Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
27 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
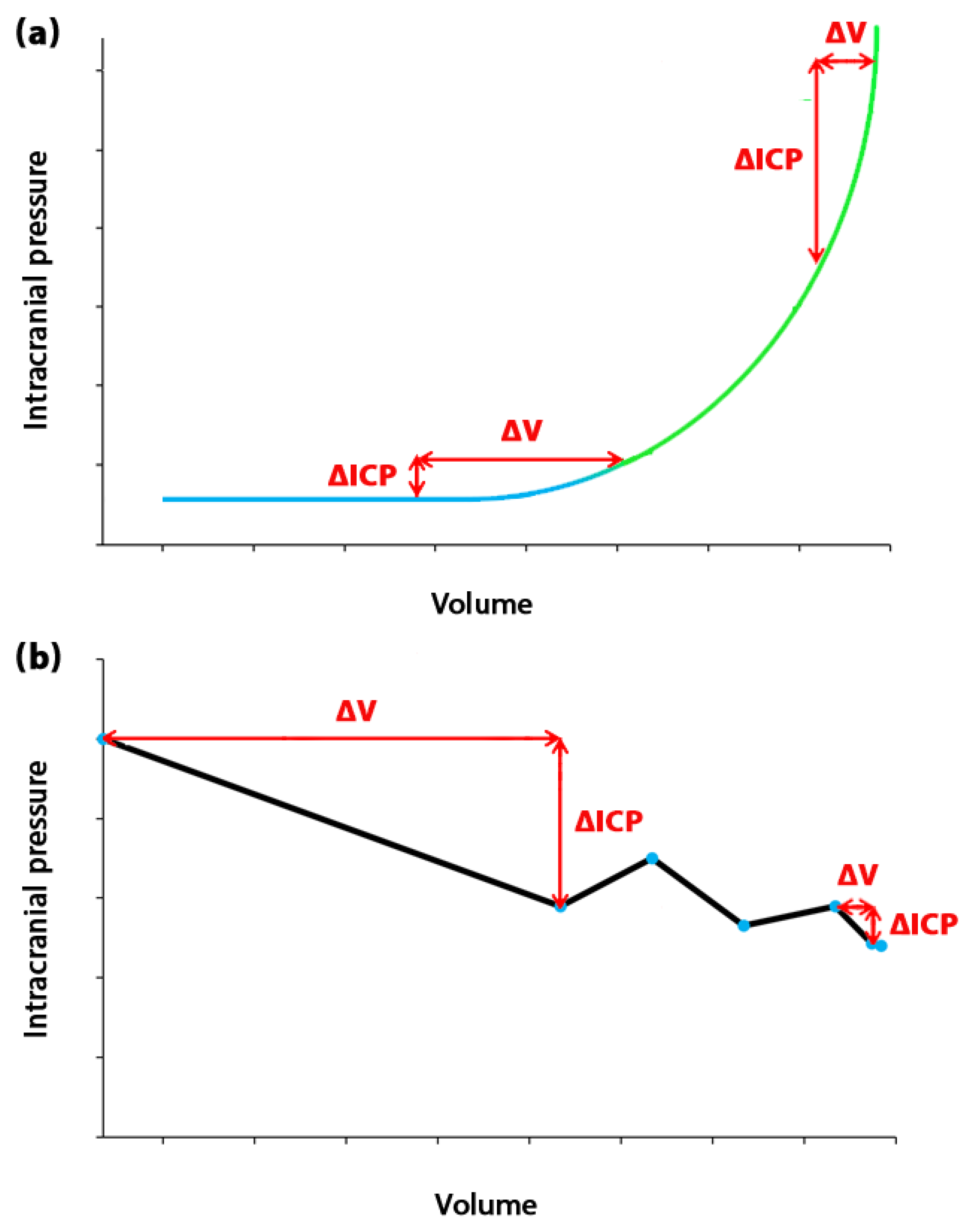
2. Measurement, calculation, and estimation of ICC
3. Viscous component of the brain
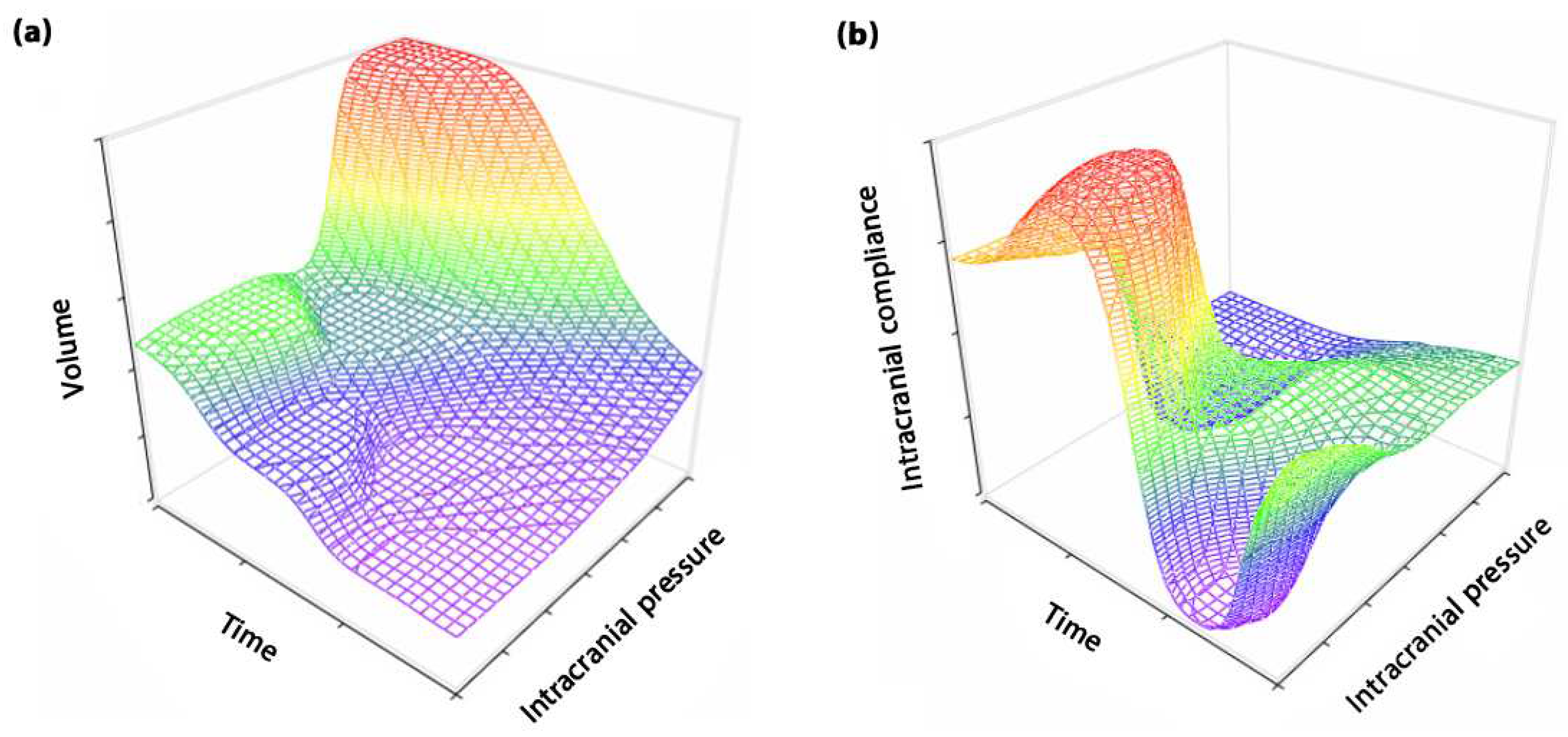
4. The role of time in ICC definition
| Brain model | Authors, year | Type of brain disorder | Solving method | Brain regions | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poroelastic | Yuan Et al, 2022 |
Healthy subjects under drug infusion | Mathematical analysis based on arbitrary Lagrange-Eulerian equations | White matter | [41] |
| Lambride Et al, 2020 |
Brain injury | Finite element method | Single region | [42] | |
| Guo Et al, 2018 |
Alzheimer’s disease | Finite element method | White matter | [43] | |
| Gholampour et al, 2014 and 2015 | Non-communicating hydrocephalus | Fluid-structure interaction | Single region | [44,45] | |
| Viscoelastic | Li et al, 2021 |
Healthy subject | Finite element method | Grey and white matter | [46] |
| Siegkas et al, 2019 |
Brain injury | Finite element method | Single region | [47] | |
| Gholampour et al, 2017 | Hydrocephalus | Fluid-structure interaction | Single region | [19,33] | |
| Harpko et al, 2006 |
Healthy subject | Mathematical analysis | White matter | [28] | |
| Hyper-viscoelastic | Menghani et al, 2023 |
Head impact | Finite element method | Basal ganglia, cerebral hemispheres, and corpus callosum | [48] |
| Wang et al, 2018 |
Brain injury | Finite element method | Grey matter, white matter, and pia mater | [49] | |
| Wilkie et al, 2012 |
Hydrocephalus | Mathematical analysis using fractional Zener model | Single region | [50] | |
| Dutta-Roy, 2011 | Normal pressure hydrocephalus | Finite element method | Single region | [51] | |
| Poro-viscoelastic | Gholampour et al, 2022 and 2023 |
Communicating hydrocephalus | Fluid-structure interaction | Single region | [16,17,31] |
| Pavan Et al, 2022 |
Brain injury | Finite element method | One region | [52] | |
| Gholampour, 2018 | Non-communicating hydrocephalus | Fluid-structure interaction | Single region | [15] | |
| Cheng et al, 2010 |
Non-communicating hydrocephalus | Finite element method | White matter | [29] | |
| Poro-hyperviscoelastic | Hosseini-Farid et al, 2020 | Healthy subject | Finite element method | Grey and white matter | [53] |
| Forte et al, 2017 |
Healthy subject | Finite element method | Grey and white matter | [54] |
5. Approaches to TE in ICC assessment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borlongan, C.V.; Burns, J.; Tajiri, N.; Stahl, C.E.; Weinbren, N.L.; Shojo, H.; Sanberg, P.R.; Emerich, D.F.; Kaneko, Y.; van Loveren, H.R. Epidemiological survey-based formulae to approximate incidence and prevalence of neurological disorders in the United States: a meta-analysis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e78490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima Giacobbo, B.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.; Bromberg, E.; de Vries, E.F. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: focus on neuroinflammation. Molecular neurobiology 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomeraniec, I.J.; Bond, A.E.; Lopes, M.B.; Jane, J.A. Concurrent Alzheimer’s pathology in patients with clinical normal pressure hydrocephalus: correlation of high-volume lumbar puncture results, cortical brain biopsies, and outcomes. Journal of neurosurgery 2016, 124, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, B.C.; Karimy, J.K.; Kundishora, A.J.; Mestre, H.; Cerci, H.M.; Matouk, C.; Alper, S.L.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M.; Kahle, K.T. Glymphatic system impairment in Alzheimer’s disease and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Trends in molecular medicine 2020, 26, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockum, K.; Virhammar, J.; Riklund, K.; Söderström, L.; Larsson, E.-M.; Laurell, K. Diagnostic accuracy of the iNPH Radscale in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. PloS One 2020, 15, e0232275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budday, S.; Ovaert, T.C.; Holzapfel, G.A.; Steinmann, P.; Kuhl, E. Fifty shades of brain: a review on the mechanical testing and modeling of brain tissue. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2020, 27, 1187–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M.; Lodi, C.A. A simple mathematical model of the interaction between intracranial pressure and cerebral hemodynamics. Journal of applied physiology 1997, 82, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiening, K.; Schoening, W.; Stover, J.; Unterberg, A. Continuous monitoring of intracranial compliance after severe head injury: relation to data quality, intracranial pressure and brain tissue PO2. British journal of neurosurgery 2003, 17, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, H.W.; Espey, F.F.; Kimbell, F.D.; Penka, E.J.; Rosenauer, A.; Podolsky, B.; Evans, J.P. The mechanism of the change in cerebrospinal fluid pressure following an induced change in the volume of the fluid space. The Journal of laboratory and clinical medicine 1953, 41, 428–435. [Google Scholar]
- Czosnyka, M.; Pickard, J.D. Monitoring and interpretation of intracranial pressure. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2004, 75, 813–821. [Google Scholar]
- Okon, M.D.; Roberts, C.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Springer, A.N.; Small, R.H.; McGregor, J.M.; Katz, S.E. Characteristics of the cerebrospinal fluid pressure waveform and craniospinal compliance in idiopathic intracranial hypertension subjects. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, M.; Roszkowski, M.; Walencik, A. Identification of the cerebrospinal compensatory mechanisms via computer-controlled drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Child's Nervous System 1995, 11, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alperin, N.J.; Lee, S.H.; Loth, F.; Raksin, P.B.; Lichtor, T. MR-Intracranial pressure (ICP): a method to measure intracranial elastance and pressure noninvasively by means of MR imaging: baboon and human study. Radiology 2000, 217, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, R.-W.; Alperin, N. Noninvasive intracranial compliance from MRI-based measurements of transcranial blood and CSF flows: indirect versus direct approach. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering 2008, 56, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S. FSI simulation of CSF hydrodynamic changes in a large population of non-communicating hydrocephalus patients during treatment process with regard to their clinical symptoms. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0196216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S.; Frim, D.; Yamini, B. Long-term recovery behavior of brain tissue in hydrocephalus patients after shunting. Communications Biology 2022, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Balasundaram, H.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Droessler, J. A mathematical framework for the dynamic interaction of pulsatile blood, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2023, 231, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Fatouraee, N. Boundary conditions investigation to improve computer simulation of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in hydrocephalus patients. Communications biology 2021, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Fatouraee, N.; Seddighi, A.; Seddighi, A. Numerical simulation of cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics in the healing process of hydrocephalus patients. Journal of Applied Mechanics and Technical Physics 2017, 58, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Bahmani, M. Hydrodynamic comparison of shunt and endoscopic third ventriculostomy in adult hydrocephalus using in vitro models and fluid-structure interaction simulation. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2021, 204, 106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Panda, N.; Swain, A.; Mathew, P.; Singla, N.; Gupta, S.; Jangra, K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Bhagat, H. Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter: Correlation With Intra-Ventricular Intracranial Measurements in Predicting Dysfunctional Intracranial Compliance. Cureus 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-C.; Sunwoo, J.; Sheriff, F.; Farzam, P.; Farzam, P.Y.; Orihuela-Espina, F.; LaRose, S.L.; Monk, A.D.; Aziz-Sultan, M.A.; Patel, N. Validation of diffuse correlation spectroscopy measures of critical closing pressure against transcranial Doppler ultrasound in stroke patients. Journal of biomedical optics 2021, 26, 036008–036008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, S.; Solla, D.J.F.; Nogueira, R.d.C.; Teixeira, M.J.; Malbouisson, L.M.S.; Paiva, W.d.S. A Novel Noninvasive Technique for Intracranial Pressure Waveform Monitoring in Critical Care. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2021, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbani, R. An Electrical Model of Hydrocephalus Shunt Incorporating the CSF Dynamics. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 9751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, J.; Chakravarty, S. A poroelastic spheroidal shell model for studying the problem of head injury. Journal of mathematical analysis and applications 1984, 103, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatelin, S.; Constantinesco, A.; Willinger, R. Fifty years of brain tissue mechanical testing: from in vitro to in vivo investigations. Biorheology 2010, 47, 255–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, G.; Bigoni, D.; Regitnig, P.; Holzapfel, G.A. Brain tissue deforms similarly to filled elastomers and follows consolidation theory. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 2006, 54, 2592–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrapko, M.; Van Dommelen, J.; Peters, G.; Wismans, J. The mechanical behaviour of brain tissue: large strain response and constitutive modelling. Biorheology 2006, 43, 623–636. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Bilston, L.E. Computational model of the cerebral ventricles in hydrocephalus. Journal of biomechanical engineering 2010, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkin, B.S.; Ilankovan, A.I.; Morrison III, B. A detailed viscoelastic characterization of the P17 and adult rat brain. Journal of neurotrauma 2011, 28, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S.; Yamini, B.; Droessler, J.; Frim, D. A New Definition for Intracranial Compliance to Evaluate Adult Hydrocephalus After Shunting. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 900644.
- Tuli, S.; O'Hayon, B.; Drake, J.; Clarke, M.; Kestle, J. Change in ventricular size and effect of ventricular catheter placement in pediatric patients with shunted hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 1999, 45, 1329–1333, discussion 1333–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, S.; Fatouraee, N.; Seddighi, A.S.; Seddighi, A. Evaluating the effect of hydrocephalus cause on the manner of changes in the effective parameters and clinical symptoms of the disease. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2017, 35, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M.; Citerio, G. Brain compliance: the old story with a new ‘et cetera’. Springer: 2012; Vol. 38, pp 925-927.
- Portella, G.; Cormio, M.; Citerio, G.; Contant, C.; Kiening, K.; Enblad, P.; Piper, I. Continuous cerebral compliance monitoring in severe head injury: its relationship with intracranial pressure and cerebral perfusion pressure. Acta neurochirurgica 2005, 147, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaohua, L.; Kimura, H. A mathematical model of intracranial pressure dynamics for brain hypothermia treatment. Journal of theoretical biology 2006, 238, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, A.; Smielewski, P.; Chambers, I.; Alperin, N.; Malm, J.; Czosnyka, M.; Marmarou, A. Assessment of cerebrospinal fluid outflow resistance. Medical & biological engineering & computing 2007, 45, 719–735. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierska, A.; Kasprowicz, M.; Czosnyka, M.; Placek, M.M.; Baledent, O.; Smielewski, P.; Czosnyka, Z. Compliance of the cerebrospinal space: Comparison of three methods. Acta Neurochirurgica 2021, 163, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czosnyka, M.; Czosnyka, Z.; Agarwal-Harding, K.J.; Pickard, J.D. Modeling of CSF dynamics: legacy of Professor Anthony Marmarou. In Hydrocephalus; Springer, 2012; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Fame, R.M.; Sadegh, C.; Sutin, J.; Naranjo, C.; Syau, D.; Cui, J.; Shipley, F.B.; Vernon, A.; Gao, F. Choroid plexus NKCC1 mediates cerebrospinal fluid clearance during mouse early postnatal development. Nature communications 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Zhan, W.; Jamal, A.; Dini, D. On the microstructurally driven heterogeneous response of brain white matter to drug infusion pressure. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology 2022, 21, 1299–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambride, C.; Christodoulou, N.; Michail, A.; Vavourakis, V.; Stylianopoulos, T. Decompressive craniectomy of post-traumatic brain injury: an in silico modelling approach for intracranial hypertension management. Scientific reports 2020, 10, 18673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Vardakis, J.C.; Lassila, T.; Mitolo, M.; Ravikumar, N.; Chou, D.; Lange, M.; Sarrami-Foroushani, A.; Tully, B.J.; Taylor, Z.A. Subject-specific multi-poroelastic model for exploring the risk factors associated with the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. Interface focus 2018, 8, 20170019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S.; Fatouraee, N.; Seddighi, A.S.; Yazdani, S.O. A Hydrodynamical Study to propose a numerical Index for evaluating the CSF conditions in cerebralventricular system. International Clinical Neuroscience Journal 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gholampour, S.; Seddighi, A.; Fatouraee, N. Relationship between Spinal fluid and Cerebrospinal fluid as an index for assessment of non-communicating hydrocephalus. Modares Mechanical Engineering 2015, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Shepherd, D.E.; Espino, D.M. Investigation of the compressive viscoelastic properties of brain tissue under time and frequency dependent loading conditions. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2021, 49, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegkas, P.; Sharp, D.J.; Ghajari, M. The traumatic brain injury mitigation effects of a new viscoelastic add-on liner. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghani, R.R.; Das, A.; Kraft, R.H. A sensor-enabled cloud-based computing platform for computational brain biomechanics. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2023, 107470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Peng, Q.; Huang, X.; Miller, K.; Wittek, A. Prediction of brain deformations and risk of traumatic brain injury due to closed-head impact: quantitative analysis of the effects of boundary conditions and brain tissue constitutive model. Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology 2018, 17, 1165–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, K.P.; Drapaca, C.S.; Sivaloganathan, S. A mathematical investigation of the role of intracranial pressure pulsations and small gradients in the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus. International journal of numerical analysis & modeling. Series B 2012, 3, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta-Roy, T. Does Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Have Mechanistic Causes? University of Western Australia; 2011.
- Pavan, P.G.; Nasim, M.; Brasco, V.; Spadoni, S.; Paoloni, F.; d'Avella, D.; Khosroshahi, S.F.; de Cesare, N.; Gupta, K.; Galvanetto, U. Development of detailed finite element models for in silico analyses of brain impact dynamics. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2022, 227, 107225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Farid, M.; Ramzanpour, M.; McLean, J.; Ziejewski, M.; Karami, G. A poro-hyper-viscoelastic rate-dependent constitutive modeling for the analysis of brain tissues. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials 2020, 102, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, A.E.; Gentleman, S.M.; Dini, D. On the characterization of the heterogeneous mechanical response of human brain tissue. Biomechanics and modeling in mechanobiology 2017, 16, 907–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldt, T.; Zoerle, T.; Teichmann, D.; Stocchetti, N. Intracranial pressure and intracranial elastance monitoring in neurocritical care. Annual review of biomedical engineering 2019, 21, 523–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, A.; Rajan, S.D.; Muthuswamy, J. Long-term changes in the material properties of brain tissue at the implant–tissue interface. Journal of neural engineering 2013, 10, 066001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulet, T.; Kelso, M.L.; Othman, S.F. Microscopic magnetic resonance elastography of traumatic brain injury model. Journal of neuroscience methods 2011, 201, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.K.; Brean, A. Cerebrospinal fluid pulse pressure amplitude during lumbar infusion in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus can predict response to shunting. Cerebrospinal fluid research 2010, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.K. The pathophysiology of chronic noncommunicating hydrocephalus: lessons from continuous intracranial pressure monitoring and ventricular infusion testing. Journal of neurosurgery 2017, 129, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mase, M.; Miyati, T.; Yamada, K.; Kasai, H.; Hara, M.; Shibamoto, Y. Non-invasive measurement of intracranial compliance using cine MRI in normal pressure hydrocephalus. In Intracranial Pressure and Brain Monitoring XII; Springer, 2005; pp. 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, U.; Bartels, P. The importance of the intrathecal infusion test in the diagnostic of normal-pressure hydrocephalus. European neurology 2001, 46, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahuquillo, J.; Rubio, E.; Codina, A.; Molins, A.; Guitart, J.; Poca, M.; Chasampi, A. Reappraisal of the intracranial pressure and cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in patients with the so-called “normal pressure hydrocephalus” syndrome. Acta neurochirurgica 1991, 112, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokossou, A.; Balédent, O.; Garnotel, S.; Page, G.; Balardy, L.; Czosnyka, Z.; Payoux, P.; Schmidt, E. ICP monitoring and phase-contrast MRI to investigate intracranial compliance. In Intracranial Pressure & Neuromonitoring XVI; Springer, 2018; pp. 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Eide, P.K. The correlation between pulsatile intracranial pressure and indices of intracranial pressure-volume reserve capacity: results from ventricular infusion testing. Journal of neurosurgery 2016, 125, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, M.; Batorski, L.; Roszkowski, M.; Tomaszewski, J.; Wocjan, J.; Walencik, A.; Zabolotny, W. Cerebrospinal compensation in hydrocephalic children. Child's Nervous System 1993, 9, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, K.; Fried, A. Pressure-volume relationships in shunt-dependent childhood hydrocephalus: The zone of pressure instability in children with acute deterioration. Journal of neurosurgery 1986, 64, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-H. The Pathophysiology of Brain Edema and Intracranial Hypertension. Journal of Neurocritical Care 2016, 9, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, I. Intracranial pressure and elastance. Head injury 1997, 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Okon, M.D.; Roberts, C.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Springer, A.N.; Small, R.H.; McGregor, J.M.; Katz, S.E. Characteristics of the cerebrospinal fluid pressure waveform and craniospinal compliance in idiopathic intracranial hypertension subjects. Fluids and Barriers of the CNS 2018, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisell, M.; Edsbagge, M.; Stephensen, H.; Czosnyka, M.; Wikkelsø, C. Elastance correlates with outcome after endoscopic third ventriculostomy in adults with hydrocephalus caused by primary aqueductal stenosis. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eide, P.; Park, E.H.; Madsen, J. Arterial blood pressure vs intracranial pressure in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta neurologica scandinavica 2010, 122, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavarajasingam, S.G.; El-Khatib, M.; Rea, M.; Russo, S.; Lemcke, J.; Al-Nusair, L.; Vajkoczy, P. Clinical predictors of shunt response in the diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurochirurgica 2021, 163, 2641–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholampour, S.; Nguyen, A.; Chaudry, S. Intracranial compliance, resistance to CSF-outflow, and pressure-volume index in hydrocephalus patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. IRBM 2023, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budday, S.; Sommer, G.; Holzapfel, G.; Steinmann, P.; Kuhl, E. Viscoelastic parameter identification of human brain tissue. Journal of the mechanical behavior of biomedical materials 2017, 74, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniak, M.; Clatterbuck, R.; Rigamonti, D.; Williams, M. Low pressure hydrocephalus and ventriculomegaly: hysteresis, non-linear dynamics, and the benefits of CSF diversion. British journal of neurosurgery 2002, 16, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G.; Vatnehol, S.A.S.; Eide, P.K. Glymphatic MRI in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Brain 2017, 140, 2691–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoka, T.; Masutani, Y.; Kawai, H.; Nakane, T.; Matsuoka, K.; Yasuno, F.; Kishimoto, T.; Naganawa, S. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Japanese journal of radiology 2017, 35, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Chen, M.J.; Plog, B.A.; Zeppenfeld, D.M.; Soltero, M.; Yang, L.; Singh, I.; Deane, R.; Nedergaard, M. Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neuroscience 2014, 34, 16180–16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Age | Type of hydrocephalus | Authors, year | Intracranial compliance measurement method | Procedure type | Intracranial compliance (ml/mmHg) | Time elapsed (minute) |
Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Noncommunicating hydrocephalus | Gholampour et al, 2021 | Computer simulation | Non-invasive | 0.78 | 0.17 | [20] |
| Eide, 2017 |
Ventricular constant-flow infusion | Invasive | 0.60 | 15.5 | [59] | ||
| Normal pressure hydrocephalus | Kazmierska et al, 2021 | Computer-assisted constant-flow infusion | Invasive | 0.27 | 13.2 | [38] | |
| Mase et al. 2005 |
Computer simulation | Non-invasive | 0.003 | --- | [60] | ||
| Meier and Bartels, 2001 | Computer-assisted constant-flow intrathecal infusion | Invasive | 0.36 | 10.5 | [61] | ||
| Sahuquillo et al, 1991 | Bolus injection, Lumbar and ventricular constant-flow infusion |
Invasive | 0.33 | 15.0 | [62] | ||
| Communicating hydrocephalus | Eide, 2017 |
Ventricular constant-flow infusion | Invasive | 0.66 | 15.5 | [59] | |
| Hydrocephalus | Lokossou et al, 2018 |
Lumbar constant-flow infusion | Invasive | 0.23 | --- | [63] | |
| Eide, 2016 |
Ventricular constant-flow infusion | Invasive | 0.6 | 15.5 | [64] | ||
| Pediatric | Noncommunicating hydrocephalus | Czosnyka et al, 1993 |
Computer-assisted lumbar infusion | Invasive | 1.27 | 6.3 | [65] |
| Acute hydrocephalus | Czosnyka et al, 1993 |
Computer-assisted lumbar infusion | Invasive | 0.97 | 6.3 | [65] | |
| Hydrocephalus | Shapiro and Fried, 1986 | Bolus withdrawal and injection | Invasive | 0.32 | --- | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





