Submitted:
25 October 2023
Posted:
26 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Binocular measurement theory and system
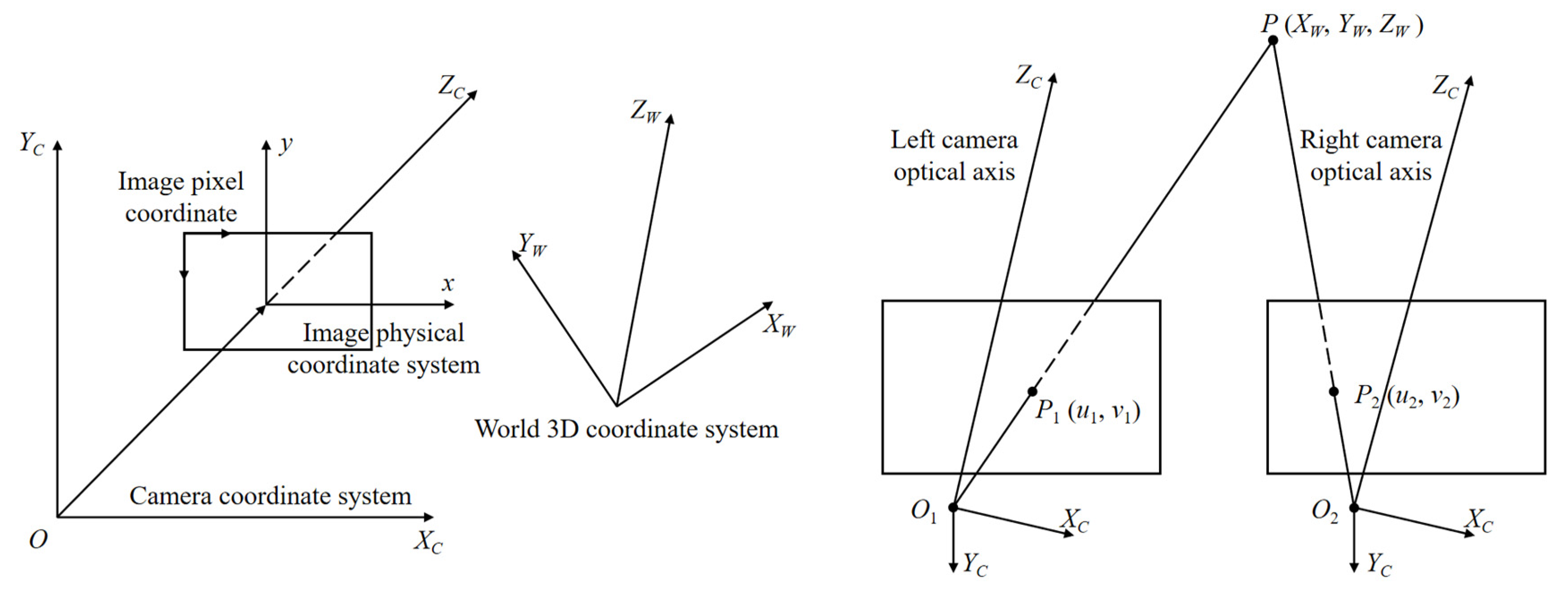
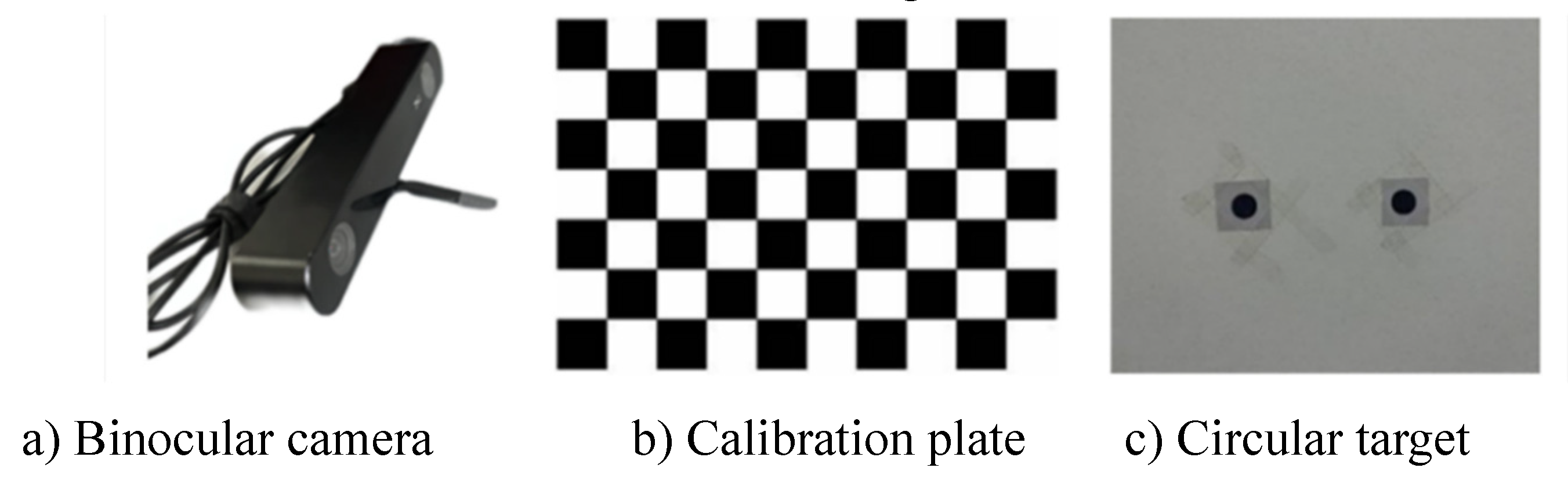
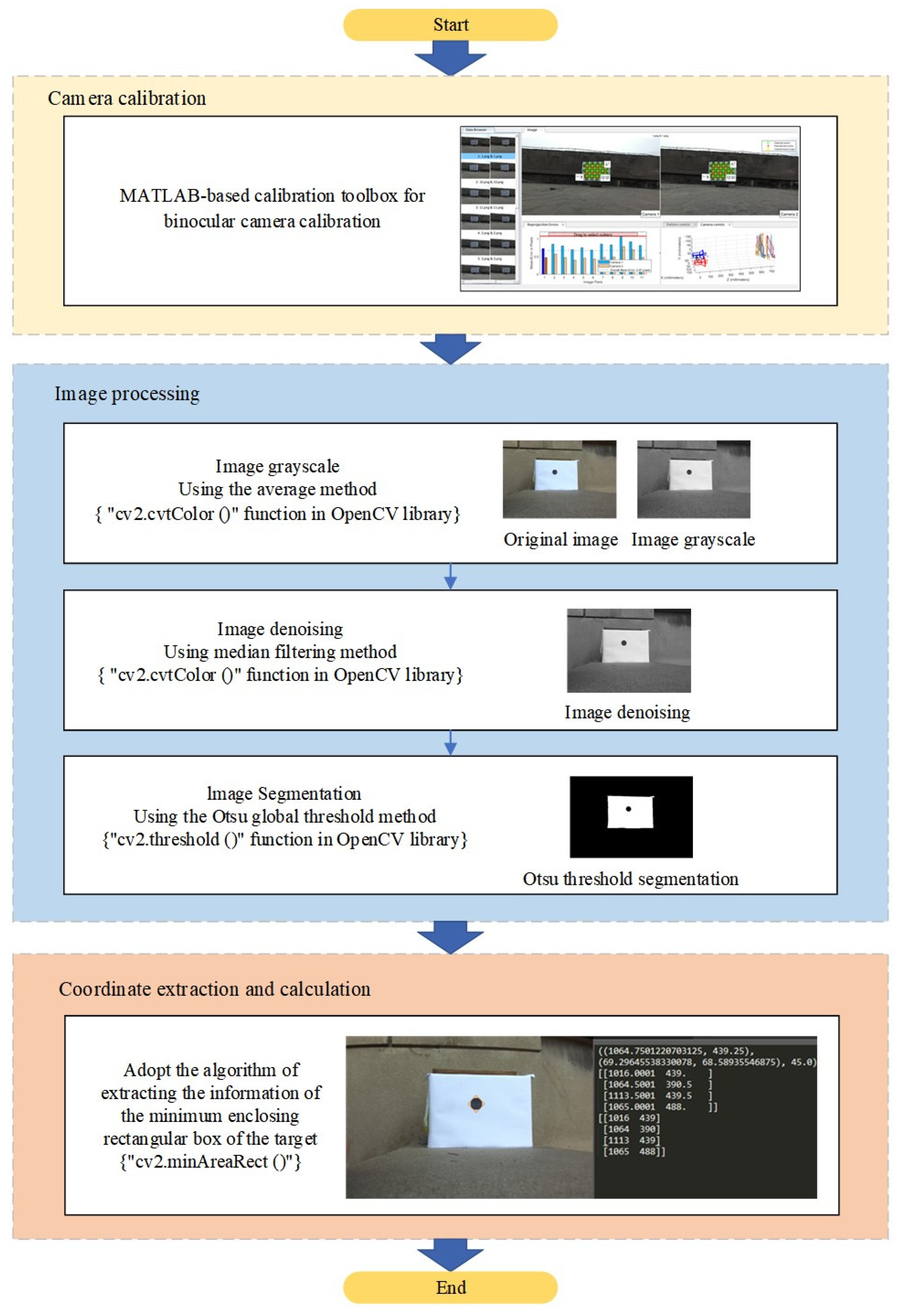
2.1. Camera calibration and feature extraction
2.2. Marker Point Matching Technology
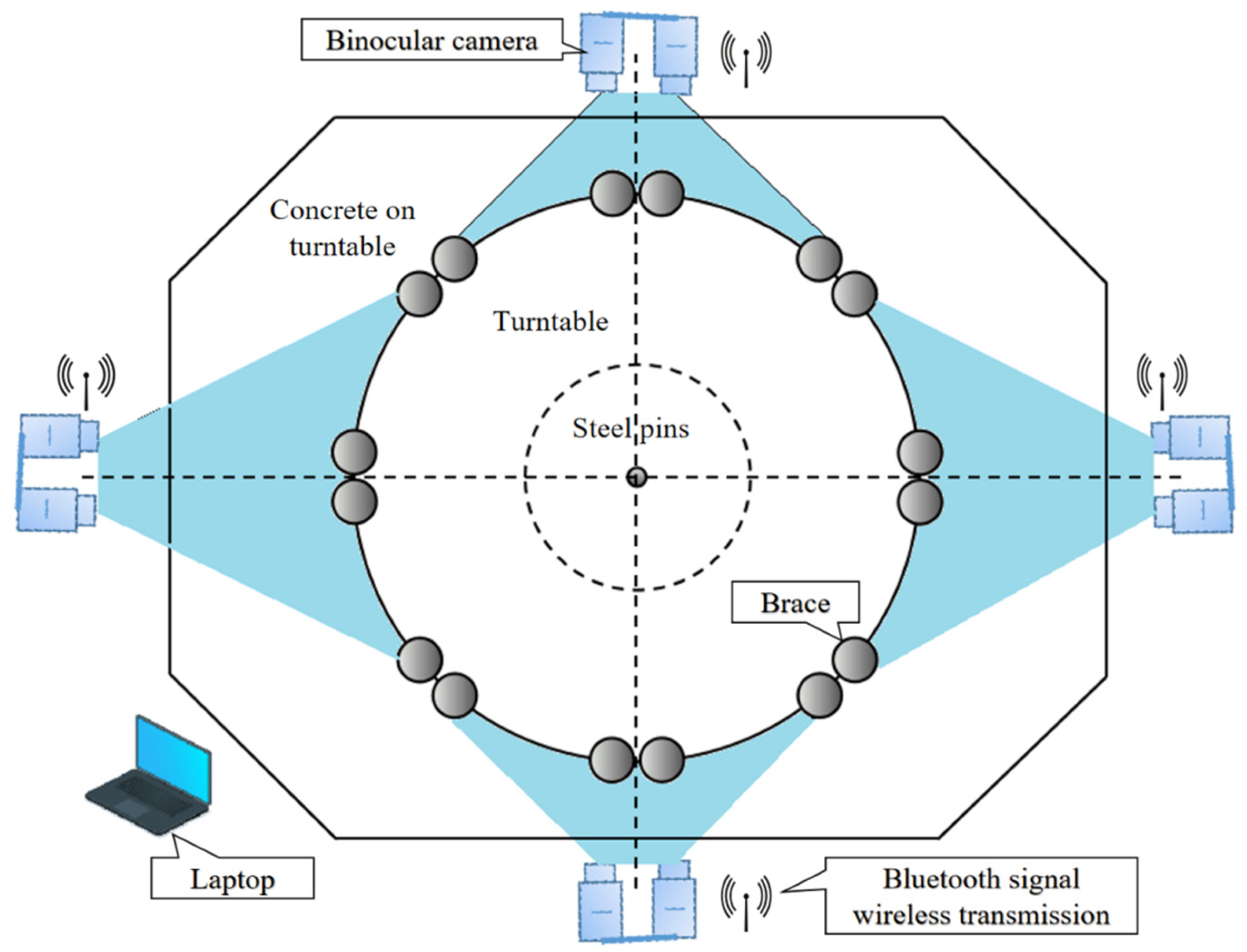
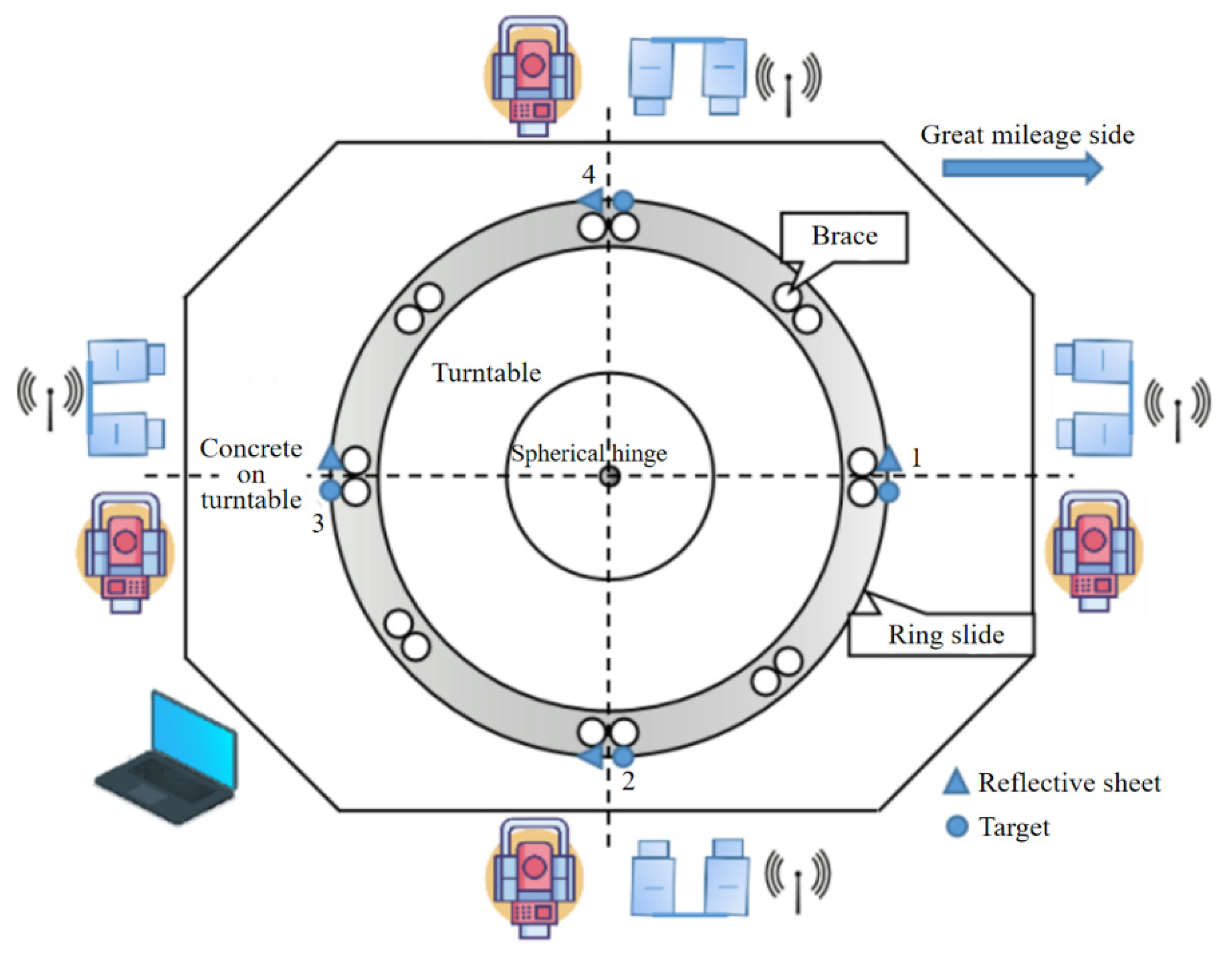
2.3. Measurement Systems
3. Test verification
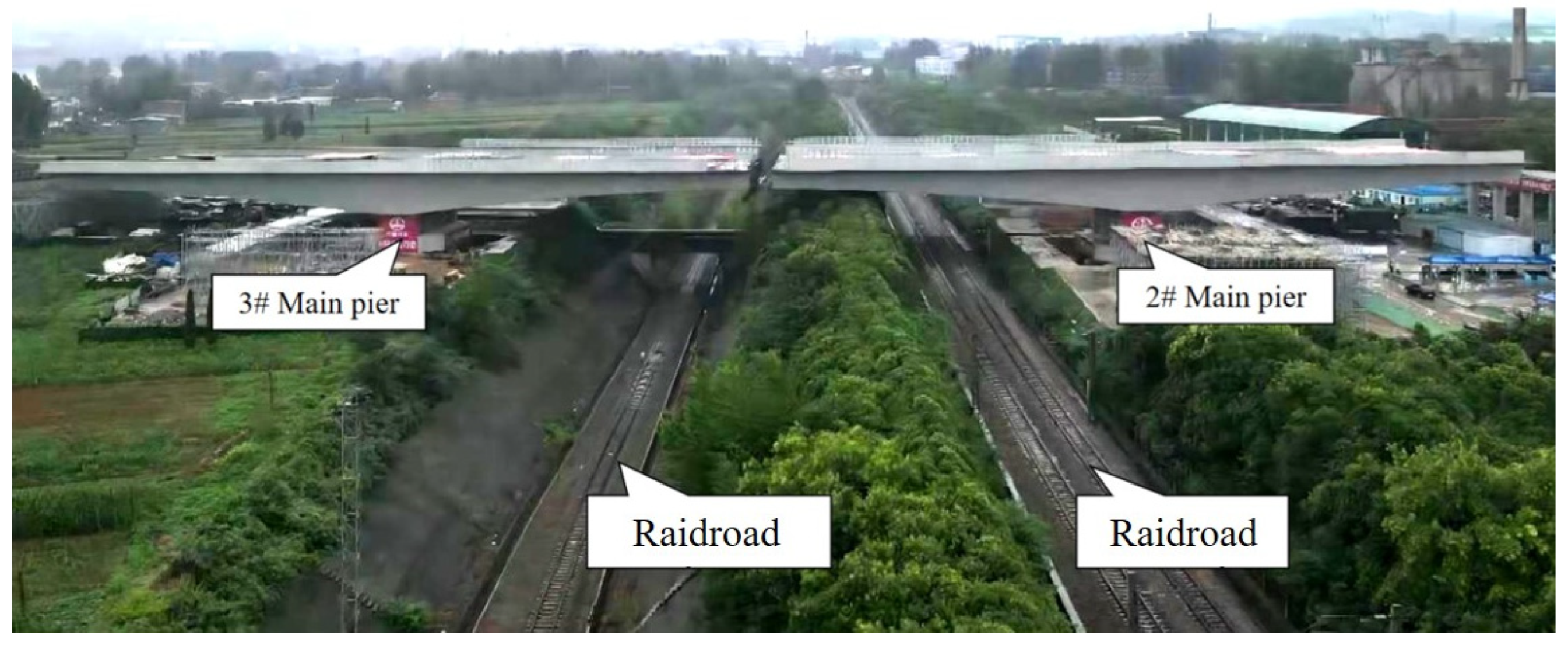
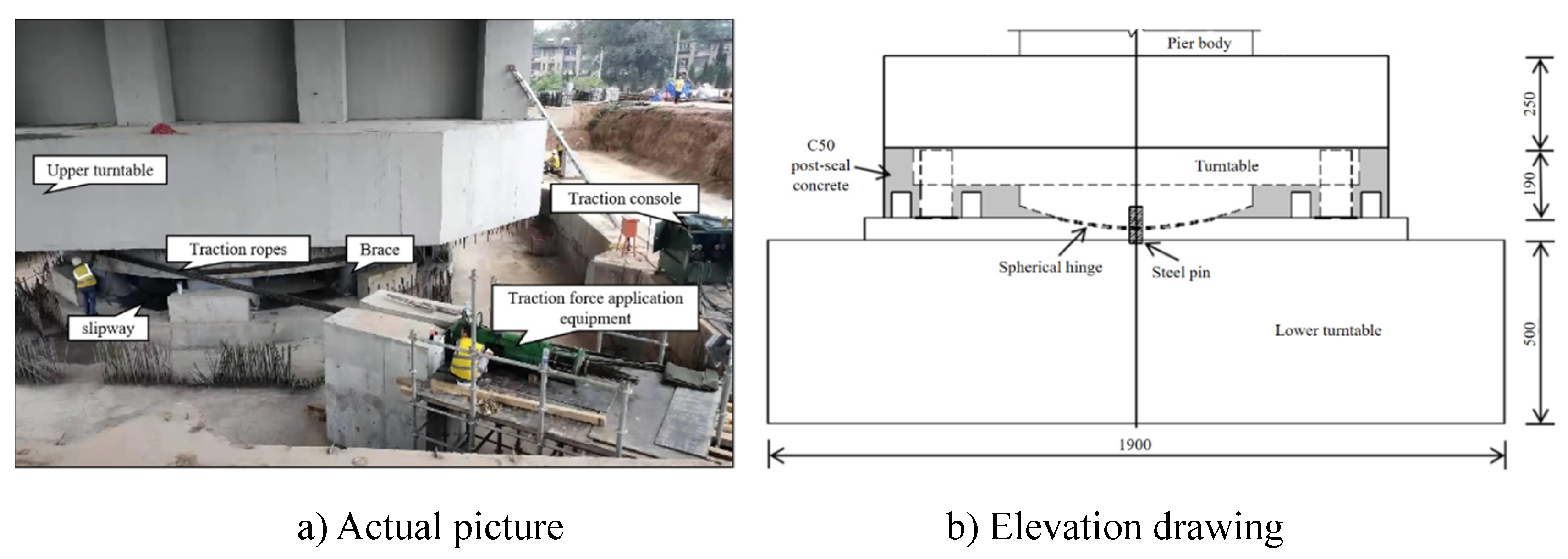
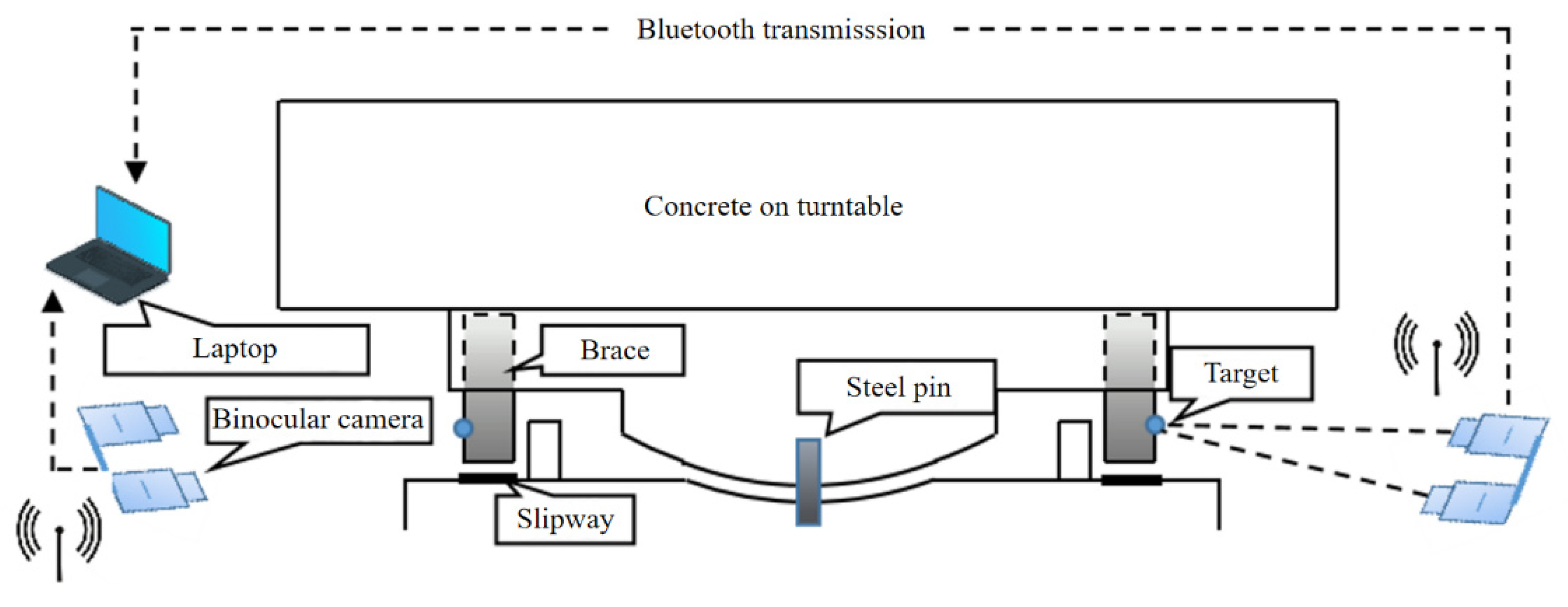
3.1. Project Introduction
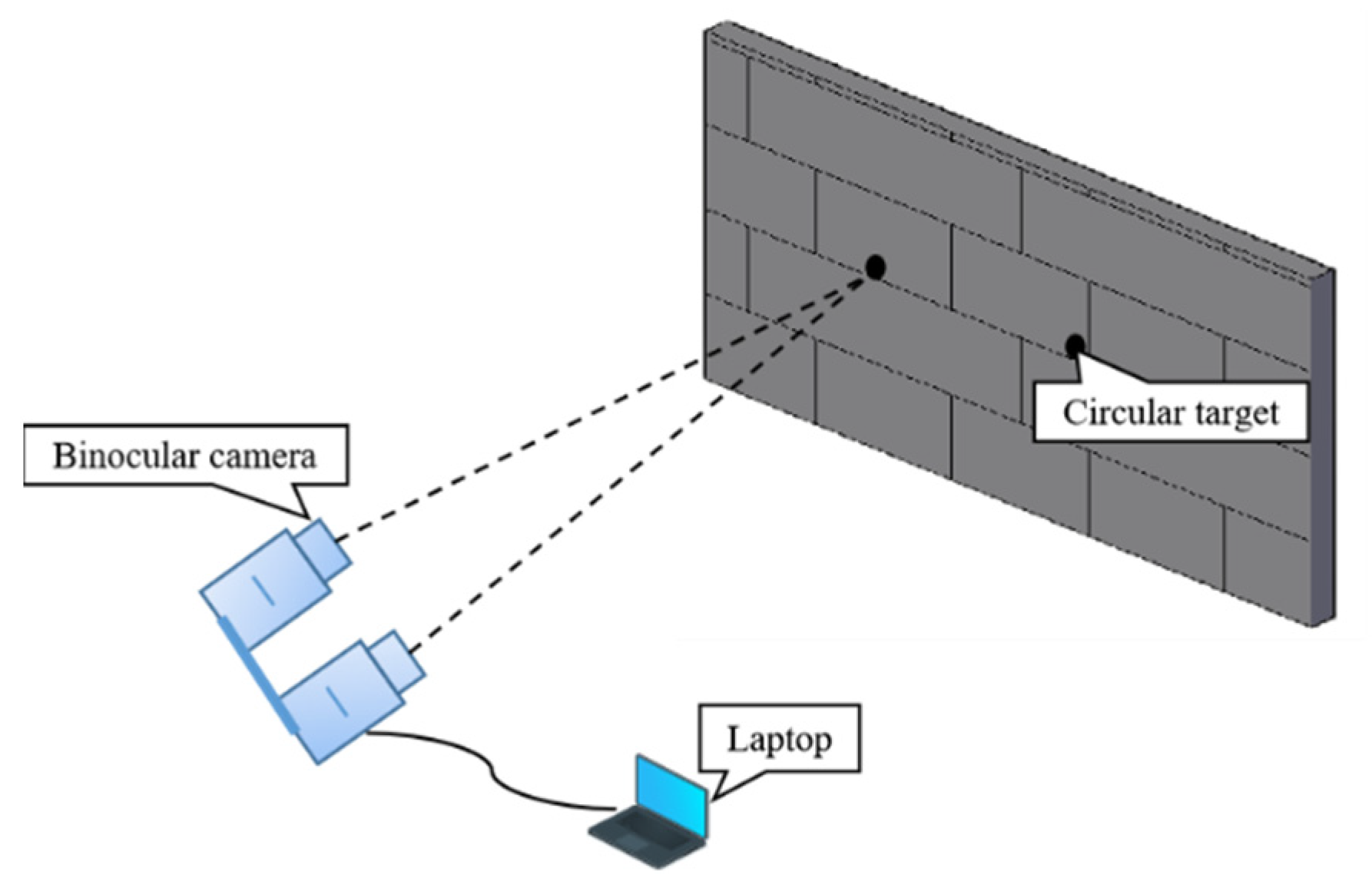
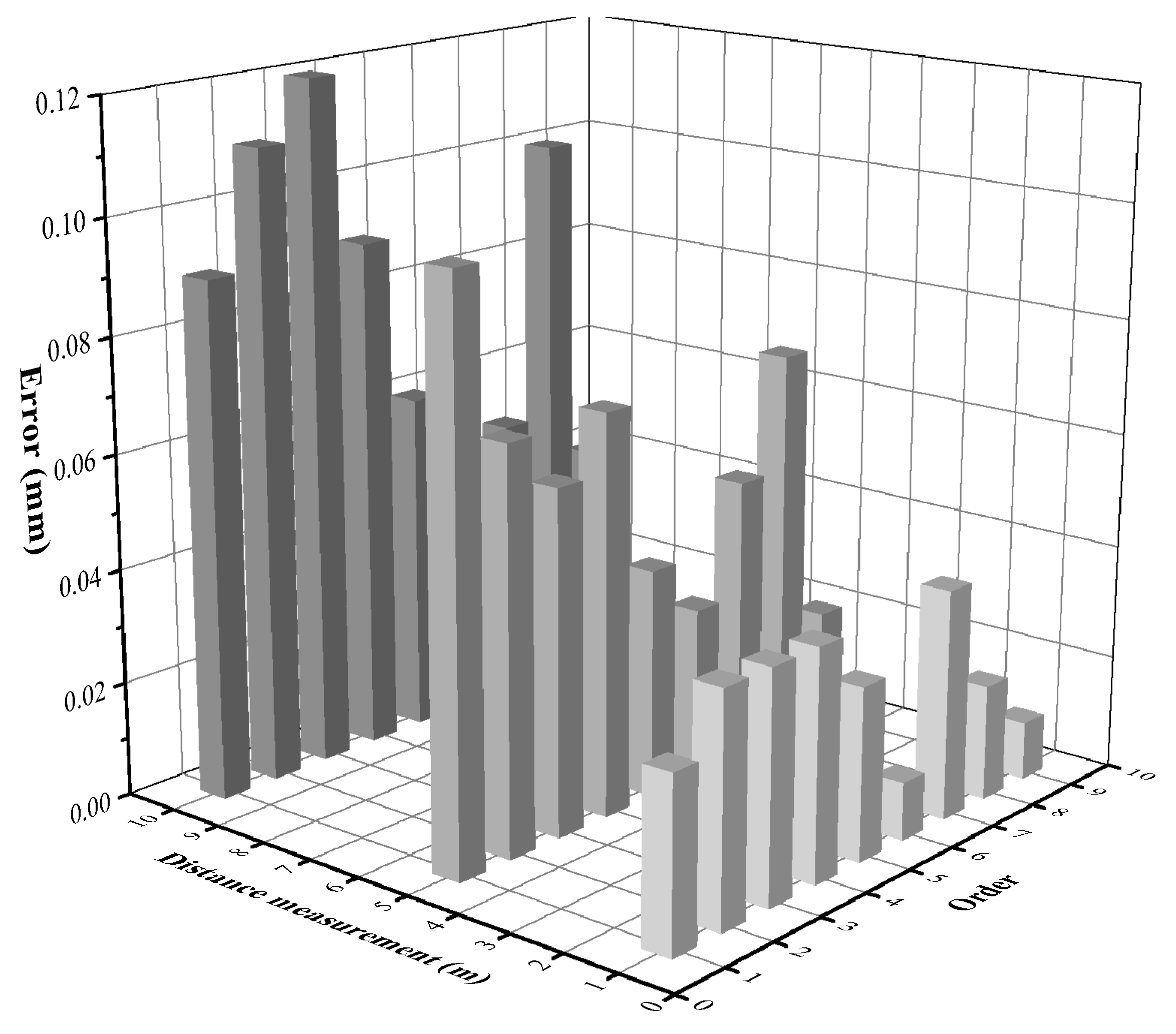
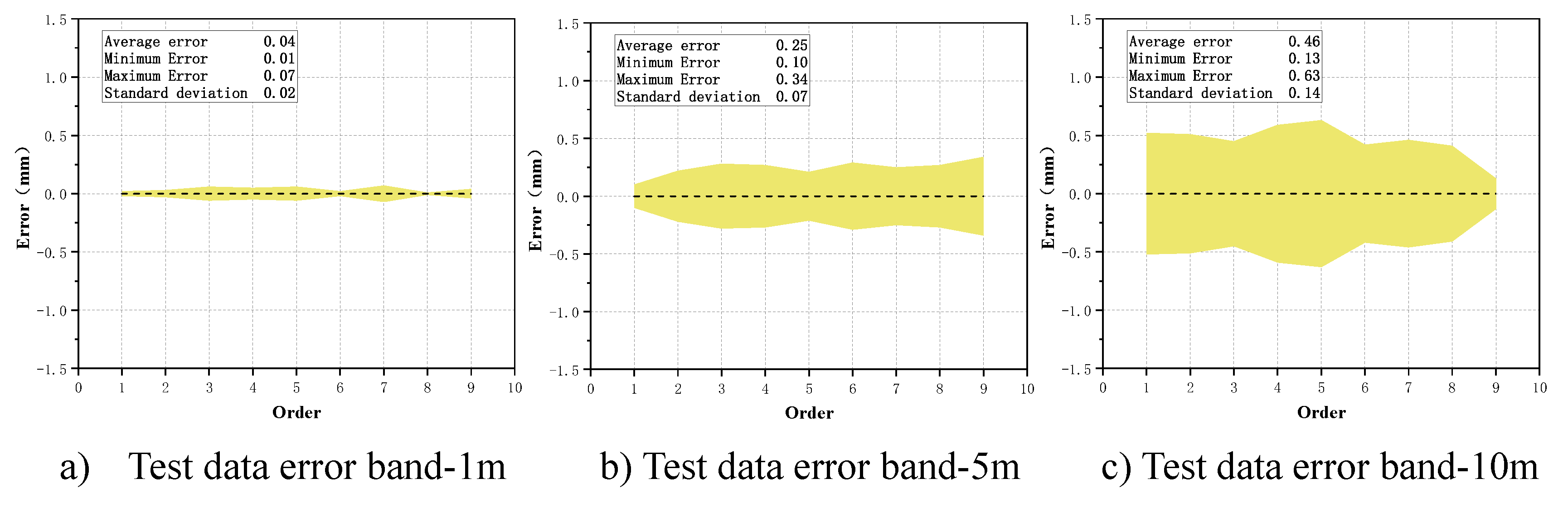
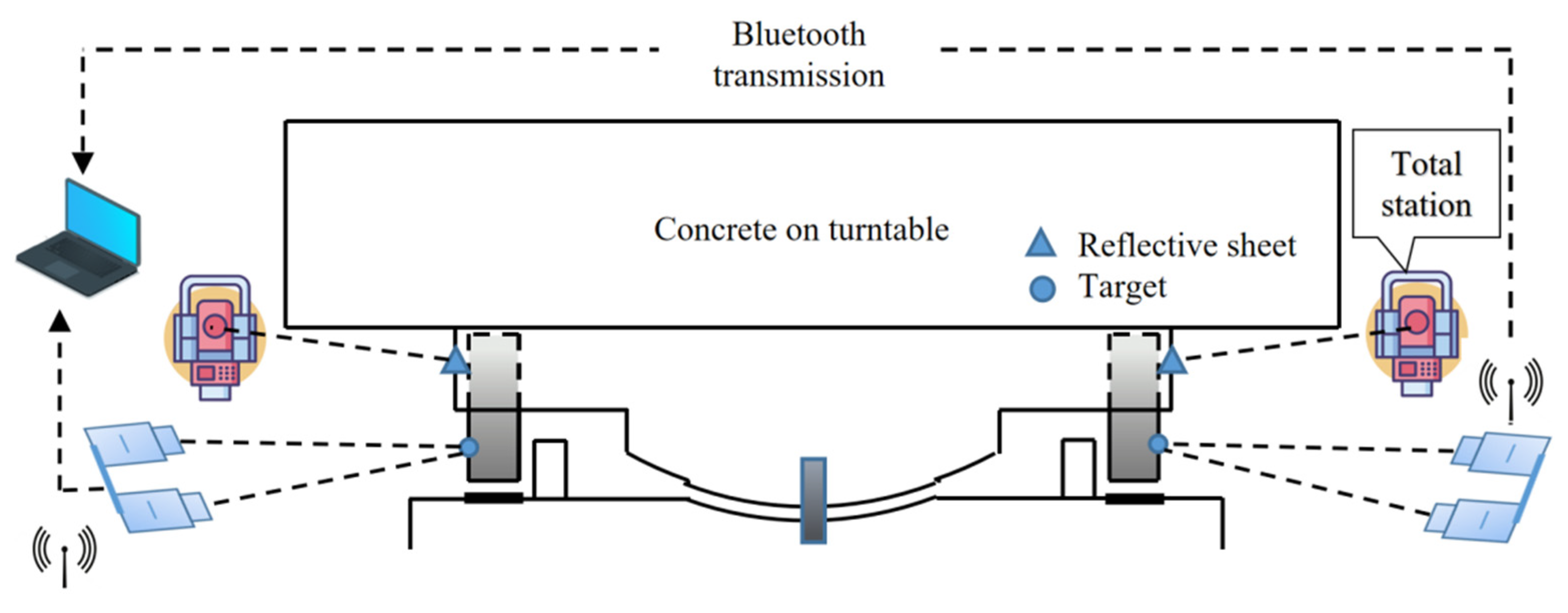
3.2. Measurement system validation
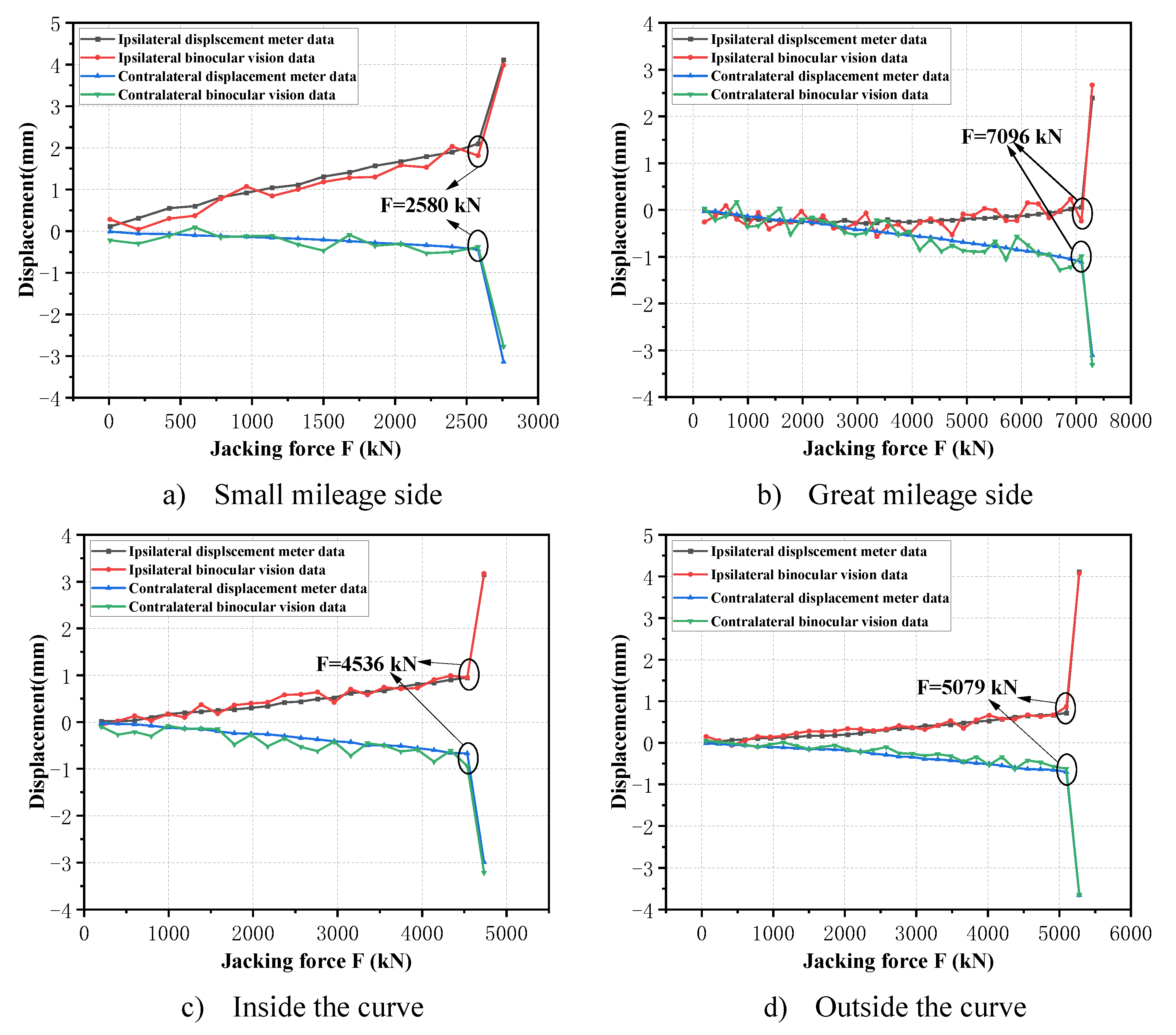
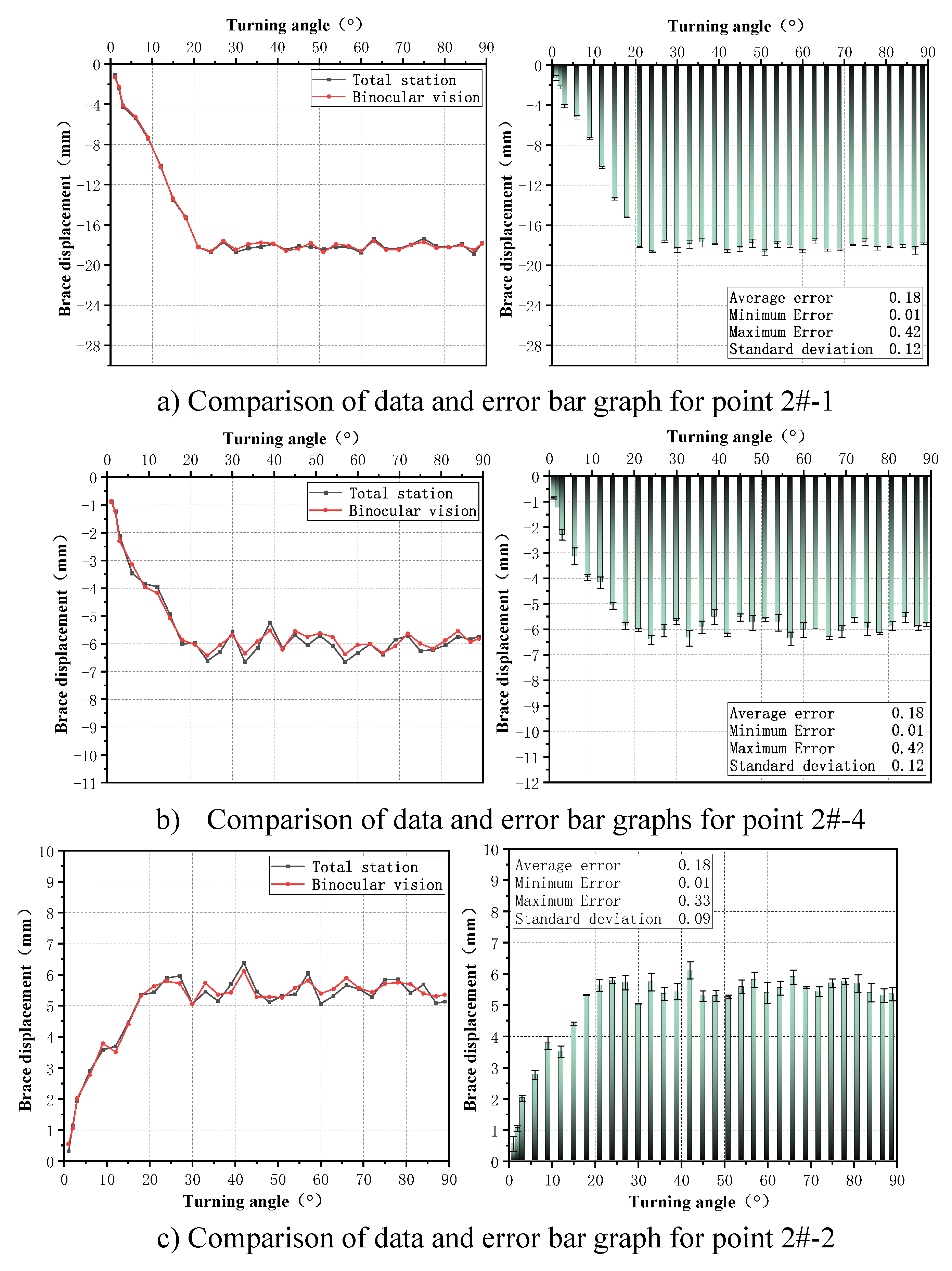
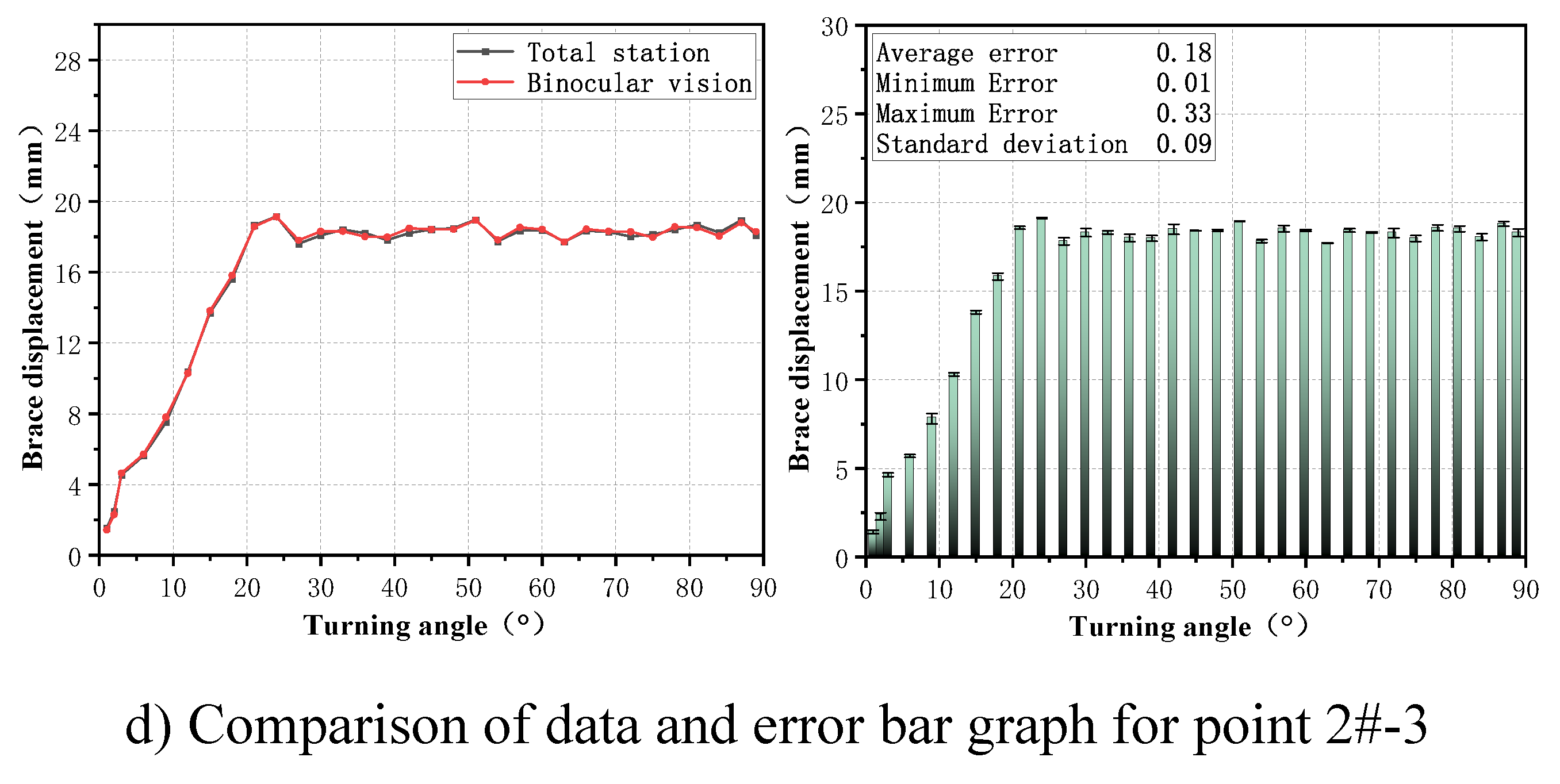
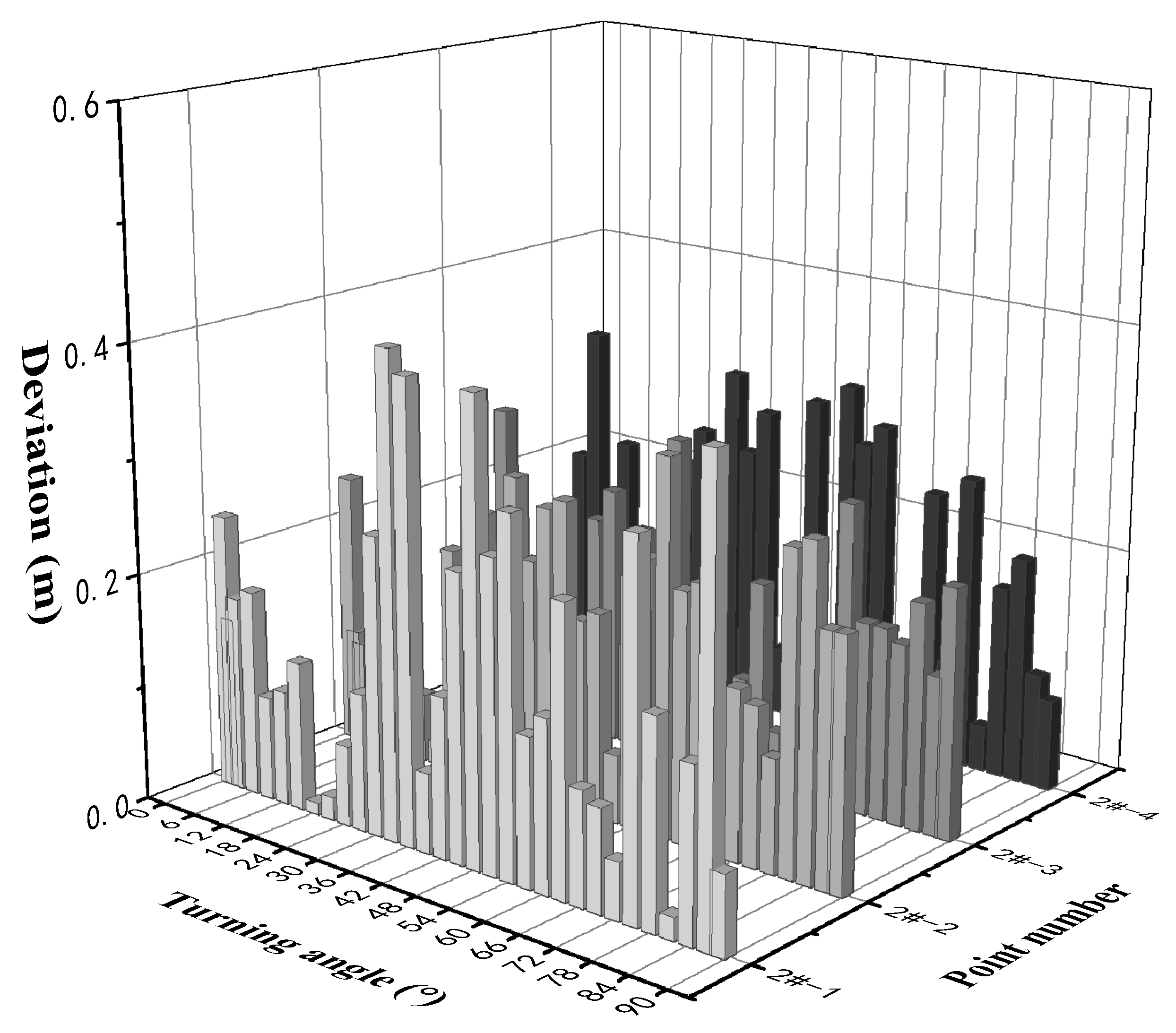
3.3. Analysis of test results
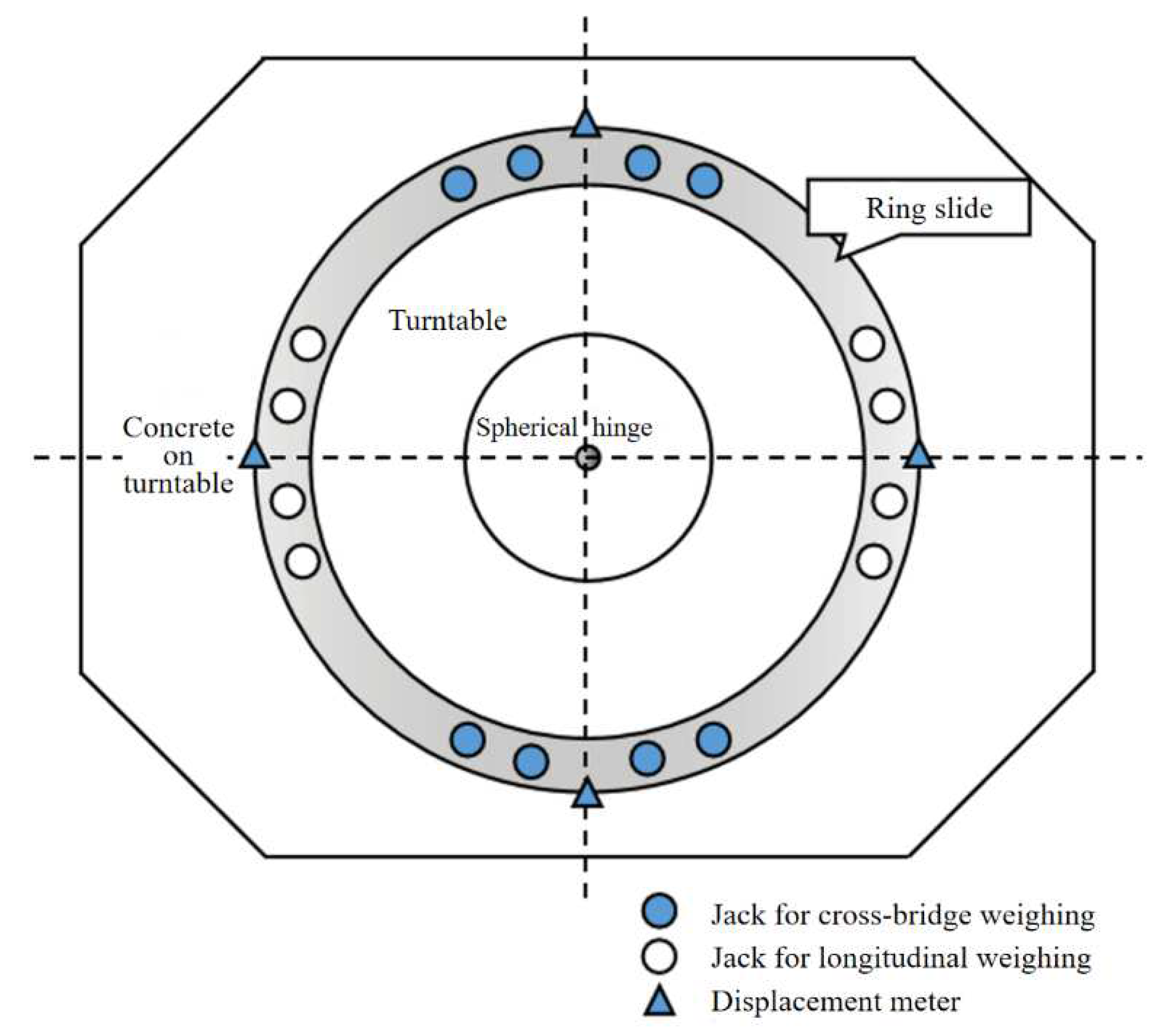
3.3.1. Weighing test and result analysis
3.3.2. Bridge swivel test and result analysis
4. Conclusion
References
- Su, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Cai, C.S.; Dai, G.L. State-of-the-art review of the development and application of bridge rotation construction methods in China. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2021, 64, 1137–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fan, J.F.; Peng, Z.Q. Central Load-Bearing Control in the Construction Process of the Concrete Spherical Joint Nandu River Swing Bridge: A Case Study. Buildings-Basel 2022, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Duan, M.J.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.Z. Research on the critical technique of synchronous rotation construction with large angle for T-shape curve rigid frame bridge. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Moreu, F.; Ozdagli, A.; Taha, M.R.; Mascarenas, D. Noncontact Dynamic Displacement Measurement of Structures Using a Moving Laser Doppler Vibrometer. J. Bridge Eng. 2019, 24, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhang, J. Radar-based multipoint displacement measurements of a 1200-m-long suspension bridge. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 167, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohut, P.; Holak, K.; Uhl, T.; Ortyl, L.; Owerko, T.; Kuras, P.; Kocierz, R. Monitoring of a civil structure’s state based on noncontact measurements. Struct. Health Monit. 2013, 12, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, C.; Bernardini, G. An interferometric radar for non-contact measurement of deflections on civil engineering structures: laboratory and full-scale tests. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2010, 6, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Qian, J.J.I.C.S.E.; Science, E. Study on The Technical Plan of Continuous Beam Rotation Construction Monitoring and Early Warning. 2021, 804, 022075 (022078pp). [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Ni, Y.Q.; Wai, T.T.; Wong, K.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Xu, F. A vision-based system for dynamic displacement measurement of long-span bridges: algorithm and verification. Smart. Struct. Syst. 2013, 12, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Zhang, B.J. Application of integrated binocular stereo vision measurement and wireless sensor system in athlete displacement test. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 4325–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.J.; Feng, Z.Y.; He, L.P.; Shou, Z.H.; Zeng, J.S.; Tan, J.; Bai, Y.; Cai, Q.J.; Gu, Y.C. Accuracy Improvement of Binocular Vision Measurement System for Slope Deformation Monitoring. Sensors 2020, 20, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Zhao, Q.K.; Fan, H.W.; Yu, H.M.; Cui, X.W.; Lv, M.; Li, T.T. Binocular stereo vision calibration based on accurate ellipse detection algorithm of direct calculation and grating conversion check. Optik 2021, 242, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, S.L.; Tang, C.T.; Jin, P. A 3D reconstruction method for pipeline inspection based on multi-vision. Measurement 2017, 98, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Feng, M.Q.; Shinozuka, M. Cost-effective vision-based system for monitoring dynamic response of civil engineering structures. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2010, 17, 918–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.A.; Costa, C.O.; Batista, J.P.J.S. Long Deck Suspension Bridge Monitoring: The Vision System Calibration Problem. 2012, 48, 108-123. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, F.; Gong, Y.; Wang, H.H.; Qin, Z. Modeling of binocular stereo vision for remote coordinate measurement and fast calibration. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 54, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.S.; Wang, S.B. Plane-Space Algorithm Based on Binocular Stereo vision With Its Estimation of Range and Measurement Boundary. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62450–62457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.W.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.J. Phase-Based Calibration Method for a Binocular Vision Sensor. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 44354–44362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, T.; Gong, Z.Q.; Yang, S.T.; Zhang, D.L.; Deng, F. Wireless Binocular Stereovision Measurement System Based on Improved Coarse-to-Fine Matching Algorithm. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 2023, 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Duan, F.J.; Fu, X.; Liu, C.W.; Li, T.Y.; Yan, M. A non-coplanar high-precision calibration method for cameras based on an affine coordinate correction model. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.Z.; Ye, X.W.; Jin, T. Identification of structural dynamic characteristics based on machine vision technology. Measurement 2018, 126, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Cigada, A.; Mazzoleni, P.; Zappa, E. Vibration Monitoring of Multiple Bridge Points by Means of a Unique Vision-Based Measuring System. Exp. Mech. 2014, 54, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.Q.; Fukuda, Y.; Feng, D.M.; Mizuta, M. Nontarget Vision Sensor for Remote Measurement of Bridge Dynamic Response. J. Bridge Eng. 2015, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.H.; Yan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y. Stereovision-based surface flaws detection experiment of foundations of Yiqiao Bridge. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.J.; Ma, M.C.; Zhong, X.; Yu, L.D. A stereovision measurement for large deformation of light structures. Measurement 2019, 136, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Wu, H.Z.; Wu, Y. Vibration monitoring of an open-type one-way tensioned membrane structure based on stereovision. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Wu, H.Z.; Shan, B.H. Application of stereovision on a saddle-shaped membrane structure in aero-elastic wind tunnel test. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.D.; Li, L.; Li, J.; An, S.J.; Hao, H. Computer vision based target-free 3D vibration displacement measurement of structures. Eng. Struct. 2021, 246, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.J.; Cai, Z.W.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, Z.C.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lin, P.J. Investigation of the super-resolution methods for vision based structural measurement. Smart. Struct. Syst. 2022, 30, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.W.; Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Yu, Q.F.; Wu, S.; Zhang, D.S. Unmanned aerial vehicle-aided stereo camera calibration for outdoor applications. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.L.; Wang, Y.W.; Wu, J.J.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, F.; Ma, M.C.; Chen, X.C.; Wang, K.Y. An effective method for camera calibration in defocus scene with circular gratings. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 114, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Z.; Xu, S.X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Localization and measurement method of continuous casting slab model based on binocular vision. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Li, L.J.; Feng, W.X.; Liu, F.; Zou, X.J.; Chen, M.Y. Binocular vision measurement and its application in full-field convex deformation of concrete-filled steel tubular columns. Measurement 2018, 130, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.J.; Yi, W.D. Curvature aided Hough transform for circle detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 51, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.P.; Tan, J.; Hu, Q.J.; He, S.S.; Cai, Q.J.; Fu, Y.T.; Tang, S. Non-Contact Measurement of the Surface Displacement of a Slope Based on a Smart Binocular Vision System. Sensors 2018, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, J.L. Practical limitations of lane detection algorithm based on Hough transform in challenging scenarios. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.B.; Zheng, X.P.; Yin, J.J.; Wang, Y.Y. Research on O-ring Dimension Measurement Algorithm Based on Cubic Spline Interpolation. Appl. Sci.-Basel 2021, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chu, Z.N.; Zhao, K. Target positioning method in binocular vision manipulator control based on improved canny operator. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 9599–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Ge, S.L.; Xie, M.Y.; Hu, F.P.; Jiang, N. An improved industrial sub-pixel edge detection algorithm based on coarse and precise location. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020, 11, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Motion Track Enhancement Method of Sports Video Image Based on OTSU Algorithm. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Li, B.; Ren, F.J.; Dong, R. High-Precision Measurement of Binocular Telecentric Vision System With Novel Calibration and Matching Methods. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54682–54692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, G.W.; Han, Z.; Li, Q.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Pan, H.H. Binocular visual dimension measurement method for rectangular workpiece with a precise stereoscopic matching algorithm. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Shuai, C.Y. Optimization of greenhouse tomato localization in overlapping areas. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 66, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Matrix |
|---|---|
| Rotation matrix R (Right camera with respect to left camera) |
|
| The translation matrix T (Right camera with respect to left camera) |
| Parameters | Left camera | Right camera |
|---|---|---|
| Focal length (fx, fy) |
[1054.28135, 1054.59429] | [1055.49768, 1056.34748] |
| Aberrations (k1, k2, p1, p2, k3) |
[-0.12773,0.35300, -0.0001,-0.00165, 0] |
[-0.05193, 0.08342, 0.00444,0.00557, 0] |
| Main Point (u0, v0) |
[932.06466, 590.30070] | [970.14869, 575.05789] |
| Beam section | Sections | Difference in pouring square volume (m³) |
Section center from bridge Distance from center (m) |
Unbalance moment (kN·m) |
Total (N·m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 2# Main beam |
A | 0 | 3 | 0 | 5517 |
| B | 6.5 | 10.5 | 1638 | ||
| C | -17 | 20.25 | -8262 | ||
| D | 12.5 | 30.75 | 9225 | ||
| E | -4.5 | 41 | -4428 | ||
| F | 6 | 51 | 7344 | ||
| Pier 3# Main beam |
A | 0 | 3 | 0 | 31404 |
| B | -3 | 10.5 | -756 | ||
| C | 19.5 | 20.25 | 9477 | ||
| D | -8.5 | 30.75 | -6273 | ||
| E | 14.5 | 41 | 14268 | ||
| F | 12 | 51 | 14688 |
| Name | Concrete quantity per extended meter (m³) | Weight per linear meter of steel (kg) | Quantity (m) | Distance from the center of the bridge (m) | Unbalance moment (kN·m) |
Total (kN·m) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 2# main beam | Wall Guardrail | 0.64 | 203.5 | 0 | — | 0 | 2753 | |
| Protective Mesh | 0 | 87.78 | 112 | — | 2753 | |||
| Hanger | 0 | 87.49 | 0 | — | 0 | |||
| Pier 3# main beam | Wall Guardrail | 0.64 | 203.5 | 5.05 | 53.48 | -4697.94 | 4326.28 | |
| Protective Mesh | 0 | 87.78 | 112 | — | 2753 | |||
| Hanger | 0 | 87.49 | 128 | 56 | 6271.28 | |||
| Name | Self-weight (kN) |
Unbalance moment (kN·m) |
Eccentricity distance (m) |
Eccentric position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 2# main beam | 165000 | 8270 | 0.05 | Offset to the southeast of the bridge center |
| Pier 3# main beam | 165000 | 35730 | 0.22 | Offset to the southeast of the bridge center |
| Name | Pre-assigned weight (t) | Pre-assigned position | Unbalance moment after pre-weighting (kN·m) | Eccentric distance after pre-weighting (m) | Eccentric position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 2# main beam | — | — | 8270 | 0.05 | Offset to the southeast of the bridge center |
| Pier 3# main beam | 55 | Located 45 m northwest of the bridge center | 10980 | 0.07 | Offset to the southeast of the bridge center |
| Beam section | Frictional moment (kN·m) |
Unbalance moment after pre-weighting (kN·m) |
Jack force arm L (m) |
Maximum jacking force (kN) | Maximum jacking force (kN) | Number of jacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pier 2# main beam | 38808 | 8270 | 5.15 | 9141 | 5930 | 4 x 400 t |
| Pier 3# main beam | 38808 | 10980 | 5.15 | 9668 | 5403 | 4 x 400 t |
| Name | Unit | Longitudinal bridge directionWeighing test value | Cross-bridge directionWeighing test value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unbalanced moment | MG | kN·m | 11019 | 1369 |
| Frictional moment | MZ | kN·m | 23609 | 23505 |
| Static friction coefficient | μ | — | 0.0183 | 0.0182 |
| Eccentricity | e | m | 0.067 | 0.008 |
| Eccentric direction | — | — | Bias to the high mileage side | Bias to the outside of the curve |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





