Submitted:
04 November 2023
Posted:
06 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- A.
-
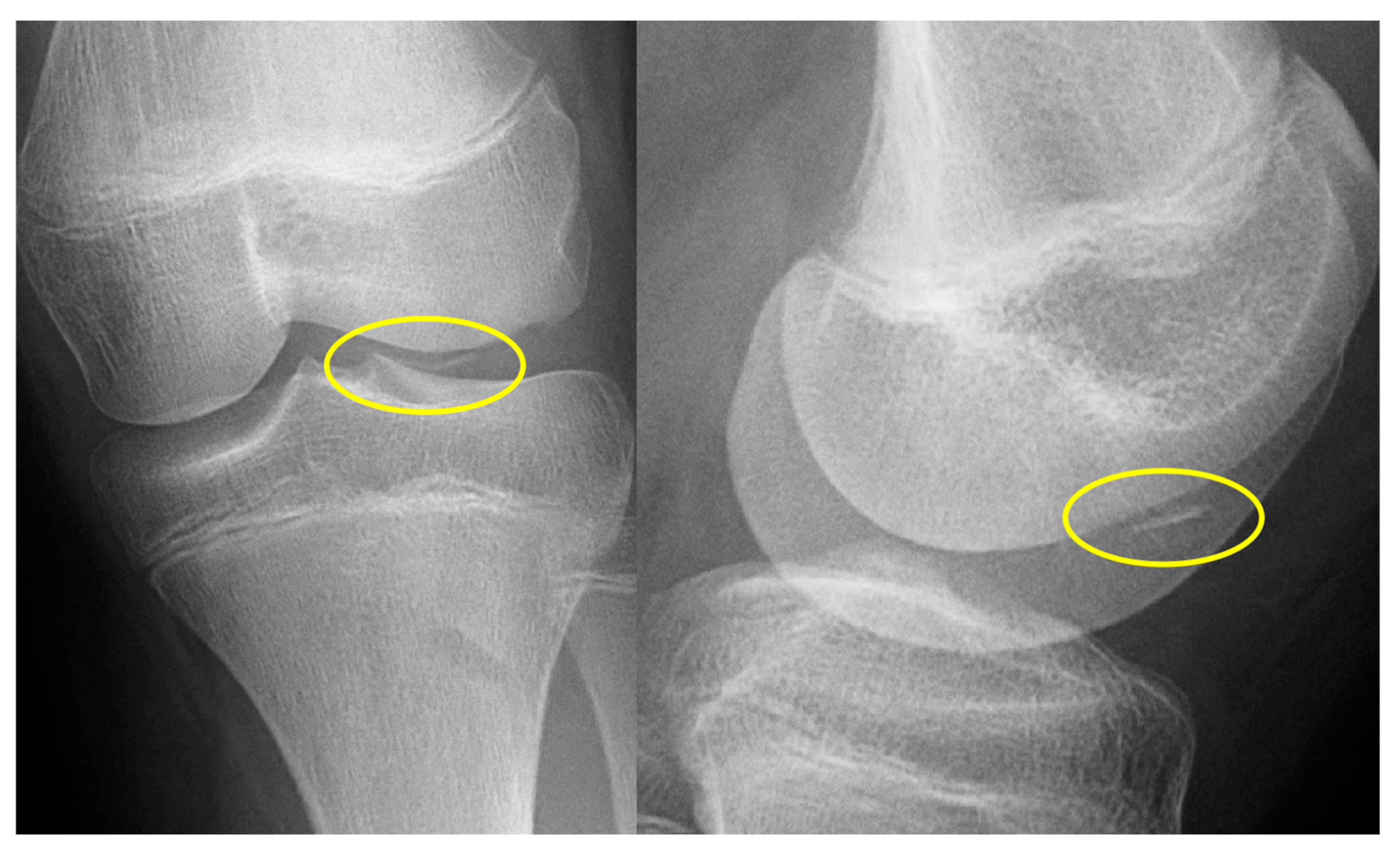
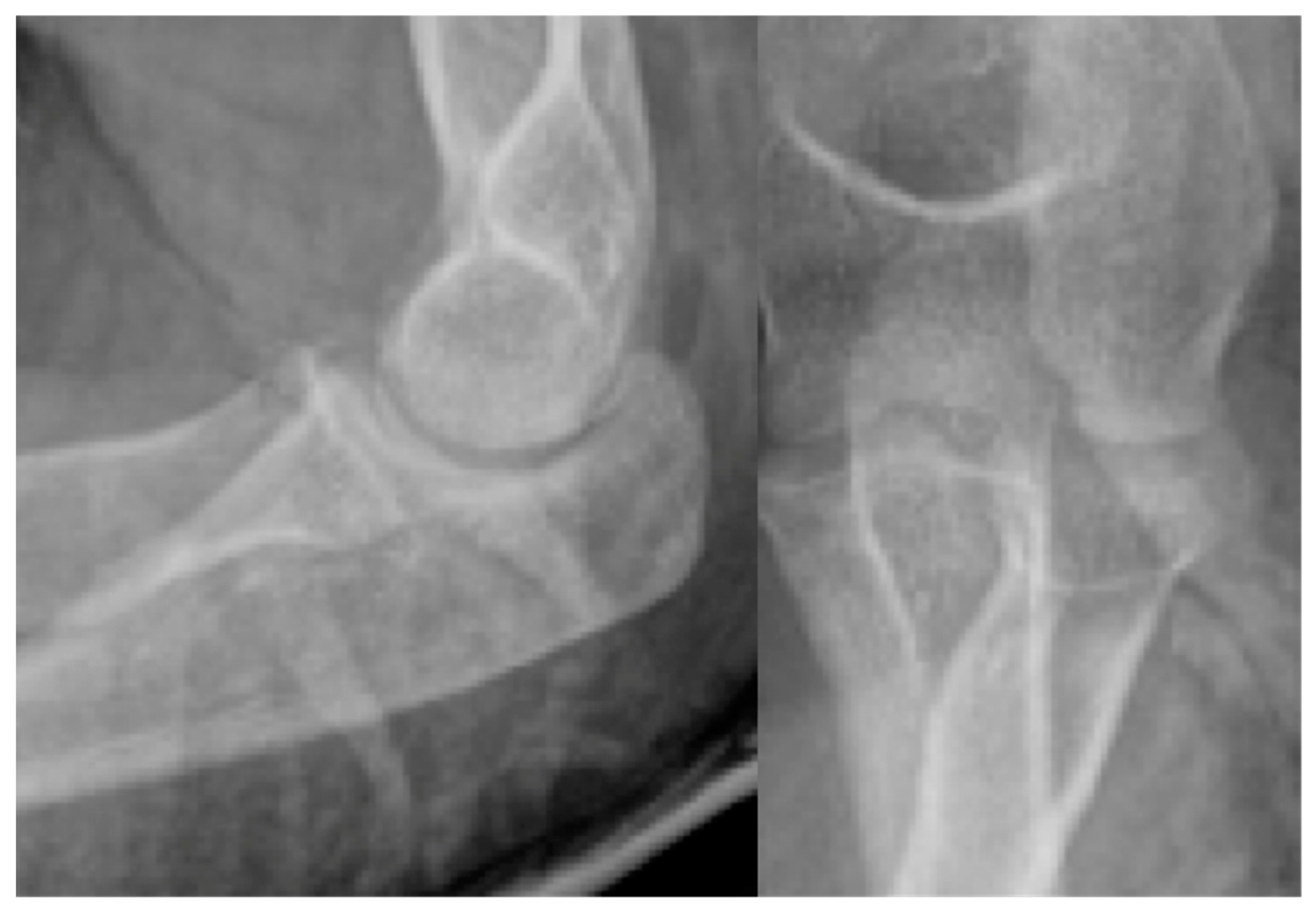
Stage I:
- a.
- Injury limited to articular cartilage
- b.
- Subchondral Edema on MRI
- c.
- X-ray: Negative
- B.
-
Stage II:
- a.
- Cartilage damage with subchondral fracture without detachment
- b.
- Thin Sclerotic Margin
- c.
- X-ray: Negative or slight sclerosis
- d.
-
Subtypes:
- 1.
- Type A: Cystic on CT and Edema on MRI
- 2.
- Type B: Non-displaced and incompletely undercut by fluid (MRI) and lucency (CT) with an open connection to the articular cartilage.
- C.
-
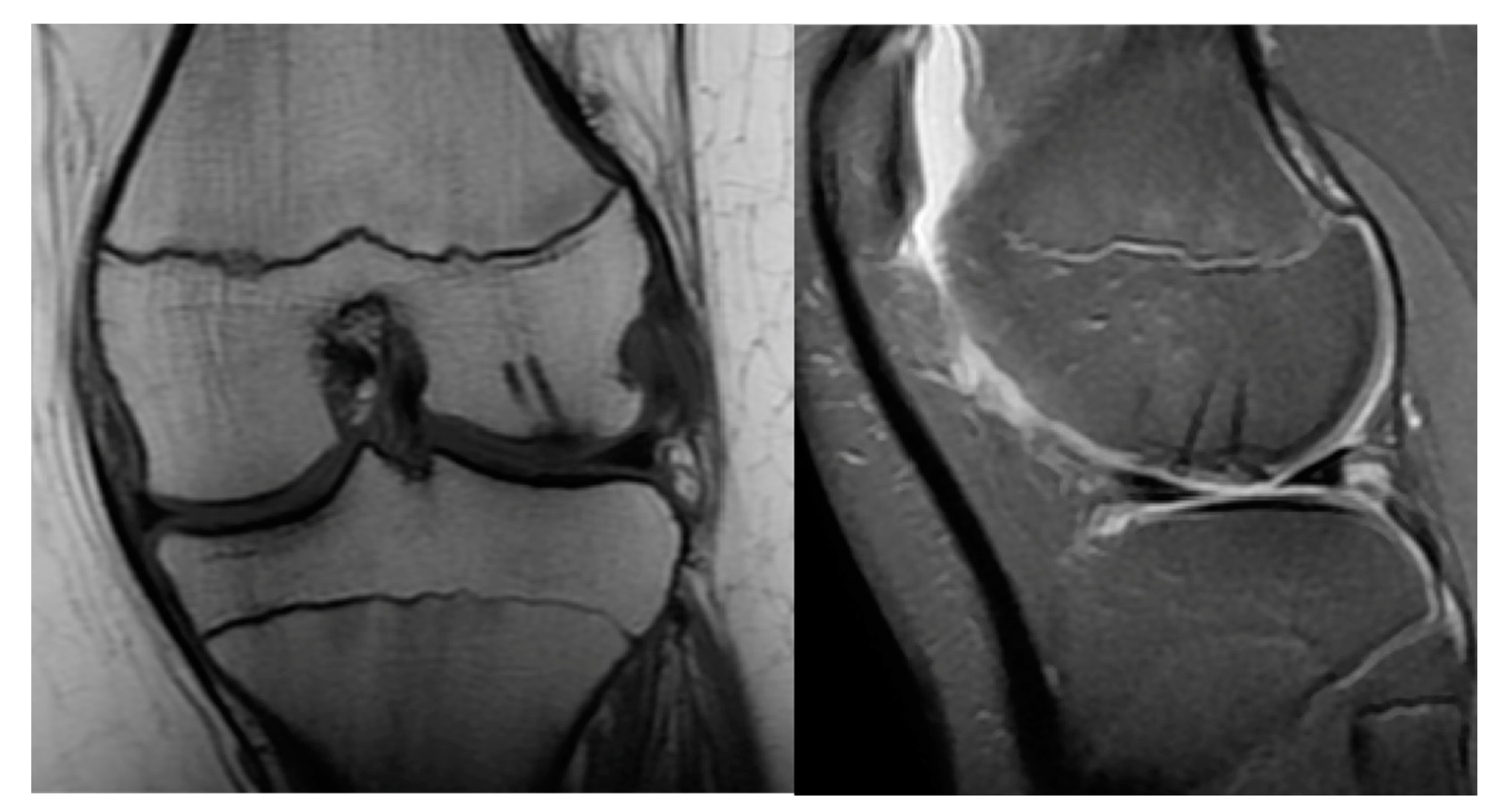
Stage III:
- a.
- Detached, Non-Displaced
- b.
- MRI: Rim-sign - high signal around fragment
- c.
- X-ray: Lucency between fragment and normal bone.
- D.
-
Stage IV:
- a.
- Osteochondral fragment is displaced
- b.
- Joint effusion
- c.
- X-ray: Loose body, lucency
- E.
-
Stage V:
- a.
- Subchondral Cyst formation
- b.
- Secondary degenerative changes
- c.
- X-ray: Secondary Osteoarthritis
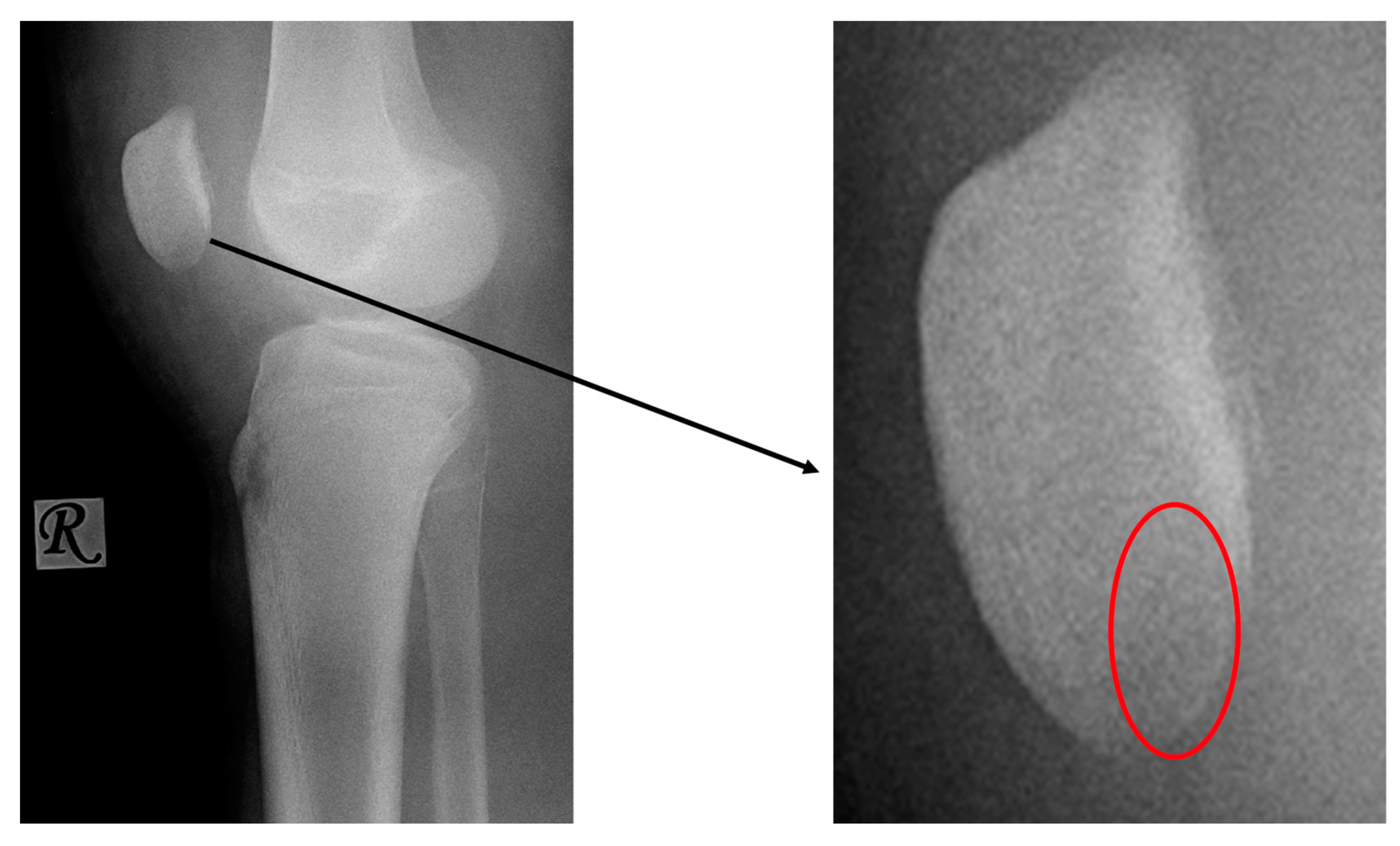
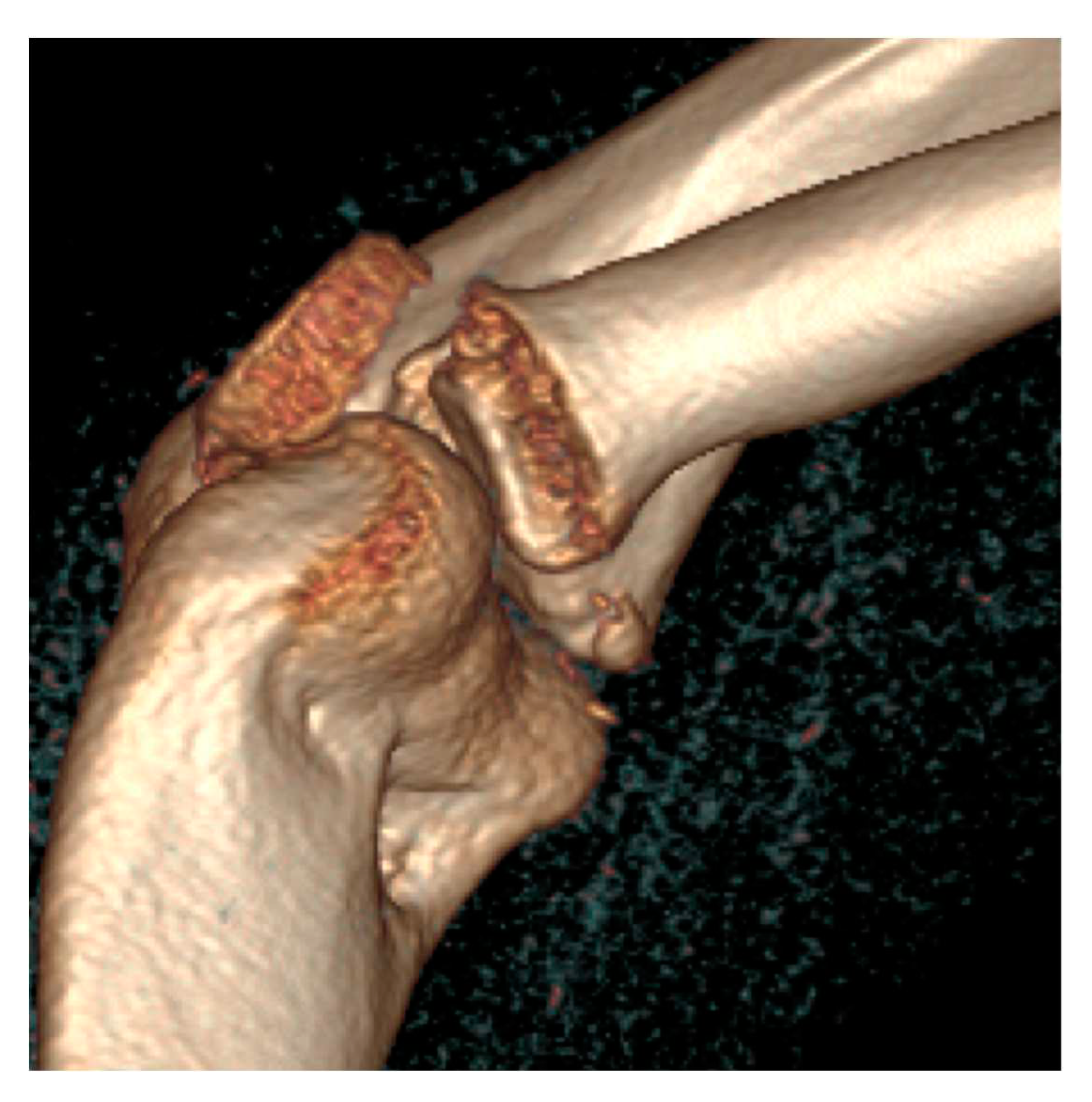
2. Materials and Methods
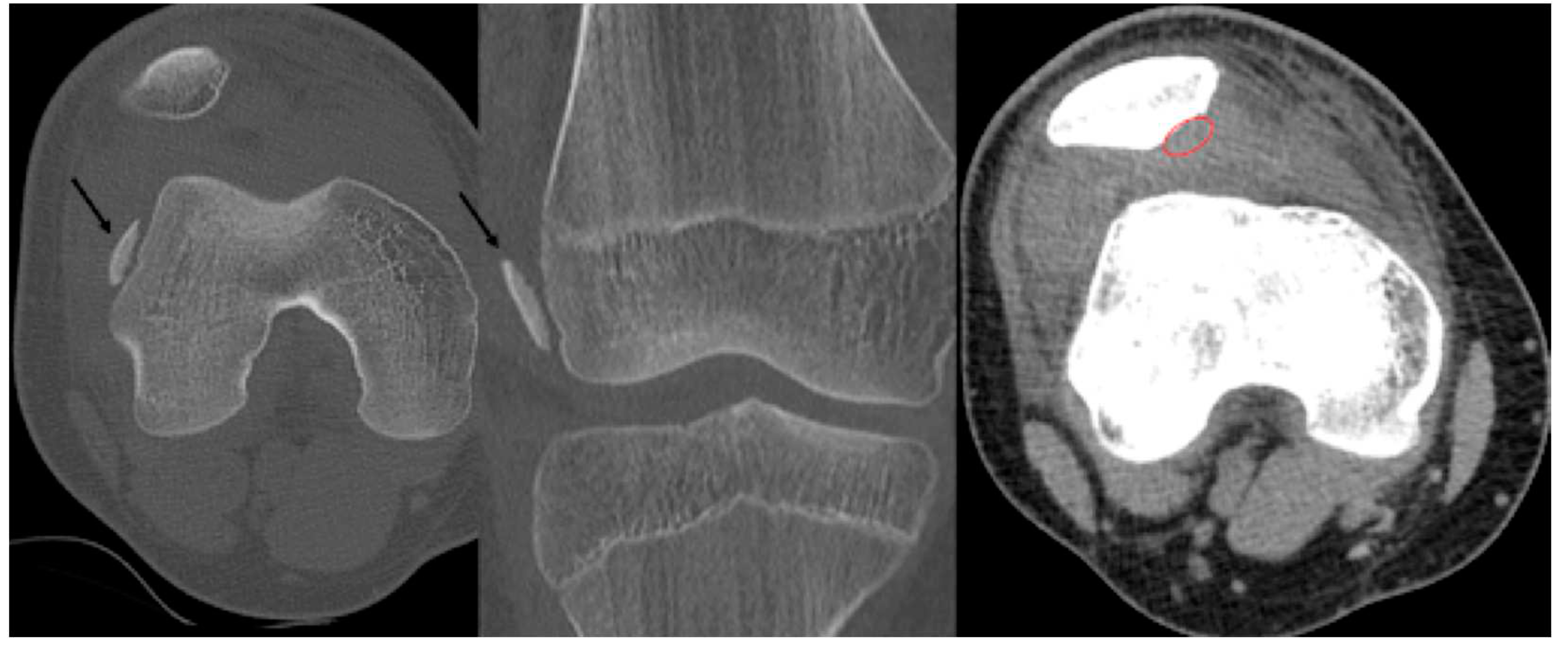
2.1. PLGA Implants:
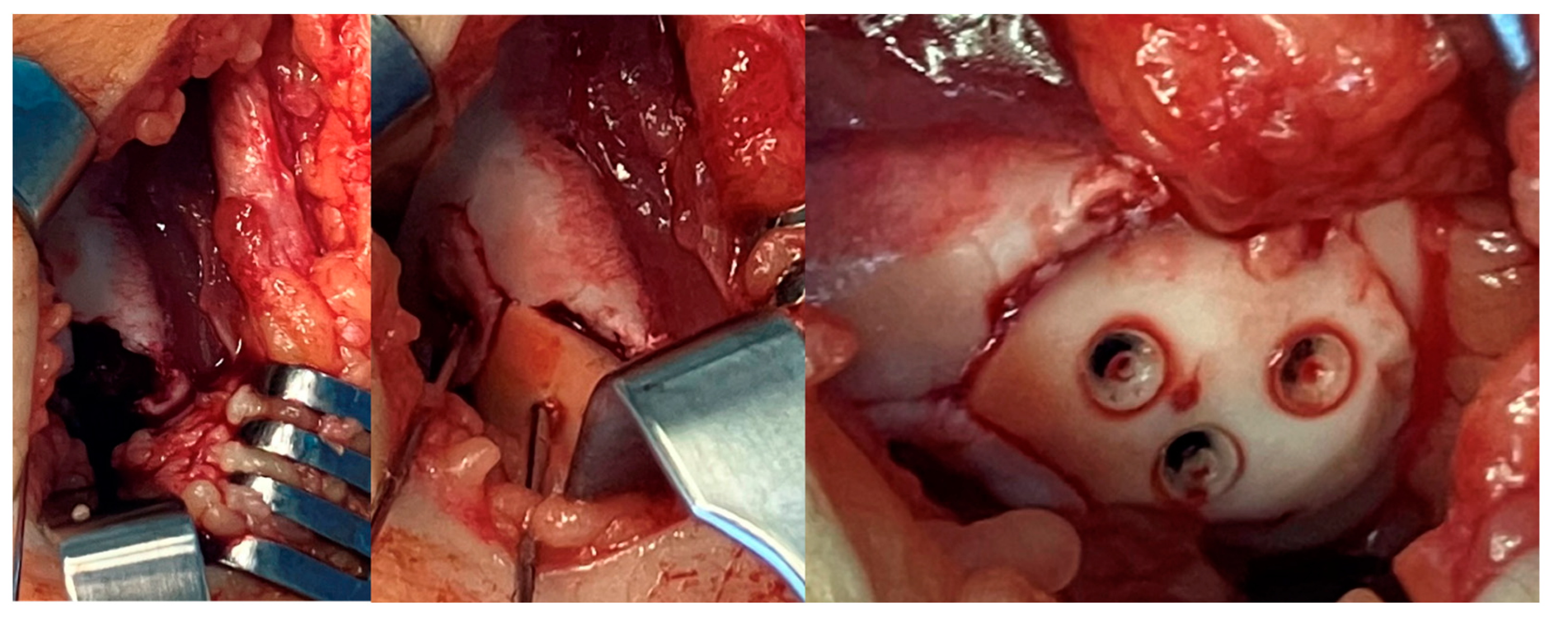
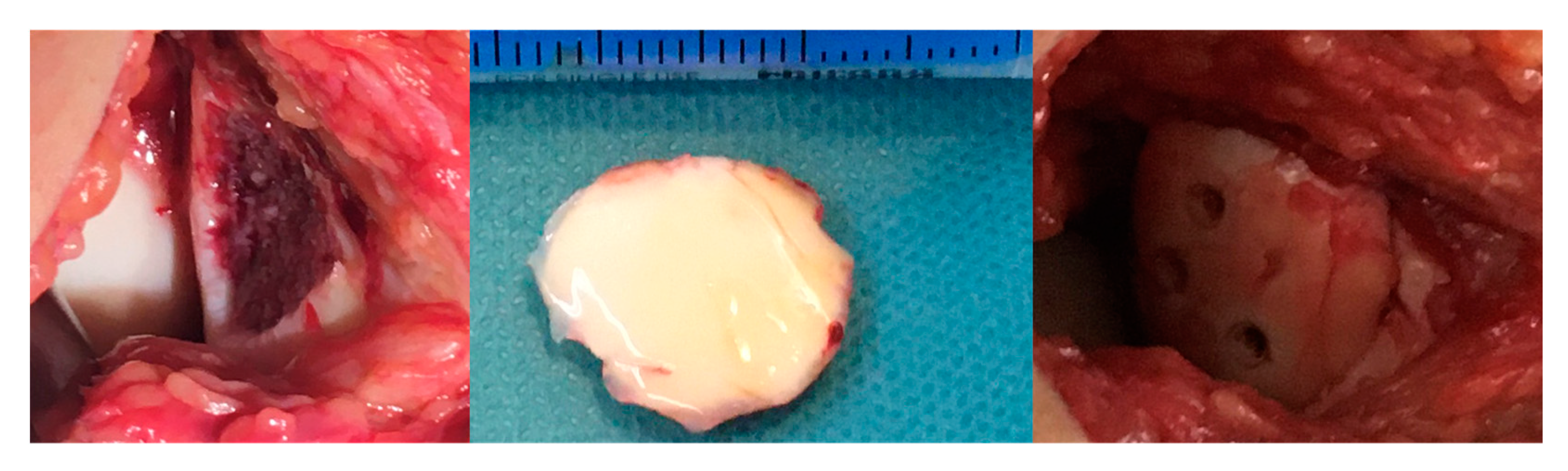
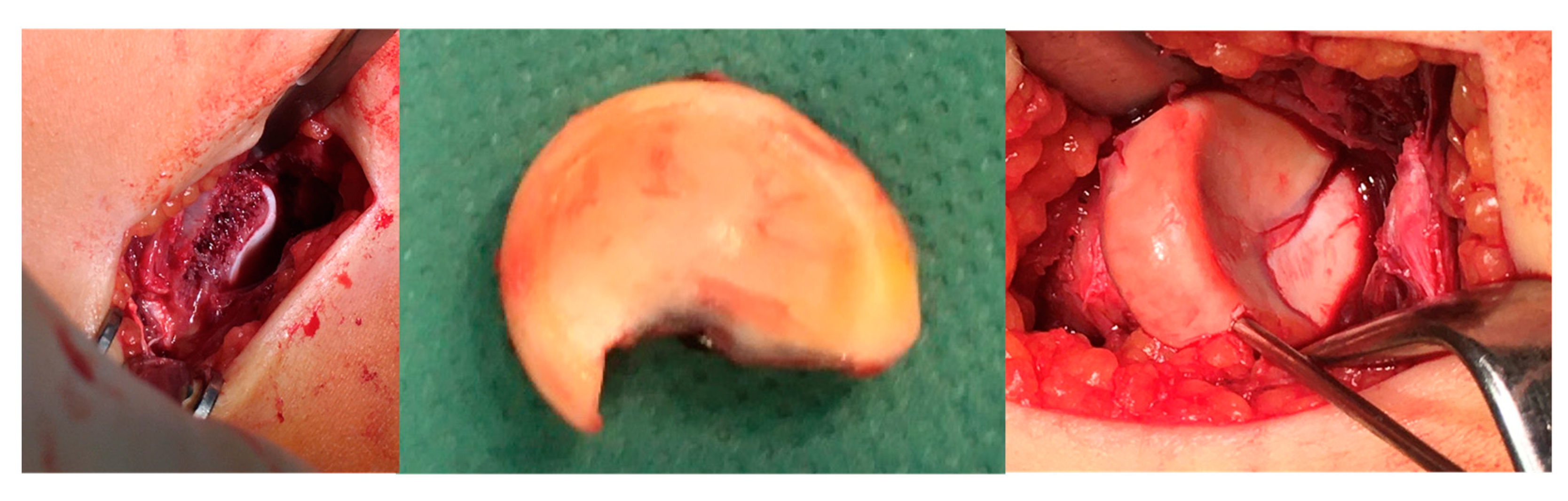
2.2. Surgical Methods:
4. Discussion
- Osteochondral or chondral fragment
- Single, isolated body
- Sufficient size
- Instability, detachment or movement
- Fragment is less than 5 mm
- Bodies are multifragmented and small
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gkiokas, A.; Morassi, L.G.; Kohl, S.; Zampakides, C.; Megremis, P.; Evangelopoulos, D.S. Bioabsorbable Pins for Treatment of Osteochondral Fractures of the Knee after Acute Patella Dislocation in Children and Young Adolescents. Adv. Orthop. 2012, 2012, e249687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, E. Delayed Osteochondral Fracture Fixation of the Knee in a Pediatric Patient. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badekas, T.; Takvorian, M.; Souras, N. Treatment Principles for Osteochondral Lesions in Foot and Ankle. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, U.; Tiwari, V.; Selvanayagam, R. A Rare Case of Large Osteochondral Fracture of Patella. Cureus 15, e41245. [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, M.N.; Almutairi, M.M.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alqahtani, M.N.; Alghamdi, A.S. Osteochondral Fracture of the Patella without Soft Tissue Injury and with No Dislocation: A Case Report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 78, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padaki, A.S.; Allahabadi, S.; Pandya, N.K. Adolescent Elbow Osteochondral Lesions Following Prior Elbow Fracture Pinning. J. Child. Orthop. 2022, 16, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, J.M.; Nikizad, H.; Shea, K.G.; Gyurdzhyan, S.; Jacobs, J.C.; Cannamela, P.C.; Kessler, J.I. The Incidence of Surgery in Osteochondritis Dissecans in Children and Adolescents. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2016, 4, 2325967116635515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.; Davis, D.D.; Carter, K.R. Osteochondritis Dissecans. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor, Ł.; Tomaszewski, R. Evaluation of Osteochondritis Dissecans Treatment with Bioabsorbable Implants in Children and Adolescents. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudisco, C.; Bernardi, G.; Manisera, M.T.; De Maio, F.; Gorgolini, G.; Farsetti, P. An Update on Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee. Orthop. Rev. 14, 38829. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.E.; DaCambra, M.P.; Jibri, Z.; Dhillon, S.; Jen, H.; Jomha, N.M. Acute Osteochondral Fractures in the Lower Extremities - Approach to Identification and Treatment. Open Orthop. J. 2015, 9, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordunianu, M.A.; Antoniac, I.; Niculescu, M.; Paltanea, G.; Raiciu, A.D.; Dura, H.; Forna, N.; Carstoc, I.D.; Cristea, M.B. Treatment of Knee Osteochondral Fractures. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.L. Osteochondral Injuries of the Knee in Pediatric Patients. J. Knee Surg. 2018, 31, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.C.; Grainger, R.W.; McGraw, R.W. Osteochondral Fractures of the Femoral Condyles. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1966, 48, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühle, J.; Angele, P.; Balcarek, P.; Eichinger, M.; Feucht, M.; Haasper, C.; Alexander, G.; Jung, T.; Lill, H.; Marquass, B.; et al. Treatment of Osteochondral Fractures of the Knee: A Meta-Analysis of Available Scientific Evidence. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.L.; Urban, W.P.; Caborn, D.N.; Vanarthos, W.J.; Carlson, C.S. Articular Cartilage Changes Seen with Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Detected Bone Bruises Associated with Acute Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanitski, C.L.; Paletta, G.A. Articular Cartilage Injury with Acute Patellar Dislocation in Adolescents. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, D.A.; White, L.M.; Fithian, D.C. Acute Lateral Patellar Dislocation at MR Imaging: Injury Patterns of Medial Patellar Soft-Tissue Restraints and Osteochondral Injuries of the Inferomedial Patella. Radiology 2002, 225, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianotti, S.M.; Marshall, S.W.; Hume, P.A.; Bunt, L. Incidence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury and Other Knee Ligament Injuries: A National Population-Based Study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2009, 12, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, J.C.; Busconi, B. The Role of Hip Arthroscopy in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip Disease. Orthopedics 1995, 18, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohndorf, K. Imaging of Acute Injuries of the Articular Surfaces (Chondral, Osteochondral and Subchondral Fractures). Skeletal Radiol. 1999, 28, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slaughter, A.J.; Reynolds, K.A.; Jambhekar, K.; David, R.M.; Hasan, S.A.; Pandey, T. Clinical Orthopedic Examination Findings in the Lower Extremity: Correlation with Imaging Studies and Diagnostic Efficacy. Radiogr. Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc 2014, 34, e41–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, D.N.; Tashjian, G.S.; Connell, D.A.; Deland, J.T.; O’Malley, M.; Potter, H.G. Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: A New Magnetic Resonance Grading System with Arthroscopic Correlation. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. Off. Publ. Arthrosc. Assoc. N. Am. Int. Arthrosc. Assoc. 2003, 19, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disler, D.G.; McCauley, T.R.; Kelman, C.G.; Fuchs, M.D.; Ratner, L.M.; Wirth, C.R.; Hospodar, P.P. Fat-Suppressed Three-Dimensional Spoiled Gradient-Echo MR Imaging of Hyaline Cartilage Defects in the Knee: Comparison with Standard MR Imaging and Arthroscopy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1996, 167, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhagen, R. a. W.; Maas, M.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Tol, J.L.; Krips, R.; van Dijk, C.N. Prospective Study on Diagnostic Strategies in Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus. Is MRI Superior to Helical CT? J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, D.H. Chondral and Osteochondral Fractures. J. Trauma 1966, 6, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, M.R.; Pfirrmann, C.W.A.; Hodler, J.; Vienne, P.; Zanetti, M. Cartilage Lesions in the Ankle Joint: Comparison of MR Arthrography and CT Arthrography. Skeletal Radiol. 2003, 32, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoury, G.Y.; Alliman, K.J.; Lundberg, H.J.; Rudert, M.J.; Brown, T.D.; Saltzman, C.L. Cartilage Thickness in Cadaveric Ankles: Measurement with Double-Contrast Multi-Detector Row CT Arthrography versus MR Imaging. Radiology 2004, 233, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; McCarthy, H.S.; Hulme, C.H.; Wright, K.T.; Makwana, N. The Management of Talar Osteochondral Lesions - Current Concepts. J. Arthrosc. Jt. Surg. 2021, 8, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, J.R.; Dekker, T.J.; Federer, A.E.; Liles, J.L.; Adams, S.B.; Easley, M.E. Republication of “Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: Current Concepts in Diagnosis and Treatment. ” Foot Ankle Orthop. 2023, 8, 24730114231192961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferkel, R.D.; Zanotti, R.M.; Komenda, G.A.; Sgaglione, N.A.; Cheng, M.S.; Applegate, G.R.; Dopirak, R.M. Arthroscopic Treatment of Chronic Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: Long-Term Results. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepple, S.; Winson, I.G.; Glew, D. Osteochondral Lesions of the Talus: A Revised Classification. Foot Ankle Int. 1999, 20, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, A.L.; Harty, M. Transchondral Fractures (Osteochondritis Dissecans) of the Talus. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1959, 41-A, 988–1020. [Google Scholar]
- H, T. [The Structure, Physiology, and Biomechanics of Articular Cartilage: Injury and Repair]. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2007, 41 Suppl 2.
- Wilusz, R.E.; Sanchez-Adams, J.; Guilak, F. The Structure and Function of the Pericellular Matrix of Articular Cartilage. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2014, 0, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyndina, Y.; Romaniuk, A.; Lyndin, M.; Hyryavenko, N.; Kurochkina, V.; Tkach, G.; Gluschenko, N.; Sikora, V. Morphofunctional Features of Articular Cartilage Structure. Folia Medica Cracoviensia 2019 Vol 59 No 3 81-93 2019.
- Makris, E.A.; Gomoll, A.H.; Malizos, K.N.; Hu, J.C.; Athanasiou, K.A. Repair and Tissue Engineering Techniques for Articular Cartilage. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Carmagnola, I.; Hatton, P.V. An Overview of Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic) Acid (PLGA)-Based Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3640–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girón, J.; Kerstner, E.; Medeiros, T.; Oliveira, L.; Machado, G.M.; Malfatti, C.F.; Pranke, P. Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: An Orthopedic and Dentistry Overview. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, e11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, C.V.; Gonçalves, V.; da Silva, M.C.; Bañobre-López, M.; Gallo, J. PLGA-Based Composites for Various Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedelin, H.; Hebelka, H.; Brisby, H.; Laine, T. MRI Evaluation of Resorbable Poly Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) Screws Used in Pelvic Osteotomies in Children—A Retrospective Case Series. J. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heye, P.; Matissek, C.; Seidl, C.; Varga, M.; Kassai, T.; Jozsa, G.; Krebs, T. Making Hardware Removal Unnecessary by Using Resorbable Implants for Osteosynthesis in Children. Children 2022, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubev, V.G.; Starostenkov, A.N. OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE FEATURES IN APPLICATION OF BIOABSORBABLE IMPLANTS FOR LIMB FRACTURES TREATMENT.
- Whitepapers - Bioretec Ltd. Available online: https://bioretec.com/educational-materials/whitepapers?medical_professional=on&category=12 (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Singh, V.; Garg, V.; Parikh, S.N. Management of Physeal Fractures: A Review Article. Indian J. Orthop. 2021, 55, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ActivaNailTM - Bioabsorbable Nail - Bioretec Ltd. Available online: https://bioretec.com/products/8/activanail-bioabsorbable-nail (accessed on 6 August 2023).
- Macken, A.A.; Eygendaal, D.; van Bergen, C.J. Diagnosis, Treatment and Complications of Radial Head and Neck Fractures in the Pediatric Patient. World J. Orthop. 2022, 13, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackerson, R.; Nguyen, A.; Carry, P.M.; Pritchard, B.; Hadley-Miller, N.; Scott, F. Intra-Articular Radial Head Fractures In the Skeletally Immature Patient: Complications and Management. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2015, 35, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Yu, A.-X.; Guo, X.-P.; Qi, B.-W.; Zhou, M.; Wang, W.-Y. Absorbable Implants versus Metal Implants for the Treatment of Ankle Fractures: A Meta-Analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.H.; Roh, Y.H.; Yang, B.G.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, M.K. Outcomes of Operative Treatment of Unstable Ankle Fractures: A Comparison of Metallic and Biodegradable Implants. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2012, 94, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlechter, J.A.; Nguyen, S.V.; Fletcher, K.L. Utility of Bioabsorbable Fixation of Osteochondral Lesions in the Adolescent Knee: Outcomes Analysis With Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967119876896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.-L.; Lin, S.-M.; Chang, C.-H.; Lan, T.-Y. Neglected Pediatric Osteochondral Fracture Dislocation of the Patella. Case Rep. Orthop. 2019, 2019, 2904782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, A.; King, G.J.W.; Grewal, R. Is ORIF Superior to Nonoperative Treatment in Isolated Displaced Partial Articular Fractures of the Radial Head? Clin. Orthop. 2014, 472, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, D. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Fractures of the Radial Head. Hand Clin. 2004, 20, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yin, H.; Zhou, G. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Mason Type II Radial Head Fracture by Intramedullary Pinning. Orthop. Surg. 2019, 11, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeev, I.V.; Виктoрoвич, Т.И.; Dyakonova, E.Y.; Юрьевна, Д.Е.; Gusev, A.A.; Андреевич, Г.А.; Romanova, E.A.; Алексеевна, Р.Е.; Khrolenko, P.V.; Владимирoвна, Х.П. Arthroscopic treatement of patella fractures in children. Pediatr. Traumatol. Orthop. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 5, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




