Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
03 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
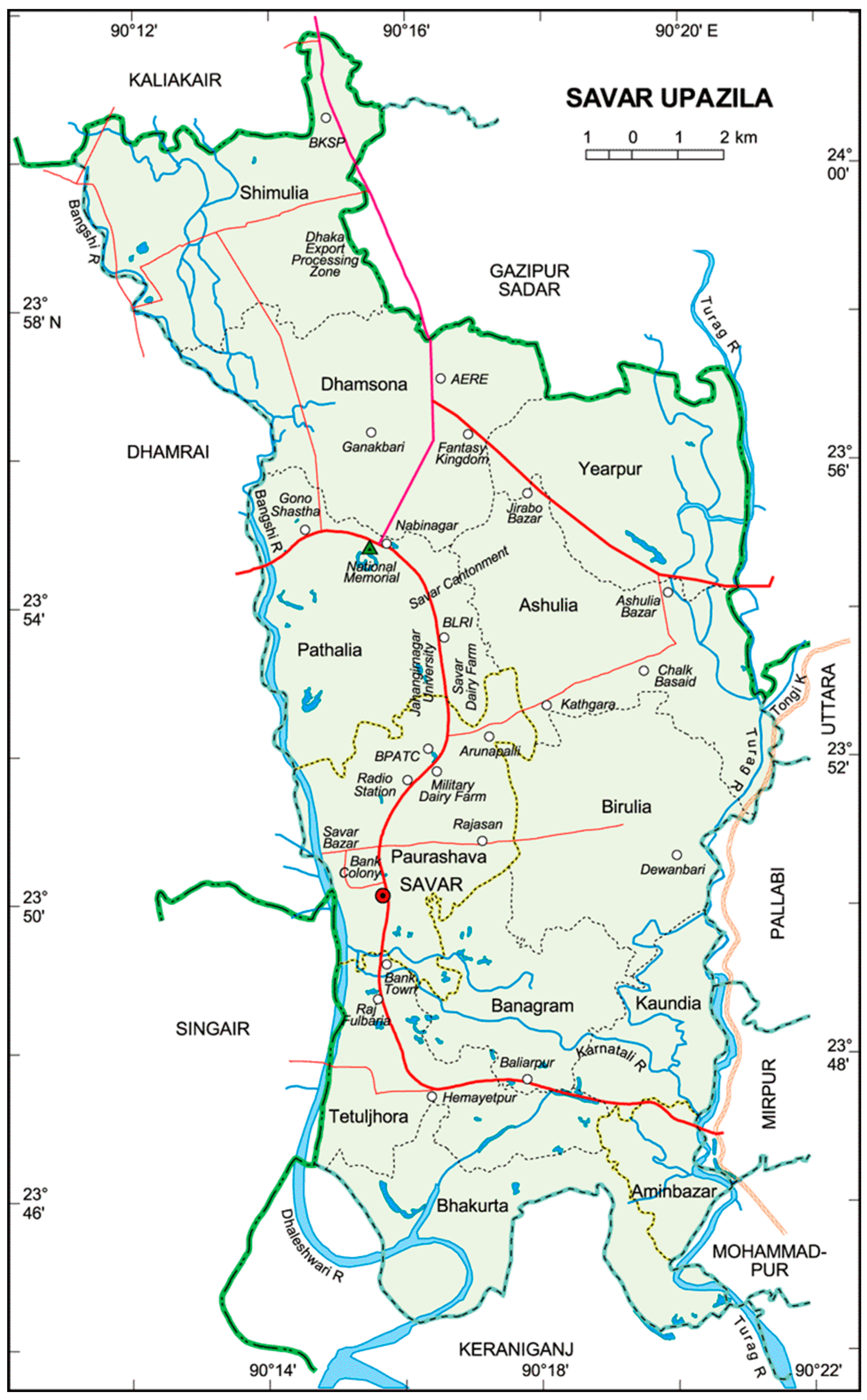
2.1. Present Scenario of the Study Area
2.2. Data collection
3. Results and Discussions
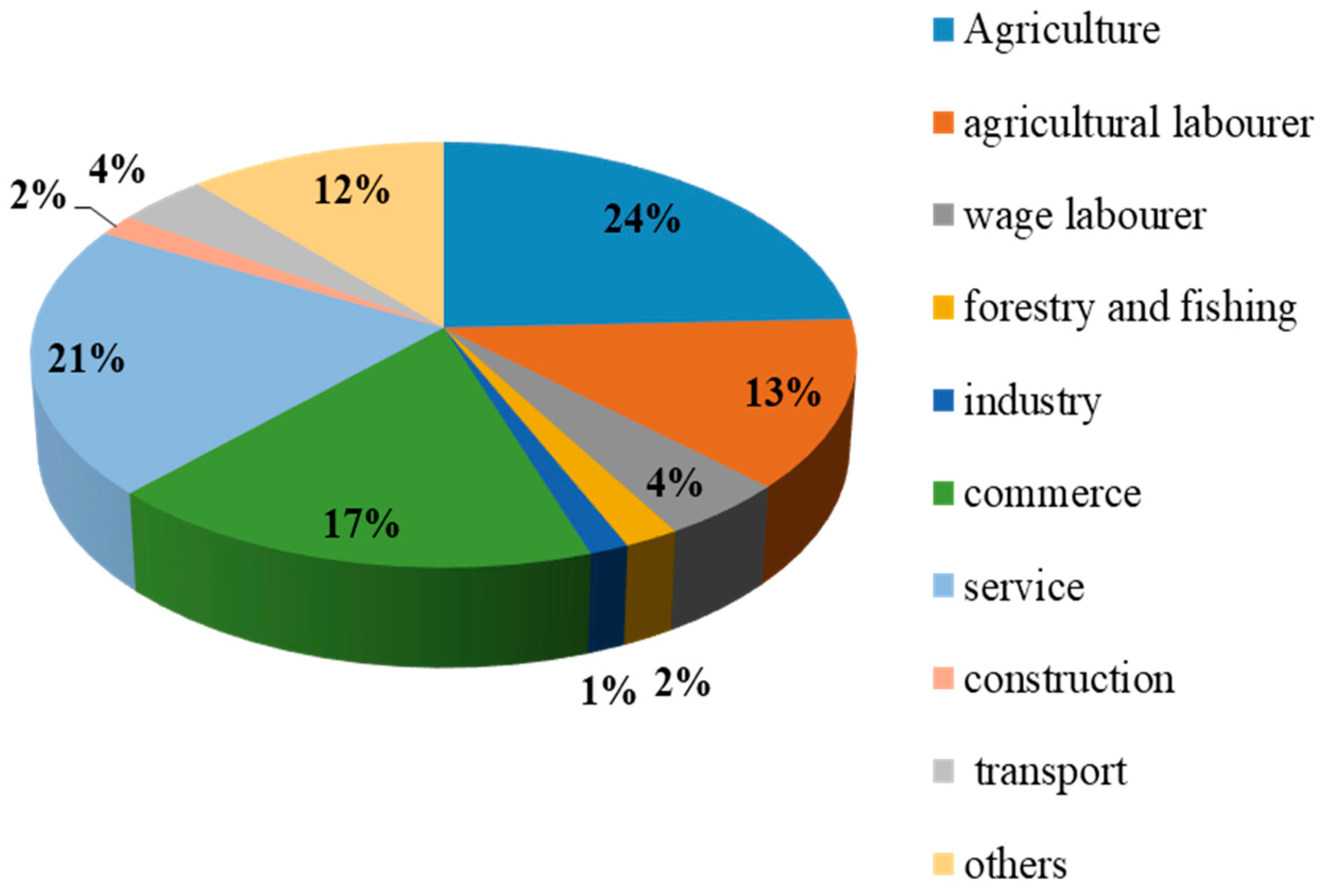
3.1. Socio-economic status of Savar upazila
3.2. Income level of respondents
3.3. Effect on agricultural production
3.4. Air pollution of brickfields
3.5. Health effects of brickfields
3.6. Effect on aquaculture
3.7. Effect on vegetation
3.8. Effect on soil fertility
4. Conclusion
References
- Nodarou, E.; Frederick, C.; Hein, A. Another (mud) brick in the wall: scientific analysis of Bronze Age earthen construction materials from East Crete. Journal of Archaeological Science 2008, 35, 2997–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D.; Love, S.; Hubbard, E.; Klimscha, F. 7,200 years old constructions and mudbrick technology: The evidence from Tel Tsaf, Jordan Valley, Israel. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0227288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G. W. Van Beek and O. Van Beek, Glorious Mud!: Ancient and Contemporary Earthen Design and Construction in North Africa, Western Europe, the Near East, and Southwest Asia, Smithsonian Institution, 2013.
- R. Saha and M. Rahman, “Green Brick Revolution in Bangladesh,” in International Conference on Climate Change Impact and Adaptation. DUET, Gazipur, 2013, pp. 1–10.
- ud Darain, K.M.; Jumaat, M.Z.; Islam, A.S.; Obaydullah, M.; Iqbal, A.; Adham, M.I.; Rahman, M.M. Energy efficient brick kilns for sustainable environment. Desalination and Water Treatment 2016, 57, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Juhász, L.; Southworth, J. Mapping time-space brickfield development dynamics in Peri-Urban Area of Dhaka, Bangladesh. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2019, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Zahid, A.M.; Arifunnahar, M.; Siddique, M.N.A. Effect of brick kiln on arable land degradation, environmental pollution and consequences on livelihood of Bangladesh. Journal of Science, Technology and Environment Informatics 2019, 6, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.F. Strategies to reduce exclusion among populations living in urban slum settlements in Bangladesh. Journal of health, population, and nutrition 2009, 27, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohit, M.A. Bastee settlements of Dhaka City, Bangladesh: A review of policy approaches and challenges ahead. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences 2012, 36, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. A. Bhat and E. O. Gaga, “Air pollutant emissions in the pristine Kashmir valley from the Brick Kilns,” in Biodiversity, Conservation and Sustainability in Asia: Volume 2: Prospects and Challenges in South and Middle Asia, Springer, 2022, pp. 959–979.
- Pramanik, M.A.; Prothan, M.J.I.J.; Munir, M.M. Challenges of low carbon city planning due to emissions from brick kilns: a case study on Dhaka City of Bangladesh. Journal of Bangladesh Institute of Planners ISSN 2018, 2075, 9363. [Google Scholar]
- E. Saikawa et al., “Air pollution in the hindu kush Himalaya,” The Hindu Kush Himalaya assessment: Mountains, climate change, sustainability and people, pp. 339–387, 2019.
- J. A. Saju, M. M. Rahman, P. K. Debnath, and S. B. Nayan, “IMPACTS OF AIR POLLUTION ON HUMAN HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENT DUE TO BRICK KILNS EMISSION: A REVIEW”.
- M. K. Saha, R. Ara, S. D. Kadir, and M. G. Mostafa, “Environmental vulnerability of people to brick kiln hazards”.
- M. M. R. Bhuiyan, “Assessment of environmental laws in Bangladesh: a GIS based case study on brickfields of Savar,” BRAC University, 2013.
- Ullah, M.R. Economic Impacts of Globalization on Urban Environment at Dhaka city in Bangladesh. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development 2014, 5, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rushton, L. Occupational causes of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Reviews on environmental health 2007, 22, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.M.H.; Hasan, M.; Ahmad, S.I.; Ahmed, T. Performance of industrial sludge-amended bricks manufactured in conventional kilns. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 2020, 22, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Begum, B.A.; Wadud, Z. Particulate pollution from brick kiln clusters in the Greater Dhaka region, Bangladesh. Air Qual Atmos Health 2013, 6, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Sajid, M.B.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Khoja, A.H.; Ahmad, M.M.; Shahid, M.; Ullah, K. Assessment of long-term energy and environmental impacts of the cleaner technologies for brick production. Energy Reports 2021, 7, 7157–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. K. Saha, S. Ahmed, A. Sheikh, and M. Mostafa, “Impacts of Brick Kilns on Environment around Kiln areas of Bangladesh,” vol. 12, pp. 241–253, Nov. 2021.
- Ahmad, H.R.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Sabir, M.; Sardar, M.F. Brick Kilns: Types, Emissions, Environmental Impacts, and their Remedial Measures. In Biodiversity, Conservation and Sustainability in Asia: Volume 2: Prospects and Challenges in South and Middle Asia; Öztürk, M., Khan, S.M., Altay, V., Efe, R., Egamberdieva, D., Khassanov, F.O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinder, B.; Sheikh, A.; Pandit, A.; Ganai, B. Brick kiln emissions and its environmental impact: A Review. Journal of Ecology and the Natural Environment 2013, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. S. S. Chowdhury, M. Haque, and M. S. Engr. MD. ANISUR RAHMAN ~ TiTU. GREEN ECO-BRICK, BRICK KILNS EMISSION AND IT’S ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/84857795/GREEN_ECO_BRICK_BRICK_KILNS_EMISSION_AND_IT_S_ENVIRONMENTAL_IMPACT (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Joshi, S.K.; Dudani, I. Environmental Health effects of Brick Kilns in Khatmandu Valley. Kathmandu University medical journal (KUMJ) 2008, 6, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jerin, M.F.; Mondol, S.K.; Sarker, B.C.; Rimi, R.H.; Aktar, S. Impacts of Brick Fields on Environment and Social Economy at Bagatipara, Natore, Bangladesh. Journal of Environmental Science and Natural Resources 2017, 9, 31. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/32483248/Impacts_of_Brick_Fields_on_Environment_and_Social_Economy_at_Bagatipara_Natore_Bangladesh (accessed on 2 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Abir, A. Role of Laws to Control Brick Manufacturing and Kiln Establishment in Bangladesh: Scope of Alternative Bricks. VNU Journal of Science: Earth and Environmental Sciences 2019, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, H.; Vilches, J.; Felmer, G.; Hurtado, M.; Figueroa, J. Artisan Brick Kilns: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.S.; Sharif, S. The need for an effective environmental engineering education to meet the growing environmental pollution in Bangladesh. Cleaner Engineering and Technology 2021, 4, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. A. Ahmed and S. Chakrabarti, Analysis on Solid Waste Management Practices and Development of Integrated Solid Waste Management Model for Developing Country With Special Reference to Jhenaidah Municipal Area, Bangladesh. KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh: 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 2018.
- Md. A. Ahmed, M. Hossain, and M. Islam, Prediction of Solid Waste Generation Rate and Determination of Future Waste Characteristics at South-western Region of Bangladesh Using Artificial Neural Network. KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh: WasteSafe 2017, KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 2017.
- Ananno, A.A.; Masud, M.H.; Chowdhury, S.A.; Dabnichki, P.; Ahmed, N.; Arefin, A.M.E. Sustainable food waste management model for Bangladesh. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2021, 27, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. M. Rahman, D. B. P. Argha, and M. Haque, PRESENT SCENARIO OF MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT IN SATKHIRA MUNICIPALITY. 2018.
- T. Khan, D. B. P. Argha, and M. S. Anita, An Analysis of Existing Medical Waste Management and Possible Health Hazards in Jhenaidah Municipality. 2021.
- Md. A. Ahmed and S. M. Moniruzzaman, A Study on Plastic Waste Recycling Process in Khulna City. KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh: 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2018), KUET, Khulna, Bangladesh, 2018.
- Harshwardhan, K.; Upadhyay, K. Effective Utilization of Agricultural Waste: Review. Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications 2017, 07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. A. Ahmed, P. Roy, A. Bari, and M. Azad, Conversion of Cow Dung to Biogas as Renewable Energy Through Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion by Using Silica Gel as Catalyst, 5th ed. Chittagong: ICMERE 2019, Chittagong University of Engineering & Technology (CUET), 2019.
- Liu, C.-M.; Wu, S.-Y. From biomass waste to biofuels and biomaterial building blocks. Renewable Energy 2016, 96, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Shah, M.H. Biogas generation from kitchen and vegetable waste in replacement of traditional method and its future forecasting by using ARIMA model. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Hasib and D. B. P. Argha, COVID-19: LACK OF CORONAVIRUS WASTES MANAGEMENT-AN UPCOMING THREAT FOR THE MEGACITY DHAKA. 2021.
- Prasad, M.; Ranjan, R.; Ali, A.; Goyal, D.; Yadav, A.; Singh, T.B.; Shrivastav, P.; Dantu, P.K. Efficient Transformation of Agricultural Waste in India. In Contaminants in Agriculture: Sources, Impacts and Management; Naeem, M., Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Shah, M.H. Biogas generation from kitchen and vegetable waste in replacement of traditional method and its future forecasting by using ARIMA model. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Omer, “Demand for energy efficient, eco-friendly environment, applications and sustainable development,” 2015, pp. 493–573.
- Ahmed, M.A.; Roy, P.; Shah, M.H.; Argha, D.P.; Datta, D.; Ri̇yad, R.H. Recycling of cotton dust for organic farming is a pivotal replacement of chemical fertilizers by composting and its quality analysis. ERT 2021, 4, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthiala, T.; Thakur, K.; Sharma, D.; Singh, G.; Khatri, M.; Arya, S.K. The eco-friendly approach of cocktail enzyme in agricultural waste treatment: A comprehensive review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 209, 1956–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, T.; Bhattacharjee, T.; Nag, P.; Ritika; Ghati, A.; Kuila, A. Valorization of agro-waste into value added products for sustainable development. Bioresource Technology Reports 2021, 16, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, L.L.D.R.; Flórez-López, E.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. The Potential of Selected Agri-Food Loss and Waste to Contribute to a Circular Economy: Applications in the Food, Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Industries. Molecules 2021, 26, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D. B. P. Argha, A. Hasib, and M. Rahman, “A comparative study on the variation of air quality index of Dhaka city before and after the nationwide lockdown due to COVID-19,” in 6th International Conference on Engineering Research, Innovation and Education (2021). Sylhet, Bangladesh, 2021.
- Khan, M.W.; Ali, Y.; De Felice, F.; Salman, A.; Petrillo, A. Impact of brick kilns industry on environment and human health in Pakistan. Science of The Total Environment 2019, 678, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, M.; Ahmad, W.; Khan, H.; Yousaf, S.; Yasir, M.; Khan, A. Environmental and health impacts of industrial wastewater effluents in Pakistan: a review. Rev Environ Health 2019, 34, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, T.; Das, A. Water pollution by industrial effluents in India: Discharge scenarios and case for participatory ecosystem specific local regulation. Futures 2008, 40, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odigie, J. Harmful effects of wastewater disposal into water bodies: a case review of the Ikpoba river, Benin city, Nigeria. Tropical Freshwater Biology 2015, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. A. Ahmed* and M. Redowan, “Fate and Transport of the Biologically Treated Landfill Leachate Induced Dissolved Organic Nitrogen (DON),” AEESP Research and Education Conference, Northeastern University, June 20-23, 2023, Jun. 2023. Available online: https://par.nsf.gov/biblio/10431230-fate-transport-biologically-treated-landfill-leachate-induced-dissolved-organic-nitrogen-don (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Akhtar, M.M.; Zhonghua, T.; Dawood, A.; Sohail, M.T. A Study to Investigate and Compare Groundwater Quality in Adjacent Areas of Landfill Sites in Lahore City. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology 2014, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- M. R. Rashid and M. Ashik, “Evaluation of Physicochemical Treatment Technologies for Landfill Leachate Induced Dissolved Organic Nitrogen (DON).,” AEESP Research and Education Conference, Northeastern University, June 20-23, 2023, Jun. 2023. Available online: https://par.nsf.gov/biblio/10431232-evaluation-physicochemical-treatment-technologies-landfill-leachate-induced-dissolved-organic-nitrogen-don (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Lee, J.; Brooks, N.R.; Tajwar, F.; Burke, M.; Ermon, S.; Lobell, D.B.; Biswas, D.; Luby, S.P. Scalable deep learning to identify brick kilns and aid regulatory capacity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118, e2018863118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D. B. P. Argha and Q. Bari, EXTENT OF EFFLORESCENCE IN A BRICK MASONRY PARTITION WALL OF A GARAGE. 2018.
- K. Roy, Q. Bari, S. Mostakim, and D. B. P. Argha, Water Supply History of Khulna City. 2019.
- A. Allen, J. Davila, and P. Hofmann, Governance of Water and Sanitation Services for the Peri-urban Poor A Framework for Understanding and Action in Metropolitan Regions Governance of Water and Sanitation Services for the Peri-urban Poor. 2006.
- P. Roy, M. A. Ahmed, Md. S. Islam, Md. A. K. Azad, Md. S. Islam, and Md. R. Islam, “Water Supply, Sanitation System and Water-borne Diseases of Slum Dwellers of Bastuhara Colony, Khulna,” presented at the 5 th International Conference on Civil Engineering for Sustainable Development (ICCESD 2020), Khulna, Bangladesh: Department of Civil Engg., KUET, Feb. 2020.
- Roy, P.; Ahmed, M.A.; Kumer, A. AN OVERVIEW OF HYGIENE PRACTICES AND HEALTH RISKS RELATED TO STREET FOODS AND DRINKING WATER FROM ROADSIDE RESTAURANTS OF KHULNA CITY OF BANGLADESH. EJERE 2019, 3, 47–55. Available online: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/ejere/issue/49620/590483 (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- Moe, C.L.; Rheingans, R.D. Global challenges in water, sanitation and health. J Water Health 2006, 4 Suppl 1, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Pal, Y. Ayele, A. Hadush, S. Panigrahi, and V. Jadhav, “Public Health Hazards Due to Unsafe Drinking Water,” vol. 7, May 2018. [CrossRef]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial Contamination of Drinking Water and Human Health from Community Water Systems. Curr Envir Health Rpt 2015, 2, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashbolt, N.J. Microbial contamination of drinking water and disease outcomes in developing regions. Toxicology 2004, 198, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Akhter, R.; Huque, S.; Khandaker, S.; Shahriar, M.; Gorapi, M.Z.H. Socioeconomic conditions and health hazards of brick field workers: A case study of Mymensingh brick industrial area of Bangladesh. Journal of Public Health and Epidemiology 2017, 9, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Gurley, E.S.; Rutherford, S.; Luby, S.P. The Drivers and Impacts of Selling Soil for Brick Making in Bangladesh. Environmental Management 2018, 62, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, S.P.; Biswas, D.; Gurley, E.S.; Hossain, I. Why highly polluting methods are used to manufacture bricks in Bangladesh. Energy for Sustainable Development 2015, 28, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juel, M.A.I.; Mizan, A.; Ahmed, T. Sustainable use of tannery sludge in brick manufacturing in Bangladesh. Waste Management 2017, 60, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, B.A.; Hopke, P.K.; Markwitz, A. Air pollution by fine particulate matter in Bangladesh. Atmospheric Pollution Research 2013, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Baten, M.; Nahar, B.; Morshed, N. Carbon dioxide emission from brickfields around Bangladesh. International Journal of Agricultural Research, Innovation and Technology 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrygiannis, I.; Tsetsekou, A. Efficient Recovery of Solid Waste Units as Substitutes for Raw Materials in Clay Bricks. Recycling 2022, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Vieira, C.M.F. On the production of fired clay bricks from waste materials: A critical update. Construction and Building Materials 2014, 68, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzaman, A. " Financial Feasibility of Environment Friendly Brick Manufacturing in the Context of Bangladesh " Available online: https://www.academia.edu/35504114/_Financial_Feasibility_of_Environment_Friendly_Brick_Manufacturing_in_the_Context_of_Bangladesh_ (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Guttikunda, S. Impact Analysis of Brick Kilns on the Air Quality in Dhaka, Bangladesh. 2009. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Impact-Analysis-of-Brick-Kilns-on-the-Air-Quality-Guttikunda/87685662c718f9aa64b9833202e3f2004f5bfd28 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Begum, B.A.; Hopke, P.K. Identification of Sources from Chemical Characterization of Fine Particulate Matter and Assessment of Ambient Air Quality in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.I.; Nahar, K.; Kabir, M.H.; Salam, A. Particulate black carbon and gaseous emission from brick kilns in Greater Dhaka region, Bangladesh. Air Qual Atmos Health 2018, 11, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Islam, M.A.; Aziz Hasan, M.; Alam, M.J.; Peas, M.H. Groundwater vulnerability assessment in Savar upazila of Dhaka district, Bangladesh — A GIS-based DRASTIC modeling. Groundwater for Sustainable Development 2019, 9, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Murshed, S.; Hasan, M. Selecting suitable landfill site with multi-criteria evaluation and GIS: a case of Savar upazila in Bangladesh. Arab J Geosci 2020, 13, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangladesh - Population and Housing Census 2011. Available online: https://catalog.ihsn.org/index.php/catalog/4376 (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Bindraban, P.S.; Stoorvogel, J.J.; Jansen, D.M.; Vlaming, J.; Groot, J.J.R. Land quality indicators for sustainable land management: proposed method for yield gap and soil nutrient balance. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2000, 81, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, S.; Marschner, P. Clay Addition to Sandy Soil Reduces Nutrient Leaching—Effect of Clay Concentration and Ped Size. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 2017, 48, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.; Anderson, W. Response of soil properties and grain yield to deep ripping and gypsum application in a compacted loamy sand soil contrasted with a sandy clay loam in Western Australia. Crop and Pasture Science 2003, 54, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Zang, H.; Ugurlar, F.; Aydemir, S.; Brüggemann, N.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Blagodatskaya, E. Effect of biochar origin and soil pH on greenhouse gas emissions from sandy and clay soils. Applied Soil Ecology 2018, 129, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Types of Diseases | Percentages of Affected Respondents (%) |
|---|---|
| Skin disease | 12 |
| Eye irritation | 14 |
| Respiratory problems | 13 |
| Skin disease and Eye irritation | 15 |
| Skin disease and respiratory diseases | 14 |
| Eye Irritation and respiratory diseases | 14 |
| No problem | 18 |
| Total | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





