Implications
Animal production sector is highly criticized due to its important environmental footprint. To become more sustainable, the use of feed additives could be a promising solution. Here, we investigate the environmental impact of manufacturing and using a Citrus extract-based additive in animal production, using life cycle assessment. Our results showed that the majority of the environmental impacts of Citrus extract-based additive manufacture came from the production of its raw materials processing and transporting to the factory. Moreover, the use of this citrus extract-based additive resulted in environmental gain in pigletand broiler production, compared to the standard production.
Highlights
Livestock environmental footprint is a big challenge which need to be improved
Life cycle assessment of a citrus extract feed additive has been assessed
The primary factor responsible for environmental impact is the production of the citrus extract feed additive’s ingredients.
The use of the additive resulted in improving 5% environmental impacts on the measured indicators, in swine and broiler production
Additives utilization is a good solution to reduce livestock environmental footprint
Introduction
According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the global population growth, urbanization, and income rise will be the key determinants of the continuous rise of livestock production in the coming decades (Robinson, 2011). Predictably, to meet the demand of about 9 billion people in 2050, there is a need for 470 million tons of meat and 1.043 million tons of milk which are twice the amount recorded in 2000. Hence, the global livestock heads are projected to exceed 100 billion with its double-feed demand compared to 2000. The shift from cattle towards monogastric species including broiler and swine is predicted to continue (Yitbarek, 2019). However, contrary to this trend, natural resources and the labor force serving animal production are not expected to expand as much due to several issues including climate change, industrialization, and demographic transition (Steinfeld et al., 2006a).
Nowadays animal production sector is the biggest user of freshwater and agricultural land which account for approximately 70 percent of water use and 30 percent ice-free surface land worldwide. Besides, this sector is responsible for 18 percent of the total greenhouse gas generated by human activities (Steinfeld et al., 2006). Among piglet and broiler supply chains, feed-producing activities share a major emission, approximately 70 percent (MacLeod et al., 2012). Although the livestock sector itself is obviously defined to bring both positive and negative impacts on the natural and social aspects (The World Bank, 2009), within its’ predicted rapid growth, livestock production still causes indeed many published concerns about environmental impacts.
Together, the situation poses a huge challenge to the livestock stakeholders to work towards the effective production systems and sustainable development strategies. Among implemented solutions, using feed additives to improve zootechnical performances could indirectly result in optimizing in-put resources as well as mitigating pollution. This approach has been proven by many studies worldwide on different species so that is considered one of the promising applications for the long term (Lewis et al., 2015). Potentially, the benefits could be multiplied in the case of natural feed additives which are exploited from plant origin or food processing byproducts thanks to reducing waste and adding value to the agro-food production chain. Citrus extract-feed additive (CEFA) is one good example. Several studies worldwide have been carried out on this food byproduct, used as a dietary additive, which demonstrated its’ benefits on zootechnical performances in broiler (Juin et al., 2004; Abbasi et al., 2015; Ebrahimi et al., 2013) and swine (Cisse et al., 2020; Cui et al., 2020; Lepont et al., 2014). However, to our knowledge, really few studies have been done to highlight the double outcome linking between its’ positive effects on animal performances and environmental impacts.
This study was conducted to assess the environmental footprint of a commercial CEFA (Nor-Spice AB®, Nor-Feed SAS) which is characterized and standardized with its’ active compounds and has been proven for the efficiency in improving broiler and swine zootechnical performances. To do that, the lifecycle assessment of the Citrus extract feed additive has been carried out, according to ISO 14,040 and 14,044 standards.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted using the Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodology as described in ISO 14,040 and ISO 14,044 standards. LCA is a method to assess the environmental impacts of a product or a service by quantifying the resources used and the emissions to the environment at several stages of its life cycle. The method combines several impact categories, allowing the identification of potential pollution transfer between impact categories. LCA comprises four phases: Goal and scope definition, Inventory analysis, Impact assessment and Interpretation.
Goal and Scope
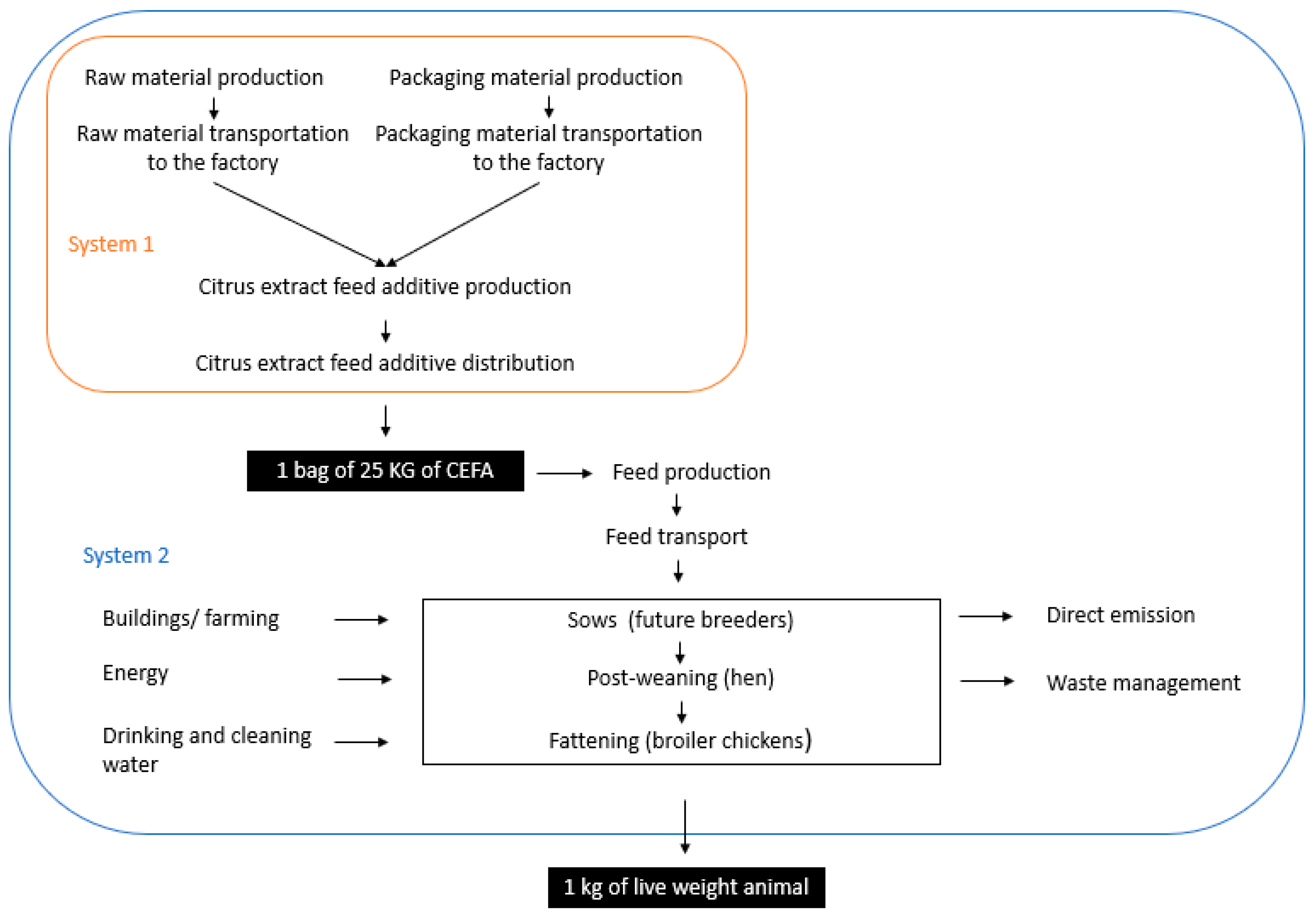
The objective of the study is to assess the environmental impact of the production and use of the CEFA. Two systems were defined, as described in Error! Reference source not found.. System 1 represents the production of CEFA. It includes the production of ingredients, their transportation to the plant where they are mixed to obtain the feed additive. System 1 also includes packaging and distribution to the end-customer. To better assess the impact of CEFA, the use phase in farms was also studied and compared to the production of meat without this additive. Two types of livestock were tested: broiler and swine. System 2 includes the production of feeds and all farming operations conducting to the production of meat at farm gate.
Two functional units were defined (one for each system). The first functional unit is “produce and distribute one bag of 25kg of CEFA”. For this functional unit, two distribution scenarios were studied: a distribution scenario in France and a distribution scenario in Thailand. The second functional unit is “produce 1kg of animal (live weight) fed with (vs. without) CEFA” in France and Thailand.
Figure 1.
overview of the system boundary and functional units.
Figure 1.
overview of the system boundary and functional units.
overview of the system boundary and functional units
Inventory Analysis
Generic data and specific data were combined to obtain inventories as described in
Table 1.
For system 1, specific data from the company were used to describe type and quantities of ingredients, quantities of energy and type of packaging used for the production of the additive (
Table 2). Background data regarding the production of ingredients and packaging, the transportation vehicles and infrastructures and the production and delivery of the energy used were obtained from Agribalyse v3.0.1 (2020) and Ecoinvent v3.6 (2020). Concerning lemon extract, lemons were produced in Spain. By lack of specific data to model the lemon extraction process, data for tomato paste (AGRYBALYSE V3.0) were adapted with a specific transformation yield of 6%. For orange peels, Spanish oranges (Ecoinvent) were used instead of Moroccan Oranges (no data available) and transformation processes including peeling and drying, were neglected. A ratio juice to peel of 40% was considered to set allocations as suggested within the AGRIBALYSE database.
Production at Nor-Feed plant in France was modelled using specific data from 2019 (
Table 3), considering a total production of 1 025 000 kg (CEFA included).
Packaging of finished product was modelled using specific data for 1 bag of 25 kg of CEFA (
Table 4).
The transportation of packaging to Nor-Feed plant considered was 1450 km. Transport distances of CEFA’s ingredients and final product distribution were estimated using Searates (
https://www.searates.com/fr/) and data used for all transports represents transportation by lorry, EURO5, 16-32 tons (Ecoinvent 3.8).
On the subject of system 2, AGRIBALYSE, a reference database of environmental impact indicators for agricultural products produced in France were used as the reference for the comparison and adapted to represent performances obtained with the used of the additive, using the MEANS InOut software which implements recommended methodologies defined for the AGRIBALYSE program (Koch & Salou, 2020).
Zootechnical performances of animals supplemented CEFA were obtained from meta-analysis of trial data conducted at different life stages of animal breeding (Clech et al, 2014). Concerning broiler production, the meta-analysis was composed of 9 trials performed in commercial or experimental farm in European countries, Canada, Taiwan and India. Animals were fed ad libitum with commercial feed containing 250 g/T of CEFA during all the production period. The AGRIBALYSE inventory for conventionally national average of broiler production was used as the reference. Zootechnical performance changes resulting from the use of the additive were implemented at fattening stage for one parameter (
Table 5). Weight of broilers was adapted to reach trial data on average daily gain (ADG) and feed conversion ratio (FCR).
In case of piglet production, the meta-analysis was composed of 10 trials performed in Denmark, The United Kingdom, Canada and Switzerland. Animals were fed ad libitum with commercial feed containing 250 g/T during post-weaning period. The AGRIBALYSE inventory for conventional, national average of piglet production was used as the reference. Zootechnical performance changes resulting from the supplementation of CEFA in feed were implemented at post-weaning stage and pig fattening stage for two parameters (
Table 6). Weight of fattened pig was adapted using trial data on ADG, and number of days at post-weaning and fattening stage was adapted to reach trial data on ADG and FCR.
Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA)
The impact assessment was performed using the Environmental Footprint method (version 2.0) (European Commission and Joint Research Centre. Institute for Environment and Sustainability, 2010), as recommended by European commission for environmental labelling. 3 indicators over the 16 were selected for being the most representative of the main contributors to the environmental impact of the two studied functions: Climate change, Land occupation and water consumption. The 3 selected indicators are described in
Table 7.
Results
Environmental Impacts within Functional Unit 1: Producing and Distributing One Bag of 25kg of CEFA
Effect on climate change, land occupation, and water consumption
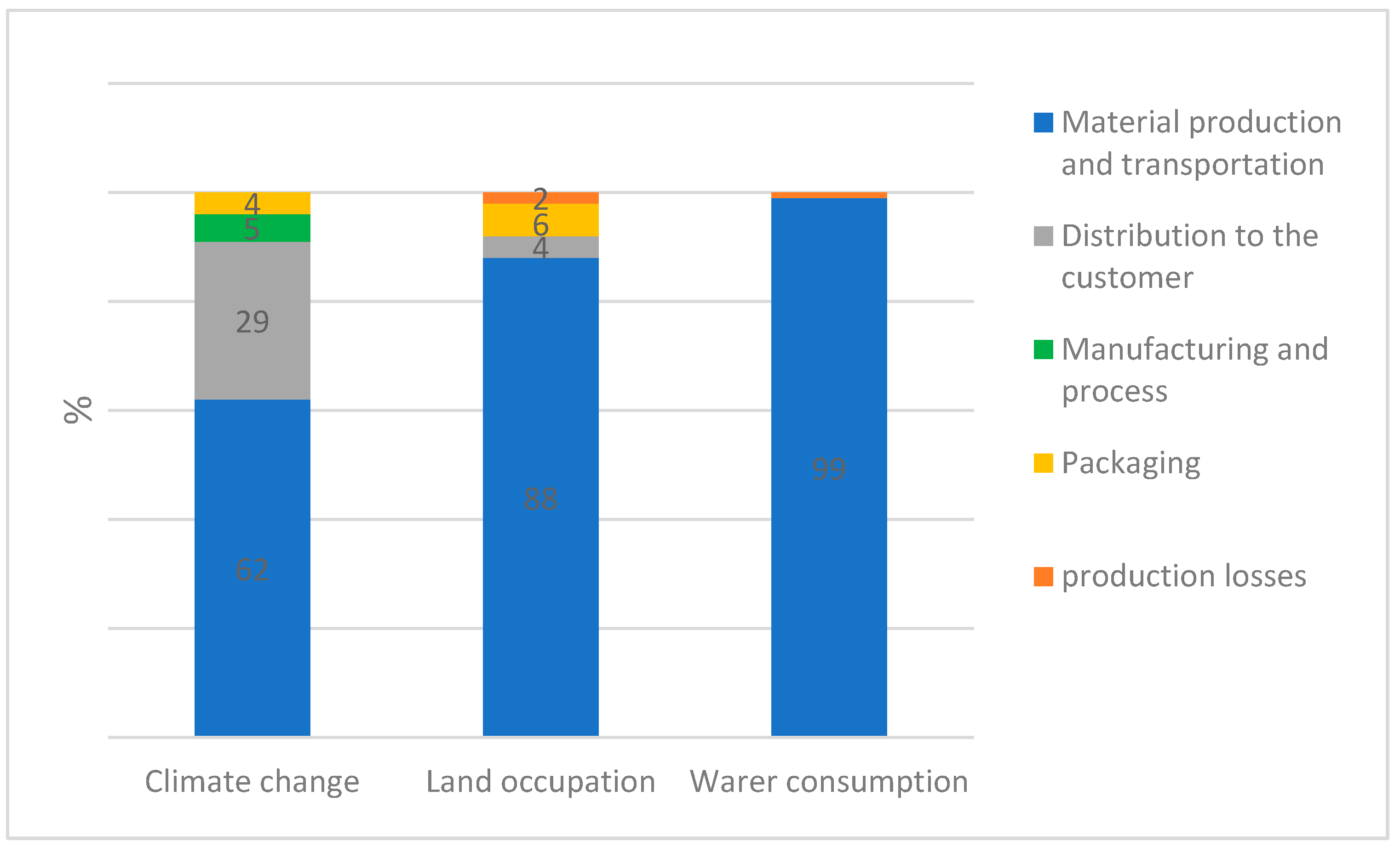
In terms of climate change, LCA analysis showed that the entire processing and distribution of 1 bag of 25kg of CEFA generates 13.1 kg CO2 eq (
Figure 2), in which, up to 8.12 kg CO2 eq is emitted during the stage of ingredients production and transportation to Nor-feed factory. Besides, distributing the product to domestic and international customers results in the emission of 3,78 kg CO2 eq, while manufacturing and packaging process to transform the raw materials to final product emits 1,18 kg CO2 eq. A similar pattern is observed in the case of land occupation (
Figure 2). The land surface used for the production of 1 bag of 25kg of CEFA along its life-cycle is estimated at 5,3 m
2 year-round which is mainly caused by the land use for Citrus agriculture (4.7 m
2). The remaining 0.6 m
2 results from the packaging (6%), the distribution to customers (4%) and production losses (2%). When it comes to water consumption, among total 66 L of water consumed for producing 1 bag of 25 kg of this CEFA, almost all of them was spent for the production and transportation of CEFA ingredients to the additive processor (
Figure 2).
Environmental impact on producing and distributing 1 bag of 25 kg of CE.
Focus on Environmental Impact of CEFA Production and Transportation to the Factory
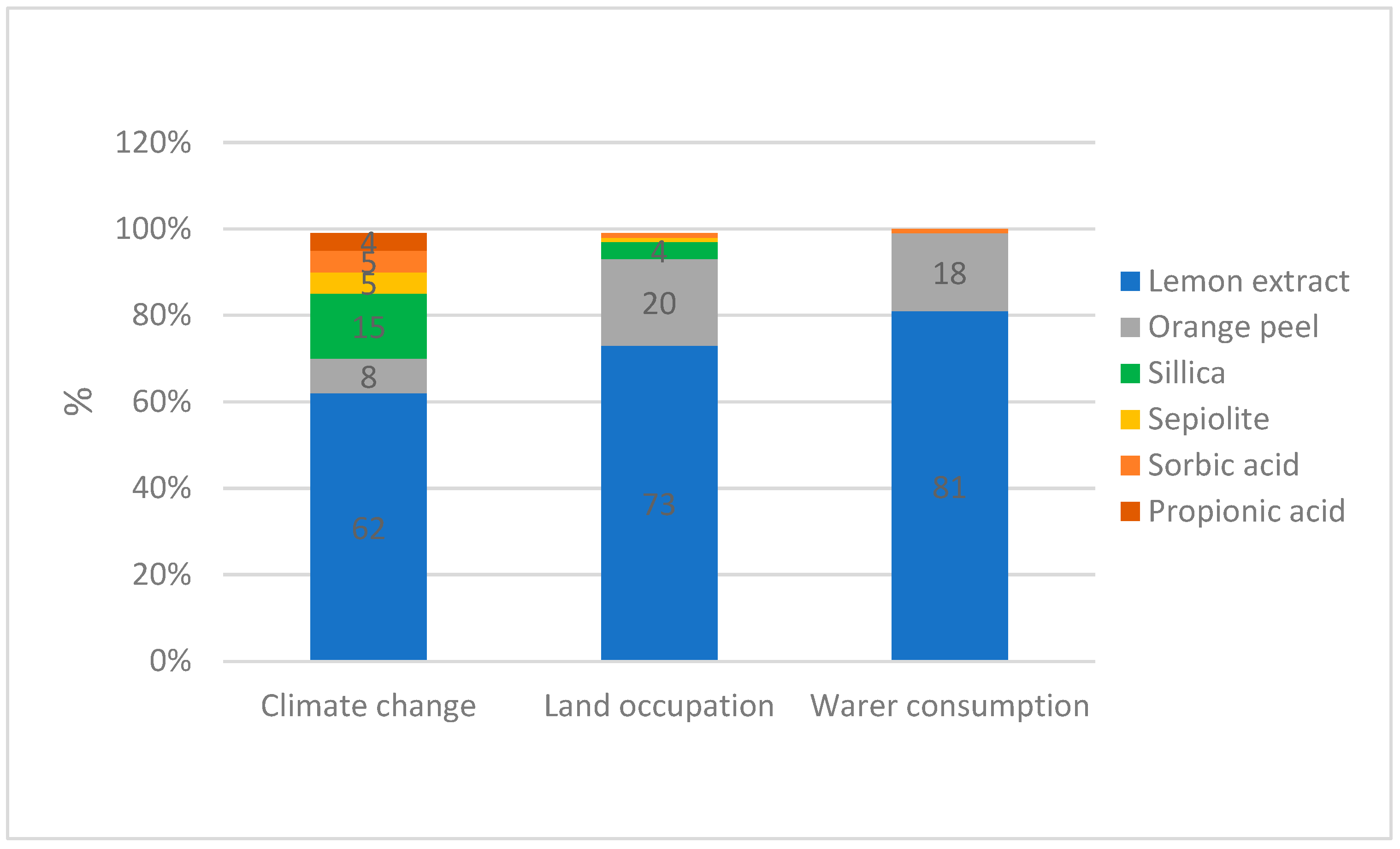
CEFA ingredients production and transportation to the factory represent 83% of the environmental impact in average, on the 3 selected indicators. As lemon extract occupies an important proportion in the composition of CEFA, it brought a considerable impact compared to others remaining raw materials (
Figure 3).
CEFA raw materials environmental impact on climate change, land occupation and water consumption.
Indeed, lemon extract represents more than 50% of CEFA formulation and generated 81% impact on water use, 73% on land occupation and 62% on climate change of the total contribution of all ingredients. The percentage of lemon extract in CEFA formulation is therefore lower than the average impact contribution in the 3 selected indicators. Agricultural activities like fertilization and irrigation are the most contributors while the transformation process of citrus fruit was considered as a minor contributor.
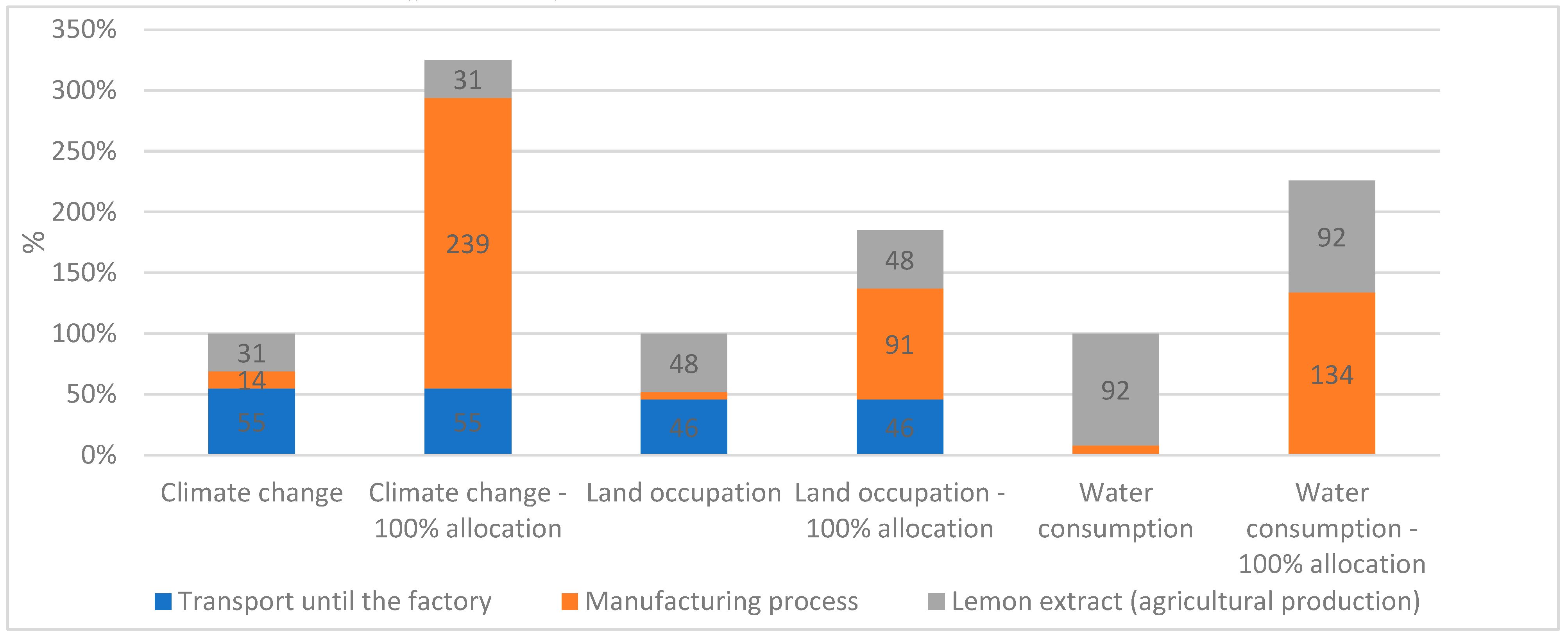
It is important to take into account that lemon extract is a co-product from juice industries. By lack of data, a proxy has been used to represent the transformation process for obtaining lemon extract from fruits. Furthermore, only 6% of this transformation process has been allocated to the lemon extract, the main ingredient of CEFA. This allocation was based on mass, other co-products considered were lemon juice and essential oil. To test the sensitivity of this parameter, we also analyzed the environment impact of CEFA when 100% of lemon extract process were allocated to the CEFA.
Results showed that the impact of 100% of lemon extract and citrus peel CEFA on climate change is multiplied by 3 while the impact on water consumption is multiplied by 2 when allocating 100% of the lemon extract transformation process to the CEFA (
Figure 4). By contrast, less changes have been observed on land occupation (
Figure 4).
CE environmental impact when 100% of lemon extract and citrus peel transformation process is allocated to the CE.
Focus on Environmental Impact of CEFA Distribution to the Final Customer
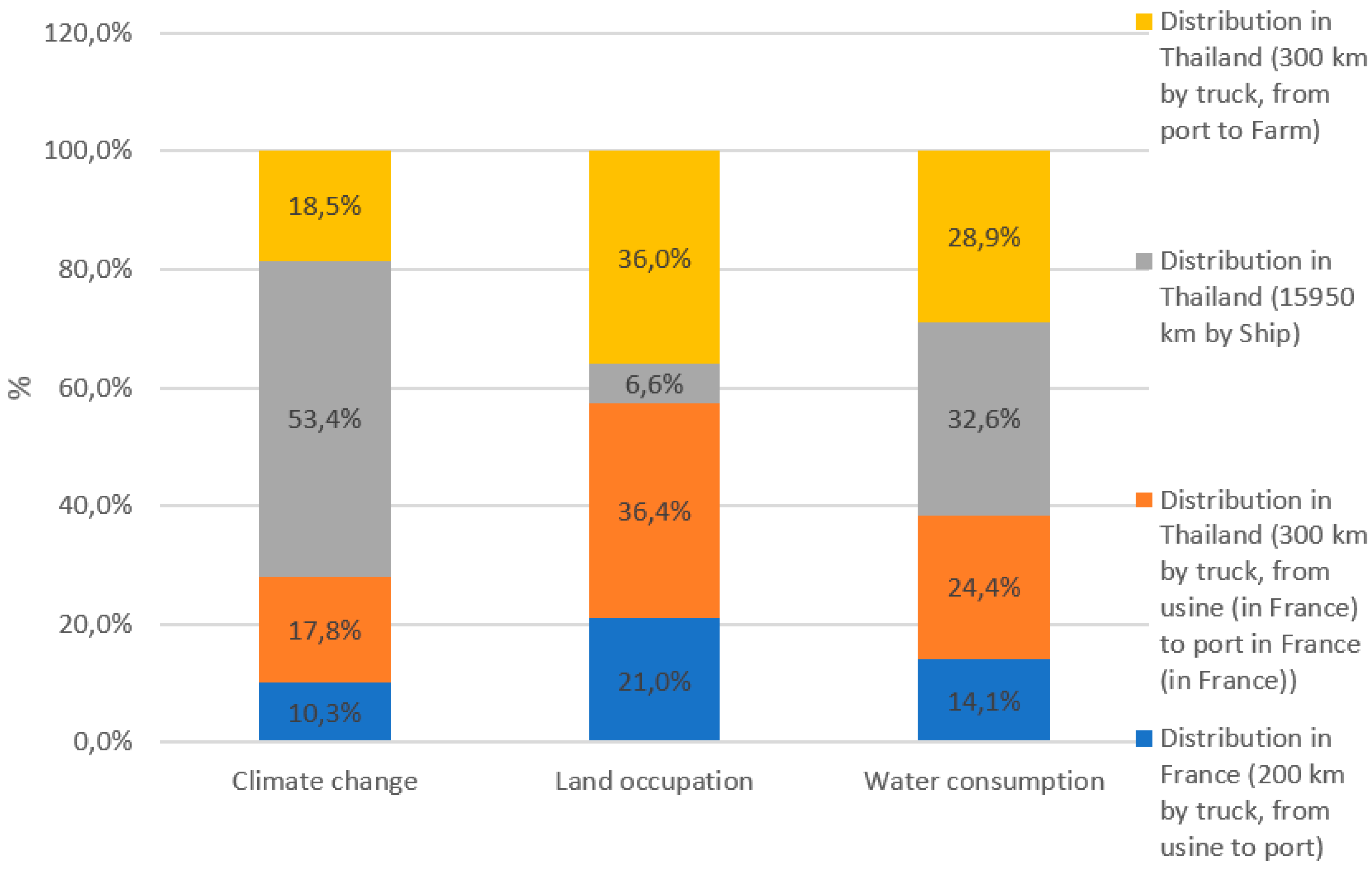
According to the results presented in the
Figure 2 CEFA’s distribution to the final customer account for 11% of the 3 environmental impacts in average, on the 3 selected indicators. The main environmental impact is observed on climate change, for which the distribution to the final customer account for 29%.
It’s important to notice that the proportion of CEFA distributed in France (46,5%) and Thailand (53,5%) is equivalent. The exportation of CEFA to Thailand generated the major effect, up to 85% of overall (
Figure 5), compared to the distribution in France (15%). In terms of distance, CEFA transportation by truck in France and Thailand represents only a small distance (600 km) compared to transportation by ship (15950 km). However, its’ effect on environmental indicators is not ignorable. Indeed, CEFA transportation by truck in France and Thailand account for 93.4% of the total environmental impact of CEFA distribution to the final customer on land occupation. It also brought a big impact on the total environmental impact of CEFA distribution to the final customer, regarding water consumption (67,4%) and climate change (46,6%).
CEFA Distribution environmental impact on climate change, land occupation and water consumption
Environmental Impacts within Functional Unit 2: Manufacture, Distribution and Utilization of 1 Bag of 25kg of CEFA in Farm
The environmental benefits resulted from the use of the CEFA in piglet and broiler productions compared to the standard condition are shown on
Figure 6 and
Figure 7.
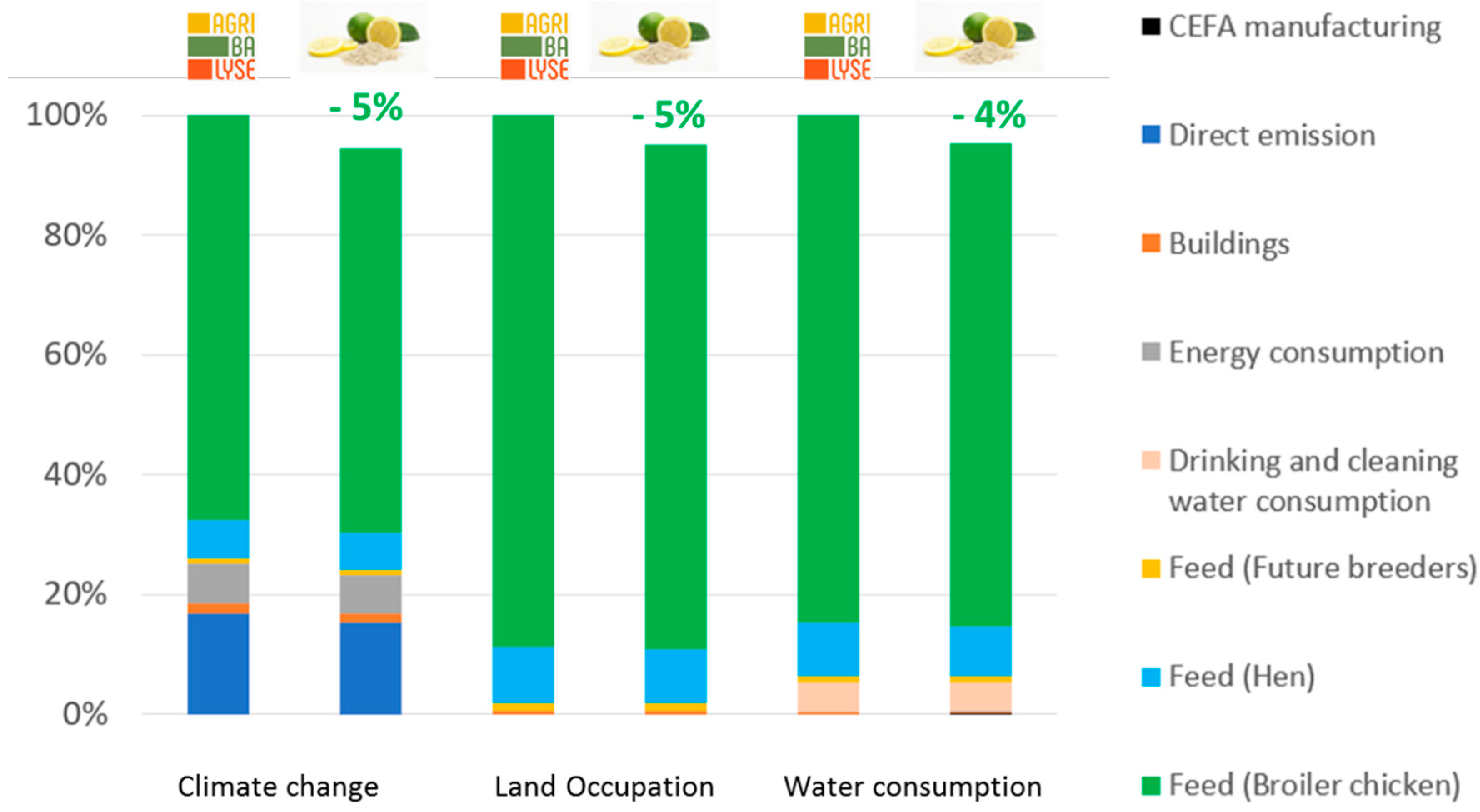
Environmental gain thanks to the use of CEFA in swine production
Figure 7.
Environmental gain thanks to the use of CEFA in broiler production.
Figure 7.
Environmental gain thanks to the use of CEFA in broiler production.
Environmental gain thanks to the use of CEFA in broiler production
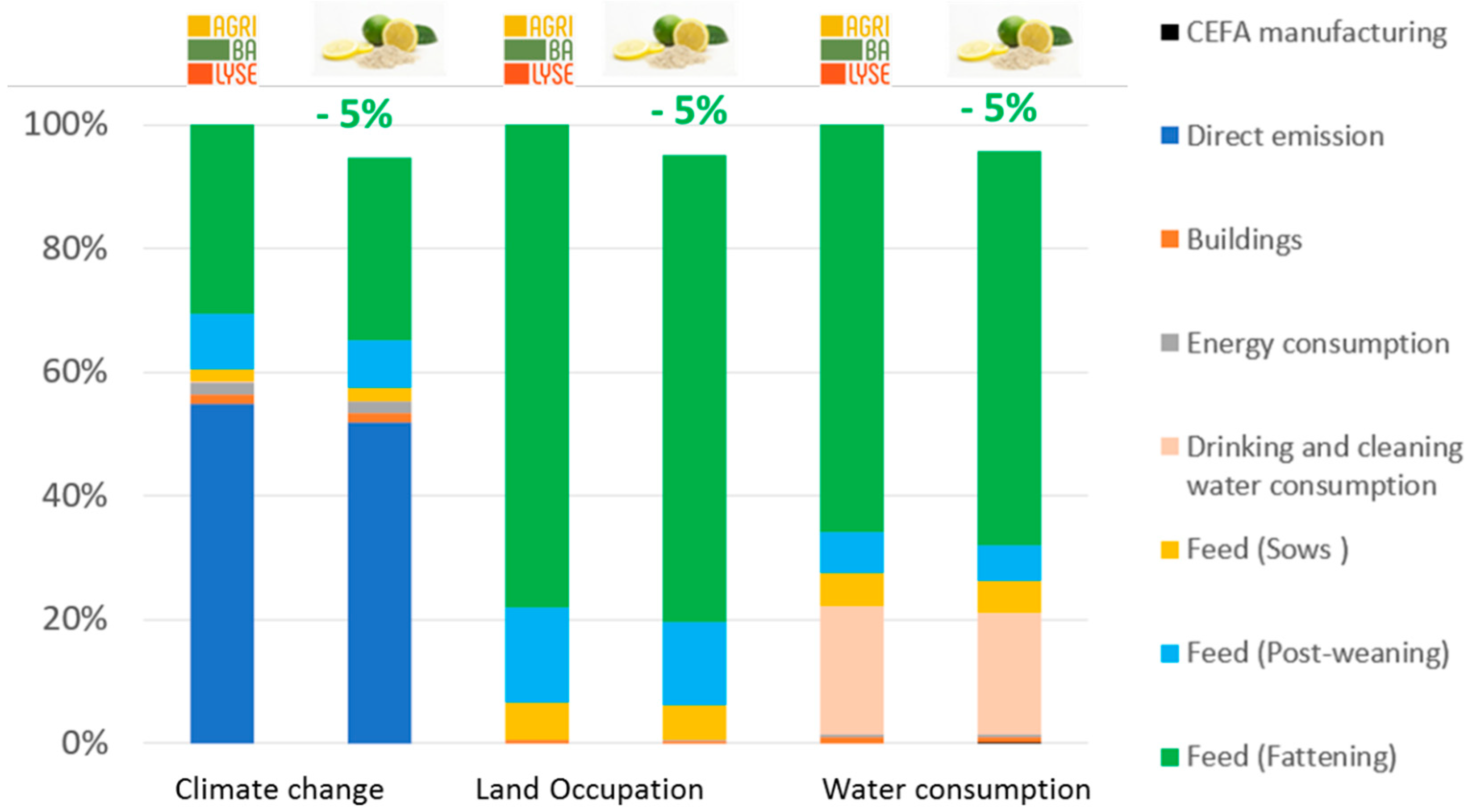
The environmental gains in both production systems fed with CEFA resulted mainly from the reduction in the quantity of feed consumed to produce the same amount of animal live weight.
With CEFA supplement, the zootechnical performances were improved which allows to reduce the husbandry duration compared to standard condition. As a result, the emissions related to husbandry including manure emission and enteric fermentation were also reduced, especially for swine production.
Effect on climate change, land occupation, and water consumption at bag scale
Citrus extract-based additive allowed to reduce the climate change of approximatively 5% in both broiler and swine. More precisely, each bag of 25 kg of Citrus extract feed additive helped reduce 6 tons of CO2 emitted from broiler production and 5 tons in case of piglet production, compared to the same situation without CEFA. In terms of land occupation, every 25 kg of Citrus extract-based additive allowed to save 7000 m2 of land used for both studied production systems. The use of 25 kg of Citrus extract-based additive had also benefits on water consumption, allowing to save up to 201 m3 and 82 m3 of water consumption in boiler and fattening pigs productions respectively which corresponded to a gain of 4% in swine production and 5% in broiler production.
Discussion
As mentioned, animal production is one of the most influential sectors on the environment. For more sustainability, it’s crucial to evaluate and reduce both the emissions of greenhouse gases and the resources needed for their production. To do that, the life cycle assessment is a good tool to evaluate the environmental footprint, with the aim of identifying areas for improvement to reduce the environmental impact.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the environmental footprint of a Citrus extract-based additive used as feed additive in animal nutrition. The main results showed that the environmental impact of producing and manufacturing 1 bag of 25 kg generates 13.1 kg CO2 eq and requires 66L of water and 5.3 m2 year-round land surface. This is mainly due to the fact that its principal raw material (lemon extract) is a co-product from juice industries. Thus, only 6% of the transformation process of Citrus fruit has been allocated to the lemon extract. These 6 % has been estimated according to the flow chart of the lemon extract. However, this estimate may constitute a bias on the environmental footprint of CEFA. Indeed, according to the percentage of transformation process which is allocated to CEFA raw material, the environmental footprint of producing and distributing CEFA may vary a lot. As example, our results showed that the environmental impact of producing and distributing 1 bag of 25 kg of CEFA is multiplied by 2 or 3 depending on the indicators, when allocating 100% of lemon extract process to the CEFA. Moreover, data for tomato process has been used as proxy to model the extraction process of lemon extract. The lack of specific reference in lemon extract regarding energy consumption, and co-products use might also induce uncertainties on final results.
Regarding transportation, our study revealed that environmental impacts generated by truck transport was significant even though it covered only short distance of the whole distributing chain. This could be a considerable stage where the environmental impact of CEFA producing and distributing could be improved. Environmentally responsible alternatives to truck transportation could be used.
Concerning the use of CEFA in broiler or swine farms, generic data used a reference (AGRIBALYSE) showed that the main factors responsible for environmental impact are feed consumption and direct emission from farming. Our results show that using CEFA in broiler or swine farms, provide benefits on the three environmental threats identified for animal production (climate change, land occupation, and water consumption), compare to a standard farming. This is mainly due to the reduction of feed consumption thanks to CEFA supplementation. Besides, in this study, we considered that there was no difference in effluent emissions per days between the CEFA supplementation situation and the standard situation (only the duration varies). However, it would be interesting to take investigate the influence of replacing a part of the food by the CEFA on the quantity and characteristics of effluent. Finally, no variation was considered in the mortality rate, however several studies show the influence of feed quality on this parameter (Gerber et al., 2013).
As shown in Fig 5 and fig 6, the environmental impact of producing and distributing CEFA is minimal compare to the environmental impact of piglet and broiler production system. This may be explained by the low inclusion rate of CEFA in feed (250 g/T) but also the low environmental footprint of producing and distributing CEFA to the final customer.
According to literature, many studies showed that additives used in animal nutrition such as CEFA, can help positively improve the environmental footprint of animal production sector, thanks to the benefits they confer on productivity. As example, Blonk evaluated the environmental footprint of using 14 feed additives including enzymes, vitamins, carotenoids, and eubiotics, on three species: broilers chickens, fattening pigs, and dairy cows, via the life cycle assessment (Blonk et al, 2021). Their results showed that the general use of feed additive can lead up to 10 % improvement of environmental footprint, due to feed additive effect on productivity and greenhouse gaze’s emissions (Blonk et al, 2021).
Conclusion
Environmental impact of producing Citrus extract-based additive is mainly linked to raw ingredient production and transportation to the factory, representing 70% out of 3 selected indicators. The manufacture and distribution of one bag of 25 kg of CEFA potentially emits 13.1 kg CO2 eq while using 5.3 m2 of land during 1 year-round and consuming 66L of water. In animal production, the use of 1 bag of 25kg of CEFA allows to reduce CO2 emission by 5 and 6 tons in swine and broiler respectively. On the other hand, it benefits 7000 m2 land surface in both broiler and swine production. In addition, water consumption was saved up to 82m3 and 201 m3 in swine and broiler production respectively. This results from the ameliorative effect of Citrus extract-based additive supplementation in swine and broiler production, allowing to increase the ADG by 10,9% and 4.3% and reduce the FCR by 7.1% and 2.4% in swine and broiler respectively. Other benefices such as the reduction of the mortality rate and the modification of effluents were not included in this study, suggesting a higher impact reduction.
Author Contributions
Hoa BUI: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft Sekhou CISSE: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft Mathilde CECCALDI: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - Original Draft Aurelie PERRIN: Conceptualization, Investigation, supervision Writing - Review & Editing Mohamed El Amine BENARBIA: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing - Review & Editing Pierre CHICOTEAU: Conceptualization, Supervision
Financial support statement
This research receives no specific grant for any funding agency, commercial, and not-for-profit section
Ethic approval
Data from meta-analysis used in this study provided from trials that have been carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations set out in the European Guidelines for accommodation and care of animals (Directive 86/609/CEE).
Declaration of interest
I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, the authors with a work within the research and development department of Nor-Feed SAS. Nor-Feed SAS commercializes a product called Nor-Spice AB which is the Citrus extract-based additive. All co-authors have seen and agree with the contents of the manuscript. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
References
- Robinson, T.P., Pozzi, F., 2011. Mapping supply and demand for animal-source foods to 2030. FAO, Rome, Italy. Animal Production and Health Working Paper. No. 2.
- Yitbarek, M., 2019. Livestock and Livestock products by 2050: review. International Journal of Animal Research, 4-30.
- Steinfeld, H., Gerber, P., Wassenaar, T., Castel, V., Rosales, M., de Haan, C., 2006a. Livestock’s long shadow. FAO, Rome, Italy, 3, 79-122.
- Steinfeld, H., Gerber, P., Wassenaar, T., Castel, V., Rosales, M., de Haan, C., 2006b. Livestock’s long shadow. FAO, Rome, Italy, 2, 23-74.
- MacLeod, M., Gerber, P., Mottet, A., 2012. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Pig and Chicken Supply Chains. AGA/FAO, Rome, Italy, 17-63.
- Minding the Stock: Bringing Public Policy to Bear on Livestock Sector Development. 2009. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, 1-77.
- Lewis, K. A., Tzilivakis, J., Green, A. & Warner, D. J., 2015. Potential of feed additives to improve the environmental impact of European livestock farming: a multi-issue analysis. International Journal of Agricultural Sustainability. 13, 55–68. [CrossRef]
- Juin, H., Elgaard, T. & Chicoteau, P., 2024. Effect of a citrus extract (NOR-SPICE AB) on broiler performances. Br. Poult. Sci. 44, 810–1. [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H., Seidavi, A., Liu, W. & Asadpour, L., 2015. Investigation on the effect of different levels of dried sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) pulp on performance, carcass characteristics and physiological and biochemical parameters in broiler chicken. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 22, 139–146. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A., Qotbi, A. A. A., Seidavi, A., Laudadio, V. & Tufarelli, V., 2013. Effect of different levels of dried sweet orange (<i>Citrus sinensis</i>) peel on broiler chickens growth performance Abbas. Arch. Anim. Breed. 56, 11–17. [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y., Tian, Z., Wang, G., Ma, X. & Chen, W., 2020. Citrus Extract Improves the Absorption and Utilization of Nitrogen and Gut Health of Piglets. Animals 10, 112. [CrossRef]
- Cisse, S. et al., 2020. Standardized Natural Citrus Extract dietary supplementation influences sows’ microbiota, welfare, and preweaning piglets’ performances in commercial rearing conditions. Transl. Anim. Sci. 4, txaa059. [CrossRef]
- Lepont, A., Budan, A. & Le, S. 2014. Mode of action and effect of a natural citrus extract on growth performances in piglets. Presented at FULDA symposium.
- Clech O., Budan, A. & Le, S., 2014. Synergistic effects of citrus extract on performance of young animals. Presented at BOKU symposium.
- Koch P. and Salou T., 2020. AGRIBALYSE®: Rapport Méthodologique- Volet Agriculture- Version 3.0 ; version initiale v1.0 ; 2014. Ed ADEME, Angers, France. 319 p.
- EUROPEAN COMMISSION. (2019). European Platform on Life Cycle Assessment. Environmental Footprint. Retrieved October 21, 2021, from https://eplca.jrc.ec.europa.eu/EnvironmentalFootprint.html.
- Blonk, H., Bosch, H., Braconi, N., Van Cauwenberghe, S., Kok, B. (2021). The applicability of LCA guidelines to model the effects of feed additives on the environmental footprint of animal production, Blonk Consultants and DSM Nutritional Products.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).