Submitted:
31 October 2023
Posted:
01 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical used
2.2. Synthesis of CdSe Quantum Dots
2.3. Extraction and purification of MSP
2.4. Synthesis of CdSe-MSP Complexes
2.5. Characterization of the synthesized CdSe QDs and CdSe-MSP complexes
2.6. Investigation of the interactions between CdSe QDs and MSPn complexes
3. Results and discussion
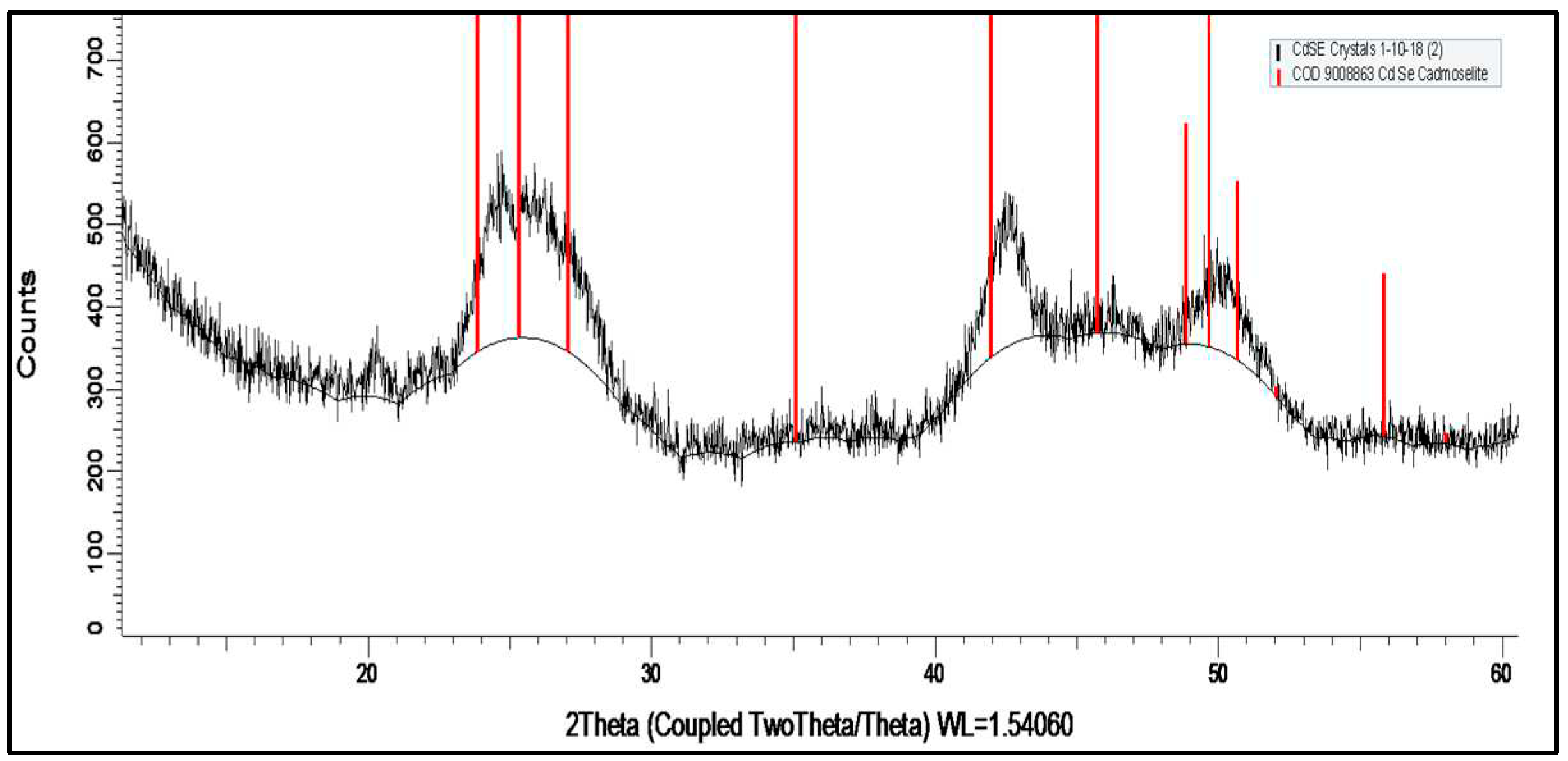
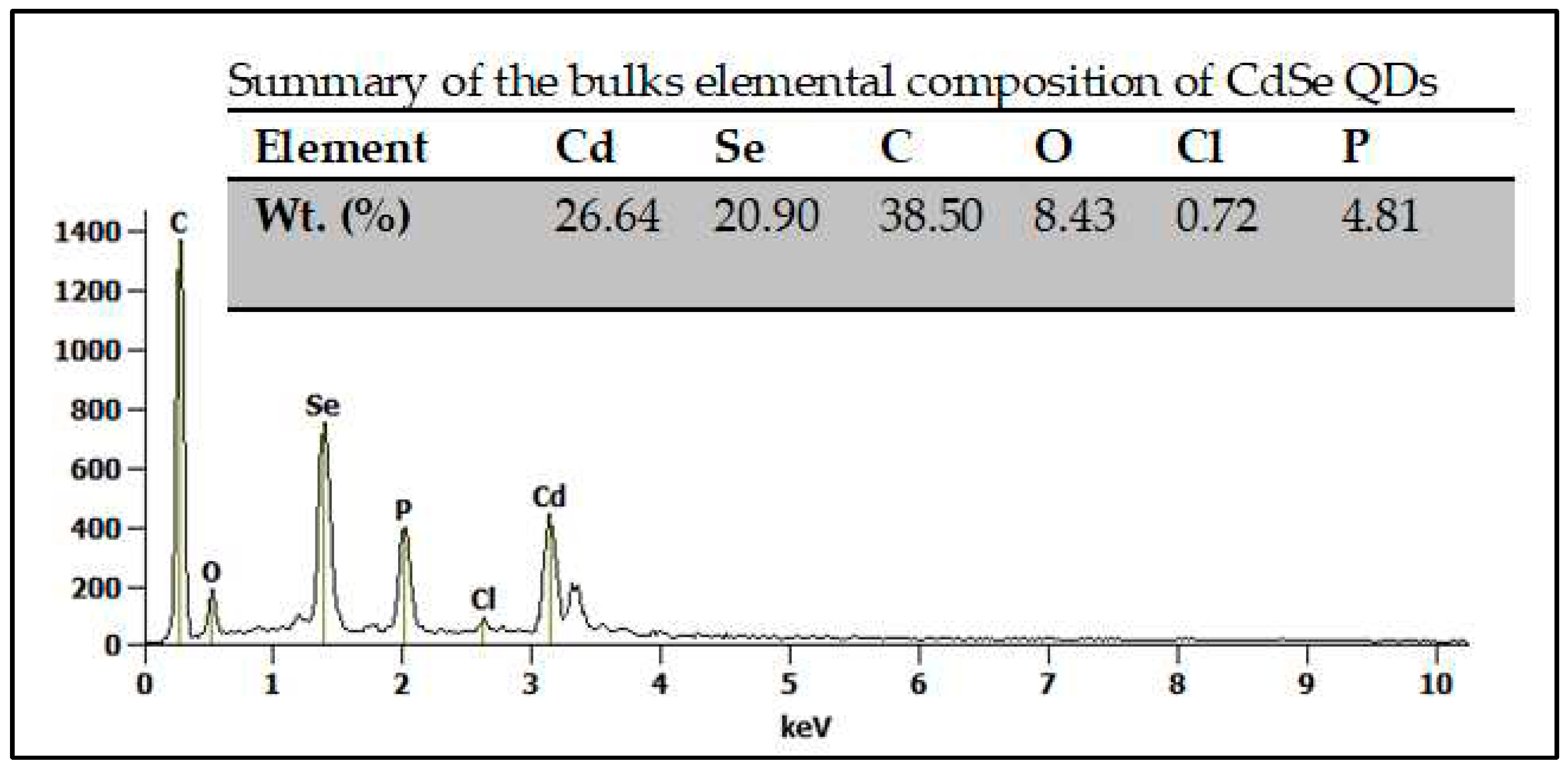
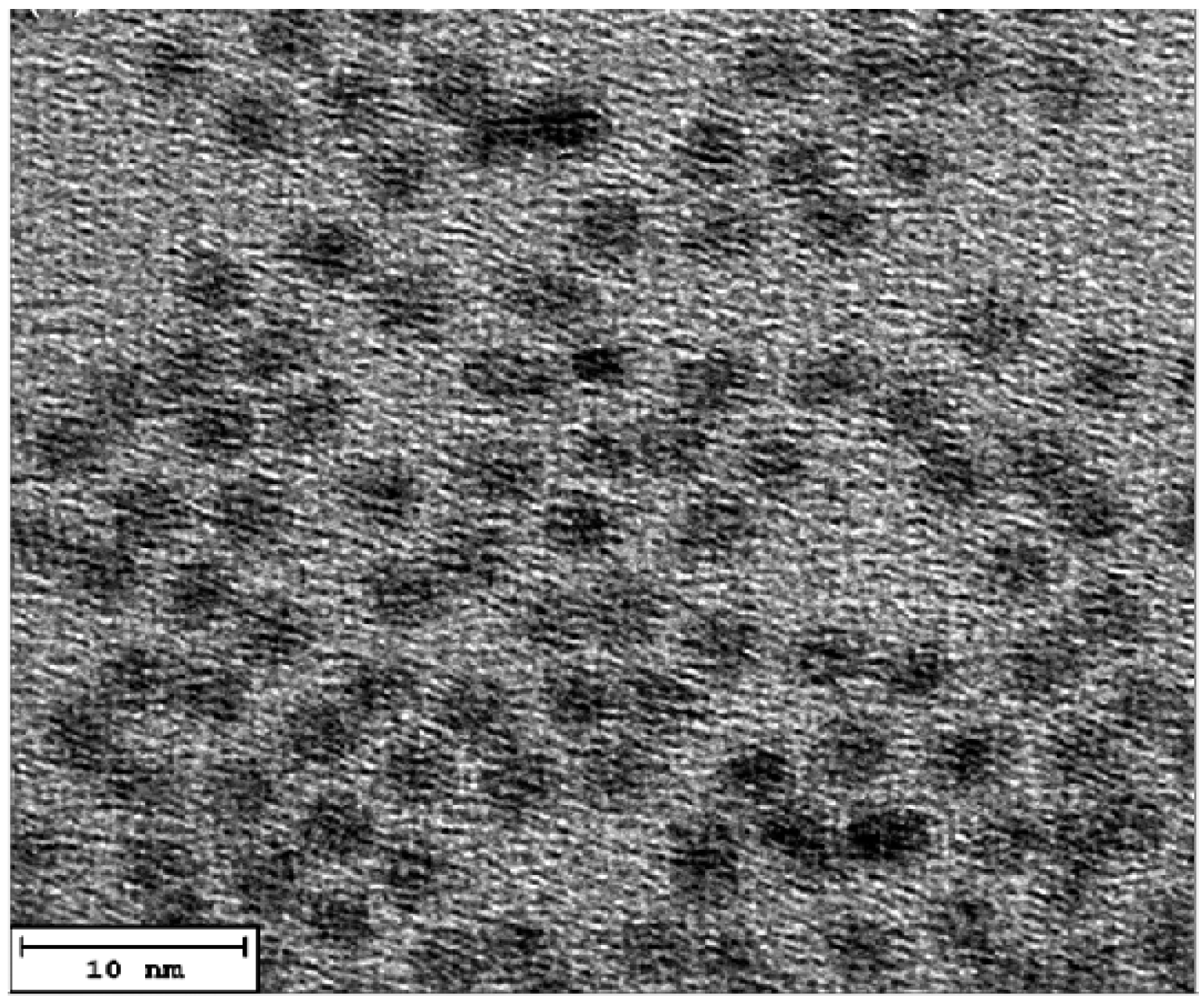
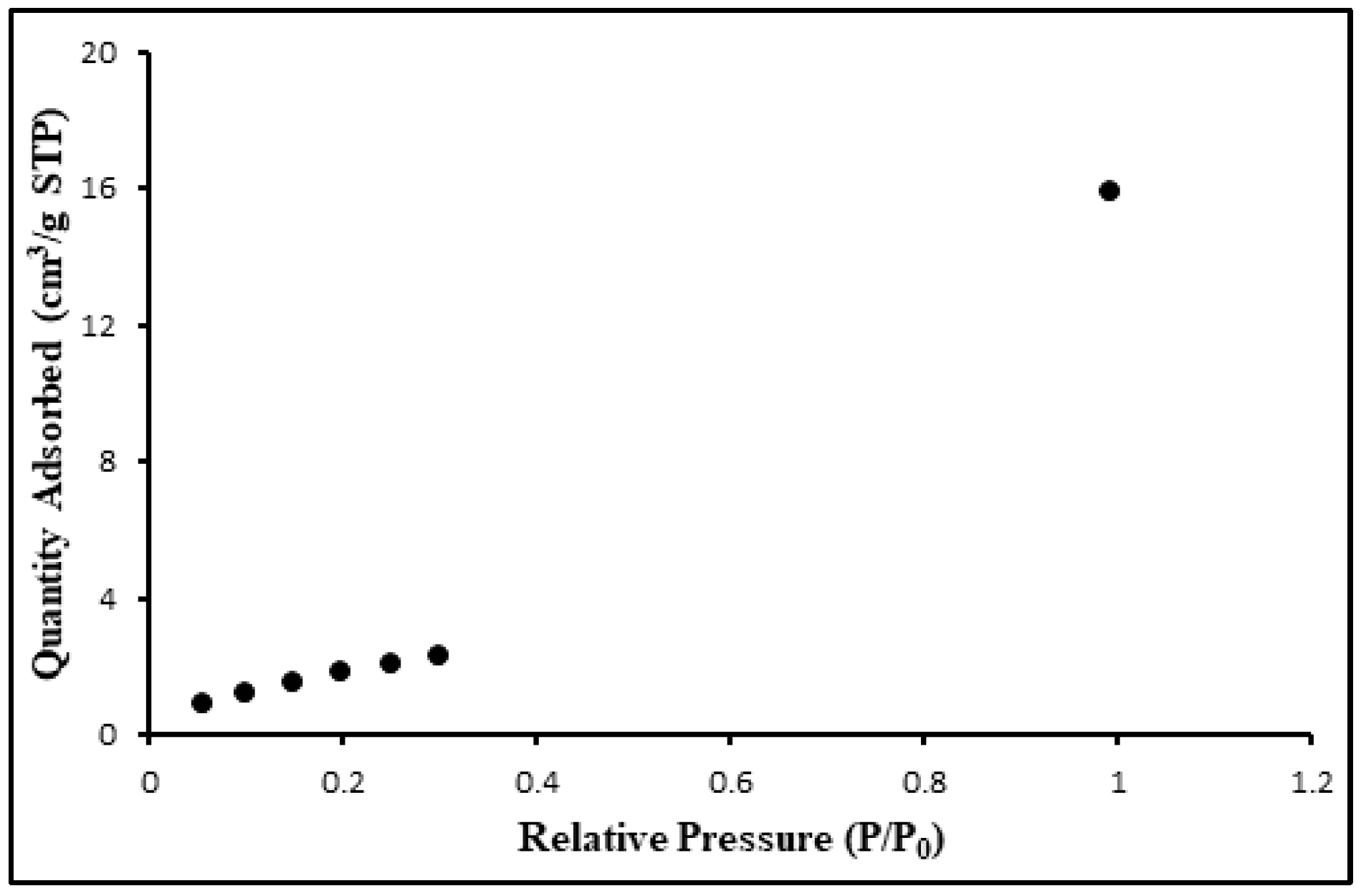
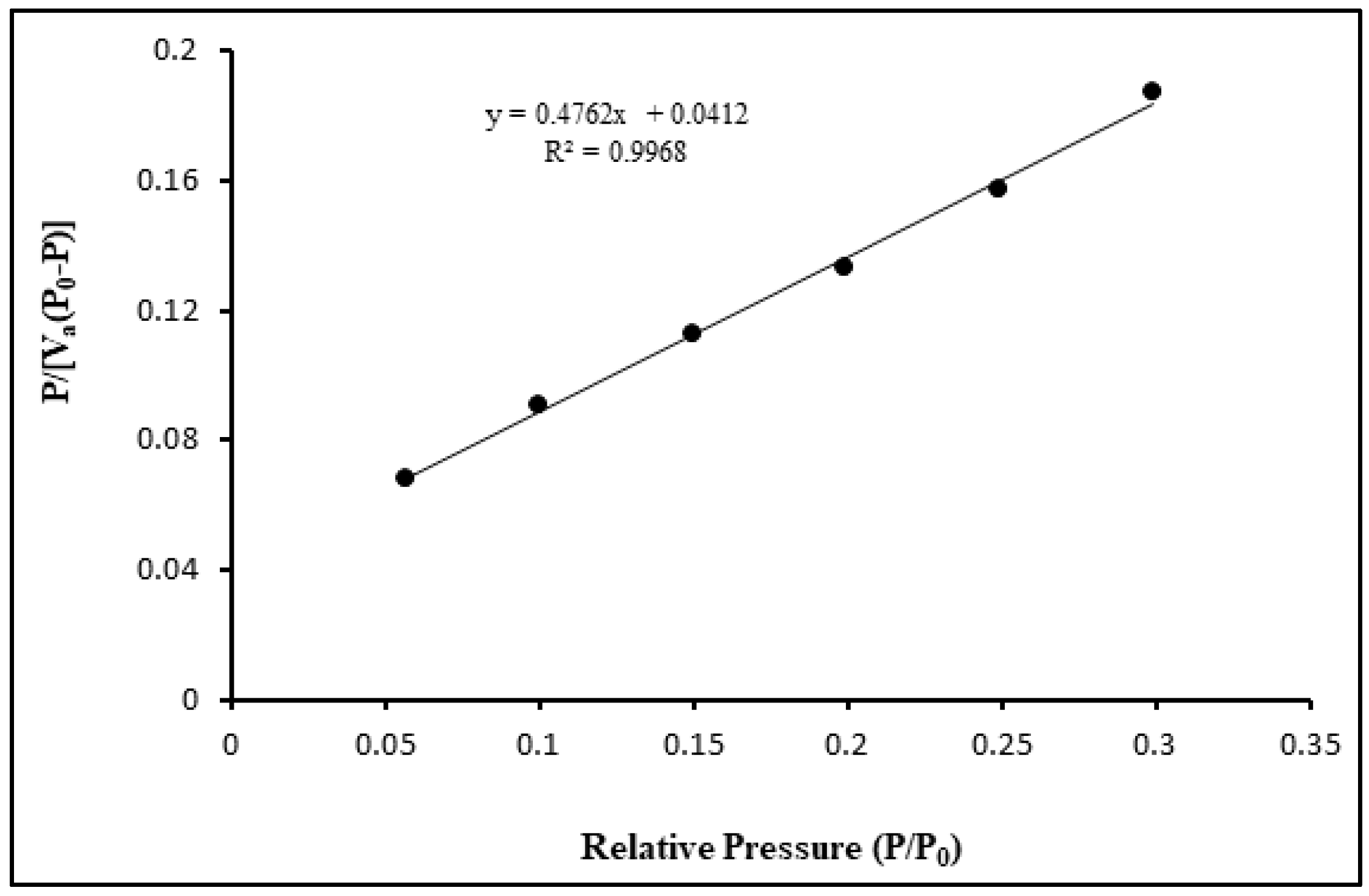
3.1. The structural and morphological characterization of CdSe QDs.
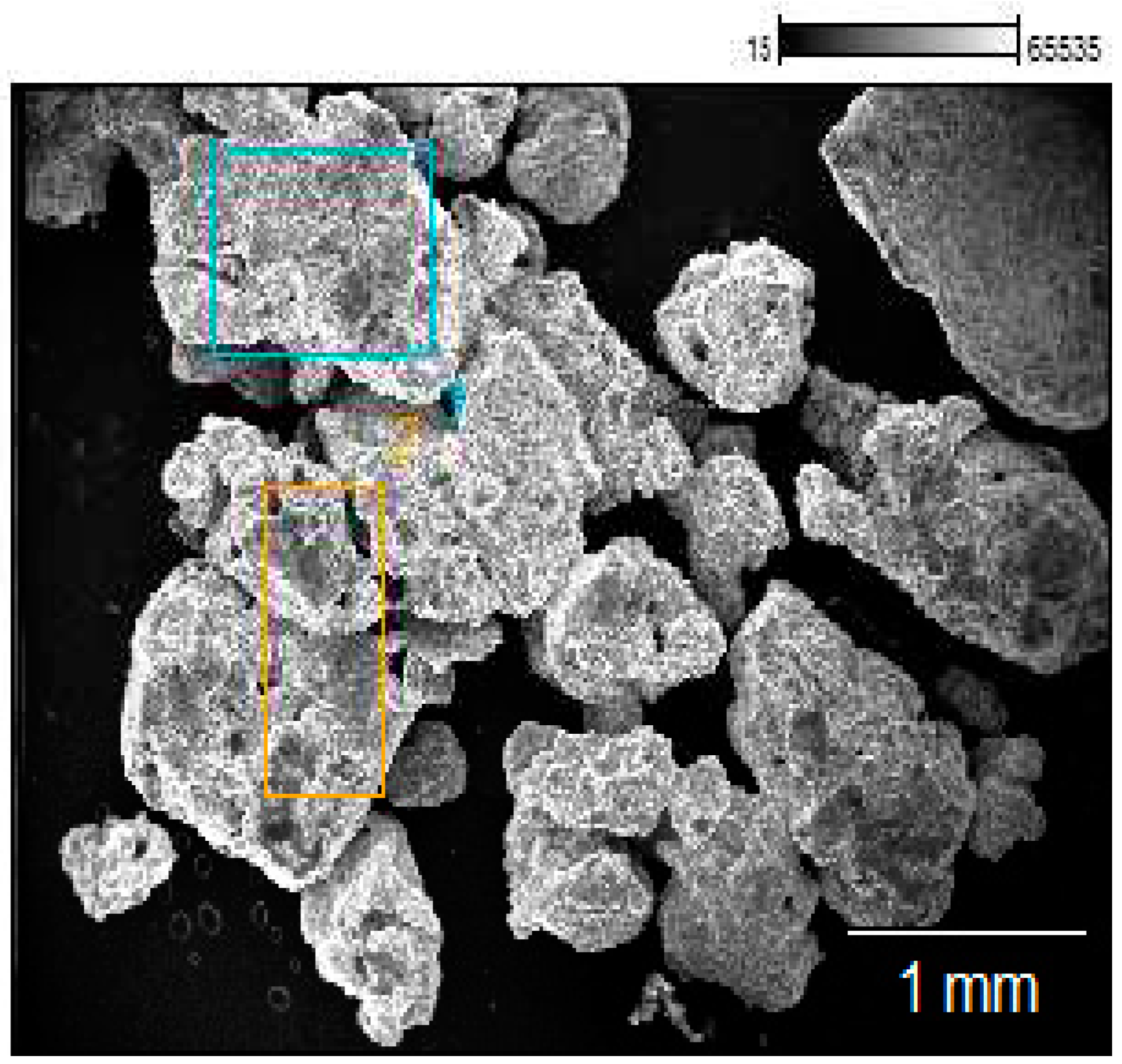
3.2. The morphological characterization of MSP and CdSe–MSP complexes.
3.3. The structural and morphological characterization of CdSe–MSCP complexes.
3.4. Interaction between CdSe QDs and MSP using the UV–Vis absorption and fluorescence spectra
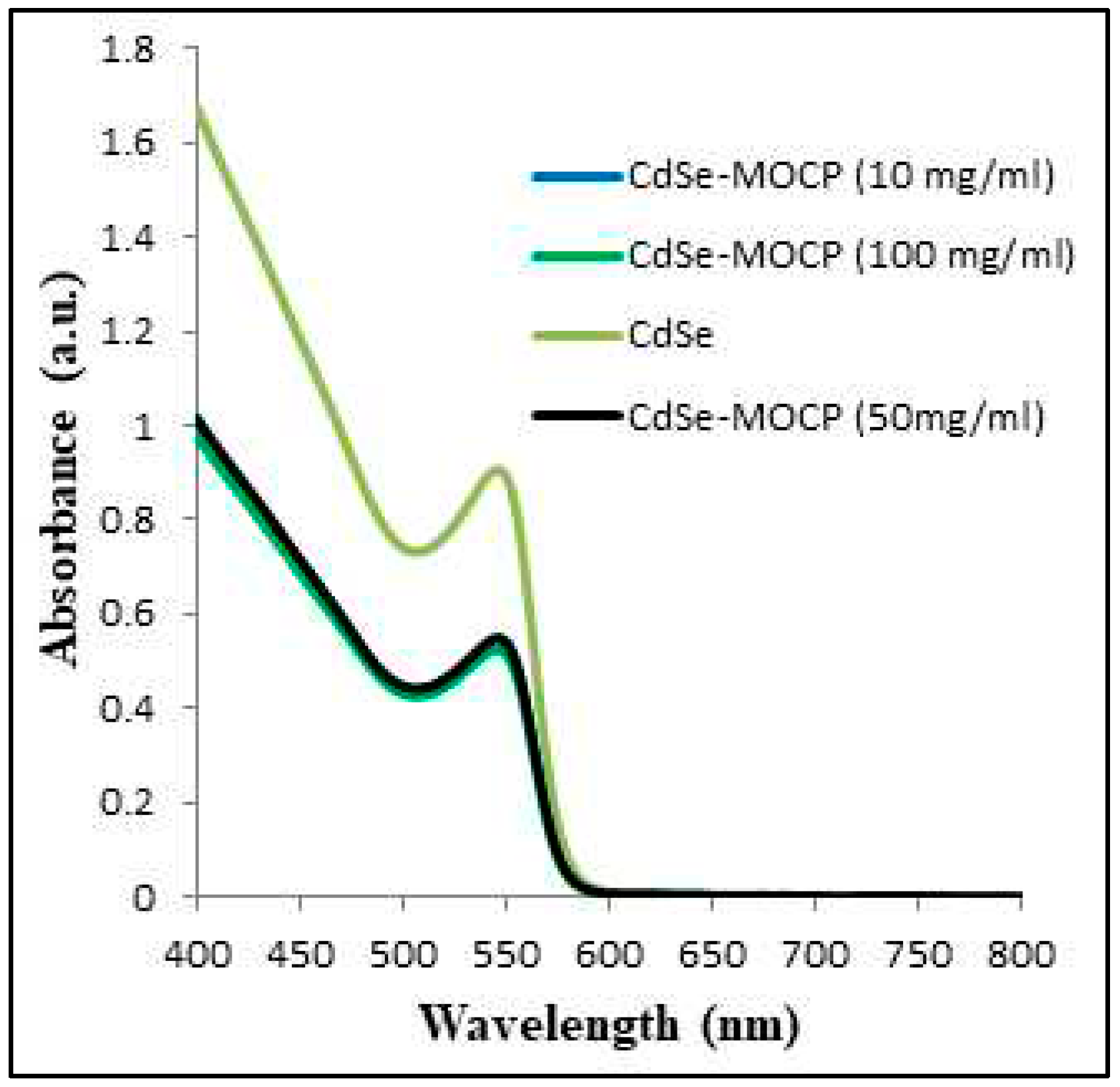
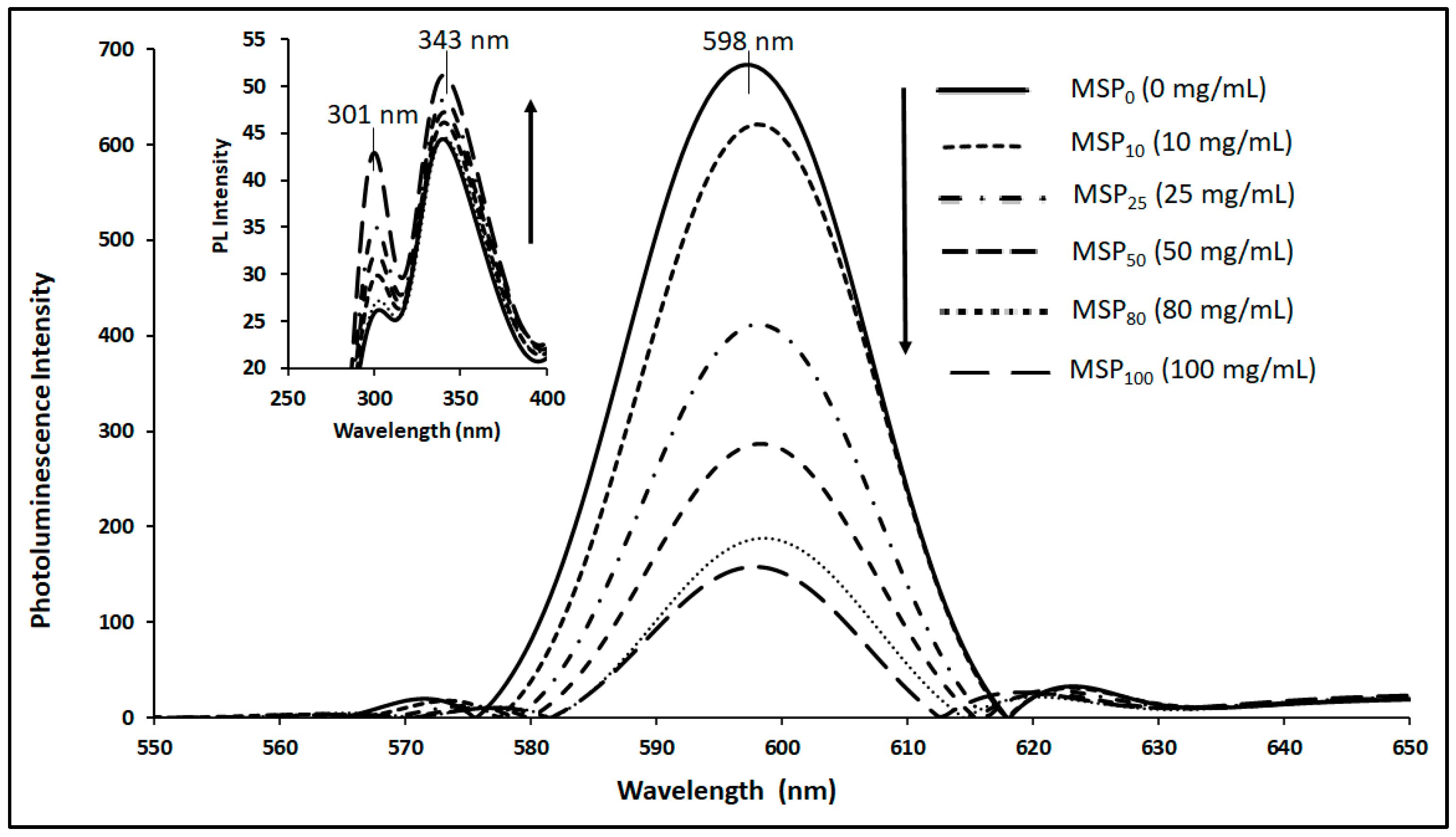
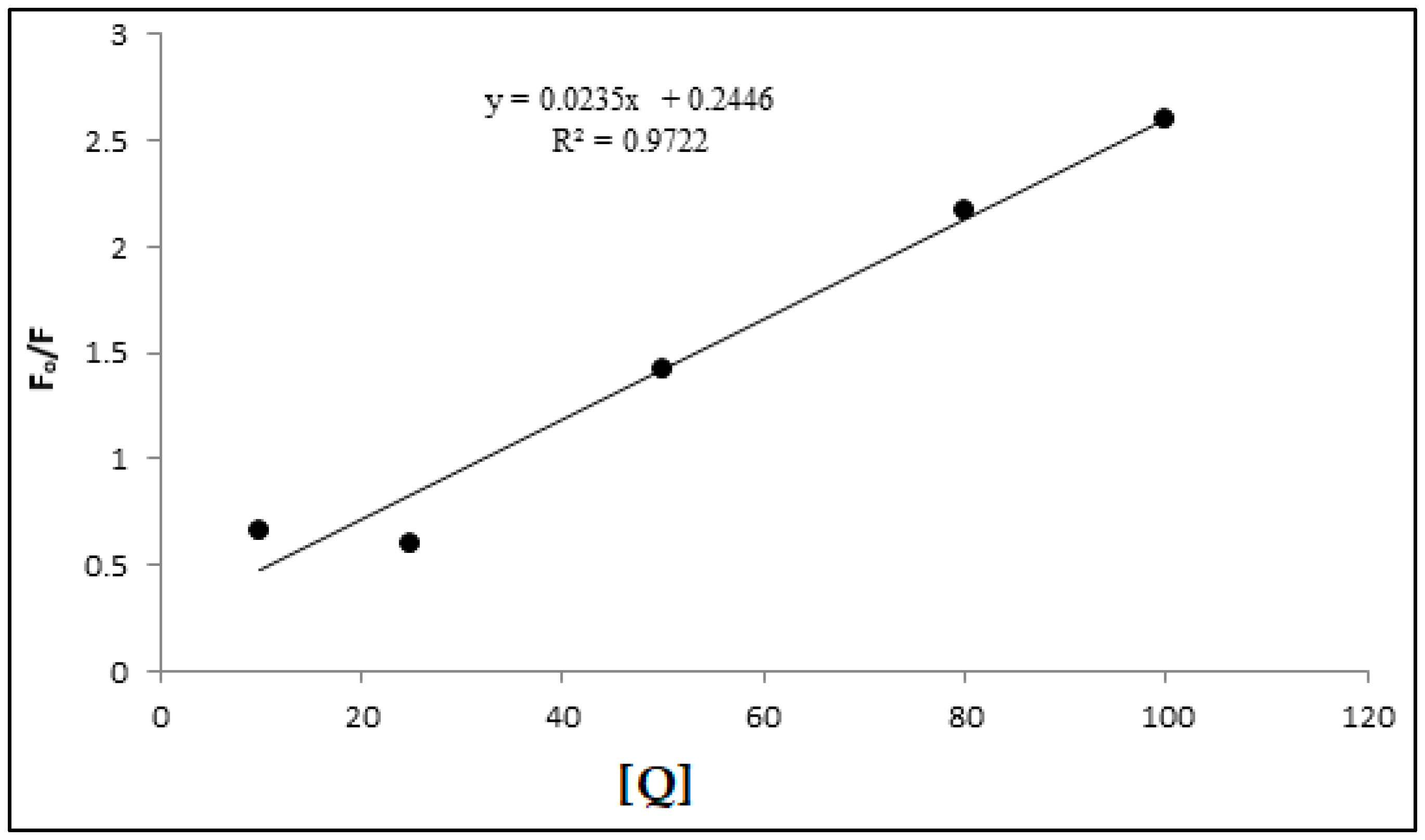
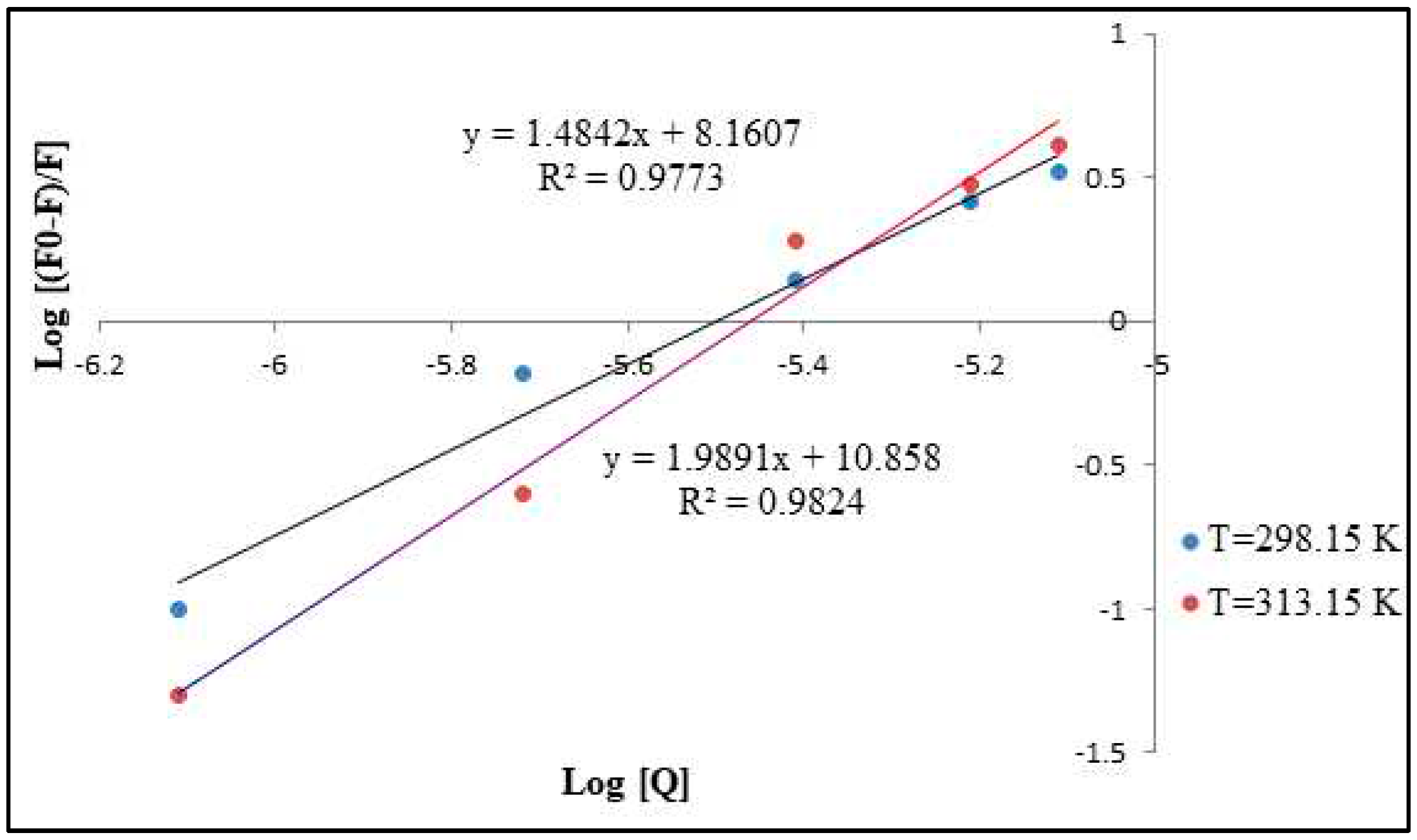
3.5. Stern-Volmer Analysis of the CdSe QDs –MSP system interactions
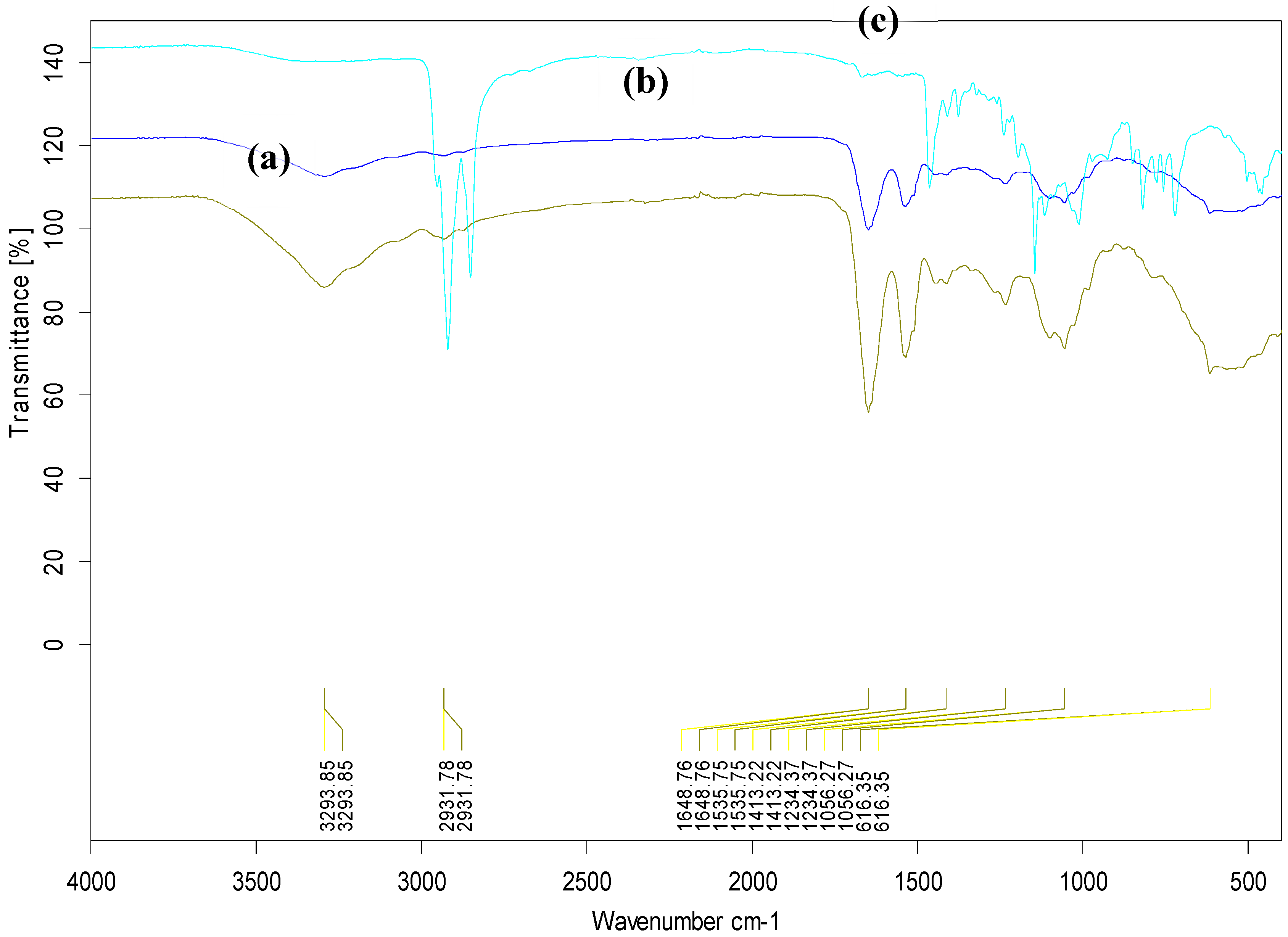
3.6. FTIR analysis of the CdSe QDs –MSP system interactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bera D, Qian L, Tseng TK, Holloway PH. Quantum dots and their multimodal applications: a review. Materials. 2010 Apr;3(4):2260-345. [CrossRef]
- Poderys V, Matulionyte M, Selskis A, Rotomskis R. Interaction of water-soluble CdTe quantum dots with bovine serum albumin. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2011 Dec;6:1-6. http://www.nanoscalereslett.com/content/6/1/9. [CrossRef]
- Joglekar SS, Gholap HM, Alegaonkar PS, Kale AA. The interactions between CdTe quantum dots and proteins: understanding nano-bio interface. AIMS Materials Science. 2017;4(1):209-22. doi: 10.3934/matersci.2017.1.209. [CrossRef]
- Shivaji, K., Sridharan, K., Kirubakaran, D. D., Velusamy, J., Emadian, S. S., Krishna-murthy, S., ... & Pitchaimuthu, S. (2023). Biofunctionalized CdS Quantum Dots: A Case Study on Nanomaterial Toxicity in the Photocatalytic Wastewater Treatment Process. ACS omega. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.3c00496. [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, D., Gaddam, R. R., Trinchi, A., & Cole, I. (2015). Core–shell quantum dots: Properties and applications. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 636, 395-404. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., & Tang, M. (2021). The cytotoxicity of core-shell or non-shell structure quantum dots and reflection on environmental friendly: A review. Environmental Research, 194, 110593. [CrossRef]
- Le, N., Zhang, M., & Kim, K. (2022). Quantum dots and their interaction with biological systems. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(18), 10763. [CrossRef]
- Ratnesh, R. K., & Mehata, M. S. (2017). Synthesis and optical properties of core-multi-shell CdSe/CdS/ZnS quantum dots: Surface modifications. Optical Materials, 64, 250-256. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G., Liang, W., Xue, X., Rosei, F., & Wang, Y. (2021). Atomic Identification of Interfaces in Individual Core@ shell Quantum Dots. Advanced Science, 8(22), 2102784. [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, S. S., Gholap, H. M., Alegaonkar, P. S., & Kale, A. A. (2017). The interactions between CdTe quantum dots and proteins: understanding nano-bio interface. AIMS Materials Science, 4(1), 209-222. [CrossRef]
- Derfus, A. M., Chan, W. C., & Bhatia, S. N. (2004). Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. Nano letters, 4(1), 11-18. [CrossRef]
- Ndabigengesere, A., Narasiah, K. S. and Talbot, B. G. (1995). Active agents and mechanism of coagulation of turbid waters using Moringa oleifera. Water Research, 29(2), 703-710. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, J., Beltrán-Heredia, J., and Peres, J. A. (2012). Improvement of the flocculation process in water treatment by using Moringa oleifera seeds extract. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 29(3), 495-502. [CrossRef]
- El Bouaidi, W., Libralato, G., Tazart, Z., Enaime, G., Douma, M., Ounas, A., ... & Loudiki, M. (2022). Nature-based coagulants for drinking water treatment: An ecotoxicological overview. Water Environment Research, 94(8), e10782.]. [CrossRef]
- Maikokera, R., & Kwaambwa, H. M. (2007). Interfacial properties and fluorescence of a coagulating protein extracted from Moringa oleifera seeds and its interaction with sodium dodecyl sulphate. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 55(2), 173-178. [CrossRef]
- Kwaambwa, H. M., & Maikokera, R. (2007). A fluorescence spectroscopic study of a coagulating protein extracted from Moringa oleifera seeds. Colloids and surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 60(2), 213-220. [CrossRef]
- Kwaambwa, H. M., & Maikokera, R. (2008). Infrared and circular dichroism spectroscopic characterisation of secondary structure components of a water treatment coagulant protein extracted from Moringa oleifera seeds. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 64(1), 118-125. [CrossRef]
- Kwaambwa, H. M., & Rennie, A. R. (2012). Interactions of surfactants with a water treatment protein from Moringa oleifera seeds in solution studied by zeta-potential and light scattering measurements. Biopolymers, 97(4), 209-218. [CrossRef]
- Kwaambwa, H. M., Hellsing, M., & Rennie, A. R. (2010). Adsorption of a water treatment protein from Moringa oleifera seeds to a silicon oxide surface studied by neutron reflection. Langmuir, 26(6), 3902-3910. [CrossRef]
- Jerri, H. A., Adolfsen, K. J., McCullough, L. R., Velegol, D., & Velegol, S. B. (2012). Antimicrobial sand via adsorption of cationic Moringa oleifera protein. Langmuir, 28(4), 2262-2268. [CrossRef]
- Kwaambwa, H. M., Hellsing, M. S., Rennie, A. R., & Barker, R. (2015). Interaction of Moringa oleifera seed protein with a mineral surface and the influence of surfactants. Journal of colloid and interface Science, 448, 339-346. [CrossRef]
- Moulin, M., Mossou, E., Signor, L., Kieffer-Jaquinod, S., Kwaambwa, H. M., Nermark, F., ... & Rennie, A. R. (2019). Towards a molecular understanding of the water purification properties of Moringa seed proteins. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 554, 296-304. [CrossRef]
- Nordmark, B. A., Bechtel, T. M., Riley, J. K., Velegol, D., Velegol, S. B., Przybycien, T. M., & Tilton, R. D. (2018). Moringa oleifera seed protein adsorption to silica: effects of water hardness, fractionation, and fatty acid extraction. Langmuir, 34(16), 4852-4860. [CrossRef]
- Nouhi, S., Pascual, M., Hellsing, M. S., Kwaambwa, H. M., Skoda, M. W., Höök, F., & Rennie, A. R. (2018). Sticking particles to solid surfaces using Moringa oleifera proteins as a glue. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 168, 68-75. [CrossRef]
- Nouhi, S., Kwaambwa, H. M., Gutfreund, P., & Rennie, A. R. (2019). Comparative study of flocculation and adsorption behaviour of water treatment proteins from Moringa peregrina and Moringa oleifera seeds. Scientific reports, 9(1), 17945. [CrossRef]
- Hellsing, M. S., Kwaambwa, H. M., Nermark, F. M., Nkoane, B. B., Jackson, A. J., Wasbrough, M. J., ... & Rennie, A. R. (2014). Structure of flocs of latex particles formed by addition of protein from Moringa seeds. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 460, 460-467. [CrossRef]
- Amuanyena, M. O., Kandawa-Schulz, M., & Kwaambwa, H. M. (2019). Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles modified with Moringa seed proteins for recovery of precious metal ions. Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology, 10(02), 142. [CrossRef]
- Drbohlavova, J., Adam, V., Kizek, R., & Hubalek, J. (2009). Quantum dots—characterization, preparation and usage in biological systems. International journal of molecular sciences, 10(2), 656-673. [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J. P., Folkard, G. K., & Grant, W. D. (1990). Natural coagulants for appropriate water treatment: a novel approach. Waterlines, 8(4), 30-32. [CrossRef]
- Thanki, A., Padhiyar, H., Singh, N. K., Yadav, M., & Christian, J. (2022). Municipal Wastewater Treatment Using Moringa oleifera Seed and Press Cake Powder: A Comparative Analysis. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water, 2100336. [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, S. J., Chang, J. C., Kovtun, O., McBride, J. R., & Tomlinson, I. D. (2011). Biocompatible quantum dots for biological applications. Chemistry & biology, 18(1), 10-24. [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, S. S., Gholap, H. M., Alegaonkar, P. S., & Kale, A. A. (2017). The interactions between CdTe quantum dots and proteins: understanding nano-bio interface. AIMS Materials Science, 4(1), 209-222. [CrossRef]
- Lohse, S. E., & Murphy, C. J. (2012). Applications of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles: from medicine to energy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 134(38), 15607-15620. [CrossRef]
- Kathiresan, R., Gopalakrishnan, S., & Kolandaivel, P. (2017). Interaction and bioconjugation of CdSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots with maltose-binding protein. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 1101, 96-101. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Zheng, J., Zhang, Z., Yuan, C., & Fu, D. (2009). CdTe nanocrystals as luminescent probes for detecting ATP, folic acid and l-cysteine in aqueous solution. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 342(1-3), 102-106. [CrossRef]
- Liang J, Cheng Y, Han H. Study on the interaction between bovine serum albumin and CdTe quantum dots with spectroscopic techniques. Journal of Molecular Structure. 2008; 892(1-3); 116-120. [CrossRef]
- Mekis, I., Talapin, D. V., Kornowski, A., Haase, M., & Weller, H. (2003). One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent CdSe/CdS core-shell nanocrystals via organometallic and “Greener” chemical approaches. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 107(30), 7454-7462. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D. K., Verma, M., Sharma, K., & Saxena, N. S. (2017). Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of CdSe/CdS and CdSe/ZnS core-shell nanoparticles. Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics (IJPAP), 55(2), 113-121. [CrossRef]
- Ndabigengesere, A., & Narasiah, K. S. (1998). Use of Moringa oleifera seeds as a primary coagulant in wastewater treatment. Environmental Technology, 19(8), 789-800. [CrossRef]
- Ndabigengesere, A., & Narasiah, K. S. (1998). Quality of water treated by coagulation using Moringa oleifera seeds. Water research, 32(3), 781-791. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G., Gomez, D., Kirkwood, N., & Mulvaney, P. (2018). Tuning single quantum dot emission with a micromirror. Nano Letters, 18(2), 1010-1017. [CrossRef]
- Naderi, M. (2015). Surface area: Brauer–emmett–teller (BET). In Progress in filtration and separation (pp. 585-608). Academic Press. [CrossRef]
- Yu, M., Saeed, M. H., Zhang, S., Wei, H., Gao, Y., Zou, C., ... & Yang, H. (2022). Luminescence enhancement, encapsulation, and patterning of quantum dots toward display applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 32(13), 2109472. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Nienhaus, K., Shang, L., & Nienhaus, G. U. (2022). Highly Luminescent Positively Charged Quantum Dots Interacting with Proteins and Cells. Chinese Journal of Chemistry, 40(22), 2685-2693. [CrossRef]
- Lima, C. N., Cabral Filho, P. E., Santos, B. S., Moura, P., & Fontes, A. (2019). Interactions of mannose binding-lectin with red blood cells by employing cationic quantum dots. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 125, 1168-1174. [CrossRef]
- Dzagli, M. M., Canpean, V., Iosin, M., Mohou, M. A., & Astilean, S. (2010). Study of the interaction between CdSe/ZnS core-shell quantum dots and bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic techniques. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 215(1), 118-122. [CrossRef]
- Lai, L., Lin, C., Xu, Z. Q., Han, X. L., Tian, F. F., Mei, P., ... & Liu, Y. (2012). Spectroscopic studies on the interactions between CdTe quantum dots coated with different ligands and human serum albumin. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 97, 366-376. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, G. A., Siddiqi, M. K., Khan, R. H., & Naeem, A. (2018). Probing the binding of phenolic aldehyde vanillin with bovine serum albumin: Evidence from spectroscopic and docking approach. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 203, 40-47. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. J., Ou-Yang, Y., Dai, C. M., Liu, Y., & Xiao, X. H. (2010). Binding of berberine to bovine serum albumin: spectroscopic approach. Molecular biology reports, 37, 3827-3832. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11033-010-0038-x. [CrossRef]
- Chu, V. H., Lien Nghiem, T. H., Le, T. H., Lam Vu, D., Nhung Tran, H., & Lien Vu, T. K. (2012). Synthesis and optical properties of water-soluble CdSe/CdS quantum dots for biological applications. Advances in natural sciences: nanoscience and nanotechnology, 3(2), 025017. [CrossRef]
- Yan, H., Wu, J., Dai, G., Zhong, A., Chen, H., Yang, J., & Han, D. (2012). Interaction mechanisms of ionic liquids [Cnmim] Br (n= 4, 6, 8, 10) with bovine serum albumin. Journal of Luminescence, 132(3), 622-628. [CrossRef]
| Direct band gap | Indirect band gap | |
|---|---|---|
| CdSe QDs | 2.27 | 2.20 |
| CdSe-MSP10 | 2.19 | 2.12 |
| CdSe-MSP50 | 2.20 | 0.85 |
| CdSe-MSP100 | 2.21 | 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





