1. Introduction
Cerebral revascularization is a microsurgical procedure that is used for the augmentation or preservation of blood flow to certain brain regions. Revascularization of brain tissue can be performed either through a bypass from the extracranial circulation to the intracranial circulation (EC-IC bypass), or through the interconnection of two intracranial vessels (IC-IC bypass). An example of the augmentation of blood flow is a bypass between the superficial temporal artery and the medial cerebral artery (STA-MCA) in patients with internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis. On the other hand, preservation of blood flow is the maintenance of an existing vascular conduit, for instance after removal of a complex brain aneurysm or a skull base tumor with vascular invasion. 1
Often, a tension free anastomosis cannot be obtained without the interposition of a vascular graft; usually the great saphenous vein (GSV) (inner diameter (ID): 4.9 ± 0.9 mm) or the radial artery (RA) (ID: 3.55 ± 0.45 mm). 2,3 The choice of vascular graft depends on the required flow delivery, the size of the recipient vessel, and the availability of the donor vessel. 4 Advantages of the GSV include its length and the absence of atherosclerosis or vasospasm. Disadvantages include its large ID, lower long-term patency rates (overall 80 %) compared to RA grafts (overall 90 %) and the thrombogenic valves and varicose veins. 5,6 Advantages of the RA include its anatomical similarity to cerebral arteries, the facilitation of surgical anastomosis, and it also allows for greater fluctuations in arterial blood pressure. Disadvantages include its short length and potential vascular compromise of the hand. 7 Additionally, harvesting of both autologous grafts can be time-consuming and invasive for the patient. Thus, there is a medical need for an effective synthetic alternative for cerebral revascularization. The advantages of a synthetic alternative graft could include a reduction in vasospasm, vasculopathy, flow-mismatch, wound infection of the donor site, and no vascular compromise or availability problems.
As the IDs of cerebral vessels typically range from 1.07 ± 0.29 mm (cortical segment of anterior inferior cerebellar artery, AICA) to 8.57 ± 1.34 mm (cervical portion of the ICA), synthetic grafts with IDs < 6 mm could offer the greatest therapeutic advantages. 8 To date, there is no or little data determining the effectiveness of small caliber (ID < 6 mm) synthetic cerebral vascular grafts. Great progress however has been made in the search for synthetic grafts in cardiovascular surgery. However, the use of classical biomaterials such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has been limited to large caliber (ID ≥ 6 mm) cardiovascular surgery. 9,10 Some animal studies using PTFE and PET grafts with ID < 6 mm have reported discouraging patency rates (overall 40 % at six months) due to dynamic non-compliance, surface thrombosis and neointimal hyperplasia (NIH), becoming more critical by gradual reduction of graft ID. 11-14
An attempt to increase patency rates in small caliber cardiovascular grafting was recently made by the use of electrospinning, a technique that produces nanoscale fibers through the acceleration of a charged polymer fluid towards a rotating collector 15. From a morphological point of view, the porosity, high surface-to-volume ratio and surface topography of electrospun grafts mimic the extracellular matrix of native blood vessels. This resemblance promotes tissue reorganization through nutrient transfer, gas exchange, and intercellular communication. In various in vitro and in vivo settings, these processes have been shown to counteract thrombosis and NIH, and improve neo-endothelialization (NE). 10,16
Many in vitro and in vivo animal electrospinning studies, using various electrospun polymeric biomaterials, have demonstrated the superior efficacy of electrospun polyurethane (ePU). ePU demonstrates anti-thrombogenic properties, biocompatibility, and a mechanical strength and elasticity that closely matches the native vessel capacities. 12,17,18 Therefore, ePU grafts are promising substitutes for small caliber vascular replacement, and indeed they are already used to gain vascular access in hemodialysis patients (ID 6 mm). 10 However, the efficacy of ePU grafts with an ID < 1.5 mm has not been determined to date. To address this important question of whether ePU grafts with an ID < 1.5 mm are clinically effective, we developed a novel ePU graft with an ID of 1.25 mm and we determined its efficacy after implantation into the infrarenal aorta of rats in a small pilot study. For this study, the infrarenal aorta was used as it has comparable dimensions and hemodynamics to human cerebral vessels and hence makes our findings clinically relevant. 19
2. Methods
In a preclinical pilot animal study, in-house generated ePU grafts were implanted into the infrarenal aorta of rats. After a period of four months, our novel ePU graft was assessed for patency, thrombosis, NIH and NE. The results of patency and thrombosis were compared to the control group of rats that underwent sham surgery. As NIH is not a natural feature of native rat aorta and endothelial coverage is typically 100%, the results of NIH and NE on histology were quantitatively only described in the intervention group. The research hypothesis was that the intervention group (ePU graft implantations) exhibited non-inferiority towards a control group (sham surgeries) regarding incidence of aortic patency and thrombosis. Second, we expected minimal differences in hemodynamic performance between the groups. Third, we expected minimal NIH, and confluent coverage of the luminal surface with NE throughout the proximal, mid portion and distal graft.
2.1. Graft production: polyurethane solution and electrospinning
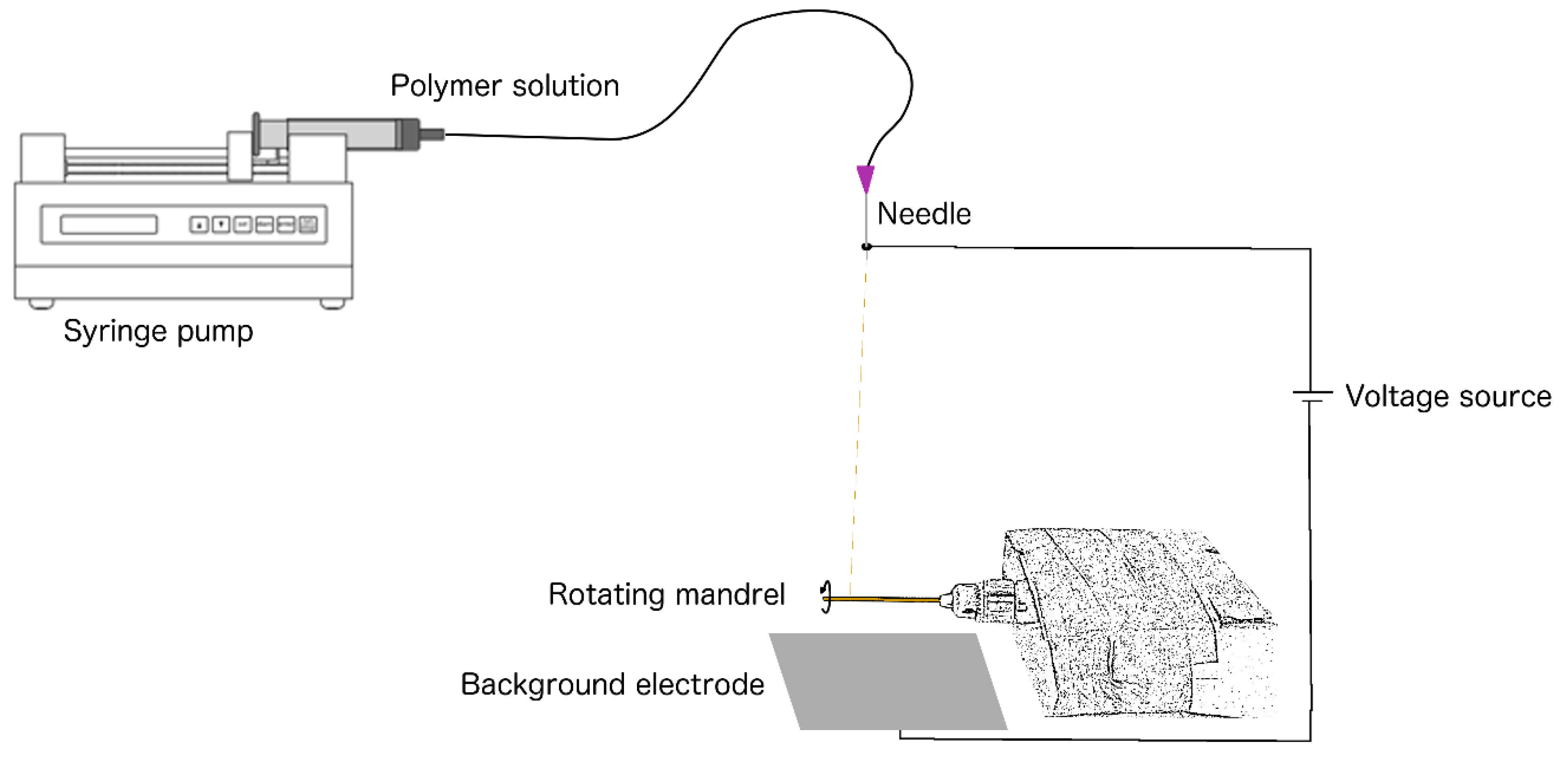
Electrospinning of the graft was performed using a novel device designed by the technical workshop (CWFW) of Ghent University – Faculty of Sciences, consisting of three main components: [1] a power supply (Glassman High Voltage, EL50P00, High Bridge, New Jersey) capable of generating a potential between 0 and 50 kV, [2] a 6 syringe motor driven pumping system (New Era Pump System, Multi-phaser NE1600, Farmingdale, New York) and [3] we added a grounded mandrel in a rotating unit for collection of the fibre jet (
Figure 1). A liquid 5 % (m/m) solution was prepared by dissolving polyurethane pellets (Carbothane®, Velox Lubrizol, Hamburg, Germany) in chloroform (Chem-lab, Zedelgem, Belgium) at room temperature (15-25 °C). A 20 ml syringe was filled with the solution and positioned in the automatic dispenser unit. The flow (flow rate: 1 ml/h) was passed through a tube which was distally mounted with a blunt end 22 Gauge needle. The needle tip was positioned vertically at a distance of 8 cm from a zinc mandrel of 1.0 mm diameter. The mandrel had been coated with molten (80 °C) polyethylene glycol (PEG, Fluka-Sigma Aldrich, Buchs, Switzerland) and dried for twenty-four hours at room temperature (15-25 °C). The PEG-coated zinc mandrel was mounted in a rotating unit (speed: 275 rotations per minute). After completion of this setup, the voltage source was set at 20 V (direct current), and consequently, the charged polyurethane solution was accelerated from the anode (needle tip) to the cathode (rotating mandrel/background electrode). Electrospinning was performed for one hour. The mandrel, circumferentially covered with a fine ePU mesh (the graft), was subsequently placed in distilled water for 1 hour to dissolve the PEG coating, facilitating detachment of the graft. The collected grafts were dried for two hours at 40 °C in atmospheric pressure to evaporate residual chloroform. The ePU grafts were sterilized in a 100 % ethylene oxide cold cycle process of 38 °C. (Sint-Jan Hospital, Bruges, Belgium).
2.2. SEM: ePU graft characterization
Before sterilization, a 1 mm piece was cut from one of the ePU grafts and sputter-coated with gold. The specimen was visualized with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Fei, Quanta Field Emission Gun 200, Hillsboro, Oregon) and the images were analyzed using ZEN 2 core software for size calibration (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany). The gross morphology, surface topography, fiber diameter, pore size and wall thickness were assessed on twenty-four randomly selected regions and expressed as the mean ± SD (in µm).
2.3. Animal characterization and grouping
For these experiments, eighteen male Wistar Han International Genetic Standard (IGS) rats (rattus norvegicus, Charles River, France) were used and this study was approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experiments at the University of Antwerp (approval number 2015-55). The rats were nine weeks of age (weighing 276-300 grams) at the start of the study and were all preoperatively healthy. All experiments were conducted according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health 20 and the experiments were reported according to the Arrive guidelines.21 All the rats were housed pairwise in the animal unit of the University of Antwerp. At the start of the study, the rats were randomly divided (using computer assistance) into two groups: the intervention group (N= 9, ePU graft surgery) and the control group (N= 9, sham surgery).
2.4. Implantation of ePU grafts
In the intervention group, an ePU graft (ID: 1.25 mm, length: 7.50 mm) was implanted into the infrarenal aorta, using a surgical microscope (Carton SPZ50, Tokyo, Japan). A midline laparotomy was made extending from the xiphoid to just above the bladder and the intestines were laid aside, exposing the retroperitoneal space. After dissection, two temporary aneurysm clamps (Peter Lazic, Tuttlingen, Germany) were placed on the infrarenal aorta, above the iliac bifurcation. The aorta was completely transected halfway in between the clamps. The last millimeters of each stump were stripped from the adventitial layer and flushed with sterile saline. The graft was implanted using two end-to-end anastomoses with circumferentially interrupted non-absorbable 10-0 sutures (Ethilon, Somerville, New Jersey). Before the last suture, the graft lumen was flushed with sterile saline. In the control group the infrarenal aorta was clamped, divided over the superior part of its circumference and reanastomosed with the same interrupted sutures. All surgeries were performed under general inhalation anesthesia using isoflurane (5 % induction and 2-3 % maintenance concentrations, Forene® Abbott, Chicago, Illinois) in an O2 enriched gas mixture. Body temperature was rectally monitored and corrected with an underlying heating pad. Vital signs were monitored using MouseOx software (Starr Life Sciences, Oakmont, Pennsylvania). No anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs were used. Subcutaneous buprenorphine (0.1 mg/ml) (Vetergesic® Ecuphar, Oostkamp, Belgium) was administered as an analgesic premedication. Postoperatively, the following products were administered: epicutaneous chlorhexidine chloride (Astrexine® Pierre Fabre, Anderlecht, Belgium), epicutaneous lidocaine hydrochloride 2 % (Xylocaine® AstraZeneca, Ukkel, Belgium), subcutaneous buprenorphine 0.1 mg/ml (Vetergesic® Ecuphar, Oostkamp, Belgium) and subcutaneous amoxicillin 150 mg/ml (Duphamox LA ® Zoetis, Zaventem, Belgium).
2.5. In vivo assessments over a 4 month period: thrombosis
Aortic thrombosis in the intervention and control group was clinically assessed over a four- month-period. The following parameters were used for the evaluation of thrombosis of the lower limb: skin/paw pad temperature (cold) and color (cyanosis/pallor), ulceration, paresis/paralysis, limb pain (biting or shaking limb). Intestinal thrombosis was evaluated by assessment of abdominal tenderness during handling, loss of appetite and alterations in fecal matter and production (blood, constipation). 22
2.6. In vivo assessments after a four-month-period: patency
In vivo evaluation of patency in the intervention and control group was performed after a four- month-period using an ultrasound system (Visualsonics, Vevo® 2100, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). This system operated at a high frequency (13-75 MHz) with a spatial resolution of ~30 microns and a temporal resolution of 1000 frames/sec. Ultrasound imaging on the rats was performed under general anesthesia using sevoflurane (5 % induction and 2 % maintenance, Sevorane® Abbvie, Wavre, Belgium) in an O2 enriched gas mixture. The abdomen was shaved and ultrasound gel at 37°C was applied. The probe was levelled perpendicular to the spine. Using pulsed-wave 40MHz Doppler in the coronal plane, patency was categorically evaluated by the presence (patent) or absence (non-patent) of pulsatile arterial flow in the aorta segment distal to the graft/control aorta. Absolute maximal flow velocity (Vmax) and Vmax decay from the proximal to distal graft/control aorta were measured in the sagittal plane and expressed as the mean ±SD (in mm/s). The inner/outer, proximal/distal diameters and systolic/diastolic diameters of graft/control aortas (IDps, IDpd, IDds, IDdd, ODps, ODpd, ODds and ODpd) were measured using the Motion-mode (in µm) and compared between the groups. Images were analysed using ImageJ software (ImageJ, National Institutes of Health). The systolic expansion was calculated using the formula [IDps - IDpd] for the proximal segment and with [IDds - IDdd] for the distal segment. The proximal to distal decay in graft/control aorta expansion [(IDps-IDpd) – (IDds-IDdd)] was calculated and compared between groups.
2.7. Retrieval surgery after a four-month-period
After ultrasound imaging, retrieval surgery of the ePU grafts/control aortas was performed. The same procedure, medication and anesthetic products were used as described for the implantation (see above). In between two temporary clamps, either the graft (intervention group) or a 7.5 mm piece of reanastomosed control aorta (control group) was retrieved. All rats were subsequently sacrificed with an intracardiac injection of 1.5 ml sodium pentobarbital 60 mg/ml (Nembutal® Ceva, Libourne, France).
2.8. In vitro assessments of retrieved ePU grafts: NIH and NE
The retrieved ePU grafts were embedded in 4 % formaldehyde for twenty-four hours and were subsequently placed in 60 % isopropyl alcohol. After dehydration and tissue preparation using an automated device (Excelsior, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Breda, The Netherlands), the samples were fixed using an automated paraffin embedding device (TES 99, Medite, Burgdorf, Germany). Two longitudinal sections of 5 µm thickness were cut from the samples. A standard light microscope (Olympus BX41) with imaging software (Leica Application Suite X, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) was used for visualization. One slide from each rat was stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), for the evaluation of NIH in the ePU grafts. NIH was quantified as the thickness (in µm) of the area between the endothelial layer and luminal graft surface. It was measured in three different regions: (1) first anastomosis, (2) mid graft and (3) second anastomosis. For each region, two measurements were performed, circumferentially at 180 degrees apart from each other. NIH was expressed as the mean ± SD for each region. The length of NIH (in mm) was also compared to the total length (in mm) of the ePU graft and expressed as a percentage (length/length %). The second slide was stained with anti-Factor VIII (anti-von Willebrand Factor, Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) antibody for the identification of endothelial cells. NE was quantified as anti-F VIII positive length (in mm), compared to the total length (in mm) of the ePU graft and expressed as a percentage (length/length %).
2.9. Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software (Statistical Package for the Social Science version 24, IBM analytics). To compare the incidence of aortic patency and thrombosis in the intervention group to the control group, no statistical analyses were performed and these parameters were quantitatively only described. Ultrasound data on hemodynamic performance were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA and Student’s t-test to compare mean values in single groups and between the two groups, respectively. Histological data of NIH were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA test to compare mean values in the intervention group. NIH and NE were quantitatively described. The assumptions of the tests were met by the data. The significance level was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Pre-implant characterization: SEM
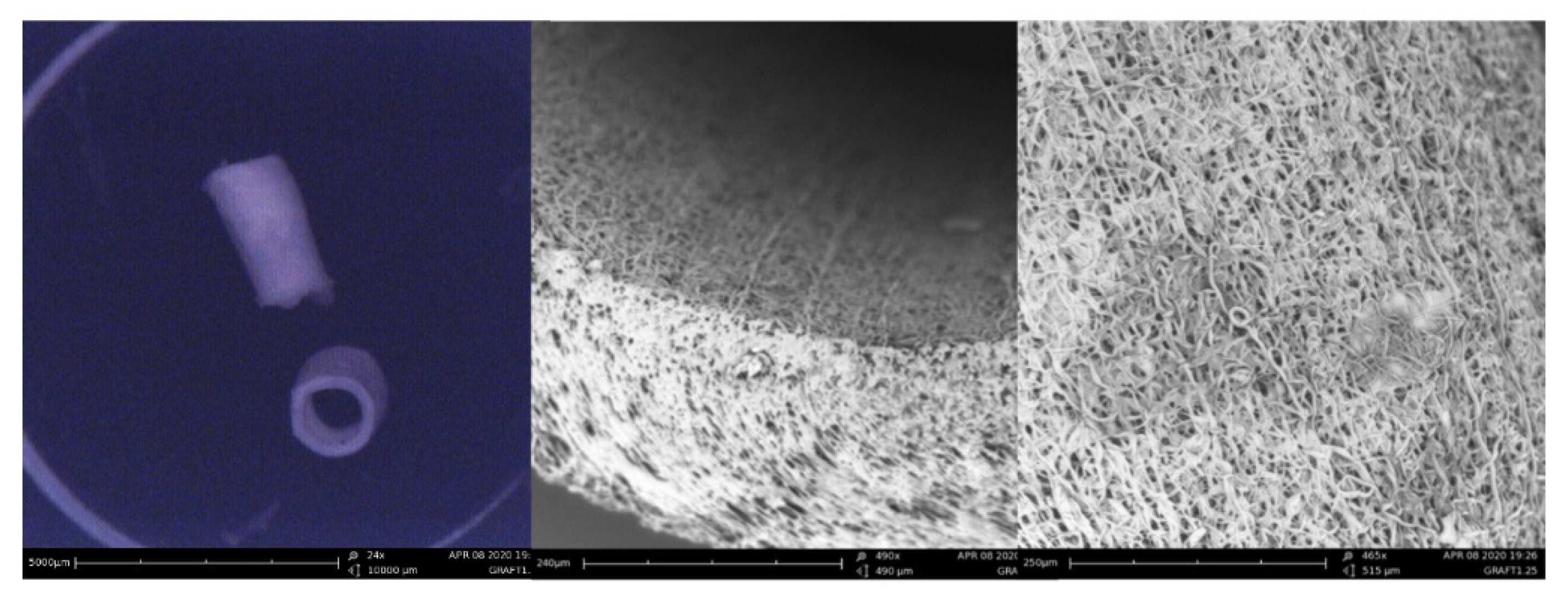
The features of one ePU graft were analyzed using SEM imaging. In
Figure 2, the tubular gross morphology and porous surface topography of the ePU graft are presented. The fibers were randomly oriented and small irregularly distributed beads were observed on the course of some fibers. The mean fiber diameter of the ePU graft was 2.02 ± 1.43 µm (minimum 0.30 µm, maximum 5.17 µm). The graft had a mean pore size of 5.65 ± 2.30 µm (minimum 2.33 µm, maximum 11.66 µm) and a wall thickness of 223 ± 18 µm (minimum 189 µm, maximum 260 µm).
3.2. Implantation of ePU grafts
All rats were preoperatively healthy, as evaluated using standardized welfare control sheets. Throughout the experiments, a total of four rats from the intervention group were excluded from the study. In two of them, surgery was prematurely terminated without interposition of a graft, due to [
1] technical problems with the microscope and [
2] inability to reach sufficient levels of anesthesia. The other two rats died because of [
3] major intraoperative bleeding due to accidental injury of the vena cava and [
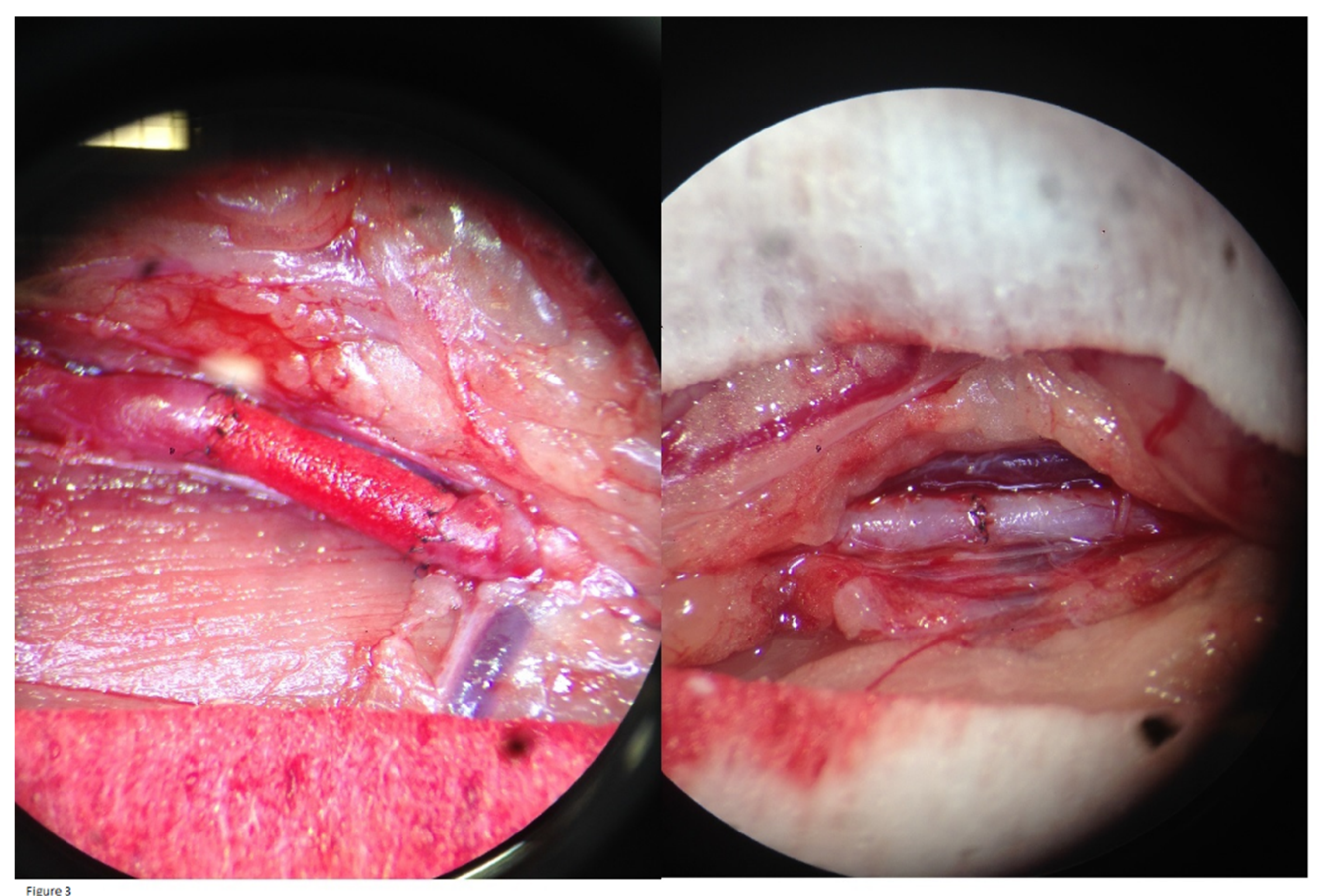
4] anesthetic intolerance. These four subjects were replaced by four unused Wistar Han IGS rats from the same lot. In the intervention and control group, all graft/control aorta anastomoses were tension-free and no major complications occurred. When releasing the vessel clamps after the procedure, an optical check of all graft/control aortas showed good expansile pulsations. The grafts became red and saturated with blood, indicating permeability to erythrocytes, but without any leakage at the anastomoses (
Figure 3). The immediate postoperative outcome for all rats was clinically favorable.
3.3. In vivo assessments: clinical parameters of thrombosis
On the first postoperative day, one rat out of nine in the intervention group developed a paraparesis of the lower limbs, suggesting graft thrombosis. Humane endpoints were met and the rat was euthanized. Postmortem ex vivo examination of the graft could not determine the cause of thrombosis. However, subsequent histological evaluations with H&E staining demonstrated a large thrombus, occluding the graft lumen. Thrombosis was likely caused by a surgical complication (see: discussion). During the four-month-study-period, no other clinical parameters of aortic thrombosis were observed, neither in the intervention nor in the control group. The paraplegic rat was considered as graft thrombosis, bringing the overall thrombosis incidence of the intervention group to 1/9 (11 %) compared to 0/9 (0 %) in the control group. Therefore, there was no significant difference in thrombosis incidence between the intervention and the control group.
3.4. In vivo assessments: patency on ultrasound
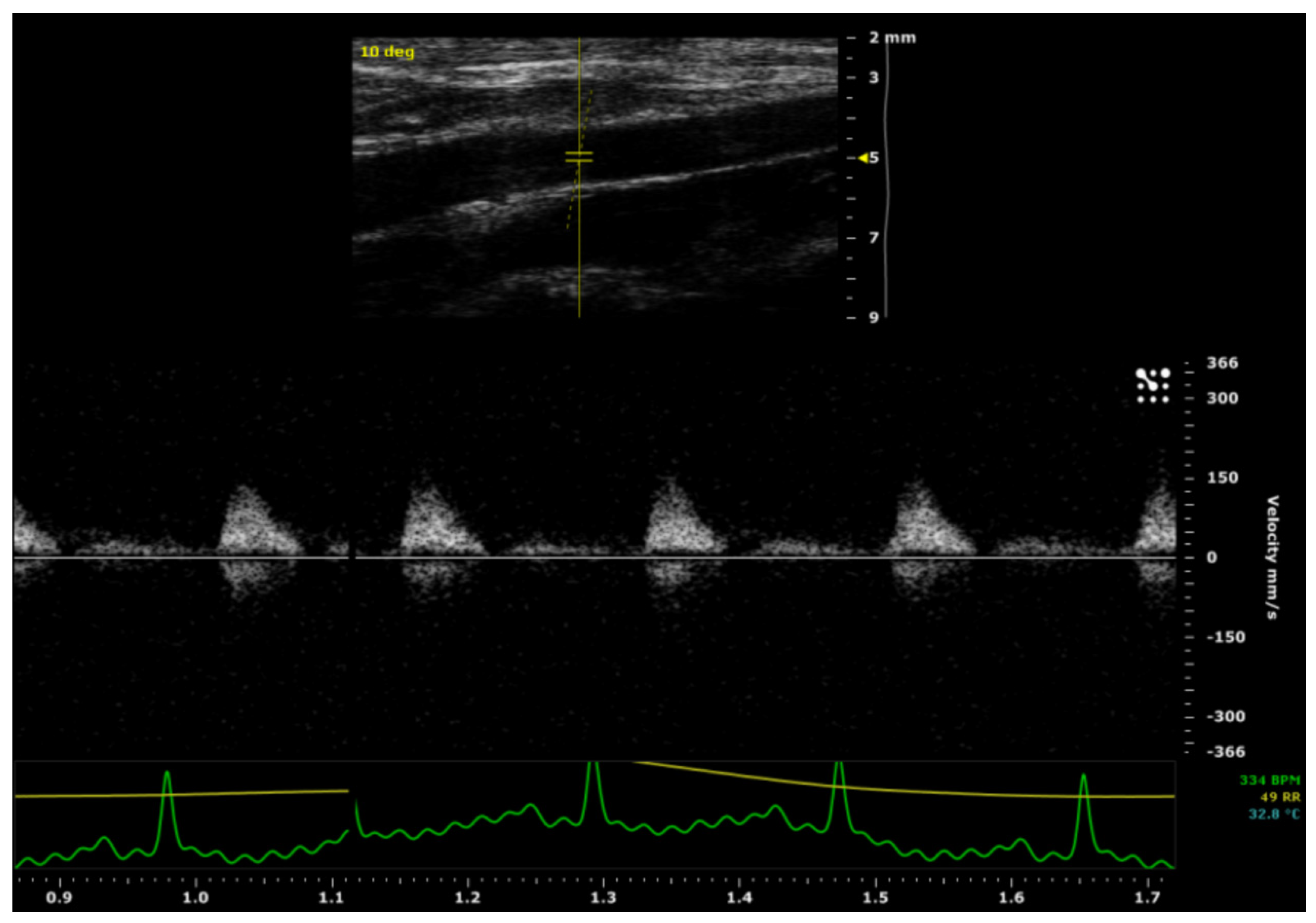
After a four-month-period, a pulsed-wave Doppler ultrasound was used to evaluate the patency of the ePU graft/control aortas. There was a pulsatile arterial flow in all aorta segments located distally from the graft/control aortas. No stenotic processes were detected over the course of the graft/control aortas and there was no evidence of ePU graft-related complications, such as graft rupture or aneurysm formation. The rat with paraparesis was clinically considered to be graft failure/non-patent, bringing the overall patency of the intervention group to 8/9 (89 %) compared to 9/9 (100 %) in the control group. Therefore, there was no significant difference in patency between the intervention and the control groups. The ultrasound imaging of the ePU grafts is demonstrated in
Figure 4.
There was no statistically significant difference between the intervention and control group for the absolute Vmax in the proximal aorta (p= 0.479) and the absolute Vmax in the distal aorta (p= 0.711). However, there was a statistically significant difference (p= 0.010) in Vmax decay (from proximal to distal), between the intervention group (mean= 49 ± 40 mm/s) and the control group (mean= -14 ± 39 mm/s). These data are shown in
Table 1.
There was no statistically significant difference (p= 0.280) in proximal aortic systolic expansion between grafts (mean= 123 ± 49 µm) and shams (mean= 157 ± 75 µm). Neither was there a significant difference (p= 0.827) in distal aortic systolic expansion between the intervention group (mean= 104 ± 64 µm) and control group (mean= 114 ± 102 µm). There was also no statistically significant (p= 0.353) difference between the intervention and control group concerning the aortic expansion decay between proximal and distal aorta [(IDps-IDpd) – (IDds-IDdd)]. However, the means showed a relevant difference between the intervention group (mean= 52 ± 110 µm) and the control group (mean= 9 ± 75 µm). These data are summarized in
Table 1.
3.5. Retrieval surgery after a four-month-period
Immediately after ultrasound imaging, retrieval surgery of the ePU grafts/control aortas was performed. In vivo evaluation demonstrated good healing of the anastomoses and good expansile pulsations in the grafts/control aortas. There were no stenotic adhesions to the surrounding retroperitoneal tissue.
3.6. In vitro evaluations: NIH and NE on histology
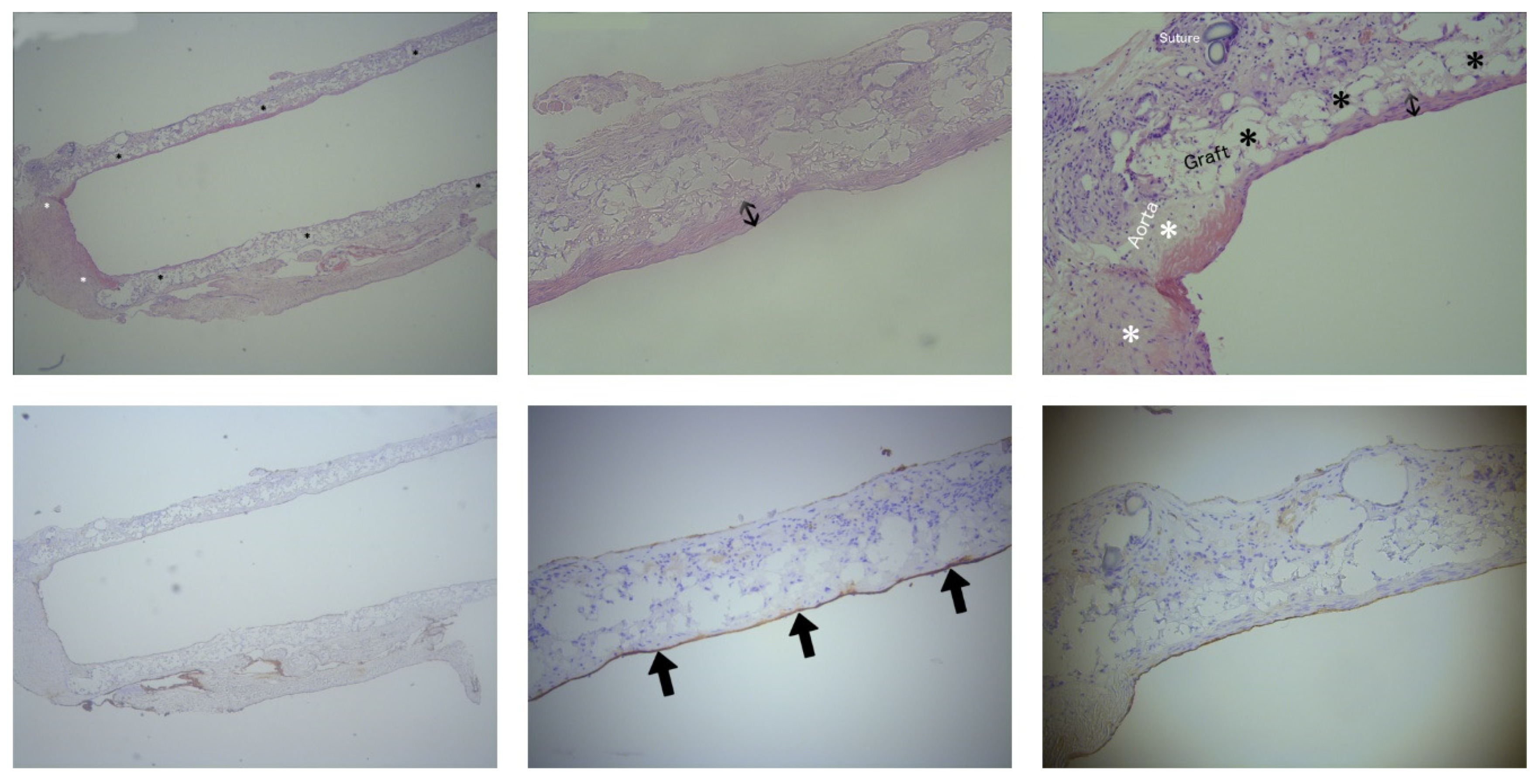
After a four-month-period, histological analyses were performed for the evaluation of NIH and NE in the intervention group. As expected on the first postoperative day, it was too soon to identify NIH or NE on the slides from the euthanized rat with paraparesis. Histological evaluation in this rat using H&E staining demonstrated a large thrombus, occluding the graft lumen. Therefore, only eight out of nine subjects were included in the histological analyses. The porous fiber mesh of the ePU graft was clearly visualized using H&E staining and it was apparent that there was an ingrowth of different cells in the graft. NIH in the intervention group was measured on the H&E stained slides of the ePU grafts. The mean neointimal thickness of the mid graft (35 ± 40 µm) was similar (p= 0.978) nearby the anastomoses (35 ± 43 µm). In 1 of 8 ePU grafts, no NIH could be observed (0 µm). The mean percentage of the longitudinal length of the graft covered with NIH was 54 ± 29 % (minimum 0 %, maximum 94 %). The absolute mean length of the graft covered with NIH was 6.02 ± 4.16 mm on a mean total graft length of 11.19 ± 2.48 mm. These data are summarized in
Table 2. An example of NIH is shown in
Figure 5.
NE in the intervention group was measured on the anti-FVIII stained sections of the ePU grafts. NE over the course of the luminal graft length was 80 ± 40 %. The mean NE length was 8.95 ± 4.64 mm, covering a mean graft length of 11.19 ± 2.48 mm. One out of eight grafts did not have NE. The proximal, mid portion and distal regions of the graft lumen were almost confluently positive for anti-FVIII staining. These data are summarized in
Table 3 (supplementary material). An example of NE is shown in
Figure 5.
4. Discussion
The current standard for small caliber (< 6 mm ID) vascular grafting in cerebral revascularization surgery is the interposition of an autologous graft, such as the GSV or the RA. 2,4 Despite the histological tissue supremacy of these autologous substitutes, technical issues and surgical complications necessitate the development of a synthetic alternative. 5-7
Yet, due to NIH and thrombosis, the use of synthetic vascular grafts with classical biomaterials such as PTFE and PET has mainly been restricted to large caliber vascular surgery. 9,10,12-14 In cardiovascular research, electrospinning is a promising technique for the development of small caliber (< 6 mm ID) vascular grafts. Several reports have suggested a superiority of in vitro and in vivo animal performance of ePU to other organic polymers in terms of patency, absence of thrombosis, NIH and NE. 23-27 To date, no studies have been performed evaluating the in vivo use of ePU grafts with an ID < 1.5 mm. Considering the introduction of synthetic grafts in cerebral revascularization surgery, we developed a novel ePU graft with an ID of 1.25 mm. Detailed feature characterization was performed using SEM. The ePU graft was implanted in the infrarenal aorta of rats and evaluated for patency, thrombosis, NIH and NE after a 4-month- period. The results were compared to the control group with sham surgery. We first hypothesized that the intervention group would exhibit non-inferiority towards the control group regarding aortic patency and thrombosis. Secondly, we expected minimal differences in hemodynamic performance on ultrasound. Thirdly, upon histological examination, we expected minimal NIH and confluent NE throughout the regions of the ePU graft.
By means of SEM imaging after electrospinning, an ePU graft with small fibers of 2.0 ± 1.43 µm was observed. The pore diameter was 5.65 ± 2.30 µm, being large enough for cellular infiltration, as demonstrated by the ingrowth of different cells on tissue slide examination. The wall thickness was 223 ± 18 µm, similar to the wall thickness of the GSV (250-370 µm), which is the current standard for small caliber vascular replacement surgery. 28,29
Some grafts showed an irregular topography with beads in the fibers. These distortions suggest the presence of electrospraying during the electrospinning process, which is the breakup of low-viscosity solutions into droplets due to surface tension effects. This can be corrected by lowering the concentration of polyurethane solution, or by altering the solvent. 30 Our study was an initial pilot study to assess efficacy of our novel ePU graft. In the future, larger animal studies will be required to fine-tune more of the appropriate settings of the electrospinning process (e.g. flow rate, rotation speed, needle diameter, voltage) and to investigate their potential clinical repercussions. Furthermore, the fiber diameter was variable (2.02 ± 1.43 µm). This could be caused by temporary decreases in voltage, interruption of the electrospinning process or by the previously mentioned electrospraying.30,31 A regular fiber diameter of < 1µm may have been preferable, as an in vitro study by Milleret et al. demonstrated less coagulation and platelet adherence with fibres < 1 µm compared to 2-3 µm, however they used in vitro ePU disks instead of in vivo tubular grafts. 32 The irregular fibre orientation can also be ameliorated by adjusting the rotation speed of the mandrel. 24
The implantation of the ePU grafts was successful, as demonstrated by a favorable postoperative outcome in eight out of nine rats after a four-month-period. One rat was euthanized for suspicion of graft thrombosis on the first postoperative day, which was later confirmed by histological examination. To determine the cause of the thrombotic event, the post-operative reports were examined, and these showed that temporary ligation of an undefined aortic branch (either iliolumbar or genital) close to the anastomosis region, and consequent excess manipulation of the endothelium, may have led to thrombosis. Secondly, a hemostatic patch (Surgicel®) was used to reduce anastomosis bleeding after clamp release. The thrombogenic hemostatic fibers may have entered the graft lumen. A third possible explanation is the early graft failure on the first postoperative day, elicited by foreign body thrombosis. However, this was unlikely as no inflammatory infiltrates were observed during histological analyses. Furthermore, immunogenic reactions are not frequently found with ePU (see introduction). Fourth, thrombosis due to NIH or insufficient NE is also unlikely, because NIH in synthetic grafts only develops after two weeks and typically peaks after one month. 33 Consequently, it was too soon to observe NIH or NE during histological analyses.
Apart from this single observed case of thrombosis, neither groups demonstrated clinical signs of graft/control aortic thrombosis, bringing the overall thrombosis rate of the intervention group to 1/9 (11 %) compared to 0/9 (0 %) in the control group, which is not significantly different. Thus, we conclude (taking the small sample size of our pilot study into account) that the incidence of thrombosis in the 1.25 mm ePU graft was comparable to the incidence of thrombosis in the native aorta after sham surgery.
During ultrasound imaging, using pulsatile arterial flow in the distal aortic segment as a criterion, there was a good patency of the ePU grafts after a period of four months. Taking into account the aforementioned single case of thrombosis, the intervention group held a patency of 8/9 (89 %) compared to 9/9 (100 %) in the control group, which was not significantly different. Therefore, the patency of the ePU grafts was comparable to the patency of native aorta after sham surgery. A recent study by Bergmeister et al. reported patency rates of 95 %, six months after implantation of 1.50 mm ID ePU grafts into the infrarenal aorta of rats. 34 A shortcoming in this study was the lack of a control group; however, the patency rates were good and were comparable to our study (89 % vs. 95 %). There are no other published in vivo studies utilizing chemically unblended ePU grafts with smaller diameters (< 1.25 mm ID). Nieponice et al. investigated the in vivo performance of 1.20 mm ID ePU grafts seeded with muscle derived stem cells, in the infrarenal aortas of rats, with patency rates of 65 % after two months, less than 89 % in our study 35.
On ultrasound, there was a statistically significant (p= 0.010) difference in Vmax decay throughout the graft between the intervention group and the control group. The difference in distal aortic systolic expansion was present but was not statistically significant (p= 0.353) between groups, however, the small sample size of our pilot study may have been a source of underestimation of the effect. The loss of velocity and the limited loss of aortic systolic expansion over the course of the ePU graft suggest a loss of energy of the blood, because of a higher resistance of the graft compared to the native aorta. A first potential cause of energy loss is graft stenosis, although this was unlikely because a stenotic segment would exhibit an increased flow velocity. The mean Vmax in the mid graft was lower than at the proximal and distal end of the graft. Leakage of the graft may have been a second potential cause, however, in vivo evaluation during retrieval revealed a watertight anastomosis. Third and more likely, is a lower elasticity of the graft compared to the native aorta, inducing an increase in resistance and loss of kinetic energy. The differences in absolute Vmax throughout the graft were not significant between the intervention and control group, neither were the proximal and distal systolic expansion.
Regardless of the fact that there was only one statistically significant hemodynamic difference between the groups (Vmax decay), the abovementioned findings suggest a slight mechanical incompatibility of the ePU graft in vivo. This may be a possible factor to take into account for future optimizations of the hemodynamic capacities of the graft.
H&E histological analyses after the 4-month-study period did not demonstrate any significant NIH in the ePU grafts (35 ± 42 µm, 54 ± 29 % of the graft length) and in 1/8 grafts, no NIH was apparent. NIH is a consequence of shear stress caused by turbulent blood flow and, as mentioned previously, normally only reaches its maximum after one month.
36 Thus, because there was only minimal NIH after a 4-month-period, it was unlikely that there would be any further increases over a longer period of time. Interestingly, in a recent report from Bergmeister et al. it was demonstrated that there were only 2/20 ePU grafts with visible NIH after 3 months (mid graft: mean 198 ± 73 μm, anastomoses: mean 159 ± 71 μm). There are two potential reasons for the smaller NIH rates that were found in the Bergmeister et al. study compared to our study: [1] size-mismatch; the ID of the infrarenal aorta of the rat ranged from 1 to 2 mm.
19 Size-mismatch in our study may have led to shear stress conditions and subsequent NIH. However, as is evident from
Figure 3, there was no size mismatch in our study.
37 [2] NIH was caused by incomplete endothelialization, which is more likely, as described below.
34
Immunohistochemistry staining with anti-FVIII for NE demonstrated 80 ± 40 % luminal coverage of the ePU graft length (mean NE length 8.95 ± 4.64 mm, covering a mean graft length of 11.19 ± 2.48 mm). This was probably an underestimation due to cutting artefacts with the microtome. The endothelial coverage is an indicator that the porous structure of the ePU graft facilitates the migration and engraftment of endothelial cells, protecting the graft from shear stress and thrombosis. Given the very low incidence of thrombotic events in our study, NE was likely to be sufficiently protective. The promotion of NE in ePU grafts has been demonstrated in previous studies by Uttayarat et al. (ID 2.10 mm), Grasl & Bergmeister et al. (ID 1.74/2.10 mm) and also in other studies that used larger IDs. 18,23,38,39 NE was demonstrated in vivo after a 1-month-study period by Bergmeister et al. (ID 1.50 mm, infrarenal aorta of rats). 34 The added value of our study is the clear evidence of similar NE in ePU grafts with ID 1.25 mm.
The ID of our graft (1.25 mm) is smaller than the ID of grafts used in previous studies to investigate the in vivo performance of ePU grafts (Bergmeister and Grasl studies, ID ≥ 1.50 mm). Some groups have performed in vivo testing using smaller IDs (starting from 0.70 mm), however they used more complex electrospun materials with the addition of multiple chemical chains. 12,40 For instance, some groups used poly(ε-caprolactone) with the addition of chitosan (ID 1 mm, Fukunishi et al.) 41, poly(glycerol sebacate) (ID 0.72 mm, Wu et al.) 42, poly(L-lactic acid) (ID 1 mm, He et al.) 43 and cysteine-alanine-glycine (ID 0.7 mm, Kuwabara et al.) 44. Other groups used amino acid-based poly(ester urea) (ID 1 mm, Gao et al.) 45, plasma-heparin-treated polycarbonate urethane (ID 1 mm, Qiu et al.) 46, polyethylene glycol and mucin (ID 1 mm, Janairo et al.) 47 or polyethylene glycol, polylactic acid and hirudin (ID 1 mm, Hashi et al.) 48. Additionally, some groups have investigated the seeding of small electrospun grafts with various cells, for instance poly(ester urethane) urea seeded with muscle stem cells (ID 1.2 mm, Nieponice et al.) 35 or poly(L-lactic acid) seeded with mesenchymal stem cells (ID 0.7 mm, Hashi et al.) 49. These studies were all single studies with limited sample sizes (three to fourty-six animals) or with a lack of adequate control groups and variable patency rates. However, some of these studies reported reasonable patency results compared to our study (89 %): Qiu et al. (common carotid artery (CCA) rats, N= 14, 86 % patency), Kuwabara et al. (CCA rats, N= 46, 77 % patency) and Janairo et al. (CCA rats, N= 8, 100 % patency). Therefore, other biomaterials may also be promising candidates together with ePU.
There are some potential limitations to our study. Firstly, there was a small sample size (N= 18) with possible over- or underestimation of the results. Secondly, the graft had a short length (7.5 mm). In future studies, it would be interesting to investigate the ePU graft on longer trajectories, because lengths starting from 2 cm provide more challenges for endothelialization. The infrarenal aorta of the Wistar rat is not long enough, so a femoral artery crossover graft could be used instead, or alternatively larger animals such as rabbits, sheep or pigs, that exhibit less spontaneous endothelialization and have a greater tendency for hypercoagulability could also be used. 19
Despite the good hemodynamic resemblance between rat aortas and cerebral blood vessels, the extrapolation of our results to humans should be done with caution. Rats have a stronger fibrinolytic system, more spontaneous endothelialization and, subsequently, there is a potential underestimation of thrombosis incidence. 19 To date, no clinical studies have been performed using ePU grafts and studies with larger sample sizes in different (larger) animal models are needed to further confirm the good in vivo performance of ePU grafts with ID < 1.50 mm. Animal studies thus far have failed to translate into clinical trials due to insufficient in vivo mechanical testing and regulatory issues. 19,50 Thus, we along with others, would like to reiterate the necessity for more and larger long-term studies on various animal models to determine the efficacy of small caliber ePU grafts. 18 This could lead to the development of more clinically efficacious graft substitutes for use in small caliber vascular surgery, such as cerebral revascularization.
5. Conclusion
Our results clearly demonstrate that ePU grafts are potentially efficacious synthetic alternatives for autologous vascular grafts. We have shown that, after fine-tuning the electrospinning process, ePU vascular grafts are also potentially good substitutes for use in small caliber vascular surgery with IDs < 1.50 mm, for example cerebral revascularization. The ePU graft possesses several good characteristics of an arterial prosthesis (as described by Abbott et al.). 51 The graft can be sterilized, is not expensive, easy to suture, easy to produce in different IDs and shows durability.
Acknowledgments
Bronwen Martin, PhD, for her thorough reviewing and English editing of our paper. Krystyna Szewczyk, PhD., Annemie Van Eetveldt, PhD., the caregivers of the animalarium and veterinary practice “De Vroente” for their knowledge of animal surgery. Siegrid Pauwels and Rita Van Den Bossche for their help with the histology. The rats, for their sacrifices, for which we are ever grateful.
Author disclosure statement
All authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Author Contributions statement
Evelynn Vergauwen, Michiel Tubeeckx and Tomas Menovsky were the major contributors in conducting the experiments and writing the manuscript. Annemie Houben and Sandra Van Vlierberghe have contributed to the technical development of the electrospun graft. Marc Demolder and Guido De Meyer have aided with ultrasound imaging, and Patrick Pauwels has provided us with insights into the histological evaluations. All authors have read and/or adjusted and approved the final manuscript.
Funding statement
This work was supported with equipment (high frequency ultrasound, VEVO® 2100, Visualsonics Inc.) funded by a Hercules grant from the Flemish Research Fund (AUHA/13/03). The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflicts of interest
none.
Abbreviations
| ePU |
electrospun polyurethane |
| GSV |
great saphenous vein |
| ID |
inner diameter |
| IDps, IDpd, IDds, IDdd, ODps, ODpd, ODds and ODpd |
inner/outer, proximal/distal diameters and systolic/diastolic diameters of graft/control aortas |
| NE |
neo-endothalialization |
| NIH |
neointimal hyperplasia |
| RA |
radial artery |
| SEM |
scanning electron microscopy |
References
- Charbel F, Amin-Hanjani S. Decision making in cerebral revascularization surgery using intraoperative CBF measurements. Cerebral revascularization. 1 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders; 2011:44.
- Liu JK, Kan P, Karwande SV, Couldwell WT. Conduits for cerebrovascular bypass and lessons learned from the cardiovascular experience. Neurosurg Focus 2003;14(3):e3. [CrossRef]
- Archie JP. Carotid endarterectomy saphenous vein patch rupture revisited: selective use on the basis of vein diameter. J Vasc Surg 1996;24(3):346-351. [CrossRef]
- Greenberg M, Abel N. Stroke and occlusive cerebrovascular disease. Greenberg handbook of neurosurgery. 8 ed. New York: Thieme; 2016:1318.
- Eddleman C, Getch C, Bendok B, Batjer H. Saphenous vein grafts for the high-flow cerebral revascularization. Cerebral revascularization. 1 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders; 2011:125-126.
- Surdell DL, Hage ZA, Eddleman CS, et al. Revascularization for complex intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 2008;24(2):E21. [CrossRef]
- Sweeney J, Sasaki-Adams D, Abdulrauf S. Radial artery harvesting for cerebral revascularization: technical pearls. Cerebral revascularization. 1 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders; 2011:119-120.
- Kawashima M, Rhoton Jr A. Surgical anatomy of EC-IC bypass procedures. Cerebral revascularization. 1 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders; 2011:66.
- Stegemann JP, Kaszuba SN, Rowe SL. Review: advances in vascular tissue engineering using protein-based biomaterials. Tissue Eng 2007;13(11):2601-2613. [CrossRef]
- Sankaran KK, Subramanian A, Krishnan UM, Sethuraman S. Nanoarchitecture of scaffolds and endothelial cells in engineering small diameter vascular grafts. Biotechnol J 2015;10(1):96-108. [CrossRef]
- Sayers RD, Raptis S, Berce M, Miller JH. Long-term results of femorotibial bypass with vein or polytetrafluoroethylene. Br J Surg 1998;85(7):934-938. [CrossRef]
- Kucinska-Lipka J, Gubanska I, Janik H, Sienkiewicz M. Fabrication of polyurethane and polyurethane based composite fibres by the electrospinning technique for soft tissue engineering of cardiovascular system. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2015;46:166-176. [CrossRef]
- Xue L, Greisler HP. Biomaterials in the development and future of vascular grafts. J Vasc Surg 2003;37(2):472-480. [CrossRef]
- Abbott WM, Vignati JJ. Prosthetic grafts: when are they a reasonable alternative? Semin Vasc Surg 1995;8(3):236-245.
- Li, D. and Xia, Y. (2004), Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel?. Adv. Mater., 16: 1151–1170. [CrossRef]
- Sill TJ, von Recum HA. Electrospinning: applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008;29(13):1989-2006.
- Uthamaraj S, Tefft BJ, Jana S, et al. Fabrication of Small Caliber Stent-grafts Using Electrospinning and Balloon Expandable Bare Metal Stents. J Vis Exp 2016(116).
- Ercolani E, Del GC, Bianco A. Vascular tissue engineering of small-diameter blood vessels: reviewing the electrospinning approach. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2015;9(8):861-888. [CrossRef]
- Byrom MJ, Bannon PG, White GH, Ng MK. Animal models for the assessment of novel vascular conduits. J Vasc Surg 2010;52(1):176-195. [CrossRef]
- Council NR. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8 ed. Washington DC: The National Academic Press; 2011.
- Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG. Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 2010;8(6):e1000412.
- Morton D, Hau J. Welfare assesment and humane endpoints. Handbook of laboratory animal science. Vol 1. 2 ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2003:468-472.
- Grasl C, Bergmeister H, Stoiber M, Schima H, Weigel G. Electrospun polyurethane vascular grafts: in vitro mechanical behavior and endothelial adhesion molecule expression. J Biomed Mater Res A 2010;93(2):716-723. [CrossRef]
- He W, Hu Z, Xu A, et al. The preparation and performance of a new polyurethane vascular prosthesis. Cell Biochem Biophys 2013;66(3):855-866. [CrossRef]
- He W, Hu ZJ, Xu AW, et al. [Assessment of the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of a new electrospun polyurethane vascular prosthesis]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2011;31(12):2006-2011.
- Wang X, Lin P, Yao Q, Chen C. Development of small-diameter vascular grafts. World J Surg 2007;31(4):682-689. [CrossRef]
- Sell SA, McClure MJ, Garg K, Wolfe PS, Bowlin GL. Electrospinning of collagen/biopolymers for regenerative medicine and cardiovascular tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2009;61(12):1007-1019. [CrossRef]
- Konig G, McAllister TN, Dusserre N, et al. Mechanical properties of completely autologous human tissue engineered blood vessels compared to human saphenous vein and mammary artery. Biomaterials 2009;30(8):1542-1550. [CrossRef]
- Donovan DL, Schmidt SP, Townshend SP, Njus GO, Sharp WV. Material and structural characterization of human saphenous vein. J Vasc Surg 1990;12(5):531-537.
- Pillay V, Dott C, Choonara Y, et al. A Review of the Effect of Processing Variables on the Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. Journal of Nanomaterials 2017;2013. [CrossRef]
- Beachley V, Wen X. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the nanofiber diameter and length. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl 2009;29(3):663-668. [CrossRef]
- Milleret V, Hefti T, Hall H, Vogel V, Eberli D. Influence of the fiber diameter and surface roughness of electrospun vascular grafts on blood activation. Acta Biomater 2012;8(12):4349-4356. [CrossRef]
- Beattie D, Davies A. Graft maintenance and graft failure. In: Barros A, Chant A, eds. Emergency vascular and endovascular surgical practice. 2 ed. London: Hodder Arnold; 2017:197-199.
- Bergmeister H, Grasl C, Walter I, et al. Electrospun small-diameter polyurethane vascular grafts: ingrowth and differentiation of vascular-specific host cells. Artif Organs 2012;36(1):54-61. [CrossRef]
- Nieponice A, Soletti L, Guan J, et al. In vivo assessment of a tissue-engineered vascular graft combining a biodegradable elastomeric scaffold and muscle-derived stem cells in a rat model. Tissue Eng Part A 2010;16(4):1215-1223. [CrossRef]
- Waltham M, Harris J. Intimal hyperplasia: the nemesis of cardiovascular intervention. ANZ J Surg 2004;74(9):719-720. [CrossRef]
- Zilla P, Bezuidenhout D, Human P. Prosthetic vascular grafts: wrong models, wrong questions and no healing. Biomaterials 2007;28(34):5009-5027. [CrossRef]
- Uttayarat P, Perets A, Li M, et al. Micropatterning of three-dimensional electrospun polyurethane vascular grafts. Acta Biomater 2010;6(11):4229-4237. [CrossRef]
- Bergmeister H, Schreiber C, Grasl C, et al. Healing characteristics of electrospun polyurethane grafts with various porosities. Acta Biomater 2013;9(4):6032-6040. [CrossRef]
- Rocco KA, Maxfield MW, Best CA, Dean EW, Breuer CK. In vivo applications of electrospun tissue-engineered vascular grafts: a review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 2014;20(6):628-640. [CrossRef]
- Fukunishi T, Best CA, Sugiura T, et al. Tissue-Engineered Small Diameter Arterial Vascular Grafts from Cell-Free Nanofiber PCL/Chitosan Scaffolds in a Sheep Model. PLoS One 2016;11(7):e0158555. [CrossRef]
- Wu W, Allen RA, Wang Y. Fast-degrading elastomer enables rapid remodeling of a cell-free synthetic graft into a neoartery. Nat Med 2012;18(7):1148-1153. [CrossRef]
- He W, Ma Z, Teo WE, et al. Tubular nanofiber scaffolds for tissue engineered small-diameter vascular grafts. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009;90(1):205-216. [CrossRef]
- Kuwabara F, Narita Y, Yamawaki-Ogata A, et al. Novel small-caliber vascular grafts with trimeric Peptide for acceleration of endothelialization. Ann Thorac Surg 2012;93(1):156-163. [CrossRef]
- Gao Y, Yi T, Shinoka T, et al. Pilot Mouse Study of 1 mm Inner Diameter (ID) Vascular Graft Using Electrospun Poly(ester urea) Nanofibers. Adv Healthc Mater 2016;5(18):2427-2436. [CrossRef]
- Qiu X, Lee BL, Ning X, et al. End-point immobilization of heparin on plasma-treated surface of electrospun polycarbonate-urethane vascular graft. Acta Biomater 2017;51:138-147. [CrossRef]
- Janairo RR, Zhu Y, Chen T, Li S. Mucin covalently bonded to microfibers improves the patency of vascular grafts. Tissue Eng Part A 2014;20(1-2):285-293. [CrossRef]
- Hashi CK, Derugin N, Janairo RR, et al. Antithrombogenic modification of small-diameter microfibrous vascular grafts. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2010;30(8):1621-1627. [CrossRef]
- Hashi CK, Zhu Y, Yang GY, et al. Antithrombogenic property of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in nanofibrous vascular grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104(29):11915-11920. [CrossRef]
- L'heureux N, Dusserre N, Marini A, et al. Technology insight: the evolution of tissue-engineered vascular grafts--from research to clinical practice. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2007;4(7):389-395. [CrossRef]
- Abbott WM, Callow A, Moore W, et al. Evaluation and performance standards for arterial prostheses. J Vasc Surg 1993;17(4):746-756.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).