Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
08 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Description of research strategy
- Studies published from 2013 to 2023.
- Observational studies (i.e. cohort, case-control, cross-sectional studies).
- Direct relation to the subject and inclusion of the specified keywords.
- Conceptual connection of keywords with the title and summary.
- Inclusion of studies with positive, negative or neutral effect on the association of maternal nutrition with placental / newborn TL and PTB.
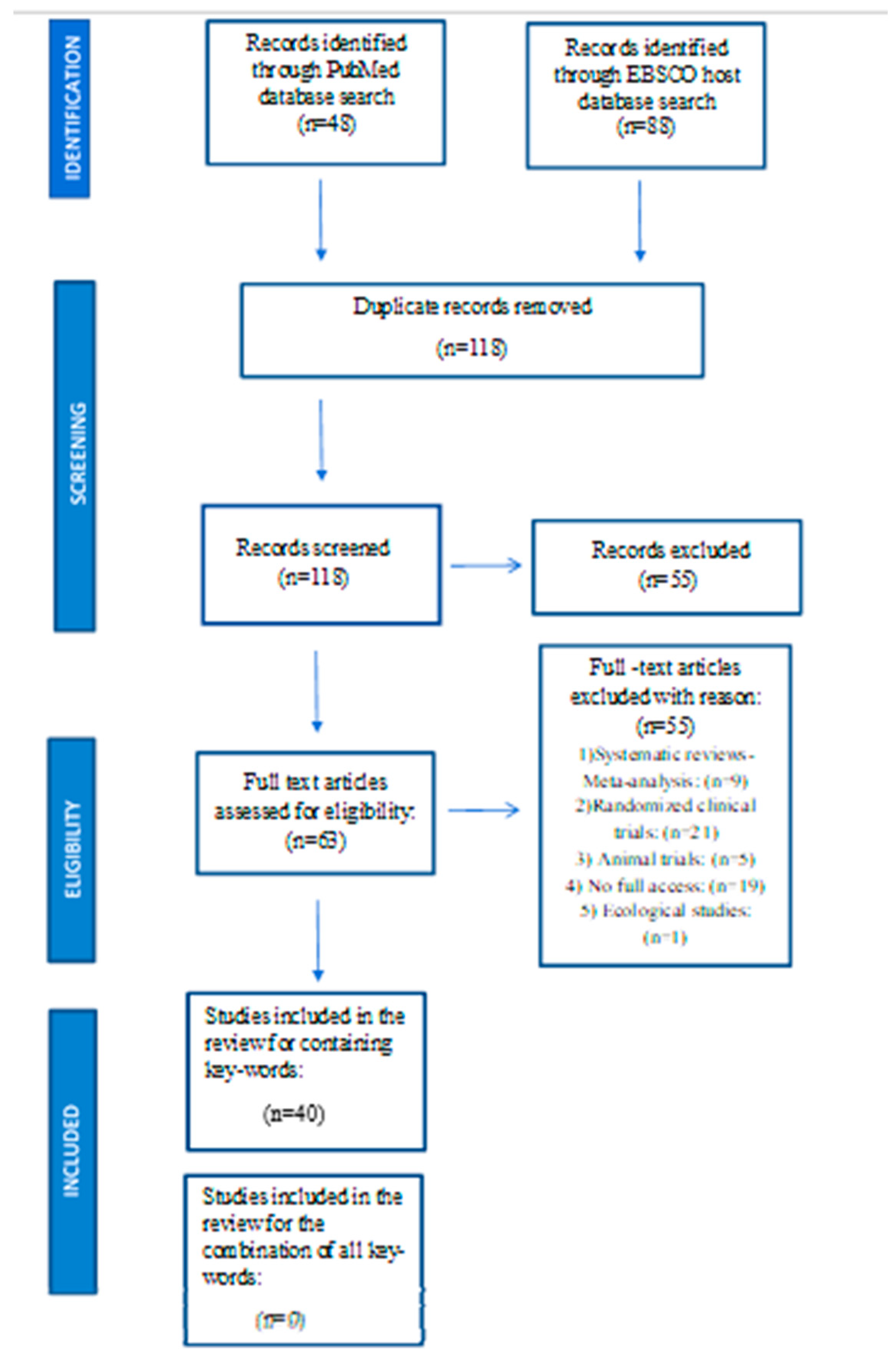
- Description of the search strategy and eligibility of studies according to the four-phase flow chart of PRISMA guidelines [71].
3. Results
3.1. Studies eligibility
3.2. Maternal nutrition and PTB
3.3. Maternal nutrition, placental and newborn telomeres
3.4. PTB, placental and newborn telomeres
3.5. Figures & Tables
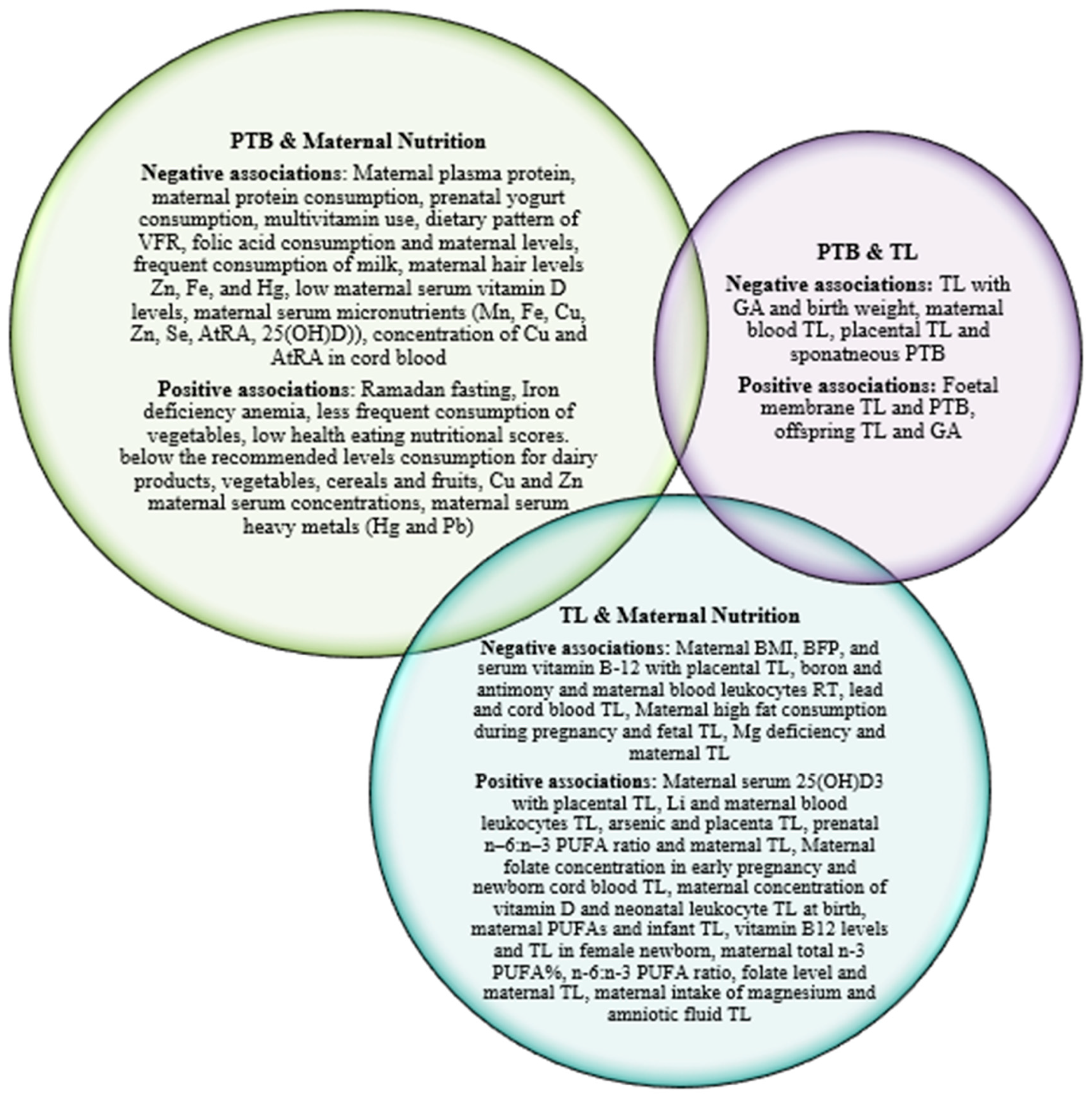
4. Discussion
Maternal nutrition and PTB
Maternal nutrition, placental and newborn telomeres
PTB, placental and newborn telomeres
Maternal nutrition, placental-newborn telomeres and PTB
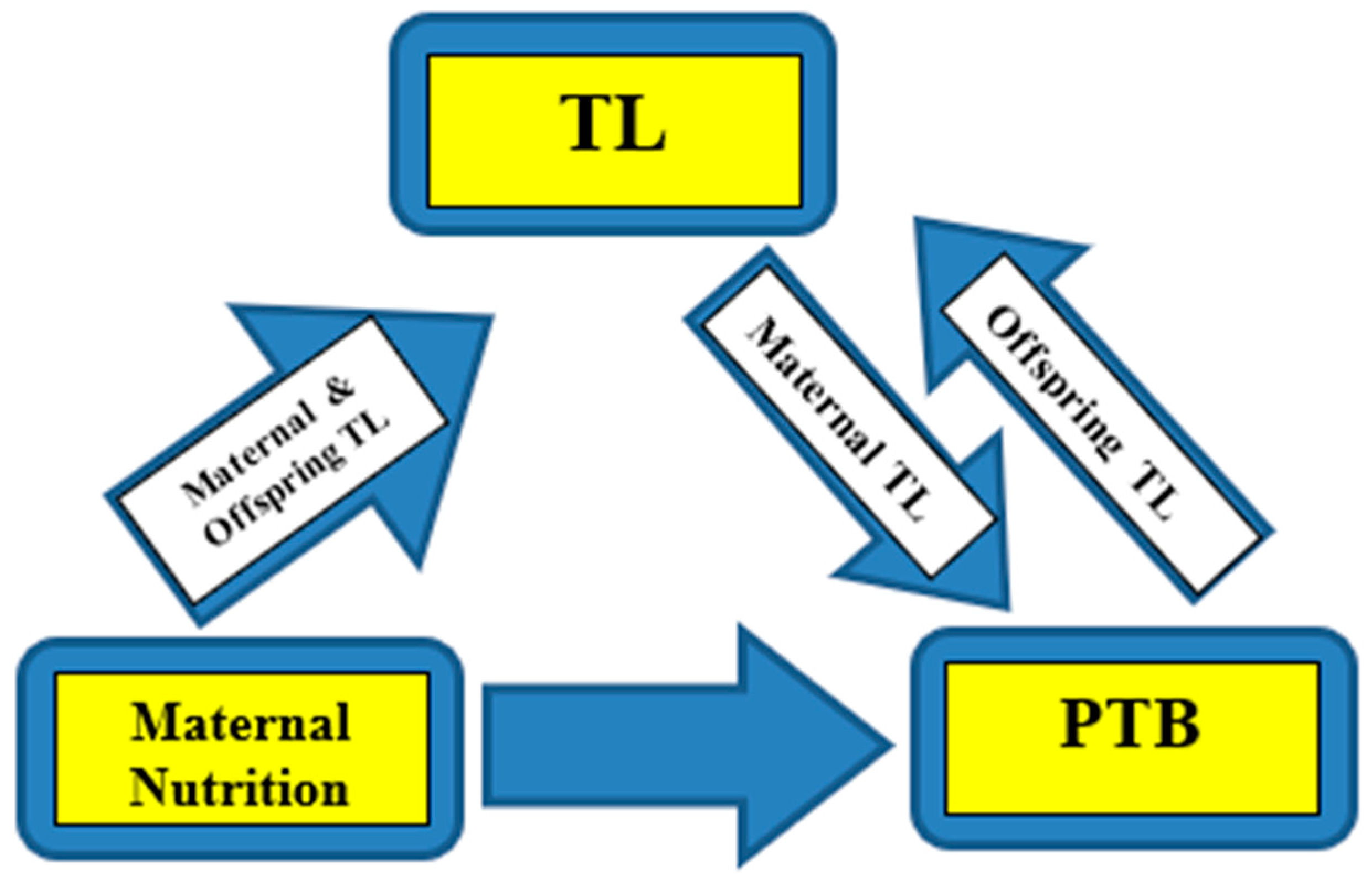
Limitations of the study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical issues
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Preterm birth, Fact sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preterm-birth#:~:text=Across%20countries%2C%20the%20rate%20of,of%20babies%20born%20in%202020 (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Goldenberg, R.; Culhane, J.F.; Iams, J.D.; Romero, R. Epidemiology and causes of PTB. The Lancet 2008, 371, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagura, P.; Wasunna, A.; Laving, A.; Wamalwa, D.; Ng’ang’a, P. Prevelance and factors associated with PTB at Kenyatta national hospital. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, V.; Luther, E. Preterm Labor. 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536939/ (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Morgan, T. Placental insufficiency is a leading cause of preterm labor. NeoReviews 2014, 15, e518–e525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, A.; Manuck, T. Screening for spontaneous PTB and resultant therapies to reduce neonatal morbidity and mortality: A review. Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2017, 23, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.B.; Buhimschi, C.S.; Norwitz, E.R. Normal labor: mechanism and duration. Obstetrics and Gynecology Clinics 2005, 32, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, W.; Challis, J.R.G. Mechanism of term and PTB. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada 2020, 23, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousiolis, A. The role of leptin and syncytin upon the placenta function. (Publication No.28617) [Doctoral thesis, University of Thessaly, Greece] National Documentation Centre 2011. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, S. Vascular Biology of the Placenta; Integrated Systems Physiology: From Molecules to Function to Disease. San Rafael (CA) 2010. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gete, D.; Waller, M.; Mishra, G. Effects of maternal diets on PTB and low birth weight: a systematic review. British Journal of Nutrition 2020, 12, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAninch, D.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Gatford, K.L.; Leemaqz, S.Y.; Andraweera, P.H.; Garrett, A.; Plummer, M.D.; Dekker, G.A.; Roberts, C.T.; Smithers, L.G.; et al. The metabolic syndrome in pregnancy and its association with child telomere length. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizgier, M.; Jarzabek-Bielecka, G.; Mruczyk, K. Maternal diet and gestational diabetes mellitus development. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2021, 34, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, E.; Ferraro, Z.M.; Yockell-Lelievre, J.; Gruslin, A.; Adamo, K.B. Maternal-Fetal nutrient transport in pregnancy pathologies :The role of the placenta. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2014, 15, 16153–16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; McCarthy, C.; McCarthy, F.P. Placental ageing in adverse pregnancy outcomes: Telomere shortening, cell senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity 2019, 2019(3095383), 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jirkovska, M.; Korabecna, M.; Lassakova, S. Telomeres and telomerase activity in the human placenta. In: Telomerase and non-Telomerase mechanisms of telomere maintenance. Morrish, T.A. Ed.; IntechOpen 2019; pp 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Connor, K.; Kibscull, M.; Matysiak-Zablocki, E.; Ngoc Nguyen, T.; Matthews, S.G.; Lye, S.; Bloise, E. Maternal malnutrition impacts placental morphology and transport. An origin for poor offspring growth and vulnerability to disease. The Journal of Biochemistry 2019, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.; Phillips, J.A.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; McAninch, D.; Goh, Z.; Anderson, P.H.; Roberts, C.T. Reduced dietary calcium and vitamin D results in PTB and altered placental morphogenesis in mice during pregnancy. Reproductive Sciences 2020, 27, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, A.; Taylor, R.N.; Tangpricha, V.; Fortunato, S.; Menon, R. Maternal micronutrient status and preterm versus term birth for black and white US women. Reproductive Sciences 2012, 19, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, K.; Robinson, S.; Barker, D.J.; Osmond, C.; Cox, V. Maternal nutrition in early pregnancy in relation to placental and fetal growth. BMJ 1996, 312, 410–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Keats, E.C.; Bhutta, Z.A. Vitamin and mineral supplementation during pregnancy on maternal birth, child health and development outcomes in low- and middle- income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2019, 419, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emond, J.; Karagas, M.R.; Baker, E.R.; Gilbert-Diamond, D. Better diet quality during pregnancy is associated with a reduced likelihood of an infant born small for gestational age: an analysis of the prospective New Hampshire birth cohort study. J Nutrients 2018, 148, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Perkins, A.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J. Maternal dietary nutrient intake and its association with PTB: A case-control study in Beijing, China. Nutrients 2017, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppe, D.; Steegers, E.A.; Timmermans, S.; den Breeijen, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Hofman, A.; Jaddoe, V.W. Maternal fish consumption, fetal growth and the risks of neonatal complications: the Generation R Study. British Journal Nutrition 2011, 105, 938–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppe, D.; van Dam, R.M.; Willemsen, S.P.; den Breeijen, H.; Raat, H.; Hofman, A.; Steegers, E.A.; Jaddoe, V.W. Maternal milk consumption, fetal growth, and the risks of neonatal complications: the Generation R Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2011, 94, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, T.; Osterdal, M.L.; Knudsen, V.K.; Haugen, M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Bakketeig, L.; Olsen, S.F. Association between a Mediterranean-type diet and risk of PTB among Danish women: a prospective cohort study. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2008, 87, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, R.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Myking, S.; Gjessing, H.K.; Sengpiel, V.; Meltzer, H.M.; Haugen, M.; Jacobsson, B. Intake of probiotic food and risk of spontaneous preterm delivery. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2011, 93, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, V.; Worsley, A.; Robinson, J.S. Dietary composition of pregnanct women is related to size of the baby at birth. The journal of nutrition 2004, 134, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, M.; Meltzer, H.M.; Brantsaeter, A.L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Osterdal, M.L.; Alexander, J.; Olsen, S.F.; Bakketeig, L. Mediterranean-type diet and risk of PTB among women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study (MoBa): a prospective cohort study. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2008, 87, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, U.; Manjrekar, R.; Rivera, J.; Gonzalez-Cossio, T.; Martorell, R. Micronutrients and pregnancy outcome : A review of the literature. Nutrition Research 1999, 9, 103–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M. Telomeres, lifestyle, cancer and aging. Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 2011, 14, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiè, S.; Canudas, S.; Muralidharan, J.; García-Gavilán, J.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Impact of nutrition on telomere health: systematic review of observational cohort studies and randomized clinical trials. Advances in Nutrition 2020, 11, 576–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballan, E.; Decottignies, A.; Deldicque, L. Physical activity and nutrition: Two promising strategies for telomere maintenance? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polettini, J.; da Silva, M. Telomere-Related disorders in fetal membranes associated with birth and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Frontiers in Physiology 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Facchinetti, F.; Saade, G.; Menon, R. Placental telomere shortening in stillbirth: a sign of premature senescence? Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2016, 29, 1283–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Boldogh, I.; Hawkins, H.K.; Woodson, M.; Polettini, J.; Ali Syed, T.; Fortunato, S.J.; Saade, G.R.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Taylor, R.N. Histological evidence of oxidative stress and premature senescence in preterm premature rupture of the human fetal membranes recapitulated in vitro. The American Journal of Pathology 2014, 184, 1740–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, Z.; Maiti, K.; Dedman, L.; Smith, R. Is there a role for placental senescence in the genesis of obstetric complications and fetal growth restriction? American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 2018, 218, S762–S773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallows, S.; Regnault, T.R.H.; Betts, D.H. The long and the short of it: The role of telomeres in fetal origins of adult disease. Journal of pregnancy 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridout, K.; Levandowski, M.; Ridout, S.J.; Gantz, L.; Goonan, K.; Palermo, D.; Price, L.H.; Tyrka, A.R. Early life adversity and telomere length: a meta-analysis. Molecular Psychiatry 2018, 23, 858–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factor-Litvak, P.; Susser, E. The importance of early life studies of telomere attrition. Paediatric and perinatal epidemiology 2015, 29, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Godara, K.; Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, S.; Maity, A.; Team, G.; Sindhu, B.; Bhatnagar, S.; Wadhwa, N.; Maitra, A.; et al. Preterm Birth is Associated with Reduction of Maternal Telomere Length During Pregnancy. Research Square 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panelli, D.; Bianco, K. Cellular aging and telomere dynamics in pregnancy. Current Opinion in Obstetrics and Gynecology 2022, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, D.S.; van der Stukken, C.; Derom, C.; Thiery, E.; Bijnens, E.M.; Nawrot, T.S. Newborn telomere length predicts later life telomere length: Tracking telomere length from birth to child-and adulthood. EBioMedicine 2021, 103164, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetos, A.; Verhulst, S.; Labat, C.; Lai, T.; Gireld, N.; Toupance, S.; Zannad, F.; Rossignol, P.; Aviv, A. Telomere length tracking in children and their parents: implications for adult onset diseases. FASEB J 2019, 33, 14248–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; de Punder, K.; Buss, C.; Wadhwa, P.D. The fetal programming of telomere biology hypothesis: an update. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Biological sciences 2018, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; Epel, E.S.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.H.; Buss, C.; Shahbaba, B.; Gillen, D.L.; Venkataramanan, R.; Simhan, H.N.; Wadhwa, P.D. Maternal folate concentration in early pregnancy and newborn telomere length. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 2015, 66, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, G.J.; Lee, D.; Ko, J.H.; Lim, I.; Bang, H.; Koes, B.W.; Seong, B.; Lee, D.C. Higher maternal vitamin D concentrations are associated with longer leukocyte telomeres in newborns. Maternal & child nutrition 2018, 14, e12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzakhani, H.; De Vivo, L.; Leeder, J.S.; Gaedigk, R.; Vyhlidal, C.A.; Weiss, S.T.; Tantisira, K. Early pregnancy intrauterine fetal exposure to maternal smoking and impact on fetal telomere length. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2017, 218, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcicki, J.; Olveda, R.; Heyman, M.B.; Elwan, D.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.; Epel, E. Cord blood telomere length in Latino infants: relation with maternal education and infant sex. Journal of Perinatology 2016, 36, 235–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellechea, M.; Fernandez-Gianotti, T.; Alvarinas, J.; Gonzalez, C.D.; Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Telomere length in the two extremes of abnormal fetal growth and the programming effect of maternal arterial hypertension. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, D.; Plusquin, M.; Gyselaers, W.; de Vivo, I.; Nawrot, T. Maternal pre-pregnancy body mass index and newborn telomere length. BMC Med 2016, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ye, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Q.; Han, C.; Ye, X.; Wang, H.; He, J.; Huang, H.; et al. Reduced fetal telomere length in gestational diabetes. Plos one 2014, 9, e8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prescott, J.; Du, M.; Wong, J.Y.Y.; Han, J.; de Vivo, I. Paternal age at birth is associated with offspring leukocyte telomere length in the nurses’ health study. Human Reproduction 2012, 27, 3622–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broer, L.; Codd, V.; Nyholt, R.D.; Deelen, J.; Mangino, M.; Willemsen, G.; Albrecht, E.; Amin, N.; Beekman, M.; de Geus, J.C.E.; et al. Meta-analysis of telomere length in 19,713 subjects reveals high heritability, stronger maternal inheritance and a paternal age effect. European Journal of Human Genetics 2013, 21, 1163–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Cherkas, L., F.; Kato, B., S.; Demissie, S.; Hjelmborg, J.B.; Brimacombe, M.; Cupples, A.; Hunkin, J.L.; Gardner, J.P.; Lu, X.; et al. Offspring’s leukocyte telomere length, paternal age, and telomere elongation in sperm. Plos Genetics 2008, 4, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordfjall, K.; Larefalk, A.; Lindgren, P.; Holmberg, D.; Roos, G. Telomere length and heredity: indications of paternal inheritance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. U S A 2005, 102, 16374–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Send, T.; Gilles, M.; Codd, V.; Wolf, I.; Bardtke, S.; Streit, F.; Strohmaier, J.; Frank, J.; Schendel, D.; Sütterlin, M.W.; et al. Telomere length in newborns is related to maternal stress during pregnancy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 2407–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; Epel, E.S.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.H.; Buss, C.; Simhan, H.N.; Wadhwa, P.D. Maternal estriol concentrations in early gestation predict infant telomere length. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2015, 100, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotlib, I.H.; LeMoult, J.; Colich, N.L.; Foland-Ross, L.C.; Hallmayer, J.; Joormann, J.; Lin, J.; Wolkowitz, O.M. Telomere length and cortisol reactivity in children of depressed mothers. Molecular psychiatry 2015, 20, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, B.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Walsh, M.C.; Hale, E.C.; Newman, N.S.; Schibler, K.; Carlo, W.A.; et al. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD neonatal research network. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 443–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, V.; Turner, K.J.; George, S.; Greenall, J.; Slijepcevic, P.; Griffin, D.K. Preterm infants have significantly longer telomeres than their term born counterparts. Plos one 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Z.; Li, K.; Xie, C.; Wen, X. Adverse birth outcomes and birth telomere length: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Pediatrics 2019, 215, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, C.; Codd, V.; Samani, N.J.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C.S. Leucocyte telomere length in young adults born preterm: Support for accelerated biological ageing. Plos one 2015, 10, e0143951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzi, L.; Giorda, R.; Fumagalli, M.; Brambilla, M.; Mosca, F.; Borgatti, R.; Montirosso, R. Telomere length and salivary cortisol stress reactivity in very preterm infants. Early Human Development 2019, 129, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tan, K.M.L.; Gong, M.; Chong, M.F.; Tan, K.H.; Chong, Y.S.; Tan, K.H.; Chong, Y.S.; Meaney, M.J.; Gluckman, P.D.; et al. Variability in newborn telomere length is explained by inheritance and intrauterine environment. BMC medicine 2022, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigal, S.; Day, K.L.; van Lieshout, R.J.; Schmidt, L.A.; Morrison, K.M.; Boyle, M.H. Health, wealth, social integration, and sexuality of extremely low-birth-weight prematurely born adults in the fourth decade of life. JAMA Pediatrics 2016, 170, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfort, M.; Qureshi, F.; Litt, J.; Bosquet Enlow, M.; De Vivo, I.; Gregory, K.; Tiemeier, H. Telomere length shortening in hospitalized preterm infants: A pilot study. Plos one 2021, 16, e0243468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzi, L.; Scotto di Minico, G.; Giorda, R.; Montirosso, R. Telomere length in preterm infants: a promising biomarker of early adversity and care in the neonatal intensive care unit? . Frontiers in endocrinology 2017, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, K.; Vasu, V.; Greenall, J.; Griffin, D.K. Telomere length analysis and preterm infant health: the importance of assay design in the search for novel biomarkers. Biomarkers in Medicine 2014, 8, 485–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadchouel, A.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Franco-Montoya, M.L.; Peaudecerf, L.; Ancel, P.Y.; Delacourt, C. Salivary Telomere Length and Lung Function in Adolescents Born Very Preterm: A Prospective Multicenter Study. Plos one 2015, 10, e0136123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009, 62, 1006–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.L.; Arocha, J.F.; Zhang, J. Thinking and reasoning in medicine. The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning 2005, 14, 727–750. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, F.; Savasi, V.M.; di Bartolo, I.; Mandia, L.; Cetin, I. Associations between first trimester maternal nutritional score, early markers of placental function, and pregnancy outcome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillesund, E.R.; Bere, E.; Sagedal, L.R.; Vistad, I.; Seiler, H.L.; Torstveit, M.K.; Øverby, N.C. Pre-pregnancy and early pregnancy dietary behavior in relation to maternal and newborn health in the Norwegian Fit for Delivery study–a post hoc observational analysis. Food & nutrition research, 2018; 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tith, R.M.; Bilodeau-Bertrand, M.; Lee, G.E.; Healy-Profitós, J.; Auger, N. Fasting during Ramadan increases risk of very PTB among Arabic-speaking women. The Journal of Nutrition 2019, 149, 1826–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriss, J.L.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Beauregard, J.L.; Phadke, V.K.; Stein, A.D.; Rivera, J.A.; Omer, S.B. Yogurt consumption during pregnancy and preterm delivery in Mexican women: A prospective analysis of interaction with maternal overweight status. Maternal & child nutrition 2018, 14, e12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.S.; He, J.R.; Chen, Q.; Lu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Q.; Chan, F.; Zhang, L.; Chen, N.; Qiu, L.; et al. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and preterm delivery: a large prospective cohort study in China. Nutrition journal 2018, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, B.; Cardoso, M.; Dias, C.C.; Pereira-da-Silva, L.; de Silva, D. Eating Habits During Pregnancy of Women Giving Birth Very Prematurely: An Exploratory Analysis. Acta Médica Portuguesa 2023, 36, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, A.R.; De Seymour, J.V.; Colega, M.; Chen, L.W.; Chan, Y.H.; Aris, I.M.; Tint, M.T.; Quah, P.L.; Godfrey, K.M.; Yap, F.; et al. A vegetable, fruit, and white rice dietary pattern during pregnancy is associated with a lower risk of PTB and larger birth size in a multiethnic Asian cohort: the Growing Up in Singapore Towards healthy Outcomes (GUSTO) cohort study. The American journal of clinical nutrition 2016, 104, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.L.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; Siega-Riz, A.M. Maternal dietary patterns during the second trimester are associated with preterm birth. The Journal of nutrition 2015, 145, 1857–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ye, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Ren, A. Periconceptional folic acid supplementation and the risk of preterm births in China: a large prospective cohort study. International Journal of Epidemiology 2014, 43, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Kong, C.; Ma, Q.; Ye, H.; Jing, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. The association between periconceptional folic acid supplementation and the risk of preterm birth: a population-based retrospective cohort study of 200,000 women in China. European Journal of Nutrition 2021, 60, 2181–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, E.O.; Sharma, A.J.; Abe, K. Association between maternal multivitamin use and PTB in 24 states, pregnancy risk assessment monitoring system, 2009–2010. Maternal and child health journal 2016, 20, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olapeju, B.; Saifuddin, A.; Wang, G.; Ji, Y.; Hong, X.; Raghavan, R.; Summers, A.; Keiser, A.; Ji, H.; Zuckerman, B.; et al. Maternal postpartum plasma folate status and PTB in a high-risk US population. Public health nutrition 2019, 22, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; An, H.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Yan, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Associations between hair levels of trace elements and the risk of PTB among pregnant women: A prospective nested case-control study in Beijing Birth Cohort (BBC), China. Environment International 2022, 158, 106965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwinda, R.; Wibowo, N.; Putri, A.S. The concentration of micronutrients and heavy metals in maternal serum, placenta, and cord blood: a cross-sectional study in PTB. Journal of pregnancy 2019, 2019, 5062365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiudzu, G.; Choko, A.T.; Maluwa, A.; Huber, S.; Odland, J. Maternal serum concentrations of selenium, copper, and zinc during pregnancy are associated with risk of spontaneous PTB: a case-control study from Malawi. Journal of Pregnancy 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perveen, S.; Soomro, T.K. Sideropaenic anaemia: Impact on perinatal outcome at tertiary care hospital. The Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2016, 66, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.W.; Lim, A.L.; Colega, M.; Tint, M.T.; Aris, I.M.; Tan, C.S.; Chong, Y.S.; Gluckman, P.D.; Godfrey, K.M.; Kwek, K.; van Dam, R.M. Maternal folate status, but not that of vitamins B-12 or B-6, is associated with gestational age and PTB risk in a multiethnic Asian population. The Journal of nutrition 2015, 145, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph, P.; Challande, P.; Raio, L.; Surbek, D. High prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency during the first trimester in pregnant women in Switzerland and its potential contributions to adverse outcomes in the pregnancy. Swiss medical weekly 2020, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahsin, T.; Khanam, R.; Chowdhury, N.H.; Hasan, A.T.; Hosen, M.B.; Rahman, S.; Roy, A.K.; Ahmed, S.; Raqib, R.; Baqui, A.H. Vitamin D deficiency in pregnancy and the risk of preterm birth: a nested case–control study. BMC pregnancy and childbirth 2023, 23, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, T.; Wu, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Gao, Q.; Hong, M.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; et al. Association between the maternal protein nutrition status during pregnancy and the risk of PTB. Maternal & Child Nutrition 2021, 17, e13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, M.J.; Souza, R.T.; Calderon, I.M.; Feitosa, F.E.; Leite, D.F.; Rocha Filho, E.A.; Vettorazzi, J.; Mayrink, J.; Fernandes, K.G.; Vieira, M.; et al. Maternal nutrition status associated with pregnancy-related adverse outcomes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shi, Q.; Fan, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, N.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, K. Associations of maternal polyunsaturated fatty acids with telomere length in the cord blood and placenta in Chinese population. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 8, 779306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeates, A.J.; Thurston, S.W.; Li, H.; Mulhern, M.S.; McSorley, E.M.; Watson, G.E.; Shamlaye, C.F.; Strain, J.J.; Myers, G.J.; Davidson, P.W.; Broberg, K. PUFA status and methylmercury exposure are not associated with leukocyte telomere length in mothers or their children in the Seychelles Child Development Study. The Journal of Nutrition 2017, 147, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, H.M.; Adegoke, K.K.; King, L.M.; Daas, R.; Paothong, A.; Pradhan, A.; Aliyu, M.H.; Whiteman, V.E. Effects of maternal carbohydrate and fat intake on fetal telomere length. Southern Medical Journal 2018, 111, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahter, M.; Broberg, K.; Harari, F. Placental and cord blood telomere length in relation to maternal nutritional status. The Journal of nutrition 2020, 150, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneels, L.; Martens, D.S.; Arredouani, S.; Billen, J.; Koppen, G.; Devlieger, R.; Nawrot, T.S.; Ghosh, M.; Godderis, L.; Pauwels, S. Maternal vitamin D and newborn telomere length. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Song, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, M.; Bi, J.; Xu, L.; Xiong, C.; Cao, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y. Association of maternal folic acid supplementation during pregnancy with newborn telomere length. Reproductive Toxicology 2022, 114, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis-Jacques, A.F.; Salihu, H.M.; King, L.M.; Paothong, A.; Sinkey, R.G.; Pradhan, A.; Riggs, B.M.; Siegel, E.M.; Salemi, J.L.; Whiteman, V.E. A positive association between umbilical cord RBC folate and fetal TL at birth supports a potential for fetal reprogramming. Nutrition Research 2016, 36, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herlin, M.; Broberg, K.; Igra, A.M.; Li, H.; Harari, F.; Vahter, M. Exploring telomere length in mother–newborn pairs in relation to exposure to multiple toxic metals and potential modifying effects by nutritional factors. BMC medicine 2019, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Caruso, M.; Giunta, G.C.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Agodi, A. The effect of nutrients on telomere length of fetal DNA: findings from the Mamma & Bambino cohort. European Journal of Public Health 2021, 31 (Supplement_3), ckab164-074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, K.O.; Ibrahimou, B.; Yusuf, K.K.; Mauck, D.E.; Salihu, H.M. The effect of maternal vitamin C intake on fetal telomere length. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2021, 34, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroyo, Y.B.; Wibowo, N.; Irwinda, R.; Prijanti, A.R.; Yunihastuti, E.; Bardosono, S.; Krisnadi, S.R.; Permata, P.I.; Wijaya, S.; Santawi, V.P.A. Oxidative stress induced damage and early senescence in preterm placenta. Journal of Pregnancy 2021, 9923761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colatto, B.N.; de Souza, I.F.; Schinke, L.A.A.; Noda-Nicolau, N.M.; da Silva, M.G.; Morceli, G.; Menon, R.; Polettini, J. Telomere length and telomerase activity in foetal membranes from term and spontaneous PTBs. Reproductive Sciences 2020, 27, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farladansky-Gershnabel, S.; Dekel, N.; Biron-Shental, T.; Shechter-Maor, G.; Amiel, A.; Weisz, A.; Benchetrit, S.; Zitman-Gal, T. Spontaneous Preterm Birth: Elevated Galectin-3 and Telomere Shortening May Reflect a Common Pathway of Enhanced Inflammation and Senescence. Reproductive Sciences 2023, 30, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarik, M.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Sinha, S.; Sachdev, H.P.S.; Tandon, N.; Roy, A.; Bhargava, S.K. Association of birth outcomes and postnatal growth with adult leukocyte telomere length: Data from New Delhi Birth Cohort. Maternal & Child Nutrition 2019, 15, e12857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumfield, M.L.; Collins, C.E. High-protein diets during pregnancy: Healthful or harmful for offspring? The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014, 100, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumfield, M.L.; Hure, A.J.; Macdonald-Wicks, L.; Smith, R.; Collins, C.E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of energy and macronutrient intakes during pregnancy in developed countries. Nutrition Reviews 2012, 70, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaki, N.; Nagata, C.; Yasuo, S.; Morokuma, S.; Kato, K.; Sanefuji, M.; Shibata, E.; Tsuji, M.; Senju, A.; Kawamoto, T.; et al. Japan Environment and Children's Study Group . Optimal protein intake during pregnancy for reducing the risk of fetal growth restriction: The Japan Environment and Children's Study. British Journal of Nutrition 2018, 120, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, E.; Mori, R.; Middleton, P.; Tobe-Gai, R.; Mahomed, K.; Miyazaki, C.; Bhutta, Z.A. Zinc supplementation for improving pregnancy and infant outcome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, 2015, CD000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Switkowski, K.M.; Jacques, P.F.; Must, A.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W.; Oken, E. Maternal protein intake during pregnancy and linear growth in the offspring. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2016, 104, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Chauhan, M.; Pandey, M.; Singh, S.; Singh, U. Energy and protein intake during pregnancy in relation to preterm birth: A case control study. Indian Pediatrics 2015, 52, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, E.; Hori, H.; Mori, R.; Tobe-Gai, R.; Farrar, D. Antenatal dietary education and supplementation to increase energy and protein intake. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, 2, CD000032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C. Folic acid and risk of preterm birth: a meta-analysis. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2019, 13, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.S.; Tao, Y.H.; Huang, K.; Zhu, B.B.; Tao, F.B. Vitamin D and risk of preterm birth: Up-to-date meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2017, 43, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bialy, L.; Fenton, T.; Shulhan-Kilroy, J.; Johnson, D.W.; McNeil, D.A.; Hartling, L. Vitamin D supplementation to improve pregnancy and perinatal outcomes: an overview of 42 systematic reviews. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e032626. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, B. Nutritional Status and the Risk of Preterm Birth. In Evidence Based Global Health Manual for Preterm Birth Risk Assessment; Anumba, D.O., Jayasooriya, S.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2022; pp. 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, S.; Azami, M.; Badfar, G.; Parizad, N.; Sayehmiri, K. The relationship between maternal anemia during pregnancy with preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2020, 33, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasricha, S.R.; Tye-Din, J.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Swinkels, D.W. Iron deficiency. Lancet 2021, 397, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L. Disordered Maternal and Fetal Iron Metabolism Occurs in Preterm Births in Human. Disease Markers 2022, 2022, 1664474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemppinen, L.; Mattila, M.; Ekholm, E.; Pallasmaa, N.; Törmä, A.; Varakas, L.; Mäkikallio, K. Gestational iron deficiency anemia is associated with preterm birth, fetal growth restriction, and postpartum infections. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 2021, 49, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Kumar, I.; Oladapo-Shittu, O.; Twose, C.; Islam, A.A.; Biswal, S.S.; Raqib, R.; Baqui, A.H. Prenatal environmental metal exposure and preterm birth: a scoping review. International journal of environmental research and public health 2021, 18, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, H.T.; Hegaard, H.K.; Huusom, L.D.; Pinborg, A.B. Multivitamin use and adverse birth outcomes in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology 2017, 217, 404-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazier, J.D.; Hayes, D.J.; Hussain, S.; D’Souza, S.W.; Whitcombe, J.; Heazell, A.E.; Ashton, N. The effect of Ramadan fasting during pregnancy on perinatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC pregnancy and childbirth 2018, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susser, E.; Ananth, C.V. Invited commentary: is prenatal fasting during Ramadan related to adult health outcomes? A novel and important question for epidemiology. American journal of epidemiology 2013, 177, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitku, A.A.; Zewotir, T.; North, D.; Jeena, P.; Naidoo, R.N. Modeling differential effects of maternal dietary patterns across severity levels of preterm birth using a partial proportional odds model. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.A.; Maslova, E.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Olsen, S.F. Characterization of dietary patterns in the Danish national birth cohort in relation to preterm birth. Plos one 2014, 9, e93644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, S.; Soltani, S.; de Souza, R.J.; Forbes, S.C.; Toupchian, O.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Associations between maternal dietary patterns and perinatal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Advances in nutrition 2021, 12, 1332–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, A.R.; Chen, L.W.; Lai, J.S.; Wong, C.H.; Neelakantan, N.; van Dam, R.M.; Chong, M.F.F. Maternal dietary patterns and birth outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Advances in Nutrition 2019, 10, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englund-Ögge, L.; Brantsæter, A.L.; Sengpiel, V.; Haugen, M.; Birgisdottir, B.E.; Myhre, R.; Meltzer, H.M.; Jacobsson, B. Maternal dietary patterns and preterm delivery: results from large prospective cohort study. BMJ 2014, 348, g1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, S. Scientific report of the 2015 dietary guidelines advisory committee. Washington, DC: US Departments of Agriculture and Health and Human Services, 2015. Advances in nutrition 2016, 7, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Saad, K.; Fraser, D. Maternal nutrition and birth outcomes. Epidemiologic reviews 2010, 32, 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, F.Q. Body mass index: Obesity, BMI, and health: a critical review. Nutrition Today 2015, 50, 117–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulhern, M.S.; Broberg, K.; McAfee, A.; Laird, E.; Li, H.; Wallace, J.M.W.; McSorley, E.M.; Myers, G.J.; Davidson, P.W.; Thurston, S.W.; et al. Vitamin D status is a predictor of telomere length during pregnancy. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2012, 71(OCE2), E124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K.; Cheng, F.; Mao, D.; Lim, C.K.; Wang, R.; Tam, C.H.; Joglekar, M.A.; Hardikar, A.A.; Jenkins, A.; Metzger, B.E.; et al. 275-OR: Maternal Vitamin D Levels during Pregnancy Is Associated with Childhood Telomere Length: Analysis from a Longitudinal Mother-Child Cohort. Diabetes, 2021; 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichetzeder, C.; Chen, H.; Föller, M.; Slowinski, T.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.P.; Lang, F.; Hocher, B. Maternal vitamin D deficiency and fetal programming-lessons learned from humans and mice. Kidney and Blood Pressure Research 2014, 39, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaset, S.; Krieger, J.P.; Richard, A.; Elgizouli, M.; Nieters, A.; Rohrmann, S.; Quack Lötscher, K.C. Vitamin D status and its determinants in healthy pregnant women living in Switzerland in the first trimester of pregnancy. BMC pregnancy and childbirth 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moores, C.J.; Fenech, M.; O’Callaghan, N.J. Telomere dynamics: the influence of folate and DNA methylation. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2011, 1229(1), 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Phoi, Y.Y.; Jankovic-Karasoulos, T.; Roberts, C.T.; Grieger, J.A. Maternal diet and offspring telomere length: a systematic review. Nutrition reviews 2021, 79, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnano San Lio, R.; Maugeri, A.; La Rosa, M.C.; Giunta, G.; Panella, M.; Cianci, A.; Caruso, M.A.T.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M. Nutrients intakes and telomere length of cell-free circulating DNA from amniotic fluid: findings from the Mamma& Bambino cohort. Sci Rep. 2022, 12, 11671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsereko, E.; Uwase, A.; Muvunyi, C.M.; Rulisa, S.; Ntirushwa, D.; Moreland, P.; Corwin, E.J.; Santos, N.; Lin, J.; Chen, J.L.; et al. Association between micronutrients and maternal leukocyte telomere length in early pregnancy in Rwanda. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valera-Gran, D.; Prieto-Botella, D.; Hurtado-Pomares, M.; Baladia, E.; Petermann-Rocha, F.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Navarrete-Muñoz, E.M. The Impact of Foods, Nutrients, or Dietary Patterns on Telomere Length in Childhood and Adolescence: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 14, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, L. Diet, nutrition and telomere length. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry 2011, 22, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenech, M.F. Nutriomes and personalised nutrition for DNA damage prevention, telomere integrity maintenance and cancer growth control. Advances in nutrition and cancer 2014, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, M.A.; Godfrey, K.M.; Lillycrop, K.A. Linking nutrition to long-term health: Epigenetic mechanisms. In Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health; Woodhead Publishing, 2022; pp. 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K.; Bardeguez, A.; Gardner, J.P.; Rodriguez, P.; Ganesh, V.; Kimura, M.; Skurnick, J.; Awad, G.; Aviv, A. Telomere length in the newborn. Pediatric research 2002, 52, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviv, A.; Chen, W.; Gardner, J.P.; Kimura, M.; Brimacombe, M.; Cao, X.; Srinisavan, R.S.; Berenson, G.S. Leukocyte telomere dynamics: longitudinal findings among young adults in the Bogalusa Heart Study. American journal of epidemiology 2009, 169, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, P.; Nagata, M.; Bullard, P.; Fogelson, N.S.; Allsopp, R. Fetal growth restriction is associated with accelerated telomere shortening and increased expression of cell senescence markers in the placenta. Placenta 2009, 30, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbers, C.C.; Garcia, M.E.; Kimura, M.; Cummings, S.R.; Nalls, M.A.; Newman, A.B.; Park, V.; Sanders, J.L.; Tranah, G.J.; Tishkoff, S.A.; et al. Comparison between southern blots and qPCR analysis of leukocyte telomere length in the health ABC study. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences 2014, 69, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, U.; Schwab, M.; Griese, E.U.; Fritz, P.; Klotz, U. Telomeres in neonates: new insights in fetal hematopoiesis. Pediatric research 2021, 49, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, M.; Hageman, G.; Pachen, D.M.F.A.; Derom, C.; Vlietinck, R.; Zeegers, M.P. Placental telomere length decreases with gestational age and is influenced by parity: a study of third trimester live-born twins. Placenta 2014, 35, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackburn, E.H. Structure and function of telomeres. Nature 1991, 350, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demerath, E.W.; Cameron, N.; Gillman, M.W.; Towne, B.; Siervogel, R.M. Telomeres and telomerase in the fetal origins of cardiovascular disease: a review. Human biology 2004, 76, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavia-García, G.; Rosado-Pérez, J.; Arista-Ugalde, T.L.; Aguiñiga-Sánchez, I.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Telomere length and oxidative stress and its relation with metabolic syndrome components in the aging. Biology 2021, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeichner, S.L.; Palumbo, P.; Feng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Gee, D.; Sleasman, J.; Goodenow, M.; Biggar, R.; Dimitrov, D. Rapid telomere shortening in children. Blood. The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 1999, 93, 2824–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenck Jr, R.W.; Blackburn, E.H.; Shannon, K.M. The rate of telomere sequence loss in human leukocytes varies with age. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1998, 95, 5607–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniali, L.; Benetos, A.; Susser, E.; Kark, J.D.; Labat, C.; Kimura, M.; Desai, K.K.; Granick, M.; Aviv, A. Telomeres shorten at equivalent rates in somatic tissues of adults. Nature communications 2013, 4, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkad, A.; Hastings, R.; Konje, J.C.; Bell, S.C.; Thurston, H.; Williams, B. Telomere length in small-for-gestational-age babies. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology 2006, 113, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabharwal, S.; Verhulst, S.; Guirguis, G.; Kark, J.D.; Labat, C.; Roche, N.E.; Martimucci, K.; Patel, K.; Heller, D.S.; Kimura, M.; et al. Telomere length dynamics in early life: the blood-and-muscle model. The FASEB journal 2018, 32, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factor-Litvak, P.; Susser, E.; Kezios, K.; McKeague, I.; Kark, J.D.; Hoffman, M.; Kimura, M.; Wapner, R.; Aviv, A. Leukocyte Telomere Length in Newborns: Implications for the Role of Telomeres in Human Disease. Pediatrics 2016, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillippe, M. Telomeres, oxidative stress, and timing for spontaneous term and preterm labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2022, 227, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pinilla, F. Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nature reviews neuroscience 2008, 9, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, J.; Gangwisch, J.E.; Borsini, A.; Wootton, R.E.; Mayer, E.A. Food and mood: how do diet and nutrition affect mental wellbeing? BMJ 2020, 369, m2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.S.; Asha, M.R.; Ramesh, B.N.; Rao, K.J. Understanding nutrition, depression and mental illnesses. Indian journal of psychiatry 2008, 50, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malouff, J.M.; Schutte, N.S. A meta-analysis of the relationship between anxiety and telomere length. Anxiety, Stress, & Coping 2017, 30, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.B.; Epel, E.; Kind, S.; Desai, M.; Parks, C.G.; Sandler, D.P.; Khazeni, N. Perceived stress and telomere length: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and methodologic considerations for advancing the field. Brain, behavior, and immunity 2016, 54, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.L.; Mezuk, B.; Bareis, N.; Lin, J.; Blackburn, E.H.; Epel, E.S. Depression, anxiety and telomere length in young adults: evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Molecular psychiatry 2015, 20, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.; Lavebratt, C.; Millischer, V.; de Jesus, R.; de Paula, V.; Pires, T.; Michelon, L.; Camilo, C.; Esteban, N.; Pereira, A.; Schalling, M.; Vallada, H. Shorter telomere length and suicidal ideation in familial bipolar disorder. Plos one 2022, 17, e0275999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpo, G.D.; Leffa, D.D.; Koehler, C.A.; Kapczinski, F.; Quevedo, J.; Carvalho, A.F. Is bipolar disorder associated with accelerating aging? A meta-analysis of telomere length studies. Journal of affective disorders 2015, 186, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayora, M.; Fraguas, D.; Abregu-Crespo, R.; Recio, S.; Blasco, M.A.; Moises, A.; Derevyanko, A.; Arango, C.; Diaz-Caneja, C.M. Leukocyte telomere length in patients with schizophrenia and related disorders: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Molecular Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P.; Prinzi, G.; Proietti, S.; Lamonaca, P.; Frustaci, A.; Boccia, S.; Amore, R.; Lorenzi, M.; Onder, G.; Marzetti, E.; Bonassi, S. Shorter telomere length in schizophrenia: evidence from a real-world population and meta-analysis of most recent literature. Schizophrenia research 2018, 202, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benetos, A.; Kark, J.D.; Susser, E.; Kimura, M.; Sinnreich, R.; Chen, W.; Steenstrup, T.; Christensen, K.; Herbig, U.; von Bornemann Hjelmborg, J.; Aviv, A. Tracking and fixed ranking of leukocyte telomere length across the adult life course. Aging cell 2013, 12, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entringer, S.; Epel, E.S.; Lin, J.; Buss, C.; Blackburn, E.H.; Simhan, H.N.; Wadhwa, P.D. Prenatal programming of newborn and infant telomere length. European Journal of psychotraumatology 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewak, M.; Buka, S.; Prescott, J.; de Vivo, I.; Loucks, E.B.; Kawachi, I.; Non, A.L.; Kubzansky, L.D. Race-related health disparities and biological aging: does rate of telomere shortening differ across blacks and whites? Biological psychology 2014, 99, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Research |
Type of study | Country | Population/ Subject characteristics |
Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Xiong et al, 2021 [92] | Cohort | China | 3,382 mother- newborn second-trimester pairs and 3,478 mother- third-trimester newborn pairs Absence of pathology |
3rd trimester MTP level, inversely associated with PTB risk and positively associated with gestational duration. The effects of the 3rd trimester MTP level on PTB risk and gestational duration, were stronger in women carrying female offspring than those carrying male. |
| 2. Kriss et al, 2018 [76] | Cohort | Mexico | 965 pregnant women 18-22 weeks gestation - follow up 2 years post-birth 18 -39 years old, Absence of pathology |
No overall association between prenatal yogurt consumption and PTB. In non-overweight women, higher prenatal yogurt consumption was associated with reduced PTB risk. |
| 3. Tith et al, 2019 [75] | Cross-sectional | Canada | 78.019 births of Arabic speaking women 3 trimesters of pregnancy during Ramadan period Absence of pathology |
Ramadan fasting during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy was associated with increased risk of very PTB (28-31 weeks gestation). |
| 4. Johnston et al, 2016 [83] | Cohort | USA | 62.443 pregnant women ≥18 weeks gestation Singleton pregnancy Absence of pathology |
Any multivitamin use in the last 3 months of pregnancy is associated with a significant reduction in PTB among non-Hispanic and African women. |
| 5. Chia et al, 2016 [79] | Cohort | Singapore | 923 pregnant women Absence of pathology |
The VFR pattern is associated with a lower incidence of PTB. The VFR pattern was also associated with a higher birth weight, higher ponderal index, and increased risk of LGA deliveries. |
| 6. Li et al, 2014 [81] | Cohort | China | 207 936 singleton live births Delivered at GAs of 20–42 weeks Absence of pathology |
Daily consumption of 400 μg folic acid alone during the periconceptional period is related to a reduced risk of spontaneous PTB. These reduced risks were greater for early-age spontaneous PTBs. |
| 7. Chen et al, 2015 [89] | Cohort | Singapore | 999 pregnant and <14 weeks gestation & post-partum women, aged 18-50 years old. Only parents of the same ethnicity Absence of pathology |
Higher maternal folate concentrations at approximately the start of the 3RD trimester significantly associated with longer duration of gestation and lower risk of PTB. Little or no correlation between ↑folic acid and SGA. Little or no correlation between ↑B6 &B12 vitamins and PTB or SGA. |
| 8. Perveen & Soomro, 2016 [88] | Cohort | Pakistan | 234 pregnant women aged 20-35 and at 35-42 weeks gestation Singleton pregnancy Absence of pathology |
Fe deficiency anemia positively associated with PTB , low newborn birth weight, fetal mortality and ↓ Apgar score at the 1st and 5th minutes of birth. |
| 9. Lu et al, 2018 [77] | Cohort | China | 7352 pregnant women <20 weeks gestation Singleton pregnancy. Absence of pathology |
Women in the high consumption of ‘Milk’ group, had greater odds of PTB, spontaneous PTB and late PTB, than those in the ‘Vegetables’ group. Compared with women in the ‘Vegetables’ group, those in the ‘Cereals, eggs, and Cantonese soups’ and ‘Fruits, nuts, and Cantonese desserts’ groups had increased odds of late PTB. Maternal pregnancy diet with frequent consumption of milk and less frequent consumption of vegetables is found to be associated with increased odds of PTB among Chinese women. |
| 10. Ren et al, 2022 [85] | Case-control study | China | 509 pregnant women: Controls: 415 pregnant women with birth at term and Cases:82 pregnant women with PTB Singleton pregnancy Absence of pathology |
Negative correlation between levels of NTMs,and PTB Especially Fe and Zn may protect against PTB occurrence. Potential protective effect of Hg. |
| 11. Parisi et al, 2020 [73] | Cohort | Italy | 112 pregnant women (11+-13+6 weeks of gestation) Absence of pathology Singleton pregnancy Natural conception Healthy neonates |
Positive association between maternal nutritional score and GA at birth. Significant increase in the risk of PTB associated with low nutritional scores. The single food items of the score calculation were not associated with both early placental markers and complex pregnancy outcomes. |
| 12. Teixeira et al, 2023 [78] | Cross-sectional | Portugal | 60 Portuguese women with a diagnosis of high-risk pregnancy Birth before 33 weeks GA |
In very PTB pregnancy-induced hypertension was associated with increased consumption of pastry products, fast food, bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes. Only bread consumption had a weak but statistically significant association with pregnancy-induced hypertension in a multivariate analysis. |
| 13. Hillesund et al, 2018 [74] | Cohort | Norway | 591 nulliparous pregnant women 18 years or older 20 weeks pregnant or less at inclusion Singleton pregnancy Absence of pathology, disabilities and substance abuse |
A higher diet score either pre-pregnancy or in early pregnancy was protectively associated with excessive GWG and PTB risk. The protective association with high birthweight was confined to pre-pregnancy diet and with preeclampsia to early pregnancy diet. No association between pre-pregnancy diet score and preeclampsia. |
| 14. Chiudzu et al, 2020 [87] | Nested case-control | Malawi | 181 pregnant women: 90/181 (49.7%) term and 91/181 (50.3%) PTBs. Singleton pregnancy Presenting in spontaneous labor with intact membranes Absence of pathology |
Copper maternal serum concentrations were above the upper normal limit in both term and PTB groups. PTB was associated with higher maternal serum concentrations of copper and zinc. |
| 15. Olapeju et al, 2019 [84] | Case - control | USA | 7675 mother–infant dyads Cases: mother–infant dyads, singleton, live, low-birth-weight (<2500 g) or preterm infants (<37 weeks of gestation) regardless of birth weight Controls: mother–infant dyads with singleton, live, term infants with birth weight of ≥2500 g or more |
Multivitamin supplement intake of at least 3 times/week throughout pregnancy was significantly associated with a reduction in the odds of PTB. Use during the third trimester associated with a greater reduction in PTB odds than use in the first trimester. No significant association between preconceptional supplement intake and PTB. Higher plasma folate levels were associated with lower risk of PTB. |
| 16. Christoph et al, 2020 [90] | Cross-sectional | Switzerland | 1382 pregnant women Supplemented with 600 IU/d orally throughout the pregnancy, and at least 1000 IU/d in cases of deficiency |
No association between the 25(OH)D serum level and, PTB, preeclampsia, postdate pregnancy, miscarriage, intrauterine growth restriction, bacterial vaginosis, mode of delivery, or neonatal birth weight and length. The lower the vitamin D maternal level, the higher the GA at birth. |
| 17. Miele et al, 2021 [93] | Nested case-control | Brazil | 1165 nulliparous pregnant women between 19 and 21 weeks of gestation Singleton pregnancies Absence of pathology Absence of medication or supplementation |
The odds of adverse outcomes were higher in non-white (p < 0.05) obese women and with high protein consumption. The anthropometric classification of obesity had a greater impact on PE and GDM, in contrast to PTB and SGA. |
| 18. Irwinda et al, 2019 [86] | Cross sectional | Indonesia | 51 pregnant women undergoing birth (term group: 25, PTB group: 26) Singleton pregnancy Absence of pathology |
PTB associated with lower concentrations of micronutrients in maternal serum. PTB associated with higher concentration of heavy metals such as Hg and Pb. Compared with PTB group, term birth group had higher maternal serum concentration of AtRA serum. Compared with PTB group, term birth group had higher placental concentration of Mn, Fe, Cu, Zn, Se, AtRA, 25(OH)D, and lower placental concentration of mercury and Pb. Compared with PTB group, term birth group had higher concentration of Cu and AtRA in cord blood. |
| 19. Wu et al, 2021 [82] | Cohort | China | 201,477 pregnant women aged 18–49 Singleton livebirth |
Periconceptional supplementation with FA was associated with a lower risk of PTB. Women who started taking FA at least 3 months before their last menstrual period were more likely to reduce the risk of PTB. |
| 20. Tahsin, et al, 2023 [91] | Nested case–control | Bangladesh | 930 pregnant women at 8–19 weeks of gestation 262 PTB and 668 term births |
Vitamin D deficiency is common in Bangladeshi pregnant women and is associated with an increased risk of PTB. |
| 21. Martin et al, 2015 [80] | Cohort | USA | 3143 pregnancies at 26–29 week of gestation | Greater adherence to a healthy dietary pattern, such as the DASH diet, reduced the odds of PTB. Greater adherence to a dietary pattern of poorer quality, such as factors 2 (i.e. high intakes of beans, corn, French fries, hamburgers or cheeseburgers, white potatoes, fried chicken, spaghetti dishes, cheese dishes, cornbread or hushpuppies, processed meats, biscuits, and ice cream) and factors 3 (i.e. high consumption of collard greens, coleslaw or cabbage, red processed meats, fried chicken, fried fish, cornbread or hushpuppies, eggs or egg biscuits, gravy, whole milk, and vitamin C-rich drinks), increased the odds of PTB. |
| Research |
Type of study | Country | Population/ Subject characteristic |
Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Vahter et al, 2020 [97] | Cohort | Argentina | 99 Pregnant women in 1st trimester, Singleton pregnancy |
Maternal BMI, BFP, and vitamin B-12 were inversely associated. 25(OH)D3 was positively associated, with placental TL. No association between the above factors was observed with cord blood TL. |
| 2. Herlin et al, 2019 [101] | Cohort | Argentina | 169 pregnant women in 1st trimester, Singleton pregnancy |
More associations with relative TL in maternal blood leukocytes during pregnancy (inverse associations with boron and antimony, positive association with lithium), than in the placenta (positive with arsenic) and cord blood (inverse with lead). Nutritional antioxidants (Zn, Se, folate, Vit D3) did not affect the associations. |
| 3. Daneels et al, 2021 [98] | Cohort | Belgium | 108 pregnant women in 1st trimester or women who are trying to conceive Absence of pathology Singleton pregnancy |
Positive association of maternal vitamin D concentration (diet and/or supplement) in the 1st trimester with TL of the newborn at birth. |
| 4. Kim et al, 2018 [47] | Cross-sectional | Seoul | 106 mother-newborn dyads. Pregnant women in 3rd trimester Absence of maternal and fetal pathology |
Positive correlation between the concentration of vitamin D of the pregnant woman and the neonatal leukocyte TL (β = .33, p < .01). |
| 5.Entringer et al, 2015 [46] | Cohort | USA | 119 mother-newborn dyads enrolled at 9.5 weeks gestation Absence of pathology or fetal abnormality Use of folic acid supplements |
Maternal total folate concentration in early pregnancy was significantly and positively associated with newborn cord blood TL. |
| 6. Yeates et al, 2017 [95] | Cohort | Seychelles | 229 mothers enrolled at 28 week gestation and followed through delivery Their children (at 5 years of age) |
No clear associations of both prenatal or postnatal PUFA status and methylmercury exposure with child TL. Higher prenatal n–6:n–3 PUFA ratio was associated with longer TL in mothers. |
| 7. Liu et al, 2022 [94] | Cohort | China | 274 mother newborn dyads. Pregnant women enrolled during 3rd trimester. Absence of pathology |
Positive association of the concentrations of DHA and total n-3 PUFAs in maternal erythrocytes with DNA methylation of the TERT promoter in the cord blood instead of the placenta. Maternal PUFAs closely correlated to infant TL and TERT promoter methylation, differently affected by maternal n-3 PUFAs between the cord blood and the placenta. High levels of maternal n-3 PUFAs during pregnancy maintain offspring TL. |
| 8. Chen et al, 2022 [65] | Cohort | Singapore | 950 mother-offspring dyads In their first trimester of pregnancy Participants with homogeneous parental ethnic backgrounds. |
TL in female newborn more susceptible to variation from maternal TL, mental health, and vitamin B12 levels. Variation in newborn male TL was more explained by their parental age, maternal education, plasma fasting glucose, DGLA%, and IGFBP3 levels. Overall, maternal TL strongly associated with antenatal factors, especially metabolic health and nutrient status. |
| 9. Magnano San Lio et al, 2022 [102] | Cohort | Italy | 174 pregnant women, at 4th–20th gestational week Singleton pregnancyAbsence of pathology and pregnancy complications Planned follow-up of their children at delivery and up to 2 years of age |
Magnesium deficiency negatively associated with maternal RTL after adjusting for the same covariates Positive association between maternal intake of magnesium and TL of cfDNA from amniotic fluid, while results on other micronutrients (i.e., vitamin B1 and Fe) were marginally significant. |
| 10. Salihu, et al, 2018 [96] | Cohort | USA | 62 women upon admission for delivery Singleton pregnancyNo indication of congenital malformations |
Shortened TL among fetuses exposed to maternal high fat consumption during pregnancy, after accounting for the effects of potential covariates. |
| 11. Fan et al, 2022 [99] | Cohort | China | 746 mother-newborn pairs < 16 weeks of pregnancy Singleton gestation |
Possible association between maternal FA supplementation during pregnancy with longer newborn TL was suggested. |
| 12. Louis-Jacques, et al, 2016 [100] | Cohort | USA | 96 maternal-fetal dyads Singleton gestation No indication of congenital malformations |
Positive association between umbilical cord RBC folate and fetal TL at birth. |
| 13. Myers et al, 2021 [103] | Cohort | USA | 96 maternal–fetal dyads Singleton gestation No indication of congenital malformations |
Positive association between maternal vitamin C intake and fetal TL. |
| Research |
Type of study | Country | Population/ Subject characteristics |
Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Vasu et al, 2017 [61] | Case-control | United Kingdom |
78 newborn (47 premature <32gestational weeks and 31 term newborns). Absence of antenatal or postnatal severe congenital malformation or unlikely to survive. |
RTL significantly negatively correlated with GA and birth weight in preterm infants. RTL highly variable in newborn infants. Preterm infants at term equivalent age, have significantly longer TLs than term born infants. Positive correlation between maternal age and T/S ratio. Longitudinal assessment in preterm infants with TL measurements available at birth and term age (n = 5) suggests that TL attrition rate is negatively correlated with increasing GA. RTL was significantly shortest in the term born control group compared with both PTB groups and longest in the PTB at birth group. In addition, TL was not significantly different between preterm infants sampled at birth and those sampled at term equivalent age. |
| 2. Hadchouel et al, 2015 [70] | Cohort | France | 274 adults Group 1:236 adults born prematurely Group 2:38 adults born full-term |
No apparent association with perinatal events. Positive association between TL and abnormal lung airflow in the population born prematurely. |
| 3. Farladansky-Gershnabel, et al, 2023 [106] | Cross sectional | Israel | 19 women with spontaneous term pregnancies and 11 with SPTB Absence of preterm premature rupture of membranes or induced preterm labor, Absence of pregnancy pathology or pregnancy complications, Nulliparous, Absence of fetal malformations |
Maternal blood and placental samples from SPTB had shorter telomeres and increased Gal-3 expression. compared with spontaneous term pregnancies group. |
| 4. Saroyo et al, 2021 [104] | Cross - sectional | Indonesia | 67 placentas (34 placentas from preterm and 33 placentas from term birth were included). Singleton pregnancy, Absence of pathology and pregnancy complications |
Similar TL due to early telomere shortening in PTB that mimics the term placenta. 8-OHdG and HMGB1, do not correlate with placental telomere ratio. HMGB1 from the placenta of both PTB and term labor has no significant difference. Equal telomere T/S ratio of the placenta from PTB and term labor. |
| 5 Colatto et al, 2020 [105] | Cross sectional | Brazil | 80 Singleton pregnancies Foetal membrane samples collected from (1) pregnant women with pPROM, (2) PTB with intact membranes, (3) term labor and (4) term not in labor (TNL). Absence of pathology and pregnancy complications |
Foetal membranes from the term group showed TL reduction compared with those from the other groups. Telomerase activity did not change in foetal membranes irrespective of pregnancy outcome. Telomere shortening in foetal membranes is suggestive of senescence associated with triggering of labor at term. |
| 6. Tarik et al, 2019 [107] | Cohort | India | 1309 offspring, Mean maternal age 39.08y (±3.29), BMI gain at 2, 11, and 29 years |
GA positively associated with offspring RTL No significant association of offspring RTL with body size at birth including birthweight, birth length, and birth BMI. Conditional BMI gain at 2 and 11 years not associated with RTL. BMI gain at 29 year was negatively associated with RTL. Born SGA was not associated with RTL in adulthood. Increased LTL attrition was observed in those born before 37 weeks of GA, as well as in those who gained weight as adults. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





