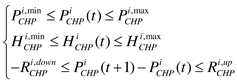1. Introduction
With the increasing global energy crisis and pollution issues, reducing carbon dioxide emissions and efficiently utilizing distributed energy sources have become major tasks for countries worldwide. However, distributed energy faces challenges such as uneven resource distribution, lack of coordination in management, and inefficient scheduling. Therefore, new technologies such as smart grids, energy hubs, integrated energy systems, and virtual power plants (VPPs) have been introduced to achieve multi-energy coordinated supply and cascaded utilization of energy resources[
1,
2]. These technologies play a crucial role in large-scale and efficient utilization of renewable energy, as well as in building efficient, secure, green, and low-carbon power systems. This paper aims to provide an academic translation of these concepts.
As a new type of technology, virtual power plants (VPPs) can aggregate distributed energy sources through advanced control, measurement, and communication technologies to achieve coordinated and optimized operation, thereby improving overall stability and competitiveness in the electricity market[
3]. As a distributed energy grid technology, VPPs can monitor and regulate flexible resources, allowing them to participate in electricity system energy trading, frequency regulation, peak load regulation, and other ancillary services as a whole. This promotes the coordinated interaction of the "source-grid-load-storage" of the new power system and can also optimize and schedule traditional thermal power, centralized renewable energy bases, or other forms of energy to promote the smooth operation of the power system. The use of market price incentive mechanisms can fully tap the potential of user-side resource regulation, and a series of hardware and software technologies such as the Internet of Things and big data can aggregate different types of operators to enable their participation in the electricity market [
3]. Existing research on VPPs has focused mainly on optimization and scheduling, increasing the consumption of new energy, reducing the impact of distributed resource fluctuations on the power system, and energy conservation and emission reduction. Future research should focus on the trading rules of VPPs in the medium and long-term electricity and spot markets, as well as in ancillary service markets, to promote the establishment of market mechanisms adapted to the new power system.
Currently, virtual power plants (VPPs) have been piloted and practiced in most provinces of China, participating in various market models such as ancillary markets and spot markets. For example, since its launch in December 2019, the Jibei VPP has participated in the North China electricity market clearance for over 3,200 hours, with a cumulative increase of 34.12 GWh of new energy generation[
4].In addition, on July 16, 2021, China's national carbon trading market was officially launched, with the power industry being the first to be included in carbon emission management[
5]. Building a new power system based on new energy and vigorously developing distributed resources is an important way for China to achieve green energy transformation, carbon neutrality, and peak carbon emissions[
6,
7]. Most researchers studying VPPs focus on operational optimization. Wang and Wu proposed a peak load optimization strategy based on a unified model of VPP adjustable space, which verified that VPPs can ensure the reliability of power system operation[
8,
9]. Falabretti and Gougheri proposed a two-stage robust optimization model considering wind power uncertainty, generating their own trading strategy. This trading strategy can realize the internal thermal power joint optimization operation of VPPs, help VPPs achieve internal resource optimization scheduling, and maximize VPP market revenue[
10,
11]. However, how to improve the consumption rate of renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions has become a key issue facing VPPs and a crucial step in promoting the green transformation of China's power system.
In recent years, carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems have received widespread attention as a new technology capable of sequestering carbon dioxide and reducing carbon emissions. MacDowell et al.[
12] provided an overview of this technology and demonstrated its potential to achieve 80%-90% emissions reduction targets. Y. Cui et al.[
13] analyzed the "energy time-shifting characteristics" of carbon capture plants and achieved peak shaving through liquid storage operation. R. Zhou et al.[
14] established a dual-carbon quantity model for liquid storage CCS systems and constructed a real-time two-stage low-carbon economic dispatch model with the goal of maximizing net revenue in the electricity and carbon trading markets. D. Chen et al.[
15] considered the operational mechanisms of CCS power plants and carbon transport systems and combined them with an economic dispatch model. In addition, W. Zhong et al.[
16] introduced CCS systems and tower-type solar thermal power plants into a virtual power plant and verified the high-efficiency coordination ability between CCS systems and renewable energy power plants. Therefore, introducing CCS systems into virtual power plants can reduce their carbon emissions and improve their flexible dispatch capabilities. At the same time, the energy consumption of carbon capture is a movable and adjustable load. By controlling it, CCS power plants have the characteristics of flexible operation and rapid power adjustment to respond to the stochastic fluctuations of wind turbine and photovoltaic power. Compared with traditional power plants, CCS power plants can reduce carbon emissions and adjust power output flexibly. Carbon trading is also one of the main measures to reduce carbon emissions in virtual power plants, and a stepped carbon trading mechanism can help the system find a balance between low-carbon and economic performance.[
17,
18,
19]introduced carbon trading costs into the dispatch models of integrated energy systems (IES) and verified the inhibitory effect of stepped carbon trading mechanisms on carbon emissions. They also studied and analyzed the impact of stepped carbon trading mechanisms on the low-carbon and economic performance of IES.[
20]compared traditional carbon trading mechanisms with stepped carbon trading mechanisms and found that stepped carbon trading mechanisms can achieve more carbon emissions reductions, and the increase in system costs for participating in stepped carbon trading mechanisms is smaller when achieving the same emissions reduction targets.[
21]combined the actual carbon emissions of gas turbines and boilers to construct a comprehensive energy system carbon trading mechanism. Finally, a low-carbon optimization operation model for integrated energy systems was established with the minimum objective function of energy purchase cost, carbon trading cost, and operation and maintenance cost. Therefore, it is evident that stepped carbon trading mechanisms play an important role in reducing carbon emissions, and this paper will introduce them to reduce carbon emissions from virtual power plants.
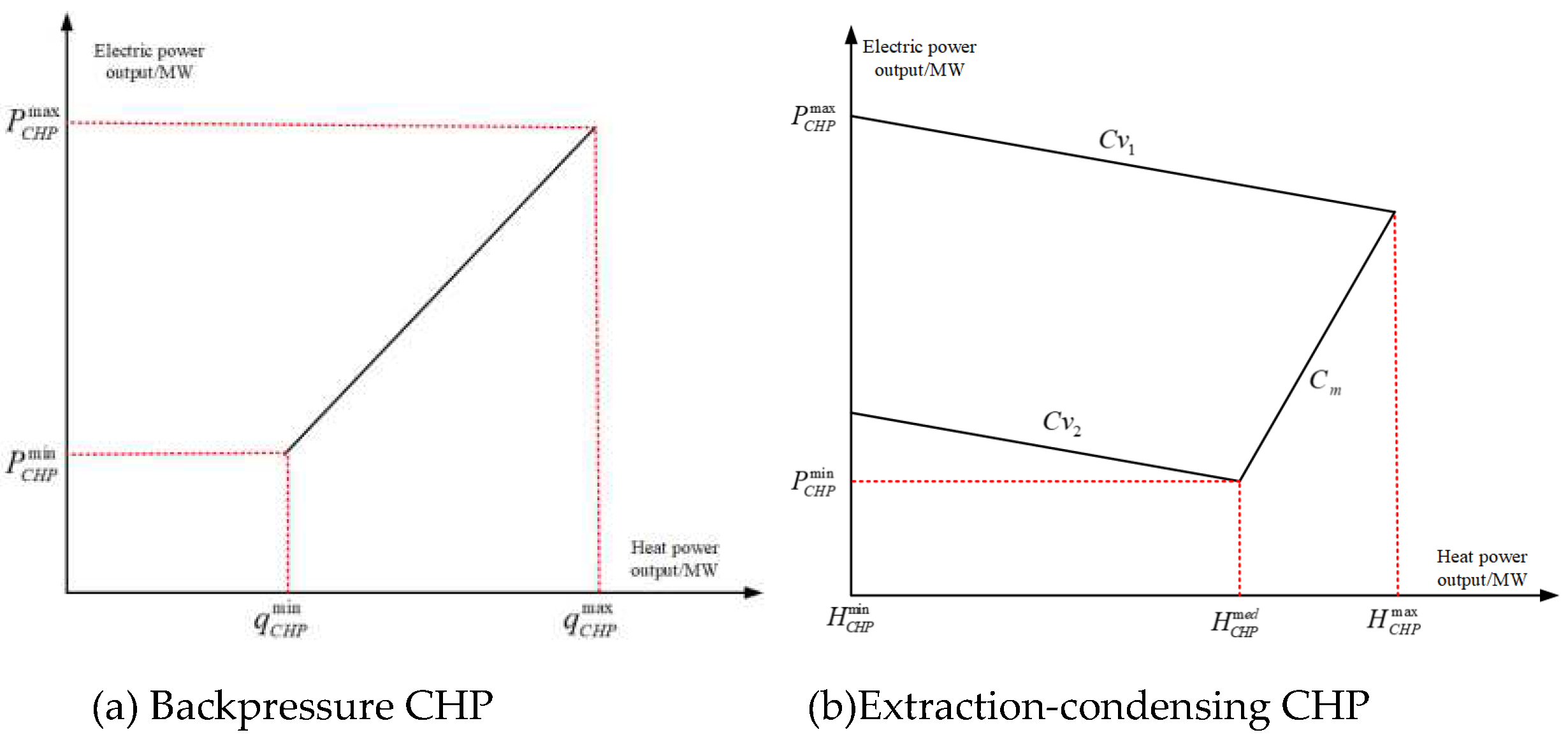
However, in the northern regions of China, the heating work in winter is usually completed by combined heat and power (CHP) units, which prioritize meeting the heat load demand and often operate in a "heat-driven" mode, resulting in the forced power output of the units being maintained at a relatively high level. Due to the thermal-electric coupling characteristics of CHP units, the range of adjustable electric output to meet user heating demand is reduced, which reduces the flexibility of CHP units and seriously affects the ability of virtual power plants (VPPs) to consume new energy sources[
22]. There are two main ways to decouple heat and electricity for CHP units: configuring thermal storage tanks and electric heating equipment, both of which can enhance the peak-shaving ability of CHP units[
23,
24]. However, the consumption of distributed energy sources such as wind and photovoltaics also needs to be addressed, and hydrogen storage as an emerging technology in recent years is composed of an electrolyzer, a fuel cell, and a hydrogen storage tank. When the load is in a valley period, the electrolyzer electrolyzes water to produce hydrogen, realizing energy conversion from electricity to hydrogen, which is injected into the hydrogen storage tank for storage; when the load is in a peak period, the stored hydrogen energy is converted into electrical energy through a hydrogen fuel cell, optimizing the operation of VPPs.[
25]established an optimal energy storage scheduling model for a wind-solar-hydrogen integrated system that includes multiple energy storage devices such as electricity, heat, and hydrogen. The results show that the proposed energy storage model can reduce the total operating cost and improve the flexibility of system regulation while ensuring safe system operation.[
26] simulated the economic efficiency of wind turbines with and without hydrogen storage devices and ultimately concluded that hydrogen storage systems can effectively improve the utilization efficiency of renewable energy sources.[
27]proposed an innovative hybrid model of a solar device based on a parabolic trough collector, proton exchange membrane electrolyzer, and fuel cell, selecting the best working fluid and ideal working conditions for the solar device with the minimum cost rate and maximum energy efficiency, demonstrating that hydrogen storage has good economic and environmental benefits as well as the ability to store energy for a long time. It can be seen that traditional energy storage and hydrogen storage are both aimed at smoothing wind power output fluctuations and reducing costs, but due to the single form of energy conversion, the role of traditional energy storage in waste heat co-utilization and carbon emission reduction is relatively limited. Compared with traditional energy storage, hydrogen storage has significant advantages in the flexibility and economy of power system regulation and seasonal energy storage, so hydrogen storage is expected to play a greater role in building low-carbon, green comprehensive energy systems. However, most studies only consider the electric-hydrogen coupling and do not consider the heat energy generated by the combustion of hydrogen gas in the hydrogen storage system's fuel cell.
(1) A new VPP structure is designed by integrating hydrogen energy storage and carbon capture into the traditional VPP. The surplus wind and solar resources are converted into hydrogen energy through hydrogen storage, and the carbon emissions from CHP generation are captured and stored or transported to MR, where CO2 is converted into CH4, achieving an optimized electric-thermal-carbon-hydrogen cycle.
(2) Based on the new VPP structure, a low-carbon economic scheduling model is established considering tiered carbon trading, which takes into account factors such as revenue, renewable energy consumption, and carbon emissions. The model is solved using a genetic algorithm.
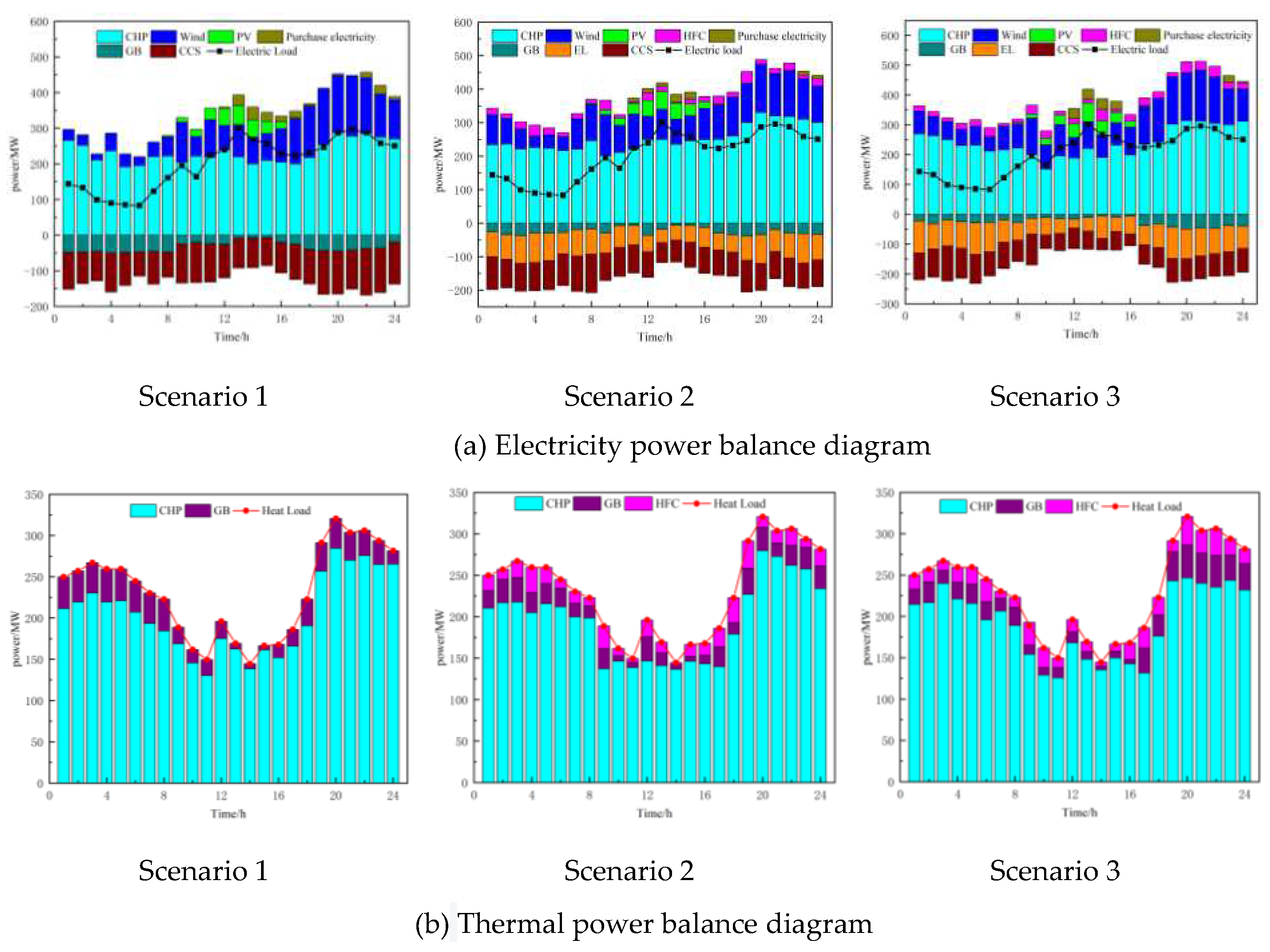
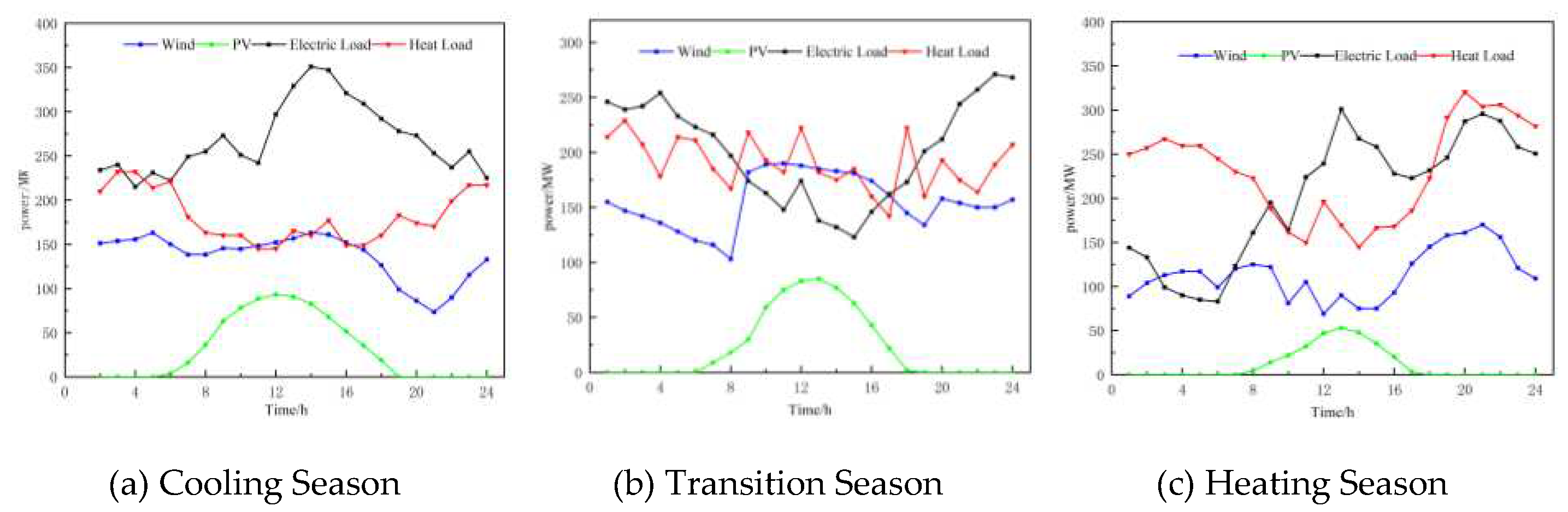
(3) Different scheduling strategies are proposed for three different scenarios: cooling season, transition season, and heating season. By selecting some parameters for comprehensive comparison, it is shown that the proposed scheduling approach has high practicality and economic benefits, effectively improving the VPP's ability to integrate renewable energy generation, mitigating the problem of mismatch between renewable energy output and load demand, achieving source-load balance, promoting VPP's low-carbon transformation, strengthening electric-thermal load coupling and complementary use, and has strong academic significance and engineering application value.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 describes the operating framework of the VPP, introduces the hydrogen energy storage system and tiered carbon trading model.
Section 3 presents the objective function and model solving process of the VPP.
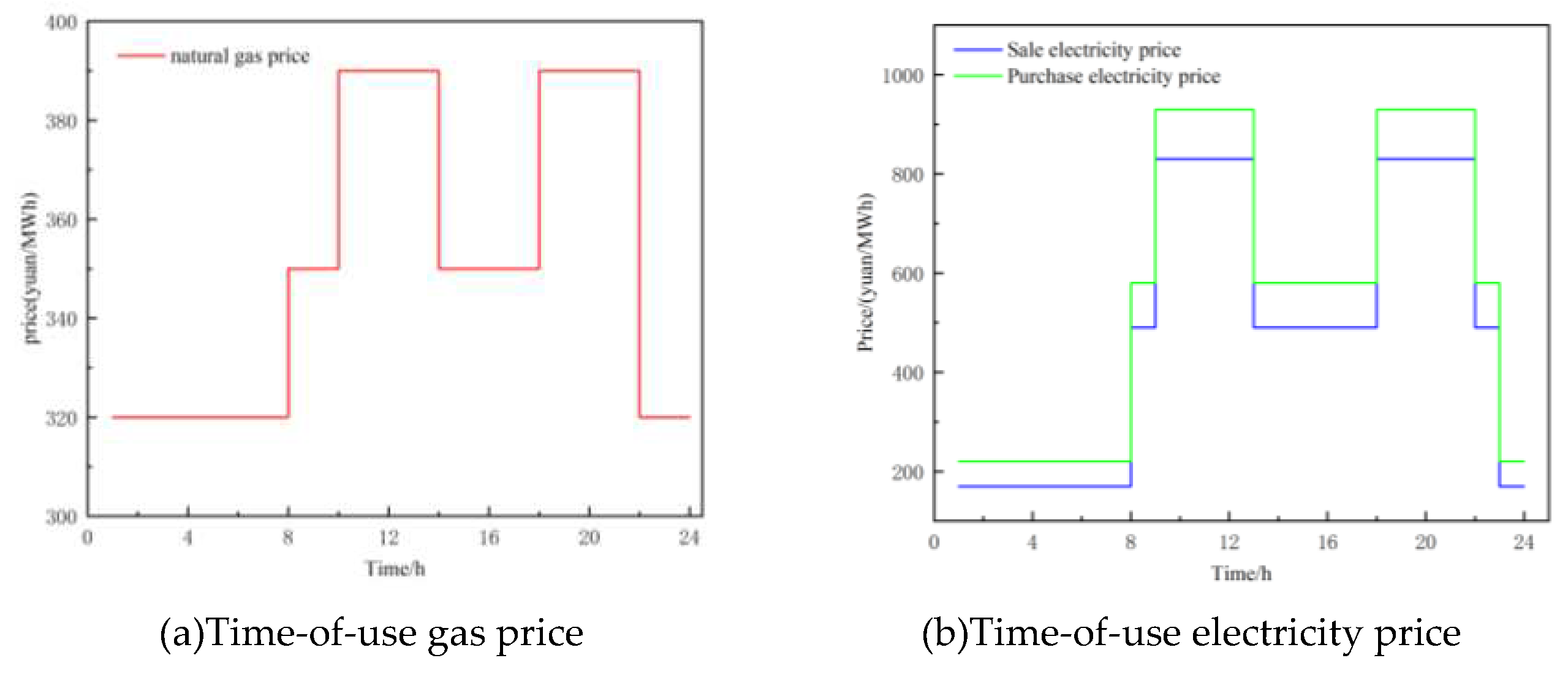
Section 4 provides the system parameters, simulation results, and analysis. Finally,
Section 5 summarizes the research results in this paper.
2. Framework for VPP Operation with Hydrogen Storage and Carbon Trading
2.1. Composition of Virtual Power Plant (VPP)
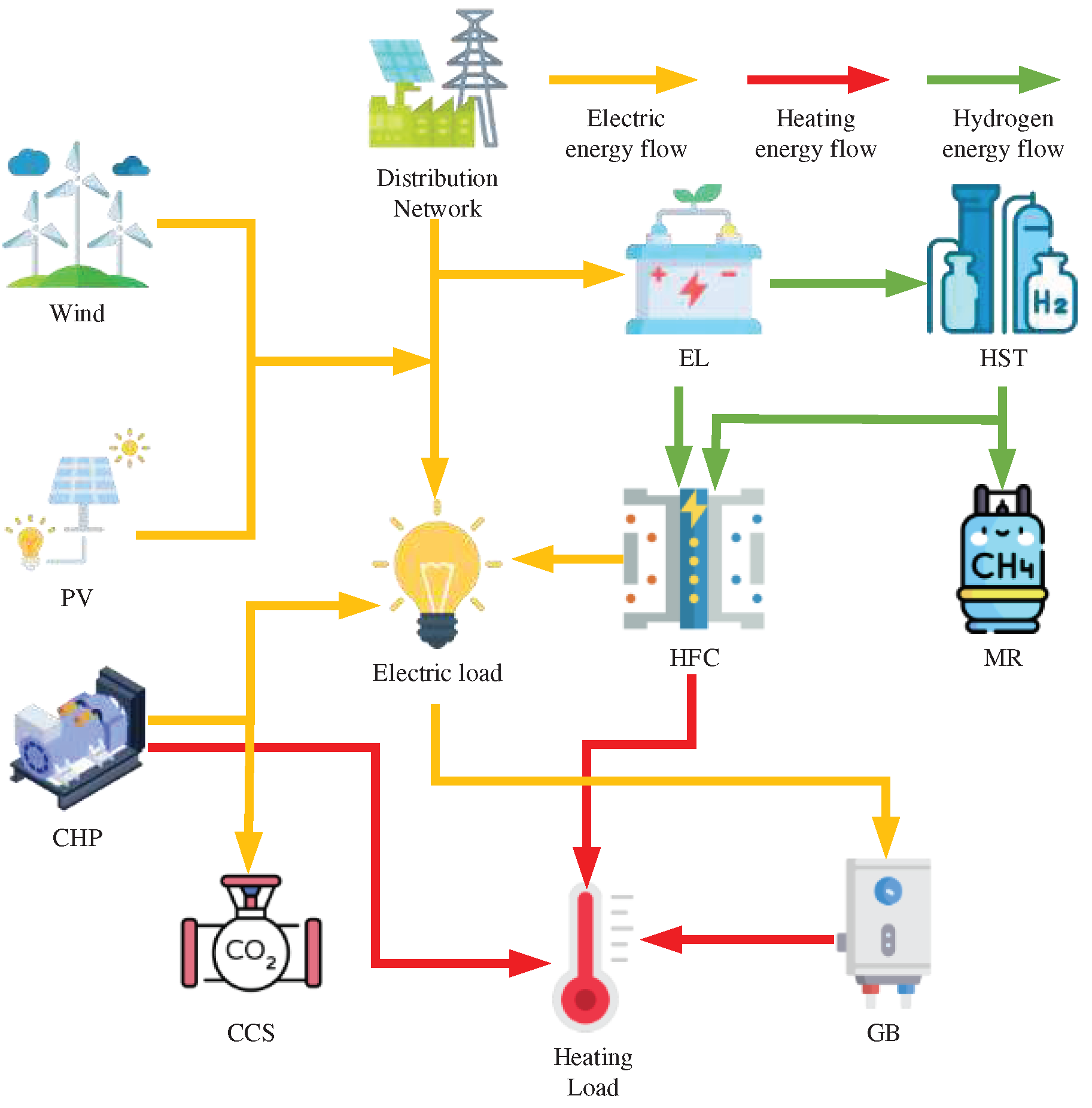
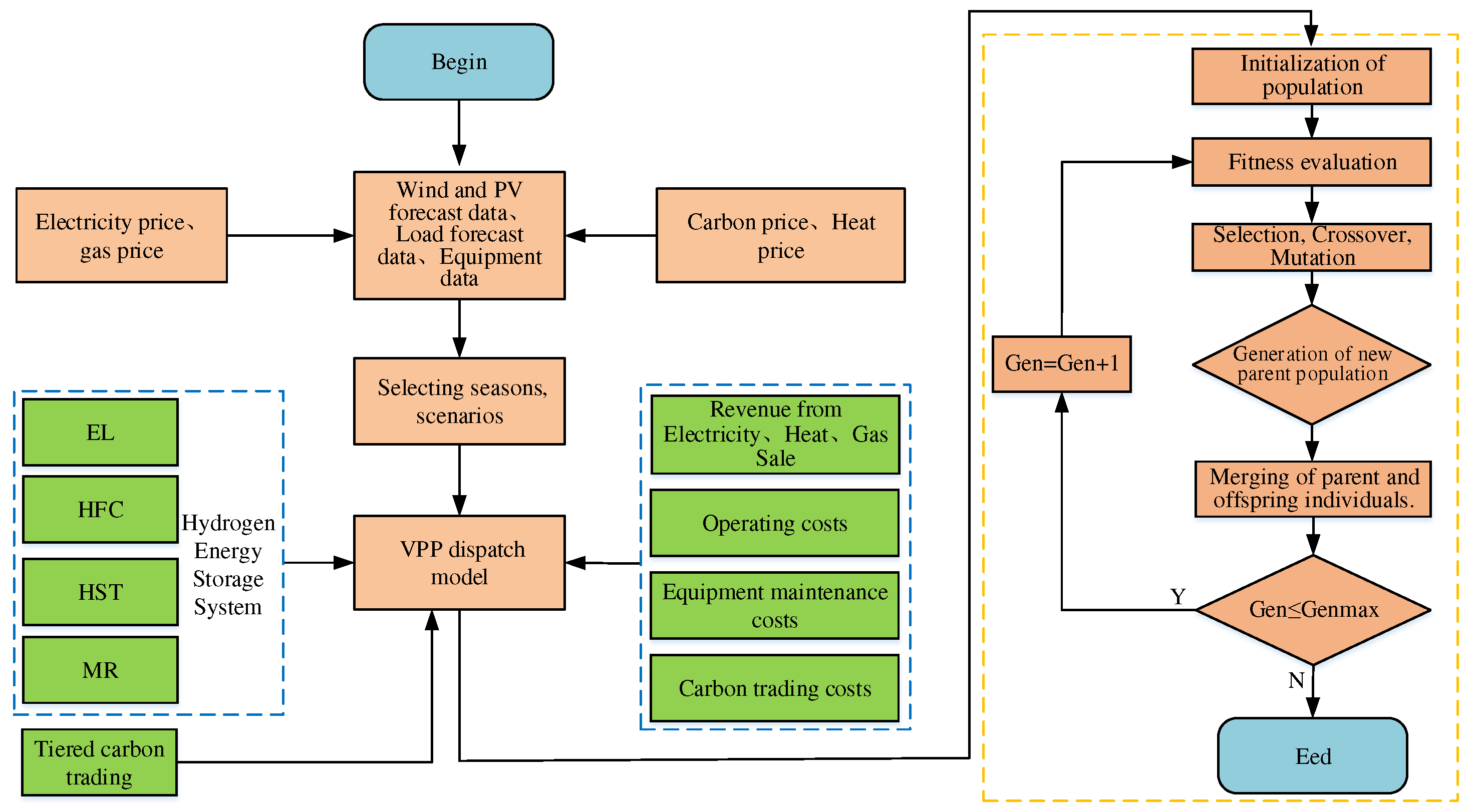
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) integrates various energy sources such as wind power, solar photovoltaic (PV), thermal power, hydropower, and natural gas within a specific region. It establishes a unified virtual control center to manage and dispatch energy resources. In a broader sense, by incorporating technologies like demand response, energy storage, electric vehicles, as well as communication and control systems, the integration of supply and demand sides can be achieved. This enables flexible coordination between power generation and consumption, and orderly integration of distributed energy sources. However, traditional VPPs heavily rely on coal-fired or combined heat and power (CHP) units, resulting in high carbon emissions and low utilization efficiency of clean energy, which hinders the implementation of China's 30-60 plan. In contrast, a combined system of carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen energy storage can effectively sequester a large amount of carbon dioxide and convert it into methane, thereby promoting a zero-carbon-oriented energy planning at the level of the power supply chain. This provides a feasible pathway for emission reduction, improving energy utilization efficiency, and implementing carbon neutrality strategies. Therefore, integrating CCS and hydrogen storage systems into the VPP can effectively control carbon emissions.
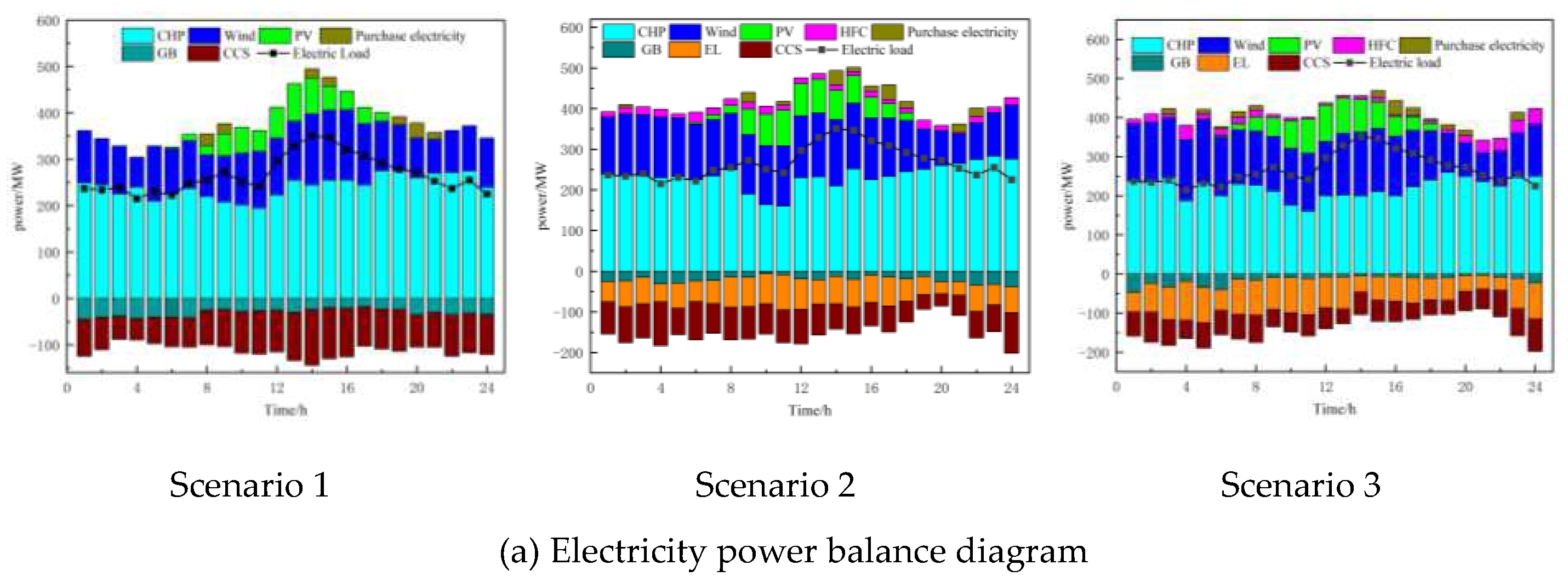
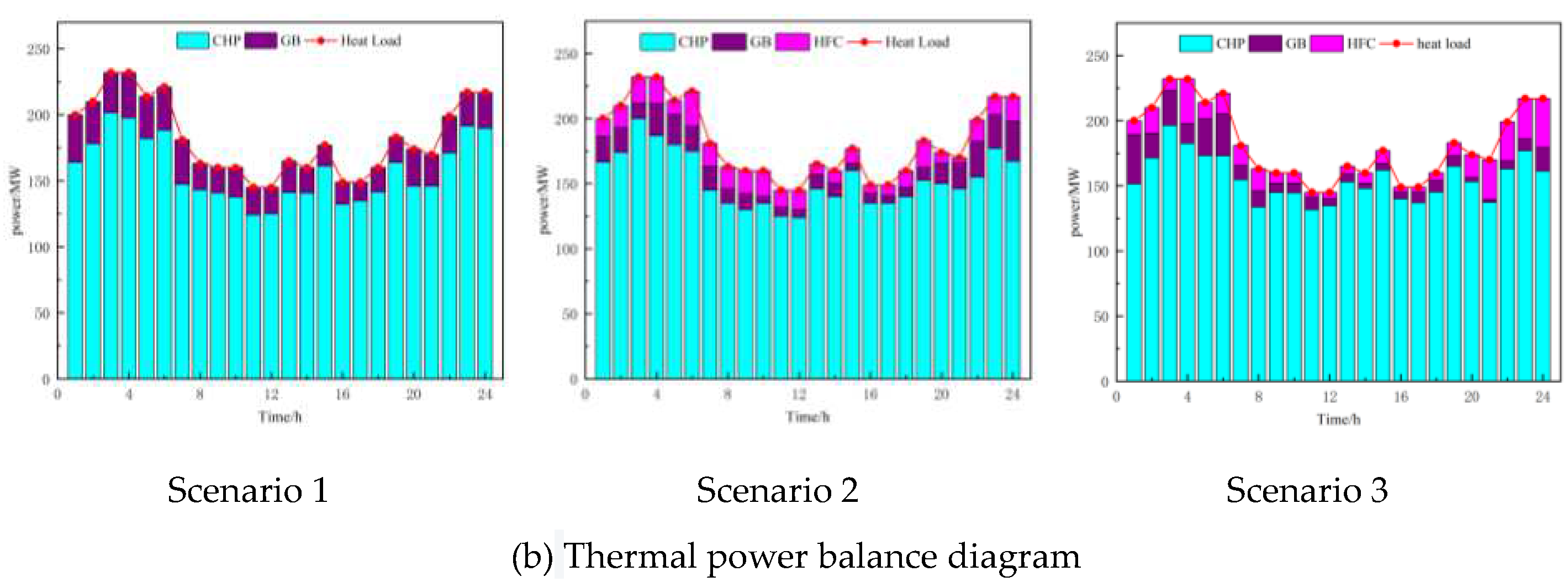
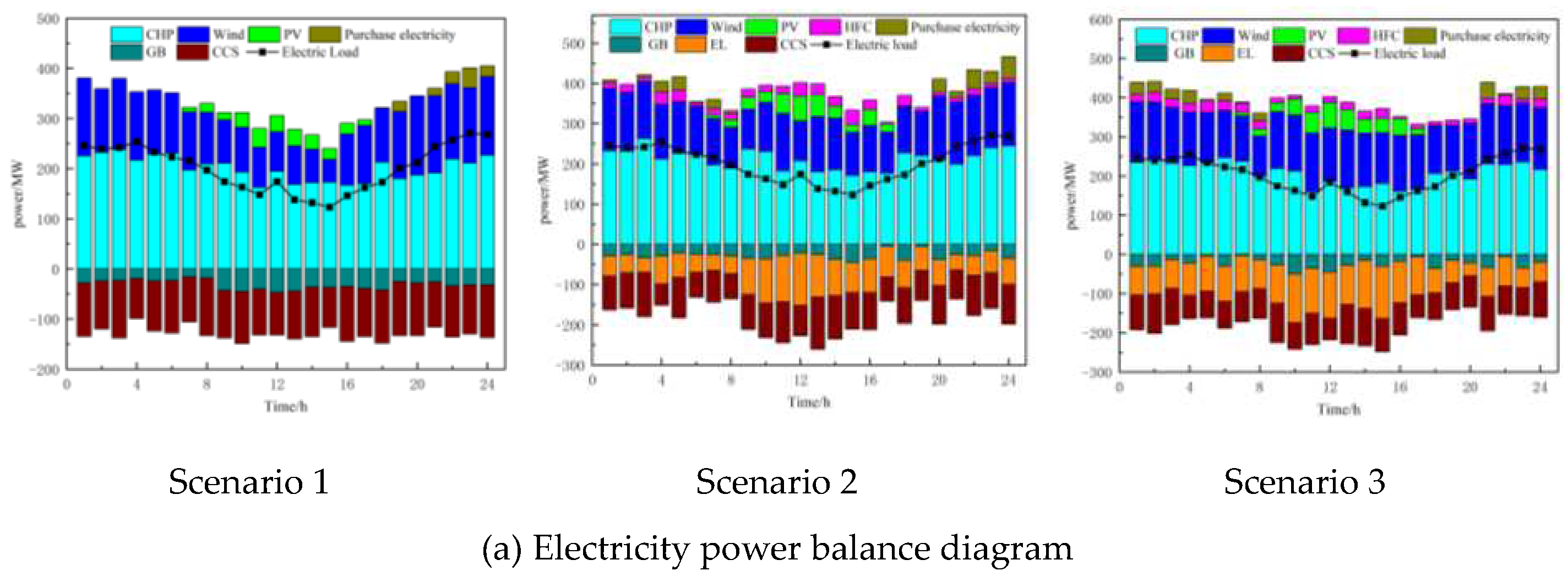
The proposed framework for the VPP, as illustrated in the figure below, includes PV, wind power, CHP, carbon capture, hydrogen storage systems, and electric boilers. By introducing hydrogen storage and electric boilers into the VPP, a portion of the CO2 emitted from the combustion of coal in CHP units can be captured and stored using carbon capture devices. Additionally, hydrogen produced by the hydrogen storage system can be converted into methane through a methanation reactor. The generated methane can be directly sold. Furthermore, the hydrogen fuel cells can generate electricity and heat by burning hydrogen, which can be operated in conjunction with electric boilers. This further decouples the CHP units from thermal-based electricity generation, leading to a reduction in carbon emissions, lowering system energy costs, and improving economic benefits.
Figure 1.
Topological Structure of Virtual Power Plant (VPP).
Figure 1.
Topological Structure of Virtual Power Plant (VPP).
2.2. Hydrogen energy storage model and methanation process.
Hydrogen Energy Storage System[
29]and the principle of carbon dioxide methanation process: EL first converts electrical energy into hydrogen energy. A portion of the hydrogen energy is inputted into the methanation reactor (MR) along with CO
2 to synthesize natural gas, while another portion is directly supplied to a hydrogen fuel cell (HFC) for conversion into electrical and thermal energy. The remaining portion is stored in hydrogen storage tanks. The direct conversion of hydrogen energy into electrical and thermal energy by HFC improves energy efficiency and does not produce CO
2. It can be seen that supplying hydrogen energy directly to HFC has multiple benefits. The energy conversion model described above can be summarized as follows in an academic paper format:
- (1)
Electrolysis cell equipment(EL)
In the equation, is the electrical energy input to EL in time period t; is the hydrogen energy output from EL in time period t; is the energy conversion efficiency of EL; and are the upper and lower limits of electrical energy input to EL, respectively; and are the upper and lower limits of EL's ramp rate.
- (2)
Hydrogen fuel cell(HFC)
In the equation,
is the hydrogen energy input to the hydrogen fuel cell (HFC) in time period t;
is the hydrogen-to-electricity conversion efficiency of the HFC;
is the hydrogen-to-thermal energy conversion efficiency of the HFC;
and
are the upper and lower limits of the hydrogen energy input to the HFC, respectively;
and
are the upper and lower limits of the ramp rate of the HFC
- (3)
Hydrogen storage tank(HST)
In the equations,
is the hydrogen charging efficiency of the hydrogen storage tank;
is the hydrogen discharging efficiency of the hydrogen storage tank;
is the hydrogen charging power of the hydrogen storage tank at time t.
and
are the hydrogen storage levels of the hydrogen storage tank at times t and t-1, respectively.
and
are the lower and upper limits of the hydrogen storage tank capacity, respectively. T is the scheduling period, which is 24 hours.
- (4)
Methane reactor(MR)
In the equation,
is the hydrogen power input to the methane reactor in time period t;
is the methane power output;
is the conversion efficiency of the methane reactor;
and
are the upper and lower limits of the hydrogen power input, respectively;
and
are the upper and lower limits of the ramp rate of the methane reactor.
2.3. Tiered carbon trading model
The carbon trading mechanism controls carbon emissions by establishing legal carbon emission rights and allowing producers to trade them on the market. Regulatory agencies first allocate carbon emission quotas to each carbon emission source, and manufacturers produce and emit carbon within their allocated quotas. If actual carbon emissions are lower than the allocated quota, the remaining quota can be traded on the carbon trading market; otherwise, additional carbon emission quotas must be purchased.
The tiered carbon trading mechanism model is mainly composed of three parts: the carbon emission quota model, the actual carbon emission model, and the tiered carbon emission trading model. The carbon emission sources in this paper mainly come from purchased electricity and CHP. Some of the carbon is captured and stored by CCS, and some is synthesized into methane by MR for sale. The rest of the emissions are optimized through the electricity-heat-carbon-hydrogen cycle to promote the low-carbon transformation of VPP.
- (1)
VPP carbon emission quota allocation model.
There are mainly two types of carbon emission sources in VPP: purchasing electricity from the superior power grid and CHP. Currently, the most commonly used quota allocation method in China is free allocation, and this paper assumes that the purchased electricity from the superior power grid is generated by coal-fired units[
30].
In the equation,
,
and
are the carbon emission quota for VPP, CHP,
and purchasing electricity from the superior power grid, respectively;
is the carbon emission quota for unit heat supply;
is the conversion factor for converting electricity generation into heat supply;
is the carbon emission quota assigned to unit purchased electricity;
and
are the thermal output and electrical output of the ith CHP in time period t;
is the electrical power input from the superior power grid to VPP.
- (2)
Actual carbon emissions of VPP
The carbon capture device can partially sequester the CO
2 generated by VPP, and additionally, the MR can absorb a portion of CO
2 during the hydrogen-to-methane conversion process. Therefore, the actual carbon emission model is as follows:
In the equation,
is the actual carbon emissions of VPP, is the carbon emissions of CHP,
is the purchased electricity from the superior power grid by VPP,
is the amount of CO
2 absorbed by MR,
is the amount of CO
2 sequestered by CCS.
is the purchased electricity power from the superior power grid by VPP in time period t.
and
are the carbon emission calculation parameters for purchased electricity power and CHP output, respectively.
and
are the electrical output and thermal output of the i-th CHP in time period t.
is the number of CHP.
is the hydrogen power input to the MR in time period t.
is the parameter for CO
2 absorption during the hydrogen-to-natural-gas conversion process in the MR equipment.
is the amount of CO
2 sequestered by CCS at time t.
- (3)
Tiered carbon trading model.
The tiered carbon trading model adopts a tiered carbon price, which sets different carbon emission ranges based on the difference between actual carbon emissions and carbon quotas. Each range corresponds to a different unit carbon trading price. When the difference between actual carbon emissions and carbon quotas exceeds the set range, the carbon trading price for the excess emissions also increases. The greater the difference, the higher the corresponding carbon trading price. The cost calculation expression for the tiered carbon trading model is as follows[
30]:
In the equation,
is the tiered carbon trading cost,
is the base carbon trading price,
is the length of the carbon emission range,
is the rate of price increase.
5. Conclusion
This paper proposes an optimization and scheduling strategy for virtual power plants (VPPs) considering the complementary use of electric and thermal energy and the decarbonization of energy in multiple scenarios. By enabling the collaborative operation of multiple devices, the VPP achieves energy complementarity and optimized scheduling, leading to carbon reuse. The following conclusions can be drawn from the proposed scheduling strategy:
(1)Introducing hydrogen energy storage systems and a tiered carbon trading mechanism based on carbon capture facilitates carbon reuse. On one hand, it reduces carbon emissions from the VPP and increases the integration of renewable energy. On the other hand, the generated methane can be supplied to the natural gas consumption system, further enhancing the economic benefits of the VPP.
(2)Through the collaborative operation of multiple units, the coupling of hydrogen energy storage and electric boilers enables the decoupling of heat and power in combined heat and power (CHP) units. This effectively optimizes the output of CHP units, improves their operational flexibility and peak shaving capabilities, reduces coal consumption costs, lowers carbon emissions, enhances the utilization of renewable energy generation, and mitigates the contradiction between renewable energy generation and electricity demand. It achieves a balance between supply and demand, optimizes the energy structure of the VPP, and improves its economic benefits.
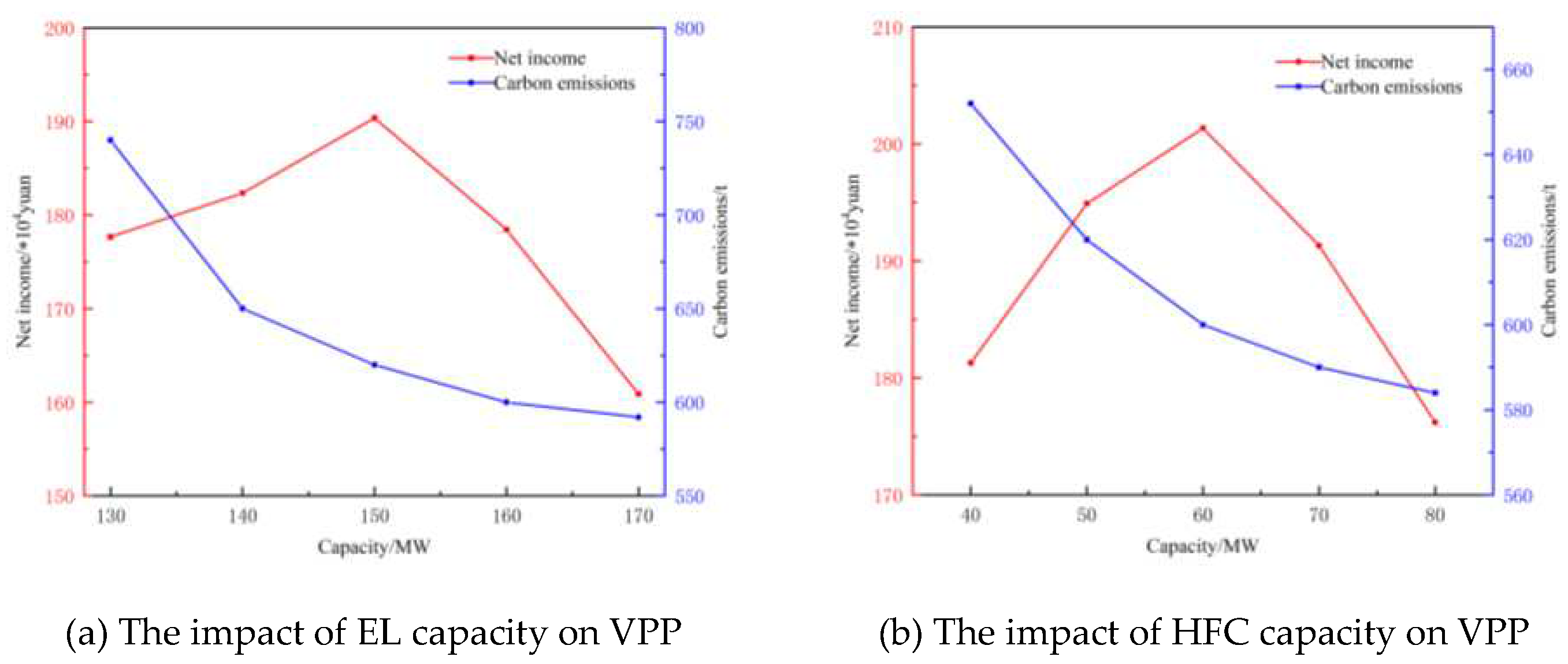
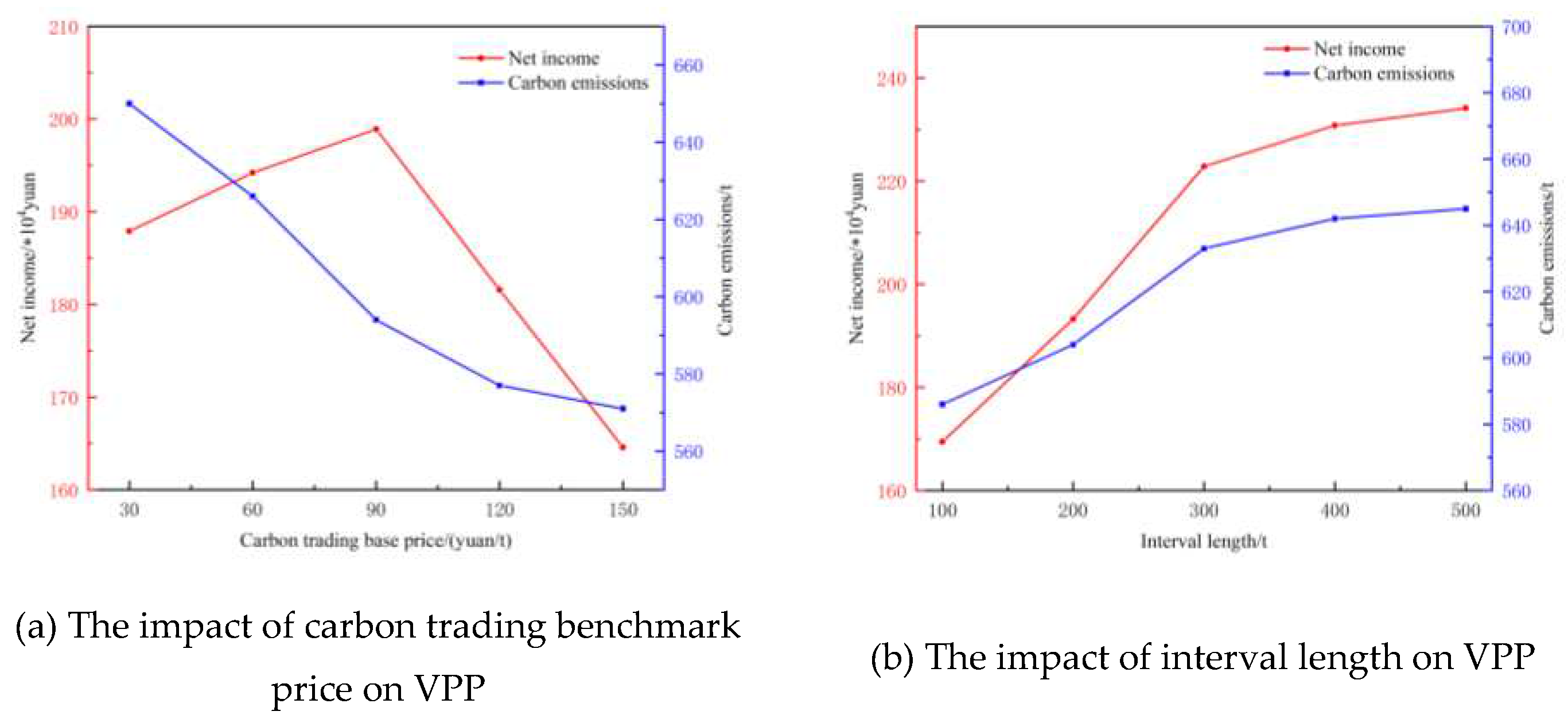
(3)Sensitivity analysis of the VPP's low-carbon economic conditions is conducted by considering different parameters for tiered carbon trading and the capacity of hydrogen energy storage devices. The results demonstrate that reasonable parameter settings and capacity configurations are more conducive to reducing carbon emissions and increasing the economic benefits of the VPP.
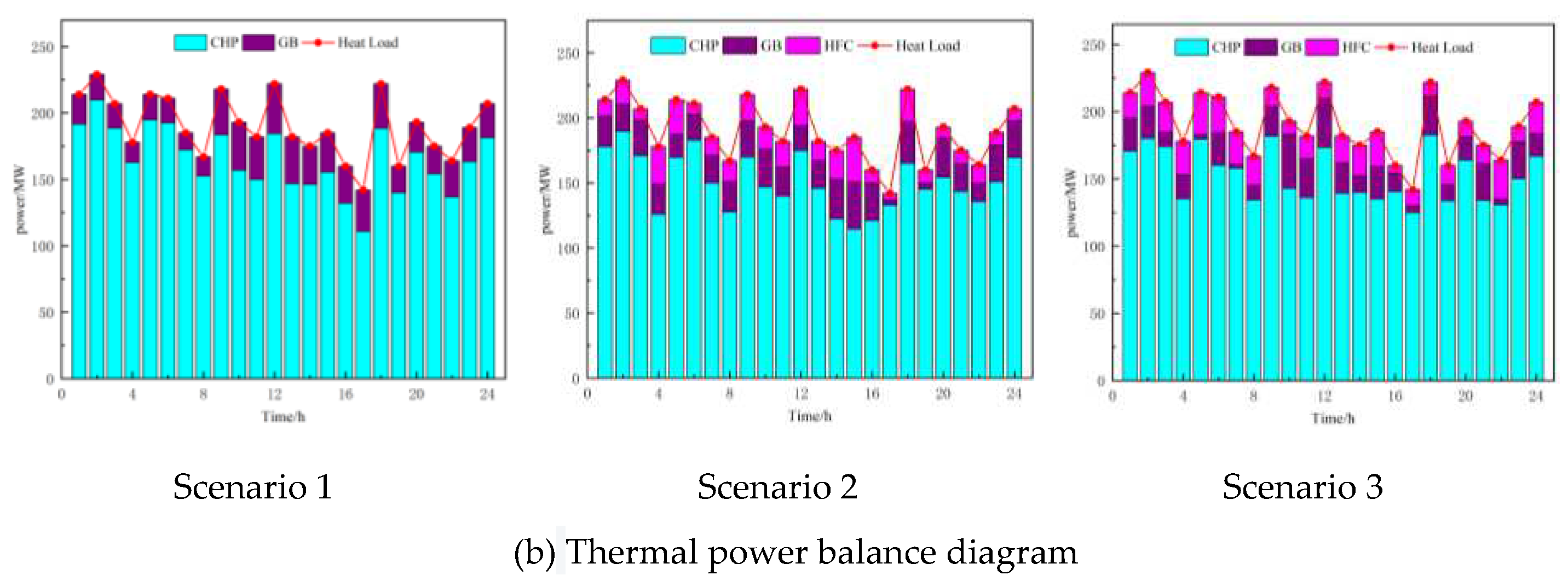
(4)Lastly, three scenarios are established to comprehensively compare the scheduling results of different scenarios in the same season, considering different load inputs. This validates the practicality of the proposed model and demonstrates that the optimization and scheduling approach has high generality and economic benefits, effectively improving the VPP's ability to integrate renewable energy generation and reduce carbon emissions.
However, this paper only considers measures to reduce carbon emissions from the supply side and does not address the demand response from the load side. Demand response has gradually matured and is of great significance for energy conservation, emission reduction, and promoting the integration of renewable energy. To tap into the resources on the load side, it is necessary to incorporate demand response into the VPP's low-carbon economic scheduling model, treating VPP devices as dispatchable assets. This enables source-load interaction and further "peak shaving and valley filling" through demand response, reducing carbon emissions in the VPP, increasing the integration of renewable energy, enhancing the operational flexibility of the VPP, and reducing the impact of fluctuations in wind and solar energy.