Submitted:
27 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture
2.2. Mouse models of NSCLC
2.3. Selection of human lncRNAs implicated in lung cancer
2.4. CpG methylation analysis of human origin lncRNAs assessed by Pyrosequencing
2.5. Expression profiles of human origin lncRNAs assessed by qPCRs
2.6. Human and mouse miRNA NSCLC profiles determined by Next Generation sequencing (NGS)
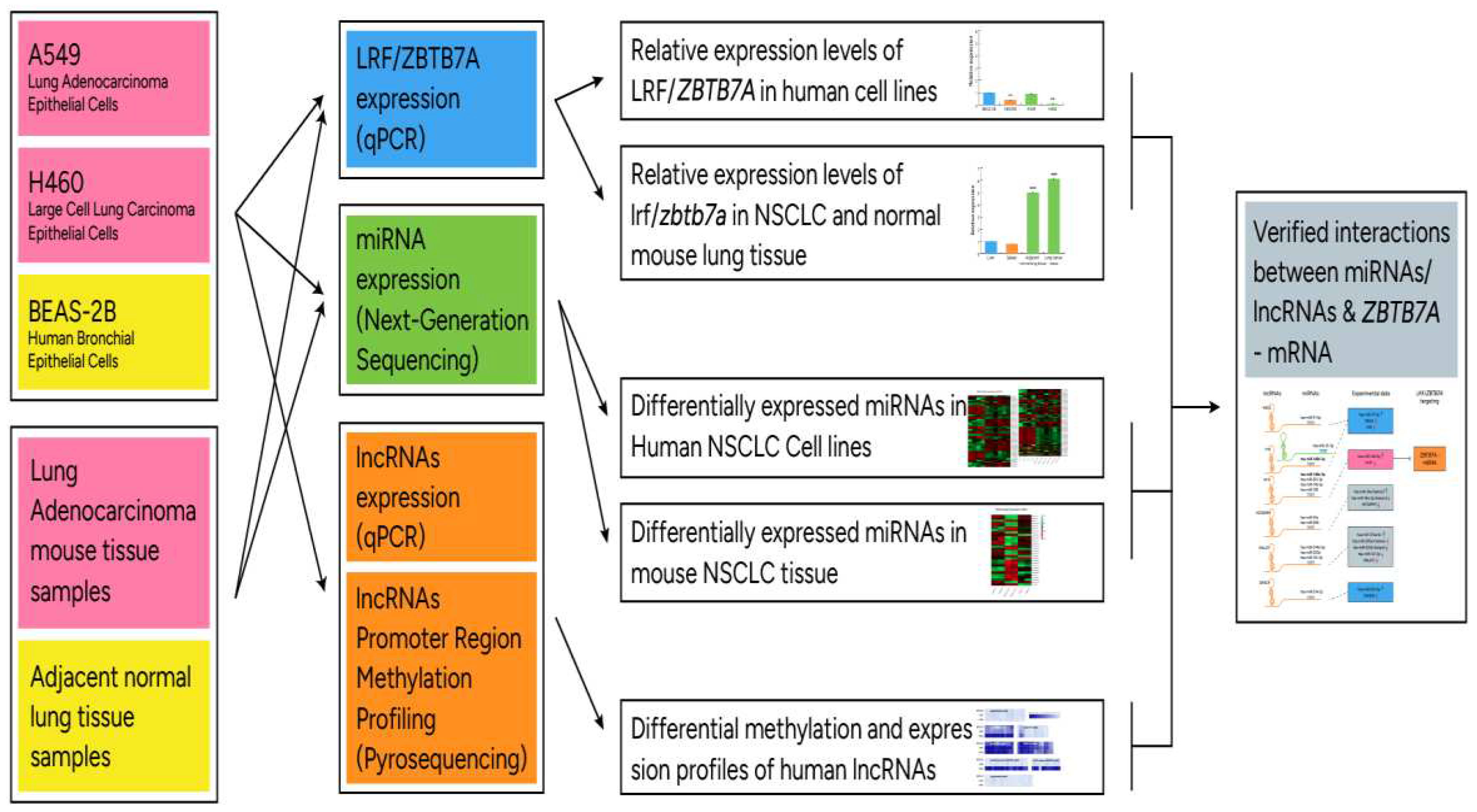
2.7. Analysis workflow
2. Results
3.1. Differential expression profiles of LRF/ZBTB7A and methylation/expression profiles of lncRNAs
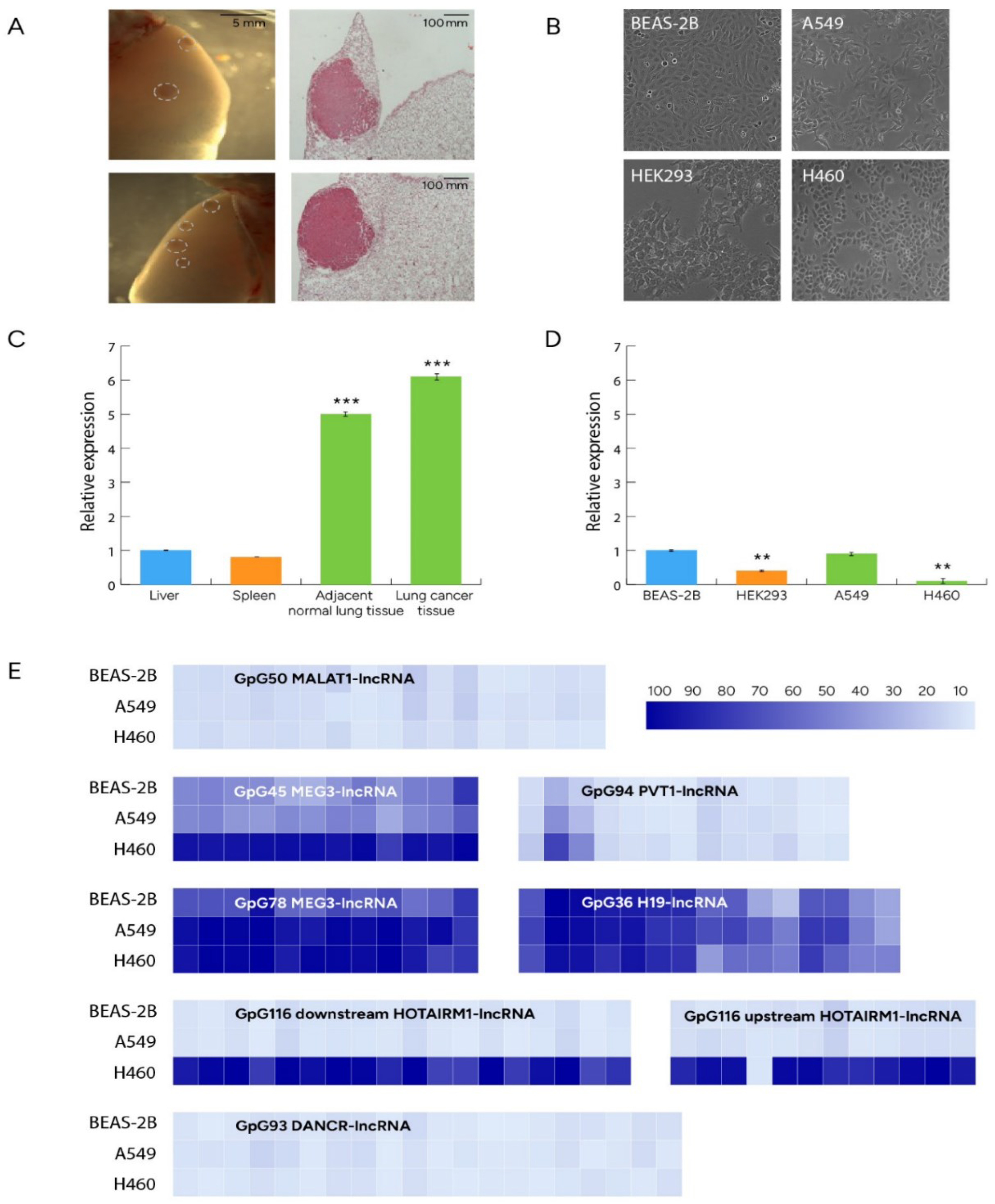
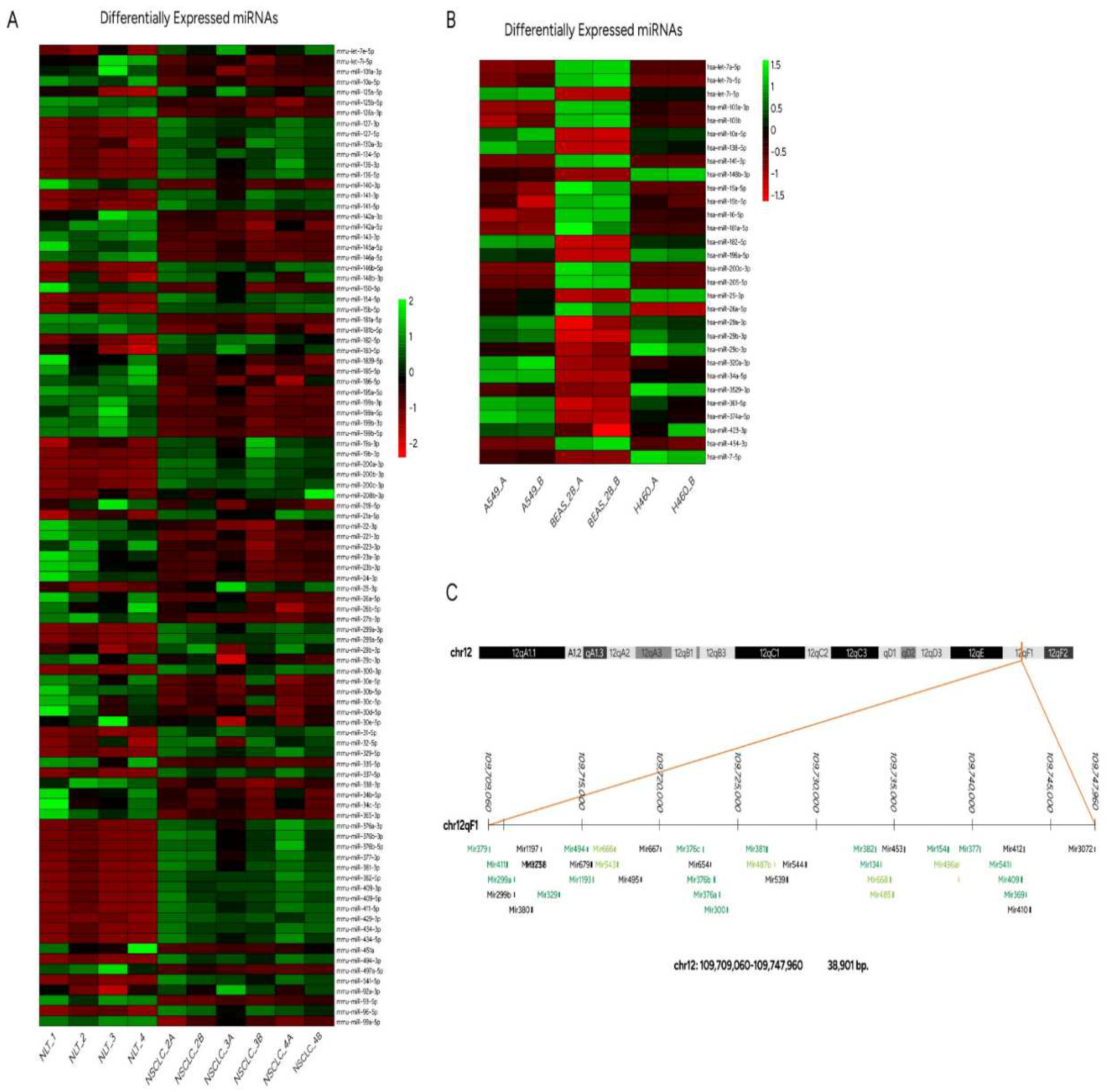
3.2. Sets of mouse miRs differentially expressed between NSCLC and normal lung tissue
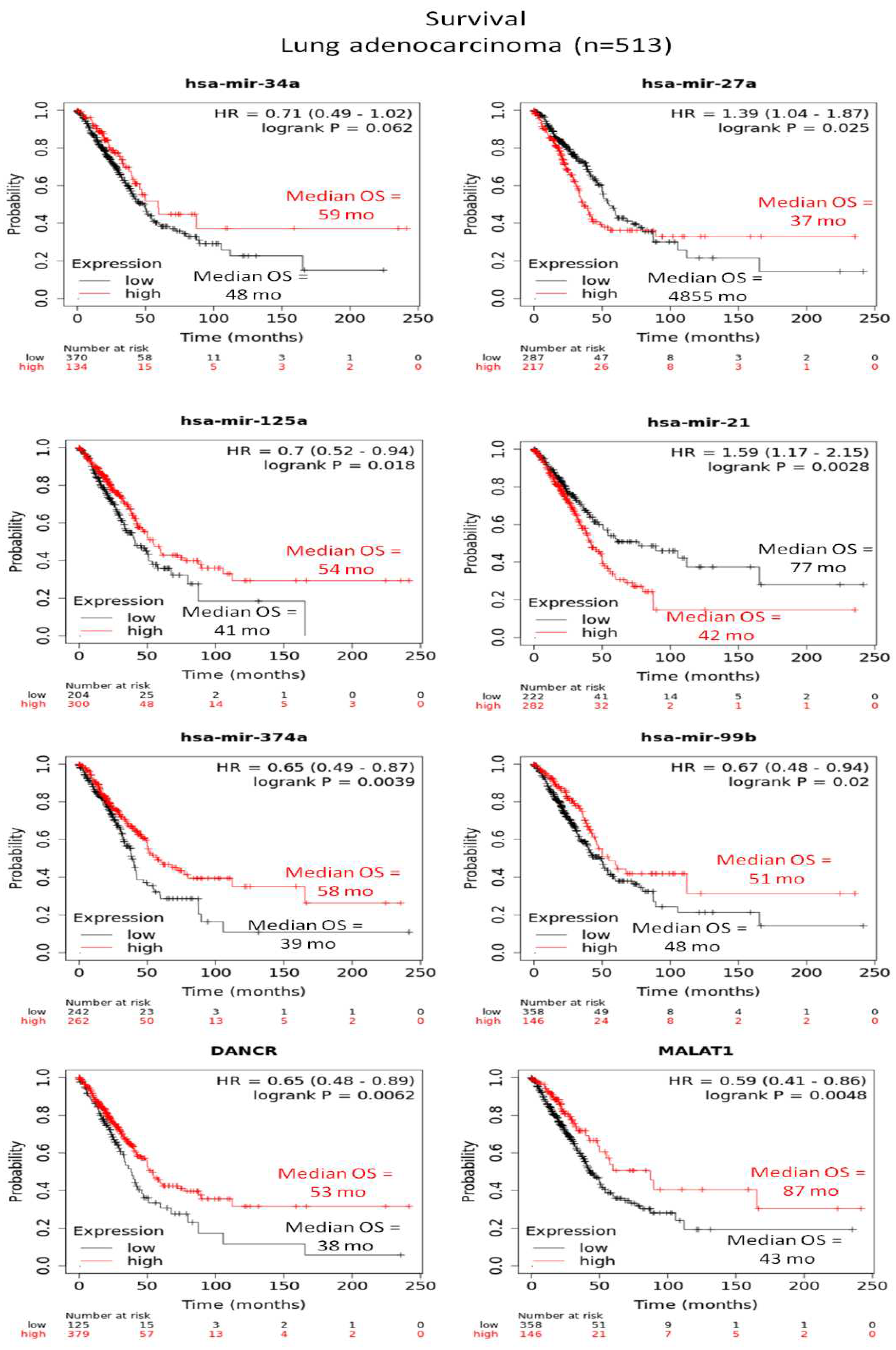
3.3. Altered expression profiles of human miRs not related to LRF/ ZBTB7A transcription factor
3.4. Human and mouse miRs targeting LRF/ZBTB7A
| Chromosome | Family | miRNA | Gene target | interaction with 3'UTR | Score/REF | Results from our study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | miR-17 | hsa-miR-20a-5p | ZBTB7A | at 912, 1205, 1230, 4309 bp | 96 | A549 downregulated |
| 19 | miR-10 | hsa-miR-125a-5p | ZBTB7A | at 547, 803, 1667, 4210 bp | 81/ [39] |
A549 upregulated |
| 12 | miR-148 | hsa-miR-148b-3p | ZBTB7A | at 1877, 2071 bp | 50 | H460 upregulated |
| 13 | miR-15 | hsa-miR-15a-5p | ZBTB7A | at 3305 bp | 65 | A549 and H460 downregulated |
| 19 | miR-10 | hsa-miR-100-5p | ZBTB7A | [48] | H460 downregulated | |
| 4 | miR-577 | hsa-miR-577 | ZBTB7A | [43] | - | |
| 7 | miR-17 | hsa-miR-106b | ZBTB7A | [49] | - | |
| 17 | miR-144 | hsa-miR-144-3p | ZBTB7A | [46] | - | |
| 19 | miR-520e | hsa-miR-520e | ZBTB7A | [44] | - | |
| 19 | miR-10 | mmu-miR-10a-5p | Zbtb7a | 68 | NSCLC mouse tissue downregulated | |
| 13 | miR-15 | mmu-miR-195a-5p | Zbtb7a | NSCLC mouse tissue downregulated | ||
| 1 and 2 | miR-181 | mmu-miR-181a-1-5p and mmu-miR-181a-2-5p | Zbtb7a | at 2907 bp | 87 | NSCLC mouse tissue downregulated |
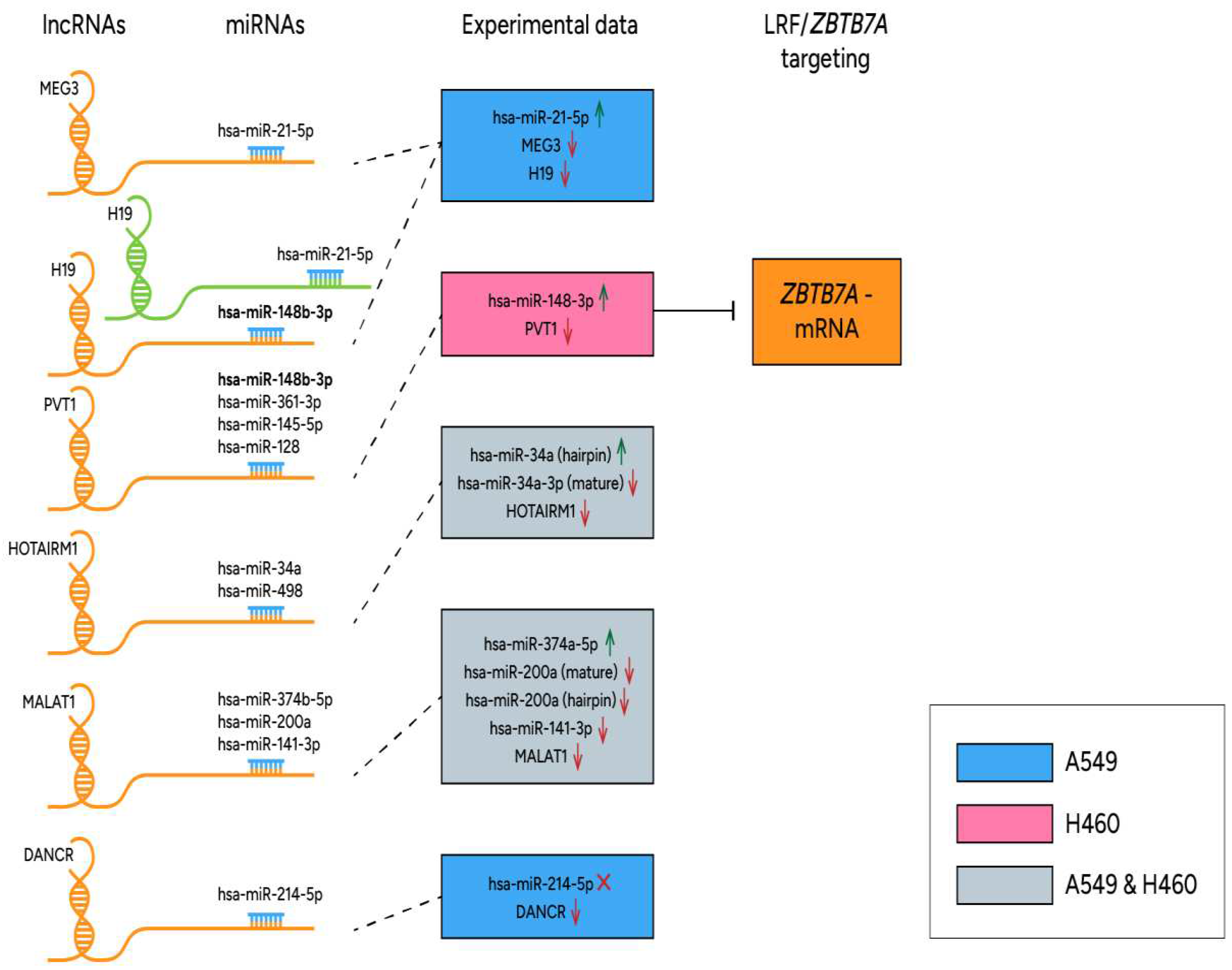
3.5. Deregulated lncRNA expression and methylation levels, and lncRNA/miR functional axes in cancer state
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascetta, P.; Marinello, A.; Lazzari, C.; Gregorc, V.; Planchard, D.; Bianco, R.; et al. KRAS in NSCLC: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Kaczkowski, B.; Ohshima, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; Noguchi, S.; Mikami, Y.; et al. Integrative CAGE and DNA Methylation Profiling Identify Epigenetically Regulated Genes in NSCLC. Mol Cancer Res 2017, 15, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A. Chemotherapy, chemoresistance and the changing treatment landscape for NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2011, 71, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2002, 3, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherafatian, M.; Arjmand, F. Decision tree-based classifiers for lung cancer diagnosis and subtyping using TCGA miRNA expression data. Oncol Lett 2019, 18, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Gao, T.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, W.; Wang, T.H.; Wu, J. Prognostic Value of Survival of MicroRNAs Signatures in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J Cancer 2019, 10, 5793–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Yuan, Y.; Song, Z.; Yan, D.; Kong, X. Expression Profiles of microRNAs in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines Using microRNA Sequencing. Cell Physiol Biochem 2018, 51, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Valdecanas, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Bhardwaj, V.; Calin, G.A.; et al. Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Mol Ther 2014, 22, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginn, L.; Shi, L.; Montagna, M.; Garofalo, M. LncRNAs in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Noncoding RNA 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Ning, S.; Wang, P. Dynamic TF-lncRNA Regulatory Networks Revealed Prognostic Signatures in the Development of Ovarian Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chondrou, V.; Shaukat, A.-N.; Psarias, G.; Athanasopoulou, K.; Iliopoulou, E.; Damanaki, A.; et al. LRF Promotes Indirectly Advantageous Chromatin Conformation via BGLT3-lncRNA Expression and Switch from Fetal to Adult Hemoglobin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Singh, A.K.; Prajapati, K.S.; Kushwaha, P.P.; Shuaib, M.; Kumar, S. Emerging role of ZBTB7A as an oncogenic driver and transcriptional repressor. Cancer Lett. 2020, 483, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, I.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Herbertz, S.; John, W.; Paz-Ares, L.; Schmid-Bindert, G. KRAS-Mutant non-small cell lung cancer: From biology to therapy. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellakis, N.I.; Giannou, A.D.; Pepe, M.A.A.; Agalioti, T.; Zazara, D.E.; Giopanou, I.; et al. Tobacco chemical-induced mouse lung adenocarcinoma cell lines pin the prolactin orthologue proliferin as a lung tumour promoter. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spella, M.; Lilis, I.; Pepe, M.A.; Chen, Y.; Armaka, M.; Lamort, A.S.; et al. Club cells form lung adenocarcinomas and maintain the alveoli of adult mice. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftabi, Y.; Ansarin, K.; Shanehbandi, D.; Khalili, M.; Seyedrezazadeh, E.; Rahbarnia, L.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs as potential biomarkers in the prognosis and diagnosis of lung cancer: A review and target analysis. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 307–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lei, T.; Chen, X.; Gu, J.; Huang, J.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z. Long non-coding RNA in lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2020, 504, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entezari, M.; Ghanbarirad, M.; Taheriazam, A.; Sadrkhanloo, M.; Zabolian, A.; Goharrizi, M.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: Potential functions in lung cancer progression, drug resistance and tumor microenvironment remodeling. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 150, 112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, L.; Gong, C.; Wu, W.; Yao, C.; Zhu, S. Long non-coding RNAs: How to regulate the metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Hou, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Gao, P. Multidimensional communication of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Han, C.; Fang, P.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer: implications for lineage plasticity-mediated TKI resistance. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. : CMLS 2021, 78, 1983–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarino, C.G.; Romanowski, V. Phenol extraction revisited: a rapid method for the isolation and preservation of human genomic DNA from whole blood. Mol. Cell. Probes 1994, 8, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaikou, A.M.; Kouroupis, D.; Sgourou, A.; Markopoulos, G.S.; Bagli, E.; Markou, M.; et al. Mechanical stress affects methylation pattern of GNAS isoforms and osteogenic differentiation of hAT-MSCs. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data [Online] Available online at:2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Smith, T.; Heger, A.; Sudbery, I. UMI-tools: modeling sequencing errors in Unique Molecular Identifiers to improve quantification accuracy. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. GigaScience 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq--a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1630–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Golpon, H.; Zardo, P.; Borlak, J. miRNAs in lung cancer. A Syst. Rev. Identifies Predict. Progn. Mirna Candidates Precis. Med. Lung Cancer. Transl. Res. 2021, 230, 164–196. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehler, D.; Høyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Lund, A.H. The miR-10 microRNA precursor family. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojo, N.; Tatsumi, N.; Moriguchi, N.; Matsumura, A.; Morimoto, S.; Nakata, J.; et al. A Zbtb7a proto-oncogene as a novel target for miR-125a. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, P.; Ma, Z. Biology of MiR-17-92 Cluster and Its Progress in Lung Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitto, L.; Ripoli, A.; Cremisi, F.; Simili, M.; Rainaldi, G. microRNA(interference) networks are embedded in the gene regulatory networks. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2458–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.B.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Han, J.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, D.H. Metformin regulates expression of DNA methyltransferases through the miR-148/-152 family in non-small lung cancer cells. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xi, J.; Peng, Y.; Bian, B.; Hao, G.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, Z. Circular RNA Circ_0016760 Modulates Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Growth Through the miR-577/ZBTB7A Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5561–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhijun, Z.; Jingkang, H. MicroRNA-520e suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cell growth by targeting Zbtb7a-mediated Wnt signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 486, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Geng, T.; Luo, S.; He, Q. MiR-106b regulates the apoptosis and tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7A (Zbtb7a). J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chou, Z.; Li, C.; Huang, K.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; et al. ZBTB7A, a miR-144-3p targeted gene, accelerates bladder cancer progression via downregulating HIC1 expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolopoulou, K.; Pateras, I.S.; Evangelou, K.; Tsantoulis, P.K.; Liontos, M.; Kittas, C.; et al. Gene amplification is a relatively frequent event leading to ZBTB7A (Pokemon) overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Pathol. 2007, 213, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.B.; Wang, Y.W.; Xing, A.Y.; Gao, J.W.; Zhang, H.; Guo, X.Y.; Gao, P. C/EBPα-induced miR-100 expression suppresses tumor metastasis and growth by targeting ZBTB7A in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Yan, Y.; Shui, S.; Wu, G.; Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, X. miR-106b regulates the 5-fluorouracil resistance by targeting Zbtb7a in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52913–52922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wan, L.; Lu, K.; Sun, M.; Pan, X.; Zhang, P.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA MEG3 Contributes to Cisplatin Resistance of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0114586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Bi, Q.; Li, Y.; Deng, J.; Wu, N.; Hao, S.; Zhao, M. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 inhibits cell migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-21-5p/PTEN axis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Sheng, B.; Xia, Q.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y. Association of long non-coding RNA H19 and microRNA-21 expression with the biological features and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Guan, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Jiang, X. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 in human cancers. Clin. Chim. Acta; Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2020, 511, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Tong, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Song, G.; Zhu, B. Overexpression of the lncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes lenvatinib resistance by downregulating miR-34a and activating autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Lung Cancer Proliferation and Gefitinib Resistance by Acting as a miR-200a Sponge. Arch. De Bronconeumol. 2019, 55, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Su, Z.Z.; Shen, Q.M. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion via miR-374b-5p/SRSF7 axis in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiong, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Long, X. A novel mechanism regulating pyroptosis-induced fibrosis in endometriosis via lnc-MALAT1/miR-141-3p/NLRP3 pathway. Biology of reproduction. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, R.; Polidori, T.; Meise, D.F.; Pulido-Quetglas, C.; Chouvardas, P.; Forster, S.; et al. Multi-hallmark long noncoding RNA maps reveal non-small cell lung cancer vulnerabilities. Cell Genom. 2022, 2, 100171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.; Wu, Y.S.; Wang, W.S.; Zhang, J.S.; Wu, Q.G. Upregulation of lncRNA DANCR functions as an oncogenic role in non-small lung cancer by regulating miR-214-5p/CIZ1 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 2539–2547. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Song, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, W.; et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1-214 promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by stabilizing Lin28 and interacting with miR-128. Oncogene 2019, 38, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Li, L. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 contributes to cell growth and metastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer by regulating miR-361-3p/SOX9 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. = Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.M.; Zhao, X.F.; Qiu, H.B.; Ming, Z.; Liu, K.; Yan, J. The long non-coding RNA PVT1/miR-145-5p/ITGB8 axis regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Shen, W.; Jin, C.; Wang, L.; Yu, B. PVT1 Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Regulating miR-148/RAB34 Signal Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1819–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Győrffy, B. Discovery and ranking of the most robust prognostic biomarkers in serous ovarian cancer. GeroScience 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| lncRNA gene | CpG island | Region analyzed |
|---|---|---|
| DANCR | 93 | Chr4: 52712612-52712726 |
| H19 | 36 | Chr11:1996329-1996211 |
|
HOTAIRM1 upstream |
116 | Chr7:27095663-27095791 |
|
HOTAIRM1 downstream |
116 | Chr7: 27096410-27096495 |
| MALAT1 | 50 | Chr11:65497584-65497709 |
| MEG3 | 45 | Chr14:100826116-100826218 |
| MEG3 | 78 | Chr14:100827449-100827521 |
| PVT1 | 94 | Chr8:127794107-127794229 |
| miR hairpin | Mature miR | Gene family | miR cluster | Chromosomal location | |
| UPREGULATED | mmu-mir-200b | mmu-mir-200b-3p | mir-8 | mmu-mir-200b mmu-mir-200a mmu-mir-429 |
chr4: 156055681-156055750 [-] chr4: 156054896-156054985 [-] chr4: 156053905-156053987 [-] |
| mmu-mir-200a | mmu-mir-200a-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-429 | mmu-mir-429-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-200c | mmu-mir-200c-3p | mmu-mir-200c mmu-mir-141 |
chr6: 124718322-124718390 [-] chr6: 124717914-124717985 [-] |
||
| mmu-mir-141 | mmu-mir-141-5p mmu-mir-141-3p |
||||
| mmu-mir-379 | mmu-mir-379-5p | mir-379 | *mmu-mir-379 mmu-mir-411 mmu-mir-299a mmu-mir-299b mmu-mir-380 mmu-mir-1197 mmu-mir-323 mmu-mir-758 mmu-mir-329 mmu-mir-494 mmu-mir-679 mmu-mir-1193 mmu-mir-666 mmu-mir-543 mmu-mir-495 mmu-mir-667 mmu-mir-376c mmu-mir-654 mmu-mir-376b mmu-mir-376a mmu-mir-300 mmu-mir-381 mmu-mir-487b mmu-mir-539 mmu-mir-544 mmu-mir-382 mmu-mir-134 mmu-mir-668 mmu-mir-485 mmu-mir-453 mmu-mir-154 mmu-mir-496a mmu-mir-377 mmu-mir-541 mmu-mir-409 mmu-mir-412 mmu-mir-369 mmu-mir-410 mmu-mir-3072 |
chr12: 109709060-109709125 [+] chr12: 109710175-109710256 [+] chr12: 109710638-109710700 [+] chr12: 109710645-109710693 [-] chr12: 109711803-109711863 [+] chr12: 109712317-109712436 [+] chr12: 109712508-109712593 [+] chr12: 109712810-109712890 [+] chr12: 109713481-109713577 [+] chr12: 109715318-109715402 [+] chr12: 109715577-109715650 [+] chr12: 109715671-109715791 [+] chr12: 109717085-109717183 [+] chr12: 109717258-109717333 [+] chr12: 109718754-109718816 [+] chr12: 109720006-109720097 [+] chr12: 109722718-109722803 [+] chr12: 109723218-109723301 [+] chr12: 109723458-109723539 [+] chr12: 109723781-109723848 [+] chr12: 109724313-109724391 [+] chr12: 109726822-109726896 [+] chr12: 109727333-109727414 [+] chr12: 109728129-109728202 [+] chr12: 109729325-109729402 [+] chr12: 109733771-109733846 [+] chr12: 109734139-109734209 [+] chr12: 109734732-109734797 [+] chr12: 109734902-109734974 [+] chr12: 109735619-109735700 [+] chr12: 109738433-109738498 [+] chr12: 109739119-109739197 [+] chr12: 109740510-109740577 [+] chr12: 109742409-109742498 [+] chr12: 109743158-109743236 [+] chr12: 109743289-109743368 [+] chr12: 109743418-109743496 [+] chr12: 109743715-109743795 [+] chr12: 109747878-109474960 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-411 | mmu-mir-411-5p | ||||
| mmu-mir-299a | mmu-mir-299a-5p mmu-mir-299a-3p |
mir-299 | |||
| mmu-mir-376c | mmu-mir-376c-3p | mir-367 | |||
| mmu-mir-376b | mmu-mir-376b-5p mmu-mir-376b-3p |
||||
| mmu-mir-376a | mmu-mir-376a-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-134 | mmu-mir-134-5p | mir-134 | |||
| mmu-mir-300 | mmu-mir-300-3p | mir-154 | |||
| mmu-mir-381 | mmu-mir-381-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-382 | mmu-mir-382-5p | ||||
| mmu-mir-154 | mmu-mir-154-5p | ||||
| mmu-mir-377 | mmu-mir-377-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-369 | mmu-mir-369-5p mmu-mir-369-3p |
||||
| mmu-mir-409 | mmu-mir-409-5p mmu-mir-409-3p |
||||
| mmu-mir-494 | mmu-mir-494-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-541 | mmu-mir-541-5p | mir-541 | |||
| mmu-mir-329 | mmu-mir-329-5p |
mir-329 |
|||
| mmu-mir-1193 | mmu-mir-1193-3p | mir-1193 | |||
| mmu-mir-337 | mmu-mir-337-5p mmu-mir-337-3p |
mir-337 | mmu-mir-337 mmu-mir-3544 mmu-mir-540 mmu-mir-665 mmu-mir-3070-1 mmu-mir-3070-2 mmu-mir-431 mmu-mir-433 mmu-mir-127 mmu-mir-434 mmu-mir-432 mmu-mir-3071 mmu-mir-136 |
chr12: 109585789-109585885 [+] chr12: 109585813-109585873 [-] chr12: 109586080-109586146 [+] chr12: 109586314-109586407 [+] chr12: 109587943-109588031 [+] chr12: 109588592-109588680 [+] chr12: 109590447-109590537 [+] chr12: 109591715-109591838 [+] chr12: 109592846-109592915 [+] chr12: 109594506-109594599 [+] chr12: 109594956-109595030 [+] chr12: 109595318-109595397 [-] chr12: 109595327-109595388 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-3544 | mir-3544 | ||||
| mmu-mir-540 |
mir-540 | ||||
| mmu-mir-127 | mmu-mir-127-5p mmu-mir-127-3p |
mir-127 | |||
| mmu-mir-434 | mmu-mir-434-5p mmu-mir-434-3p |
mir-434 | |||
| mmu-mir-431 | mmu-mir-431-5p | mir-431 | |||
| mmu-mir-136 | mmu-mir-136-3p mmu-mir-136-5p |
mir-136 | |||
| mmu-mir-3071 | no family | ||||
| mmu-mir-19b-1 mmu-mir-19b-2 |
mmu-mir-19b-3p | miR-19 | mmu-miR-17 mmu-miR-18a mmu-miR-19a mmu-miR-20a mmu-miR-19b-1 mmu-miR-92a-1 |
chr14: 115043671-115043754 [+] chr14: 115043851-115043946 [+] chr14: 115044000-115044081 [+] chr14: 115044157-115044263 [+] chr14: 115044305-115044391 [+] chr14: 115044427-115044506 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-31 | mmu-mir-31-5p | mir-31 | mmu-mir-31 | chr4: 88910557-88910662 [-] | |
| mmu-mir-146b | mmu-miR-146b-5p | mir-146 | mmu-miR-146b | chr19: 46342762-46342870 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-21a | mmu-miR-21a-5p | mir-21 | mmu-miR-21a | chr11: 86584067-86584158 [-] | |
| mmu-mir-32 | mmu-mir-32-5p | mir-32 | mmu-mir-32 | chr4: 56895226-56895298 [-] | |
| mmu-mir-96 | mmu-mir-96-5p | mir-96 | mmu-mir-183 mmu-mir-96 mmu-mir-182 |
chr6: 30169668-30169737 [-] chr6: 30169446-30169551 [-] chr6: 30165918-30165992 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-208b | mmu-mir-208b-3p | mir-208 | mmu-mir-208b | chr14: 54975700-54975776 [-] | |
| mmu-mir-341 | mmu-mir-341-3p | mir-341 | mmu-mir-341 mmu-mir-1188 mmu-mir-370 |
chr12: 109611500-109611595 [+] chr12: 109611822-109611941 [+] chr12: 109618258-109618336 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-674 | mmu-mir-674-5p | mir-674 | mmu-mir-674 | chr2: 117185127-117185226 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-184 | mmu-mir-184-3p | mir-184 | mmu-mir-184 | chr9: 89802260-89802328 [-] | |
| DOWNREGULATED | mmu-mir-126a | mmu-mir-126a-3p | mir-126 | mmu-mir-126a mmu-mir-126b |
chr2: 26591357-26591429 [+] chr2: 26591363-26591420 [-] |
| mmu-mir-126a-5p | |||||
| mmu-mir-126b | mmu-mir-126b-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-126b-5p | |||||
| mmu-mir-142a | mmu-mir-142a-3p mmu-mir-142a-5p |
mir-142 | mmu-mir-142a mmu-mir-142b |
chr11: 87756864-87756927 [+] chr11: 87756841-87756955 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-143 | mmu-mir-143-3p mmu-mir-143-5p |
mir-143 | mmu-mir-143 mmu-mir-145a |
chr18: 61649196-61649258 [-] chr18: 61647825-61647894 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-145a | mmu-mir-145a-5p mmu-mir-145a-3p |
mir-145 | |||
| mmu-mir-199b | mmu-mir-199b-3p mmu-mir-199b-5p |
mir-199 | mmu-mir-3154 mmu-mir-199b |
chr2: 32318265-32318343 [+] chr2: 32318460-32318569 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-199a-1 mmu-mir-199a-2 |
mmu-mir-199a-3p mmu-mir-199a-5p |
mmu-mir-199a-2 mmu-mir-214 |
chr1: 162217814-162217923 [+] chr1: 162223368-162223477 [+] |
||
| mmu-mir-10a | mmu-mir-10a-5p | mir-10 | mmu-mir-10a | chr11: 96317165-96317274 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-146a | mmu-mir-146a-5p | mir-146 | mmu-mir-146a | chr11: 43374397-43374461 [-] | |
| mmu-mir-497a | mmu-mir-497a-5p | mir-497 | mmu-mir-497b mmu-mir-497a mmu-mir-195a |
chr11: 70234692-70234816 [-] chr11: 70234717-70234800 [+] chr11: 70235042-70235135 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-497b | |||||
| mmu-mir-195a | mmu-mir-195a-5p | mir-15 | |||
| mmu-mir-335 | mmu-mir-335-5p | mir-335 | mmu-mir-335 | chr6: 30741299-30741396 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-365-1 mmu-mir-365-2 |
mmu-mir-365-3p | mir-365 | mmu-mir-193b mmu-mir-365-1 |
chr16: 13449523-13449601 [+] chr16: 13453840-13453926 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-150 | mmu-mir-150-5p | mir-150 | mmu-mir-150 mmu-mir-5121 |
chr7: 45121757-45121821 [+] chr7: 45126918-45126991 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-181a-1 mmu-mir-181a-2 |
mmu-mir-181a-5p | mir-181 | mmu-mir-181a-1 mmu-mir-181a-2 |
chr1: 137966455-137966541 [+] chr2: 38852735-38852810 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-23a | mmu-mir-23a-3p | mir-23 | mmu-mir-23a mmu-mir-27a mmu-mir-24-2 mmu-mir-3074-2 |
chr8: 84208518-84208592 [+] chr8: 84208672-84208758 [+] chr8: 84208815-84208921 [+] chr8: 84208825-84208907 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-27a | mmu-mir-27a-3p | mir-27 | |||
| mmu-mir-3074-5p | mir-3074 | ||||
| mmu-mir-144 mmu-mir-451a mmu-mir-451b |
mmu-mir-144-3p mmu-mir-451a |
mir-451 | mmu-mir-144 mmu-mir-451b mmu-mir-451a |
chr11: 78073005-78073070 [+] chr11: 78073170-78073241 [-] chr11: 78073170-78073241 [+] |
|
| mmu-mir-222 | mmu-mir-222-3p | mir-221 | mmu-mir-222 mmu-mir-221 |
chrX: 19146893-19146971 [-] chrX: 19146294-19146388 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-221 | mmu-mir-221-3p | ||||
| mmu-mir-223 | mmu-mir-223-3p | mir-223 | mmu-mir-223 | chrX: 96242817-96242926 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-34b mmu-mir-34c |
mmu-mir-34b-5p mmu-mir-34c-5p |
mir-34 | mmu-mir-34b mmu-mir-34c |
chr9: 51103562-51103645 [-] chr9: 51103034-51103110 [-] |
|
| mmu-mir-3065 | mir-3065 | mmu-mir-3065 mmu-mir-338 |
chr11: 120014767-120014853 [+] chr11: 120014765-120014862 [-] |
||
| mmu-mir-338-3p | mir-338 | ||||
| mmu-mir-140 | mmu-mir-140-3p mmu-mir-140-5p |
mir-140 | mmu-mir-140 | chr8: 107551244-107551313 [+] | |
| mmu-mir-187-3p | mir-187 | mmu-mir-187 | chr18: 24429110-24429170 [-] | ||
| A549 vs BEAS-2B | H460 vs BEAS-2B | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR hairpin | Mature miR | miR family | miR cluster | Chromosomal location | miR hairpin | Mature miR | miR family | miR cluster | Chromosomal location | ||
| UPREGULATED | hsa-mir-34a | hsa-mir-34a-5p | mir-34 | hsa-mir-34a | chr1: 9151668-9151777 [-] | hsa-mir-7-1 hsa-mir-7-2 hsa-mir-7-3 |
hsa-mir-7-5p | mir-7 | hsa-mir-7-5p | chr9: 83969748-83969857 [-] | |
| hsa-mir-23b | mir-27 | hsa-mir-23b hsa-mir-27b hsa-mir-3074 hsa-mir-24-1 |
chr9: 95085208-95085304 [+] chr9: 95085445-95085541 [+] chr9: 95086014-95086094 [-] chr9: 95086021-95086088 [+] |
hsa-mir-182 | hsa-mir-182-5p | mir-182 | hsa-mir-183 hsa-mir-96 hsa-mir-182 |
chr7: 129774905-129775014 [-] chr7: 129774692-129774769 [-] chr7: 129770383-129770492 [-] |
|||
| hsa-mir-27b | hsa-mir-27b-3p | hsa-mir-3529 | hsa-mir-3529-3p | mir-3529 | hsa-mir-3529 hsa-mir-7-2 hsa-mir-1179 |
chr15: 88611847-88611924 [-] chr15: 88611825-88611934 [+] chr15: 88608107-88608197 [+] |
|||||
| hsa-mir-21 | hsa-mir-21-5p hsa-mir-21-3p |
mir-21 | hsa-mir-21 | chr17: 59841266-59841337 [+] | hsa-mir-155 | hsa-mir-155-5p | mir-155 | hsa-mir-155 | chr21: 25573980-25574044 [+] | ||
| hsa-mir-374a | hsa-mir-374a-5p | mir-374 | hsa-mir-374a hsa-mir-545 |
chrX: 74287286-74287357 [-] chrX: 74287104-74287209 [-] |
hsa-mir-374a | hsa-mir-374a-5p | mir-374 | hsa-mir-374a hsa-mir-545 |
chrX: 74287286-74287357 [-] chrX: 74287104-74287209 [-] |
||
| hsa-mir-99b | hsa-mir-99b-5p | mir-10 | hsa-mir-99b hsa-let-7e hsa-mir-125a |
chr19: 51692612-51692681 [+] chr19: 51692786-51692864 [+] chr19: 51693254-51693339 [+] |
hsa-mir-148b | hsa-mir-148b-3p | mir-148 | hsa-mir-148b | chr12: 54337216-54337314 [+] | ||
| hsa-mir-125a | hsa-mir-125a-5p | hsa-let-7i | hsa-let-7i-5p | let-7 | hsa-let-7i | chr12: 62603686-62603769 [+] | |||||
| hsa-let-7e | hsa-let-7e-5p | let-7 | hsa-let-7c | hsa-let-7c-5p | hsa-let-7c | chr21: 16539828-16539911 [+] | |||||
| hsa-let-7i | hsa-let-7i-5p | hsa-let-7i | chr12: 62603686-62603769 [+] | hsa-mir-34a | hsa-mir-34a-5p | mir-34 | hsa-mir-34a | chr1: 9151668-9151777 [-] | |||
| hsa-mir-182 | hsa-mir-182-5p | mir-182 | hsa-mir-183 hsa-mir-96 hsa-mir-182 |
chr7: 129774905-129775014 [-] chr7: 129774692-129774769 [-] chr7: 129770383-129770492 [-] |
hsa-mir-126 | mir-126 | hsa-mir-126 | chr9: 136670602-136670686 [+] | |||
| hsa-mir-25 | mir-25 | hsa-mir-106b hsa-mir-93 hsa-mir-25 |
chr7: 100093993-100094074 [-] chr7: 100093768-100093847 [-] chr7: 100093560-100093643 [-] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-1307 | mir-1307 | hsa-mir-1307 | chr10: 103394253-103394401 [-] | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-423 | mir-423 | hsa-mir-423 hsa-mir-3184 |
chr17: 30117079-30117172 [+] chr17: 30117086-30117160 [-] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-3184 | |||||||||||
| hsa-mir-138-5p | mir-138 | hsa-mir-138 | chr3: 44114212-44114310 [+] | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-196a-5p | mir-196 | hsa-mir-196a | chr17: 48632490-48632559 [-] | ||||||||
| DOWNREGULATED | hsa-mir-205 | hsa-mir-205-5p | mir-205 | hsa-mir-205 | chr1: 209432133-209432242 [+] | hsa-mir-205 | hsa-mir-205-5p | mir-205 | hsa-mir-205 | chr1: 209432133-209432242 [+] | |
| hsa-mir-200a | hsa-mir-200a-3p | mir-8 | hsa-mir-200b hsa-mir-200a hsa-mir-429 |
chr1: 1167104-1167198 [+] chr1: 1167863-1167952 [+] chr1: 1169005-1169087 [+] |
hsa-mir-221 | hsa-mir-221-3p | mir-221 | hsa-mir-222 hsa-mir-221 |
chrX: 45747015-45747124 [-] chrX: 45746157-45746266 [-] |
||
| hsa-mir-200c | hsa-mir-200c-3p | hsa-mir-200c hsa-mir-141 |
chr12: 6963699-6963766 [+] chr12: 6964097-6964191 [+] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-222 | hsa-mir-222-3p | ||||||||||
| hsa-mir-141 | hsa-mir-141-3p | hsa-mir-141 | hsa-mir-141-3p | mir-8 | hsa-mir-200c hsa-mir-141 |
chr12: 6963699-6963766 [+] chr12: 6964097-6964191 [+] |
|||||
| hsa-let-7c | hsa-let-7c-5p | let-7 | hsa-mir-99a hsa-let-7c |
chr21: 16539089-16539169 [+] chr21: 16539828-16539911 [+] |
hsa-mir-200c | hsa-mir-200c-3p | |||||
| hsa-mir-200a | hsa-mir-200a-3p | ||||||||||
| hsa-mir-100 | hsa-mir-100-5p | mir-10 | hsa-mir-100 hsa-mir-10526 hsa-let-7a-2 |
chr11: 122152229-122152308 [-] chr11: 122152103-122152156 [-] chr11: 122146522-122146593 [-] |
|||||||
| hsa-let-7d | hsa-let-7d-5p | hsa-let-7a-1 hsa-let-7f-1 hsa-let-7d |
chr9: 94175957-94176036 [+] chr9: 94176347-94176433 [+] chr9: 94178834-94178920 [+] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-15a-5p | mir-15 | hsa-mir-15a hsa-mir-16-1 |
chr13: 50049119-50049201 [-] chr13: 50048973-50049061 [-] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-20a-5p | mir-17 | hsa-mir-17 hsa-mir-18a hsa-mir-19a hsa-mir-20a hsa-mir-19b-1 hsa-mir-92a-1 |
chr13: 91350605-91350688 [+] chr13: 91350751-91350821 [+] chr13: 91350891-91350972 [+] chr13: 91351065-91351135 [+] chr13: 91351192-91351278 [+] chr13: 91351314-91351391 [+] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-27a | mir-27 | hsa-mir-23a hsa-mir-27a hsa-mir-24-2 |
chr19: 13836587-13836659 [-] chr19: 13836440-13836517 [-] chr19: 13836287-13836359 [-] |
||||||||
| hsa-mir-130a | hsa-mir-130a-3p | mir-130 | hsa-mir-130a | chr11: 57641198-57641286 [+] | |||||||
| hsa-mir-21-3p | mir-21 | hsa-mir-21 | chr17: 59841266-59841337 [+] | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-15a | hsa-mir-15a-5p | mir-15 | hsa-mir-15a hsa-mir-16-1 |
chr13: 50049119-50049201 [-] chr13: 50048973-50049061 [-] |
|||||||
| hsa-mir-454-3p | mir-454 | hsa-mir-454 | chr17: 59137758-59137872 [-] | ||||||||
| hsa-mir-378a-3p | mir-378 | hsa-mir-378a | chr5: 149732825-149732890 [+] | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





