Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
03 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Location modeling for emergency medical facility planning
2.2. Integration facility dispersion models with other location problems
3. Methodology
3.1. The p-dispersed-median (p-DIME) model
-
Indexi, j: index for candidate facilities for LEMIs,k: index for demand area k,N: a set of the candidate facilities for LEMIs, andL: a set of the demand areas.
-
Decision variablesYi: 1 if a LEMI is located at the candidate facility site i; 0 otherwise,Xik: 1 if demand k is served by facility site i; 0 otherwise,Zij: 1 if LEMIs are located at i and j; 0 otherwise, andD: the smallest separation distance between any pair of assigned facilities.
-
Parameter inputsp: the number of facility sites to be open for LEMIs,dij: the shortest path (travel-time) distance between facilities i and j,fk: weights at demand area k (a measure of the population in our models),M: a large number that exceeds the maximum value of dij, anddopt: the optimal objective value pre-obtained from the p-dispersion model at p.
3.2. Auxiliary pre-informed lower bound (APRIL) constraint
3.3. Defining a service coverage standard of LEMIs
3.4. Data
4. Analysis and Implications
4.1. Assessment of service coverage by planning scenarios
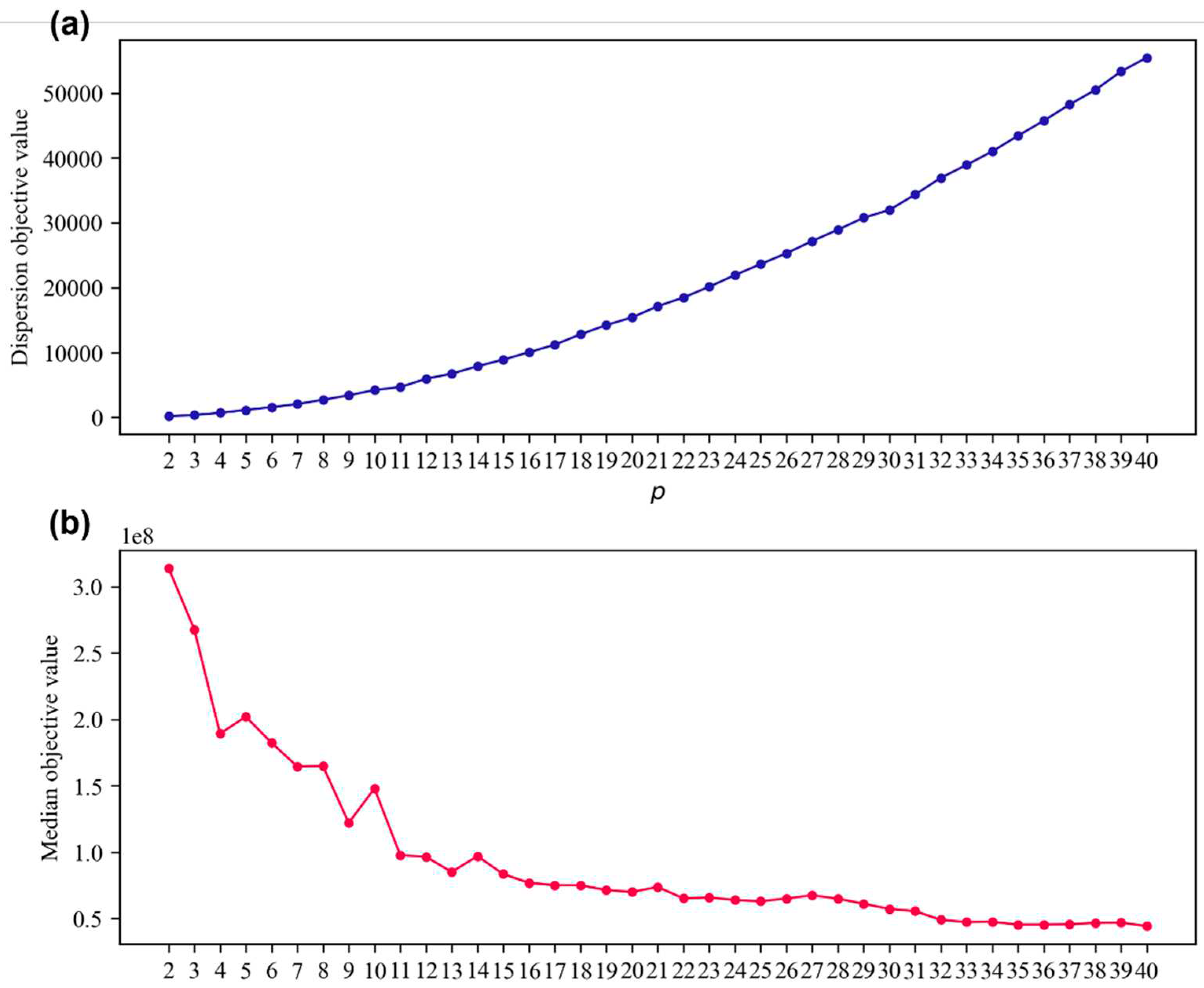
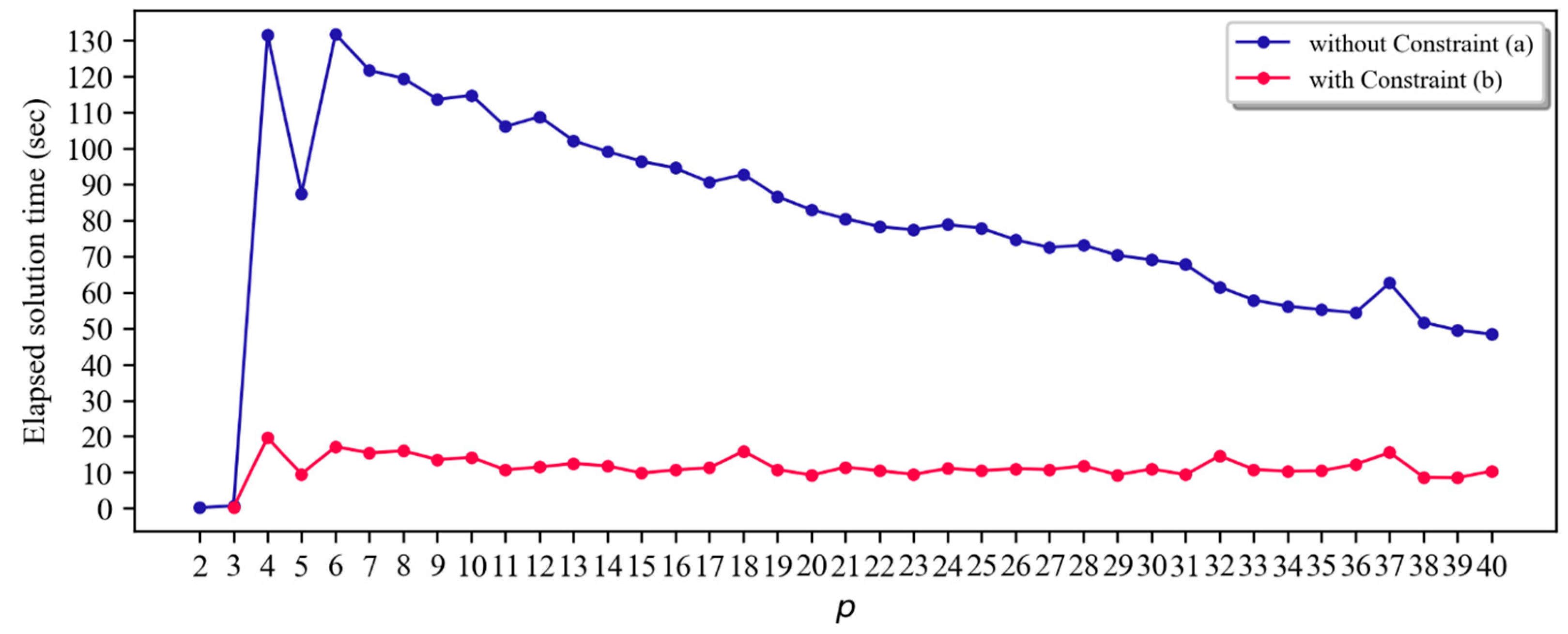
4.2. Computational efficience of the p-DIME models for planning scenarios
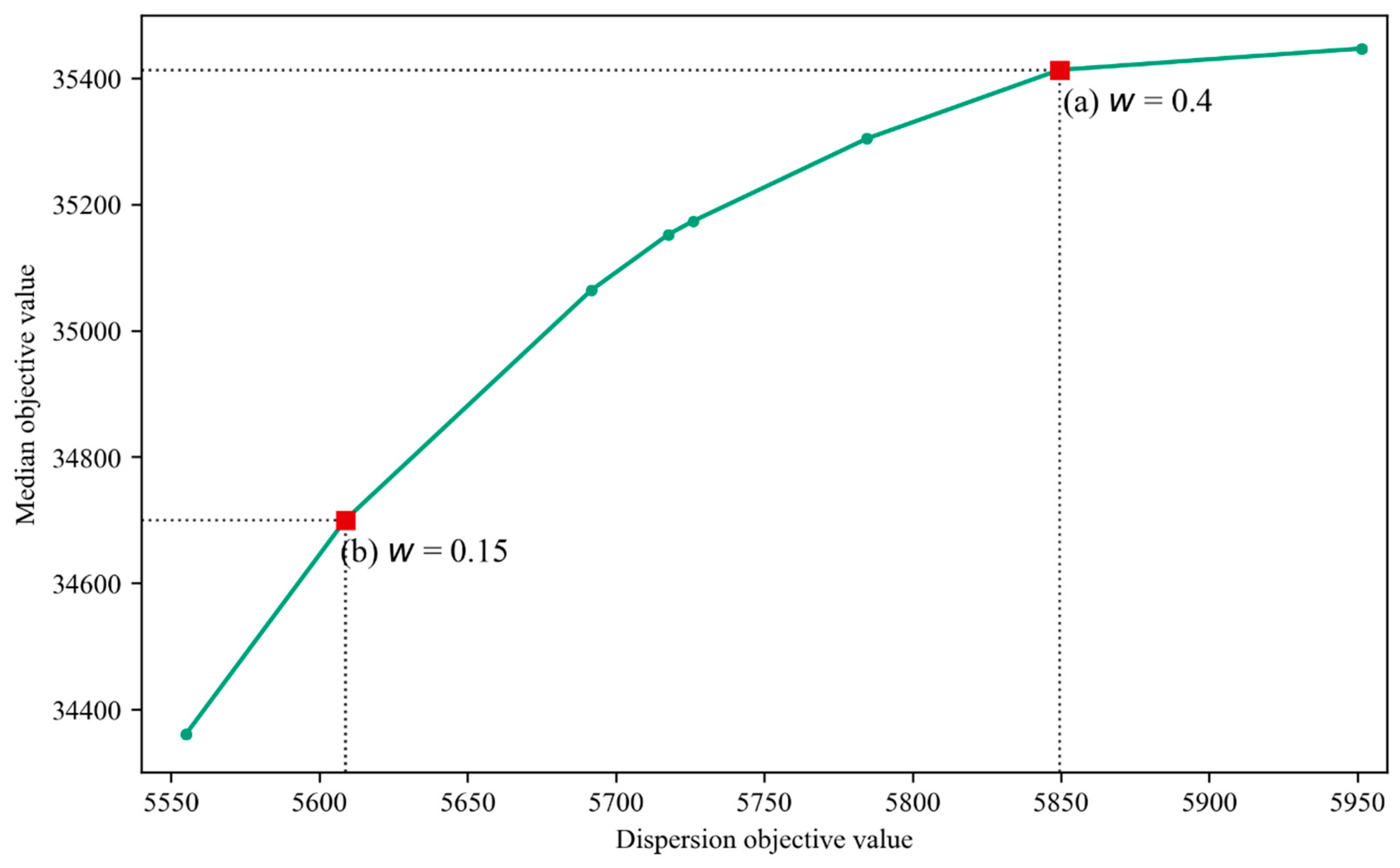
4.3. Trade-off between dispersion and median of LEMIs
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin SD, Ong MEH, Tanaka H, Ma MH-M, Nishiuchi T, Alsakaf O, Karim SA, Khunkhlai N, Lin C-H, Song KJ, Ryoo HW, Ryu HH, Tham LP, Cone DC. Comparison of Emergency Medical Services System Across Pan-Asian Countries: A Web-based Survey. Prehospital Emergency Care 2012, 16(4), 477-496. [CrossRef]
- Arnold JL, Song HS, Chung, JM. The Recent Development of Emergency Medicine in South Korea. Annals of Emergency Medicine 1998, 32(6), 730-735. [CrossRef]
- 3Herbert A, Gilbert R, González-Izquierdo A, Pitman A, Li L. 10-y Risks of Death and Emergency Re-admission in Adolescents Hospitalised with Violent, Drug- or Alcohol-Related, or Self-Inflicted Injury: A Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS Med 2015, 12(12),e1001931. [CrossRef]
- Chea H. Kim H. Shaw S. Chun Y. Assessing trauma center accessibility for healthcare equity using anti-covering approach. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19(3), 1459. [CrossRef]
- Lee H. Spatial Distribution of the Emergency Medical Facilities and Spatial Disparity of the Demand-Supply Level for the Emergency Medical Service. Journal of the Korean Association of Regional Geographers 2004, 10(3), 606-623.
- Cho J, You M, Yoon Y. Characterizing the influence of transportation infrastructure on Emergency Medical Services (EMS) in urban area – A case study of Seoul, South Korea. PloS ONE 2017, 12(8), e0183241. [CrossRef]
- Khubchandani JA, Shen C, Ayturk D, Kiefe CI, Santry HP. Disparities in access to emergency general surgery care in the United States. Surgery 2017, 163, 243-250. [CrossRef]
- Ge E, Su M, Zhao R, Huang Z, Shan Y, Wei X. Geographical disparities in access to hospital care in Ontario, Canada: a spatial coverage modelling approach. BMJ open 2021, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Mao L, Nekorchuk D. Measuring spatial accessibility to healthcare for populations with multiple transportation modes. Health & place 2013, 24, 115-122. [CrossRef]
- Im J, Park J. Spatial Distribution of Underserved Emergency Medical Service Areas and Their Residents’ Atrributes – Focusing on Chungnam Province. Journal of Korea Planning Association 2016, 51(1), 63-75. [CrossRef]
- Yun SB, Kim S, Ju S, Noh J, Kim C, Wong MS, Heo J. Analysis of accessibility to emergency rooms by dynamic population from mobile phone data: Geography of social inequity in South Korea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(4), e0231079. [CrossRef]
- National Geographic Information Institute. 2020 National Territorial Monitoring Report, NGII, Suwon: South Korea; 2021.
- Ahmadi-Javid A. Seyedi P. Syam SS. A Survey of Healthcare Facility Location. Computers & Operations Research 2017, 79, 223-263. [CrossRef]
- Kuby MJ. Programming Models for Facility Dispersion: The p-Dispersion and Maxisum Dispersion Problems. Geographical Analysis 1987, 19(4), 315-329. [CrossRef]
- Hakimi SL. Optimum Locations of Switching Centers and the Absolute Centers and Medians of a Graph. Operations Research 1964, 12(3), 450-459. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Zhao Z, Zhu X, Wyatt. T. Covering models and optimization techniques for emergency response facility location and planning: a review. Mathematical Methods of Operations Research 2011, 74, 281-310. [CrossRef]
- Toregas C, Swain R, ReVelle C, Bergman, L. The Location of Emergency Service Facilities. Operations Research 1971, 19(6), 1363-1373. [CrossRef]
- Church R, ReVelle C. The maximal covering location problem. In Papers of the regional science association 1974, 32(1), 101-118.
- Church RL, Murray AT. Business Site Selection, Location Analysis and GIS. Hoboken. NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2009.
- Daskin M, Stern E. A Hierarchical Objective Set Covering Model for Emergency Medical Service Vehicle Deployment. Transportation Science 1981, 15(2), 137-152. [CrossRef]
- Eaton D, Daskin M, Simmons D, Bulloch B, Jansma G. Determining Emergency Medical Service Vehicle Deployment in Austin, Texas. Interfaces 1985, 15(1), 96-108. [CrossRef]
- Jia H, Ordones F, Dessouky M. A Modeling Framework for Facility Location of Medical Services for Large-Scale Emergencies. IIE Transactions 2007, 39(1), 41-55. [CrossRef]
- Ye H, Kim H. Locating healthcare facilities using a network-based covering location problem. GeoJournal 2016, 81, 875–890. [CrossRef]
- ReVelle, CS, Swain RW. Central facilities location. Geographical Analysis 1970, 2(1), 30-42. [CrossRef]
- Caccetta L, Dzator M. Heuristic Methods for Locating Emergency Facilities. Proceedings Modsim 2005.
- Indriasari V, Mahmud AR, Ahmad N, Shariff ARM. Maximal Service Area Problem for Optimal Siting of Emergency Facilities. International Journal of Geographical Information Science 2010, 24(2), 213-230. [CrossRef]
- Daskin MS. Network and discrete location: models, algorithms and applications. Hoboken. NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 1995.
- Shier DR. A min-max theorem for p-center problems on a tree, Transportation Science, 1977, 11(3), 243-252.
- Lei TL, Church RL. A Unified Model for Dispersing Facilities. Geographical Analysis 2013, 45, 401-418. [CrossRef]
- Curtin KM. Church RL. A Family of Location Models for Multiple-Type Discrete Dispersion. Geographical Analysis 2006, 38, 248-270. [CrossRef]
- Erkut E, Neuman S. Analytical Models for Locating Undesirable Facilities. European Journal of Operational Research 1989, 40, 277-291. [CrossRef]
- Curtin KM, Church RL. Optimal Dispersion and Central Places. Journal of Geographical Systems 2007, 9, 167-187. [CrossRef]
- Erkut E. Neuman S. Comparison of Four Models for Dispersing Facilities. INFOR: Information Systems and Operational Research 1991, 29(2), 68-86. [CrossRef]
- Erkut E. Neuman S. A multiobjective model for locating undesirable facilities. Annals of Operations Research 1992, 40, 209-227. [CrossRef]
- Maliszewski PJ. Kuby MJ. Horner MW. A Comparison of Multi-objective Spatial Dispersion Models for Managing Critical Assets in Urban Areas. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 2012, 36, 331-341. [CrossRef]
- Erkut E. The discrete p-dispersion problem. Journal of Operational Research 1990, 46(1), 48-60. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, O’Kelly ME. Reliable p-hub location problems in telecommunication networks. Geographical Analysis 2009, 41(3), 283-306. [CrossRef]
- Garey MR, Johnson DS. Computers and intractability. San Francisco: Freeman; 1979.
- Akinc U, Khumawala BM. An Efficient Branch and Bound Algorithm for the Capacitated Warehouse Location Problem. Management Science 1977, 23(6), 585-594. [CrossRef]
- IBM. Branch and Cut in CPLEX, ILOG CPLEX Optimization Studio 12.10.0 Documentation; 2019. https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/icos/12.10.0?topic=concepts-branch-cut-in-cplex.
- Guzelsoy M, Nemhauser G, Savelsbergh M. Restrict-and-relax search for 0-1 mixed-integer programs. European Journal on Computational Optimization 2013, 1, 201–218. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, Chun Y, Kim K. Delimitation of Functional Regions Using a p-Regions Problem Approach. International Regional Science Review 2015, 38(3), 235-263. [CrossRef]
- Lerner EB, Moscati RM. The Golden Hour: Scientific Fact or Medical “Urban Legend”?. Academic Emergency Medicine 2001, 8, 758-760. [CrossRef]
- Vanderschuren M, McKune D. Emergency Care Facility Access in Rural Areas within the Golden Hour?: Western Cape Case Study. International Journal of Health Geographics 2015, 14(5), 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Cohon JL. Multiobjective programming and planning. New York: Academic Press; 1978.
- Griffith D, Chun Y, Kim H. Spatial autocorrelation informed approaches to solving location–allocation problems. Spatial Statistics 2022. [CrossRef]
- Jenks GF. Optimal data classification for choropleth maps. Department of Geography, University of Kansas Occasional Paper 1977.
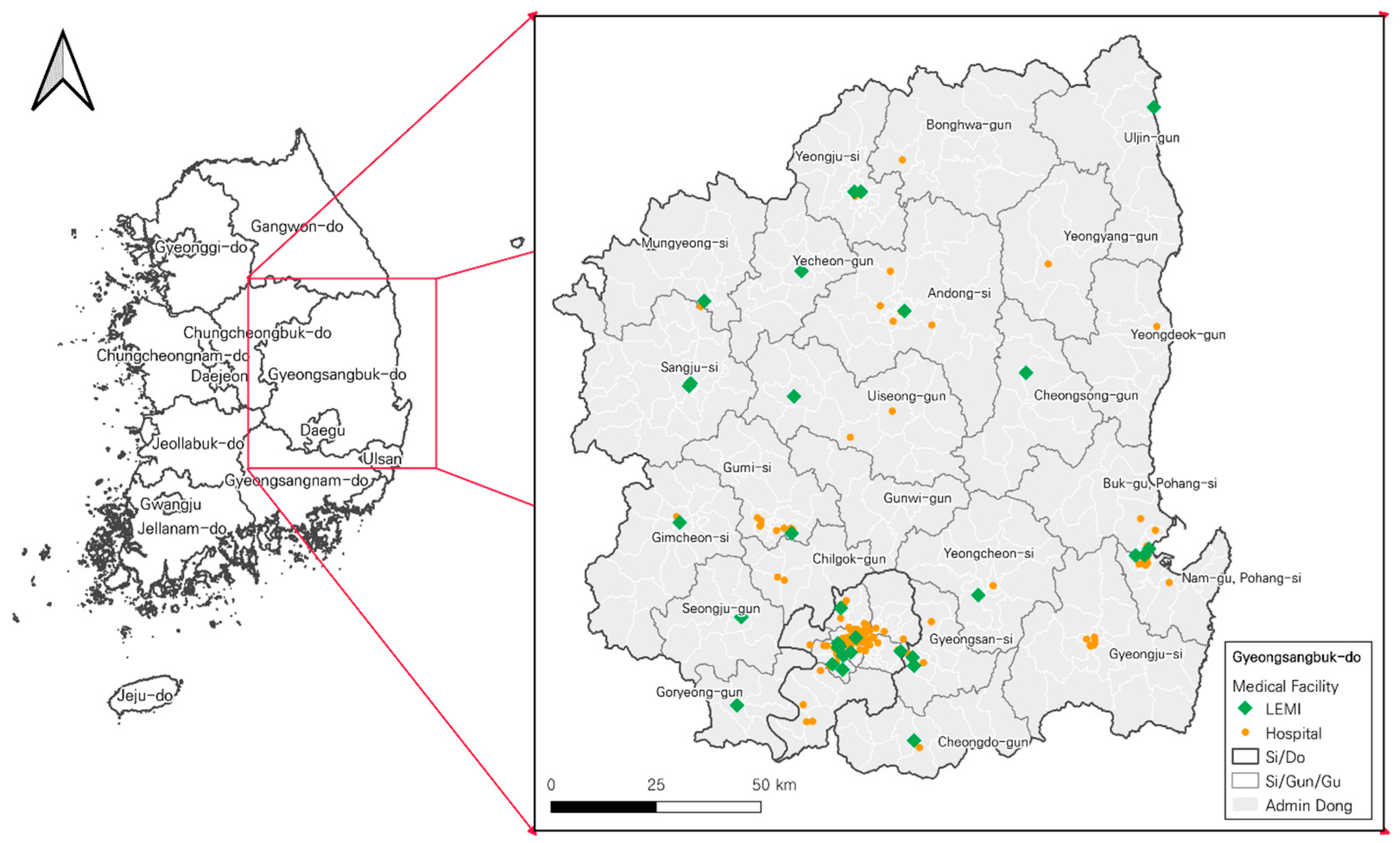
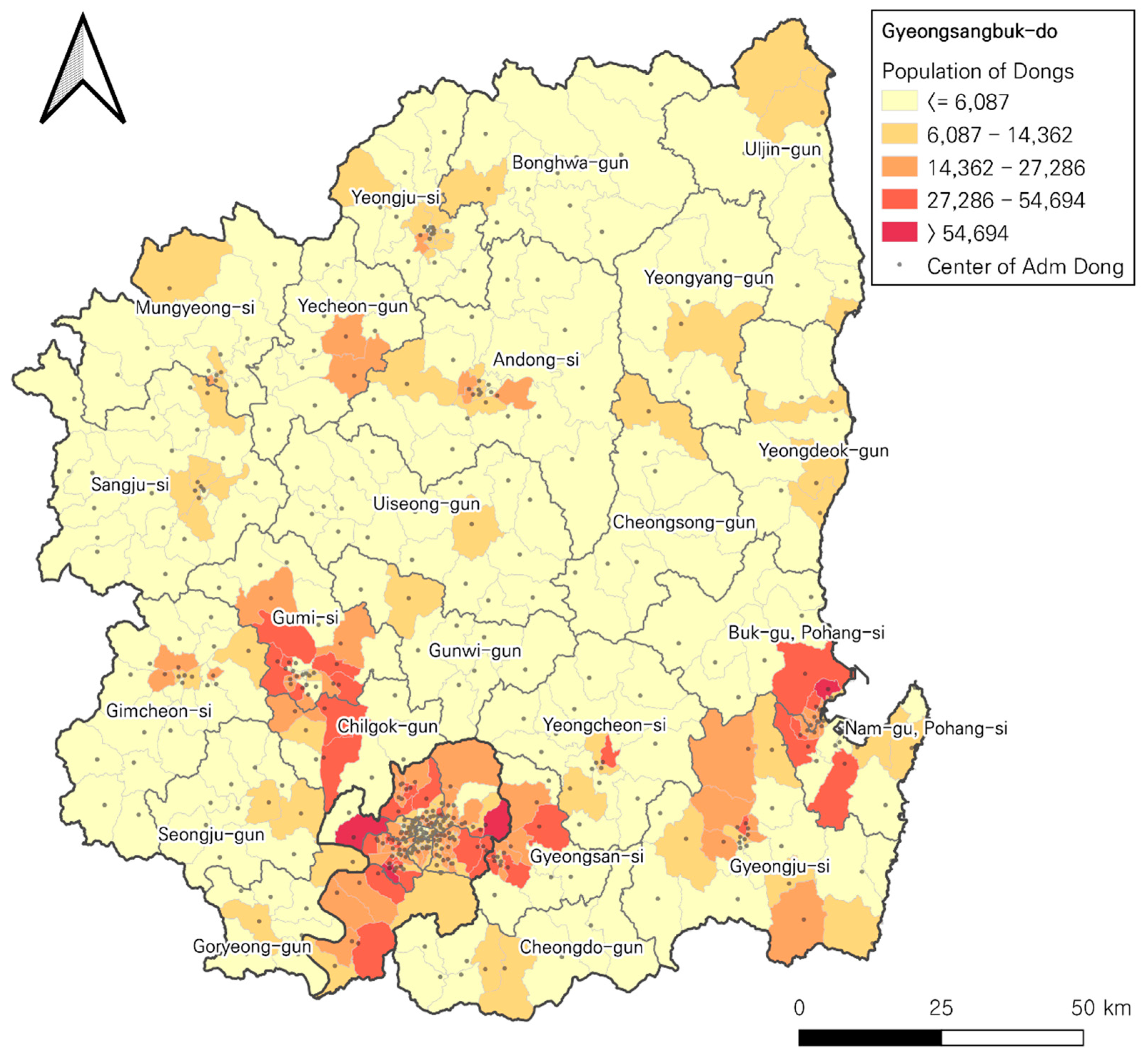
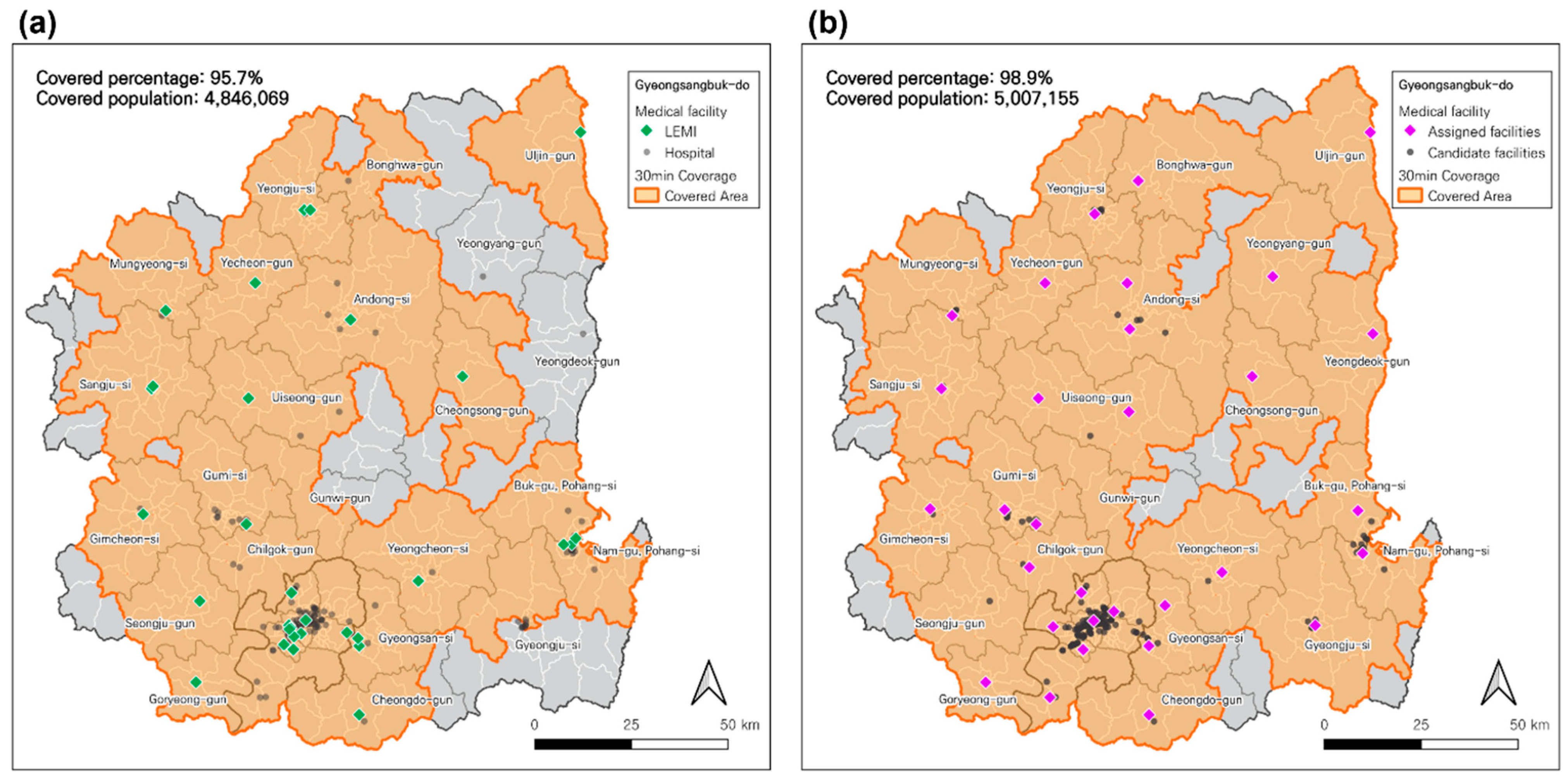
| p | Maxisum Dispersion (A) | p-DIME (B) | Current location of the LEMIs (C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covered population | % | Covered population | % | Covered population | % | |
| 2 | 196,780 | 3.9 | 196,780 | 3.9 | - | - |
| 10 | 1,861,864 | 36.8 | 2,138,988 | 42.2 | - | - |
| 20 | 4,942,982 | 97.6 | 4,967,938 | 98.1 | - | - |
| 30 | 4,980,951 | 98.3 | 4,999,462 | 98.7 | - | - |
| 31 | 4,980,951 | 98.3 | 5,007,155 | 98.9 | 4,846,069 | 95.7 |
| 40 | 4,986,485 | 98.5 | 5,011,482 | 98.9 | - | - |
| p | Objective Value | p-DIME without APRIL (A) | p-DIME with APRIL (B) | Sol. Time reduction | ||||
| Time(s) (c) | Nodes | Iterations | Time(s) (d) | Nodes | Iterations | |||
| 2 | 173.6 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | - | 0 | - | - |
| 3 | 368.1 | 0.7 | 0 | 1,785 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 50.7 |
| 10 | 4,213.7 | 114.7 | 0 | 25,583 | 14.2 | 0 | 25,932 | 87.6 |
| 20 | 15,411.7 | 82.9 | 0 | 18,868 | 9.2 | 0 | 18,057 | 88.9 |
| 30 | 31,978.6 | 69.0 | 0 | 17,697 | 11.0 | 0 | 18,484 | 84.1 |
| 31 | 34,360.8 | 67.7 | 0 | 22,218 | 9.4 | 0 | 22,031 | 86.2 |
| 40 | 55,478.5 | 48.4 | 0 | 21,181 | 10.4 | 0 | 20,045 | 78.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





