1. Introduction
According to the National Fire Dada System (NFDS) of the Republic of Korea (ROK), out of 197,480 total fires from 2018 to 2022, 128,390 fires in building structures accounted for 65% of the total. In addition, the total number of human casualties as a result of fires was 10,047, with 1,354 deaths. [
1] The most common casualty of all fires was burns, with 1,065 cases in 2022, an increase of more than 8% from 986 cases in 2018.[
2] In addition, there was an increase of 158 cases of smoke and toxic gas inhalation, from 685 cases in 2018 to 843 cases in 2022, showing a trend of increasing heat and smoke hazards.
Internationally, a 2021 report by The International Association of Fire & Rescue Services (CTIF) found that fire losses in 16 countries accounted for more than 83% of deaths and 70% of injuries in residential dwellings. [
3].
The fire resistance performance of building materials has gained global attention because it is a critical factor in fire response and evacuation. Variables such as fire resistance, durability, smoke emissions, and toxicological hazards of building materials are critical to increasing the likelihood of escape and survival for occupants of residential buildings.
One of the most commonly used building materials is polyurethane (PU) material, which is molded into a foam shape, called PU Foams (PUFs).[
5] PUFs are porous polymers and are often used for thermal insulation in building materials.[
6] Although these PUFs have low thermal conductivity, which makes them excellent for thermal insulation, PUFs are flammable and can contribute to the spread of fire. To compensate for these shortcomings, research is underway to introduce various types of flame retardants.[
7] In addition, the manufacturing method based on chemical foaming has harmful effects on the environment and human health, which has become a global issue.[
8,
9] These issues have led to the globalization of building materials.
Due to these issues, research on basic materials for building materials is underway worldwide. Among them, studies based on cellulose are attracting attention.
In a study by Youngjoo Kim et al, samples of building materials were made using expanded graphite and magnesium hydroxide based on cellulose extracted from waste paper. The basic data was collected based on the ISO 5660-1 test for the samples. The results of the FDS simulation based on the amount of oxygen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide showed a fractional effective dose (FED) value that met the life safety standards of the National Fire Safety Codes 203 and did not exceed a maximum of 0.001. In addition, the cellulose-based building materials reduced the amount of smoke generated, thereby improving the escape time of occupants [
10].
In a study by Sun, J et al, a blend of cellulose, aerogel, and montmorillonite showed higher THR values during the first 62 seconds of the test compared to the results of the cone calorimeter test for a blend of cellulose and aerogel, but the THR values were evaluated as lower after the end of the test. Furthermore, the addition of ammonium hydrogen phosphate resulted in a decrease of 73.33% in the maximum PHRR value and 45.9% in the THR value compared to the cellulose and aerogel blended sample. This showed that the flame retardancy improved as the amount of ammonium hydrogen phosphate ((NH4)2HPO4) added increased.
Methods and manufacturing techniques for additive materials are also being studied. In a study by Rawers, J et al, new materials were prepared by compressing Fe-Al and Fe-C powders using hot-pressing, and the results showed that the microstructural changes contributed to the strength improvement.[
12] Candan, Z et al showed that when paulownia boards were thermally compressed using an experimental hot-press, the moisture content decreased and the density and hardness increased, suggesting that hot-press manufacturing is an alternative method for producing high-performance wood with an environmentally friendly approach.
In addition, according to a study by Han-Hsi, L et al, the toxicity index of organic foam, polyurethane, and polyethylene building materials was evaluated to be higher than 10, indicating a high risk of smoke toxicity. Therefore, it was evaluated that non-combustible materials should be constructed along with building materials to ensure safety against smoke toxicity poisoning caused by fire.
In this study, we tried to produce a building material with a low toxicity index by using ceramic binder and expanded graphite as a flame retardant material based on cellulose from waste paper. In addition, we tried to remove the moisture of the material by using a laboratory-scale hot-press manufacturing method as in previous studies, and to shape the board through the binding force of the ceramic binder. In this study, we used waste paper to formulate flame retardant additives to produce a board using a hot-press manufacturing method in a laboratory, and evaluated its thermal properties using the ISO-5660-1 test and toxicity using the NES-713 test.
2. Method and Materials
2.1. Hot Press Overview
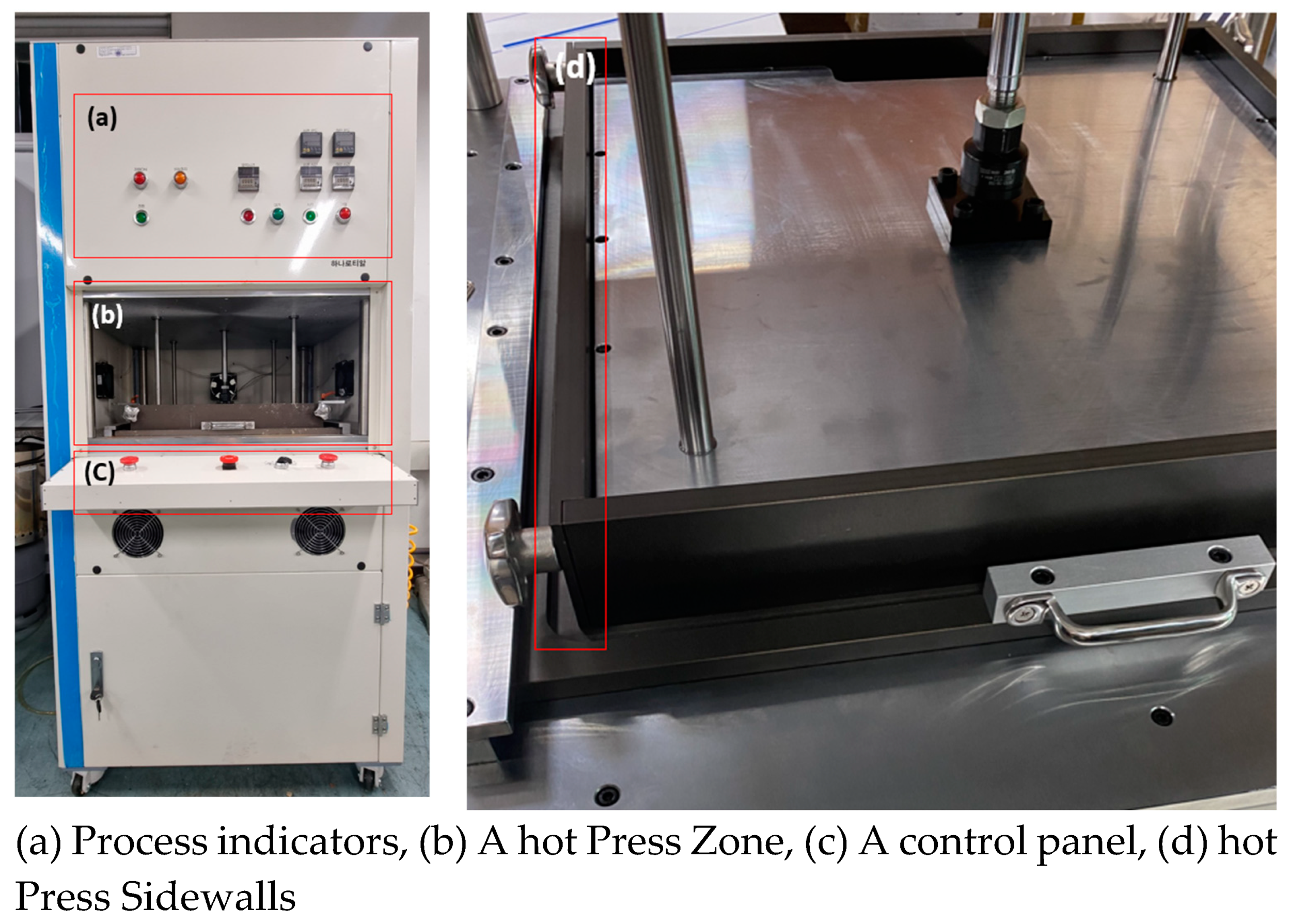
The structure of the hot press used to produce the specimens in this experiment is shown in
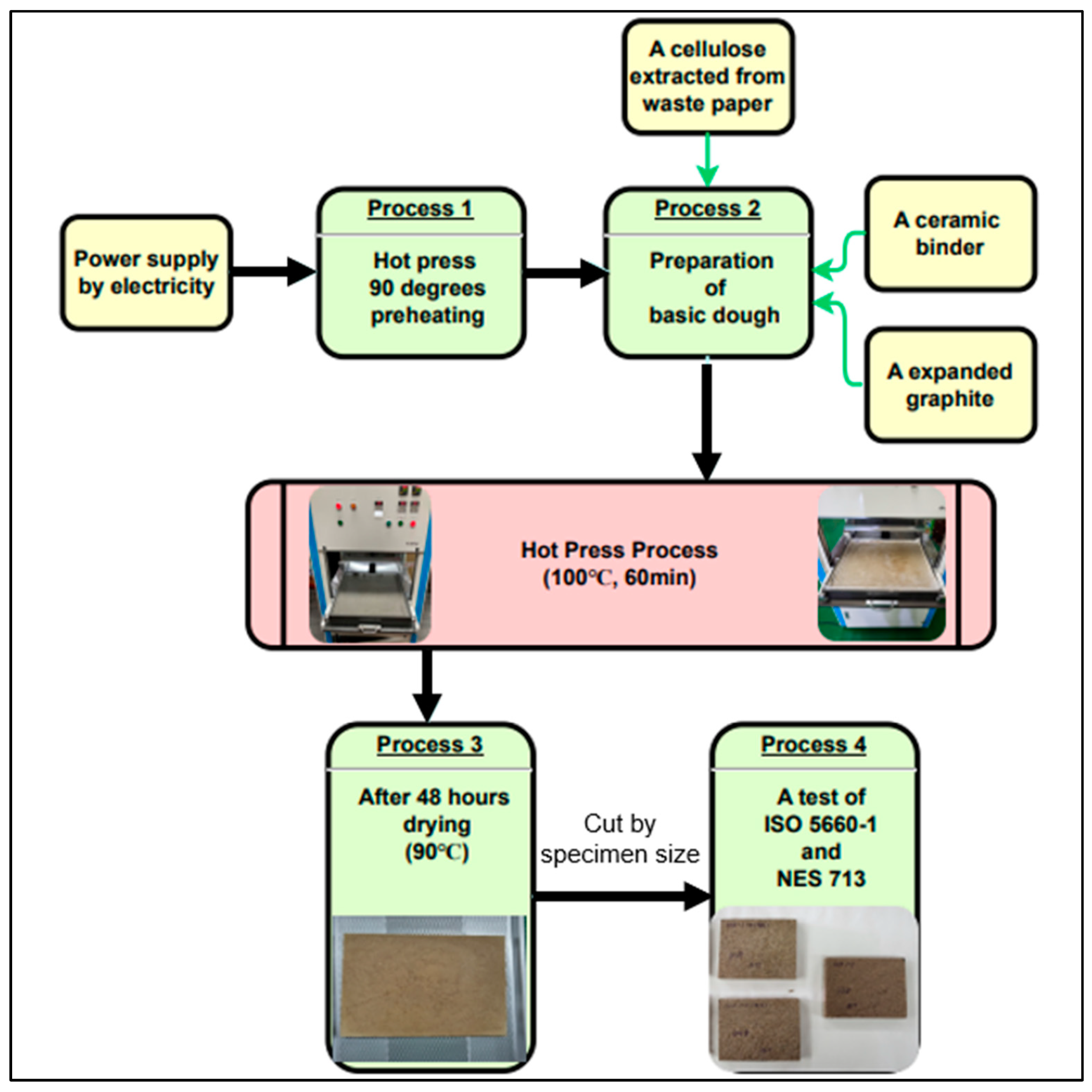
Figure 2. The laboratory hot-press has a structure in which the upper and lower plates can be individually adjusted to a temperature of 150 degrees, and the upper plate rises and falls. In addition, the side walls can be assembled to facilitate the removal of plate-like specimens after they are produced. This function is to prevent damage to the flame retardant board when removing the flame retardant board without sufficient moisture release from the bottom plate. The temperature is equipped with a control system that operates and inhibits the operation at the temperature set by the researcher through a PLC, and the upper and lower operations of the top plate are carried out with positive operation to ensure the safety of the experimenter from pinching and burns. For effective discharge of steam during the process, a steam release line was constructed on the top plate. The kneaded composites were placed in a laboratory hot-press, where the temperature was increased from 90 to 100 for the first 30 minutes to provide pressure and heat for 1 hour. The resulting specimens were dried in a desiccator for 24 hours before being cut to size and used as specimens.
Figure 1.
Lab-scale hot press equipment.
Figure 1.
Lab-scale hot press equipment.
2.2. Plate Flame Retardant Board Specimen Materials
Waste paper was used by purchasing corrugated cardboard from a local recycling center. Expanded graphite and ceramic binder were used as flame retardant materials to reduce the heat emission rate and toxicity index of the plate-shaped flame retardant board. The ceramic binder is 'FP-100' from Sunjin Chemical Co. of Korea. The ceramic binder is composed of 48% MgO, 17% SiO2, 14.6% Al2O3 and other components. In addition, expanded graphite is a 100-mesh product sold by Samjung C&E in Korea.
2.3. Basic dough for flame-retardant boards
The pulping was performed using a pulper with a mixture of waste paper and water. The pulper was operated at a motor speed of 360 RPM for 60 minutes, with a maximum capacity of 16L.
After the pulping process was completed, the primary dehydration process was performed. Basic dough was prepared by mixing cellulose flame retardant materials with a certain amount of moisture removed. The base dough was made into a laboratory-scale plate-shaped building material by hot-pressing. Additives were applied at the rate of 100 Wt.% by weight of waste paper. The units were expressed as Weight % (wt%). The content of ceramic binder was added at 30 Wt.% and 40 Wt.%. In addition, expanded graphite proportions of 40 Wt.% and 50 Wt.% were mixed according to the matrix in
Table 1. In order to check the fire properties of the cellulose-only board, specimens without additives were also prepared as a control.
2.4. The hot press specimen making process
First, the hot-press machine was preheated to a temperature of 90℃. Then, the top and bottom plates were covered with paper foil to prevent the plate-like building materials from sticking to the machine after the process. The base dough was then applied to the bottom plate.
When the second application was completed, the top plate was manipulated to the bottom plate by operating the two-handed button to press the weight of the top plate through pneumatic pressure. The temperature was then raised to 100 °C for 30 minutes to maintain a constant temperature. After that, pressing was carried out for 60 minutes while maintaining the temperature of 100 °C.
Finally, once the process was complete, the top plate was pneumatically lifted upward. The bottom plate was then positioned in front of the researcher to remove the sidewalls, and the plate-like specimen was transferred to a drying plate for post-process drying. The plate was then placed in a dryer to dry at a temperature of 90°C for 48 hours.
Figure 2 shows the process flow chart of the hot pressing process. The plate-like flame retardant board was cut at three random points to meet the specifications of the test specimens for ISO-5660-1 and NES-713 tests.
2.5. NES-713 Experimental Materials
In this experiment, among the products distributed and used as building interiors, PF Board (inner core only), compressed polystyrene foam, MDF, and hot-pressed panel board produced in-house using waste paper were used as specimens. The appearance and components of the specimens are shown in
Table 2. The specimens were cut to a weight of 1±0.2g.
3. Fire and Toxicity Assessment
3.1. Description of ISO 5660-1 test
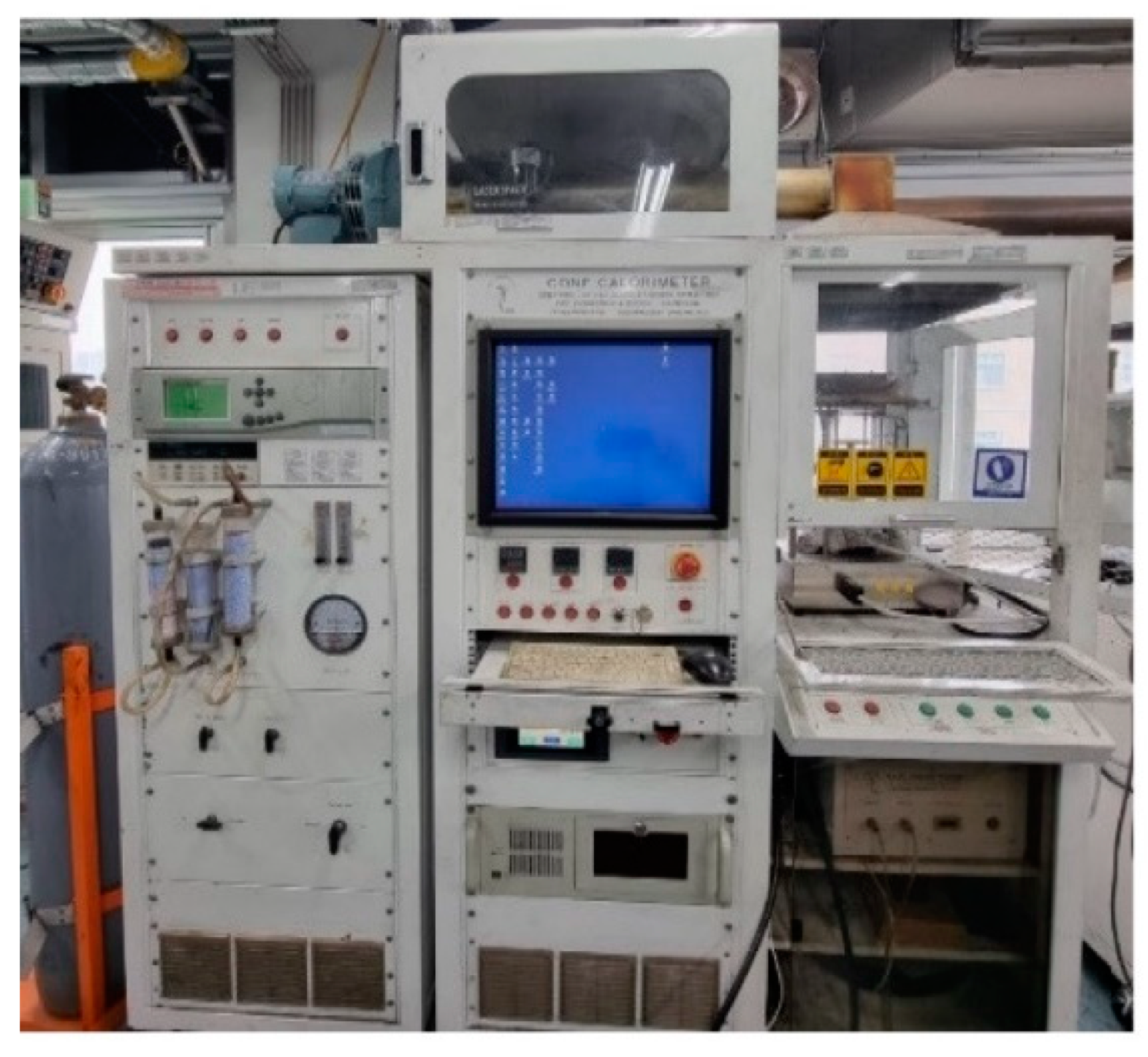
Cone calorimeter testers are often used in small-scale experiments to test the fire behavior of building materials.
Figure 3 shows the cone calorimeter tester used in this experiment. The International Organization for Standardization has adopted the cone calorimeter tester as a standard for measuring the heat release rate (HRR) of test materials. The standard is specified in ISO-5660-1. Huggett, C confirmed that the heat released from building materials is proportional to the oxygen consumed during combustion. He also confirmed that most fuels produce about 13.1 MJ of energy per kilogram of oxygen, based on experiments with different types of test materials. [
15] Based on these results, the amount of oxygen consumed is measured to collect data such as Heat Release Rate (HRR) and Total Heat Release (THR), which are important parameters in fire experiments and fire risk assessment.
The experiments were conducted as follows The specimen dimensions required by the standard are 100 x 100 mm². The specimen is wrapped in aluminum foil, which is joined to a holder so that only the top is exposed to the heat emitted by the heating element in the concalorimeter tester. A spark igniter is placed over the specimen surface and baseline data is collected for 60 seconds before the actual combustion test begins. The experimental data is then measured relative to this baseline.[
16]
Table 3.
A Grade Table of Fire-Resistant Materials according to Fire Characteristics of Building Materials in korea and Japan.
Table 3.
A Grade Table of Fire-Resistant Materials according to Fire Characteristics of Building Materials in korea and Japan.
| Standard |
Korea class |
Japan class |
Heating
Time(min) |
Evaluation Criteria |
ISO 5660-1
(Cone CalorimeterMethod) |
No criteria |
Fire retardancy
Class 1
(non-combustible) |
20 |
- Total Radiant Heat (THR) Heating is 8 MJ/m².
- Max. Heat Radiant Rate does not Exceed 200 kW/m² for Longer than 10 Consecutive Seconds.
- There shall not be Crack that Penetrates Sample, Hole, or Melting (for Mixed Content Materials, Includes Melting and Dissipation of all Core Materials) after Heating for 10 minutes. |
Semi-
Non-combustible
Material |
Fire retardancy
Class 2
(Limited combustible) |
10 |
Fire Retardant
Material |
Fire retardancy
Class 3
(fire retardant)) |
5 |
3.2. Description of NES 713 test
NES 713 tests were conducted to determine the smoke toxicity of currently used building materials and specimens. NES 713 tests are conducted to determine the composition and emission of toxic gases in building materials. The methodology of the NES 713 toxicity test is based on the Naval Engineering Standard code. [
20] The NES 713 test provides a relative toxicity index for concentrations that can cause death after 30 minutes of exposure to a total of 13 gases.
The test is performed using the apparatus shown in
Figure 4. The NES 713 tester consists of a chamber, control panel, and sampling tube. The chamber contains a specimen support, a Bunsen burner to control the flame, a mixing fan to equalize the gas atmosphere in the chamber after combustion, a gas sampling ring tube, and a forced air extraction for internal ventilation after the end of the test. Each sample was cut to ±1g and stored in a constant temperature and humidity chamber at 23±1℃ and 50±5% relative humidity for 24 hours before testing. The prepared specimens were subjected to complete combustion for 2 minutes in a 100-120 mm high flame at a temperature of 1150±25℃ by adjusting the ratio of oxygen and methane gas. After combustion, the mixing fan was operated and the gas was detected through the gas detection tube using a gas detector.
Table 4 shows the concentration values of 13 gases (HF, HCl, HBr, SO
2, H
2S, HCN, HCHO, CH
2CHCN, CO, CO
2, NOX, NH
3, C
6H
5OH) that are lethal after 30 minutes of exposure. Based on these values, the concentration of the gas (Cθ) is calculated using equation (1). In the calibration experiment conducted for 2 minutes before this experiment, carbon dioxide (CO2) was detected at 4,200 ppm, carbon monoxide (CO) at 10 ppm, and nitrogen oxide (NOX) at 1 ppm, and the calculated values were applied as calibration values. The values of 13 individual toxic gases calculated through this are converted to the Toxicity Index using equation (2).
C1 : The Detected gas concentration (ppm), V : Chamber volume (m
3), m : Test specimen mass(g)
1, 2, 3 … n : Converted gas concentration, C
fn : Lethal Concentration for 30 Minutes Exposure(ppm) [
20]
4. Result of Reaction to fire tests and toxicity test
4.1. Result of Reaction to fire tests
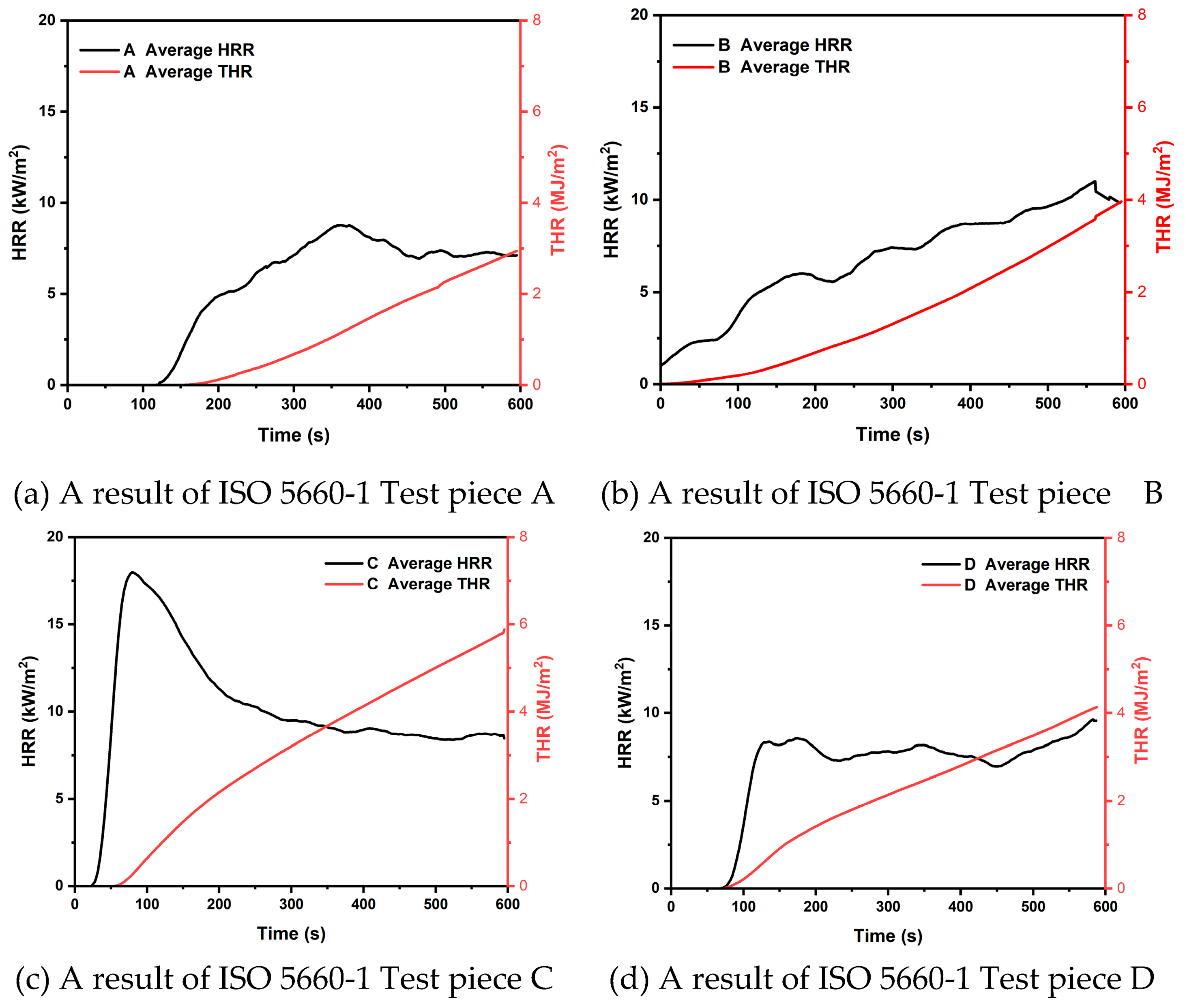
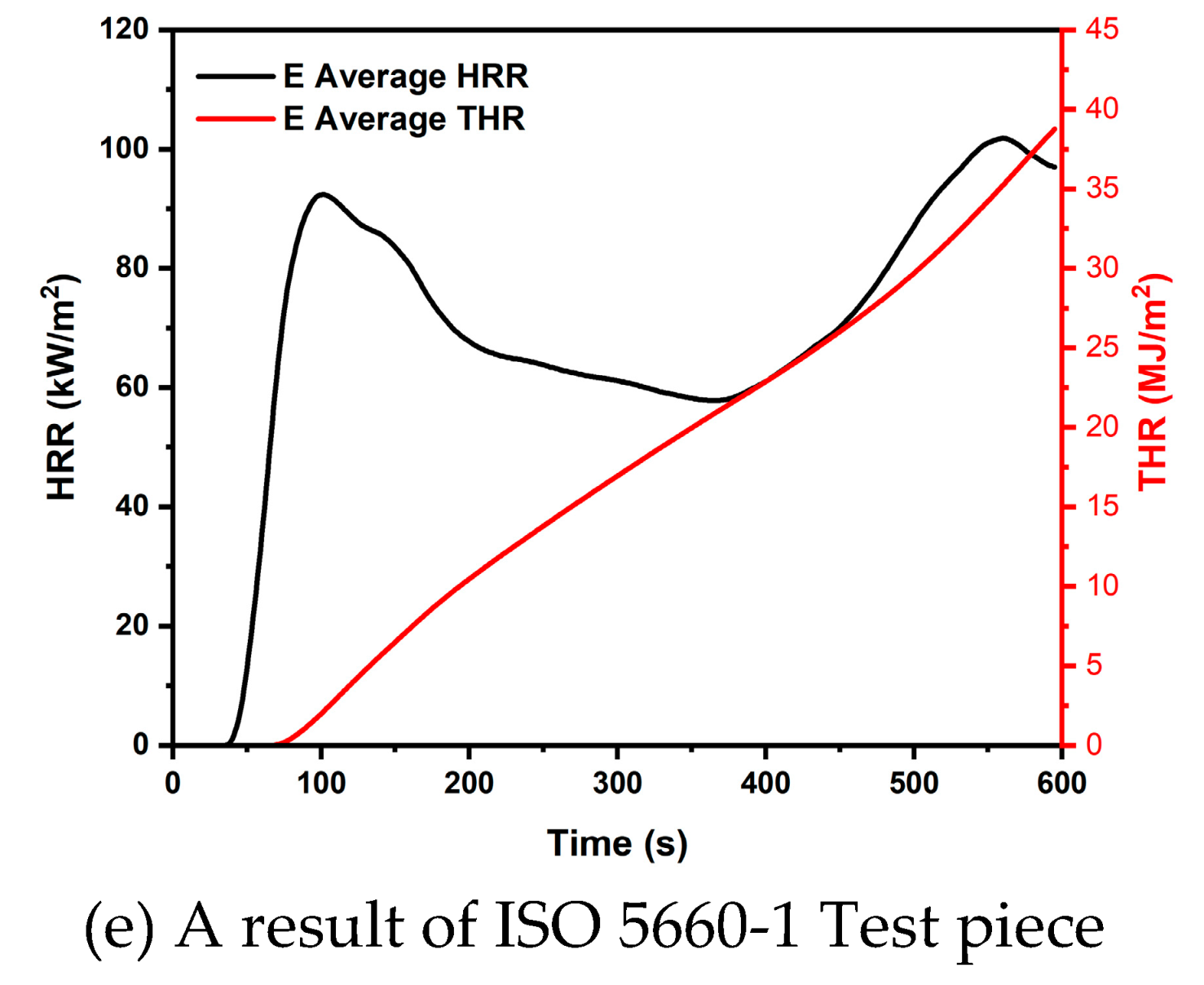
Figure 5 shows the results of the 10 minute THR of the flat board specimens. The average THR value of specimen A was the lowest at 2.9 MJ, and the average THR value of each specimen was 3.9 MJ for specimen B, 5.8 MJ for specimen C, and 4.2 MJ for specimen D. In addition, all four specimens containing additives were not found to have a THR value of more than 8 MJ when tested for 10 minutes, which is the safety standard used in Korea and Japan.
In addition, the HRR values of specimens A, B, and D showed a moderate increase and maintenance after the initial ignition. However, specimen C showed a sharp increase in HRR after the initial ignition, followed by a decrease and maintenance within about 90 seconds. The average Initial Ignition Time (IIT) of the specimens was found to be 70s. For each specimen, the IIT was 116s for specimen A, 31s for specimen B, 42s for specimen C, and 91s for specimen D. The average initial ignition time was 70s.
All the specimens used in this test showed THR values of 8 MJ or less for 10 minutes, which is rated as Semi-Non-combustible Material according to Korean standards. Also. Japan's flame retardant performance standard Class 2 was confirmed.
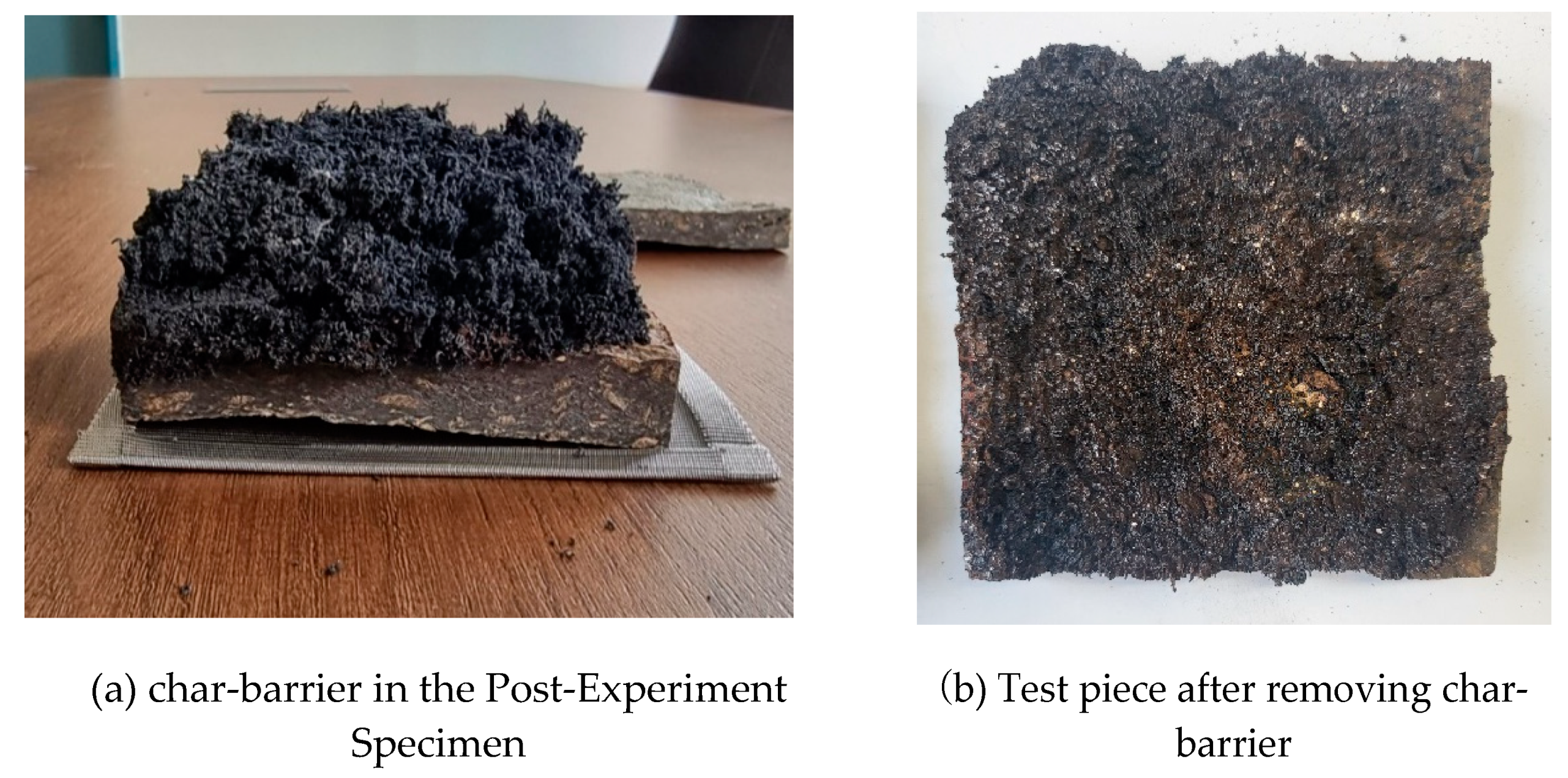
Figure 6 shows the appearance of the specimen after the end of the test. It was visually confirmed that there were no holes or cracks in the specimen through the carbonization surface. This shows the characteristics of the carbonized surface, which prevents the propagation of flame by forming a char film as the expanded graphite expands.
4.2. Result of toxicity test
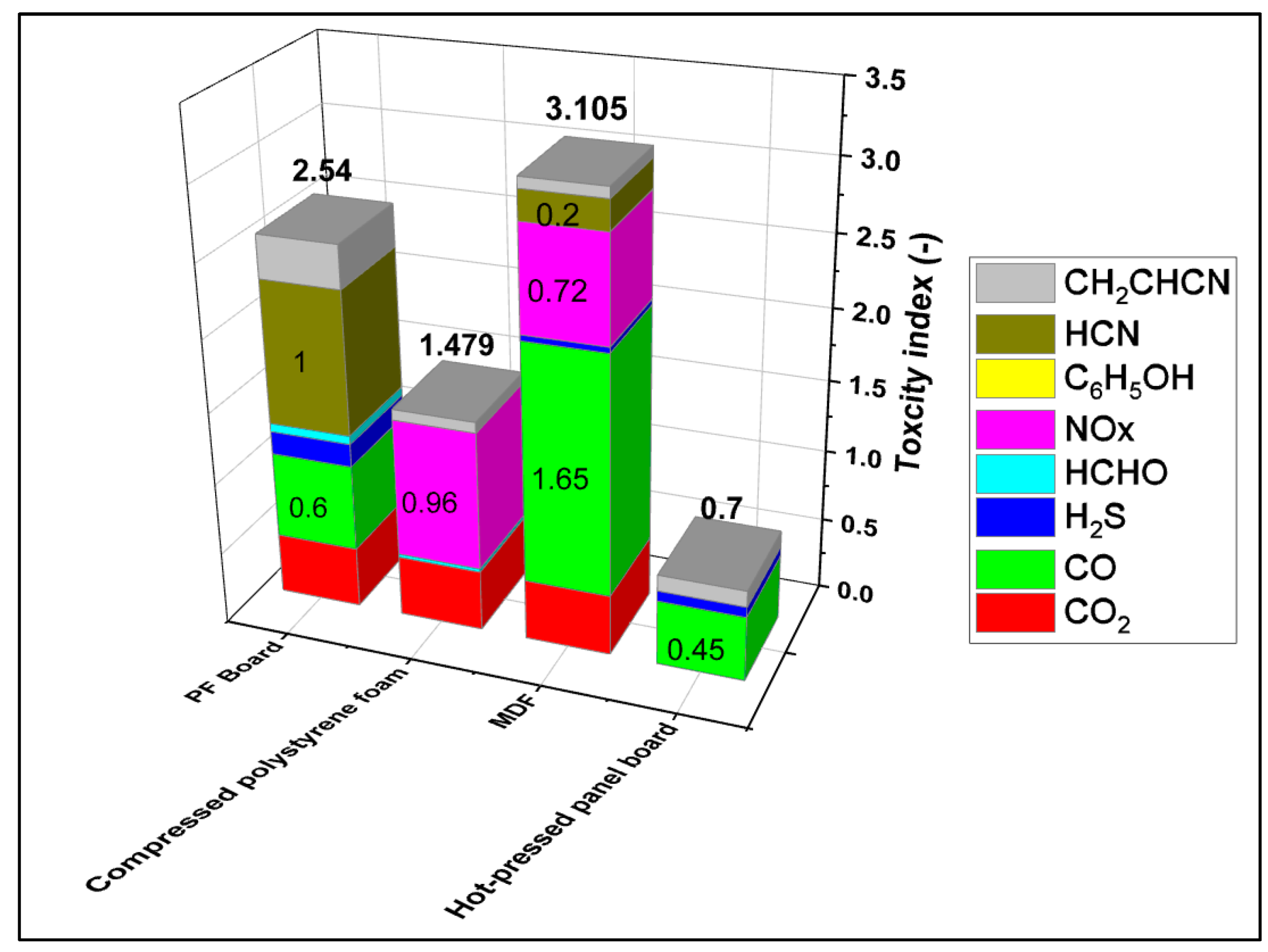
The results of the toxicity evaluation showed that out of a total of 13 gases, only 8 gases were detected except NH3, HCl, SO2, HBr, and HF. The detection results and toxicity indexes are shown in
Table 5.
4. Discussion
4.1. Reliability of specimens
To ensure that the specimens have the same fire characteristics, the standard deviation (SD) was calculated from the THR values of the given specimens. The formula is shown in Equation (3) below. Then, the Relative Standard Deviation (RSD) value was calculated, which was utilized in the study of Ahn et al.
Table 6 shows the mean, SD, and RSD values for the THR values obtained in this study.
where, SD= Standard Deviation, n= Number of data, M= mean
4.2. Toxicity Evaluation Results
The toxicity evaluation results were measured using a detector for a total of 13 gases. However, only 8 gases were detected: Carbon Dioxide (CO
2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Hydrogen Sulfide (H
2S), Formaldehyde (HCHO), Acrylonitrile (CH
2CHCN), Nitrogen-Oxides (NOX), Phenol (C
6H
5OH), and Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN). Among them, the most toxic factors were CO (23.6%) for PF board, CO
2 (28.4%) for compressed polystyrene foam, CO (53.1%) for MDF, and CO (64.3%) for hot-pressed panel board.
Table 7 shows the toxicity index of NES-713 obtained in this study and the ratio of the toxicity index of each building material.
In addition, the evaluation of the overall toxicity index is shown in
Figure 7. Hot-pressed panel board using waste paper was evaluated as having a lower toxicity index than conventional building materials. This shows that the safety of smoke toxicity in case of fire is secured.
The toxicity index of the hot-pressed panel board is 0.7, and the safety against smoke toxicity is about 4.4 times higher than the toxicity index of MDF, which is about 3.1. This is believed to shorten the time of loss of consciousness due to smoke toxicity of fire victims in the event of a fire and improve the evacuation time (A-SET) of fire victims to increase the probability of survival.
5. Conclusion
The following conclusions were drawn from this study.
First, the plate-like flame retardant board produced by hot-pressing based on waste paper showed consistent flame retardant properties and satisfied the semi-non-combustible material of Korea's fire performance standard for building materials and the fire retardancy class 2 of Japan's fire performance standard for building materials.
Second, specimen A showed the lowest THR value and delayed initial ignition time at 50wt% expanded graphite and 40wt% ceramic binder, indicating flame retardant performance.
Third, the plate-like flame retardant board produced in this experiment showed low heat release rate and toxicity value compared to conventional building materials, which suggests the possibility of securing the time required for human evacuation in case of fire.
Through further research, it can be utilized as a basic research for sustainable architecture if the manufacturing method of building materials for mass production is secured instead of a laboratory unit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.R.; Methodology, D.R.; Software, D.P.; Validation, J.H. and D.P.; Analysis, D.R and J.H.; Resources, J.H.; Writing, J.H. and D.P.; Review & Editing, D.R. and J.H.; Visualization, J.H and D.P.; Supervision, D.R.; Project Administration, D.R.; Funding Acquisition, D.R.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Incheon National University Reserch Grant in 2019.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- National Fire Dada System(NFDS) Fire Type - National Statistics Overview - Fire Type 2018-2022. https://www.nfds.go.kr/stat/general.do.
- National Fire Dada System(NFDS) Fire Trend Analysis - National Statistical Overview - Cause of Death 2018-2022. https://www.nfds.go.kr/stat/trend.do.
- N.N, B.; M., A.; S.V., S.; P., W. 2021CTIF No26. World Fire Statistics Magazine issue no 26, 2021.
- Mullins-Jaime, C.; Smith, T.D. Nanotechnology in Residential Building Materials for Better Fire Protection and Life Safety Outcomes. Fire 2022, 5, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyurethane Production, Pricing and Market Demand. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/720449/globalpolyurethane-market-size-forecast/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Ter-Zakaryan, K.A.; Zhukov, A.D.; Bobrova, E.Y.; Bessonov, I.V.; Mednikova, E.A. Foam Polymers in Multifunctional Insulating Coatings. Polymers 2021, 13, 3698 [Google Scholar]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Wicklein, A. Kocjan, G. Salazar-Alvarez, F. Carosio, G. Camino, M. Antonietti and L. Bergström, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2015, 10, 277 —283 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. B. Borrelle, J. Ringma, K. L. Law, C. C. Monnahan, L. Lebreton, A. McGivern, E. Murphy, J. Jambeck, G. H. Leonard, M. A. Hilleary, M. Eriksen, H. P. Possingham and C. M. Rochman, Science, 2020, 1518, 1515 —1518 Search PubMed.
- Plant bio-inspired laminar cellulose-based foam with flame retardant, thermal insulation and excellent mechanical properties.
- Kim, Y.; Park, D.; Rie, D. Evaluation of the Flame-Retardant Performance and Fire Risk of Cellulose Building Finishing Material Due to the Particle Size of Expandable Graphite. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Z.; An, B.; Ma, C.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Thermal-Insulating, Flame-Retardant and Mechanically Resistant Aerogel Based on Bio-Inspired Tubular Cellulose. Composites Part B: Engineering 2021, 220, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawers, J.; Slavens, G.; Krabbe, R.; Groza, J. HOT-PRESS CONSOLIDATION and TENSILE STRENGTH CHARACTERIZATION of MECHANICALLY ALLOYED NANOSTRUCTURED Fe-A! And Fe-C POWDER.
- Candan, Z.; Korkut, S.; Unsal, O. Effect of Thermal Modification by Hot Pressing on Performance Properties of Paulownia Wood Boards. Industrial Crops and Products 2013, 45, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-H.; Ho, M.-C. Toxicity Characteristics of Commercially Manufactured Insulation Materials for Building Applications in Taiwan. Construction and Building Materials 2007, 21, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, C. Estimation of Rate of Heat Release by Means of Oxygen Consumption Measurements. Fire and Materials 1980, 4, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Standards Institution Reaction-to-Fire Tests. Heat Release, Smoke Production and Mass Loss Rate. Part 1, Heat Release Rate (Cone Calorimeter Method) and Smoke Production Rate (Dynamic Measurement). 2021.
- Korea Industrial Standards Committee Reaction-to-Fire Tests — Heat Release, Smoke Production and Mass Loss Rate — Part 1: Heat Release Rate(Cone Calorimeter Method) and Smoke Production Rate (Dynamic Measurement) 2021.
- TAKAHASHI; M. MORITA; M. SAITO; T. HANDA Characterization on Factors in Estimating Fire-Hazardness of Organic Interior Building Materials by Furnace-Test Based on the Pattern in the Modeling of Fire : Part (III) Characterization on the Mode of Combustion of Plywood Panels in JIS A 1321 Type (ISO-Type) Test Furnace. 1973, 23, 23.
- Standard Guide for Understanding and Using Information Related to Installation of Firestop Systems; 2023; Vol. 04.12.
- Ministry of Defense Naval Engineering Standards NES 713, Determination of the Toxicity Index of the Products of Combustion from Small Specimens of Materials 1990.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).