Submitted:
29 October 2023
Posted:
30 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Analysis
2.3. Kidney Type Prediction
2.3.1. Feature Selection
2.3.2. Model Selection & Hyperparameter Tuning
2.3.3. Model Training & Evaluation
2.4. PFAS Accumulation Model
2.4.1. Feature Selection
2.4.2. Model Selection & Hyperparameter Tuning
2.4.3. Model Training & Evaluation
2.5. Glomerular Total Surface Area vs Proximal Tubule Predictor
2.5.1. Feature Selection
2.5.2. Model Selection & Hyperparameter Tuning
2.5.3. Model Training & Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy
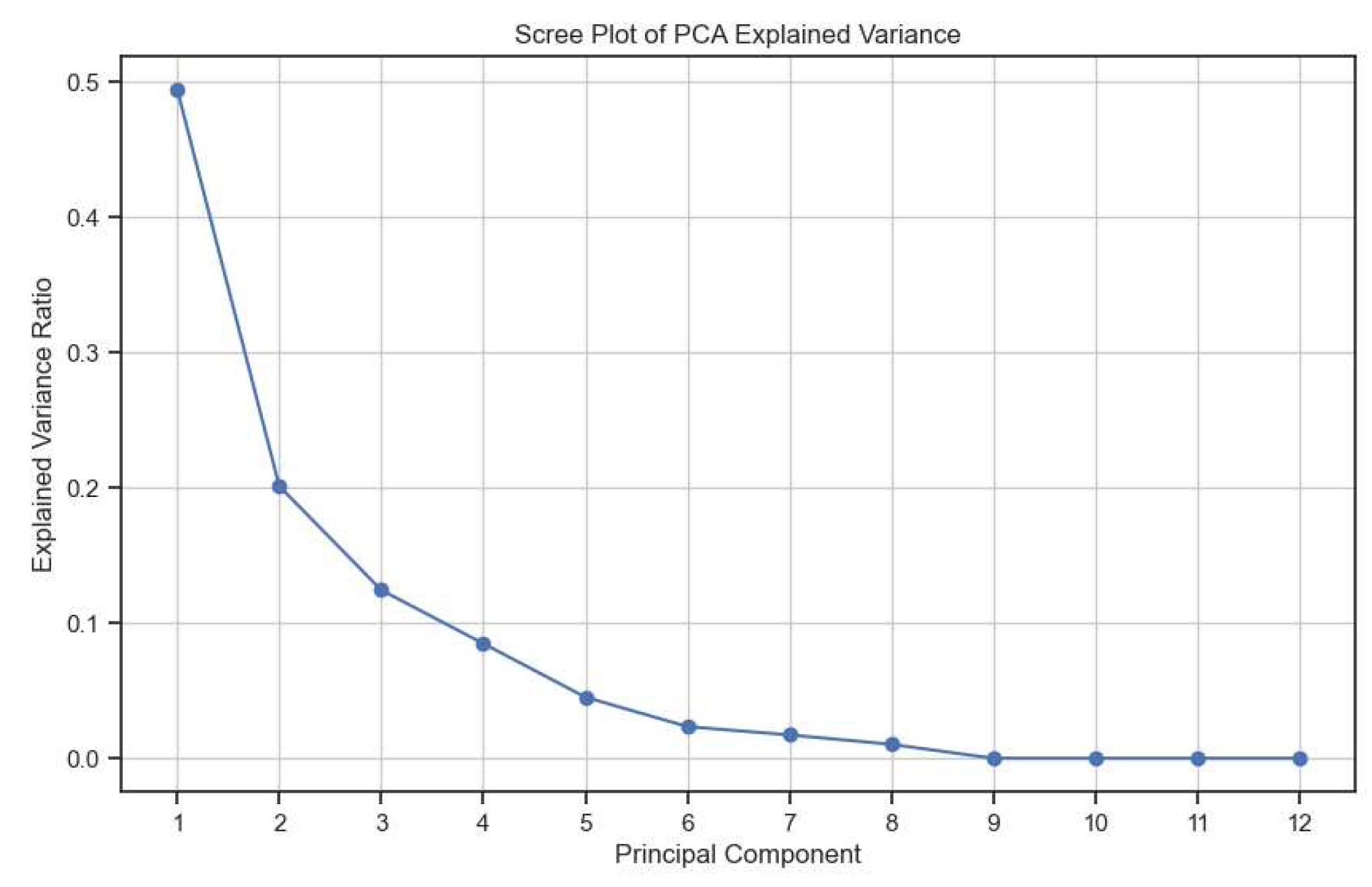
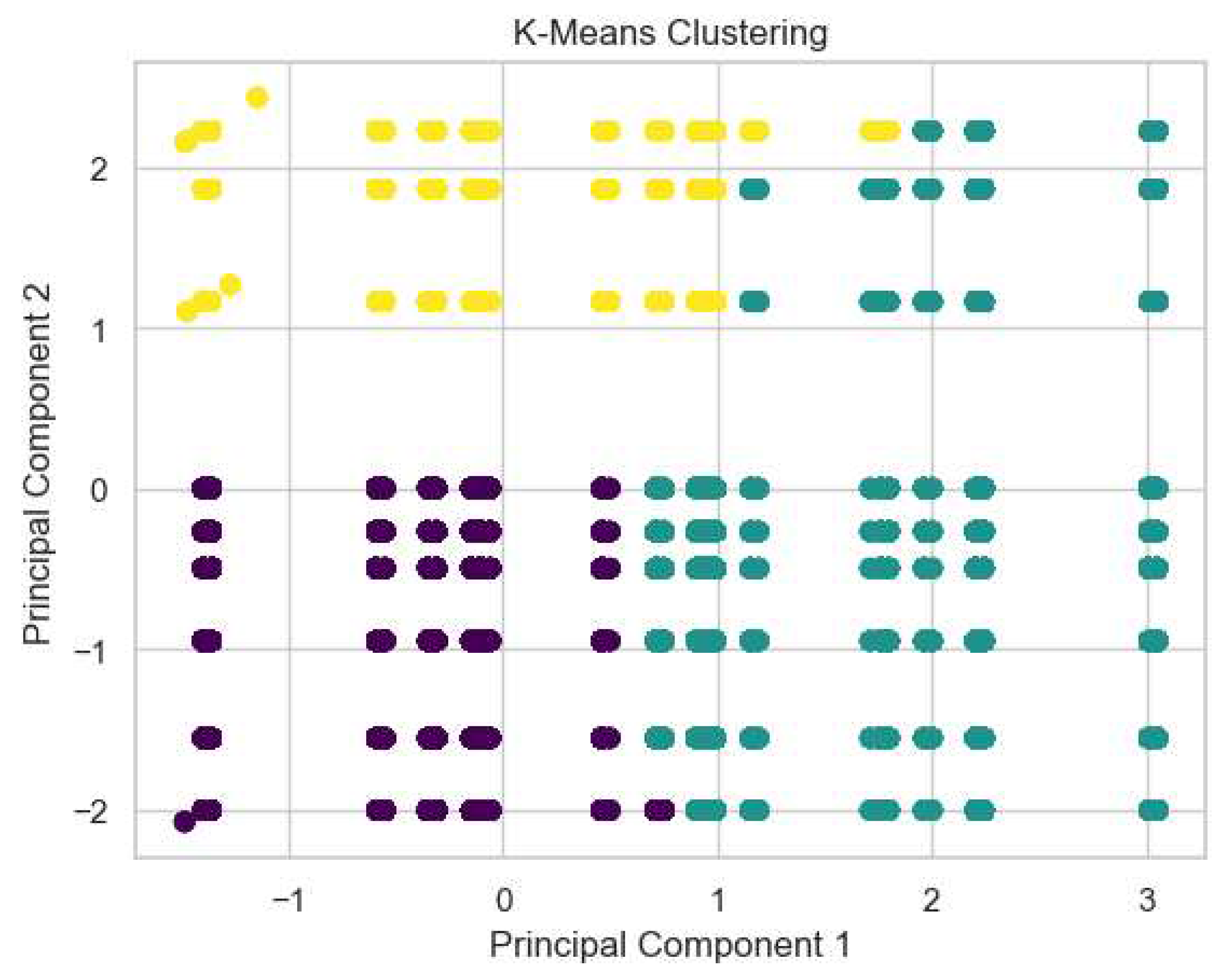
3.1.1. Kidney Type Prediction
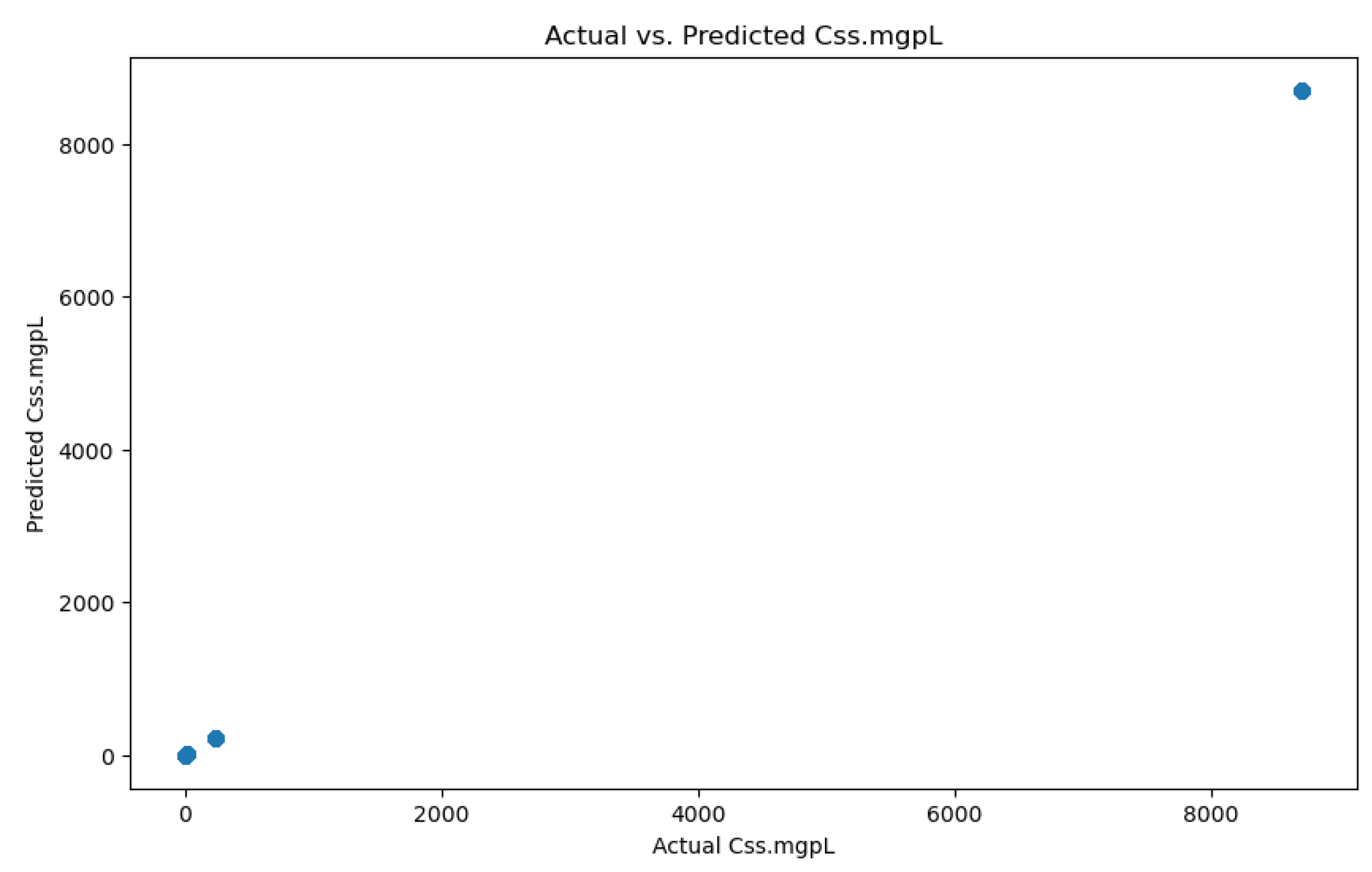
3.1.2. PFAS Accumulation Model
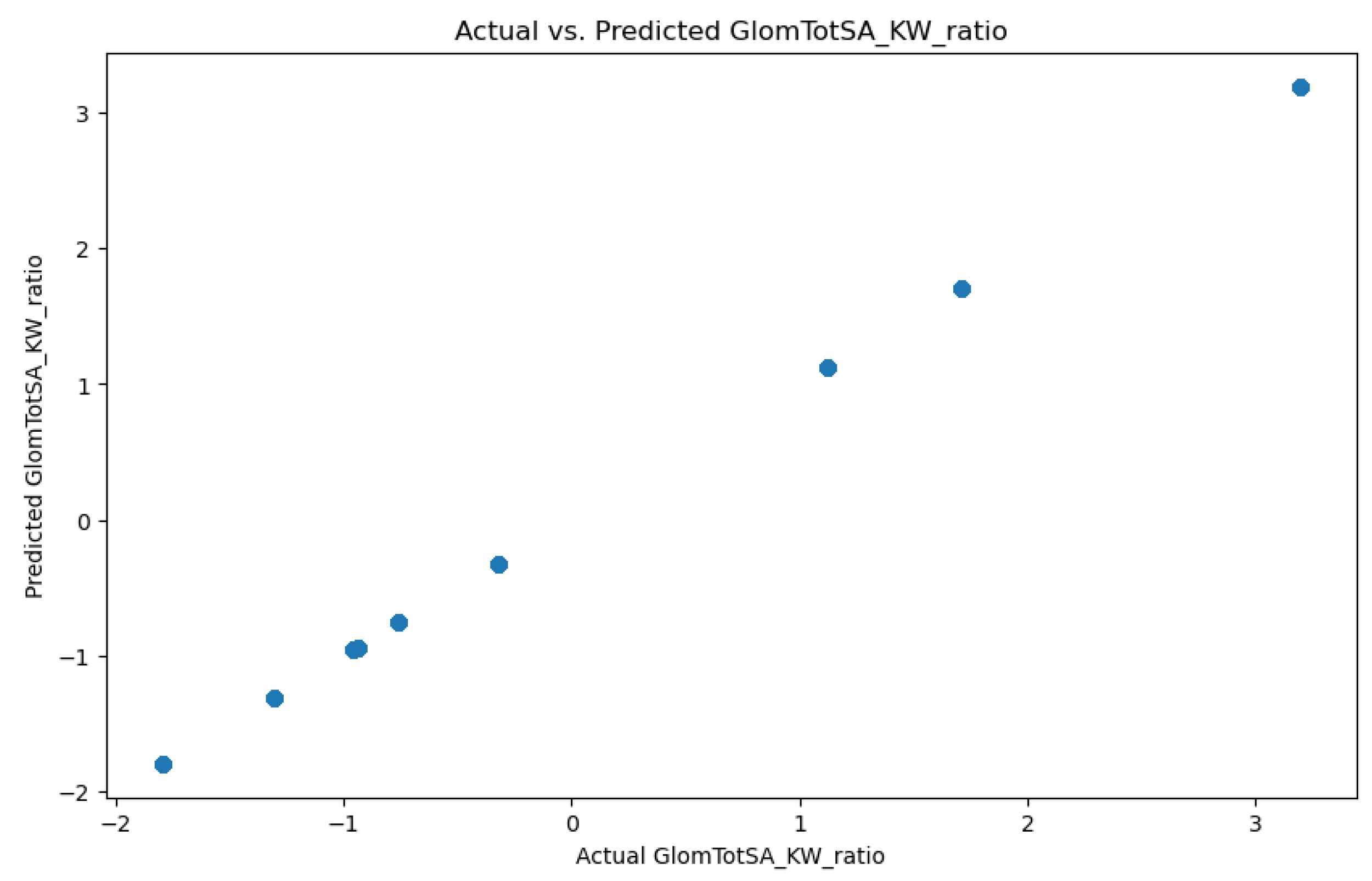
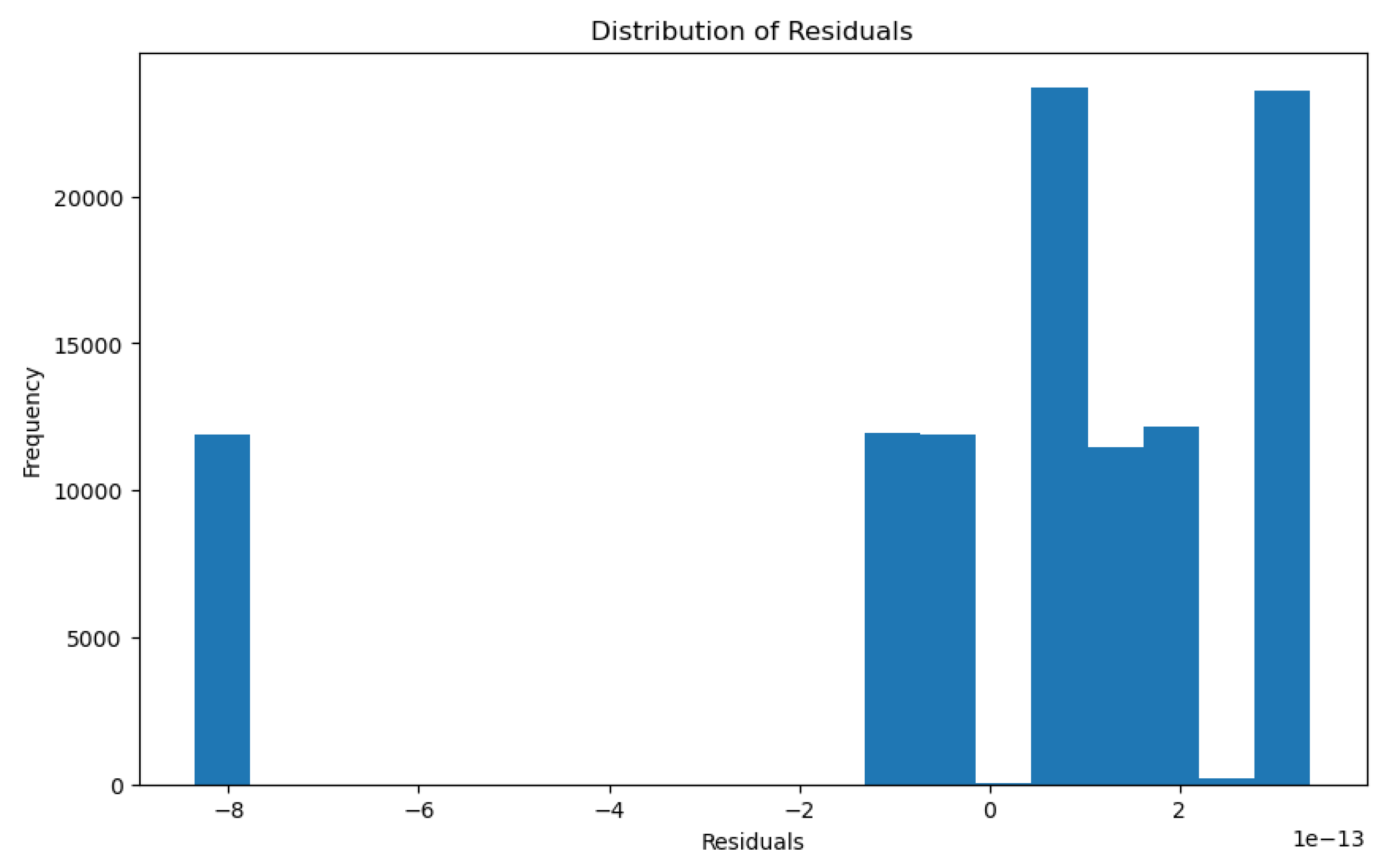
3.1.3. Glomerular Total Surface Area vs Proximal Tubule Predictor
3.2. Feature Importance
3.2.1. Kidney Type Prediction
3.2.2. PFAS Accumulation Model
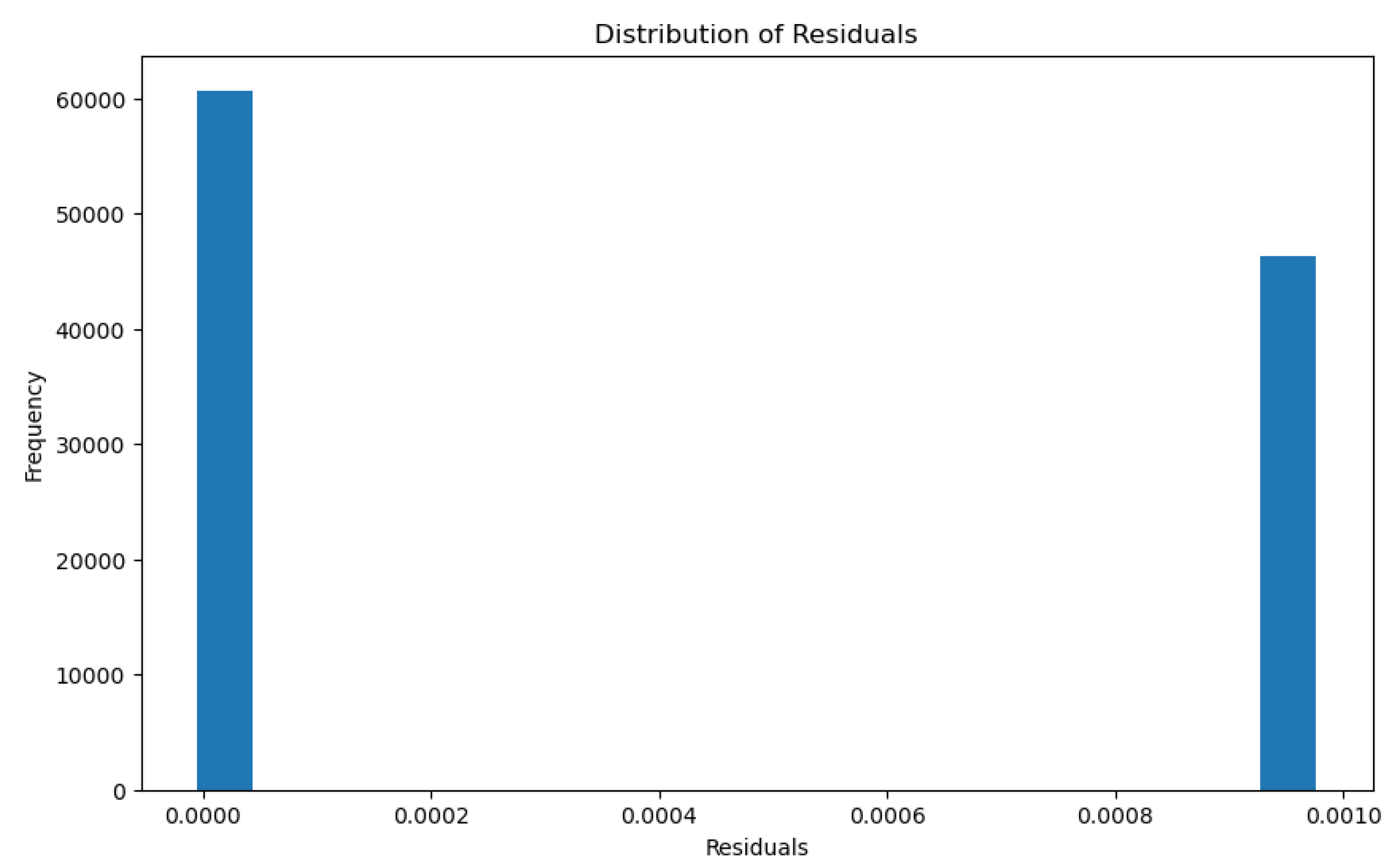
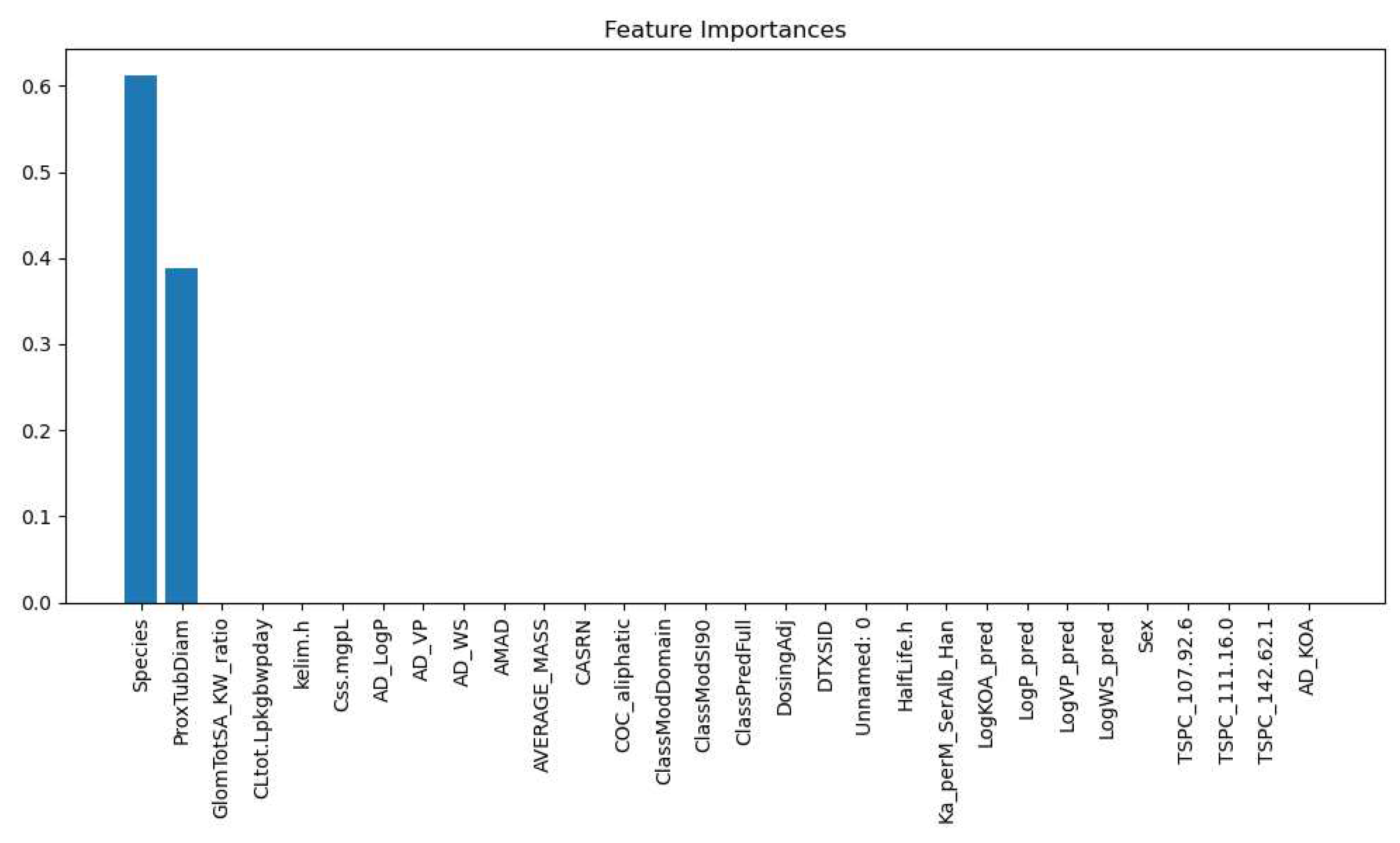
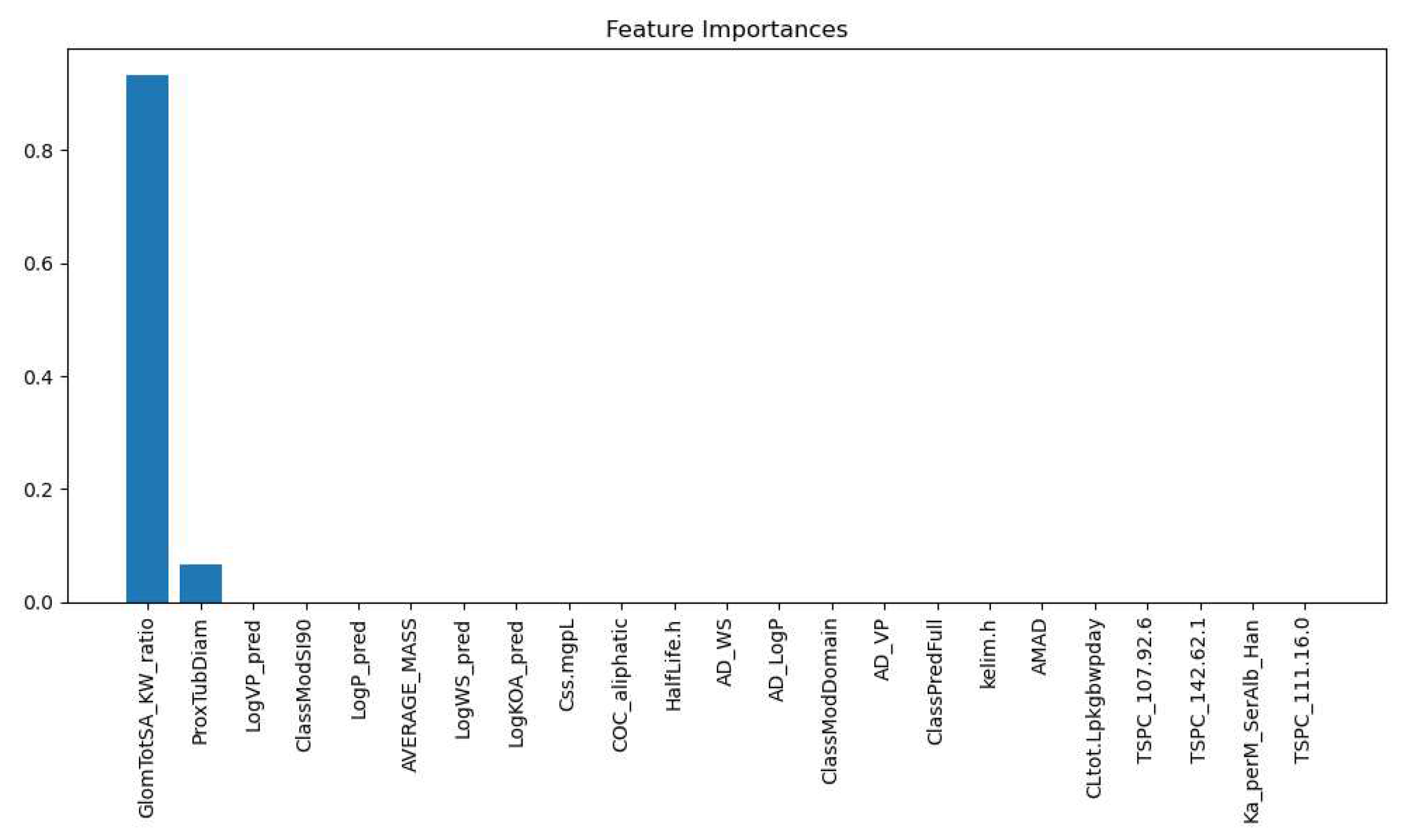
3.2.3. Glomerular Total Surface Area vs Proximal Tubule Predictor
4. Biological Significance
5. Conclusion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFAS | Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| RFR | Random Forest Regressor |
| XGBC | Extreme Gradient Boost Classifier |
| XGBR | Extreme Gradient Boost Regressor |
| GlomTotSA | Glomerular Total Surface Area |
| Proximal Tubule | ProxTubTotVol |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
References
- Glüge, J.; Scheringer, M.; Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Ng, C.A.; Trier, X.; Wang, Z. An overview of the uses of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 2020, 22, 2345–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewapriya, P.; Chadwick, L.; Gorji, S.G.; Schulze, B.; Valsecchi, S.; Samanipour, S.; Thomas, K.V.; Kaserzon, S.L. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in consumer products: Current knowledge and research gaps. Journal of Hazardous Materials Letters 2023, 4, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Fenton, S.E. Early life exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and latent health outcomes: A review including the placenta as a target tissue and possible driver of peri- and postnatal effects. Toxicology 2020, 443, 152565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renfrew, D.; Pearson, T.W. The Social Life of the “Forever Chemical”. Environment and Society 2021, 12, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthoff, M.; Müller, J.; Jürling, H.; Schlummer, M.; Fiedler, D. Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances in consumer products. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2015, 22, 14546–14559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bălan, S.A.; Mathrani, V.C.; Guo, D.F.; Algazi, A.M. Regulating PFAS as a Chemical Class under the California Safer Consumer Products Program. Environmental Health Perspectives 2021, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsan, M.N.; Riza, M.; Pervez, M.N.; Khyum, M.M.O.; Liang, Y.; Naddeo, V. Environmental and health impacts of PFAS: Sources, distribution and sustainable management in North Carolina (USA). Science of The Total Environment 2023, 878, 163123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat-Palau, J.; Vidal, M.; Rigol, A. Examining sorption of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in biochars and other carbon-rich materials. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, G.; Kankarla, V.; McLennon, E.; Pal, S.; Sihi, D.; Dari, B.; Diaz, D.; Nocco, M. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Integrated Crop–Livestock Systems: Environmental Exposure and Human Health Risks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021, 18, 12550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Pinney, S.M.; Hines, E.P.; Fenton, S.E.; Ferguson, K.K. Associations between longitudinal serum perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) levels and measures of thyroid hormone, kidney function, and body mass index in the Fernald Community Cohort. Environmental Pollution 2018, 242, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubicic, M.L.; Madsen, A.; Juul, A.; Almstrup, K.; Johannsen, T.H. The Application of Principal Component Analysis on Clinical and Biochemical Parameters Exemplified in Children With Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonato, M.; Corrà, F.; Bellio, M.; Guidolin, L.; Tallandini, L.; Irato, P.; Santovito, G. PFAS Environmental Pollution and Antioxidant Responses: An Overview of the Impact on Human Field. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17, 8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraley, K.M.; Fraley, H.N.; Arthur, D.; Walther, E.J. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances ( PFAS ): Anglers May Be Exposed to Harmful Chemicals in Their Catch. Fisheries 2020, 45, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderko, L.; Pennea, E. Exposures to per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS): Potential risks to reproductive and children’s health. Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care 2020, 50, 100760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.H.; Kinde, A. The Pathway to a Green New Deal: Synthesizing Transdisciplinary Literatures and Activist Frameworks to Achieve a Just Energy Transition. Environs: Environmental Law and Policy Journal 2020, 44, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.I.D.; Cardenas, A.; Hauser, R.; Gold, D.R.; Kleinman, K.P.; Hivert, M.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Webster, T.F.; Horton, E.S.; Oken, E. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and kidney function: Follow-up results from the Diabetes Prevention Program trial. Environment International 2021, 148, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PFALLER, W.; RITTINGER, M., QUANTITATIVE MORPHOLOGY OF THE RAT KIDNEY; Elsevier, 1980; pp. 17–22. [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Jang, E.C.; Kwon, S.C.; Min, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J. The association of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and kidney function in Korean adolescents using data from Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) cycle 4 (2018–2020): a cross-sectional study. Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 2023, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanifer, J.W.; Stapleton, H.M.; Souma, T.; Wittmer, A.; Zhao, X.; Boulware, L.E. Perfluorinated Chemicals as Emerging Environmental Threats to Kidney Health. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2018, 13, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.; Badders, A.; Costacou, T.; Arthur, J.; Innes, K. Perfluoroalkyl substances and kidney function in chronic kidney disease, anemia, and diabetes. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy 2018, 11, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Ricci, G.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M.; Imbriani, M.; Chiovato, L. Thyroid Disrupting Effects of Old and New Generation PFAS. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Bardhan, S.; Xu, L.; Yamijala, S.S.R.K.C.; Lian, C.; Kwon, H.; Wong, B.M. A Machine Learning Approach for Predicting Defluorination of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) for Their Efficient Treatment and Removal. Environmental Science & Technology Letters 2019, 6, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Lu, R.; Iqbal, U.; Lin, S.H.; Nguyen, P.A.; Yang, H.C.; Wang, C.F.; Li, J.; Ma, K.L.; Li, Y.C.; Jian, W.S. A richly interactive exploratory data analysis and visualization tool using electronic medical records. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making 2015, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.E.; Lau, C.; Pradeep, P.; Sayre, R.R.; Judson, R.S.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Wambaugh, J.F. A Machine Learning Model to Estimate Toxicokinetic Half-Lives of Per- and Polyfluoro-Alkyl Substances (PFAS) in Multiple Species. Toxics 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Hoque, A.S.M.L. Clustering medical data to predict the likelihood of diseases. 2010 Fifth International Conference on Digital Information Management (ICDIM), 2010, pp. 44–49. [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, L.; Fong, S.; Xu, Q.; Wen, T.; Liu, Z. Comparative Research of Swarm Intelligence Clustering Algorithms for Analyzing Medical Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 137560–137569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yu, Z.; Qu, Y.; Xu, J.; Cao, Y. Application of the XGBoost Machine Learning Method in PM2.5 Prediction: A Case Study of Shanghai. Aerosol and Air Quality Research 2020, 20, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Jiang, K.; Yan, T.A.; Chen, G.H. XGBoost: An Optimal Machine Learning Model with Just Structural Features to Discover MOF Adsorbents of Xe/Kr. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; An, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Zhou, X.; ao Geng, Y. Application of XGBoost algorithm in the optimization of pollutant concentration. Atmospheric Research 2022, 276, 106238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunleye, A.; Wang, Q.G. XGBoost Model for Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics 2020, 17, 2131–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, C.; Gao, C.; Malin, B.A.; Chen, Y. Predicting Missing Values in Medical Data Via XGBoost Regression. Journal of Healthcare Informatics Research 2020, 4, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir-Pichhadze, R.; Kaplan, B. Seeing the Forest for the Trees: Random Forest Models for Predicting Survival in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2020, 104, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Alickovic, E.; Kevric, J. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease by Using Random Forest; 2017; pp. 589–594. [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Rahman, M.S.; Rahman, M.S. A Random Forest based predictor for medical data classification using feature ranking. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2019, 15, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, P.G.; Muratov, E.N.; Artemenko, A.G.; Kolumbin, O.G.; Muratov, N.N.; Kuz’min, V.E. Application of Random Forest Approach to QSAR Prediction of Aquatic Toxicity. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2009, 49, 2481–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrochategui, E.; Lacorte, S.; Tauler, R.; Martin, F.L. Perfluoroalkylated Substance Effects in Xenopus laevis A6 Kidney Epithelial Cells Determined by ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Chemometric Analysis. Chemical Research in Toxicology 2016, 29, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Hinton, P.; Chen, J.; Jiang, J. Causal inference for the effect of environmental chemicals on chronic kidney disease. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2020, 18, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.B.; Ducatman, A. Associations between the concentrations of α-klotho and selected perfluoroalkyl substances in the presence of eGFR based kidney function and albuminuria: Data for US adults aged 40–79 years. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 838, 155994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, B.M.; Troy, J.L.; Daugharty, T.M.; Ueki, I.F.; Nicholas, D.P.; Wong, C.F. On the Mechanism of Inhibition in Fluid Reabsorption by the Renal Proximal Tubule of the Volume-Expanded Rat. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1971, 50, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, R. Androgens stimulate proximal tubule transport. Gender Medicine 2008, 5, S114–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, A.; Chakravarty, S.; Chen, J.K.; Chen, J.C.; Loleh, S.; Saini, N.; Harris, R.C.; Capdevila, J.; Quigley, R. Androgens augment proximal tubule transport. American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology 2004, 287, F452–F459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, A.A. Mechanisms of proximal tubule sodium transport regulation that link extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology 2010, 298, R851–R861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaissling, B.; Hegyi, I.; Loffing, J.; Hir, M. Morphology of interstitial cells in the healthy kidney. Anatomy and Embryology 1996, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Radermecker, R.P.; Rorive, M.; Depas, G.; Krzesinski, J.M. Indexing glomerular filtration rate for body surface area in obese patients is misleading: concept and example. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2005, 20, 2024–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyengaard, J.R.; Bendtsen, T.F. Glomerular number and size in relation to age, kidney weight, and body surface in normal man. The Anatomical Record 1992, 232, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, C.C.; Woo, Y.M.; Brady, S. Glomerular filtration rate what is the rationale and justification of normalizing GFR for body surface area? Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2007, 23, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, G.; Veldman, B.; Berden, J.H.M.; Smits, P.; Wetzels, J.F.M. Glomerular hyperfiltration in type 1 diabetes mellitus results from primary changes in proximal tubular sodium handling without changes in volume expansion. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2005, 35, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula-Abed, W.A.S.; Rasadi, K.A.; Riyami, D.A. Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR): A Serum Creatinine-Based Test for the Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease and its Impact on Clinical Practice. Oman Medical Journal 2012, 27, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayego-Mateos, S.; Rodrigues-Diez, R.; Morgado-Pascual, J.L.; Valentijn, F.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Goldschmeding, R.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Its Ligands in Kidney Inflammation and Damage. Mediators of Inflammation 2018, 2018, 8739473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, N.; Tolbert, E.; Ponnusamy, M.; Ma, L.; Gong, R.; Bayliss, G.; Yan, H.; Zhuang, S. Sustained Activation of EGFR Triggers Renal Fibrogenesis after Acute Kidney Injury. The American Journal of Pathology 2013, 183, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Callaghan, C.A.; Shine, B.; Lasserson, D.S. Chronic kidney disease: a large-scale population-based study of the effects of introducing the <em>CKD-EPI</em> formula for eGFR reporting. BMJ Open 2011, 1, e000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, N.; Harris, K.; Whitfield, M.; O’Donoghue, D.; Lewis, R.; Mansell, M.; Thomas, S.; Townend, J.; Eames, M.; Marcelli, D. The impact of population-based identification of chronic kidney disease using estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) reporting. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 2008, 23, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.A.; Montes, M.D.L.A.V.; Taylor, C.J.; Ordóñez-Mena, J.M.; Ogburn, E.; Sharma, V.; Shine, B.; James, T.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Impact of a single eGFR and eGFR-estimating equation on chronic kidney disease reclassification: a cohort study in primary care. British Journal of General Practice 2018, 68, e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
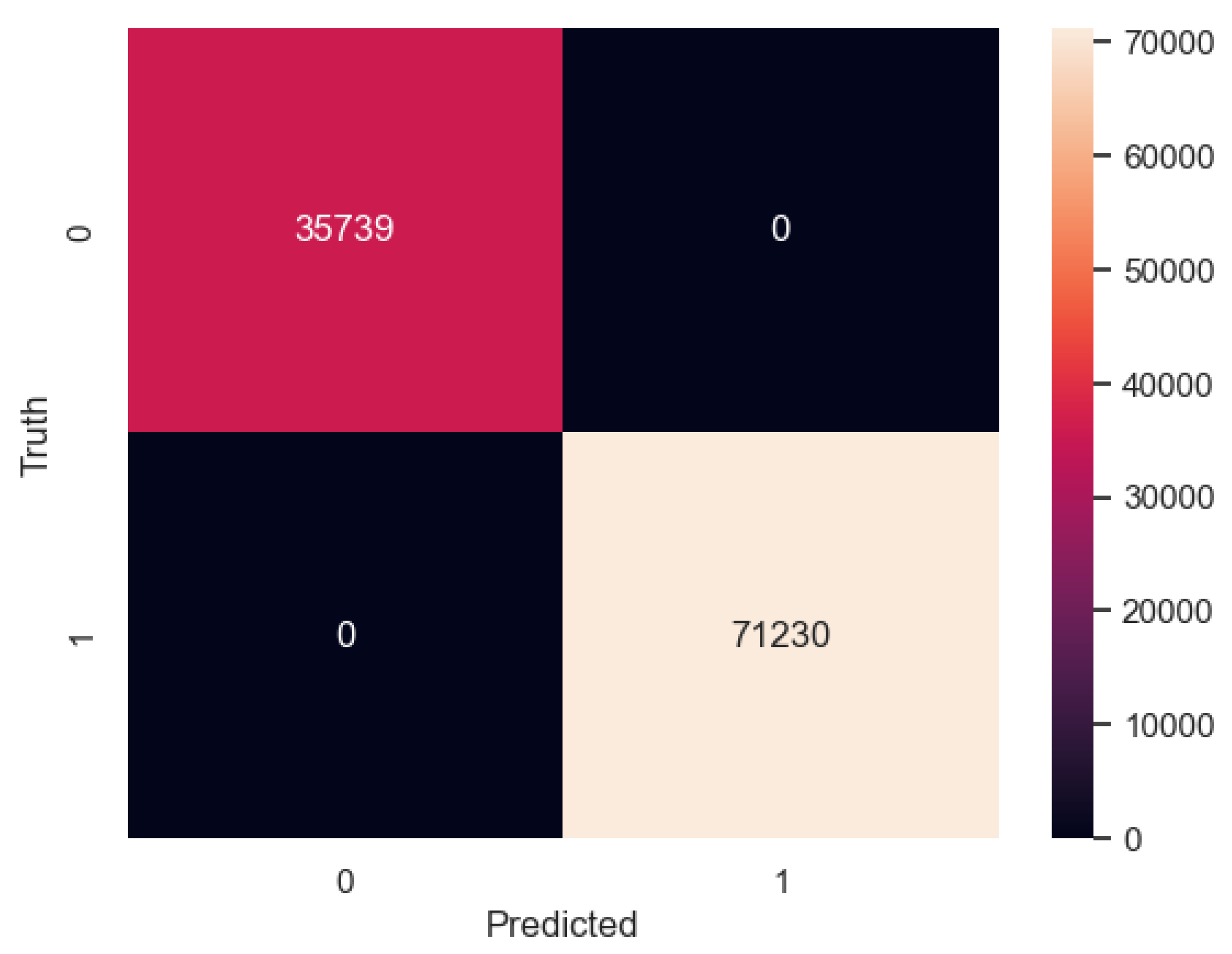
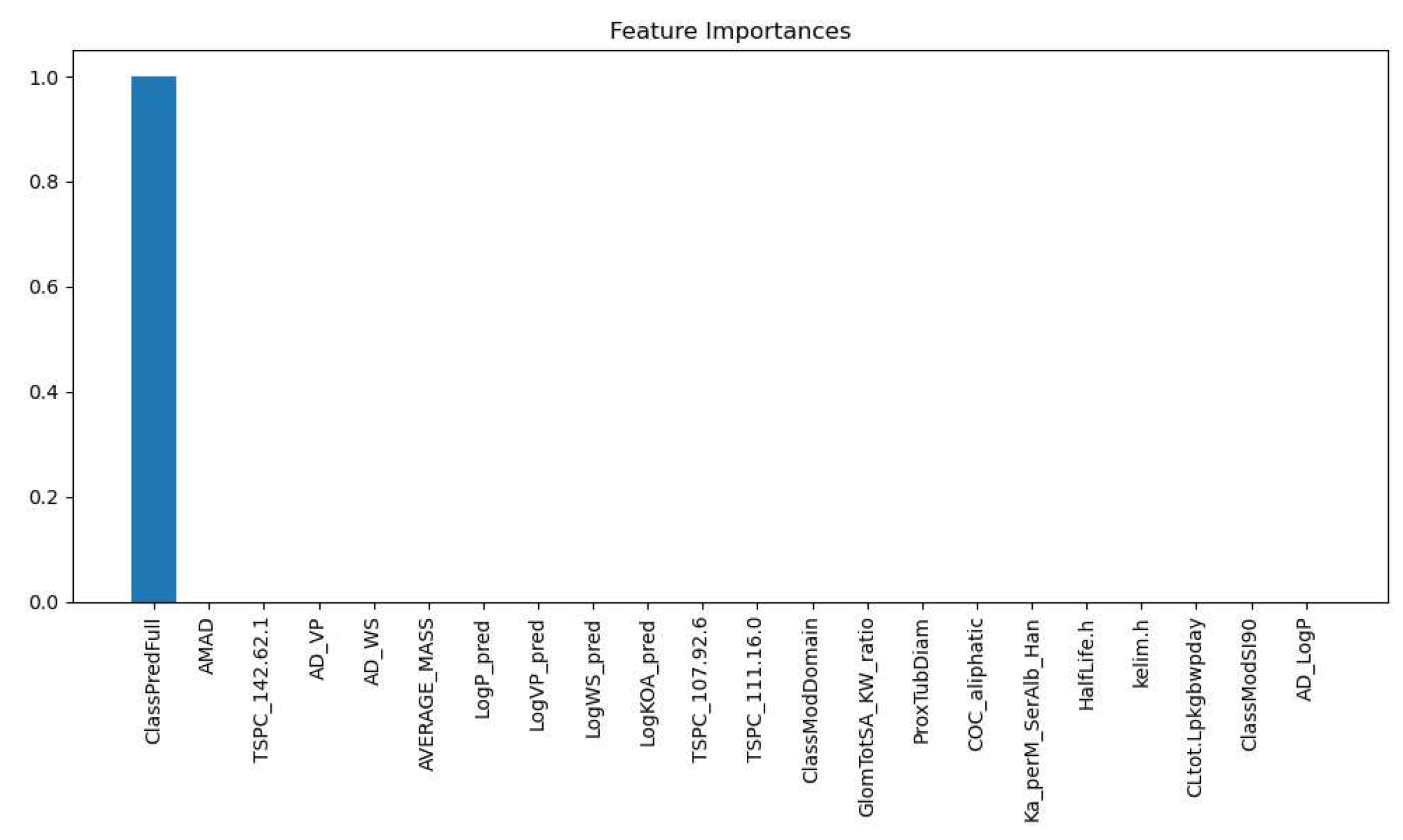
| Labels | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multirenculated | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 35739 |
| Unipapillary | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 71230 |
| Accuracy | 1.00 | 106969 | ||
| Macro Average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 106969 |
| Weighted Average | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 106969 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




