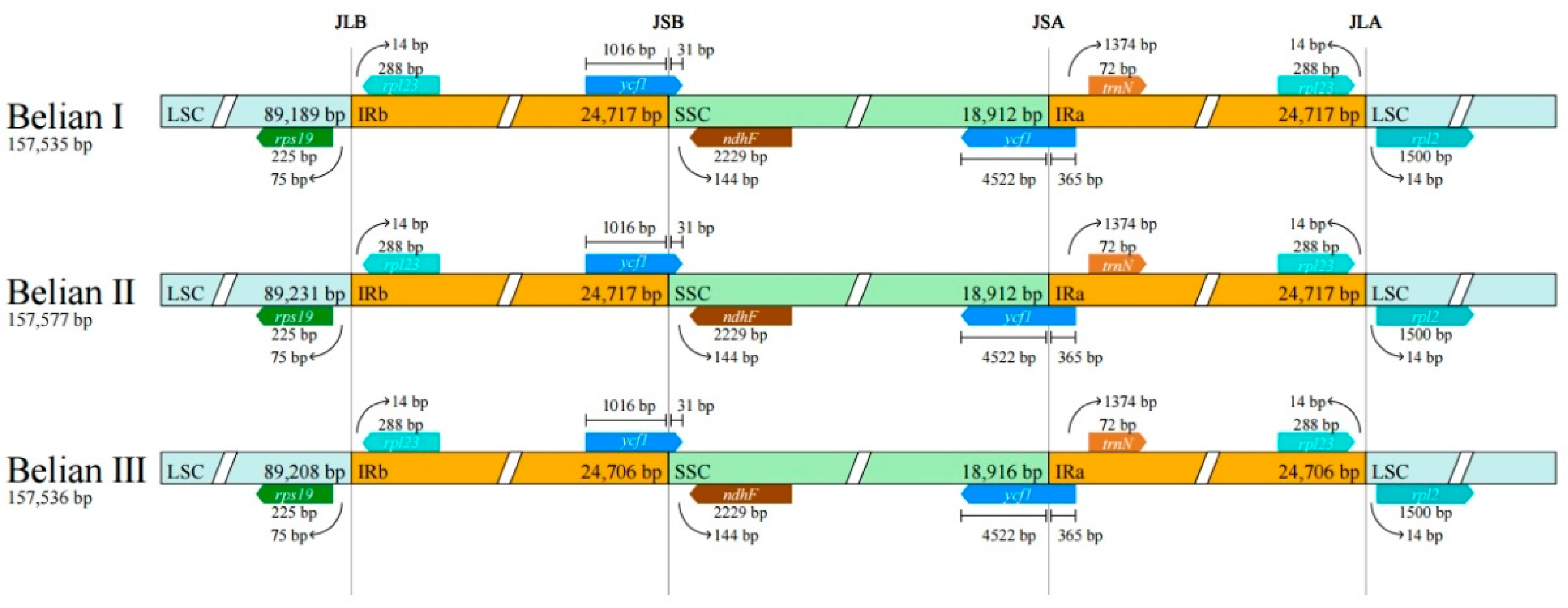
3.4. Inverted repeat contraction and expansion
Differences in IR boundaries of the three Belian chloroplast genomes were compared using CPJSdraw software. The results showed no difference in IR boundaries among the three individuals (
Figure 6). LSC/IRb(JLB), IRb/SSC(JSB), SSC/IRa(JSA), and IRa/LSC(JLA) boundary junctions are mainly associated with six genes,
rsp19,
rpl23,
ycf1,
ndhF,
trnN, and
rpl2.
rsp19 and
rpl23 were distributed on both sides of the LSC/IRb(JLB), the intact
ycf1 connects to the SSC/IRa(JSA) boundary, the
ycf1 fragment connects to the IRb/SSC(JSB) boundary, and
rpl23 and
rpl2 were distributed near the IRa/LSC(JLA) boundary.
3.5. Mutations in the Belian chloroplast genomes
Between the Belian I and Belian III plastomes, we found 143 mutation events, including five microinversions, 40 InDels, and 98 substitutions. Compared to the Belian Ⅱ, we accurately located six microinversions, 53 InDels, and 111 substitutions in these Belian plastomes. Among the SNPs, 46 were located in the gene-coding regions, which included 21 transitions (Ts) and 25 transversions (Tv), while 65 were found in non-coding regions, comprising 27 Ts and 38 Tv (Supplementary Table S3). The transition/transversion ratio (Ts/Tv) was calculated to be 0.76. Of the 53 InDels, 40 were in the LSC region, 13 in the SSC region, and four in the IR regions. The sizes of all InDels varied from 1 to 15 bp. There were 50 in intergenic regions, three in the gene coding regions, and none in introns. The greatest InDel, 15 bp in size, was found in the atpF-atpH intergenic region. There were also four microinversions in the psbC-trnS, petA-psbJ, rrn5S-trnR, and ccsA-ndhD intergenic areas, as well as two microinversions in the rpl16 and ycf1 coding regions.
SNP and InDel events of Belian II and Belian III were detected using Belian I as a reference, and their densities in each region were calculated (
Table 2). Belian II possesses 31 SNPs (5 Ts, 26 Tv) and 20 InDels, while Belian III holds 98 SNPs (44 Ts, 54 Tv) and 40 InDels. The number of SNPs in Belian III was 3.16 times that of Belian II, and the SNP count was double that of Belian II. Compared to the other two regions, the SSC region of Belian II had the highest density of SNPs and InDels. The highest SNP density was observed in the LSC regions of BelianIII, whereas the highest InDel density was identified in the SSC region. In all of them, the density of the IR regions is low.
3.6. Nucleotide diversity (pi) analysis
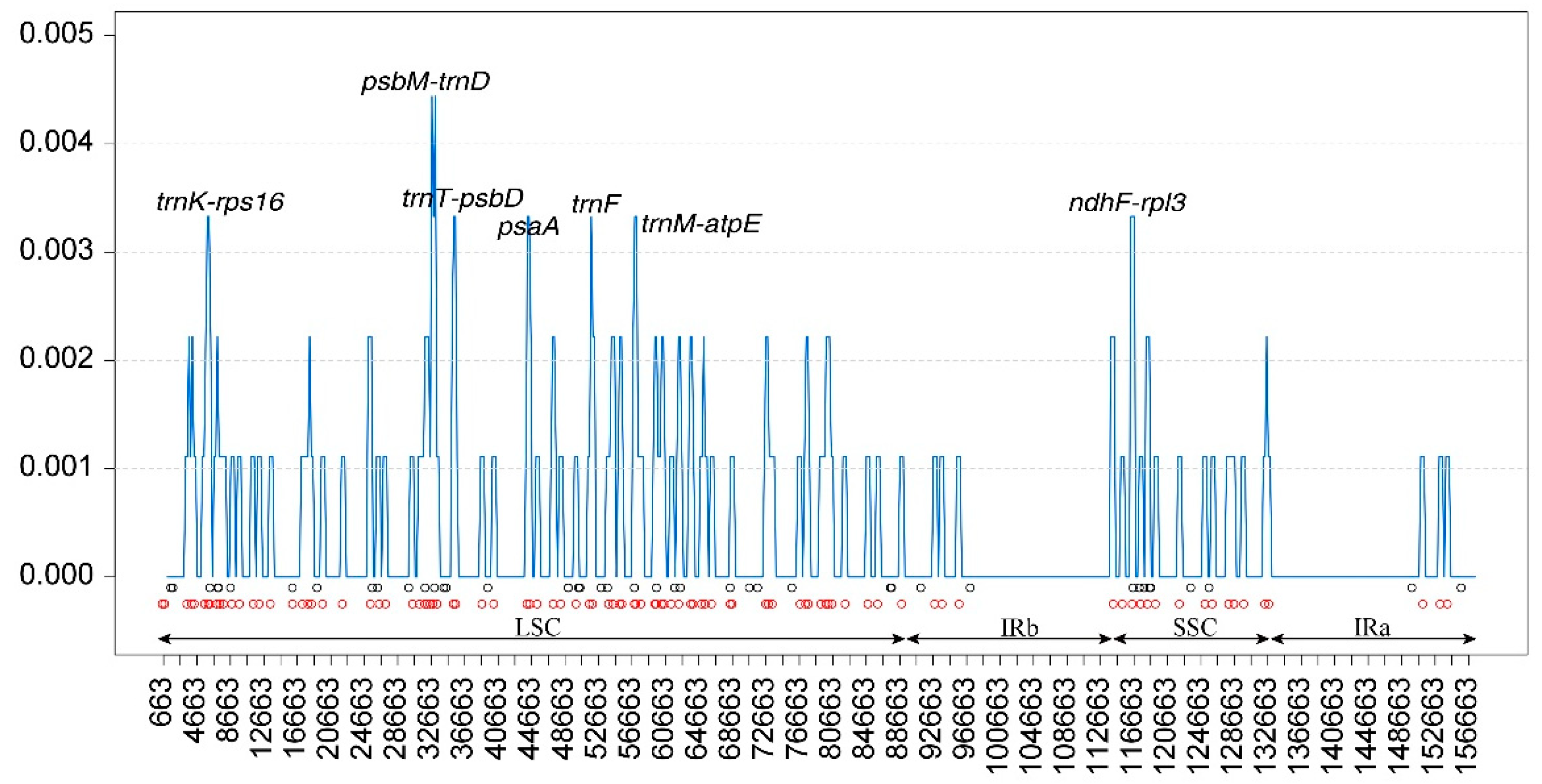
The nucleotide diversity (pi) values of three Belian plastomes were calculated using DNAsp version 6.12 software. In the three Belian plastomes, Pi values ranged from 0 to 0.0044, with a mean of 0.0005. Thirty-five variable loci (Pi > 0.002) were identified (
Figure 7), of which 10 hypervariable regions (Pi > 0.003), including
trnK,
trnK-rps16,
psbM-trnD,
trnT-psbD,
psaA,
trnF,
trnM-atpE,
atpE,
ndhF, and
ndhF-rpl32. Among these variable loci, eight were located in the LSC, two in the SSC, and none in the IRs. The value of
psbM-trnD was the highest (Pi > 0.004). These ten variable loci were all found in the LSC region and SSC region, and were ideal candidates for phylogenetic study.
3.7. Phylogenetic analysis
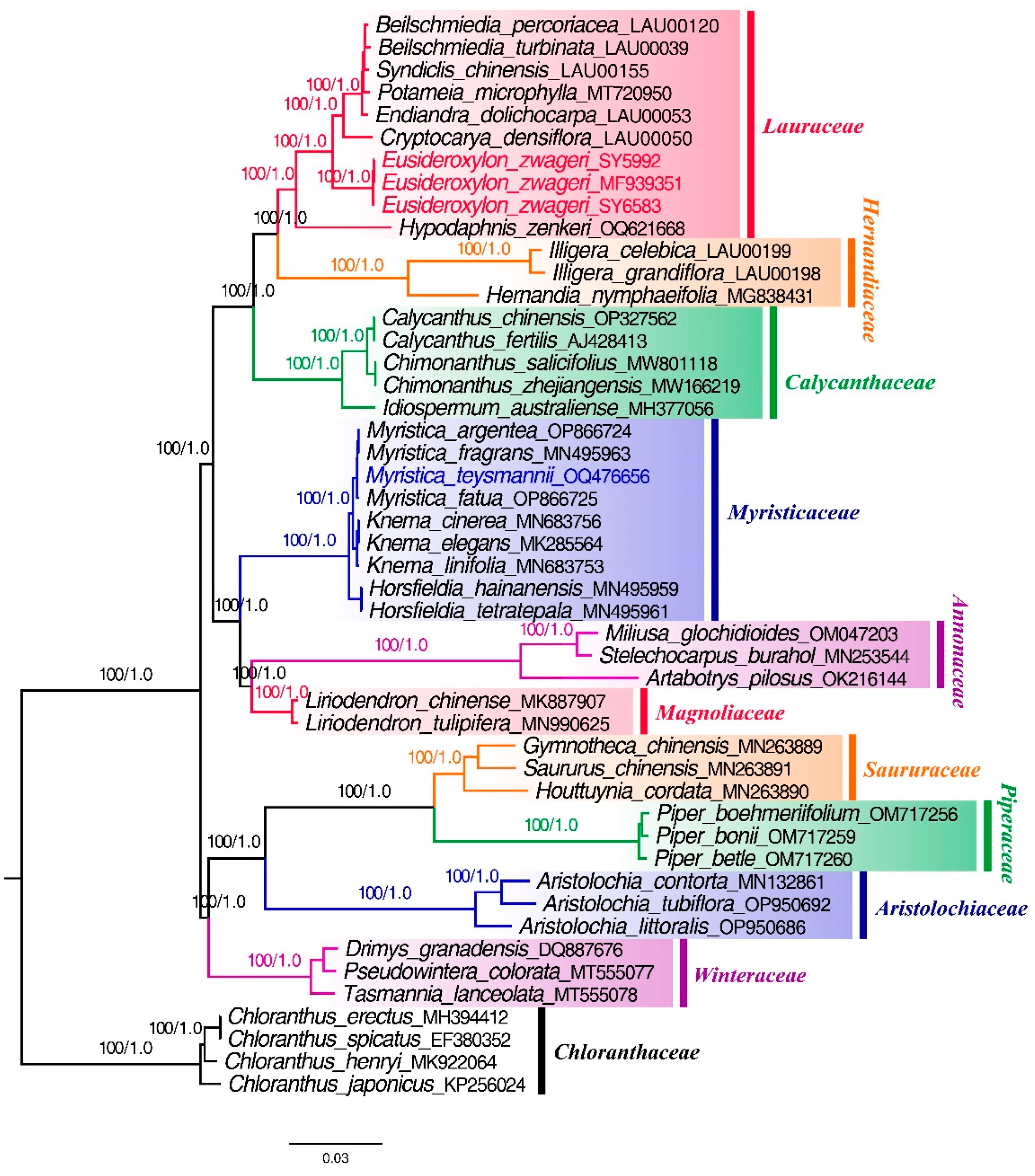
To determine the phylogenetic location of Belian in Lauraceae, the phylogenetic relationships among two Belian plastomes and 42 plastomes from ten families of the Magnoliids were reconstructed based on the chloroplast genomes, with
Chloranthus erectus,
C. spicatus,
C. henryi, and
C. japonicus as outgroup. The topologies, using the Bayesian inference (BI) and maximum likelihood (ML) methods, were nearly identical and both well-supported (
Figure 8). Overall, the 44 samples were divided into ten branches, corresponding Lauraceae, Hernandiaceae, Calycanthaceae, Myristicaceae, Annonaceae, Magnoliaceae, Saururaceae, Piperaceae, Aristolochiaceae, and Winteraceae (
Figure 8). The three plastomes of Belian were clustered into one branch in the Lauraceae clade with high support (ML-BS=100%, BI-PP=1.0).
In addition, we compared the trnL-trnF (GenBank accession No. AF268718), psbA-trnH (GenBank accession No. AF268820), rpl16 (GenBank accession No. AF268252) sequences used by Chanderbali et al. (2001) and the trnK (GenBank accession No. AJ627926) sequence used by Rohwer and Rudolph (2005) with the Belian sequence (GenBank accession No. MF939351). The trnL-trnF sequence was identical, and the psbA-trnH, rpl16, and trnK sequences contained 1 to 3 bp mutations. When we compared the genomes of the three Belian, we found similar mutations in these three regions. Furthermore, we constructed the phylogenetic tree using the same methods and sequences as in the Ariati et al. (2023) study, and added two additional Belian sequences. We get a different topological structure than they do. The three Belians clustered with Cinnamomum camphora, litsea coreana, and litsea auriculata, all located in the Lauraceae family, not the Myristiaceae (Supplementary Figure S1). We also constructed a phylogenetic tree based on the complete genome using ML and BI methods to get the same result.
4. Discussion
The chloroplast genome is second only to the nuclear genome regarding genetic information [36]. The similarity in size, content, and structure of the chloroplasts of most land plants is due to the common ancestor of the plant kingdom and the relative stability of the chloroplasts, which enables the chloroplast genome to be widely compared and analyzed in the plant kingdom, thereby revealing the plant's relatives and evolutionary history [37-39]. In this study, the chloroplast genomes of two Belians from Java and Kalimantan were newly assembled and compared with another previously published one. The chloroplast genome of Belian had a typical quadripartite structure with a size of 157,535~157,577 bp, containing a total of 130 genes, including 85 CDS genes, 37 tRNA genes and eight rRNA genes, which was similar to the chloroplast genomes of other Lauraceae species [40,41]. Song et al. (2017) found that the chloroplasts of the core Lauraceae were 150,749 bp to 152,739 bp in length, with
trnI-CAU, rpl23,
rpl2, and
ycf2 fragments and their intergenic regions lost in the IRb region, and that the chloroplasts of the basal Lauraceae were 157,577 bp to 158,530 bp in length, with
rpl2 lost in the IRa region [17], which is supported by the results of the present study. The chloroplast genomes of most land plants are highly conserved, and differences in the size of IR regions and intergenic spacer regions result in differences in chloroplast genomes [42]. The three Belian chloroplast genomes differed in size mainly owing to base insertion and deletion in the intergenic spacer region. In addition, it has been demonstrated that the
ycf1 and
ycf2 genes are located at the junction of the IR regions with the LSC and SSC regions, and these two genes have partial duplication [40,43]. In this study, only the
ycf1 gene occurs at the junction of the IR regions with the LSC and SSC regions, the complete
ycf1 gene occurs at the junction of the SSC and IRa, and the
ycf1 gene fragment occurs at the junction of the LSC and IRb (
Figure 6). This result was also seen in the genus
Atractylodes [44].
Codon preference varies significantly among different species and different genes in the same species. The utilization of biased codons is a significant indication in studying species evolution [45]. The usage of synonymous codons is biased, in many biological groups due to natural selection, base mutation, gene drift, and gene expression level differences [46]. Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) is an important index to study codon usage preference. A total of 78 289 codons were detected in the protein-coding genes of the three Belian chloroplast genomes, with 26 095~26 099 codons detected in each genome. There are 31 codons with high relative synonymous usage with RSCU>1, 29 of which end in A/U, indicating that the chloroplast genome of Belian is more inclined to employ codons ending in A or U, which is consistent with the results of previous studies [47].
Although the chloroplast plastids of most land plants are generally similar in size, content and structure, certain plant species have developed significantly rearranged chloroplast plastids. Inversions, internal inversions, and IR boundary shifts are the principal causes of such structural alterations, with repeat sequences playing a key role in the evolution and rearrangement of chloroplast genomes [48,49]. In the chloroplast genome of Belian, the number of repeats with a length of 25~29bp was the largest, followed by 30~39bp. The majority of the repeats were palindromic repeats and forward repeats, with reverse repeats and complement repeats discovered primarily in the of 25 bp to 29 bp and in a small number, which is similar to the results of Avocado (Persea americana) [50]. Furthermore, the repeat distribution in Belian chloroplast genomes were unbalanced, with the most repeats in LSC region and fewer repeats in SSC region and IRs region. This unbalanced distribution may be related to the distribution of chloroplast genes, where genes related to photosynthesis were predominantly located in the LSC, while rRNAs were all located in the IRs region.
Simple sequence repeats are highly variable in different species of the same genus, play an important role in the identification of plant genetic relationships and taxonomic status, and are considered to be one of the main sources of molecular markers [51]. 176 SSRs were detected in the three Belian chloroplast genomes, with 56 to 61 SSRs detected in each Belian individual. The number of mono-nucleotide repeats was the largest, and the A/T repeats were the main, while the di-nucleotide repeats were TA, AT, AG and CT. The preference of SSRs to be rich in A/T bases may be due to the fact that there are only two hydrogen bonds between A/T, whereas there are three hydrogen bonds between G/C, so it is more difficult to break the G/C bond to produce mutations [52].
The IRs region is the most conserved region in the chloroplast genomes, however, the expansion and contraction of the IRs region boundary is a common evolutionary phenomenon, which is the primary mechanism leading to the change of chloroplast genome size [53,54]. By comparing the differences in the IR boundaries of the three Belian chloroplast genomes, the results show that they were identical. This result reaffirms the highly conserved nature of the IRs region.
SNP and InDel are essential sources of genetic variation, leading to differences in gene structure, which reflect the adaptability of individuals to environmental changes [55]. In this study, we examined mutations in two other Belian chloroplast genomes using Belian I as a reference sequence and 170 mutation events were identified, including six microinversions, 53 InDels, and 111 substitutions. The distribution of mutation events in Belian is similar to that in other angiosperms; most of them are located in the non-coding region, and the number of mutation events is the highest in the LSC region, and the number of mutation events is the least or even none in the IR regions. However, the density of SNPs and InDels in each region of Belian Ⅱ and Belian Ⅲ showed that the maximum density of the SSC region of Belian Ⅱ was 5.56/kb, and the maximum density of the LSC region of Belian Ⅲ was 8.43/kb, which was similar to the results of Liu et al. [56].
Chloroplast genomes contain highly variable regions that help to distinguish closely related species or genera and are considered potential molecular marker material for phylogenetic analyses [57]. In the three Belian genomes, thirty-five variable loci (Pi > 0.002) were identified by DnaSP version 6.12, of which ten hypervariable regions (Pi > 0.003), including trnK, trnK-rps16, psbM-trnD, trnT-psbD, psaA, trnF, trnM-atpE, atpE, ndhF, and ndhF-rpl32. The highly variable region petA-psbJ is considered a hotspot of variation in Neocinnamomum [58], and Litsea glutinosa [59], but not in Belian. IRs region has lower genetic polymorphism than the LSC region and SSC region, and the coding region is more conserved than the non-coding region in Belian chloroplast genomes. This result is consistent with the chloroplast genome studies of other higher plants.
The chloroplast genome is essential for the study of phylogenetic relationships and species identification of angiosperms and for determining their taxonomic status [60,61]. Chanderbali et al. (2001) constructed a phylogenetic tree of the Lauraceae using chloroplast sequence fragments and ribosomal sequence 26S of Belian, where Belian and Potoxylon melaganga form a sister branch with good support [13]. They are morphologically very similar, with a deep, vase-shaped receptacle cup that develops into a deep cup enclosing the drupe with only a tiny apical hole [13]. Rohwer et al. (2014) used Bayesian and maximum likelihood methods to construct developmental trees based on trnK and ITS sequences, and Belian and Potoxylon melaganga also constituted sister branches [62]. Song et al. (2019) reconstructed phylogenetic trees of Lauraceae based on nine plastid fragments and obtained the same results [63]. The complete chloroplast genome of Potoxylon has not yet been reported, and we expect more researchers to pay attention to it. In this study, the phylogenetic relationships among two Belian plastomes and 42 plastomes from ten families of the Magnoliids were reconstructed based on the chloroplast genomes. The topology of Lauraceae clades is similar to that of previous studies, especially the location of Belian, which is located at the base of Lauraceae [13,14,17,19]. Furthermore, it is worth noting that we have reason to question the speculation of Ariati et al. (2023) that the Belian (GenBank accession No. MF939351) sequence we submitted to GenBank may be located in Myristicaceae rather than Lauraceae [20]. Here, our results provided sufficient evidence to confirm the accuracy of the sequence. We speculate that the reasons for the errors of Ariati et al. (2023) may include inadequate sampling, sequence errors, sequence alignment errors, and inaccurate phylogenetic analysis.
5. Conclusions
The present study sequenced, assembled, and annotated two Belian chloroplast genomes from Java and Kalimantan, and analyzed them with another previously published Belian genome from Sulawesi. Through comparative analysis of the genomes, it was found that the Belian genomes in three different places were conserved in gene content, gene sequence and GC content. The rapidly evolving differentiation regions, repeats and mutation sites identified in this study may serve as potential molecular markers for phylogenetic studies. The location of Belian in Lauraceae was determined based on the whole chloroplast genome sequence, which further confirmed the placement of our previously published Belian sequence within the Lauraceae, not Myristicaceae. In summary, our study has deepened our understanding of the Belian chloroplast genome and provided a foundation for taxonomic identification, phylogenetic studies, and conservation of genetic resources.
Author Contributions
Y.S. and P.X. conceived and designed the experiments. Y.S. and P.X. revised the manuscript. W.Z. performed the data analysis and drafted the manuscript. Y.T. and X.Z. contributed materials. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32260060, 32060710), Key Technologies Research for the Germplasm of Important Woody Flowers in Yunnan Province (No. 202302AE090018), and Yunnan Science and Technology Talents and Platform Program (No. 202205AF150022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nurtjahjaningsih, I.L.G.; Sukartiningsih; Kurokochi, H.; Saito, Y.; Ide, Y. Genetic Structure of the Tropical Tree Eusideroxylon zwageri in Indonesia Revealed by Chloroplast DNA Phylogeography. Forests 2017, 8. [CrossRef]
- Asian Regional Workshop (Conservation & Sustainable Management of Trees, Viet Nam, August 1996). Eusideroxylon zwageri. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 1998. [CrossRef]
- Irawan, B.; Gruber, F.; Finkeldey, R.; Gailing, O. Linking indigenous knowledge, plant morphology, and molecular differentiation: the case of ironwood (Eusideroxylon zwageri Teijsm. et Binn.). Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 2015, 63, 1297-1306. [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol 2016, 17, 134. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Raubeson, L.A.; Boore, J.L.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Chumley, T.W.; Haberle, R.C.; Wyman, S.K.; Alverson, A.J.; Peery, R.; Herman, S.J.; et al. Methods for obtaining and analyzing whole chloroplast genome sequences. Methods Enzymol 2005, 395, 348-384. [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu Rev Genet 1985, 19, 325-354. [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lee, S.B.; Grevich, J.; Saski, C.; Quesada-Vargas, T.; Guda, C.; Tomkins, J.; Jansen, R.K. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Solanum bulbocastanum, Solanum lycopersicum and comparative analyses with other Solanaceae genomes. Theor Appl Genet 2006, 112, 1503-1518. [CrossRef]
- Walker, T. Plant Diversity and Evolution. Genotypic and Phenotypic Variation in Higher Plants. Edited by R. J. Henry. Wallingford UK: CABI Publishing (2005), pp. 332, £65.00. ISBN 0-85199-904-2. Experimental Agriculture 2006, 42, 121-121. [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Nugent, J.M.; Herbon, L.A. Unusual structure of geranium chloroplast DNA: A triple-sized inverted repeat, extensive gene duplications, multiple inversions, and two repeat families. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1987, 84, 769-773. [CrossRef]
- Dyall, S.D.; Brown, M.T.; Johnson, P.J. Ancient invasions: from endosymbionts to organelles. Science 2004, 304, 253-257. [CrossRef]
- Clegg, M.T.; Gaut, B.S.; Learn, G.H., Jr.; Morton, B.R. Rates and patterns of chloroplast DNA evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 6795-6801. [CrossRef]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Peery, R.; Chumley, T.W.; Dziubek, C.; Fourcade, H.M.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Comparative chloroplast genomics: analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus. BMC Genomics 2007, 8, 174. [CrossRef]
- Chanderbali, A.S.; van der Werff, H.; Renner, S.S. Phylogeny and Historical Biogeography of Lauraceae: Evidence from the Chloroplast and Nuclear Genomes. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 2001, 88. [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, J.G.; Rudolph, B. Jumping Genera: The Phylogenetic Positions of Cassytha, Hypodaphnis, and Neocinnamomum (Lauraceae) Based on Different Analyses of trnK Intron Sequences. Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden 2005, 92, 153-178.
- Kurokochi, H.; Nurtjahjaningsih, I.L.G.; Sukartiningsih; Tan, E.; Asakawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Ide, Y. Development of polymorphic chloroplast DNA markers for the endangered tree Eusideroxylon zwageri through chloroplast isolation and next-generation sequencing. Conservation Genetics Resources 2015, 7, 845-850. [CrossRef]
- Md-Isa, S.F.; Yien Yong, C.S.; Saleh, M.N.; Go, R. An assessment of genetic variation in vulnerable Borneo Ironwood Eusideroxylon zwageri Teijsm. & Binn. in Sarawak using SSR markers. Journal of Threatened Taxa 2021, 13, 18588-18597. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, W.B.; Tan, Y.; Liu, B.; Yao, X.; Jin, J.; Padmanaba, M.; Yang, J.B.; Corlett, R.T. Evolutionary Comparisons of the Chloroplast Genome in Lauraceae and Insights into Loss Events in the Magnoliids. Genome Biol Evol 2017, 9, 2354-2364. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-F.; Ma, H.; Ci, X.-Q.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, H.-W.; Wang, S.-L.; Qu, X.-J.; Hu, J.-L.; et al. Can plastid genome sequencing be used for species identification in Lauraceae? Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 2021, 197, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ferguson, D.K.; Yang, Y. New insights into the plastome evolution of Lauraceae using herbariomics. BMC Plant Biol 2023, 23, 387. [CrossRef]
- Ariati, S.R.; Priyadi, A.; Hariri, M.R.; Risna, R.A. The complete chloroplast genome of Myristica teysmannii (Myristicaceae), an endemic and endangered species from Indonesia. Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity 2023. [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. PHYTOCHEMICAL BULLETIN 1987, v.19(1):11-15.
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; dePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol 2020, 21, 241. [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Schultz, M.B.; Zobel, J.; Holt, K.E. Bandage: interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3350-3352. [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, W65-W73. [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, W59-W64. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlic, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol Ecol Resour 2020, 20, 348-355. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xue, Q. Comparative studies on codon usage pattern of chloroplasts and their host nuclear genes in four plant species. J Genet 2005, 84, 55-62. [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res 2001, 29, 4633-4642. [CrossRef]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.K.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of gene-derived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 2003, 106, 411-422. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, L.; Gao, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X. CPJSdraw: analysis and visualization of junction sites of chloroplast genomes. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15326. [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sanchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sanchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol Biol Evol 2017, 34, 3299-3302. [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief Bioinform 2019, 20, 1160-1166. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol 2015, 32, 268-274. [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 2012, 61, 539-542. [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 772-772. [CrossRef]
- Spalik, K.; Downie, S.R. Intercontinental disjunctions in Cryptotaenia (Apiaceae, Oenantheae): an appraisal using molecular data. Journal of Biogeography 2007, 34, 2039-2054. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Mehmood, F.; Shahzadi, I.; Waseem, S.; Mirza, B.; Ahmed, I.; Waheed, M.T. Chloroplast genome of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Malvaceae): Comparative analyses and identification of mutational hotspots. Genomics 2020, 112, 581-591. [CrossRef]
- Dobrogojski, J.; Adamiec, M.; Luciński, R. The chloroplast genome: a review. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 2020, 42. [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, C.L.; Abdullah; Ahmed, I.; Carlsen, M.M.; Zuluaga, A.; Croat, T.B.; McKain, M.R. Evolutionary dynamics of chloroplast genomes in subfamily Aroideae (Araceae). Genomics 2020, 112, 2349-2360. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Dong, W.; Liu, B.; Xu, C.; Yao, X.; Gao, J.; Corlett, R.T. Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genome sequences of two tropical trees Machilus yunnanensis and Machilus balansae in the family Lauraceae. Front Plant Sci 2015, 6, 662. [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Peng, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, B. The Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Machilus chuanchienensis (Lauraceae): Genome Structure and Phylogenetic Analysis. Genes (Basel) 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Mardanov, A.V.; Ravin, N.V.; Kuznetsov, B.B.; Samigullin, T.H.; Antonov, A.S.; Kolganova, T.V.; Skyabin, K.G. Complete sequence of the duckweed (Lemna minor) chloroplast genome: structural organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. J Mol Evol 2008, 66, 555-564. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ma, P.F.; Wen, J.; Yi, T.S. Complete sequencing of five araliaceae chloroplast genomes and the phylogenetic implications. PLoS One 2013, 8, e78568. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, H.; Kong, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; et al. Phylogenomic analyses based on the plastid genome and concatenated nrDNA sequence data reveal cytonuclear discordance in genus Atractylodes (Asteraceae: Carduoideae). Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 1045423. [CrossRef]
- Shabalina, S.A.; Spiridonov, N.A.; Kashina, A. Sounds of silence: synonymous nucleotides as a key to biological regulation and complexity. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41, 2073-2094. [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; He, J.; Jia, X.; Qi, Q.; Liang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Ping, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, J. Analysis of codon usage bias of mitochondrial genome in Bombyx mori and its relation to evolution. BMC Evol Biol 2014, 14, 262. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Long, W.; Li, X. Patterns of synonymous codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of seed plants. Forestry Studies in China 2008, 10, 235-242. [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Ming, Z.; Junrui, W.; Li, F.; Sha, L.; Hongbo, P.; Lan, Q.; Jing, L.; Yan, S.; Weihua, Q.; Lifang, Z.; et al. Inferring the evolutionary mechanism of the chloroplast genome size by comparing whole-chloroplast genome sequences in seed plants. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 1555. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Guo, W.; Gupta, S.; Fan, W.; Mower, J.P. Evolutionary dynamics of the plastid inverted repeat: the effects of expansion, contraction, and loss on substitution rates. New Phytol 2016, 209, 1747-1756. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yao, X.; Tan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Corlett, R.T. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of the avocado: gene organization, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationships with other Lauraceae. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 2016, 46, 1293-1301. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, B.; Zhu, W.; Sun, L.; Tian, J.; Wang, X. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Mahonia bealei (Berberidaceae) reveals a significant expansion of the inverted repeat and phylogenetic relationship with other angiosperms. Gene 2013, 528, 120-131. [CrossRef]
- Dodsworth, S.; Chase, M.W.; Kelly, L.J.; Leitch, I.J.; Macas, J.; Novak, P.; Piednoel, M.; Weiss-Schneeweiss, H.; Leitch, A.R. Genomic repeat abundances contain phylogenetic signal. Syst Biol 2015, 64, 112-126. [CrossRef]
- dePamphilis, C.W.; Palmer, J.D. Loss of photosynthetic and chlororespiratory genes from the plastid genome of a parasitic flowering plant. Nature 1990, 348, 337-339. [CrossRef]
- McCoy, S.R.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Raubeson, L.A. The complete plastid genome sequence of Welwitschia mirabilis: an unusually compact plastome with accelerated divergence rates. BMC Evol Biol 2008, 8, 130. [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Xue, Y. Genome-wide intraspecific DNA-sequence variations in rice. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2003, 6, 134-138. [CrossRef]
- Muraguri, S.; Xu, W.; Chapman, M.; Muchugi, A.; Oluwaniyi, A.; Oyebanji, O.; Liu, A. Intraspecific variation within Castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) based on chloroplast genomes. Industrial Crops and Products 2020, 155. [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35071. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yang, L.; Xin, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xin, P. Comparative and phylogenetic analysis of complete chloroplast genomes from seven Neocinnamomum taxa (Lauraceae). Front Plant Sci 2023, 14, 1205051. [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, D.D.; Strijk, J.S. Toward phylogenomics of Lauraceae: The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Litsea glutinosa (Lauraceae), an invasive tree species on Indian and Pacific Ocean islands. Plant Gene 2017, 9, 71-79. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: from gene to genome. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 2015, 90, 157-166. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Guan, Y.; Ma, X. Corrigendum: Species Identification of Dracaena Using the Complete Chloroplast Genome as a Super-Barcode. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 51. [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, J.G.; De Moraes, P.L.R.; Rudolph, B.; Werff, H.V.D. A phylogenetic analysis of the Cryptocarya group (Lauraceae), and relationships of Dahlgrenodendron, Sinopora, Triadodaphne, and Yasunia. Phytotaxa 2014, 158. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, W.B.; Tan, Y.H.; Jin, J.J.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.B.; Liu, B.; Corlett, R.T. Plastid phylogenomics improve phylogenetic resolution in the Lauraceae. Journal of Systematics and Evolution 2019, 58, 423-439. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).