Submitted:
02 November 2023
Posted:
03 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental combination
2.2. Laboratory animals
2.3. Experimental groups
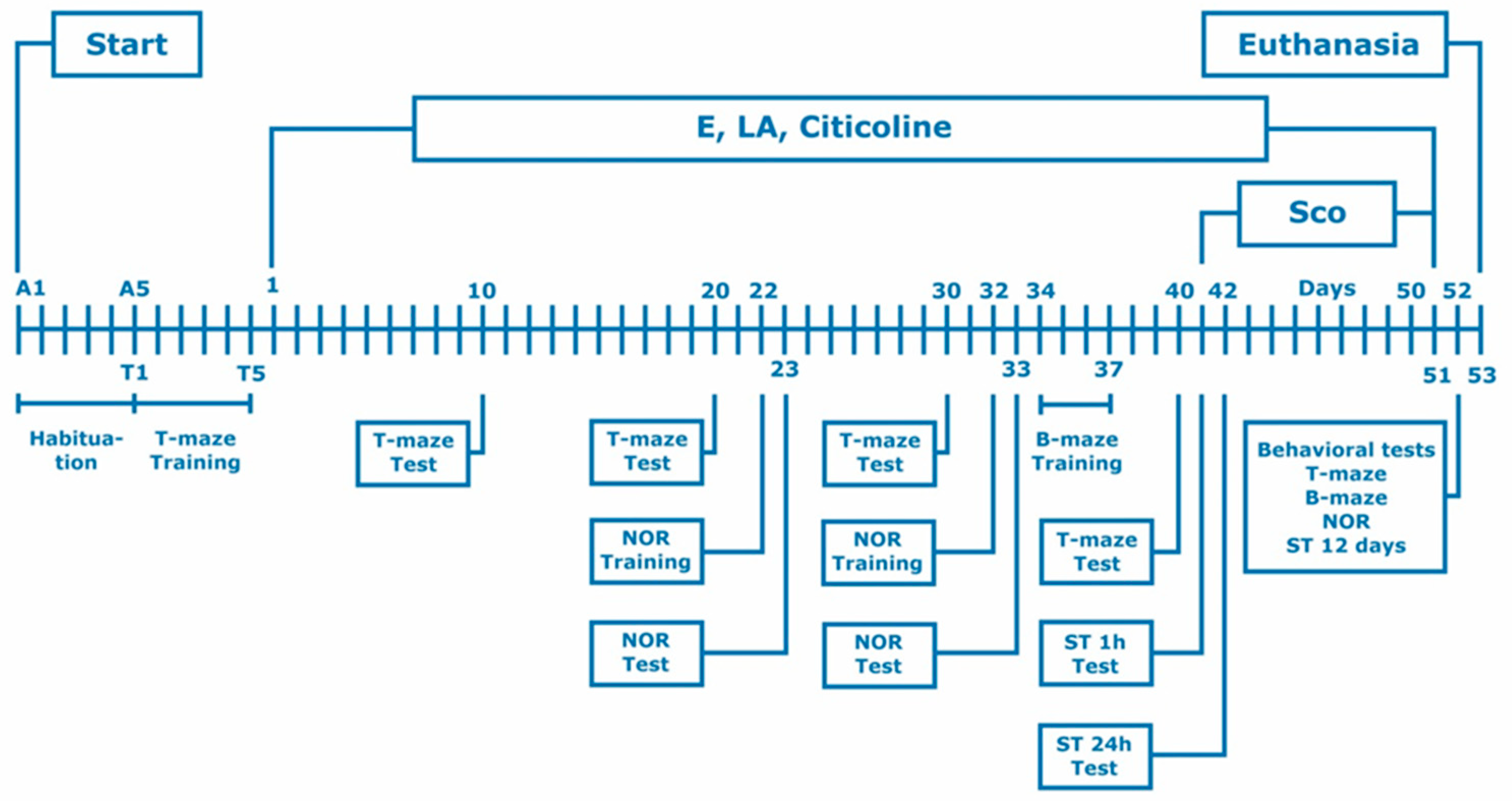
2.4. Experimental design
2.5. Behavioral experimental methods
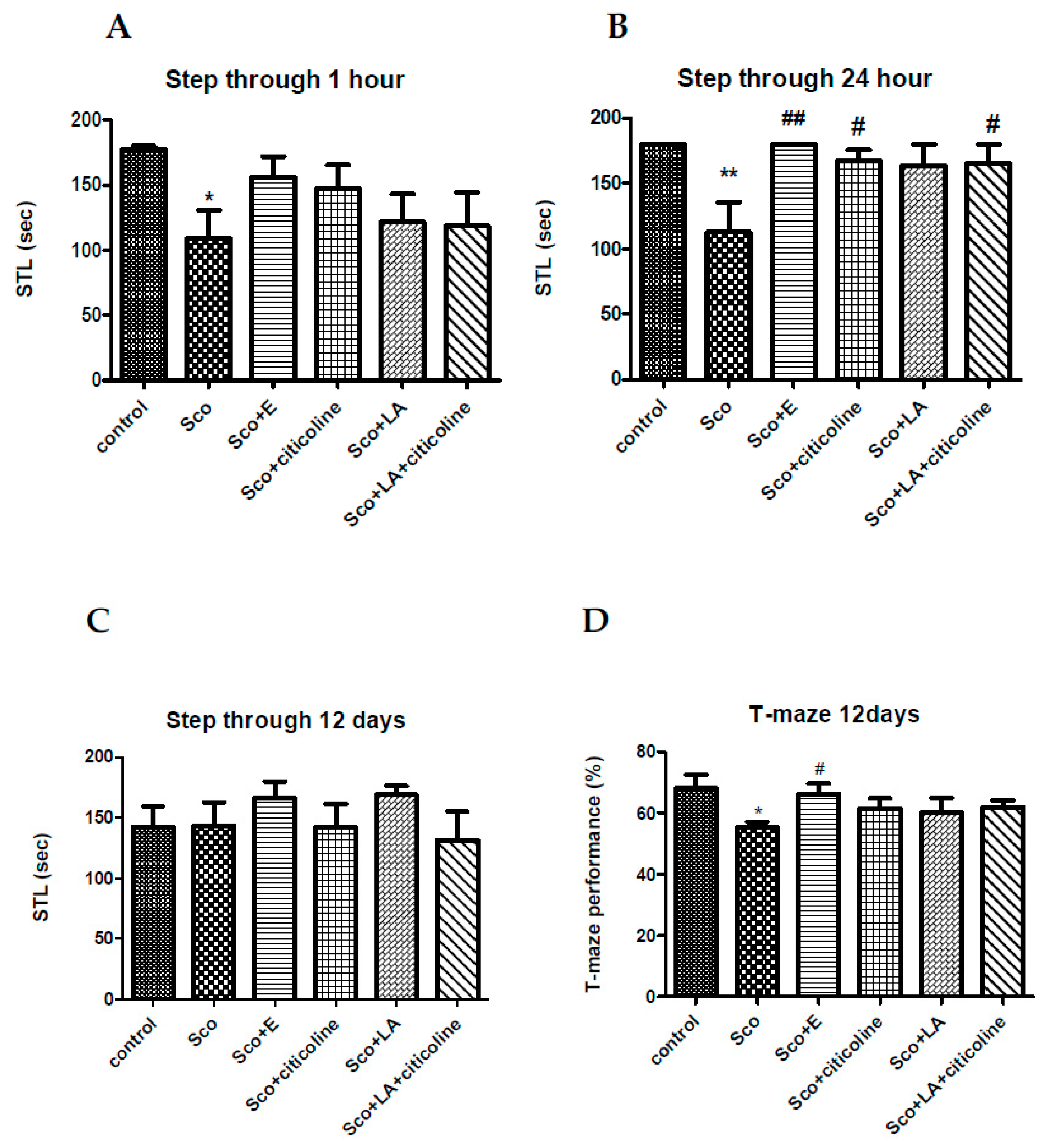
2.5.1. Step-through passive avoidance
2.5.2. T-maze
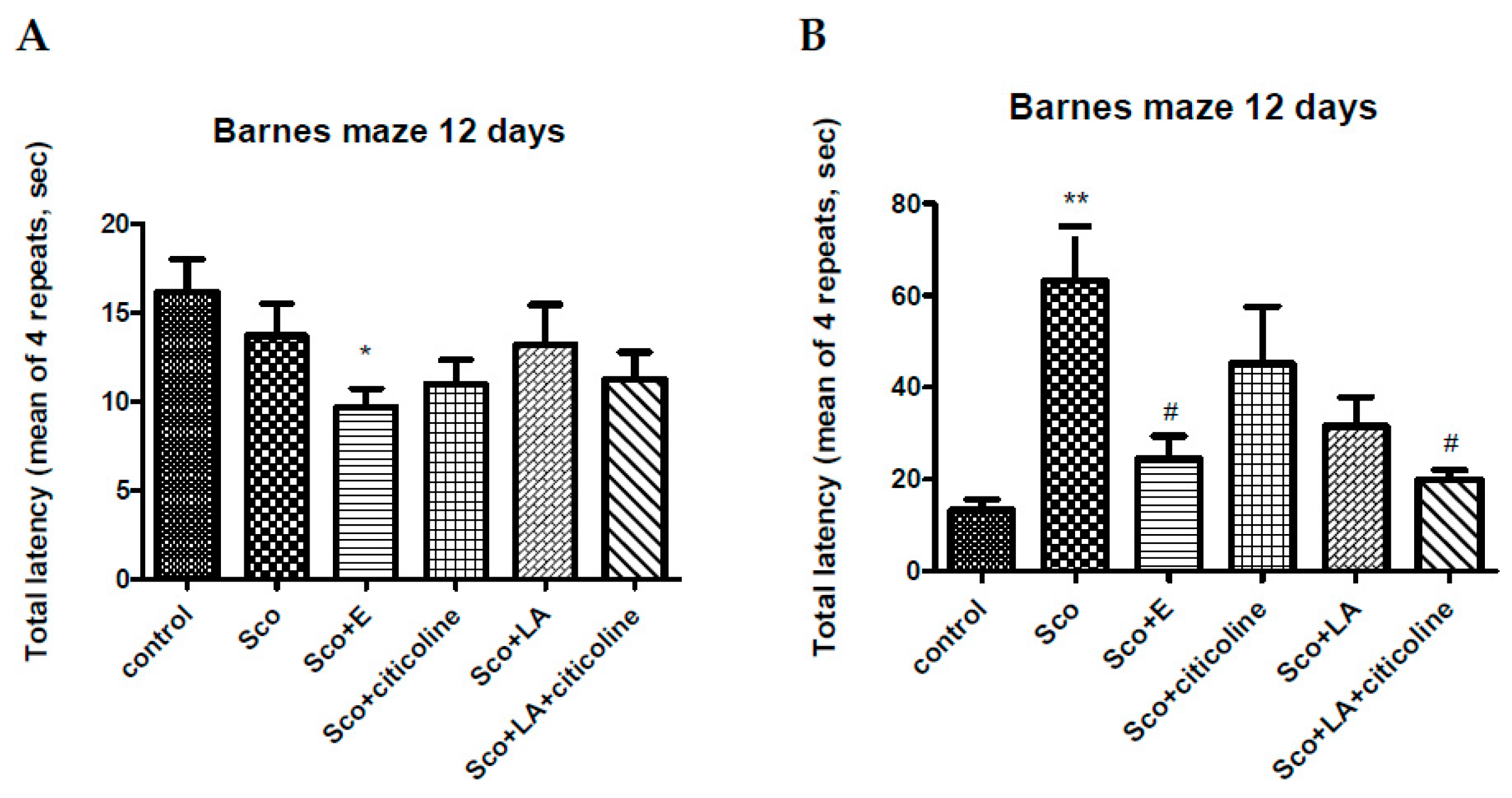
2.5.3. Barnes maze (B-maze)
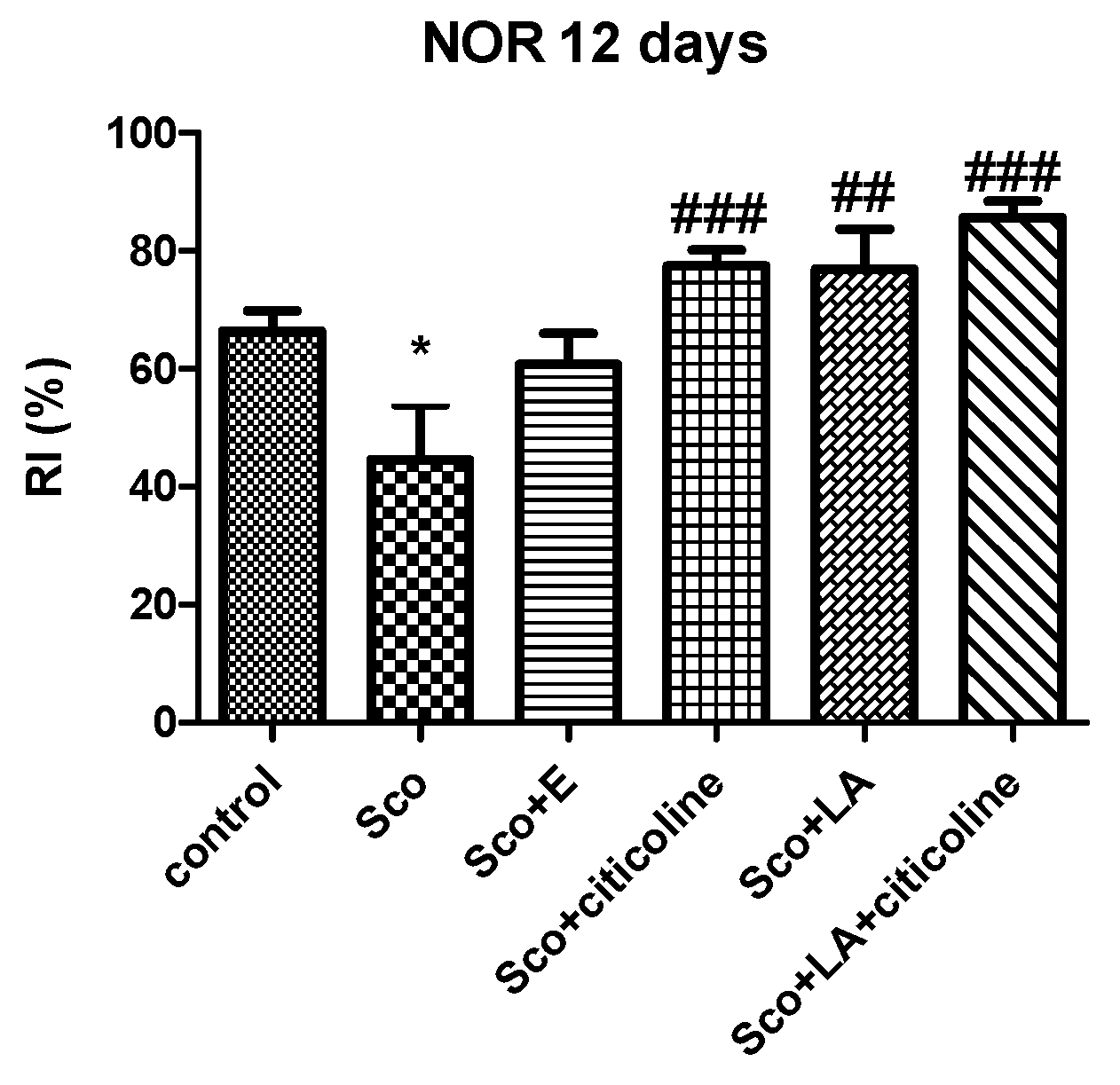
2.5.4. The Novel Object Recognition (NOR)
2.6. Biochemical methods
2.6.1. Tissue preparation
2.6.2. AChE activity
2.7. Histological studies
2.8. Statistical analysis
3. Results
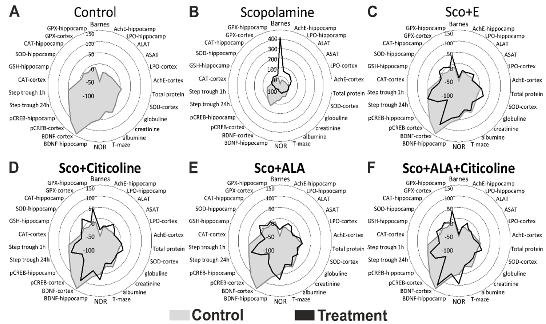
3.1. Behavioural assessment of the effects of the experimental combination on learning and memory
3.2. Biochemical assessment of the effects of the experimental combination
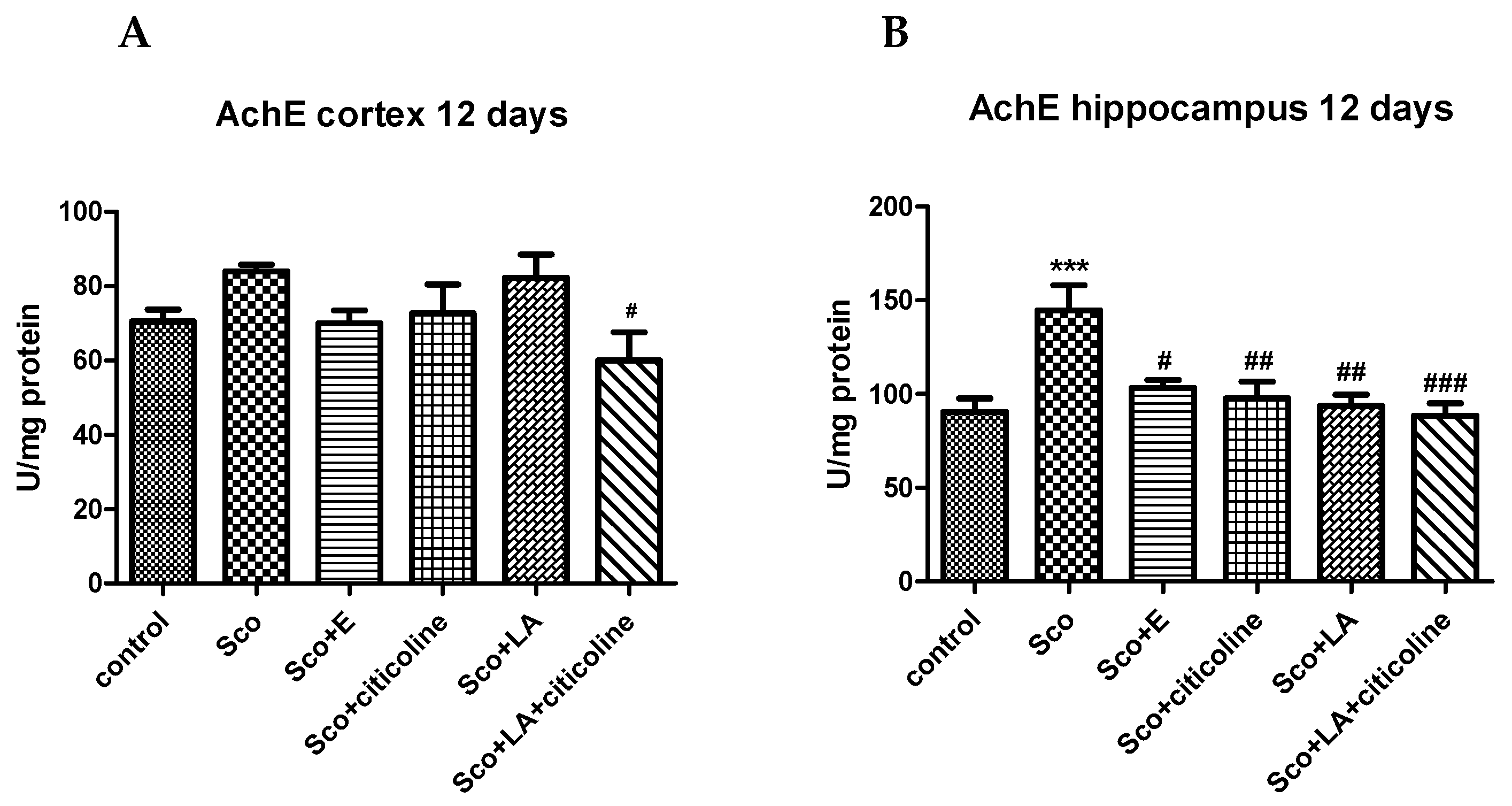
3.2.1. Effect of the experimental combination and its components on brain AChE activity
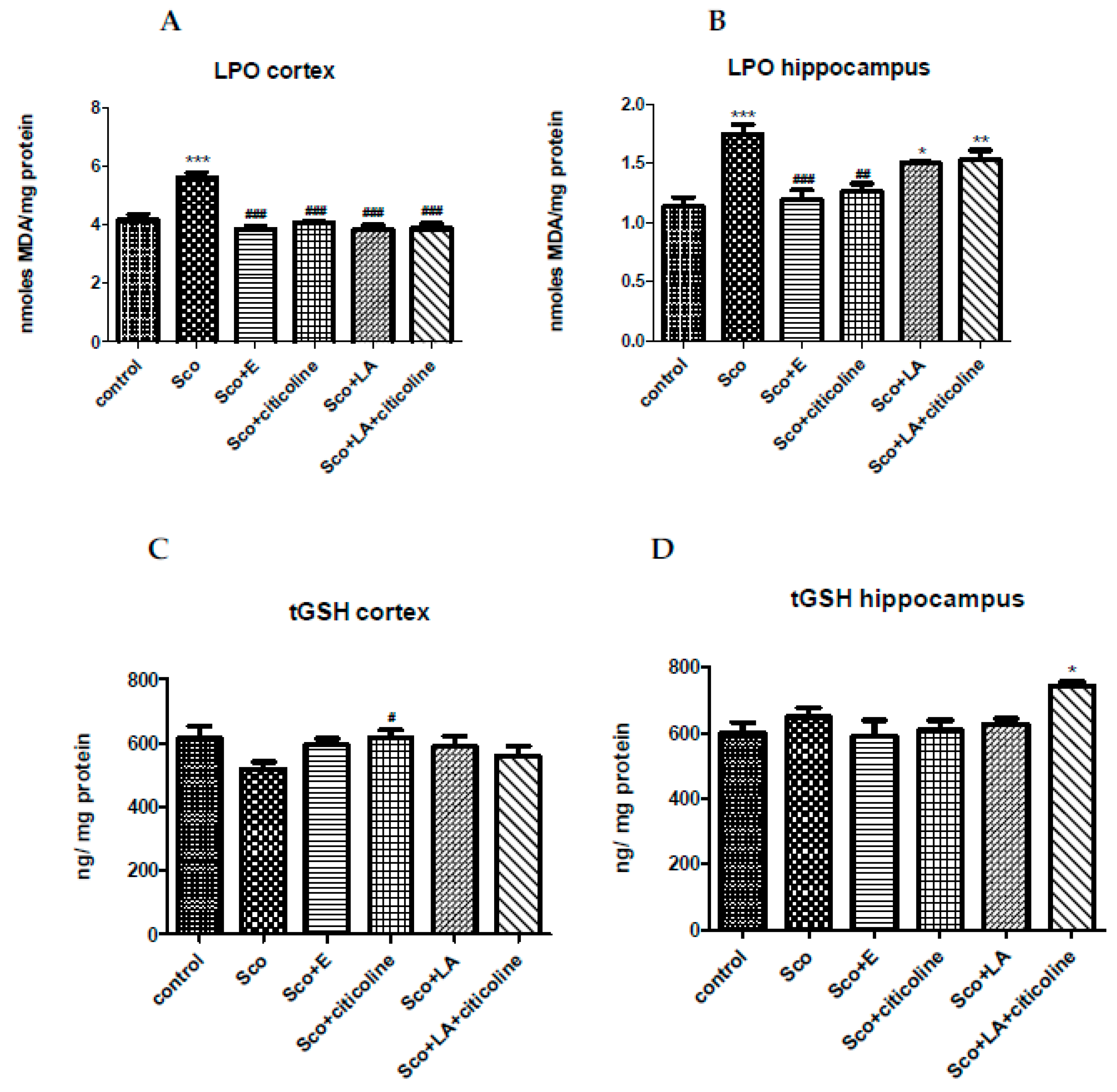
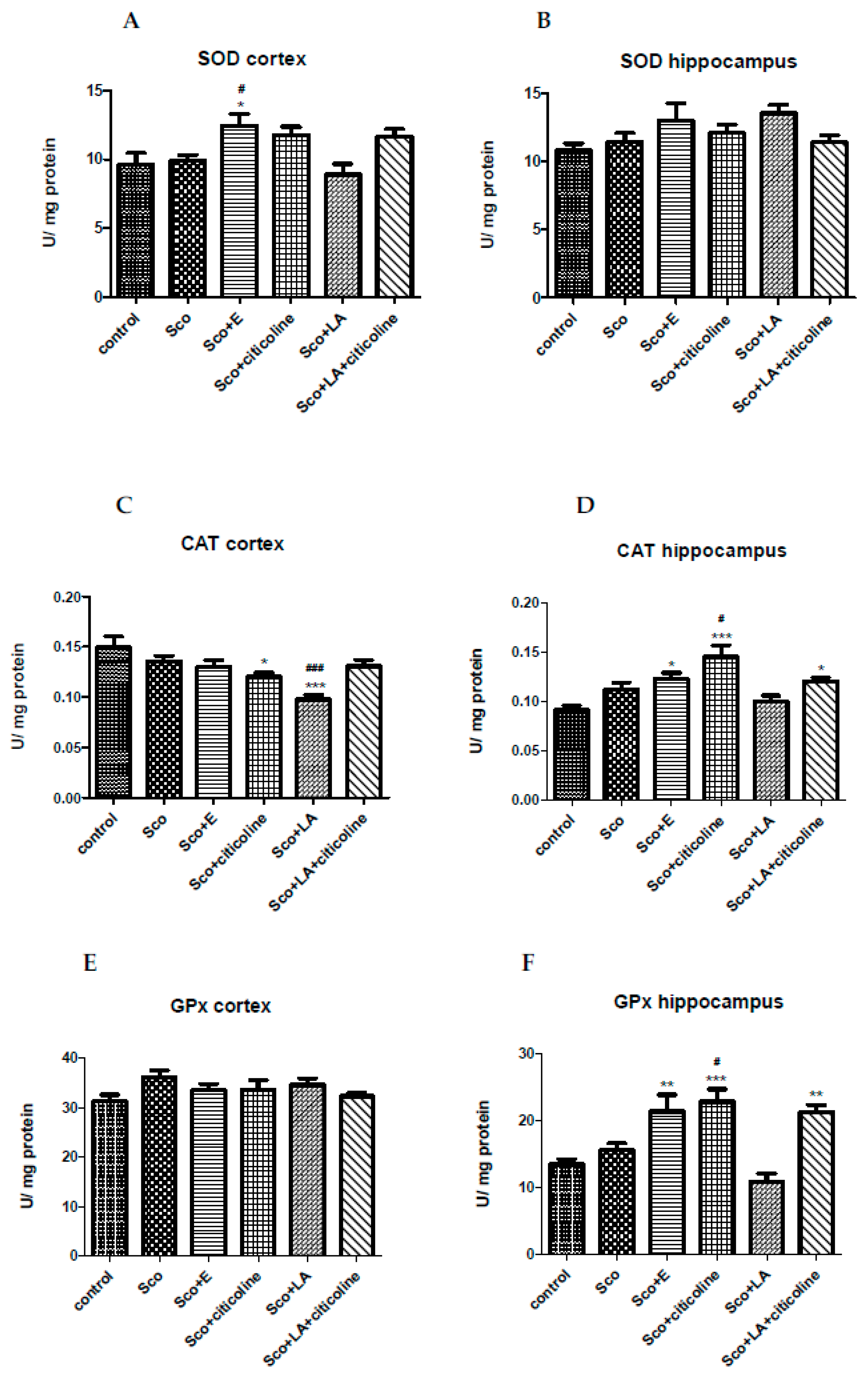
3.2.2. Antioxidant potential of the experimental combination and its components
3.2.3. Effect of the experimental combination and its components on SOD, catalase and GPx activity
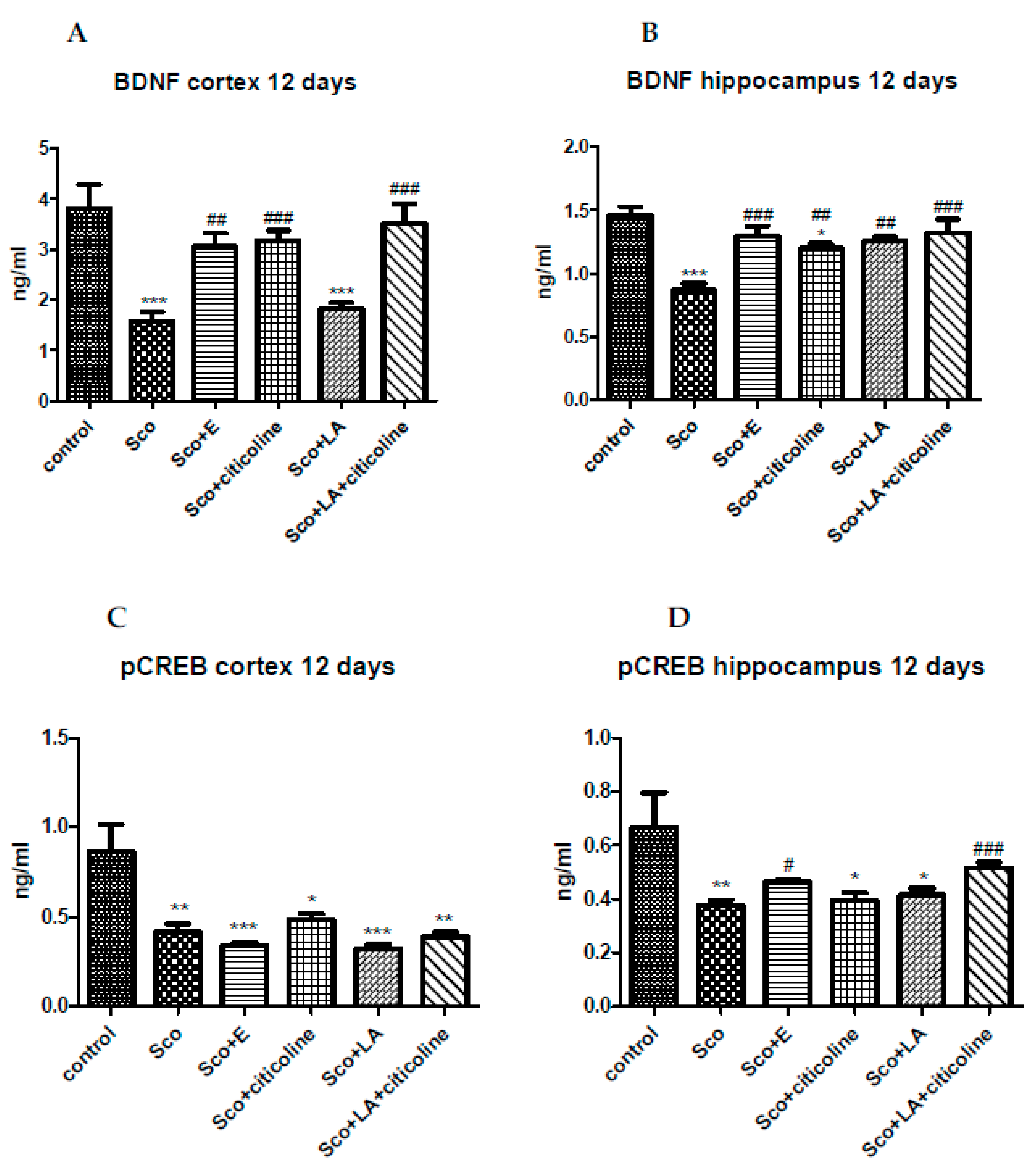
3.3. Effect of the experimental combination and its components on the brain BDNF/CREB signaling pathway
3.4. Histological evaluation of pathological changes in stomach, small intestine, liver and kidney of male Wistar rats treated with the еxperimental combination and its components
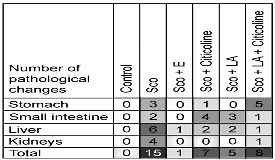
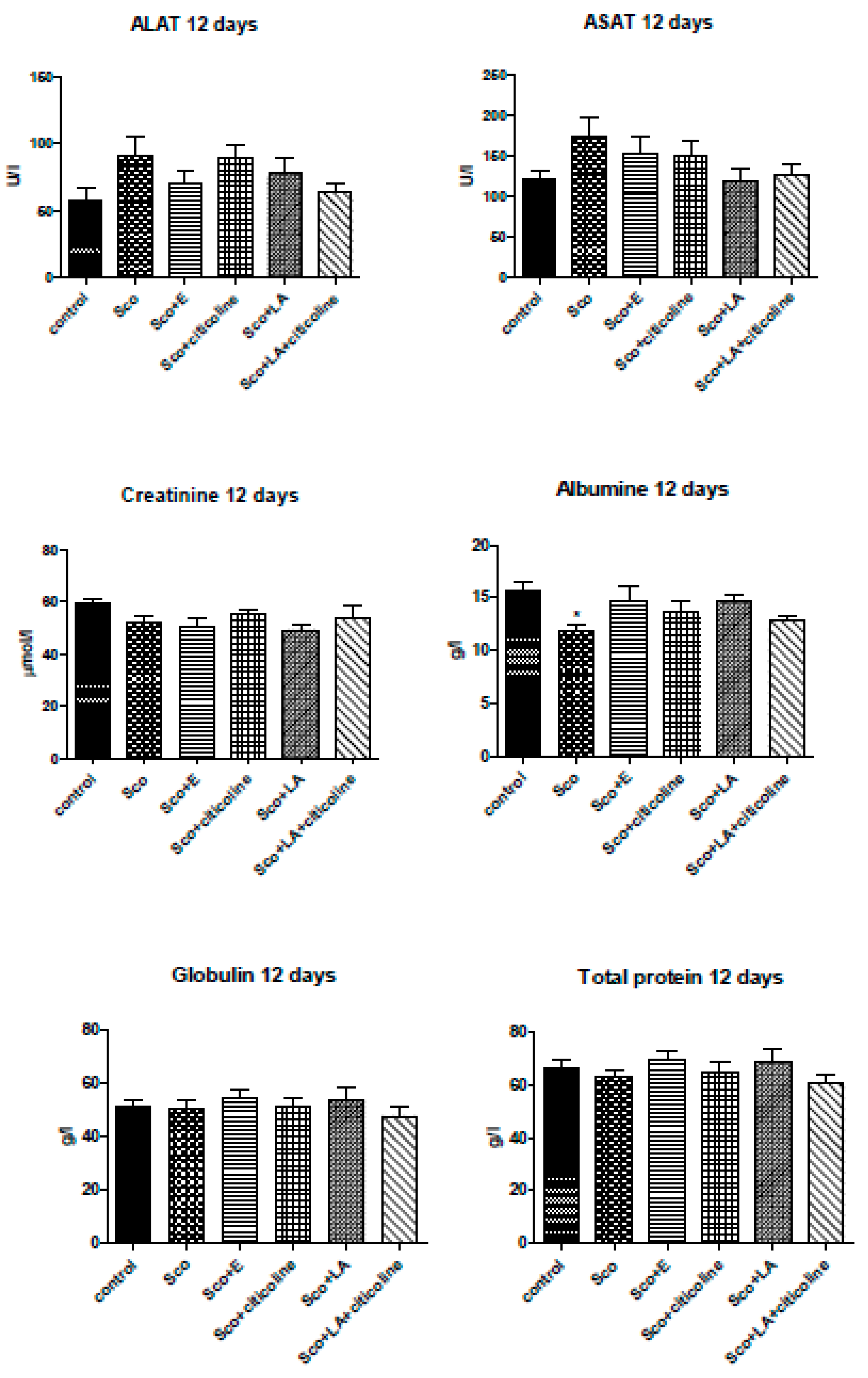
3.5. Biochemical evaluation of toxicity of the experimental combination and its components (ALAT, ASAT, creatinine, albumin, globulin, total protein assays)
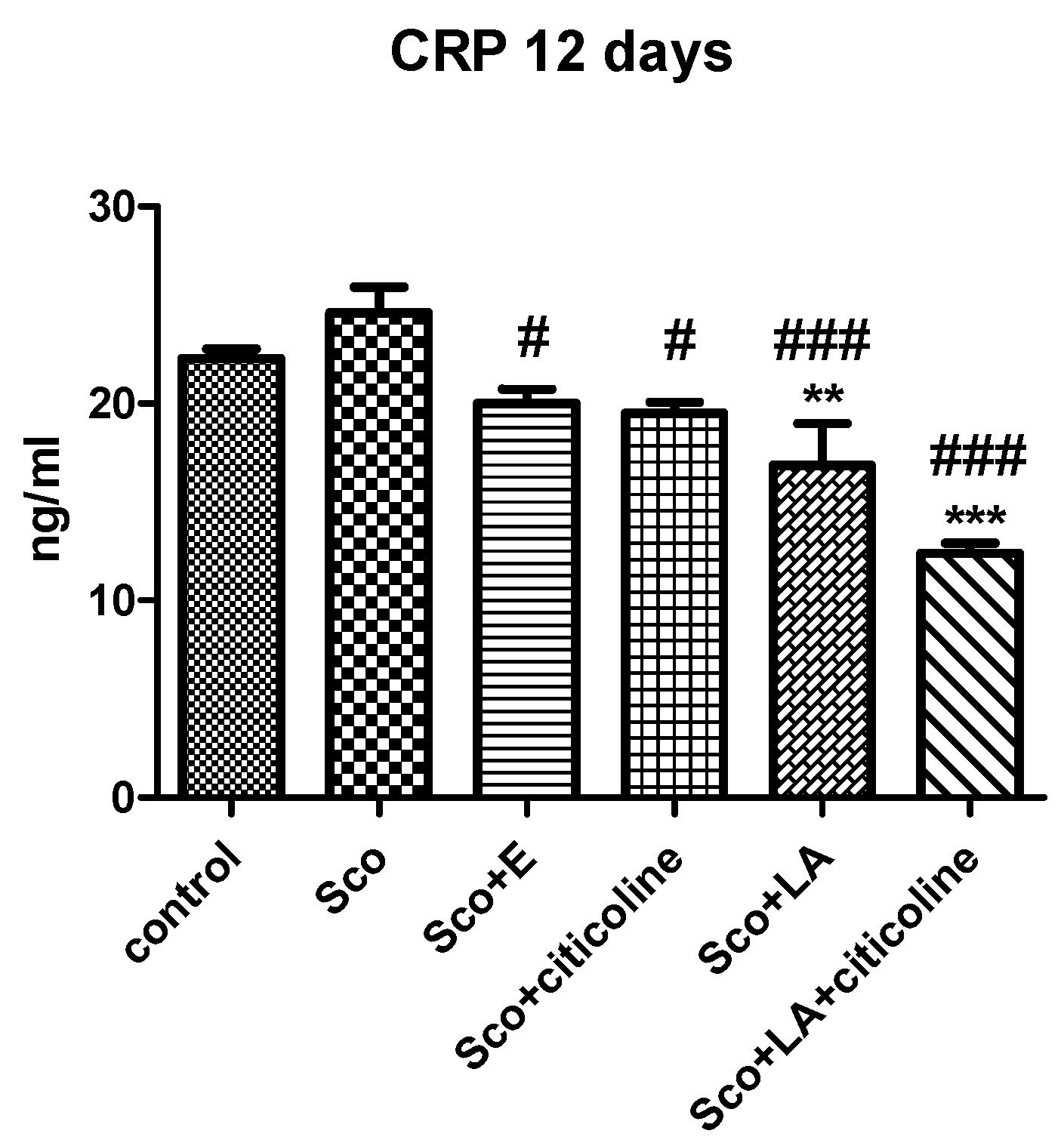
3.6. Evaluation of the anti-inflammatory effect of the combination and its components (C-reactive protein assay)
3.7. Mathematical processing of the experimental data
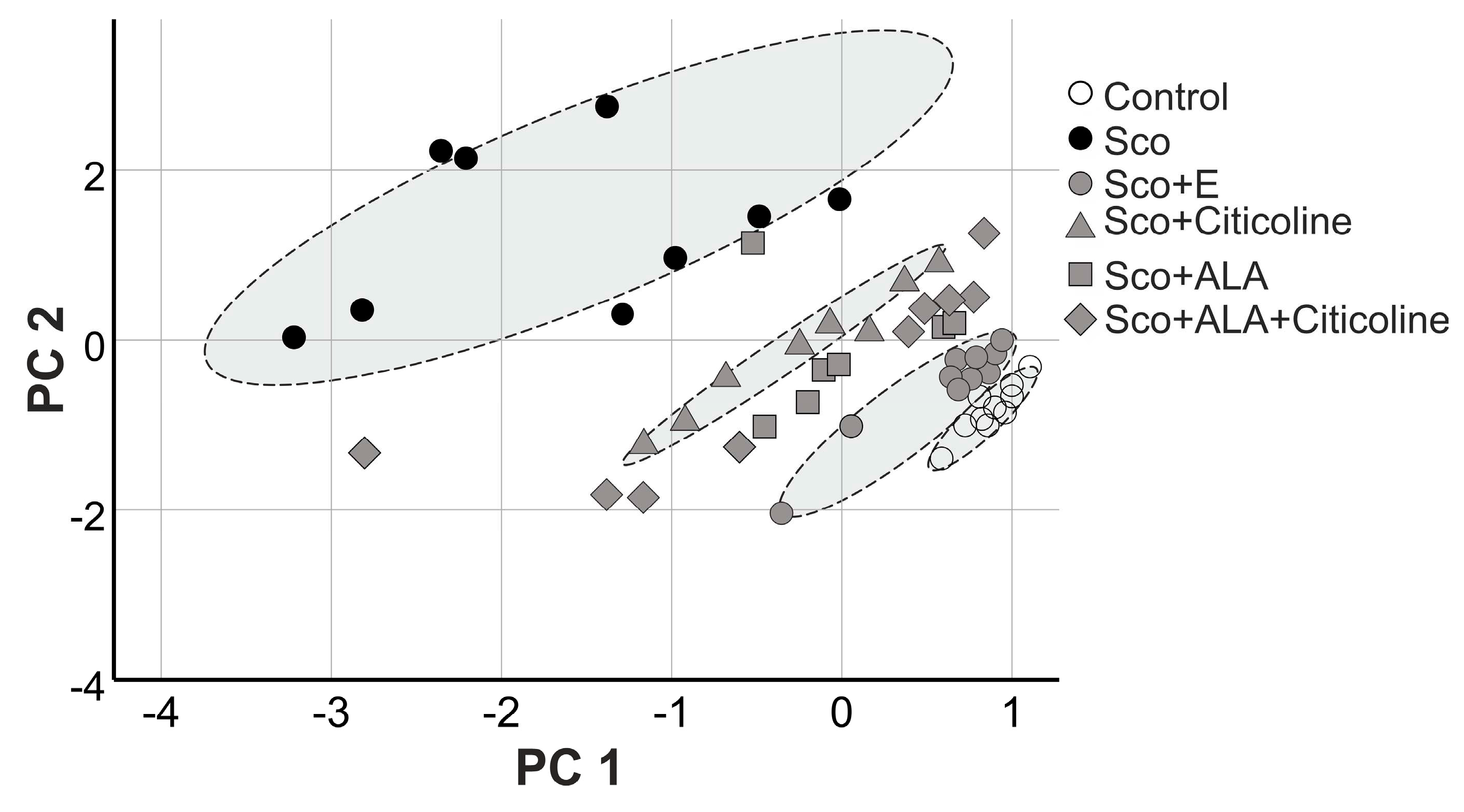
3.7.1. Evaluation of grouping of the experimental data into separate clusters
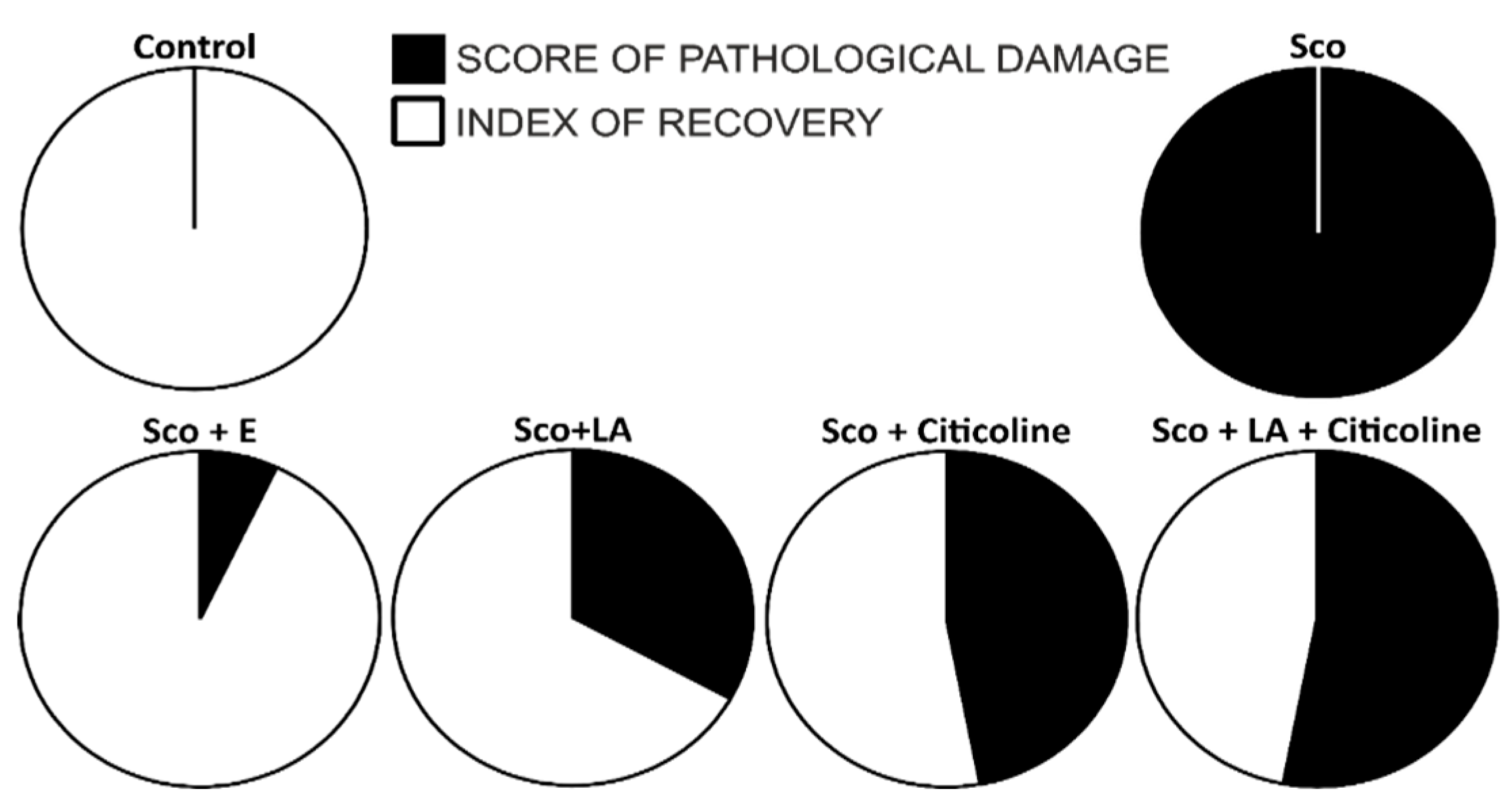
3.7.2. Relationship between pathological changes and rate of recovery-combined behavioural and histology data
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 6, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munafò, A.; Burgaletto, C.; Di Benedetto, G.; Di Mauro, M.; Di Mauro, R.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. Repositioning of Immunomodulators: A Ray of Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 614643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.D.; Carney, J.M.; Starke-Reed, P.E.; Oliver, C.N.; Stadtman, E.R.; Floyd, R.A.; Markesbery, W.R. Excess brain protein oxidation and enzyme dysfunction in normal aging and in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10540–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldeiras, I.; Santana, M.T.; Garrucho, R.; Pascoal, A.; Rodrigues, D.; Duro, C.R.; Oliveira. Peripheral oxidative damage in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2008, 15, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Hritcu, L.; Stoica, B.; Bild, W.; Stefanescu, C. Changes of some oxidative stress markers in the serum of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Rai, S.; Swarnkar, S.; Tota, S.; Nath, C.; Tyagi, N. Mechanism of oxidative stress and synapse dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Understanding the therapeutics strategies. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verri, M.; Pastoris, O.; Dossena, M.; Aquilani, R.; Guerriero, F.; Cuzzoni, G.; Venturini, L.; Ricevuti, G.; Bongiorno, A.I. Mitochondrial alterations, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshan-Barmatz, V.; Nahon-Crystal, E.; ShteinferKuzmine, A.; Gupta, R. VDAC1, mitochondrial dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimić, G.; Babić Leko, M.; Wray, S.; Harrington, C.R.; Delalle, I.; Jovanov-Milošević, N.; Bažadona, D.; Buée, L.; de Silva, R.; Di Giovanni, G.; Wischik, C.M.; Hof, P.R. Monoaminergic neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 151, 101–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.Q.; Wu, D.W.; Zhang, C.X.; Yan, R.; Yang, C.; Rong, C.P.; Zhang, L.; Chang, X.; Su, R.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; He, W.Q.; Qu, Z.; Li, S.; Su, Z.R.; Chen, Y.B.; Wang, Q.; Fang, S.H. Bushen-Yizhi formula ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative stress-related neuronal apoptosis in scopolamine-induced senescence in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amelio, M.; Rossini, P.M. Brain excitability and connectivity of neuronal assemblies in Alzheimer’s disease: from animal models to human findings. Prog Neurobiol. 2012, 99, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yin, Y.L.; Liu, X.Z.; Shen, P.; Zheng, Y.G.; Lan, X.R.; Lu, C.B.; Wang, J.Z. Current understanding of metal ions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Varma, V.R.; Varma, S.; Casanova, R.; Dammer, E.; Pletnikova, O.; Chia, C.W.; Egan, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Troncoso, J.; Levey, A.I.; Lah, J.; Seyfried, N.T.; Legido-Quigley, C.; O’Brien, R.; Thambisetty, M. Evidence for brain glucose dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018, 14, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadang, F.S.A.; Nguezeye, Y.; Kom, C.W.; Betote, P.H.D.; Mamat, A.; Tchokouaha, L.R.Y.; Taiwe, G.S.; Agbor, G.A.; Bum, E.N. Scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice: Neuroprotective effects of Carissa edulis (Forssk.) Valh (Apocynaceae) aqueous extract. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 6372059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Batool, Z.; Ahmad, S.; Siddiqui, R.A.; Haleem, D.J. Walnut supplementation reverses the scopolamine-induced memory impairment by restoration of cholinergic function via mitigating oxidative stress in rats: a potential therapeutic intervention for age related neurodegenerative disorders. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, J.E.; Sung, J.E.; Lee, H.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Bae, C.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Hwang, D.Y. α-Isocubebenol alleviates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment by repressing acetylcholinesterase activity. Neurosci Lett. 2017, 638, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puangmalai, N.; Thangnipon, W.; Soi-Ampornkul, R.; Suwanna, N.; Tuchinda, P.; Nobsathian, S. Neuroprotection of N-benzylcinnamide on scopolamine-induced cholinergic dysfunction in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Neural Regen Res. 2017, 12, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Eun, C.S.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.P.; Yang, S.A. The protective effect of fermented Curcuma longa L. on memory dysfunction in oxidative stress-induced C6 gliomal cells, proinflammatory-activated BV2 microglial cells, and scopolamine-induced amnesia model in mice. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, X.; Chen, J.; Yi, X.; Nie, D.; Sun, X.; et al. Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Prevent Memory and Neurogenesis Impairments in Scopolamine-Treated Rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, V.V.; Thandavarayan, R.A.; Sato, S.; Ko, K.M.; Konishi, T. Prevention of scopolamine-induced memory deficits by schisandrin B, an antioxidant lignan from Schisandra chinensis in mice. Free Radic. Res. 2011, 45, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.L.; Yeo, E.T.Y.; Wong, K.W.L.; See, M.L.; Wong, K.Y.; Gan, S.Y. Piper sarmentosum Roxb. Root Extracts Confer Neuroprotection by Attenuating Beta Amyloid-Induced Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Released from Microglial Cells. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2019, 16, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshahi, M.; Nickmahzar, E.G.; Babakordi, F. The effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on scopolamine-induced apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats. Anat. Sci. Int. 2013, 88, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarova, M.; Tancheva, L.; Alexandrova, A.; Tsvetanova, E.; Georgieva, A.; Stefanova, M.; Tsekova, D.; Vezenkov, L.; Kalfin, R.; Uzunova, D.; Petkova-Kirova, P. Effects of New Galantamine Derivatives in a Scopolamine Model of Dementia in Mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 84, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, S.; Alexova, R.; Dragomanova, S.; Kalfin, R.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P.; Petralia, M.C.; Mangano, K.; Tancheva, L. Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum L. Polyphenols in Neurological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Lazarova, M.; Munkuev, A.; Suslov, E.; Volcho, K.; Salakhutdinov, N.; Bibi, A.; Reynisson, J.; Tzvetanova, E.; Alexandrova, A.; Georgieva, A.; Uzunova, D.; Stefanova, M.; Kalfin, R.; Tancheva, L. New Myrtenal-Adamantane Conjugates Alleviate Alzheimer’s-Type Dementia in Rat Model. Molecules. 2022, 27, 5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomanova, S.; Pavlov, S.; Marinova, D.; Hodzev, Y.; Petralia, M.C.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; Lazarova, M.; Tzvetanova, E.; Alexandrova, A.; Kalfin, R.; Tancheva, L. Neuroprotective Effects of Myrtenal in an Experimental Model of Dementia Induced in Rats. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staykov, H.; Lazarova, M.; Hassanova, Y.; Stefanova, M.; Tancheva, L.; Nikolov, R. Neuromodulatory Mechanisms of a Memory Loss-Preventive Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid in an Experimental Rat Model of Dementia. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 72, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancheva, L.; Lazarova, M.; Velkova, L.; Dolashki, A.; Uzunova, D.; Minchev, B.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Hassanova, Y.; Gavrilova, P.; Tasheva, K.; Taseva, T.; Hodzhev, Y.; Atanasov, A.G.; Stefanova, M.; Alexandrova, A.; Tzvetanova, E.; Atanasov, V.; Kalfin, R.; Dolashka, P. Beneficial Effects of Snail Helix aspersa Extract in an Experimental Model of Alzheimer’s Type Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancheva, L.P.; Popatanasov, A.B.; Dragomanova, S.D.; Tzvetanova, E.R.; Aleksandrova, S.M.; Alova, L.G.; Stefanova, M.; Kalfin, R.E. New mechanisms in preventive effect of ellagic acid on cognition in mice with Alzheimer’s disease type dementia. Bul. Chem. Commun. 2018, 50, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksandrova, S.M.; Tancheva, L.; Dragomanova, S.; Alova, L.; Stefanova, M.; Georgieva, A.; Simeonova, L.; Pavlova, E.; Kalfin, R. Preventive effect of ellagic acid on cognitive disorders in two mouse models of oxidative stress (influenza infection and scopolamine-induced dementia). Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1651–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Shinto, L.; Quinn, J.; Montine, T.; Dodge, H.H.; Woodward, W.; Baldauf-Wagner, S.; Waichunas, D.; Bumgarner, L.; Bourdette, D.; Silbert, L.; Kaye, J. A randomized placebo-controlled pilot trial of omega-3 fatty acids and alpha lipoic acid in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 38, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharman, M.J.; Gyengesi, E.; Liang, H.; Chatterjee, P.; Karl, T.; Li, Q.X.; Wenk, M.R.; Halliwell, B.; Martins, R.N.; Münch, G. Assessment of diets containing curcumin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate, docosahexaenoic acid and α-lipoic acid on amyloid load and inflammation in a male transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: Are combinations more effective? Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 124, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molz, P.; Schröder, N. Potential Therapeutic Effects of Lipoic Acid on Memory Deficits Related to Aging and Neurodegeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Tritschler, H.J.; Wessel, K. Neuroprotection by the metabolic antioxidant alpha-lipoic acid. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadvand, H.; Jamor, P. Effects of alpha lipoic acid on level of NO and MPO activity in diabetic rats. Ann. Res. Antioxid. 2017, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Seifar, F.; Khalili, M.; Khaledyan, H.; et al. α-Lipoic acid, functional fatty acid, as a novel therapeutic alternative for central nervous system diseases: a review. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, P.; Tritschler, H.J.; Wolff, S.P. Thioctic (lipoic) acid: a therapeutic metal-chelating antioxidant? Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Chigurupati, S.; Alhowail, A.; Abdeen, A.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; Sachdeva, M.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Bungau, S. Decrypting the potential role of α-lipoic acid in Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Atwood, C.S.; Hartshorn, M.A.; Multhaup, G.; Goldstein, L.E.; Scarpa, R.C.; Cuajungco, M.P.; Gray, D.N.; Lim, J.; Moir, R.D.; Tanzi, R.E.; Bush, A.I. The A beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease directly produces hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 7609–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, K.; Luan, T.; Zang, B. Alpha-lipoic acid exerts anti-inflammatory effects on lipopolysaccharidestimulated rat mesangial cells via inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Inflammation 2015, 38, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmquist, L.; Stuchbury, G.; Berbaum, K.; Muscat, S.; Young, S.; Hager, K.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. Lipoic acid as a novel treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.S.; Feitosa, C.M.; Saldanha, G.B.; TomÃ, A.D.; Feng, D.; de Freitas, R.M. Lipoic acid inhibits caspasedependent and -independent cell death pathways and is neuroprotective against hippocampal damage after pilocarpine-induced seizures. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 97, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivazhagan, P.; Panneerselvam, C. Neurochemical changes related to ageing in the rat brain and the effect of DL-alpha-lipoic acid. Exp. Gerontol. 2002, 37, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xing, G.Q.; Barker, J.L.; Chang, Y.; Maric, D.; Ma, W.; Li, B.S.; Rubinow, D.R. Alpha-lipoic acid protects rat cortical neurons against cell death induced by amyloid and hydrogen peroxide through the Akt signalling pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 312, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.F.; Bussiere, J.R.; Hammond, R.S.; Montine, T.J.; Henson, E.; Jones, R.E.; Stackman, R.W., Jr. Chronic dietary alpha-lipoic acid reduces deficits in hippocampal memory of aged Tg2576 mice. Neurobiol. Aging. 2007, 28, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; et al. Activation of Nrf2/ARE pathway alleviates the cognitive deficits in PS1V97L-Tg mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease through modulation of oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. Res., 2019, 97, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, J.; Miklossy, J.; Atwood, C.; Martins, R. The severity of cortical Alzheimer’s type changes is positively correlated with increased amyloid-beta levels: resolubilization of amyloid-beta with transition metal ion chelators. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2001, 3, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, K.; Kenklies, M.; McAfoose, J.; Engel, J.; Münch, G. Alpha-lipoic acid as a new treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease--a 48th months follow-up analysis. J. Neural. Transm. 2007, Suppl. 72, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Fava, A.; Pirritano, D.; Plastino, M.; Cristiano, D.; Puccio, G.; Colica, C.; Ermio, C.; De Bartolo, M.; Mauro, G.; Bosco, D. The Effect of Lipoic Acid Therapy on Cognitive Functioning in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 2013, 454253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parachikova, A.; Green, K.N.; Hendrix, C.; LaFerla, F.M. Formulation of a medical food cocktail for Alzheimer’s disease: beneficial effects on cognition and neuropathology in a mouse model of the disease. PLoS One 2010, 5, e14015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secades, J.J.; Gareri, P. Citicoline: pharmacological and clinical review, 2022 update. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 75(s05), S1–S89. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, X.A.; Sampedro, C.; Lozano, R.; Cacabelos, R. Citicoline protects hippocampal neurons against apoptosis induced by brain beta-amyloid deposits plus cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 21, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauss AG, Nakazaki E.; 67 - Citicoline (CDP-Choline), Editor(s): Joseph E. Pizzorno, Michael T. Murray, Textbook of Natural Medicine (Fifth Edition), Churchill Livingstone, 2020, Pages 515-525.
- Adibhatla, R.M.; Hatcher, J.F. Citicoline decreases phospholipase A2 stimulation and hydroxyl radical generation in transient cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 73, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuki, H.; Okuda, S. Arachidonic acid as a neurotoxic and neurotrophic substance. Prog. Neurobiol. 1995, 46, 607–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Q. Arachidonic acid metabolism in health and disease. Med. Comm. 2023, 4, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasielski, P.; Piędel, F.; Piwek, M.; Rocka, A.; Petit, V.; Rejdak, K. Application of citicoline in neurological disorders: a systematic review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secades, J.J. Citicoline: pharmacological and clinical review. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 63, S1–S73. [Google Scholar]
- Gareri, P.; Castagna, A.; Cotroneo, A.M.; Putignano, S.; De Sarro, G.; Bruni, A.C. The role of citicoline in cognitive impairment: pharmacological characteristics, possible advantages, and doubts for an old drug with new perspectives. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvicini, M.; Travaglini, S.; Lelli, D.; Antonelli Incalzi, R.; Pedone, C. Is Citicoline Effective in Preventing and Slowing Down Dementia: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, P.E.; Dorado, R.; Zea-Sevilla, M.A. Role of Citicoline in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurosci. Insights 2023, 18, 26331055231152496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piamonte, B.L.C.; Espiritu, A.I.; Anlacan, V.M.M. Effects of Citicoline as an Adjunct Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I. Research Paper: Citicoline Improves Human Vigilance and Visual Working Memory: The Role of Neuronal Activation and Oxidative Stress. Basic Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Rayman, M.P. The importance of selenium to human health. The Lancet 2000, 356, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.A.; Hoffmann, P.R. The human selenoproteome: recent insights into functions and regulation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2457–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, L.V.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A.; Khanna, K.K. From selenium to selenoproteins: synthesis, identity, and their role in human health. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2007, 9, 775–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaraly, N.T.; Hininger-Favier, I.; Carriere, I.; Arnaud, J.; Gourlet, V.; Roussel, A.N.; Berr, C. Plasma selenium over time and cognitive decline in the elderly. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smorgon, C.; Mari, E.; Atti, A.R.; Dalla Nora, E.; Zamboni, P.F.; Calzoni, F.; Passaro, A.; Fellin, R. Trace elements and cognitive impairment: an elderly cohort study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2004, 9, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, B.R.; Ong, T.P.; Jacob-Filho, W.; Jaluul, O.; Freitas, M.I.; Cozzolino, S.M. Nutritional status of selenium in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, H.; Demirin, H.; Kara, Y.; Eren, I.; Delibas, N. Alterations of plasma magnesium, copper, zinc, iron and selenium concentrations and some related erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2010, 24, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loef, M.; Schrauzer, G.N.; Walach, H. Selenium and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 26, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, A.R.; Park, J.-S.; Park, J.-H.; Baik, S.-H.; Jeong, H.-Y.; Hyun, D.-H.; Park, K.W.; Jo, D.-G. Selenium attenuates A beta production and A beta-induced neuronal death. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q. Potential Roles of Selenium and Selenoproteins in the Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Iqbal, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Shen, L. Se-Methylselenocysteine (SMC) Improves Cognitive Deficits by Attenuating Synaptic and Metabolic Abnormalities in Alzheimer’s Mice Model: A Proteomic Study. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1112–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ni, J.-Z.; Song, G.-L. Selenomethionine Attenuates the Amyloid-Beta Level by Both Inhibiting Amyloid-Beta Production and Modulating Autophagy in Neuron-2a/AbetaPPswe Cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 59, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Zheng, R.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Hoffmann, P.R.; Ni, J.-Z.; Song, G.-L. Selenomethionine Mitigates Cognitive Decline by Targeting Both Tau Hyperphosphorylation and Autophagic Clearance in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Grosso, G.; Giampieri, F.; Lipari, V.; Sánchez-González, C.; Battino, M.; Quiles, J.L. Molecular Mechanisms of the Protective Effects of Olive Leaf Polyphenols against Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.M.; Al-Shami, K.M.; Yang, E.; Wang, J.; Guillaume, C.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleuropein-Rich Olive Leaf Extract Attenuates Neuroinflammation in the Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1002–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Liang, G. Oleanolic acid exerts neuroprotective effects in subarachnoid hemorrhage rats through SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 893, 173811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.P.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.T.; Luo, Z.Q. The protective effect of oleanolic acid on NMDA-induced MLE-12 cells apoptosis and lung injury in mice by activating SIRT1 and reducing NF-κB acetylation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 70, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde-Salazar, V.; Ruiz-Gabarre, D.; García-Escudero, V. Alzheimer’s Disease and Green Tea: Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate as a Modulator of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, L.D.; Thibault, V.; Chen, K.C.; Langub, M.C.; Landfield, P.W.; Porter, N.M. Vitamin D hormone confers neuroprotection in parallel with downregulation of L-type calcium channel expression in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexianu, M.E.; Robbins, E.; Carswell, S.; Appel, S.H. 1Alpha, 25 dihydroxyvitamin D3-dependent up-regulation of calcium-binding proteins in motoneuron cells. J. Neurosci Res. 1998, 51, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcion, E.; N Wion-Barbot, C.N. Montero-Menei, F. Berger, D. Wion, New clues about vitamin D functions in the nervous system. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masakazu, I.; Hideyuki, S.; Miki, N.; et al. Protective effects of 1 alpha,25-(OH)(2)D(3) against the neurotoxicity of glutamate and reactive oxygen species in mesencephalic culture. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 761–771. [Google Scholar]
- Ndrepepa, G.; Colleran, R.; Kastrati, A. Gamma-glutamyl transferase and the risk of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 476, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Meng, X. Vitamin D and neurodegenerative diseases. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasoń, W.; Jantas, D.; Leśkiewicz, M.; Regulska, M.; Basta-Kaim, A. The Vitamin D Receptor as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases Such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Narrative Review. Cells 2023, 12, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balion, C.; Griffith, L.E.; Strifler, L.; et al. Vitamin D, cognition, and dementia: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Neurology 2012, 79, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, D.J.; Lang, I.A.; Langa, K.M.; et al. Vitamin D and risk of cognitive decline in elderly persons. Arch Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, M.; Kos, K.; Lang, I.A.; Jones, K.; Melzer, D.; Llewellyn, D.J. Vitamin D and cognitive function. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2012, 72, 79–82. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.M.; Tajar, A.; Ulubaev, A.; Pendleton, N.; O’Neill, T.W.; O’Connor, D.B.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Bouillon, R.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. Association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and cognitive performance in middle-aged and older European men. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohns, T.J.; Henley, W.E.; Lang, I.A.; Annweiler, C.; Beauchet, O.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Fried, L.; Kestenbaum, B.R.; Kuller, L.H.; Langa, K.M.; et al. Vitamin D and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2014, 83, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Navarro, S.G.; Mimenza-Alvarado, A.J.; Jiménez-Castillo, G.A.; Bracho-Vela, L.A.; Yeverino-Castro, S.G.; Ávila-Funes, J.A. Association of Vitamin D with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s dementia in older Mexican adults. Rev. Invest. Clin. 2019, 71, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinzon, R.T.; Handayani, T.; Wijaya, V.O.; Buana, R.B. Low vitamin D serum levels as risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Egypt J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2023, 59, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayedi, A.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. Vitamin D status and risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis of dose-response. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, B.; Gao, F.; Wu, R.; Dong, T.; Gu, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y. Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: an updated meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2019, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarvik, M.E.; Kopp, R. An improved one-trial passive avoidance learning situation. Psychol. Rep. 1967, 21, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenk, G.L. Assessment of spatial memory using the T maze. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. Chapter 2001, 8. Unit 8.5B. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezu, M.; Malikovic, J.; Kristofova, M.; Engidawork, E.; Hoger, H.; Lubec, G.; Korz, V. Spatial working memory in male rats: Pre-experience and task dependent roles of dopamine D1- and D2- like receptors. Front Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, A.M.; Bezu, M.; Korz, V. Evaluating working memory on a T-maze in male rats. Bio. Protoc. 2018, 8, e2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, C.A. Memory deficits associated with senescence: a neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1979, 93, 74–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaceur, A.; Delacour, J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 31, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, J.R.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colori-metric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.W.; Rosenbrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randal, R.J. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 256–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budni, J.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; Mina, F.; Garcez, M.L.; Zugno, A.I. The involvement of BDNF, NGF and GDNF in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Aging Dis. 2015, 6, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanila, H. The role of BDNF in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 97 Pt B, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liskowsky, W.; Schliebs, R. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor inhibition in transgenic Alzheimer-like Tg2576 mice by scopolamine favours the amyloidogenic route of processing of amyloid precursor protein. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihaqi, S.W.; Singh, A.P.; Tiwari, M. Supplementation of Convolvulus pluricaulis attenuates scopolamineinduced increased tau and amyloid precursor protein (AbetaPP) expression in rat brain. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, H.H.; Arab, S.M.; Rizk, S.A. El-Maraghy, Bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells protect against scopolamine-induced Alzheimer-like pathological aberrations. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, D.K.; CA Ismail, D.A. Ghareeb, Differential metformin dose-dependent effects on cognition in rats: role of Akt. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, C.; Maddalena, A.; Heuser, I.; Naber, D.; Oertel, W.; Von Der Kammer, H.; Wienrich, M.; Raschig, A.; Deng, M.; Growdon, J.H.; Nitsch, R.M. Treatment with the selective muscarinic agonist talsaclidine decreases cerebrospinal fluid levels of total amyloid beta-peptide in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 920, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsch, R.M.; Deng, M.; Tennis, M.; Schoenfeld, D.; and Growdon, J.H. The selective muscarinic M1 agonist AF102B decreases levels of total Abeta in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzini, C.A.; Baldi, E.; Bucherelli, C.; Sacchetti, B.; Tassoni, G. Role of dorsal hippocampus in acquisition, consolidation and retrieval of rat’s passive avoidance response: a tetrodotoxin functional inactivation study. Brain Res 1996, 730, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, M.M.; Blake, M.G.; Acosta, G.B.; Baratti, C.M. Atropine, an anticholinergic drug, impairs memory retrieval of a high consolidated avoidance response in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 345, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, I.; da Cunha, C.; Rosat, R.; Jerusalinsky, D.; Ferreira, M.B.; Medina, J.H. Neurotransmitter receptors involved in post-training memory processing by the amygdala, medial septum, and hippocampus of the rat. Behav. Neural. Biology, 1992, 58, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeruzalinsky, D.; Cervenansky, C.; Walz, R.; Bianchin, M.; Izquierdo, I. A peptide muscarinic toxin from the Green Mamba venom shows agonist-like action in an inhibitory avoidance learning task. Eur. J. Pharm. 1993, 240, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, M.G.; Lana, D.; Pepeu, G. The integrated role of ACh, ERK and mTOR in the mechanisms of hippocampal inhibitory avoidance memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2015, 119, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Morales, S.E.; Duran-Arevalo, M.; Diaz Del Guante, M.A.; Quirarte, G.; PradoAlcalá, R.A. A threshold for the protective effect of over-reinforced passive avoidance against scopolamine-induced amnesia. Behav. Neural. Biology 1992, 57, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Saito, H.; Matsuki, N. Role of cholinergic neurotransmission in the amygdala on performances of passive avoidance learning in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 17, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, M.G.; Pazzagli, M.; Malmberg-Aiello, P.; Della, C.L.; Rakovska, A.D.; Cerbai, F.; et al. Inhibition of acetylcholine-induced activation of extracellular regulated protein kinase prevents the encoding of an inhibitory avoidance response in the rat. Neuroscience 2005, 136, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, D.; Cerbai, F.; Di Russo, J.; Boscaro, F.; Giannetti, A.; Petkova-Kirova, P.; Pugliese, A.M.; Giovannini, M.G. Hippocampal long-term memory: effect of the cholinergic system on local protein synthesis. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2013, 106, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holscher, C. Stress impairs performance in spatial water maze learning tasks. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 100, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.G.; Garrud, P.; Rawlins, J.N.; O’Keefe, J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature, 1982, 297, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.E.; Broadbent, N.J.; Squire, L.R. Impaired remote spatial memory after hippocampal lesions despite extensive training beginning early in life. Hippocampus 2005, 15, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffard, J.P.; Jarrard, L.E. Acquisition of a complex place task in rats with selective ibotenate lesions of hippocampal formation: combined lesions of subiculum and entorhinal cortex versus hippocampus. Behav. Neurosci. 1988, 102, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Zambon, N.J.; Gibbs, R.B. Selective lesion of cholinergic neurons in the medial septum by 192 IgG-saporin impairs learning in a delayed matching to position T-maze paradigm. Brain Res. 2002, 943, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, J.J.; Salamone, J.D.; Simpson, J.; Iversen, S.D.; Morris, R.G. Place navigation in rats is impaired by lesions of medial septum and diagonal band but not nucleus basalis magnocellularis. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 27, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandner, C.; Schenk, F. Septal lesions impair the acquisition of a cued place navigation task: attentional or memory deficit? Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 1998, 69, 106–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, L.S.; Glasier, M.M.; Fulop, Z.; Stein, D.G. Intraseptal injections of 192 IgG saporin produce deficits for strategy selection in spatial-memory tasks. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 90, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, O.; Grottick, A.J.; Cassel, J.C.; Higgins, G.A. A double dissociation between serial reaction time and radial maze performance in rats subjected to 192 IgGsaporin lesions of the nucleus basalis and/or the septal region. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandeis, R.; Dachir, S.; Sapir, M.; Levy, A.; Fisher, A. Reversal of age-related cognitive impairments by an M1 cholinergic agonist, AF102B. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1990, 36, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, D.B., Jr.; Lindner, M.D.; Hogan, J.B.; Jones, K.M.; Markus, E.J. Scopolamine induced deficits in a battery of rat cognitive tests: comparisons of sensitivity and specificity. Behav. Pharmacol. 2009, 20, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.; Harper, D.N.; Hunt, M. Differential effects of MDMA and scopolamine on working versus reference memory in the radial arm maze task. Neurobiol. Learn. Memory, 2010, 93, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Ma, S.X.; Joo, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jang, C.G. Inhibitory Effects of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Bark on Scopolamine-Induced Learning and Memory Deficits in Mice. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2013, 21, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spowart-Manning, L.; van der Staay, F. The T-maze continuous alternation task for assessing the effects of putative cognition enhancers in the mouse. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 151, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadang, F.S.A.; Nguezeye, Y.; Kom, C.W.; Betote, P.H.D.; Mamat, A.; Tchokouaha, L.R.Y.; Taiwe, G.S.; Agbor, G.A.; Bum, E.N. Scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice: Neuroprotective effects of Carissa edulis (Forssk.) Valh (Apocynaceae) aqueous extract. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis 2020, 6372059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Ng, C.P.; O’Callaghan, M.; Jensen, G.S.; Wong, H.J. In vitro and ex-vivo cellular antioxidant protection and cognitive enhancing effects of an extract of Polygonum minus Huds (Lineminus™) demonstrated in a Barnes Maze animal model for memory and learning. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Nishizawa, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Sakata, S.; Kobayashi, K. Distinct roles of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in spatial and object recognition memory. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kwon, D.A.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, W.K. Standardized Extract (HemoHIM) Protects against Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia in a Murine Model. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 8884243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Sevilla, D.; Núñez, A.; Buño, W. Muscarinic Receptors, from Synaptic Plasticity to its Role in Network Activity. Neuroscience 2021, 456, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drever, B.D.; Riedel, G.; Platt, B. The cholinergic system and hippocampal plasticity. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.E.; Vazdarjanova, A.; McGaugh, J.L. Muscarinic cholinergic influences in memory consolidation. Neurobiol. Learn Mem. 2003, 80, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.Q.; Xu, Y.J.; Yang, C.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Cai, H.B.; Hou, B.N.; Chen, H.F.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.G.; Zhang, S.J. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunctions via improving cholinergic system. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9852536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Tamboli, R.S.; Seth, B.; Kanhed, A.M.; Tiwari, S.K.; Agarwal, S.; Nair, S.; Giridhar, R.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Yadav, M.R. Neuroprotective role of novel triazine derivatives by activating Wnt/ catenin signaling pathway in rodent models of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyemi, A.J.; Oboh, G.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Ogunsuyi, O. Anti-amnestic effect of curcumin in combination with donepezil, an anticholinesterase drug: Involvement of cholinergic system. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.; Kaundal, M.; Banslav, V. Caffeic acid attenuates oxidative stress, learning and memory deficit in intra-cerebroventricular streptozotocin induced experimental dementia in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 81, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoupaye, G.T.; Yassi, F.B.; Bahane, D.A.N.; Bum, E.N. Combined corticosterone treatment and chronic restraint stress lead to depression associated with early cognitive deficits in mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 33, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.E.; Perez, D.R.; Alvarez, A.; Garrido, J.; Gentry, M.K.; Doctor, B.P.; Inestrosa, N.C. A monoclonal antibody against acetylcholinesterase inhibits the formation of amyloid fibrils induced by the enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.; Alarcon, R.; Opazo, C.; Campos, E.O.; Munoz, F.J.; Calderon, F.H.; Dajas, F.; Gentry, M.K.; Doctor, B.P.; De ´ Mello, F.G.; Inestrosa, N.C. Stable complexes involving acetylcholinesterase and amyloid-beta peptide change the biochemical properties of the enzyme and increase the neurotoxicity of Alzheimer’s fibrils. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Takahashi, T.; Sumitani, K.; Takatsu, H.; Urano, S. Glucocorticoid generates ROS to induce oxidative injury in the Hippocampus, leading to impairment of cognitive function of rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 47, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Irving, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Han, W.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, T.; Song, F.; Zhao, X.; Xie, K. Oxidative Stress Mediated Hippocampal Neuron Apoptosis Participated in Carbon Disulfide-Induced Rats Cognitive Dysfunction. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.R.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, A.; Meena, R.C.; Nanda, S.; Mishra, K.P.; Singh, S.B. Heat stress induced oxidative damage and perturbation in BDNF/ERK1/2/CREB axis in hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 396, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, C. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Bull. 2014, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, A.; Doctrow, S.; Baudry, M. Prevention of cognitive defcits and brain oxidative stress with superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetics in aged mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, L.; Raber, J.; Kekonius, L.; Yan, F.; Yu, G.Q.; Bien-Ly, N.; Puoliväli, J.; Scearce-Levie, K.; Masliah, E.; Mucke, L. Reduction in mitochondrial superoxide dismutase modulates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and accelerates the onset of behavioral changes in human amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5167–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibhatla, R.M.; Hatcher, J.F.; Dempsey, R.J. Citicoline: neuroprotective mechanisms in cerebral ischemia. J. Neurochem. 2002, 80, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminzadeh, A.; Salarinejad, A. Citicoline protects against lead-induced oxidative injury in neuronal PC12 cells. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2019, 97, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikravesh, M.; Mahdavinia, M.; Neisi, N.; Khorsandi, L.; Khodayar, M.J. Citicoline ameliorates arsenic-induced hepatotoxicity and diabetes in mice by overexpression of VAMP2, PPAR-γ, As3MT, and SIRT3. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 192, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamro, A.A.; Alsulami, E.A.; Almutlaq, M.; Alghamedi, A.; Alokail, M.; Haq, S.H. Therapeutic Potential of Vitamin D and Curcumin in an In Vitro Model of Alzheimer Disease. J. Cent. Nerv. Sys. Dis. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, O.; Amit, T.; Mandel, S.; Youdim, M.B. Neuroprotective molecular mechanisms of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: a reflective outcome of its antioxidant, iron chelating and neuritogenic properties. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somova, L.I.; Shode, F.O.; Ramnanan, P.; Nadar, A. Antihypertensive, antiatherosclerotic and antioxidant activity of triterpenoids isolated from Olea europaea, subspecies africana leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekanski, D.; Selaković, V.; Piperski, V.; Radulović, Z.; Korenić, A.; Radenović, L. Protective effect of olive leaf extract on hippocampal injury induced by transient global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in Mongolian gerbils. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghari, A.A.; Hosseini, M.; Bafadam, S.; Rakhshandeh, H.; Farazandeh, M.; Mahmoudabady, M. Olea europaea L. (olive) leaf extract ameliorates learning and memory deficits in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2022, 12, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Nabeshima, T. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB signaling in memory processes. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2003, 91, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia, S.; Silhol, M.; Moulière, F.; Meffre, J.; Höllinger, I.; Maurice, T.; Tapia-Arancibia, L. Protective effect of BDNF against beta-amyloid induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo in rats. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 31, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.; Lee, K.Y.; Huh, J.; Choi, J.H.; Yang, H.; Jeong, E.J.; Kim, H.P.; Sung, S.H. Cognitive-enhancing effects of Rhus verniciflua bark extract and its active flavonoids with neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 58, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastropasqua, L.; Agnifili, L.; Ferrante, C.; Sacchi, M.; Figus, M.; Rossi, G.C.M.; Brescia, L.; Aloia, R.; Orlando, G. Citicoline/Coenzyme Q10/Vitamin B3 Fixed Combination Exerts Synergistic Protective Effects on Neuronal Cells Exposed to Oxidative Stress. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, W.J.; Alonso, M.; Bramham, C.R.; Pozzo-Miller, L.D. From the acquisition to consolidation: on the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in hippocamal-dependent learning. Learn. Mem. 2002, 9, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolotti, N.; Lazarov, O. CREB signals as PBMC-based biomarkers of cognitive dysfunction: A novel perspective of the brain-immune axis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 78, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Mizuno, M.; Nabeshima, T. Role for Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci. 2002, 70, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Rossetti, A.C.; Brandwein, C.; Riva, M.A.; Gass, P.; Elsner, P.; Hesse-Macabata, J.; Hipler, U.C.; Smesny, S.; Milleit, B. Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Deficiency is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Elevated Phospholipase A2 Activity in Plasma of Mice. Neuroscience 2022, 480, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarelainen, T.; Pussinen, R.; Koponen, E.; Alhonen, L.; Wong, G.; Sirviö, J.; Castrén, E. Transgenic mice overexpressing truncated trkB neurotrophin receptors in neurons have impaired long-term spatial memory but normal hippocampal LTP. Synapse 2000, 38, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.-S.; Li, W.-P.; Yao, Z.-B.; Zhou, X.-F. Deprivation of endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor results in impairment of spatial learning and memory in adult rats. Brain Res. 1999, 835, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Vianna, M.R.M.; Depino, A.M.; e Souza, T.M.; Pereira, P.; Szapiro, G.; Viola, H.; Pitossi, F.; Izquierdo, I. and Medina JH: BDNF-triggered events in the rat hippocampus are required for both short- and long-term memory formation. Hippocampus 2002, 12, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.R.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, A.; Meena, R.C.; Nanda, S.; Mishra, K.P.; Singh, S.B. Heat stress induced oxidative damage and perturbation in BDNF/ERK1/2/CREB axis in hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 396, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourtchuladze, R.; Frenguelli, B.; Blendy, J.; Cioffi, D.; Schutz, G.; Silva, A.J. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell 1994, 79, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




