Submitted:
02 November 2023
Posted:
03 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
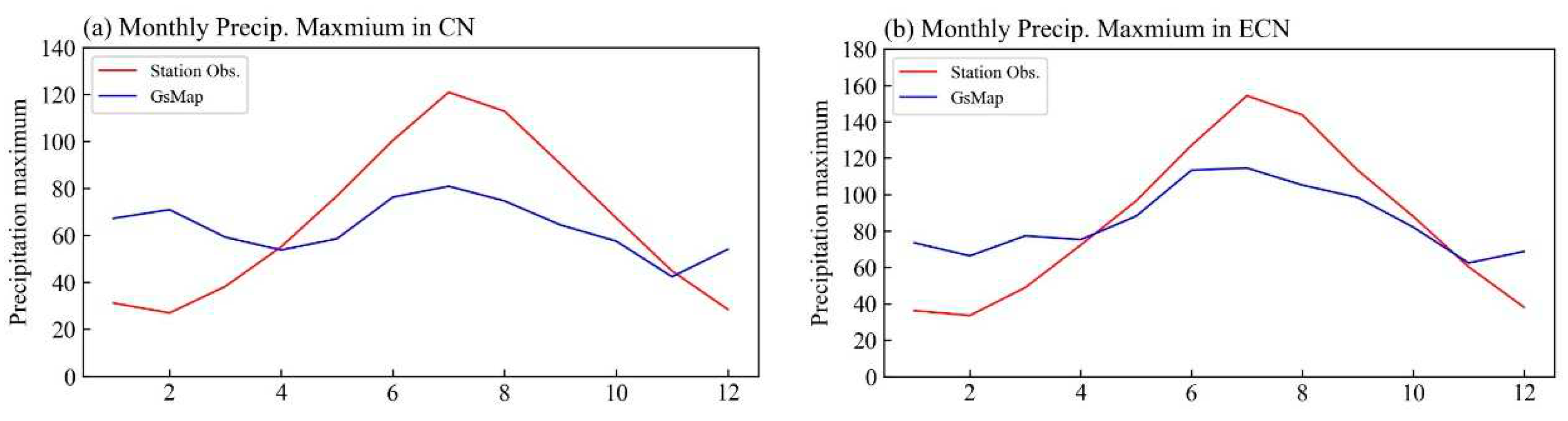
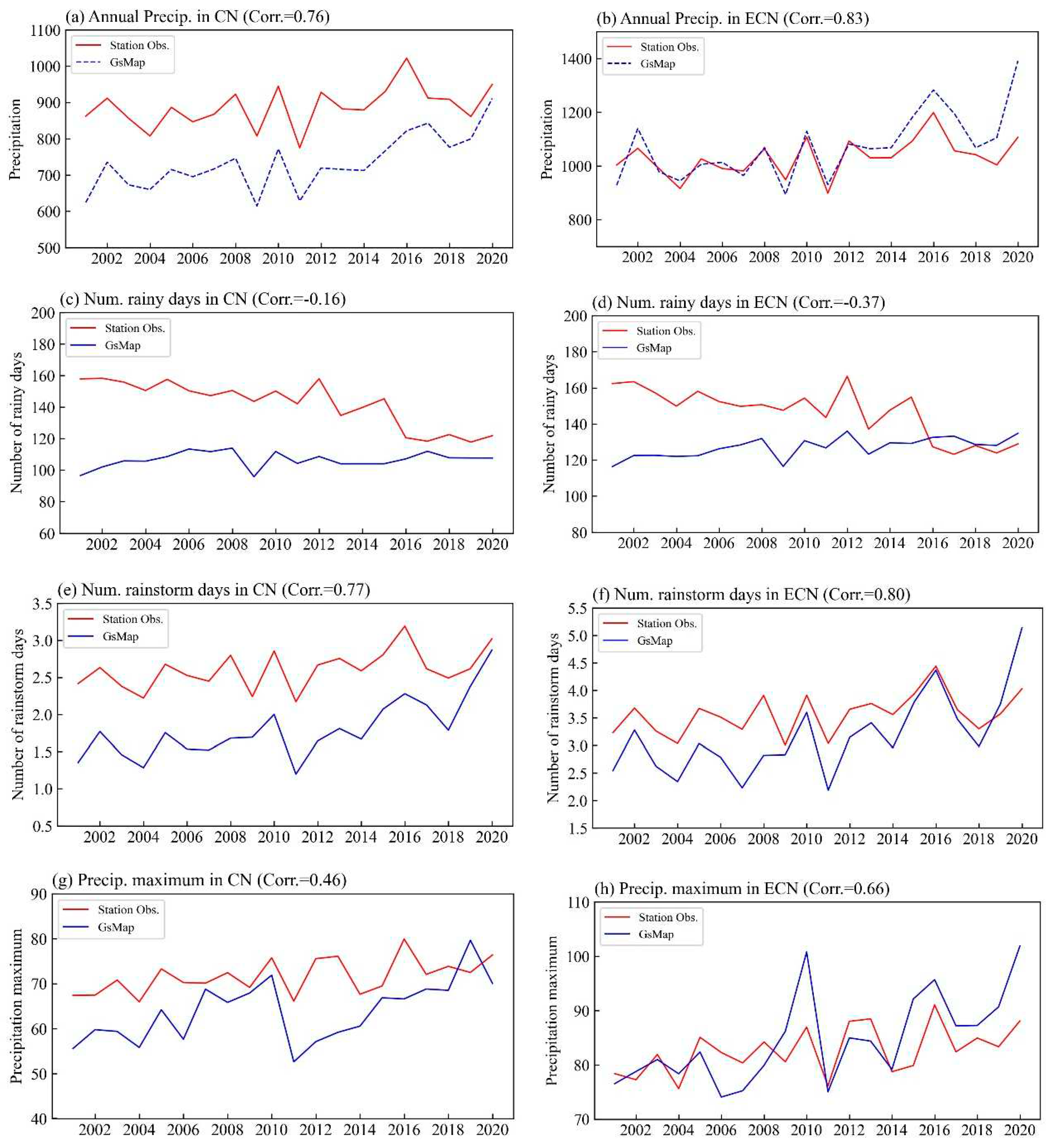
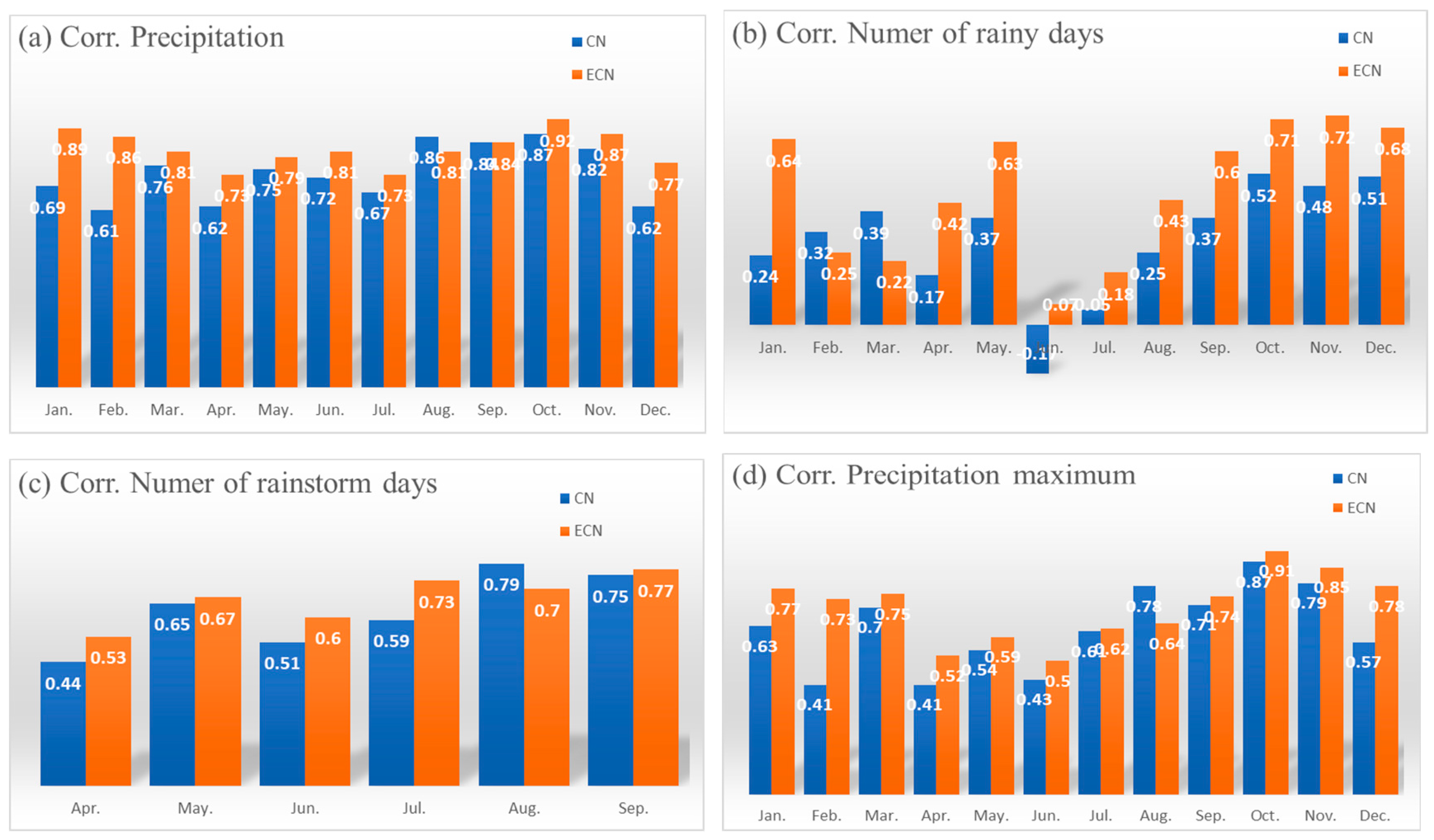
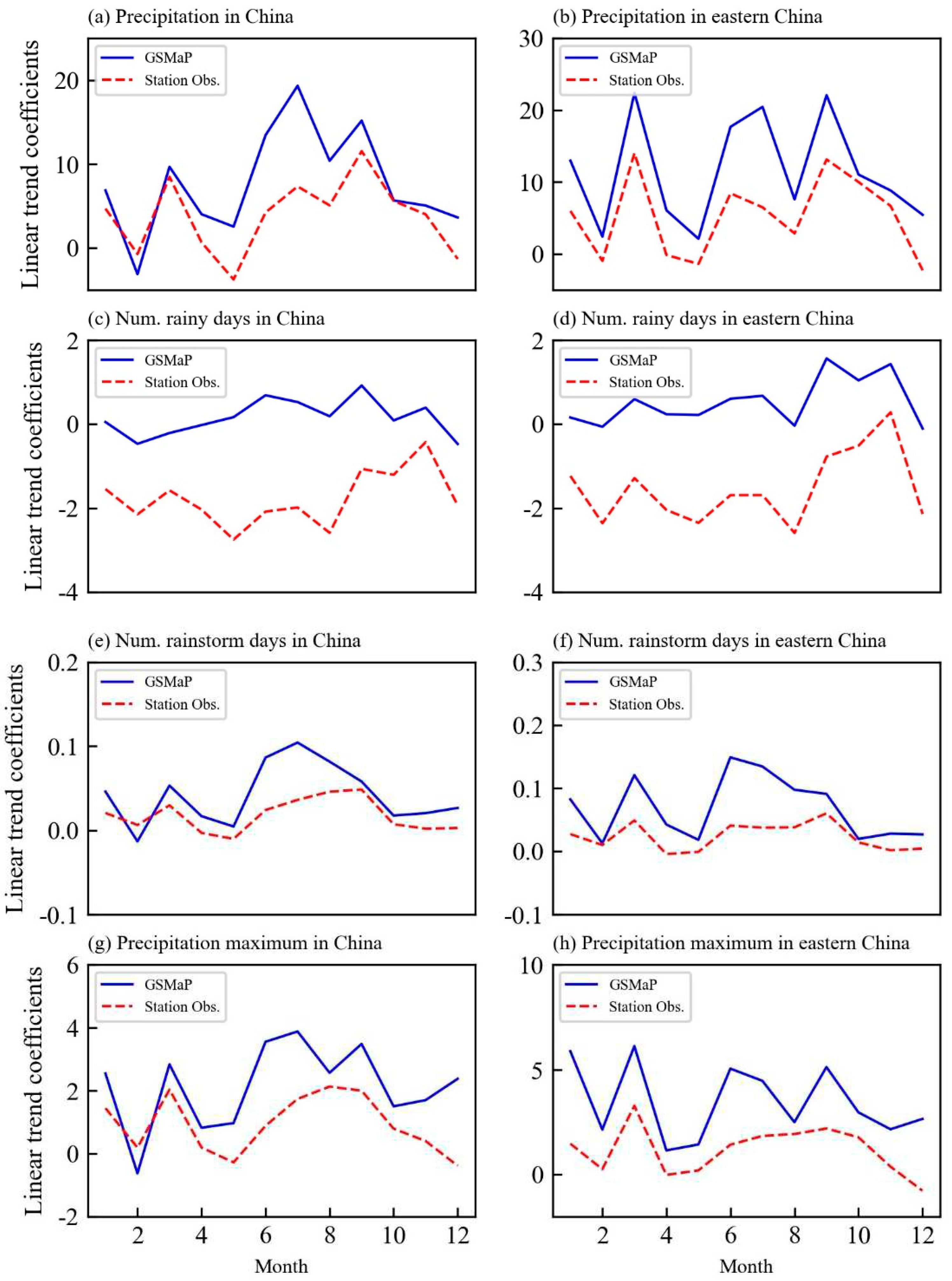
3. Results
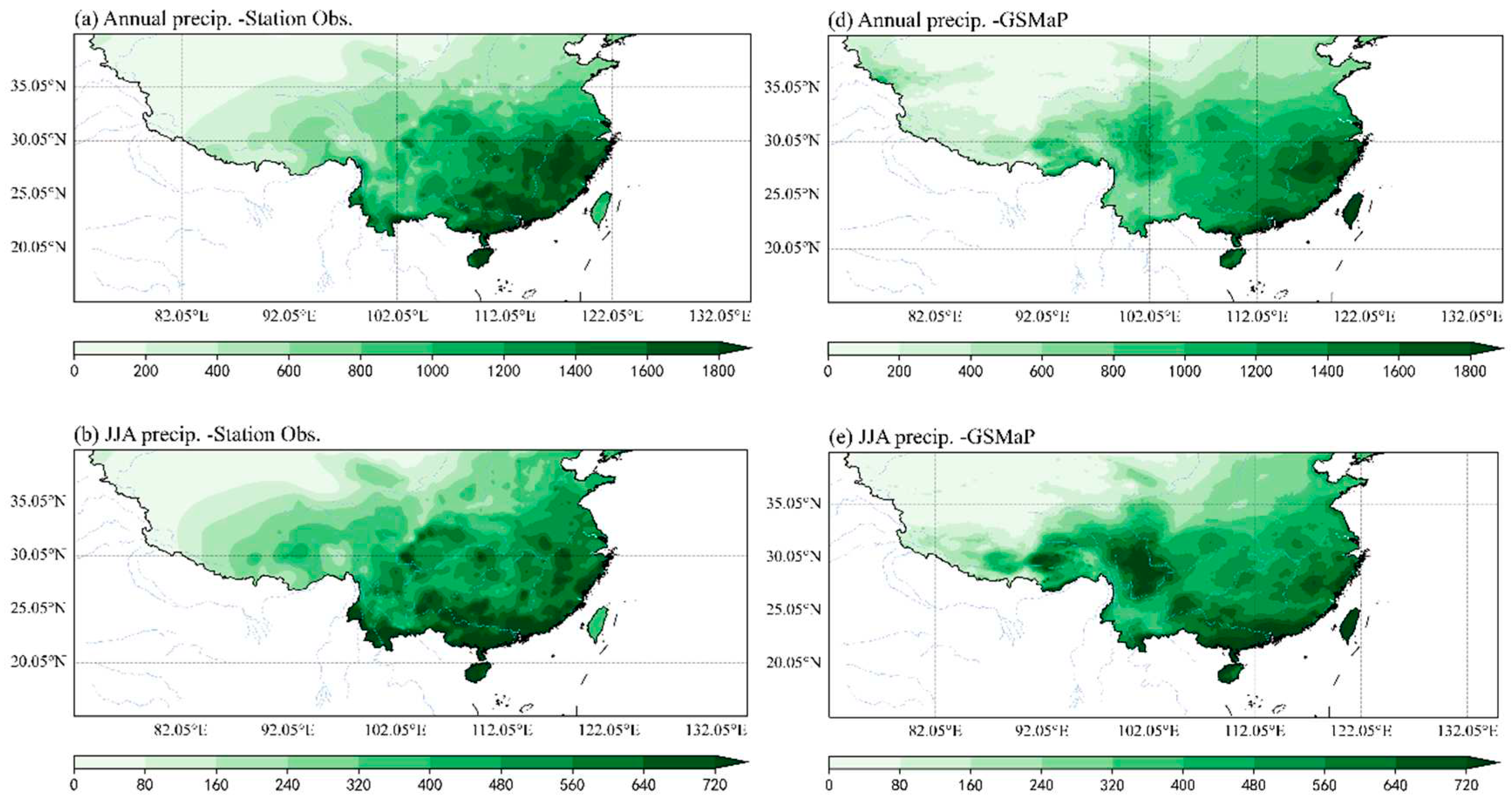
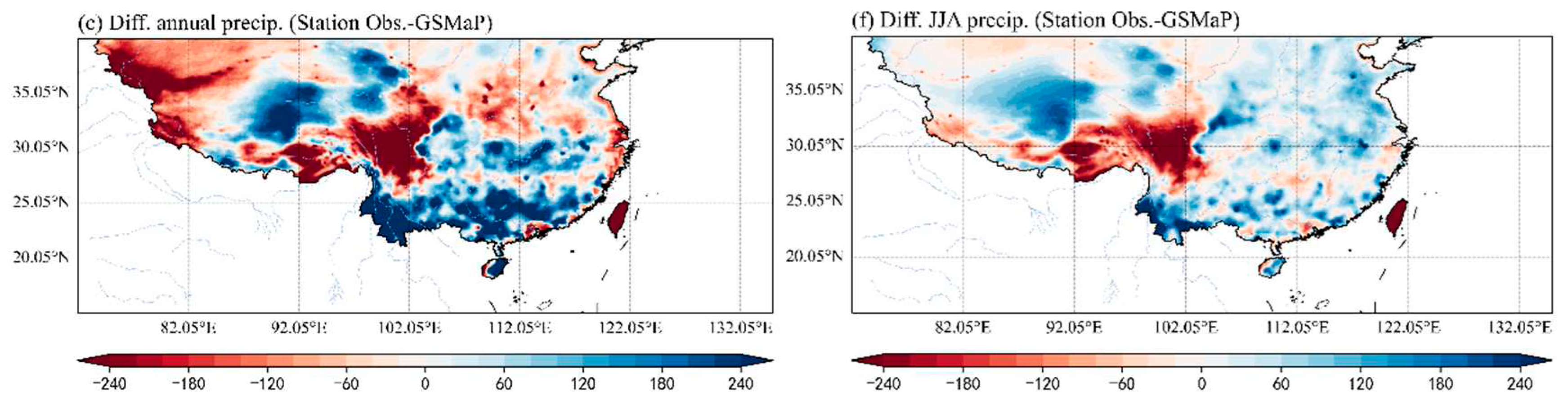
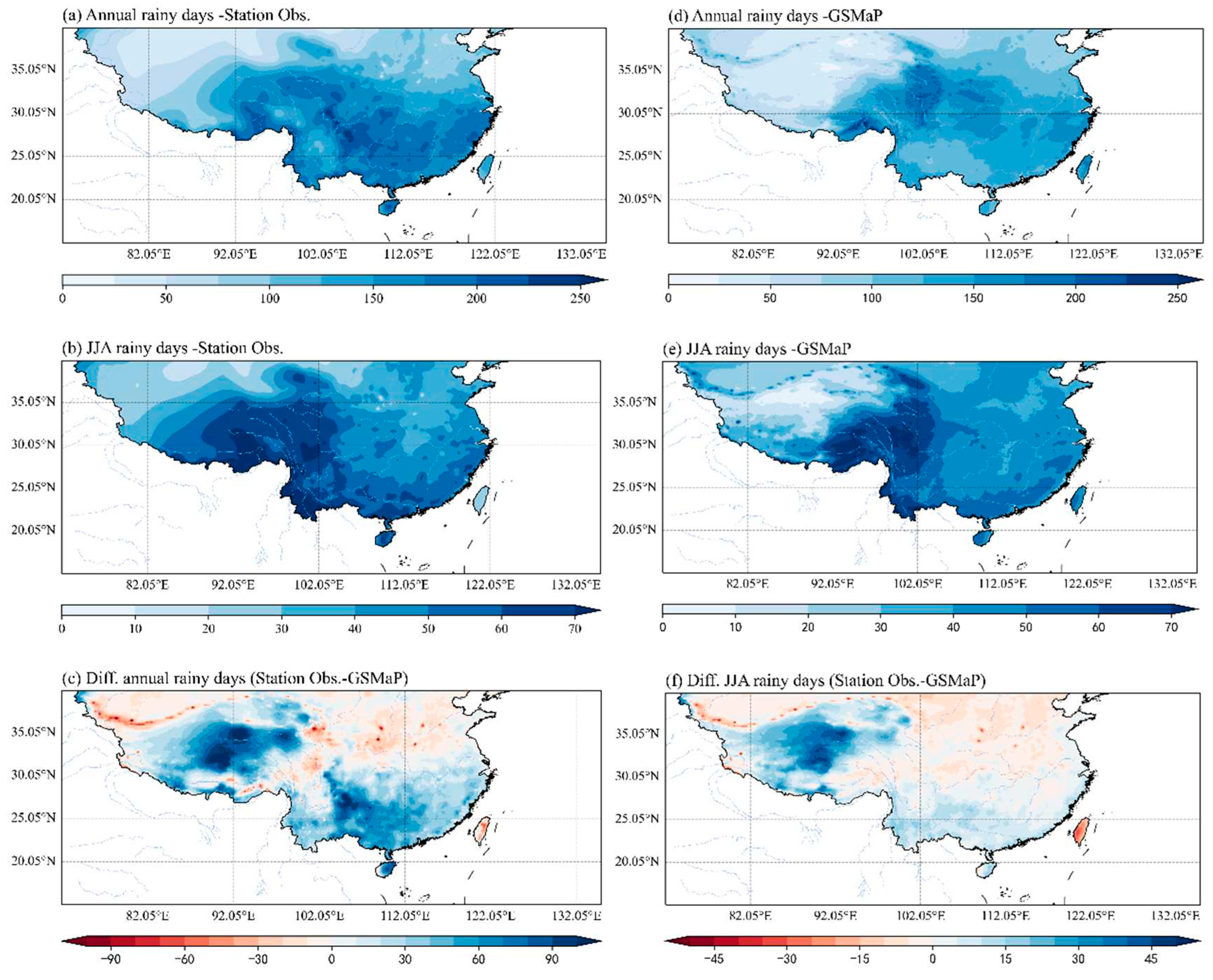
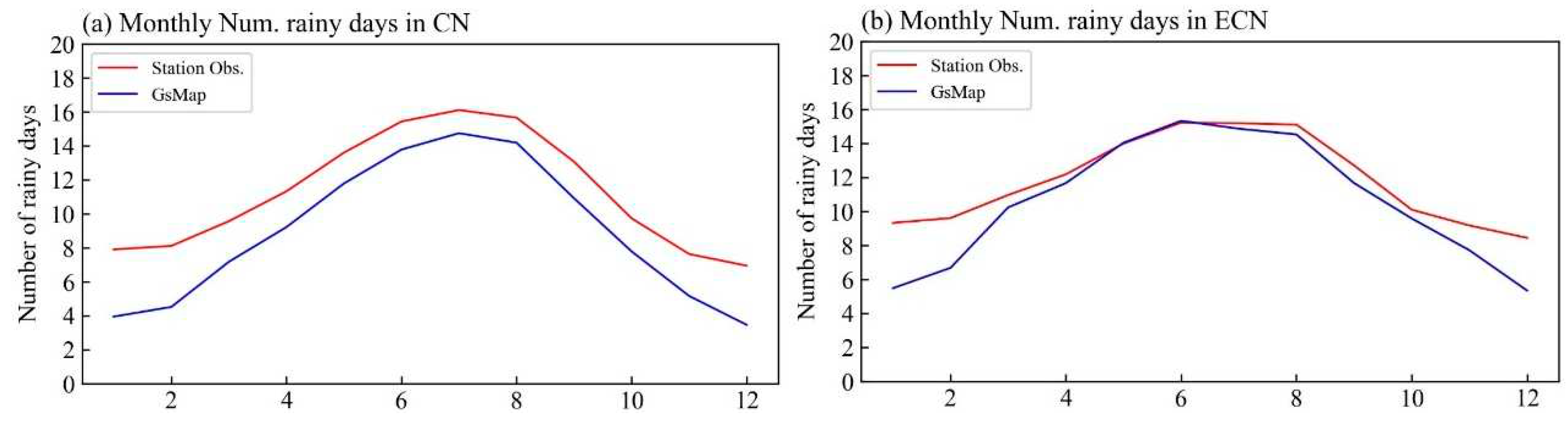
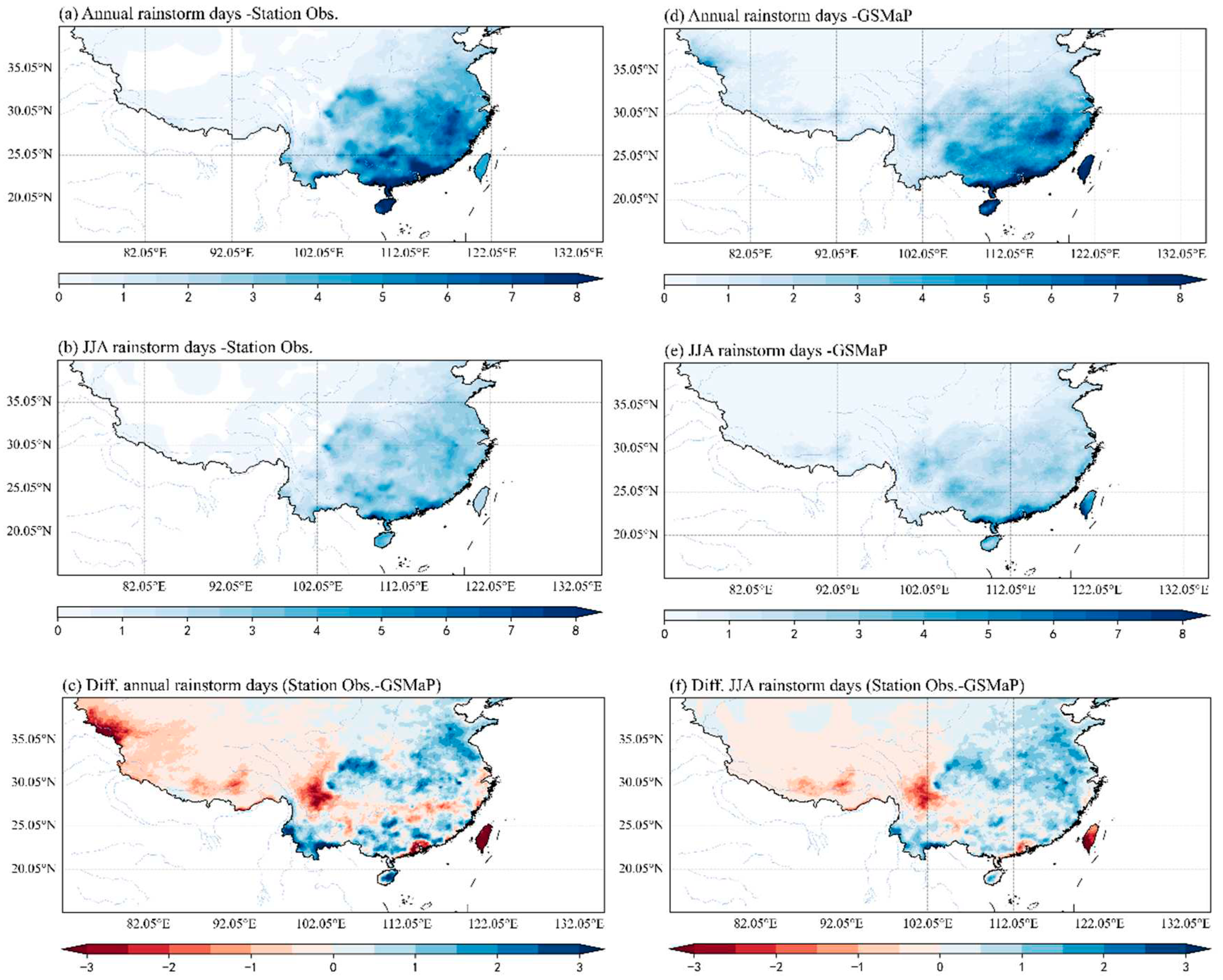
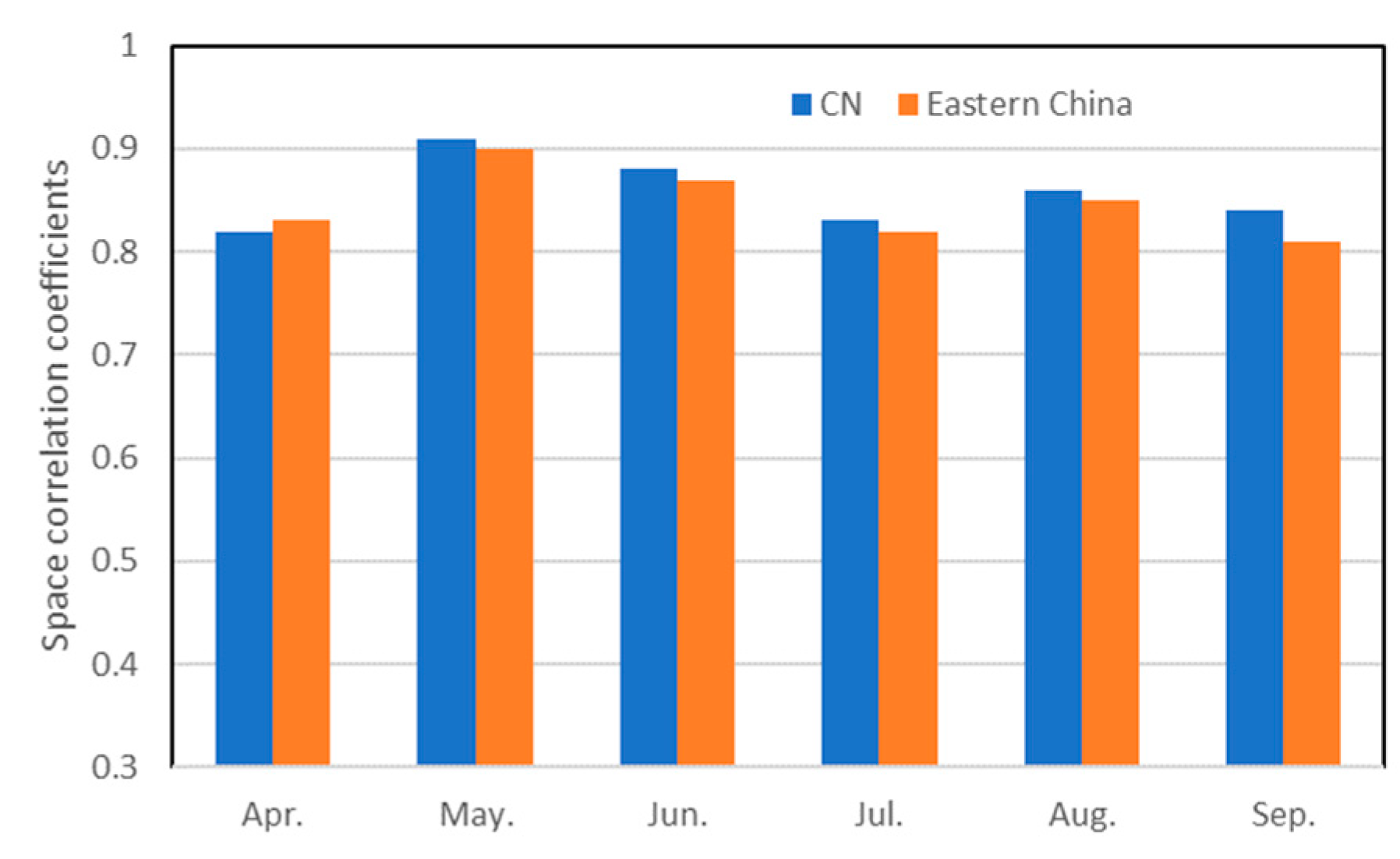
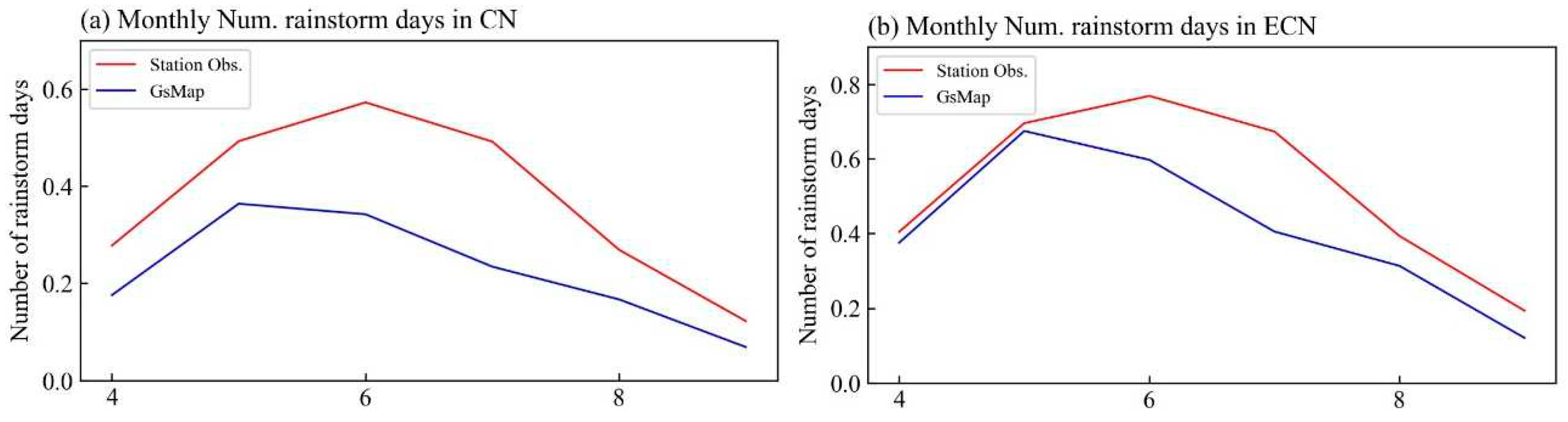
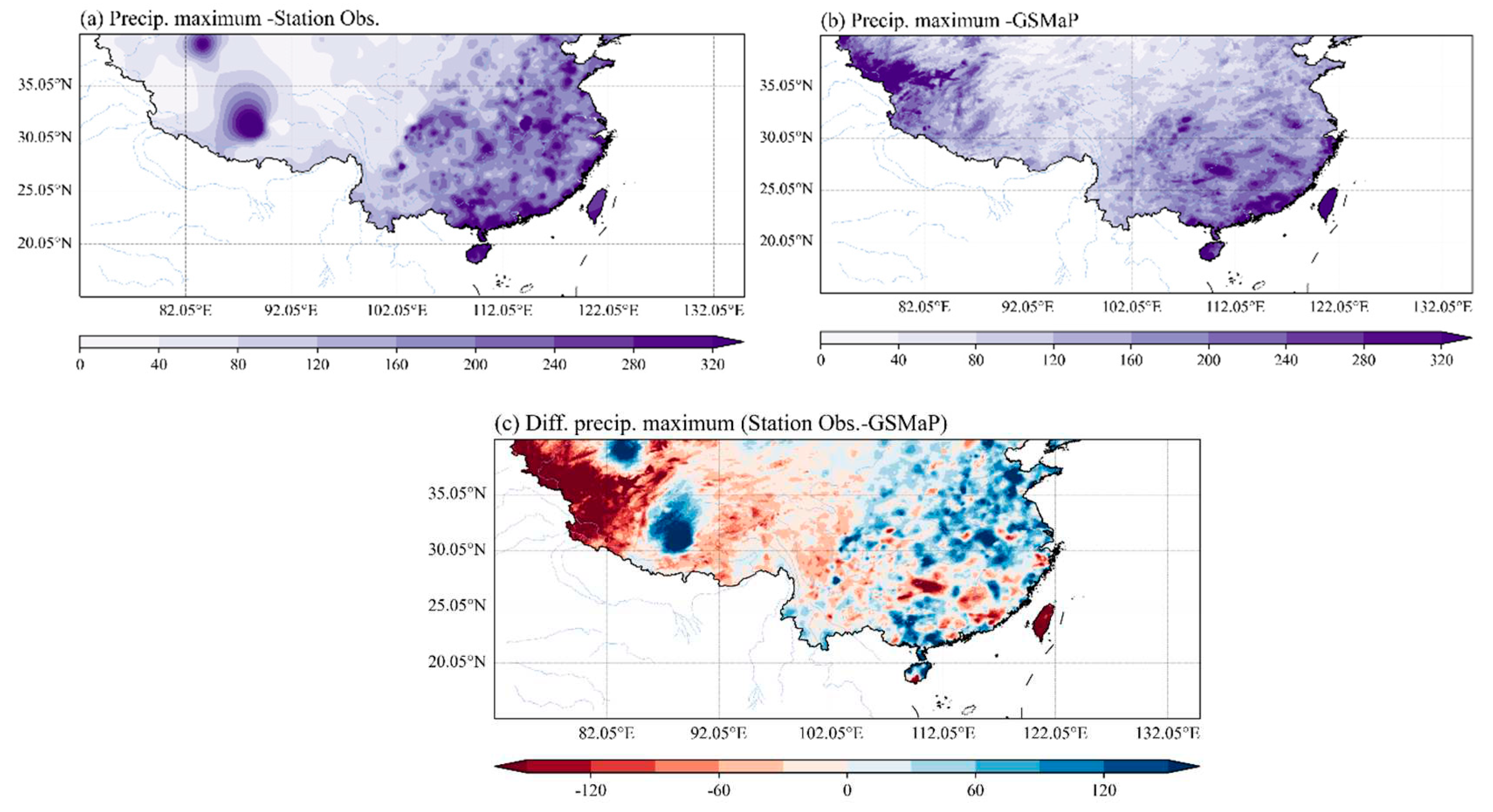
3.1. Comparison of climatology
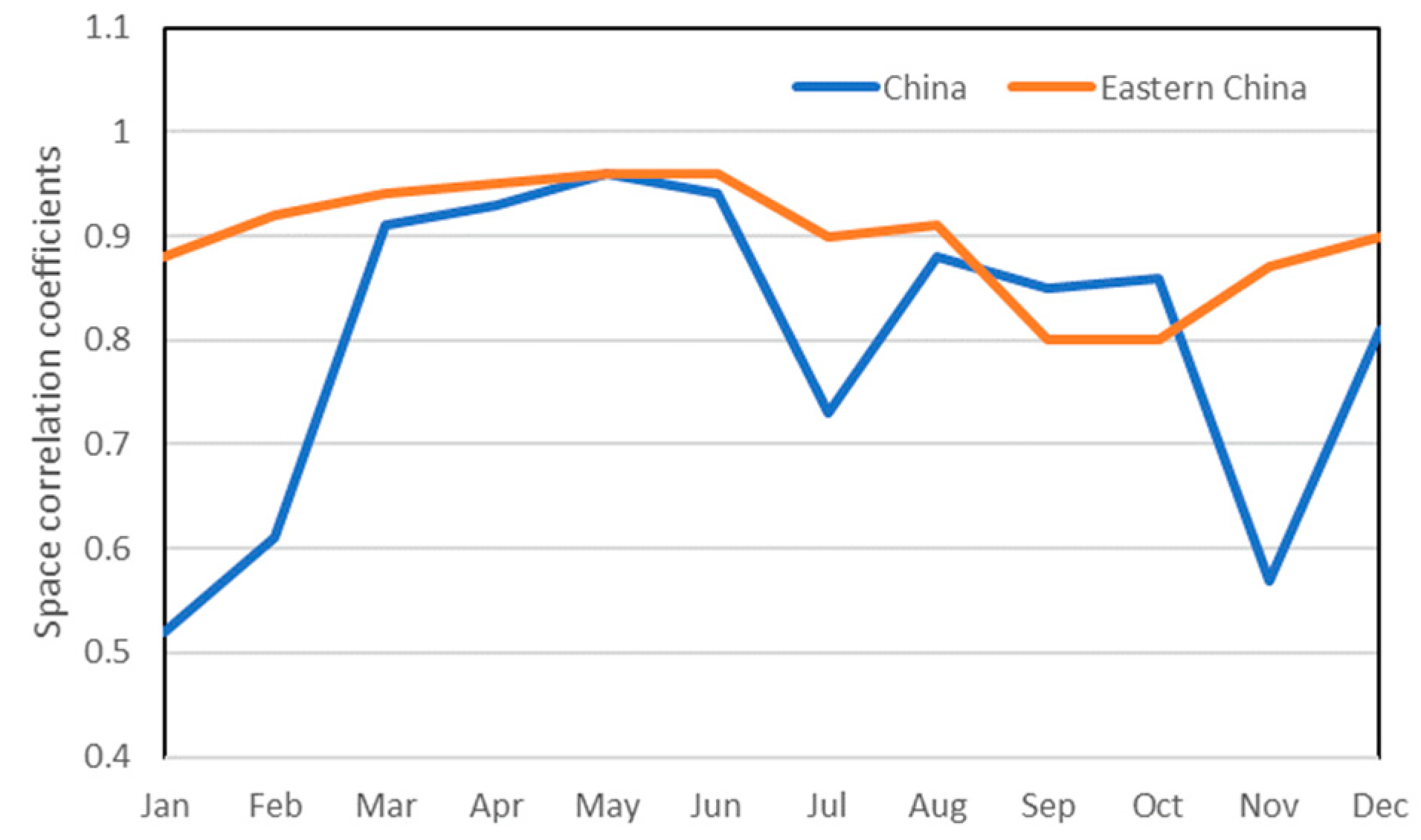
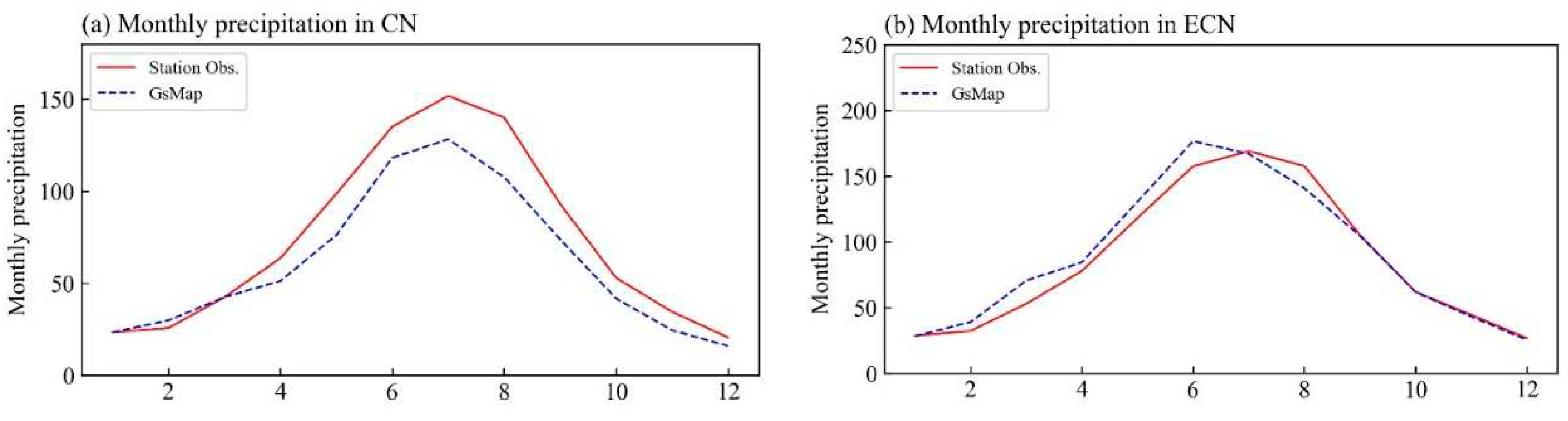
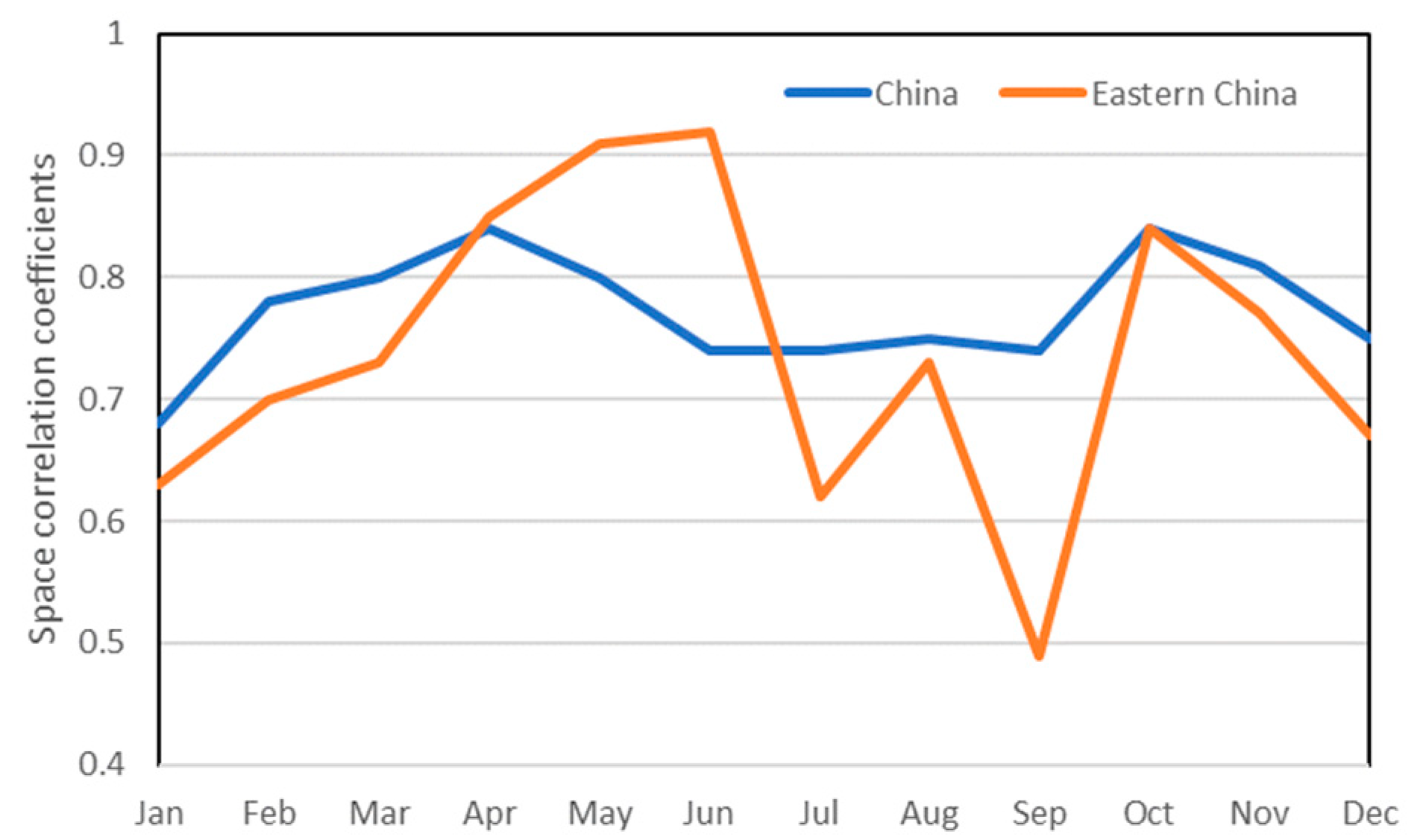
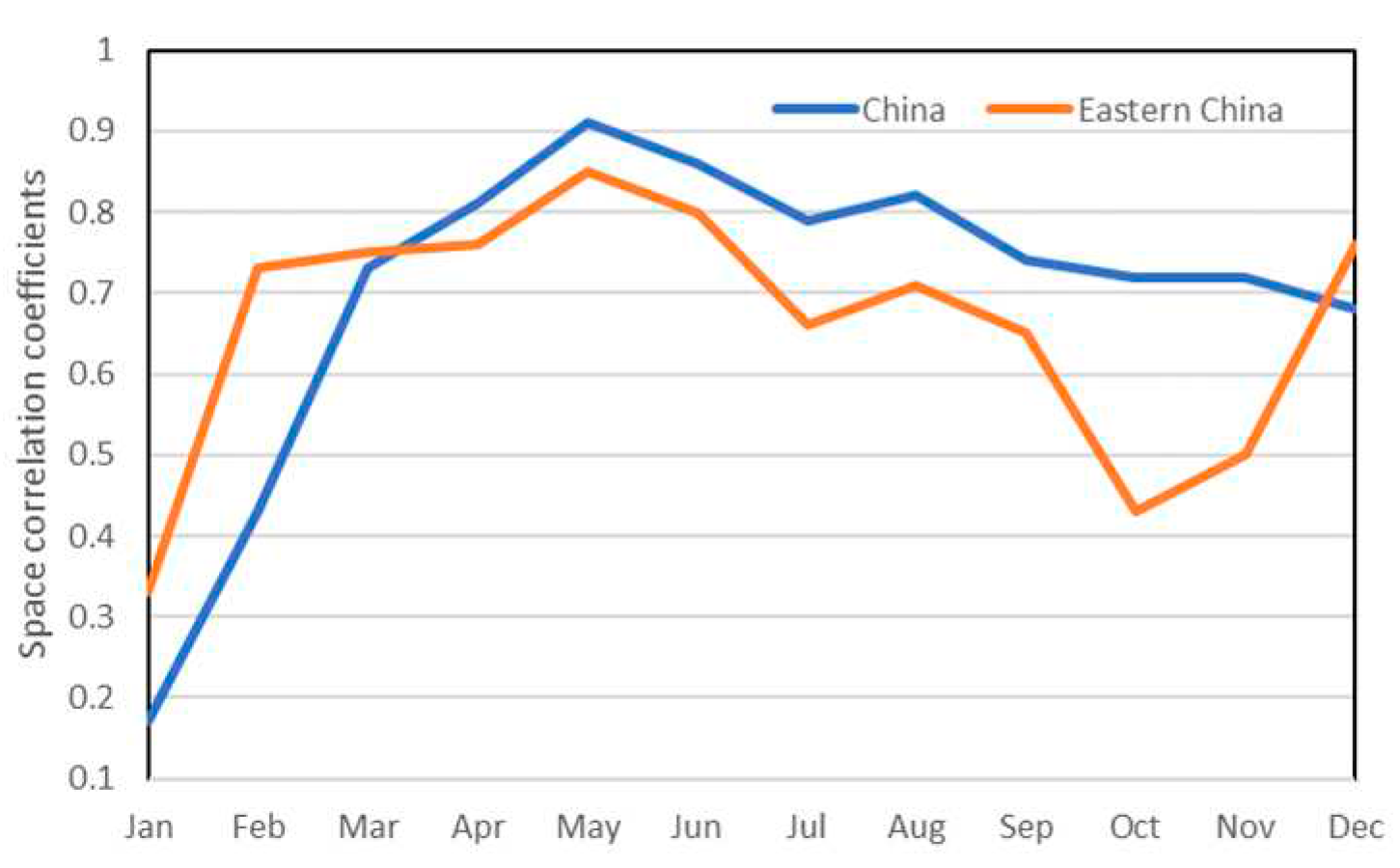
3.2. Comparison of climate variability
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schär, C.; Frei, C. Orographic precipitation and climate change. Global change and mountain regions: an overview of current knowledge 2005, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Douben, K. J. Characteristics of river floods and flooding: a global overview, 1985–2003. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55(S1), S9–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petley, D. Global patterns of loss of life from landslides. Geology 2012, 40, 927–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Mahendran, R.; Koirala, S.; Konoshima, L.; Yamazaki, D.; Watanabe, S.; Kim, H.; Kanae, S. Global flood risk under climate change. Nature. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, C. A.; Santi, P. M. Debris flows and their toll on human life: a global analysis of debris-flow fatalities from 1950 to 2011. Nat. Hazards 2014, 71, 203–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T. H.; Gong, D. H.; Chin, C. T.; Jui, Y. H. Using rainfall thresholds and ensemble precipitation forecasts to issue and improve urban inundation alerts. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, x.; Rankin, C.; Gangrade, S.; Zhao, G.; Lander, K.; Voisin, N.; Shao, M.; Morales-Hernández, M.; Kao, S. C.; Gao, H. Evaluating precipitation, streamflow, and inundation forecasting skills during extreme weather events: A case study for an urban watershed. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K. E. The impact of climate change and variability on heavy precipitation, floods, and droughts. Encyclopedia of hydrological sciences 2005, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, A. Drought under global warming: a review. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change 2011, 2(1), 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Trenberth, K. E. Climate change and drought: a perspective on drought indices. Current climate change reports 2018, 4, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. Climate Change and Drought: a Precipitation and Evaporation Perspective. Curr. Clim. Change 2018, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, S.; Wang, P. Interdecadal variation of the number of days with drought in China based on the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index (SPEI). J. Clim. 2022, 35(6), 2003–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebaldi, C.; Hayhoe, K.; Arblaster, J. M.; Meehl, G. A. Going to the extremes. Clim. Change 2006, 79, 185–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Kemfert, C.; Höppe, P. The impact of socio-economics and climate change on tropical cyclone losses in the USA. Reg. Environ. Change 2010, 10, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; Midgley, P. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis: Working Group I contribution to the Fifth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press). 2013, 167-178.
- Mullan, D.; Favis-Mortlock, D.; Fealy, R. Addressing key limitations associated with modelling soil erosion under the impacts of future climate change. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 156, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, G.; Bonada, N.; Brown, L. E.; Death, R. G.; Durance, I.; Gray, C.; Hladyz, S.; Ledger, M. E.; Milner, A. M.; Ormerod, S. J. The effects of climatic fluctuations and extreme events on running water ecosystems. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H. W.; Crosswell, J. R.; Van, D. B.; Hall, N. S.; Rossignol, K. L.; Osburn, C. L.; Hounshell, A. G.; Sloup, R. S.; Harding, L. W. Two decades of tropical cyclone impacts on North Carolina’s estuarine carbon, nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics: implications for biogeochemical cycling and water quality in a stormier world. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M. R.; Ingram, W. J. Constraints on future changes in climate and the hydrologic cycle. Nature 2002, 419, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santer, B. D.; Mears, C.; Wentz, F.; Taylor, K.; Gleckler, P.; Wigley, T.; Barnett, T.; Boyle, J.; Brüggemann, W.; Gillett, N. Identification of human-induced changes in atmospheric moisture content. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 15248–15253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S. K.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F. W.; Hegerl, G. C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderick, T. P.; Wasko, C.; Sharma, A. Atmospheric moisture measurements explain increases in tropical rainfall extremes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wu, X.; Liu, B. Global changes in the spatial extents of precipitation extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16(5), 054017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, P. A.; Ardanuy, P. E. Estimating climatic-scale precipitation from space: A review. J. Clim. 1989, 2(11), 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K. E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R. M.; Parsons, D. B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Halbleib, M.; Smith, J. I.; Gibson, W. P.; Doggett, M. K.; Taylor, G. H.; Curtis, J.; Pasteris, P. P. Physiographically sensitive mapping of climatological temperature and precipitation across the conterminous United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 2031–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, S.; Levizzani, V.; Anagnostou, E.; Bauer, P.; Kasparis, T.; Lane, J. E. Precipitation: measurement, remote sensing, climatology and modeling, Atmos. Res., 2009, 94, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, G. L.; L'Ecuyer, T.; Forbes, R.; Gettelmen, A.; Golaz, J. C.; Bodas-Salcedo, A.; Suzuki, K.; Gariel, P.; Haynes, J. Dreary state of precipitation in global models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F. J.; Turk, F. J.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A. Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L. A. T.; Angelis, C. F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. J.; Castro, M. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K. L. A review of global precipitation data sets: Data sources, estimation, and intercomparisons. Rev. Geophy. 2018, 56(1), 79–107. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, H. E.; Vergopolan, N.; Pan, M.; Levizzani, V.; Dijk, A. I. J. M.; Weedon, G. P.; Brocca, L.; Pappenberger, F.; Huffman, G. J.; Wood, E. F. Global-scale evaluation of 22 precipitation datasets using gauge observations and hydrological modeling. Satellite Precipitation Measurement. 2020, 2, 625–653. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P. A. Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1997, 78(11), 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C. Satellite rainfall climatology: A review. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21(9), 1041–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturaro, G. A. Closer look at the climatological discontinuities present in the NCEP/NCAR reanalysis temperature due to the introduction of satellite data. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 21, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Hagemann, S.; Hodges, K. I. Can climate trends be calculated from reanalysis data? , J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chelliah, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Higgins, W.; Janowiak, J.; Mo, K. c.; Ropelewski, C.; Wang, J.; Leetmaa, A.; Reynolds, R.; Jenne, R.; Joseph, D. (1996). The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77(3), 437–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woolen, J.; Yang, S. K.; Hnilo, J. J.; Fiorino, M.; Potter, G. L. NCEP–DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 83(11), 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppala, S. M.; KÅllberg, P. W.; Simmons, A. J.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V. D. C.; Fiorino, M.; … Woollen, J. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2005, 131(612), 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D. P.; Uppala, S. M.; Simmons, A. J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; … Vitart, F. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quarterly Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2011, 137(656), 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2020, 146(730), 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.; Hersbach, H.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Dahlgren, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nocolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; Soci, C.; Villaume, S.; Bidlot, J. R.; Haimberger, L.; Woollen, J.; Buontempo, C.; Thépaut, J. H. The ERA5 global reanalysis: Preliminary extension to 1950. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc. 2021, 147(741), 4186–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H. L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P. , Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; … Goldberg, M. The NCEP climate forecast system reanalysis. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2010, 91(8), 1015–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha S, Moorthi S; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y. T.; Chuang, H.; … Becher, E. The NCEP climate forecast system version 2. J. clim. 2014, 27(6), 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebita, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Moriya, M.; Kumabe, R.; Onogi, K.; … Ishimizu, T. The Japanese 55-year Reanalysis “JRA-55”: An interim report. SOLA 2011, 7, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, T.; Kubota, T.; Mega, T.; Ushio, T.; Oki, R. Precipitation Extremes Monitoring Using the Near-Real-Time GSMaP Product. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2020, 13, 5640–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R. J.; Janowiak, J. E.; Arkin, P. A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive nicrowave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydro. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G. J.; Bolvin, D. T.; Nelkin, E. J.; Wolff, D. B.; Adler, R. F.; Gu, G.; … Stocker, E. F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydro. 2007, 8(1), 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K. L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. G. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed imagery using an artificial neural network cloud classification system. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43(12), 1834–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K. L.; Gao, X. G.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H. V. Precipitation estimation from remotely sensed information using artificial neural networks. J. Appl. Meteor. 1997, 36(9), 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K. L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H. V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite-based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2000, 81(9), 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Kachi, M. Kalman filtering applications for global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP). In M. Gebremichael & F. Hossain (Eds.), Satellite rainfall applications for surface hydrology, 2010, 105–123). New York: Springer.
- Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K.; Ushio, T.; Shige, S.; Takayabu, Y. N.; Kachi, M.; Arai, Y.; Tashima, T.; Makaki, T.; Kawamoto, N.; Mega, T.; Yamamoto, M. K.; Hamada, A.; Yamaji, M.; Liu, G.; Oki, R. Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) products in the GPM era. Satellite Precipitation Measurement 2020, 1, 355–373. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, N.; Behrangi, A.; Alexander, L. V. Large uncertainties in observed daily precipitation extremes over land. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122(2), 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaranom, A. B.; Masunaga, H. Origins of heavy precipitation biases in the TRMM PR and TMI products assessed with CloudSat and reanalysis data. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2019, 58(1), 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunaga, H.; Schröder, M.; Furuzawa, F. A.; Kummerow, C.; Rustemeier, E.; Schneider, U. Inter-product biases in global precipitation extremes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14(12), 125016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A. Y.; Kakar, R. K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A. A.; Kummerow, C. D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2014, 95(5), 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W. A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E. F.; Krischbaum, D. B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S. A.; Huffman, G. J.; Iguchi, T.; Kirstetter, P. E.; Kummerow, C.; Meneghini, R.; Oki, R.; Olson, W. S.; Takayabu, Y. N.; Furukawa, K.; Wilheit, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission for science and society. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2017, 98(8), 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawati, M. D.; Miura, F.; Aryastana, P. Validation of Hourly GSMaP and ground base estimates of precipitation for flood monitoring in Kumamoto, Japan. Geospatial technology for water resource applications 2016, 130–143. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C. D.; Adler, R. F.; Kubota, T.; Ushio, T. Evaluation of GSMaP precipitation estimates over the contiguous United States. J. Hydro. 2010, 11(2), 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qin, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of global satellite mapping of precipitation project daily precipitation estimates over the Chinese mainland. Adv. Meteor. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Song, F.; Udmale, P.; Jin, J.; Thapa, B. R.; Ishidaira, H. Error analysis and evaluation of the latest GSMap and IMERG precipitation products over Eastern China. Adv. Meteor. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. A preliminary assessment of the gauge-adjusted near-real-time GSMaP precipitation estimate over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12(1), 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Guo, B.; Xing, W.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Xu, Y. Comprehensive evaluation of latest GPM era IMERG and GSMaP precipitation products over mainland China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 246, 105132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, Z. W.; Kuleshov, Y.; Watkins, A. Evaluation of satellite precipitation estimates over Australia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12(4), 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiyoko, A.; Osawa, T.; Nuarsa, I. W. Evaluation of GSMaP precipitation estimates over Indonesia. Int. J. Environ. Geosci 2019, 3, 26–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshov, Y.; Kurino, T.; Kubota, T.; Tashima, T.; Xie, P. "WMO space-based weather and climate extremes monitoring demonstration project (SEMDP): First outcomes of regional cooperation on drought and heavy precipitation monitoring for Australia and South-East Asia", [online] Available: https://www.intechopen.com/books/rainfall-extremes-distribution-and-properties/wmo-space-based-weather-and-climate-extremes-monitoring-demonstration-project-semdp-first-outcomes-o.
- Zheng, D.; Yao, T. D. Research progress on formation and evolution of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its environmental and resource effects (in Chinese). Chinese Basic Science 2004, 6, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Chan, J. C. L. The East Asian summer monsoon: an overview. Meteor. Atmos. Phys 2005, 89(1-4), 117–142. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X. Y.; and Shi, X. H. Climatological characteristics of summertime moisture budget over the southeast part of Tibetan Plateau with their impacts (in Chinese). J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2008, 19, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. A study of rainy seasons in China. Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 100(1-4), 121–138. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W. W.; Beek, L. P. V.; Bierkens, M. F. Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 2010, 328, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. A climatological northern boundary index for the East Asian summer monsoon and its interannual variability. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. D.; Dong, L. L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. J. Effects of the Asian Water Tower over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the characteristics of atmospheric water circulation (in Chinese). Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2830–2841. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, X.; Chen, J. The modulation of westerlies-monsoon interaction on climate over the monsoon boundary zone in East Asia. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3049–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yong, B.; Ke, L.; Wang, G.; Ren, L.; Chen, X. Tracing the error sources of global satellite mapping of precipitation for GPM (GPM-GSMaP) over the Tibetan Plateau, China. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2018, 11(7), 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Yin, J.; Qiao, Z.; Peng, W.; Peng, H. Multiscale comparative evaluation of the GPM and TRMM precipitation products against ground precipitation observations over Chinese Tibetan Plateau. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2020, 14, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Atmospheric simulation-based precipitation datasets outperform satellite-based products in closing basin-wide water budget in the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42(14), 7252–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Achberger, C.; Linderholm, H. W. Rain-season trends in precipitation and their effect in different climate regions of China during 1961–2008. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6(3), 034025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, C.; Lian, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Long-term change of wet and dry climatic conditions in the southwest karst area of China. Glob. Planet. Change 2015, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Xu, M.; Zhao, F.; Tijjani, S.B. Spatial and temporal variations in precipitation amount, frequency, intensity, and persistence in China, 1973–2016. J. Hydro. 2019, 20(11), 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, M.; Moussa, A.; Hassan, Q. K.; El-Sheimy, N.; et al. Performance assessment of sub-daily and daily precipitation estimates derived from GPM and GSMaP products over an arid environment. Remote Sens. 2019, 11(23), 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yong, B. Evaluation and hydrological utility of the latest GPM IMERG V5 and GSMaP V7 precipitation products over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10(12), 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




