1. Introduction
In order to meet the national and European targets to reach a climate-neutral economy by 2050 [
1], countries like Poland have to implement an adequate strategy for the development of renewable energy sources. Currently, solar and onshore wind systems have been developing most rapidly, replacing conventional power plants in the global energy mix. In the mid-term the development and application of energy storage will help to provide balancing abilities for these intermittent renewables. The development of offshore wind technologies, which have more stable generation due to better wind conditions and are located in close vicinity of water that may be used for hydrogen production via electrolysis brings the growing attention of policy makers and investors. From these reasons the offshore wind market is the most dynamically growing markets, especially in Europe. In 2021 3.3 GW were added, and the overall capacity of offshore wind farms (OWFs) in Europe reached 28.3 GW. There are predictions that by 2030 only the United Kingdom will own 40 GW, while all of the European countries are expected to have up to 135 GW of offshore wind power [
2]. Both onshore and offshore technologies are characterized by technical maturity and their environmental impact is not significant if the necessary precautions have been taken. Better quality of wind resources in the sea makes it possible to install higher turbines with bigger rotor diameters that have a capacity of up to 15 MW/turbine [
3,
4]. The first step while developing a new wind project should be the selection of an optimal location. This could be performed using supportive tools to assess the energy potential of the area. To do this, it is necessary to process the meteorological data, especially wind parameters such as velocity, direction, and power. There are numerous papers describing different approaches to resource assessment. The examples are the resource estimation model and Geographical Information System (GIS). Data collection is a former step, and the methods are on-site measurements, weather station networks, and numerical climate models. Typically, the measurements in offshore regions are performed using different types of buoys (met buoys or moored buoys, depending on the water depth). Examples of remote sensing measurements are SODAR and LIDAR. Another possible option is to employ satellite data and combine it with the surface wind recording data accumulated using devices like scatterometers, altimeters, passive microwave remote sensors, and synthetic aperture radars (SAR). The raw data is then inserted into the mathematical model to create data sets. The next step is to employ an estimation model or Geographical Information System (GIS) approach. The objective is to investigate which parameters would affect offshore wind farm locations [
5].
According to Wind Europe, today there is over 30 GW of offshore wind power installed in European waters. The capacity of projects carried out in the Baltic Sea is around 2.8 GW [29]. By 2030, total capacity could increase up to 11 GW or even 14 GW. There are predictions that by 2050, in the Baltic Sea, there will be 85 GW of offshore wind installed. As a result, the Baltic Sea would be the second-largest basin for offshore wind in Europe, after the North Sea [38]. The offshore wind technical potential of the Polish part of the Baltic Sea (EEZ) is estimated to be 116 GW according to [23]. The total value of the mentioned potential is then divided to be suitable for fixed (60 GW) and for floating (56 GW) technologies. Nevertheless, the realistic potential is much smaller, according to PEP2040 11 GW [
2], and 33 GW based on the PSEW report [39].
In this paper the factors that determine offshore wind farm location were analysed and incorporated into a multi-criteria model developed with the use of QGIS software. The abilities of the model were then demonstrated for the area covering part of the Baltic Sea, namely the Exclusive Economic Zone of Poland. As a result of the investigation, the optimal sites for offshore wind farm development were proposed. Moreover, the study helped to answer to the following research questions:
What are the key aspects that should be considered while deciding on the offshore wind farm location?
Which spatial data sets are crucial to determine the optimal offshore wind farm locations using QGIS software?
What are the suitable sites for offshore wind farm development in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea other than those proposed in the Act
[6]?
What is the technical potential of offshore wind in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea?
The novelty of this paper lies in the fact that for the first time the technical potential of offshore wind in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea was estimated using the GIS-based approach described in the paper. In this process the unique set of constraints was considered. This potential has been estimated for the different spatial configurations for the deployment of individual wind turbines. An original set of assumptions used in the Analytic Hierarchy Process in order to depict the most favorable locations for offshore wind investments. Determinants with the greatest influence on the choice of location were identified. The prosed methodology was validated based on the real investment plans.
2. Optimization of offshore wind farm locations
The implementation of different locational restrictions for offshore wind farms depends primarily on the specifics of the area. The constraints for the Chinese coast are not necessarily the same as for the UK. For example,
[7] indicates the need to maintain a distance from seismic fault lines, which is specific to the Turkish coast and will not apply to the North Sea, for example. Nevertheless, some restrictions apply to the majority of areas predisposed to offshore wind energy like wind energy potential or water depth. For the purpose of optimisation, the restrictions should be identified and then formulated as constraints. The following step would be to assign the possible and/or required outcome. For example, the wind speed should be maximised while conservation areas and bird migratory routes should be excluded
[7]. The constraints could be divided into three types of limitation factors: technical, regulatory, and economical
[8]. Similarly, Kim et al. have classified the criteria for offshore wind farm site selection using four categories: energy resources and profitability, conservation area and view protection, human activities, marine environment, and marine ecology
[9].
2.1. Energy resources and profitability
Among the constraints that could be assigned to the category energy resources and profitability are aspects regarding wind energy potential and water depth. In general, wind energy potential is considered a determining factor and its value should be maximized
[7]. The minimum wind speed that is perceived as suitable for offshore energy use is around 6.5 m/s at a height of 100 m
[7]. Another way in which the wind potential can be determined is by calculating the wind power density. An annual power density of approximately 200 W/m
2 is accepted as a suitable value
[9]. The water depth constraint determines the possibility for the development of fixed or floating technology. There is no universal foundation type, and various technologies are applied depending on water depth as well as the consistency of the seabed. In shallow waters (below 30 m) monopile foundations are most commonly used, and where the sea is deeper (30-60 m), jacket foundations are usually applied. Floating technology is promising for deep waters above 60 m
[10]. The constraint of the water depth might be formulated as less or equal to 100 m with the objective of minimising the value
[7]. Another constraint is distance to the coast, which determines the costs of cabling, transportation of the turbines, substations, and other necessary equipment. Additionally, the offshore and onshore grid infrastructure should be considered, cables that already exist reduce the cost significantly. The same applies the existing onshore power substations infrastructure.
2.2. Conservation area and view protection
Another group of constraints covers conservation areas and view protection. An example of such restriction would be seabird conservation areas, as wind turbines pose a threat to birds flying nearby. Despite the use of safeguards in the form of motion detectors, sensors, acoustic signals, etc., the problem has not yet been fully eliminated. For this reason, offshore wind farms are usually not located in protected bird habitat areas and a buffer of 3-5 km is suggested
[11]. Another example of a constraint is the natural environment conservation area. Areas such as Natura 2000, which were established to protect plant and animal species, usually cannot be used for other purposes, including OWFs. For example,
[12] introduces the following buffers: 1 km for a near-shore scenario and 2 km for a far-shore scenario. Other protected areas are taken into account as well
[7,9,12]. Additionally, coastal landscapes should be considered. Revised papers offer a buffer from land to protect the marine view of 2 km
[9] or even 8-16 km
[11]. The distance from various types of conservation areas should therefore be maximised.
2.3. Human activities
Human activities other than offshore wind farms include fishing areas, harbour developments, shipping routes, anchorages, shipwrecks, submarine cables and pipelines, oil and gas infrastructure, existing wind farms, military units, and marine leisure activities
[7,9,10,11,12]. In this category, as a rule, the buffers are proposed. For example, for anchorages and fishing areas
[12] proposes a 1-2 km buffer while
[7] suggests a 1 km buffer from shipwrecks and offshore petroleum and natural gas wells, and at least 750 m buffer from subsea communication cables and subsea pipelines. The distance maintained from densely used shipping routes should be at least 1 km according to
[7]. The buffer is applied in order to decrease the risk of a collision with the infrastructure.
2.4. Marine environment and marine ecology
Last but not least, there are constraints from the category of marine environment and marine ecology. In the study presented in
[9] marine water quality was analysed and excluded areas with 1st-grade dissolved oxygen (7.5 mg/l). Similarly, the areas with increased activity of marine benthos and marine mammals were disregarded. As it has been mentioned, offshore wind farms have an influence on birds. OWF can affect birds in terms of collision risk, short-term and long-term habitat loss, barriers to movement, and disconnection of ecological units
[13]. To prevent and reduce the damages, numerous papers exclude and/or apply a buffer from birds' migratory routes
[7,9,11].
3. Methodology
3.1. Proposed framework
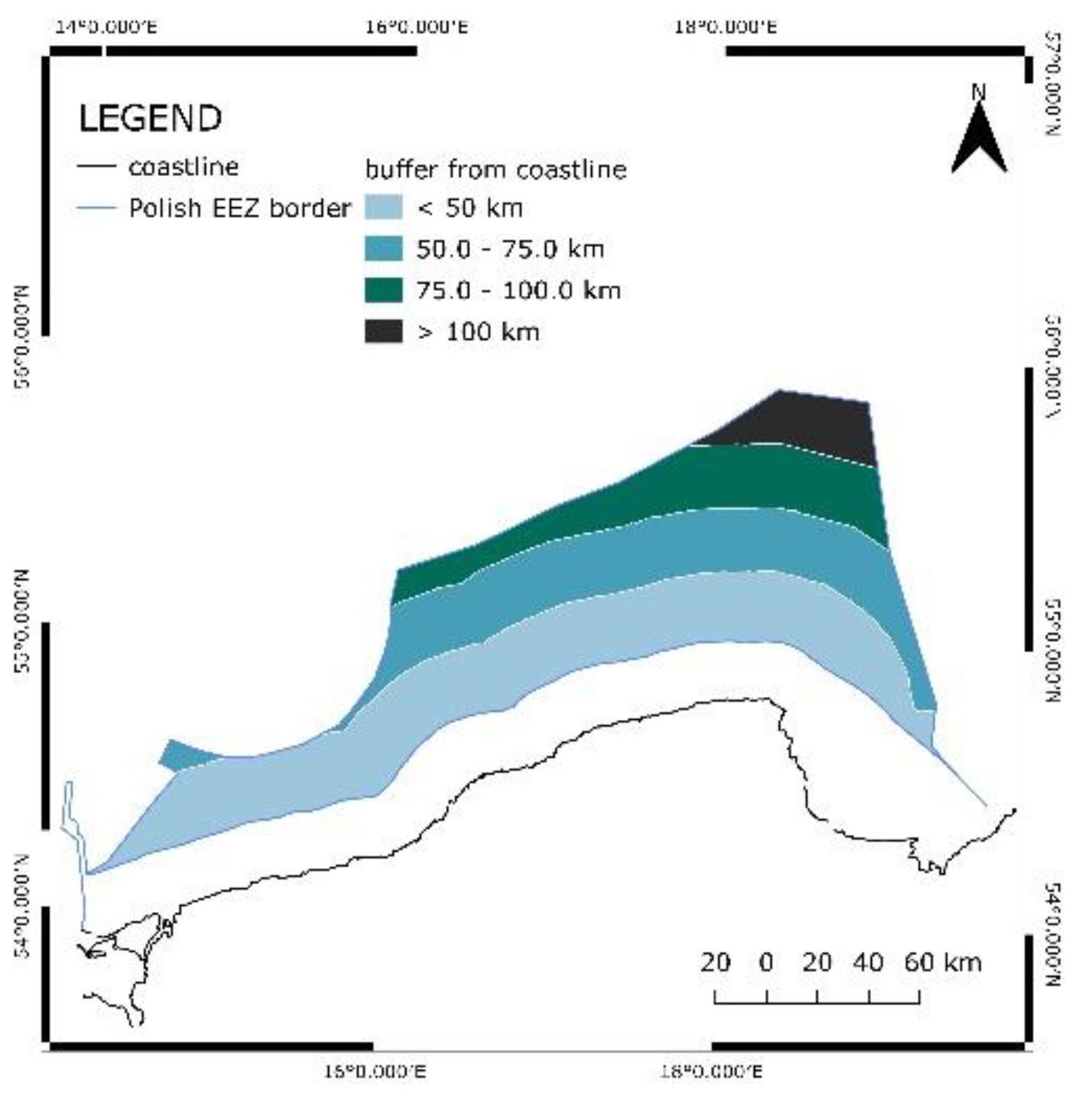
The study concerns the Polish part of the Baltic Sea, more specifically the Exclusive Economic Zone of Poland. The area under analysis is presented in
Figure 1. In order to find optimal locations for offshore wind farms, a model in QGIS was developed. Before developing the model, solutions proposed in articles and publications were reviewed. This led to a preliminary selection of location factors on which the feasibility of siting offshore wind farms depends. Then, the availability of source data was verified, and in this way, the final constraints were selected. The data was obtained from different sources and in vector or raster format. The individual layers containing the constraints were imported into QGIS software and their properties were adjusted. To receive the final layers tools like buffer, cut, aggregate, and others were used. At the same time, the importance of each constraint was assessed, and the pairwise matrix was created using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). As a result, weights were assigned to each constraint. In QGIS software, data from all layers was then aggregated into one grid layer of a 1 km x 1 km spatial resolution. Similarly, areas where offshore wind farms cannot be located, were rejected, and the excluded areas were combined. The sites with the best properties were selected to show the wind farm location suitability.
3.2. Criteria selection
The literature mentions different criteria that can help with the site assessment process. Four categories could be applied regarding all of the constraints: Energy resources and profitability, Conservation area and view protection, Human activities, and Marine environment and marine ecology. Various sources provide the data that could be later processed using QGIS software. For the constraints described below the data was obtained from the following sources
[14,15,16]. However, not all of the data was stored in vector format, which is more suitable for the analysis. Some layers were available only in raster format and in low quality. For that reason, the values could not be very precise. Moreover, not all of the data could be collected. For example, data about bird migratory routes or some of the human activities like military units or anchorages is not considered in the study.
Table 1 contains the final nine constraints assigned to four categories and the source of raw data implemented to QGIS software.
3.3. Analytic Hierarchy Process
In order to assess the offshore wind potential, it is crucial to recognise the location constraints. Later, one should group the criteria and assign the importance to each one. To address the matter, an Analytic Hierarchy Process could be applied. The AHP is a tool developed by Saaty to investigate complex problems. AHP is an example of a multi-criteria decision-making method (MCDM) and aims to assign priority using relative weights of criteria that influence a complex decision
[17,18]. Additionally, the AHP method is one of the most commonly used to analyse the current state of the technology. Other examples of tools include technology readiness level, S-curve analysis, and key technologies. The main purpose of the AHP tool is to reduce the uncertainty of the data accuracy and to facilitate the selection process. Typically, the methodology involves two steps: (1) a hierarchical structure development of the decision-making process; and (2) the criteria and options evaluation within the hierarchical structure. To compare the elements on each level of the hierarchical model, the pairs are considered using the relative scale from 1 to 9. As a result, the importance rating among all elements is determined
[19].
Among the advantages of the AHP method are the following:
provides a straightforward solution;
can be applied in computer software;
can address a wide range of complex decision problems;
ability to assess consistency while using the method
[7,20].
In this study, the first step while performing the analysis using the AHP method was to develop the hierarchical structure taking into account the main goal of the process, then criteria (constraints) and alternatives. Optimal locations for offshore wind farm development recognition were formulated as the main goal. Nine criteria were selected and analysed, eight of which were used in the AHP method. The latter step was to determine the relative importance of the different criteria considering the main goal. The individual decision elements were compared on a scale from 1 to 9. Then, the model has been built as a pairwise comparison matrix (rating matrix). The length of the pairwise matrix is equivalent to the number of criteria, - in this study, 8x8. The ninth criterion, EEZ area is not considered in the AHP calculations. The whole Exclusive Economic Zone of Poland is under analysis, and all sites are equally important. The following step was to create the normalised pairwise matrix. As a result, criteria weights that represent the relative importance of the chosen criteria were calculated. The next step was to investigate the consistency to check whether the values were accurate. The characteristic value, λ
max is calculated as the arithmetic mean value of the weighted sum and criteria weights ratio divided by the number of elements n according to Equation (1).
Then, consistency index CI is calculated according to Equation (2).
The consistency coefficient takes into account previously calculated CI value and a random index RI (Equation (3)). Values of RI depend on the number of considered elements, in this case RI = 1.41
[17].
Table 2 presented below summarize the received results. The criteria weights are in range 0.030 – 0.349 and ranked from 1 to 8. Wind velocity was revealed the most significant criterion in the study, while fishing areas emerged to be the least important one. λmax value was calculated at 8.866 and CI was at 0.124. As a result, the CR was equal to 8.8%, which corresponds with the theory (CR ≤ 10%).
3.4. Criteria classification
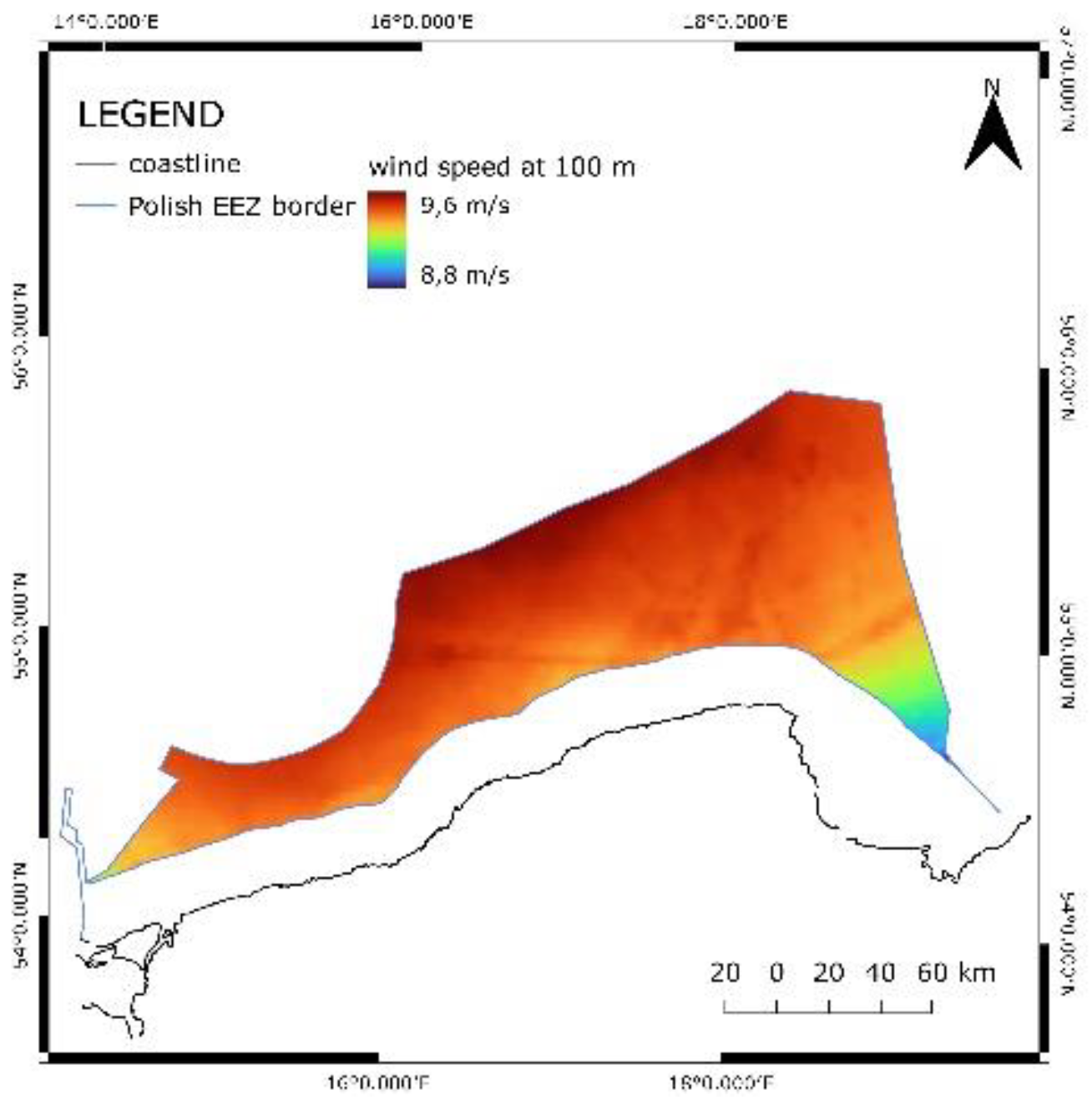
For wind energy potential, the input layer was in a raster format, and it presented the data for the whole Baltic Sea region. First, it was clipped to fit the EEZ borders, and then the map was created. As it was mentioned, usually areas with the mean value of 6.5 m/s or more are considered suitable for offshore wind development. The whole area of the EEZ has a wind velocity of 8.85 m/s or more, as it is shown in
Figure 2. The most promising areas, with the highest values of wind speed, are in the north of the Polish EEZ. The lowest value was 8.85 m/s, and as a result, no area was excluded from the study according to the wind velocity constraint. Nevertheless, the three ranges which correspond to the suitability were proposed. For marginally suitable areas the assigned value was 1, and for highly suitable 3.
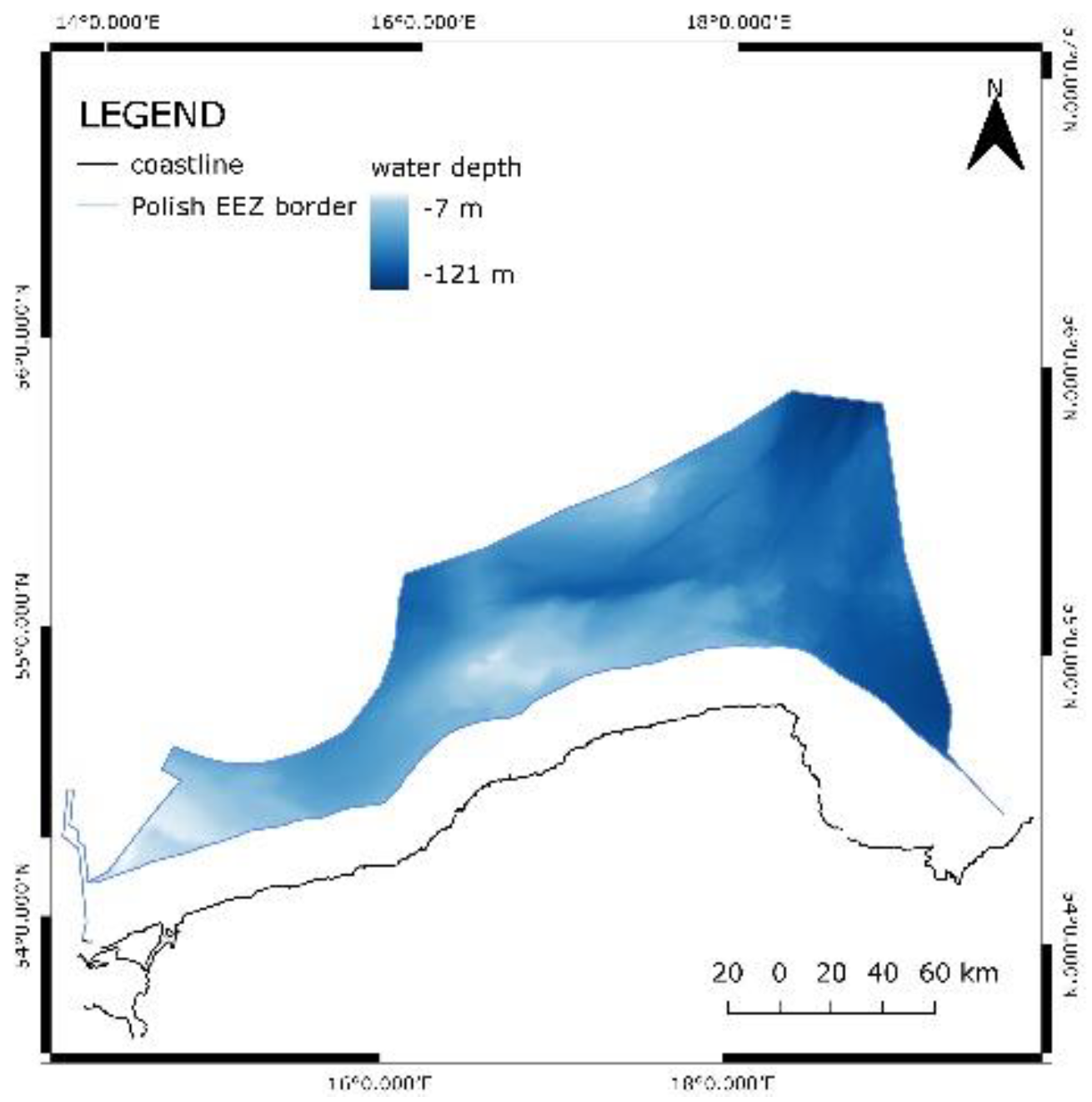
Similarly, for water depth the obtained data was in raster format, and first, it was necessary to convert it into vector format. As a continuance, the layer was clipped to fit EEZ borders. The water depth in the EEZ is within the range of 0 – 121 m. For offshore wind development, the appropriate value would be 100 m or less. Moreover, for fixed foundations, the maximal depth should be around 60 m, and for depths 60 – 100 m floating foundations would be preferred. Areas where the water depth is more than 100 m were excluded.
Figure 3 shows the seabed characteristics.
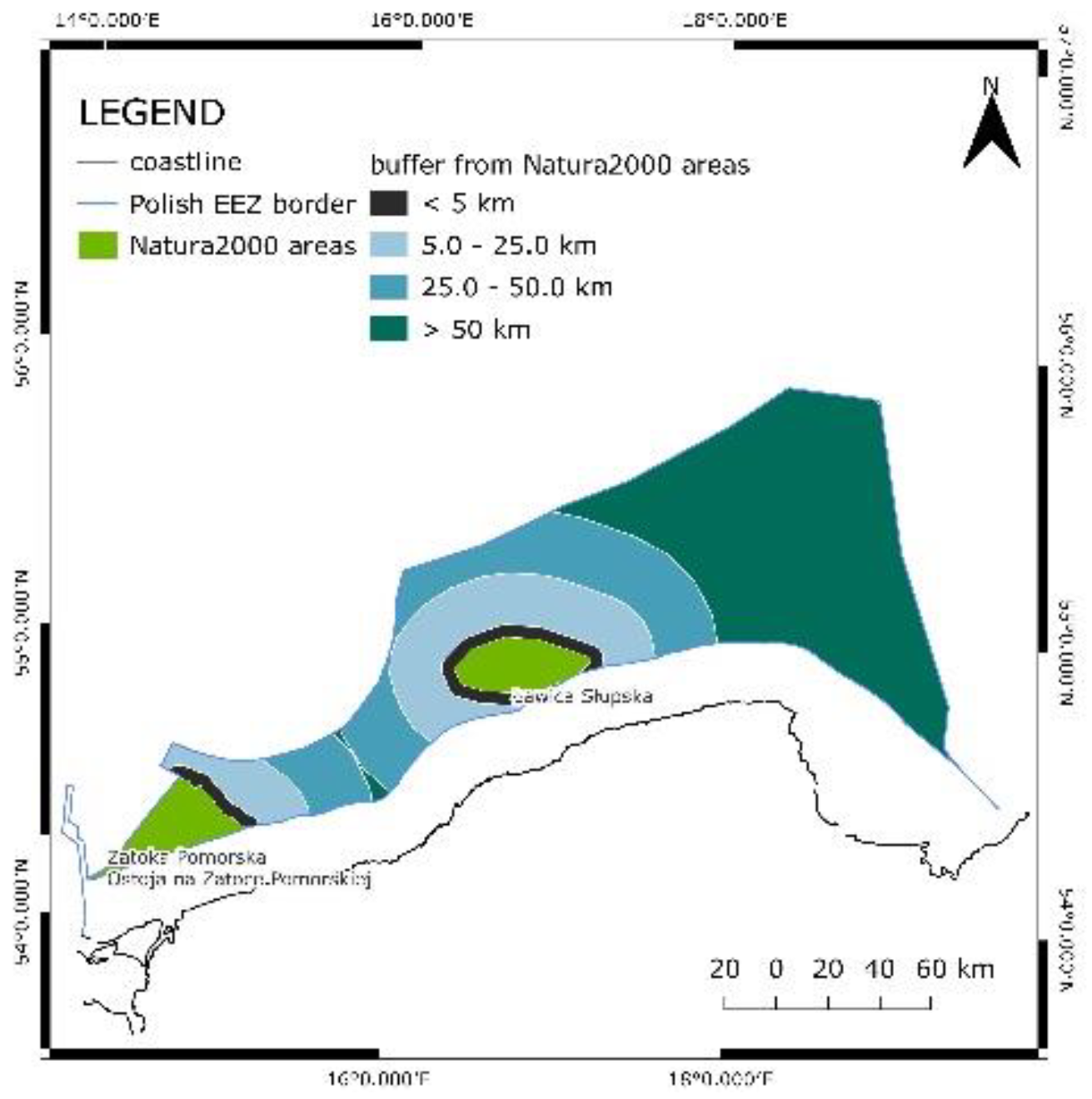
In the EEZ there are two types of nature conservation areas protected under Natura2000: conservation under the Bird Directive and conservation under the Habitats Directive. Three areas were identified however, two of them cover the same area. The names of the protected sites are: Obszar specjalnej ochrony siedlisk “Ostoja na Zatoce Pomorskiej”, Obszar specjalnej ochrony ptaków “Zatoka Pomorska”, Obszar specjalnej ochrony ptaków “Ławica Słupska”. For the mentioned areas, the data was stored in a vector format (polygon). It was necessary to clip the areas to fit the EEZ area. As a continuance, a buffer of 5 km was applied. The protected area as well as the 5 km buffer are excluded for offshore wind farm development. Taking into account the constrain regarding conservation areas, the area was divided into four ranges, and for each one, the value was assigned.
Figure 4 presents the mentioned approach.
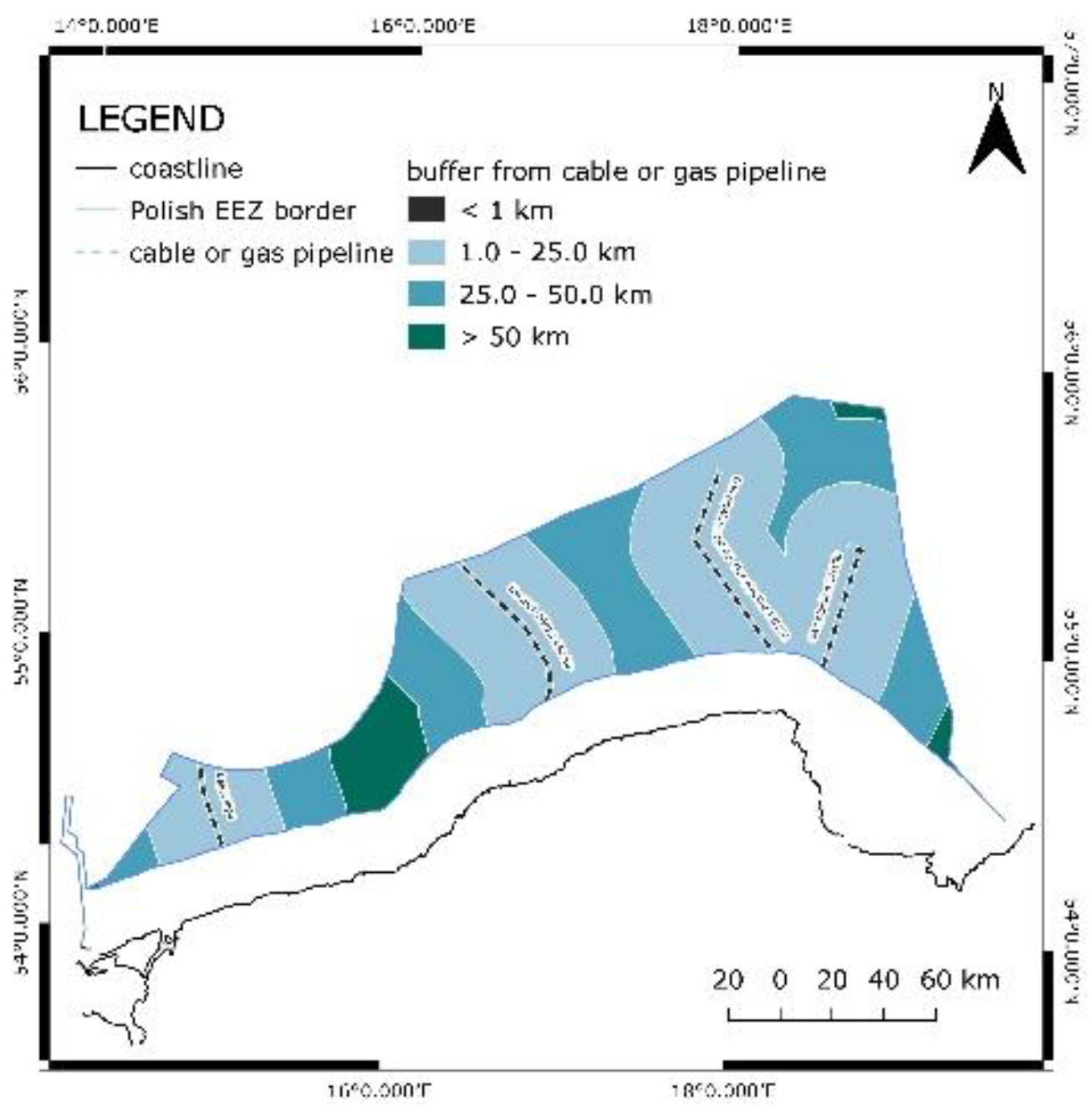
For submarine cables and gas pipelines, a buffer of 1 km was applied. Only existing cables and gas pipelines were taken into account.
Figure 5 presents (from the left) the Baltic Pipe (gas pipeline), the high voltage cable 450 kV connecting Sweden and Poland, gas pipelines DN200 and DN250, and gas pipeline DN100.
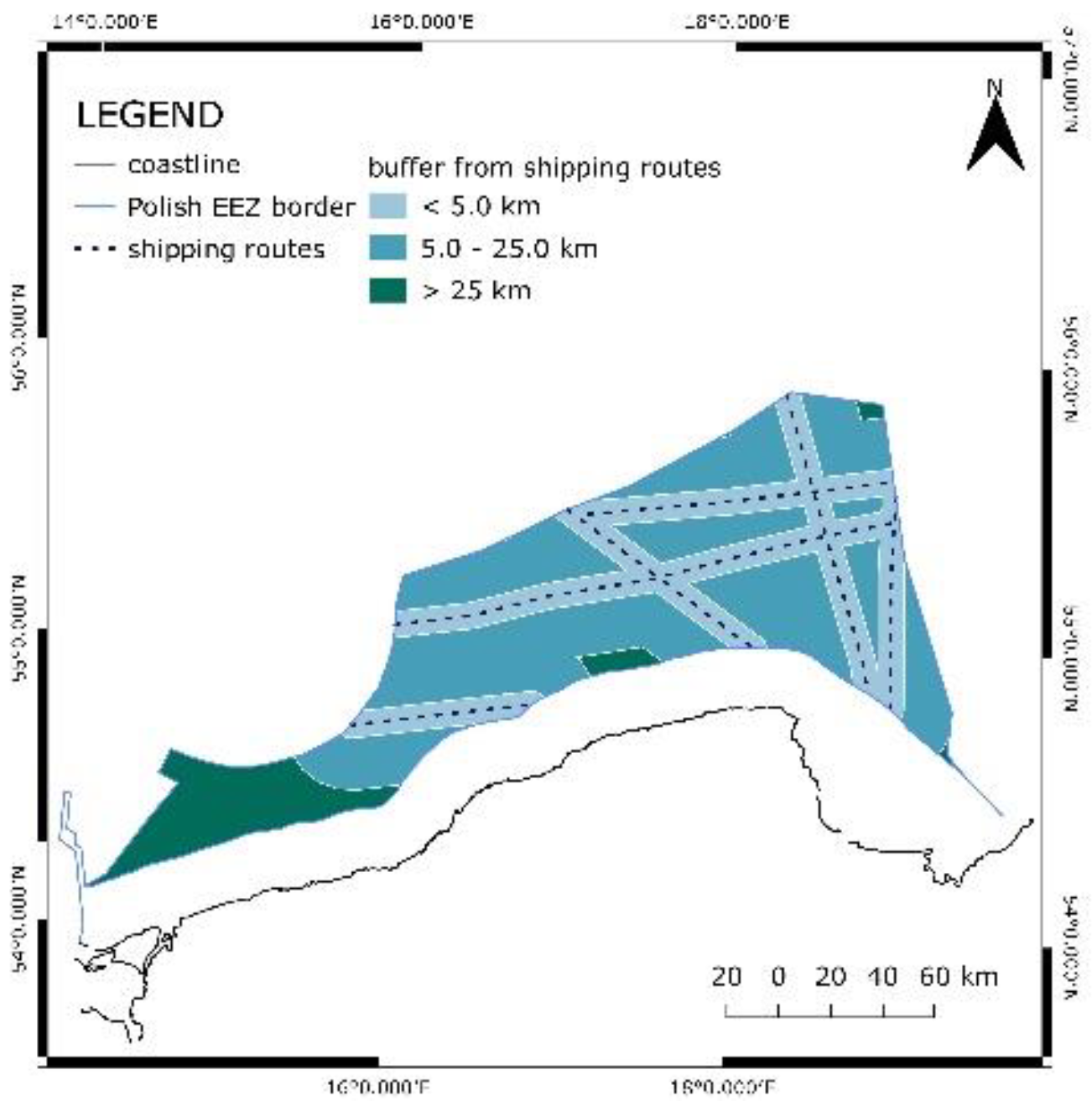
The data about the most commonly used shipping routes was downloaded in a low-quality raster format. For that reason, the data was transformed into a vector layer. However, the precision of the presented shipping routes is not high, and therefore, should not be considered a crucial constraint. No area was excluded due to the lack of reliable data. For typical shipping routes, a line was drawn in the middle and then a buffer of 5 km was applied. However, these sites received marginally suitable rank, not excluded.
Figure 6. presents the shipping routes as well as the applied buffers.
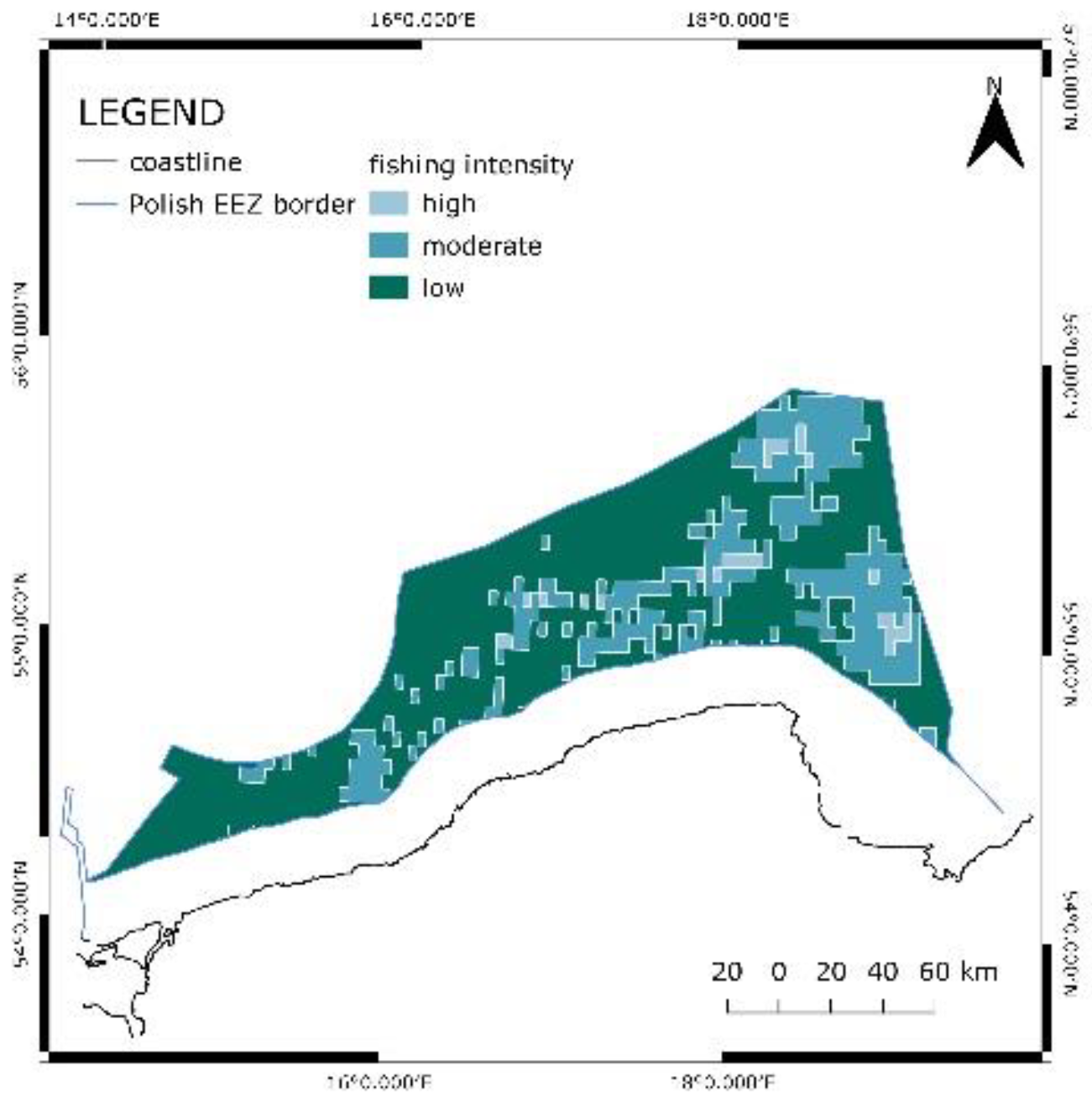
For fishing areas, the data considering the most frequently used sites was downloaded in raster format. The conversion to vector format was possible with the use of a tool in QGIS software. The areas were divided into three ranges that describe the fishing intensity: high, moderate, and low. Due to the uncertainty, no site is excluded.
Figure 7. is the map of fishing intensity.
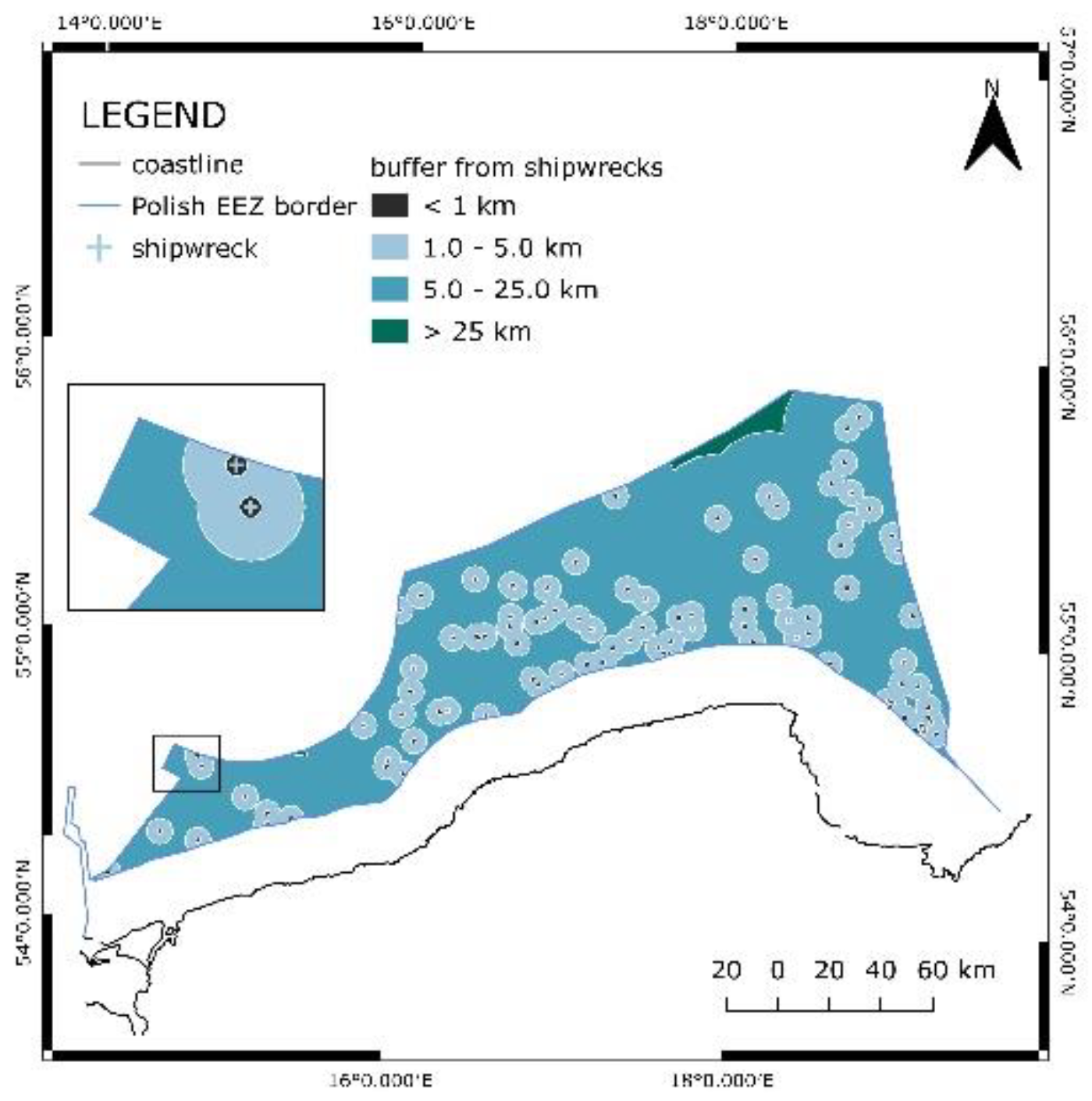
The data about shipwrecks was obtained in a vector format, more specifically, in points. First, these of the pointes that lied inside the EEZ area were selected. Then, the buffer of 1 km was applied, in order to find the excluded sites.
Figure 8 presents the EEZ area with shipwreck locations. Additionally, a detailed frame that shows the applied buffer is provided.
Distances from the coast were determined using the buffer tool. Areas close to the land were considered to be the most optimal.
Figure 9. shows the distribution of distances.
3.5. Assumptions
To estimate the offshore wind energy potential for the Polish EEZ, certain assumptions have to be made. As a result of the mapping and calculations performed in QGIS, an area was obtained where the location of offshore wind farms would be possible. Two important assumptions had to be made for the evaluation of the power generation potential, i.e. the electrical capacity of a single turbine and the spatial distribution of the turbines. The use of turbines with a nominal capacity of 15 MW, manufactured by Vestas, was assumed
[4]. Similar components are planned to be used for the Baltic Power offshore wind farm planned in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea. In addition, it has been proposed to lay the turbines 2 km apart from each other to minimise the risk of wake effect. The literature recommends a distance between 10 and 15 D, where D is the rotor diameter
[21,22,23].
4. Results
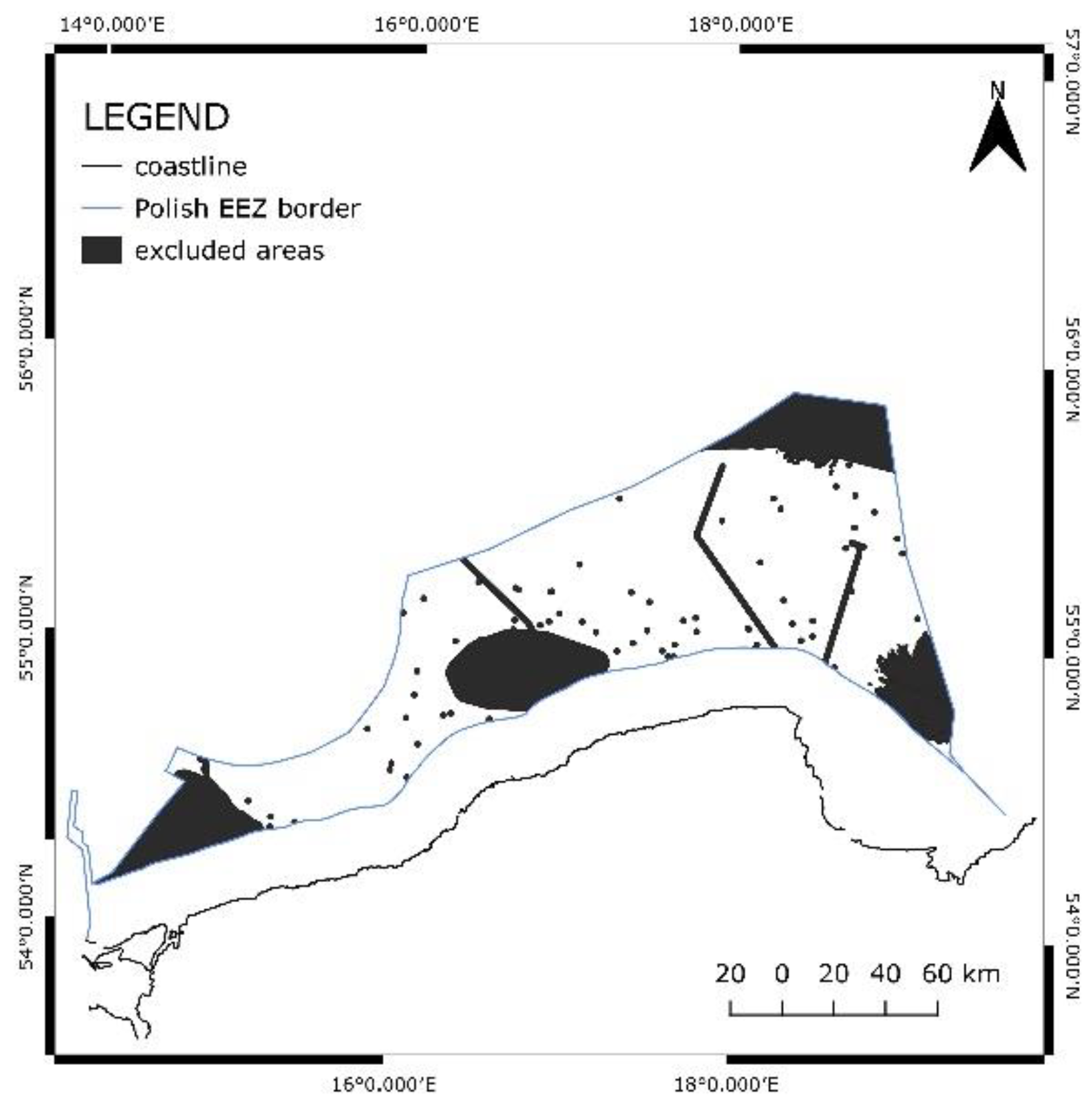
4.1. Excluded areas
In the study, the Exclusive Economic Zone of Poland is considered. However, not the whole area (approx. 22 500 km
2) is suitable for offshore wind development. Numerous constraints restrict the area. During the preliminary analysis, it was determined which criteria are related to the exclusion of sites. These areas were then mapped in QGIS software according to the proposed methodology. For water depth areas with the depth of 100 m or more were excluded due to lack of appropriate foundation technology. The development of Nature conservation areas protected under the Natura 2000 programme is prohibited. Additionally, a 5 km buffer from these areas was not considered. Submarine cables, gas pipelines and shipwrecks’ locations were excluded as well as a 1 km buffer from them. Since data about shipping routes and fishing areas was not highly reliable no sites were removed from further study in relation to these constraints. Nevertheless, distance from the coast should not exceed 100 km, and further areas were excluded from the study. Areas in proximity to the shore have not been disregarded as only the EEZ is taken into account. Moreover, there are areas not considered in the study due to more than one constraint. The total value of the excluded area equals to 5018.852 km
2 which is 22.3% of the EEZ of Poland (
Figure 10).
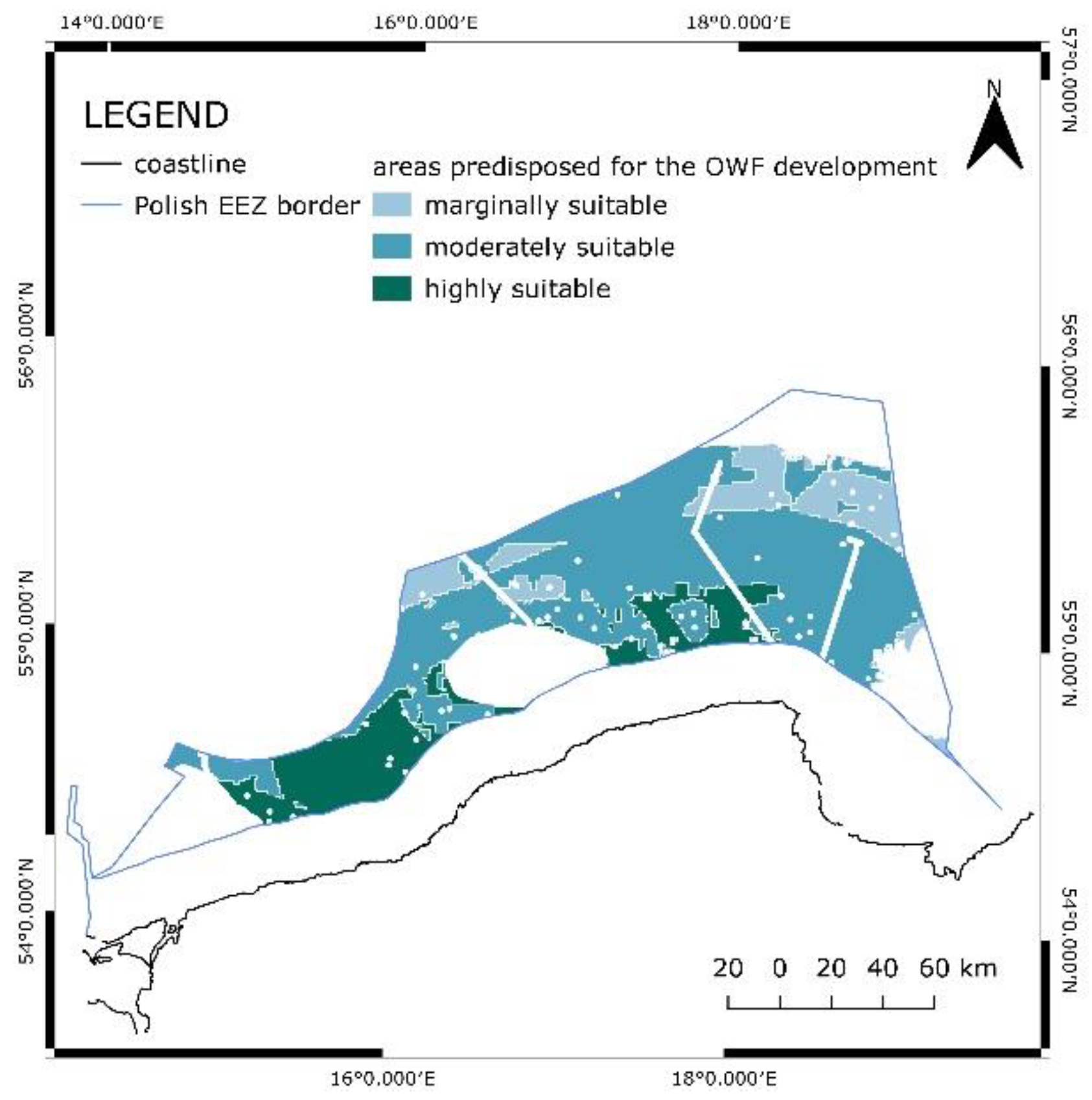
4.2. Suitable areas
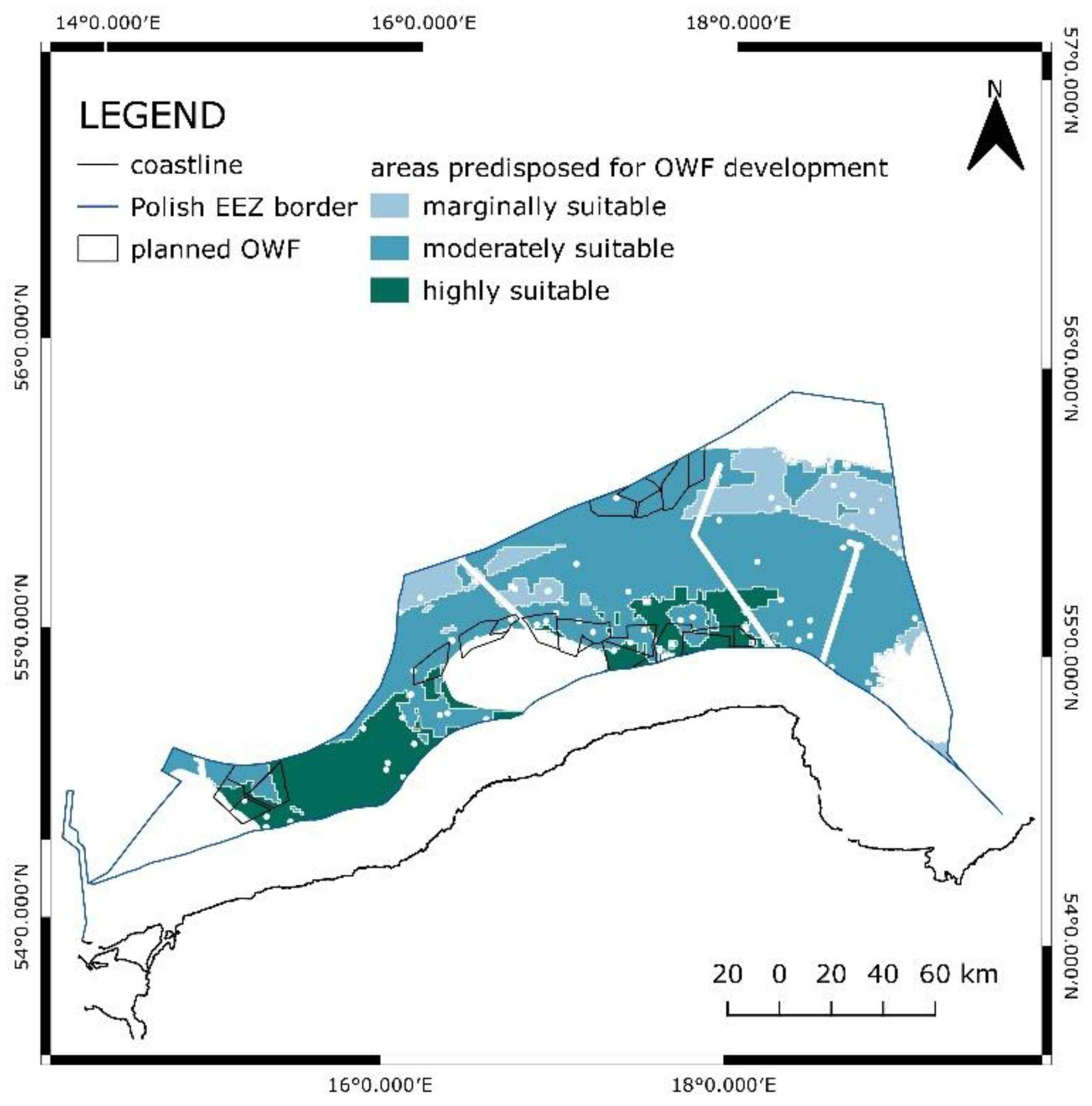
A spatial resolution of 1 km x 1 km was applied over the domain covering the EEZ to map the detailed results. After the summation of all layers’ values and weights obtained from the AHP process, final values were obtained. The results were in a range from 1.494 to 2.801 (
Table 3). It was decided to divide the results into three groups, namely, marginally, moderately, and highly suitable. The sites marginally suitable covered an area of 2178.97 km
2 which is equal to 10.26% of the total EEZ area. Moderately suitable was an area of 10312.76 km
2, and a share of 48.56%. Moreover, highly suitable was an area of 3726.90 km
2, a share of 17.55%. The total area predisposed for OWF development was 16218.67 km
2. As mentioned, the minimal value observed was 1.494, and the maximal 2.801. The mean value was 2.272, and the median was 2.217. The standard deviation was 0.227. The areas suitable for OWF development are distributed as shown in the map (
Figure 11). Areas highly suitable are in the south of the EEZ.
4.3. Offshore wind potential of the EEZ of Poland
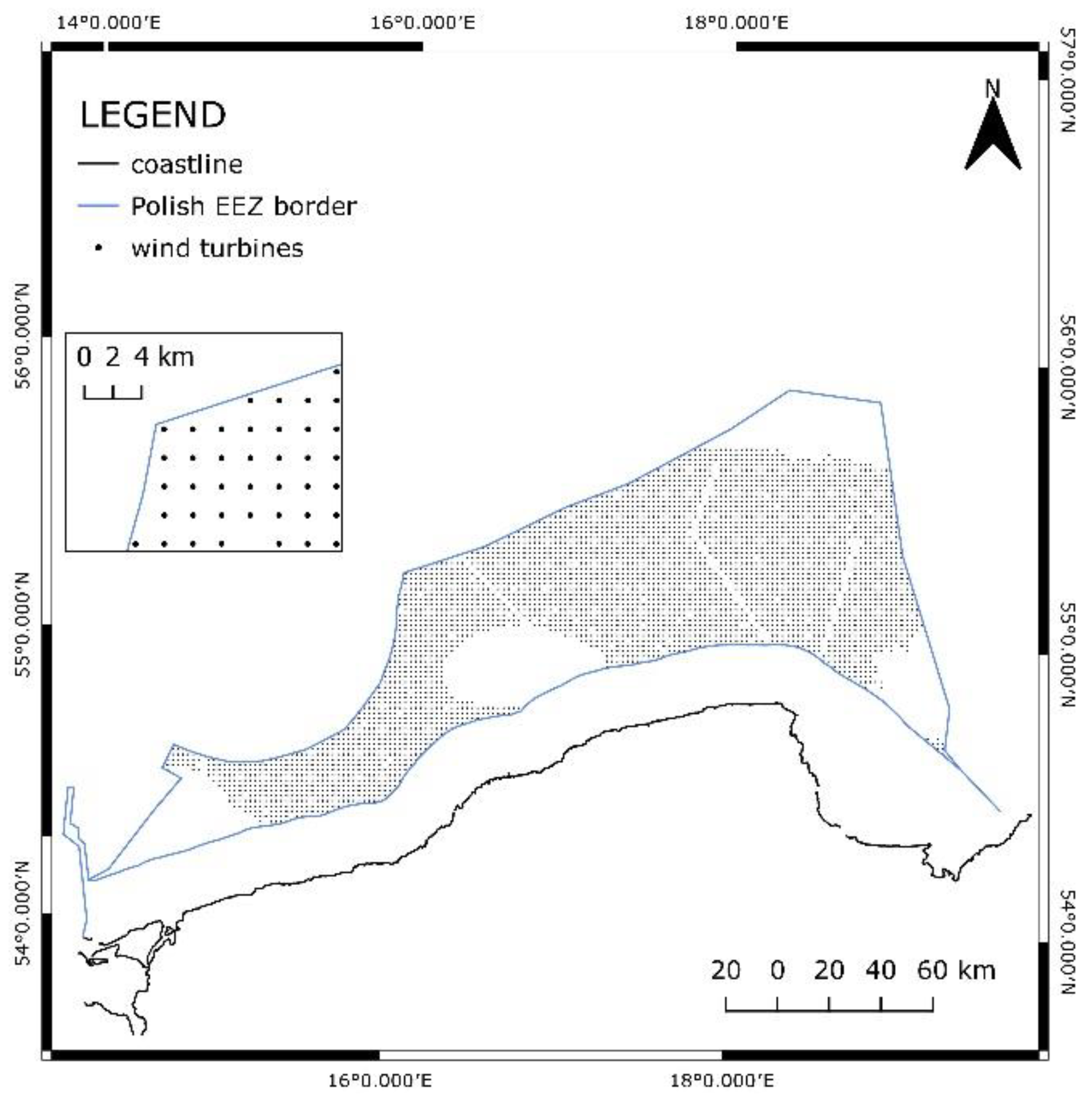
To assess the offshore wind potential of the Polish part of the Baltic Sea, two different spatial configurations for the deployment of individual wind turbines were considered.
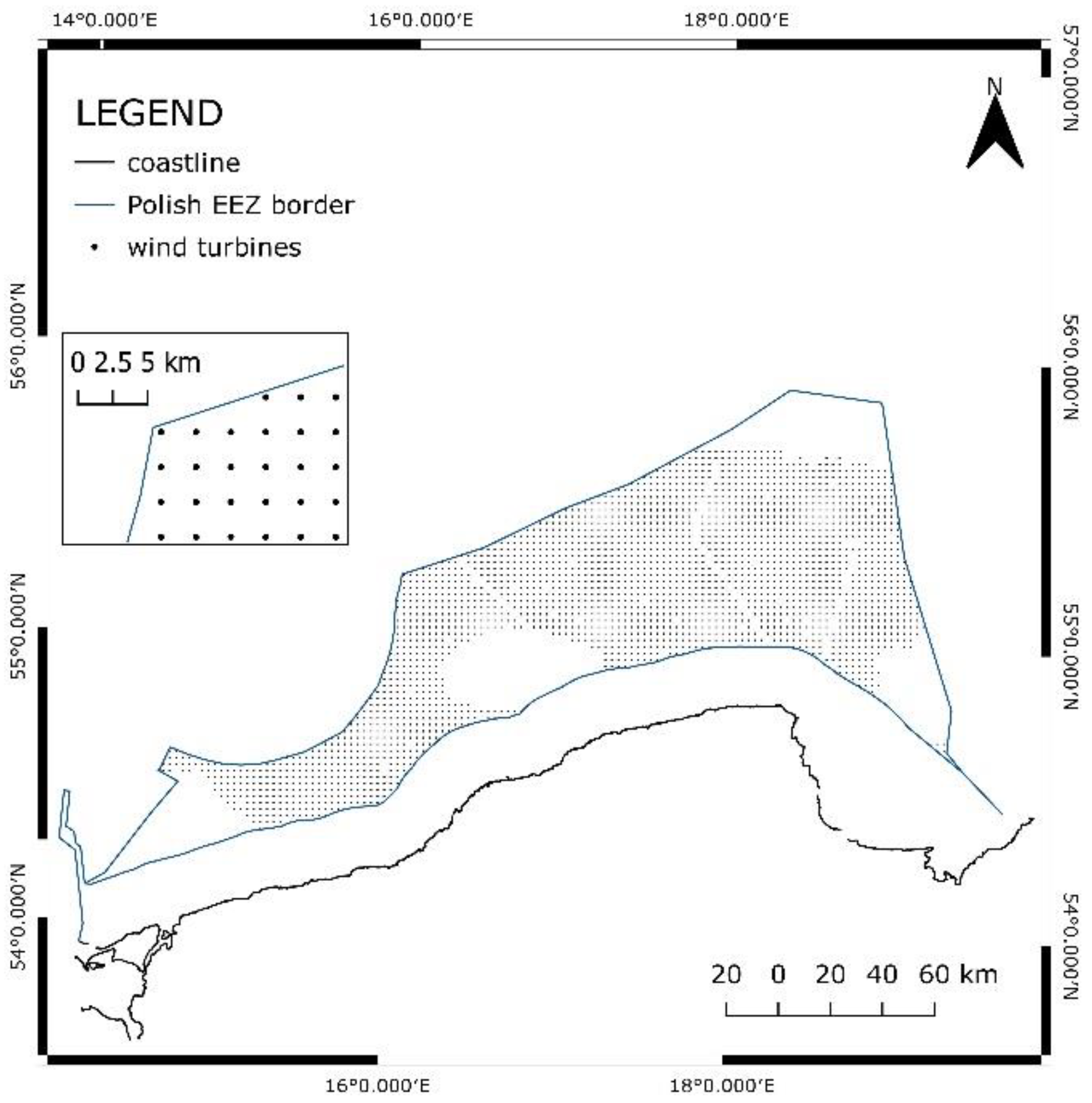
In the first one, wind turbines with a nominal capacity of 15 MW were laid out 2 km apart from each other only in the suitable areas of EEZ. The dots presented in
Figure 12 depict the locations of the turbines with such a layout. In total, such an area can accommodate 3664 turbines with overall electrical capacity equal to 54.96 GW. The technical potential only in highly suitable areas would be equal to 15.24 GW.
In the second spatial configuration, wind turbines of the same size were laid out 2.5 km apart from each in the suitable areas of EEZ. The dots presented in
Figure 13. depict the locations of the turbines with such a layout. In total, such an area can accommodate 2347 turbines with overall electrical capacity equal to 35.2 GW. The technical potential only in highly suitable areas would be equal to 9.15 GW.
4.3. Validation of the results against real investment plans
The most advanced investments projects in offshore wind farms in EEZ are listed in
Table 4. All of them obtained the location permit, some of them also received an environmental decision, a grid-connection agreement or other required permits. Highly-developed projects are Baltic Power, Baltica I, Baltica II, Baltica III, BC-WIND, F.E.W. Baltic II, MFW Bałtyk I, MFW Bałtyk II, and MFW Bałtyk III. Less advance ones include five areas granted to the PGE Group, and other five locations awarded to the Orlen Group [41].
As shown in
Figure 14, outlines of planned investments overlaps with highly suitable areas for OWF development indicated in this study.
5. Discussion
The technical potential for offshore wind farms was estimated from 15 GW (highly suitable areas) to almost 55 GW (all suitable areas). These values were obtained assuming that wind turbines were laid out 2 km apart from each other and located in suitable areas. If the distance between turbines was 2.5 km, the technical potential would be equal to 35.2 GW. The areas of the Polish EEZ suitable for OWFs were identified using QGIS software taking into account several constraints. Although a numerous constraints can be found in literature, there is no universal set of such constraints and it would be different for each location. Such an original set of constraints which, according to the Authors, are relevant for the EEZ was proposed. This set included constraints such as distance from nature conservation areas (Natura 2000), distance from submarine cables and gas pipelines, and distance from shipping routes, fishing areas, and distance from shipwrecks were taken into account in this study. Some of the geospatial data was downloaded in raster format and it was necessary to convert it into vector format. Impact maps with distances were created for each constraint. The assessment of the importance of the selected constraints was performed with AHP. This revealed three most significant criteria in the study were: wind velocity, distance from coastline, and water depth. The least important criteria were fishing areas, mostly due to the lack of precise data. A spatial resolution of 1 km x 1 km was applied over the domain covering the EEZ to map the detailed AHP results. The results were divided into three groups, namely, marginally, moderately, and highly suitable are for the development of the offshore OWFs. The most optimal conditions for are in the south of the EEZ of Poland due to the proximity to the coast, relatively shallow waters, and appropriate wind conditions. On the other hand, the marginally suitable areas for OWF are located in the north of the EEZ of Poland, further from the coast, where the sea is deeper.
6. Summary and conclusions
Offshore wind market is one of the most dynamically growing markets, especially in Europe. This research was aimed at estimating the total technical potential of the Poland's Exclusive Economic Zone of the Baltic Sea and identifying the optimal locations for offshore wind farms (OWFs).
Site selection for the development of an OWF project is complex and needs to take into consideration different numerous constraints. The paper proposes a GIS-based methodology in which a unique set of constraint-related criteria was employed to select the bests sites. These criteria included wind velocity, water depth, distance from nature conservation areas, distance from submarine cables and gas pipelines, distance from shipping routes, distance from fishing areas, distance from shipwrecks, distance from coastline.
In the Analytic Hierarchy Process, at first each criteria were first given a score. Then, the rating matric was formed containing the weights from their pairwise comparison. Finally the weights were rank (the minimal value was 1.494, and the maximal 2.801) and divided into three groups, namely, marginally, moderately, and highly suitable. The total area predisposed for OWF development was 16218.67 km2. The sites marginally suitable covered an area of 2178.97 km2 which is equal to 10.26% of the total EEZ area. Moderately suitable was an area of 10312.76 km2, and a share of 48.56%. Moreover, highly suitable was an area of 3726.90 km2, a share of 17.55%. Three most significant criteria in the study were: wind velocity, distance from coastline, and water depth. The results were presented in the form of maps over the domain covering with spatial resolution of 1 km x 1 km. Two different spatial configurations for the deployment of individual wind turbines were considered to assess the offshore wind potential, in which wind turbines with a nominal capacity of 15 MW were laid out: (i) 2 km and (ii) 2.5 km apart from each, respectively. First configuration could accommodate 3664 turbines with overall electrical capacity equal to 54.96 GW, whereas the second one 2347 turbines with overall electrical capacity equal to 35.2 GW. The technical potential only in highly suitable areas was equal to 15.24 GW and 9.15 GW, respectively. The study provides new insight on the development of offshore wind farms in the Polish part of the Baltic Sea. The methodology presented in this paper could be easily applied to estimate the technical potential and select best sites for OWFs in other locations. The electricity produced by offshore wind farms could play a very important role in replacement of hard coal and lignite in the Polish power generation mix, thus helping the country to reach its decarbonization targets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Prz., A.W and J.Z.; methodology, M.Prz. and A.W.; software, M.Prz., M.R and J.Z..; validation, M.Prz.; formal analysis, M.Prz.; investigation, M.Prz. and A.W.; resources, M.Prz.; data curation, M.Prz.,M.P. and M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Prz.; writing—review and editing, A.W.; visualization, M.Prz. and M.P; supervision, A.W.; project administration, A.W.; funding acquisition, A.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by AGH University of Krakow, Faculty of Energy and Fuels (grant number 16.16.210.476) with the financial support of the “Excellence Initiative—Research University” program.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- ‘“Fit for 55”: delivering the EU’s 2030 Climate Target on the way to climate neutrality. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions’, European Commission, Brussels, COM(2021) 550 final, 2021.
- ‘Offshore wind energy 2021 statistics’, Wind Europe, 2022.
- M. D. Esteban, J. J. Diez, J. S. López, and V. Negro, ‘Why offshore wind energy?’, Renewable Energy, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 444–450, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- ‘https://www.vestas.com/en/products/offshore/V236-15MW; Accessed: may 2023’.
- E. E. Michaelides, Alternative Energy Sources. in Green Energy and Technology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2012. [CrossRef]
- ‘Ustawa z dnia 17 grudnia 2020 r. o promowaniu wytwarzania energii elektrycznej w morskich farmach wiatrowych’, Dz.U. 2021 poz. 234, Dec. 2020.
- E. Caceoğlu, H. K. Yildiz, E. Oğuz, N. Huvaj, and J. M. Guerrero, ‘Offshore wind power plant site selection using Analytical Hierarchy Process for Northwest Turkey’, Ocean Engineering, vol. 252, p. 111178, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Chaouachi, C. F. Covrig, and M. Ardelean, ‘Multi-criteria selection of offshore wind farms: Case study for the Baltic States’, Energy Policy, vol. 103, pp. 179–192, Apr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. Kim, J.-I. Park, and J. Maeng, ‘Offshore wind farm site selection study around Jeju Island, South Korea’, Renewable Energy, vol. 94, pp. 619–628, Aug. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Cavazzi and A. G. Dutton, ‘An Offshore Wind Energy Geographic Information System (OWE-GIS) for assessment of the UK’s offshore wind energy potential’, Renewable Energy, vol. 87, pp. 212–228, Mar. 2016. [CrossRef]
- L. Hong and B. Möller, ‘Offshore wind energy potential in China: Under technical, spatial and economic constraints’, Energy, vol. 36, no. 7, pp. 4482–4491, Jul. 2011. [CrossRef]
- B. Möller, L. Hong, R. Lonsing, and F. Hvelplund, ‘Evaluation of offshore wind resources by scale of development’, Energy, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 314–322, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Exo K.M., Hüppop O., Garthe S., ‘Birds and offshore wind farms: A hot topic in marine ecology’, Wader Study Group Bulletin, vol. 100, pp. 50–53, Nov. 2003.
- ‘https://globalwindatlas.info/en/; Accessed: april 2023’.
- ‘https://sipam.gov.pl/; Accessed: june 2023’.
- ‘https://emodnet.ec.europa.eu/; Accessed: may 2023’.
- R. W. Saaty, ‘The analytic hierarchy process—what it is and how it is used’, Mathematical Modelling, vol. 9, no. 3–5, pp. 161–176, 1987. [CrossRef]
- T. L. Saaty and K. P. Kearns, ‘The Analytic Hierarchy Process’, in Analytical Planning, Elsevier, 1985, pp. 19–62. [CrossRef]
- K. Halicka, Prospektywna analiza technologii: metodologia i procedury badawcze. Białystok: Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Białostockiej, 2016.
- Atanasova-Pacemska, Tatjana & Pachemska, – & Lapevski, Martin & Timovski, Riste, ‘ANALYTICAL HIERARCHICAL PROCESS (AHP) METHOD APPLICATION IN THE PROCESS OF SELECTION AND EVALUATION’, presented at the UNITECH International Scientific Conference, Gabrovo, Nov. 2014.
- R. J. A. M. Stevens, B. F. Hobbs, A. Ramos, and C. Meneveau, ‘Combining economic and fluid dynamic models to determine the optimal spacing in very large wind farms: Combining economic and fluid dynamic models to determine the optimal spacing in very large wind farms’, Wind Energ., vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 465–477, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Meyers and C. Meneveau, ‘Optimal turbine spacing in fully developed wind farm boundary layers: Optimal turbine spacing in wind farm boundary layers’, Wind Energ., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 305–317, Mar. 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. J. A. M. Stevens, D. F. Gayme, and C. Meneveau, ‘Effects of turbine spacing on the power output of extended wind-farms’, Wind Energ., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 359–370, Feb. 2016. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).