Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
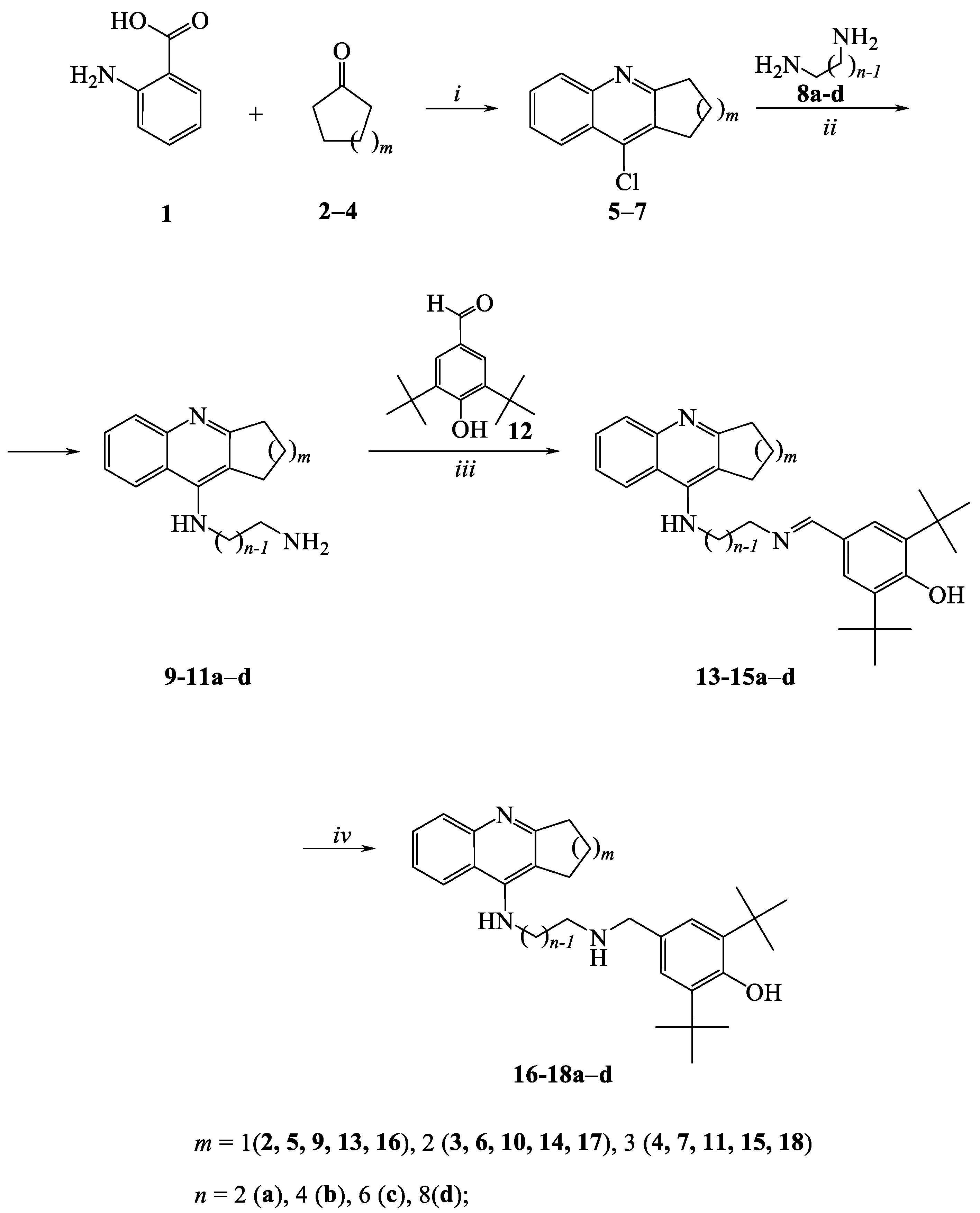
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological studies
2.2.1. Studies of AChE, BChE and CES Inhibition. Structure-Activity Relationships
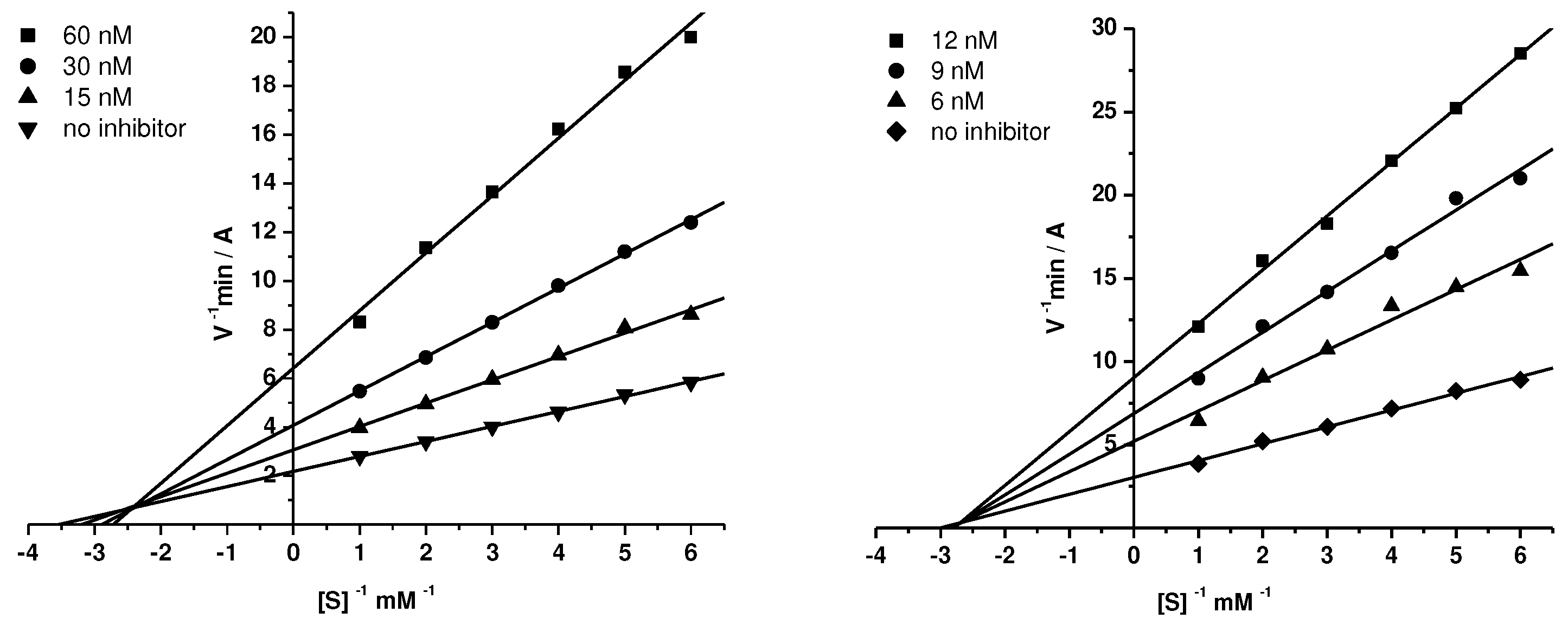
2.2.2. Kinetic Studies of AChE and BChE Inhibition
| Compound | AChE | eqBChE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ki, nM | αKi, nM | Ki, nM | αKi, nM | |
| 15a | 1580±100* | 4300±20* | 164±5* | 437±10* |
| 15c | 69.8±5.0 | 108±3 | 5.13±0.10 | 9.34±0.62 |
| 15d | 19.9±0.8 | 31.4±2.4 | 4.91±0.42 | 5.68±0.06 |
| 18c | 83.1±1.4 | 101±5 | 7.83±0.76 | 17.3±0.2 |
| 18d | 13.0±1.0 | 25.1±0.2 | 4.25±0.33 | 6.06±0.41 |
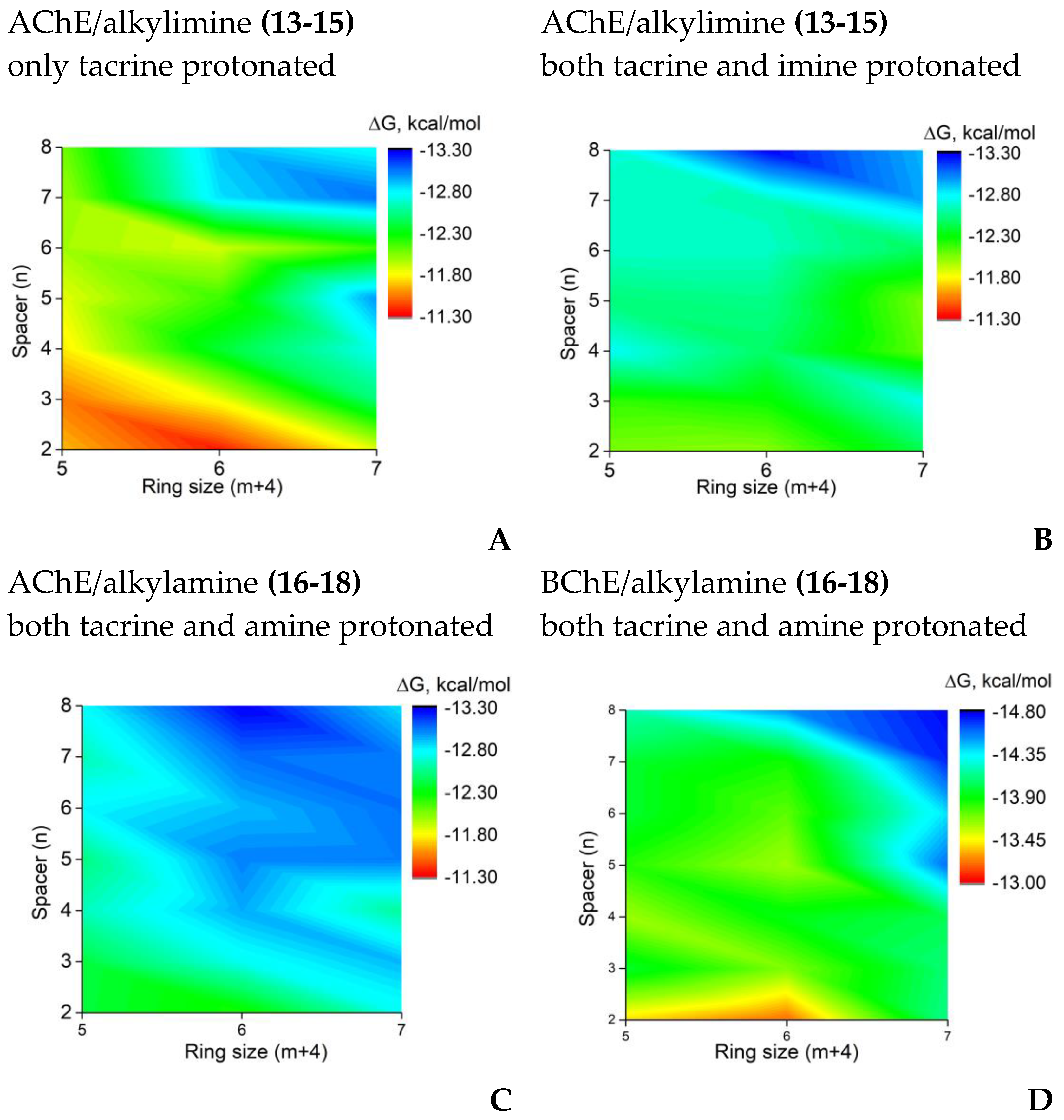
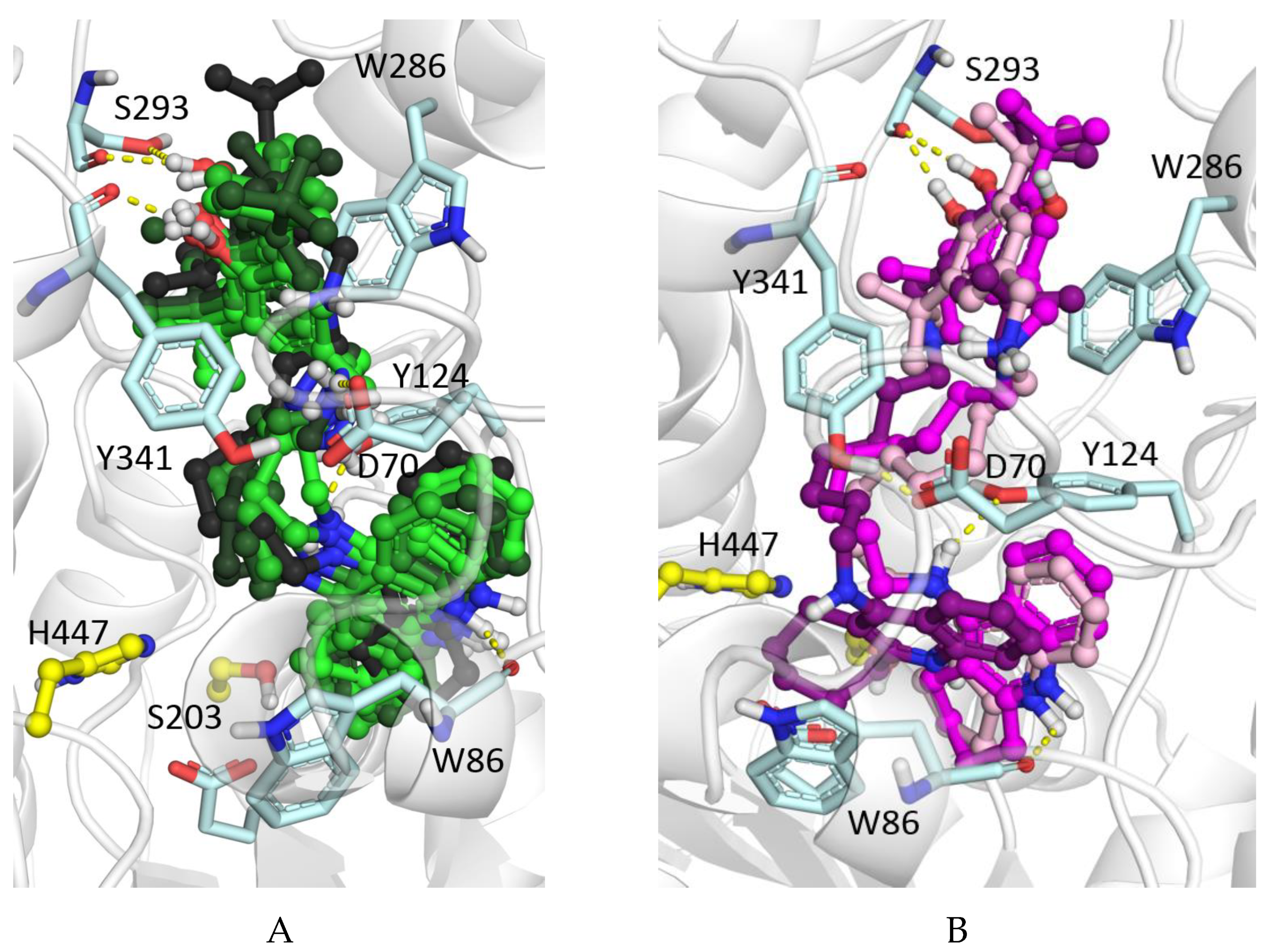
2.2.3. Molecular docking to AChE and BChE
2.2.4. Displacement of Propidium from the PAS of EeAChE
2.2.5. Inhibition of β-amyloid (1–42) (Aβ42) self-aggregation
2.2.6. Molecular docking to Aβ42
2.2.7. Antioxidant activity
2.2.7.1. ABTS assay
2.2.7.2. FRAP assay
2.2.8. Antioxidant activity of conjugates in a biological system
| No | m | n | Radical scavenging capacity, luminol chemiluminescence assay | Inhibition of spontaneous lipid peroxidation in mouse brain homogenate, TBARS assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50, µM | IC50, μM | |||
| 14d | 2 | 8 | 1.9±0.1 | 20.4±2.3 |
| 15d | 3 | 8 | 3.0±0.1 | 29.1±2.4 |
| 15c | 3 | 6 | 2.3±0.3 | 27.6±1.7 |
| 17d | 2 | 8 | 11.3±1.5 | 17.4±2.1 |
| 18c | 3 | 6 | 14.6±0.8 | 24.6±2.8 |
| 18d | 3 | 8 | 9.2±0.6 | 20.2±3.3 |
| Tacrine | n.a. | n.a. | ||
| BHT | 70.4±4.1 | 6.9±0.3 | ||
2.2.8.1. Radical scavenging activity in mouse brain homogenate. Luminol CL assay.
2.2.8.2. Inhibition of spontaneous LP in mouse brain homogenate. TBARS assay
2.2.9. Quantum-Chemical Calculations
| Compound | BDE1 | IP | EA | PDE1 | PDE2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHT | 75.1 | 105.3 | -12.7 | 41.0 | n.a |
| 14bts | 83.7 | 113.9 | 38.1 | 26.7 | 31.4 |
| 17bts | 79.2 | 114.0 | 27.3 | 37.0 | 32.9 |
2.2.9.1. Luminol chemiluminescence
2.2.9.2. Inhibition of spontaneous lipid peroxidation
2.2.9.3. ABTS and FRAP tests
2.3. Predicted ADMET Profiles and PAINS Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General procedure for the preparation of derivatives 13–15a-d and 16–18a-d
3.1.2. Synthesis of compounds
3.2. Biological testing
3.2.1. In vitro AChE, BChE and CES inhibition
3.2.2. Propidium displacement from EeAChE PAS
3.2.3. Effect on β-Amyloid self-aggregation
3.2.4. Antioxidant Activity
3.2.4.1. ABTS radical cation scavenging activity assay
3.2.4.2. Ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay
3.2.4.3. Tissue preparation
3.2.4.4. Luminol chemiluminescence assay of radical-scavenging activity of conjugates in mouse brain homogenate
3.2.4.5. TBARS Assay of the effect of compounds on spontaneous LP
3.3. Molecular Modeling Studies
3.3.1. Molecular docking
3.3.2. QM calculation of antioxidant activity
3.3.3. Prediction of ADMET, Physicochemical, and PAINS Profiles
3.4. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Huang, Y.; Mucke, L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 2012, 148, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. Alzheimer's Disease: Epidemiology and Clinical Progression. Neurol Ther 2022, 11, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, 391–460. [CrossRef]
- Weller, J.; Budson, A. Current understanding of Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and treatment. F1000Res 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreiras, M.C.; Mendes, E.; Perry, M.J.; Francisco, A.P.; Marco-Contelles, J. The multifactorial nature of Alzheimer's disease for developing potential therapeutics. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Freschi, M.; de Camargo Nascente, L.; Salerno, A.; de Melo Viana Teixeira, S.; Nachon, F.; Chantegreil, F.; Soukup, O.; Prchal, L.; Malaguti, M.; et al. Sustainable Drug Discovery of Multi-Target-Directed Ligands for Alzheimer's Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 4972–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaikie, L.; Kay, G.; Kong Thoo Lin, P. Current and emerging therapeutic targets of alzheimer's disease for the design of multi-target directed ligands. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 2052–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaszczyk, J.W. Pathogenesis of Dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, C.; Greig, N.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Enz, A.; Darvesh, S. Cholinesterases: Roles in the Brain During Health and Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2005, 2, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatonovic-Kustrin, S.; Kettle, C.; Morton, D.W. A molecular approach in drug development for Alzheimer's disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreta, M.P.; Burgos-Alonso, N.; Torrecilla, M.; Marco-Contelles, J.; Bruzos-Cidón, C. Efficacy of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors on Cognitive Function in Alzheimer's Disease. Review of Reviews. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGleenon, B.M.; Dynan, K.B.; Passmore, A.P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruangritchankul, S.; Chantharit, P.; Srisuma, S.; Gray, L.C. Adverse Drug Reactions of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in Older People Living with Dementia: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Ther. Clin. Risk. Manag. 2021, 17, 927–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieff, M.G.; Nam, G.; Kang, J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, M.; Lim, M.H. Development of multifunctional molecules as potential therapeutic candidates for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the last decade. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1221–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease as a target for therapy. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2018, 119, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, L.; Fernandez, F.; Johnson, J.B.; Naiker, M.; Owoola, A.G.; Broszczak, D.A. Oxidative stress in alzheimer’s disease: A review on emergent natural polyphenolic therapeutics. Complement Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmann, B.; Behl, C. Antioxidants as treatment for neurodegenerative disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2002, 11, 1407–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufunmilayo, E.O.; Gerke-Duncan, M.B.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.; Bogdanovic, N.; Winblad, B.; Portelius, E.; Andreasen, N.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Zetterberg, H. Pathways to Alzheimer's disease. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 275, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.; Du, X.G.; Geng, M.Y. Small molecule inhibitors of amyloid beta peptide aggregation as a potential therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremic, D.; Jimenez-Diaz, L.; Navarro-Lopez, J.D. Past, present and future of therapeutic strategies against amyloid-beta peptides in Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ferrari, G.V.; Canales, M.A.; Shin, I.; Weiner, L.M.; Silman, I.; Inestrosa, N.C. A structural motif of acetylcholinesterase that promotes amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 10447–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, M.; Bertucci, C.; Cavrini, V.; Andrisano, V. β-Amyloid aggregation induced by human acetylcholinesterase: inhibition studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inestrosa, N.C.; Dinamarca, M.C.; Alvarez, A. Amyloid-cholinesterase interactions. Implications for Alzheimer's disease. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lushchekina, S.V.; Kots, E.D.; Novichkova, D.A.; Petrov, K.A.; Masson, P. Role of Acetylcholinesterase in β-Amyloid Aggregation Studied by Accelerated Molecular Dynamics. BioNanoScience 2017, 7, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Ruiz, P.; Rubio, L.; García-Palomero, E.; Dorronsoro, I.; del Monte-Millán, M.; Valenzuela, R.; Usán, P.; de Austria, C.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Dual Binding Site Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: New Disease-Modifying Agents for Alzheimer's Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, P.; Formosa, X.; Galdeano, C.; Gomez, T.; Munoz-Torrero, D.; Ramirez, L.; Viayna, E.; Gomez, E.; Isambert, N.; Lavilla, R.; et al. Tacrine-based dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors as potential disease-modifying anti-Alzheimer drug candidates. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 187, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zueva, I.; Dias, J.; Lushchekina, S.; Semenov, V.; Mukhamedyarov, M.; Pashirova, T.; Babaev, V.; Nachon, F.; Petrova, N.; Nurullin, L.; et al. New evidence for dual binding site inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase as improved drugs for treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 2019, 155, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Risacher, S.L.; Nho, K.; Kim, S.; Swaminathan, S.; Shen, L.; Foroud, T.M.; Hakonarson, H.; Huentelman, M.J.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. APOE and BCHE as modulators of cerebral amyloid deposition: a florbetapir PET genome-wide association study. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvesh, S. Butyrylcholinesterase as a diagnostic and therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016, 13, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylowska, M.; Dzierzbicka, K.; Kowalski, S.; Chmielewska, K.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Therapeutic Potential of Multifunctional Derivatives of Cholinesterase Inhibitors. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 19, 1323–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spilovska, K.; Korabecny, J.; Nepovimova, E.; Dolezal, R.; Mezeiova, E.; Soukup, O.; Kuca, K. Multitarget tacrine hybrids with neuroprotective properties to confront Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1006–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameem, B.; Saeedi, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Shafiee, A. A review on tacrine-based scaffolds as multi-target drugs (MTDLs) for Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 128, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylowska, M.; Kowalski, S.; Dzierzbicka, K.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Therapeutic Potential of Multifunctional Tacrine Analogues. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 472–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubley, A.; Erofeev, A.; Gorelkin, P.; Beloglazkina, E.; Majouga, A.; Krasnovskaya, O. Tacrine-Based Hybrids: Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Astakhova, T.Y.; Rudakova, E.V.; Proshin, A.N.; Serkov, I.V.; Radchenko, E.V.; Palyulin, V.A.; et al. New Hybrids of 4-Amino-2,3-polymethylene-quinoline and p-Tolylsulfonamide as Dual Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase and Potential Multifunctional Agents for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Rudakova, E.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Grishchenko, M.V.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Astakhova, T.Y.; Serebryakova, O.G.; Timokhina, E.N.; Zhilina, E.F.; et al. Conjugates of Tacrine and Salicylic Acid Derivatives as New Promising Multitarget Agents for Alzheimer's Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, R.; Mao, X.; Chao, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, M.; Duan, X.; Ye, M.; Chen, X.; Mei, Z.; Liu, P.; et al. Tacrine-6-ferulic acid, a novel multifunctional dimer, inhibits amyloid-beta-mediated Alzheimer's disease-associated pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 2012, 7, e31921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepovimova, E.; Korabecny, J.; Dolezal, R.; Babkova, K.; Ondrejicek, A.; Jun, D.; Sepsova, V.; Horova, A.; Hrabinova, M.; Soukup, O.; et al. Tacrine-Trolox Hybrids: A Novel Class of Centrally Active, Nonhepatotoxic Multi-Target-Directed Ligands Exerting Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant Activities with Low In Vivo Toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8985–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scipioni, M.; Kay, G.; Megson, I.L.; Kong Thoo Lin, P. Synthesis of novel vanillin derivatives: novel multi-targeted scaffold ligands against Alzheimer's disease. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan-Pena, J.M.; Romero-Real, V.; Hicke, J.; Maya, I.; Franconetti, A.; Lagunes, I.; Padron, J.M.; Petralla, S.; Poeta, E.; Naldi, M.; et al. Tacrine-O-protected phenolics heterodimers as multitarget-directed ligands against Alzheimer's disease: Selective subnanomolar BuChE inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 181, 111550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkov, I.V.; Proshin, A.N.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Rudakova, E.V.; Makhaeva, G.F.; Bachurin, S.O. Synthesis and properties of new derivatives of 4-amino-2,3-polymethylenequinolines with antioxidant function. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2023, 72, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Rudakova, E.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Faingold, II; Poletaeva, D.A.; Soldatova, Y.V.; Kotelnikova, R.A.; Serkov, I.V.; et al. New Multifunctional Agents Based on Conjugates of 4-Amino-2,3-polymethylenequinoline and Butylated Hydroxytoluene for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, P.R.; Han, Y.F.; Chow, E.S.; Li, C.P.; Wang, H.; Lieu, T.X.; Wong, H.S.; Pang, Y.P. Evaluation of short-tether bis-THA AChE inhibitors. A further test of the dual binding site hypothesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1999, 7, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Rudakova, E.V.; Serebryakova, O.G.; Aksinenko, A.Y.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Bachurin, S.O.; Richardson, R.J. Esterase profiles of organophosphorus compounds in vitro predict their behavior in vivo. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 259, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Rudakova, E.V.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Proshin, A.N.; Shchegolkov, E.V.; Burgart, Y.V.; Saloutin, V.I. Cholinesterase and carboxylesterase inhibitors as pharmacological agents. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2019, 68, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Rudakova, E.V.; Stupina, T.S.; Terentiev, A.A.; Serkov, I.V.; Proshin, A.N.; Radchenko, E.V.; et al. Conjugates of tacrine and 1,2,4-thiadiazole derivatives as new potential multifunctional agents for Alzheimer's disease treatment: Synthesis, quantum-chemical characterization, molecular docking, and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Proshin, A.N.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Rudakova, E.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Astakhova, T.Y.; Serkov, I.V.; Kalashnikova, I.P.; Bachurin, S.O. Synthesis and study of the biological activity of thiourea-containing amiridine derivatives as potential multi-target drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2022, 71, 2404–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokar, S.; Erfani, M.; Bavi, O.; Khazaei, S.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Hajiramezanali, M.; Beiki, D.; Shamloo, A. Design of peptide-based inhibitor agent against amyloid-beta aggregation: Molecular docking, synthesis and in vitro evaluation. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 102, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, K.M.; Tian, X.; Xie, J. Hurdles and pitfalls in measuring antioxidant efficacy: A critical evaluation of ABTS, DPPH, and ORAC assays. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Schaich, K.M. Effects of molecular structure on kinetics and dynamics of the trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity assay with ABTS(+*). J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2013, 61, 5511–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Meo, S.; Venditti, P.; Piro, M.C.; De Leo, T. Enhanced luminescence study of liver homogenate response to oxidative stress. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 1995, 103, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, A.; Cedrowski, J.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Ratkiewicz, A.; Witkowski, S. Synthesis, DFT Calculations, and In Vitro Antioxidant Study on Novel Carba-Analogs of Vitamin E. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; An, L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Y. Density functional theory study of the structure-antioxidant activity of polyphenolic deoxybenzoins. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, J.; Pal, T.K.; Hasan, T. Theoretical investigations on the antioxidant potential of 2,4,5-trihydroxybutyrophenone in different solvents: A DFT approach. Results Chem. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marković, Z.; Tošović, J.; Milenković, D.; Marković, S. Revisiting the solvation enthalpies and free energies of the proton and electron in various solvents. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2016, 1077, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedouhène, S.; Moulti-Mati, F.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; My-Chan Dang, P.; El-Benna, J. Luminol-amplified chemiluminescence detects mainly superoxide anion produced by human neutrophils. Am. J. Blood Res. 2017, 7, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Villaverde, A.; Netherton, J.; Baker, M.A. From Past to Present: The Link Between Reactive Oxygen Species in Sperm and Male Infertility. Antioxidants (Basel) 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudin, A.P.; Malinska, D.; Kunz, W.S. Sites of generation of reactive oxygen species in homogenates of brain tissue determined with the use of respiratory substrates and inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1777, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuvanshi, R.S. Superoxide Anion Radical, A Multipotent Reagent: A Review. Nat. Volatiles & Essent. Oils 2020, 7, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Galano, A.; Vargas, R.; Martinez, A. Carotenoids can act as antioxidants by oxidizing the superoxide radical anion. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Shakeel, F. Antioxidant activity coefficient, mechanism, and kinetics of different derivatives of flavones and flavanones towards superoxide radical. Czech J. Food Sci. 2012, 30, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, R.; Yan, X.; Fan, K. Superoxide dismutase nanozymes: an emerging star for anti-oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 6939–6957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahan, A.; Shiroudi, A. Oxidation reaction mechanism and kinetics between OH radicals and alkyl-substituted aliphatic thiols: H-abstraction pathways. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 2020, 45, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Mishra, P.C. Modeling the activity of glutathione as a hydroxyl radical scavenger considering its neutral non-zwitterionic form. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroka, S.; Zimmeck, S.; Troya, D.; Tanko, J.M. How solvent modulates hydroxyl radical reactivity in hydrogen atom abstractions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valgimigli, L. Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant Protection. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacique, A.P.; Barbosa, É.S.; de Pinho, G.P.; Silvério, F.O. Miniaturized Methodologies for Determining the Total Phenol and Flavonoid Concentrations and the Antioxidant Activity. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosokha, S.V.; Kochi, J.K. Continuum of outer- and inner-sphere mechanisms for organic electron transfer. Steric modulation of the precursor complex in paramagnetic (ion-radical) self-exchanges. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3683–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Shen, D.X.; Meng, M.; Mallick, S.; Cao, L.; Patmore, N.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Zou, S.F.; Chen, H.W.; Qin, Y.; et al. Efficient electron transfer across hydrogen bond interfaces by proton-coupled and -uncoupled pathways. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Serebryakova, O.G.; Rudakova, E.V.; Ustyugov, A.A.; Bachurin, S.O.; Shchepochkin, A.V.; Chupakhin, O.N.; Charushin, V.N.; et al. 9-Substituted acridine derivatives as acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors possessing antioxidant activity for Alzheimer's disease treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5981–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Lappi, S. Interaction of fluorescence probes with acetylcholinesterase. Site and specificity of propidium binding. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Lwebuga-Mukasa, J.; Lappi, S.; Rademacher, J. Propidium—a fluorescence probe for a peripheral anionic site on acetylcholinesterase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1974, 10, 703–708. [Google Scholar]
- LeVine, H. 3rd. Quantification of beta-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 309, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhaeva, G.F.; Elkina, N.A.; Shchegolkov, E.V.; Boltneva, N.P.; Lushchekina, S.V.; Serebryakova, O.G.; Rudakova, E.V.; Kovaleva, N.V.; Radchenko, E.V.; Palyulin, V.A.; et al. Synthesis, molecular docking, and biological evaluation of 3-oxo-2-tolylhydrazinylidene-4,4,4-trifluorobutanoates bearing higher and natural alcohol moieties as new selective carboxylesterase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of "antioxidant power": the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterborg, J.H. The Lowry Method for Protein Quantitation. in Walker J.M. (eds) The Protein Protocols Handbook. Springer Protocols Handbooks. Humana Press. 2002, pp, 7-10. [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Ji, C. MolGpka: A Web Server for Small Molecule pKa Prediction Using a Graph-Convolutional Neural Network. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3159–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comp. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwdin, P.-O. On the nonorthogonality problem. In Advances in Quantum Chemistry, Per-Olov, L., Ed. Academic Press: New York, London, 1970; Vol. Volume 5, pp. 185-199.
- Cheung, J.; Rudolph, M.J.; Burshteyn, F.; Cassidy, M.S.; Gary, E.N.; Love, J.; Franklin, M.C.; Height, J.J. Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10282–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, Y.; Lockridge, O.; Masson, P.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C.; Nachon, F. Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41141–41147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, P.; Lushchekina, S.; Schopfer, L.M.; Lockridge, O. Effects of viscosity and osmotic stress on the reaction of human butyrylcholinesterase with cresyl saligenin phosphate, a toxicant related to aerotoxic syndrome: kinetic and molecular dynamics studies. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzi, O.; Tomaselli, S.; Guerrini, R.; Salvadori, S.; D'Ursi, A.M.; Temussi, P.A.; Picone, D. Solution structure of the Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) in an apolar microenvironment. Similarity with a virus fusion domain. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 5642–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comp. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comp. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H. Gaussian 16 Revision C. 01. 2016, Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA: 2016.
- Laikov, D.N.; Ustynyuk, Y.A. PRIRODA-04: a quantum-chemical program suite. New possibilities in the study of molecular systems with the application of parallel computing. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2005, 54, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laikov, D.N. PRIRODA. Electronic Structure Code, 19; 2020.
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Toward reliable density functional methods without adjustable parameters: The PBE0 model. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 6158–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Huber, C.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted Gaussian basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 5829–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular Dichroism Spectra Using Density Functional Force Fields. J. Phys. Chem. 2002, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassolov, V.A.; Ratner, M.A.; Pople, J.A.; Redfern, P.C.; Curtiss, L.A. 6-31G* basis set for third-row atoms. J. Comp. Chem. 2001, 22, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Antony, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Krieg, H. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 154104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACS Chem NeurosciActa NeuropatholMarenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushko, I.; Novotarskyi, S.; Korner, R.; Pandey, A.K.; Rupp, M.; Teetz, W.; Brandmaier, S.; Abdelaziz, A.; Prokopenko, V.V.; Tanchuk, V.Y.; et al. Online chemical modeling environment (OCHEM): web platform for data storage, model development and publishing of chemical information. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2011, 25, 533–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radchenko, E.V.; Dyabina, A.S.; Palyulin, V.A.; Zefirov, N.S. Prediction of human intestinal absorption of drug compounds. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2016, 65, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyabina, A.S.; Radchenko, E.V.; Palyulin, V.A.; Zefirov, N.S. Prediction of blood-brain barrier permeability of organic compounds. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 470, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchenko, E.V.; Dyabina, A.S.; Palyulin, V.A. Towards Deep Neural Network Models for the Prediction of the Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability for Diverse Organic Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchenko, E.V.; Rulev, Y.A.; Safanyaev, A.Y.; Palyulin, V.A.; Zefirov, N.S. Computer-aided estimation of the hERG-mediated cardiotoxicity risk of potential drug components. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 473, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ADMET Prediction Service. http://qsar.chem.msu.ru/admet/ (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Bickerton, G.R.; Paolini, G.V.; Besnard, J.; Muresan, S.; Hopkins, A.L. Quantifying the chemical beauty of drugs. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RDKit: open-source cheminformatics software. Available online: http://www.rdkit.org (accessed on 15 June 2022).
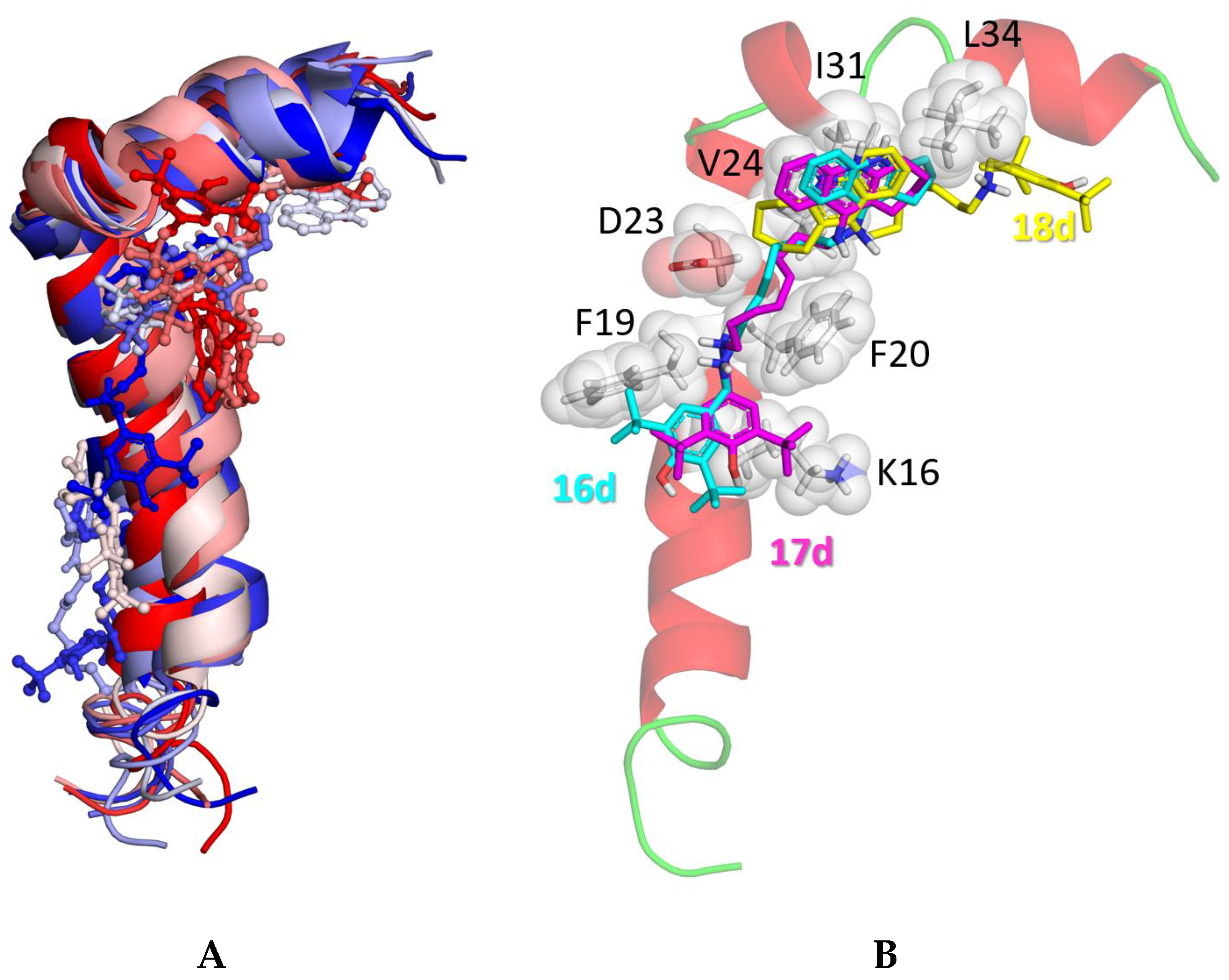

| No | m | n | Inhibitory activity against AChE, BChE and CES IC50, μM or % inhibition at 20 μM |
Propidium displacement, (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AChE | BChE | CES | ||||
| 13a | 1 | 2 | 4.86±0.01* | 1.92±0.11* | 26.1±0.7%* | 18.1±1.6* |
| 13b | 1 | 4 | 1.30±0.07 | 0.351±0.001 | 32.7±1.9% | 20.0±1.6 |
| 13c | 1 | 6 | 0.210±0.010 | 0.172±0.017 | 31.3±2.1% | 16.5±1.3 |
| 13d | 1 | 8 | 0.107±0.009 | 0.0417±0.0003 | 26.3±1.7% | 15.1±0.9 |
| 14a | 2 | 2 | 5.98±0.13* | 1.61±0.04* | 28.6±1.6%* | 18.2±1.6* |
| 14b | 2 | 4 | 0.424±0.022 | 0.385±0.031 | 26.6±2.2% | 17.6±1.4 |
| 14c | 2 | 6 | 0.0712±0.0012 | 0.055±0.005 | 25.1±1.9% | 19.7±1.5 |
| 14d | 2 | 8 | 0.0171±0.0016 | 0.00939±0.00042 | 28.8±2.0% | 14.8±1.0 |
| 15a | 3 | 2 | 4.03±0.03* | 0.419±0.040* | 30.1 ± 2.5%* | 16.3±1.3* |
| 15b | 3 | 4 | 0.524±0.020 | 0.131±0.004 | 26.3±0.4% | 18.4±1.4 |
| 15c | 3 | 6 | 0.151±0.013 | 0.0106±0.0002 | 25.4±0.9% | 16.8±1.2 |
| 15d | 3 | 8 | 0.0260±0.0024 | 0.00624±0.00054 | 25.5±1.1% | 14.9±1.2 |
| 16a | 1 | 2 | 3.50±0.33* | 0.652±0.05* | 19.6±1.3%* | 16.4±1.4* |
| 16b | 1 | 4 | 0.912±0.016 | 0.177±0.017 | 17.2±3.3% | 17.5±1.5 |
| 16c | 1 | 6 | 0.205±0.012 | 0.0488±0.0005 | 18.7±0.7% | 15.8±1.4 |
| 16d | 1 | 8 | 0.094±0.006 | 0.0170±0.0016 | 17.2±0.2% | 13.9±1.1 |
| 17a | 2 | 2 | 2.88±0.19 | 0.464±0.041 | 18.4±1.1% | 13.4±1.1 |
| 17b | 2 | 4 | 0.279±0.022 | 0.111±0.009 | 15.8±1.4% | 15.4±1.3 |
| 17c | 2 | 6 | 0.0702±0.0011 | 0.0361±0.023 | 18.5±1.6% | 16.1±1.1 |
| 17d | 2 | 8 | 0.0151±0.002 | 0.00756±0.00042 | 23.6±2.1% | 13.4±1.2 |
| 18a | 3 | 2 | 1.90±0.26* | 0.0838±0.0082* | 26.0±3.9%* | 13.6±1.2* |
| 18b | 3 | 4 | 0.436±0.016 | 0.0678±0.0061 | 21.4±1.8% | 15.7±1.2 |
| 18c | 3 | 6 | 0.103±0.004 | 0.0149±0.0003 | 16.8±0.5% | 12.5±0.9 |
| 18d | 3 | 8 | 0.0308±0.0002 | 0.00596±0.00058 | 13.9±1.2% | 12.3±0.8 |
| Tacrine | 0.601±0.047 | 0.0295±0.0002 | n.a. | 4.4 ± 0.6 | ||
| BHT | 6.0±1.5% | 18.9±1.7% | 5.6±0.2% | n.d. | ||
| BNPP | n.a. | n.a. | 99.1±0.9%1 | n.d. | ||
| Donepezil | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | 11.9 ± 0.9 | ||
| No | m | n | Inhibition of Aβ42 Self- aggregation, % 1 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13d | 1 | 8 | 49.4±4.3 | |
| 14c | 2 | 6 | 62.4±4.9 | |
| 14d | 2 | 8 | 70.4±5.6 | |
| 15c | 3 | 6 | 43.4±3.9 | |
| 15d | 3 | 8 | 63.5±5.0 | |
| 16d | 1 | 8 | 54.6±3.9 | |
| 17c | 2 | 6 | 64.1±5.7 | |
| 17d | 2 | 8 | 71.4±4.9 | |
| 18c | 3 | 6 | 47.8±3.8 | |
| 18d | 3 | 8 | 59.6±4.7 | |
| Tacrine | 5.9±0.5 | |||
| Myricetin | 73.2±5.8 | |||
| Propidium iodide | 89.3±7.1 | |||
| No | m | n | ABTS•+-scavenging activity |
Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEAC | IC50, µM | TE | |||
| 13a | 1 | 2 | 0.92±0.03* | 22.3±1.5 | 0.51±0.03* |
| 13b | 1 | 4 | 0.78±0.04 | 25.4±1.6 | 0.60±0.02 |
| 13c | 1 | 6 | 0.98±0.04 | 19.4±0.9 | 0.59±0.01 |
| 13d | 1 | 8 | 0.85±0.03 | 22.7±1.2 | 0.71±0.03 |
| 14a | 2 | 2 | 1.13±0.05* | 17.8±1.5 | 0.58±0.03* |
| 14b | 2 | 4 | 1.00±0.05 | 19.7±0.9 | 0.72±0.03 |
| 14c | 2 | 6 | 1.10±0.05 | 18.6±0.9 | 0.71±0.02 |
| 14d | 2 | 8 | 1.06±0.03 | 18.2±0.7 | 0.70±0.03 |
| 15a | 3 | 2 | 1.11±0.04* | 18.8±0.8 | 0.52±0.01* |
| 15b | 3 | 4 | 0.89±0.04 | 22.5±1.4 | 0.46±0.01 |
| 15c | 3 | 6 | 0.90±0.03 | 22.3±1.1 | 0.52±0.02 |
| 15d | 3 | 8 | 1.00±0.03 | 19.6±0.8 | 0.73±0.02 |
| 16a | 1 | 2 | 1.39±0.05* | 14.6±0.8 | 0.57±0.02 |
| 16b | 1 | 4 | 0.90 ±0.04 | 23.6±1.3 | 0.44±0.02 |
| 16c | 1 | 6 | 1.50±0.06 | 13.4±0.7 | 0.51±0.02 |
| 16d | 1 | 8 | 1.00±0.03 | 21.3±1.2 | 0.61±0.01 |
| 17a | 2 | 2 | 1.20±0.05 | 16.7±0.8 | 0.52±0.02 |
| 17b | 2 | 4 | 1.40±0.06 | 14.3±0.6 | 0.46±0.01 |
| 17c | 2 | 6 | 1.32±0.08 | 15.7±0.6 | 0.44±0.02 |
| 17d | 2 | 8 | 1.27±0.05 | 15.2±0.7 | 0.57±0.01 |
| 18a | 3 | 2 | 1.35±0.06* | 15.3±0.6 | 0.44±0.06 |
| 18b | 3 | 4 | 1.36±0.06 | 14.6±0.5 | 0.38±0.01 |
| 18c | 3 | 6 | 1.00±0.03 | 21.6±1.1 | 0.43±0.02 |
| 18d | 3 | 8 | 1.20±0.05 | 15.8±0.6 | 0.45±0.01 |
| BHT | 0.98 ± 0.03 | 22.4±1.4 | 0.96±0.02 | ||
| Trolox | 1.0 | 20.1±1.2 | 1.0 | ||
| Compound | m | n | MW | LogPow | pSaq | LogBB | HIA, % | hERG pKi | hERG pIC50 | QED |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13a | 1 | 2 | 443.63 | 5.82 | 6.82 | 0.24 | 100 | 6.22 | 6.17 | 0.35 |
| 13b | 1 | 4 | 471.69 | 6.35 | 7.39 | 0.48 | 100 | 6.18 | 6.55 | 0.28 |
| 13c | 1 | 6 | 499.74 | 6.99 | 7.96 | 0.40 | 100 | 6.09 | 6.95 | 0.23 |
| 13d | 1 | 8 | 527.79 | 7.38 | 8.24 | 0.77 | 100 | 6.45 | 7.39 | 0.19 |
| 14a | 2 | 2 | 457.66 | 6.14 | 7.19 | 0.27 | 100 | 6.27 | 6.06 | 0.32 |
| 14b | 2 | 4 | 485.71 | 6.64 | 7.65 | 0.51 | 100 | 6.22 | 6.43 | 0.27 |
| 14c | 2 | 6 | 513.77 | 7.31 | 8.10 | 0.43 | 100 | 6.13 | 6.82 | 0.22 |
| 14d | 2 | 8 | 541.82 | 7.55 | 8.56 | 0.79 | 100 | 6.49 | 7.26 | 0.19 |
| 15a | 3 | 2 | 471.69 | 6.40 | 7.44 | 0.30 | 100 | 6.27 | 6.17 | 0.23 |
| 15b | 3 | 4 | 499.74 | 6.98 | 7.96 | 0.54 | 100 | 6.22 | 6.55 | 0.20 |
| 15c | 3 | 6 | 527.79 | 7.36 | 8.32 | 0.46 | 100 | 6.13 | 6.95 | 0.17 |
| 15d | 3 | 8 | 555.85 | 7.70 | 8.72 | 0.82 | 100 | 6.49 | 7.39 | 0.14 |
| 16a | 1 | 2 | 445.65 | 5.33 | 5.68 | 0.22 | 100 | 5.87 | 5.83 | 0.39 |
| 16b | 1 | 4 | 473.70 | 5.89 | 6.23 | 0.49 | 100 | 6.43 | 6.29 | 0.31 |
| 16c | 1 | 6 | 501.76 | 6.42 | 6.80 | 0.48 | 100 | 6.23 | 6.43 | 0.25 |
| 16d | 1 | 8 | 529.81 | 6.88 | 7.30 | 0.84 | 100 | 6.60 | 6.81 | 0.21 |
| 17a | 2 | 2 | 459.68 | 5.65 | 5.96 | 0.25 | 100 | 5.92 | 5.74 | 0.36 |
| 17b | 2 | 4 | 487.73 | 6.18 | 6.51 | 0.52 | 100 | 6.47 | 6.19 | 0.29 |
| 17c | 2 | 6 | 515.78 | 6.67 | 7.06 | 0.51 | 100 | 6.27 | 6.33 | 0.24 |
| 17d | 2 | 8 | 543.84 | 7.11 | 7.50 | 0.87 | 100 | 6.64 | 6.71 | 0.20 |
| 18a | 3 | 2 | 473.70 | 5.92 | 6.28 | 0.28 | 100 | 5.93 | 5.82 | 0.27 |
| 18b | 3 | 4 | 501.76 | 6.40 | 6.81 | 0.55 | 100 | 6.47 | 6.28 | 0.22 |
| 18c | 3 | 6 | 529.81 | 6.85 | 7.28 | 0.54 | 100 | 6.28 | 6.43 | 0.18 |
| 18d | 3 | 8 | 557.86 | 7.39 | 7.68 | 0.90 | 100 | 6.64 | 6.82 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





