1. Introduction
All European Union (EU) Member States are working towards achieving climate neutrality by 2050. In pursuit of this objective, the European Green Deal introduces a collection of measures outlining the EU's approach to achieving this goal. Within these initiatives, the road transport sector plays an important role. According to the European Environment Agency (EEA), by 2019, the greenhouse gas emissions from road transport have risen by 28% concerning 1990 levels, whereas the EU has witnessed a substantial reduction of 24% in its overall emissions (EEA, 2022). Within this sector, light commercial vehicle (LCV) emissions stand out with a contribution of almost 12%. The environmental impact of road transportation becomes notably pronounced in urban areas, largely owing to the dense populace and concentrated economic endeavors that characterize these regions (Aditjandra et al., 2016).
Additionally, the company's environmental commitment is becoming increasingly relevant (Evangelista et al., 2017). The contribution of logistic activities to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is measured through its carbon footprint. Quantifying a company's carbon footprint involves measuring its direct and indirect GHG emissions expressed in units of CO2 equivalent weight (kg CO2e). Therefore, the emissions reduction in transportation improves the sustainability of the logistic activities, but it can additionally contribute to enhancing the company's financial outcomes and bolstering its reputation (Albitar et al., 2023).
In this context, transport companies are engaged in a process of change to improve efficiency and reduce the carbon footprint of logistics activities (Seroka-Stolka, 2014). Accordingly, one of the most important measures is to prioritize the adoption of electric vehicles and therefore the van fleet renewal is becoming a key factor in the fleet management strategy (Di Foggia, 2021). Nevertheless, the path to fleet electrification is complex, entailing numerous decisions, ranging from the selection of vehicles and energy supply infrastructure to the management of operations. The use of electric vehicles for urban delivery activities is heavily reliant on their cost effectiveness (Tsakalidis et al., 2020), where fleet operators consider the total discounted cost of ownership (TDCO) as the determining factor. Typically, TDCO methodology integrates the present value of all the vehicle costs to accurately assess the actual expenses of employing a specific vehicle alternative (Ellram, 1995).
Therefore, it is evident that appropriate fleet management requires an analysis that incorporates both financial and non-financial information (Karaman et al., 2020; Ortiz-Martínez et al., 2022), considering the integrated information derived from the interaction between economic data and non-financial information like Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) expressed through the annual sustainability company report. This holistic approach is the key to making appropriate fleet replacement decisions.
To this end, the authors have developed an optimization model to efficiently explore viable fleet renewal strategies over a defined planning horizon for the achievement of two conflicting objectives: cost and emission reduction. Considering organizational boundaries it is evaluated the competitiveness of different types of powertrains for light commercial vehicles, such as natural gas (CNG), battery electric (BEV), hydrogen fuel cell (FCEV) and hydrogen fuel cell range extender (FCEREV). The developed model is based on a Multi-Objective Linear Programming (MOLP) and applies a hybrid cost analysis taking into account the vehicle and on-site energy supply infrastructure costs and also the emissions reported in each inventory scope following the Greenhouse Gas Protocol guidelines (GreenHouse Gas Protocol, 2022).
The comprehensive numerical simulations carried out over different study scenarios in Spain demonstrate that the optimization approach not only shows effective fleet renewal strategies but also identifies critical factors that impact the fleet's competitiveness. Additionally, the optimized fleet mix is compared with a fleet composed only of CNG vans. In this sense, the fleet operator managers could analyze the effect of tailored model fleet parameters, such as the van purchase price, van ownership period, the annual mileage demand, and the price and emissions intensity of the energy for van fueling. The investigation approach considers the particular characteristics of electric LCVs, the corporate emissions boundaries, and the on-site van energy supply pathway. Furthermore, to assess the robustness of the optimized strategies and to reduce the model parameters uncertainty, it is conducted a sensitivity scenario analysis of the critical fleet factors.
From this perspective, this study introduces a novel approach by integrating MOLP and the GHG Protocol corporate accounting and reporting standards assessing various types of electric delivery trucks and their on-site refueling infrastructure. Therefore, the fleet operator managers could improve the van replacement decision-making process, optimizing fleet costs and carbon footprint from a sustainability report point of view according to corporate policy.
The organization of the paper is developed as follows: the literature background section is focused on fleet replacement problems with GHG emissions considerations in previous investigations. The methodology and materials are in the following section, explaining the optimization model, the economic and environmental evaluation, the scenario definition, and the data used in the investigation. The following is the results and discussion section. Finally, conclusions are placed in the foreground.
2. Literature background
In fleet management, a critical concern of fleet renewal problems is determining the optimal timing and type of vehicles for replacement. Contrary to earlier research studies that concentrated on fleet optimization models for reducing long-term expenses (Redmer, 2020), the optimization model outlined in this study places its emphasis on reaching the optimal fleet mix minimizing cost and emissions throughout the entire service life in the fleet from the corporate point of view.
Despite some research investigations that explore the environmental and economic effectiveness of using electric vehicles (Lee et al., 2013; Giordano et al., 2018; Onat et al., 2021; Lal et al., 2023), there is scarce literature that has investigated strategies for vehicle replacement considering GHG emission reduction and economic viability simultaneously.
Table 1 summarizes the research studies analyzed and how the authors’ research fits within the existing literature. As can be seen, most of the optimization methods utilized for fleet renewal management challenges relied on a linear programming (LP) model, also the optimization problem is expressed in single (SO) or multiple (MO) objective functions taking into account specific country market characteristics. However, for SO approximation is not possible to achieve a balance between economic and environmental objectives and the optimal solution is highly dependent on the economic magnitude of the vehicle ownership costs. Moreover, the models are subjected to certain constraints considering that the fleet has an adequate number of vehicles to fulfill transportation requirements and satisfy a budget limit.
In general, the economic evaluation is conducted using the TDCO approach, and the environmental impact is evaluated through the GHG emissions converted to a cost function using a carbon tax. However, the research works differ on the cost and emissions quantification scope. In the case of the total cost of ownership, the studies consider the vehicle acquisition and operating costs but dismiss the on-site energy supply infrastructure for electric vans, and this is an important fact due to the limited availability of high-capacity public recharging points and the virtual absence of urban hydrogen refueling stations (HRS). Concerning emission quantification, some of the studies expand the vehicle emissions during operation and incorporate emissions associated with some of the basic phases in the lifecycle analysis (LCA) of a product defined by ISO 14040:2006 (ISO, 2004) such as manufacturing, operation, maintenance and disposal, and even some investigations include emissions associated with the extraction of raw materials, fuel production or manufacture and installation of the necessary energy supply infrastructure. Nevertheless, all the studies analyzed sum up all the emissions and none of them consider the corporate carbon footprint reporting scopes (Scopes 1, 2 and 3) for assessing and quantifying sources of emissions. Additionally, BEVs receive full attention while fuel cell vehicles are dismissed.
Therefore, the developed optimization model allows to efficient exploration of viable fleet renewal strategies over a defined planning horizon for the achievement of two conflicting objectives: cost and emission reduction from the corporate perspective. Considering organizational boundaries, it is assessed at the same time the competitiveness of different types of electric powertrains taking into account the vehicle and energy supply infrastructure costs and focusing on the scopes of the emissions computed in the carbon footprint corporate report. In this light, the conducted research offers a novel approximation to fleet replacement problems enabling a break-down analysis for costs and emissions scopes.
3. Methodology and materials
The multi-objective linear replacement optimization model is based on two cost-objective functions to be minimized: the total cost of ownership and the corporate carbon footprint focused on transport activities at the organizational level.
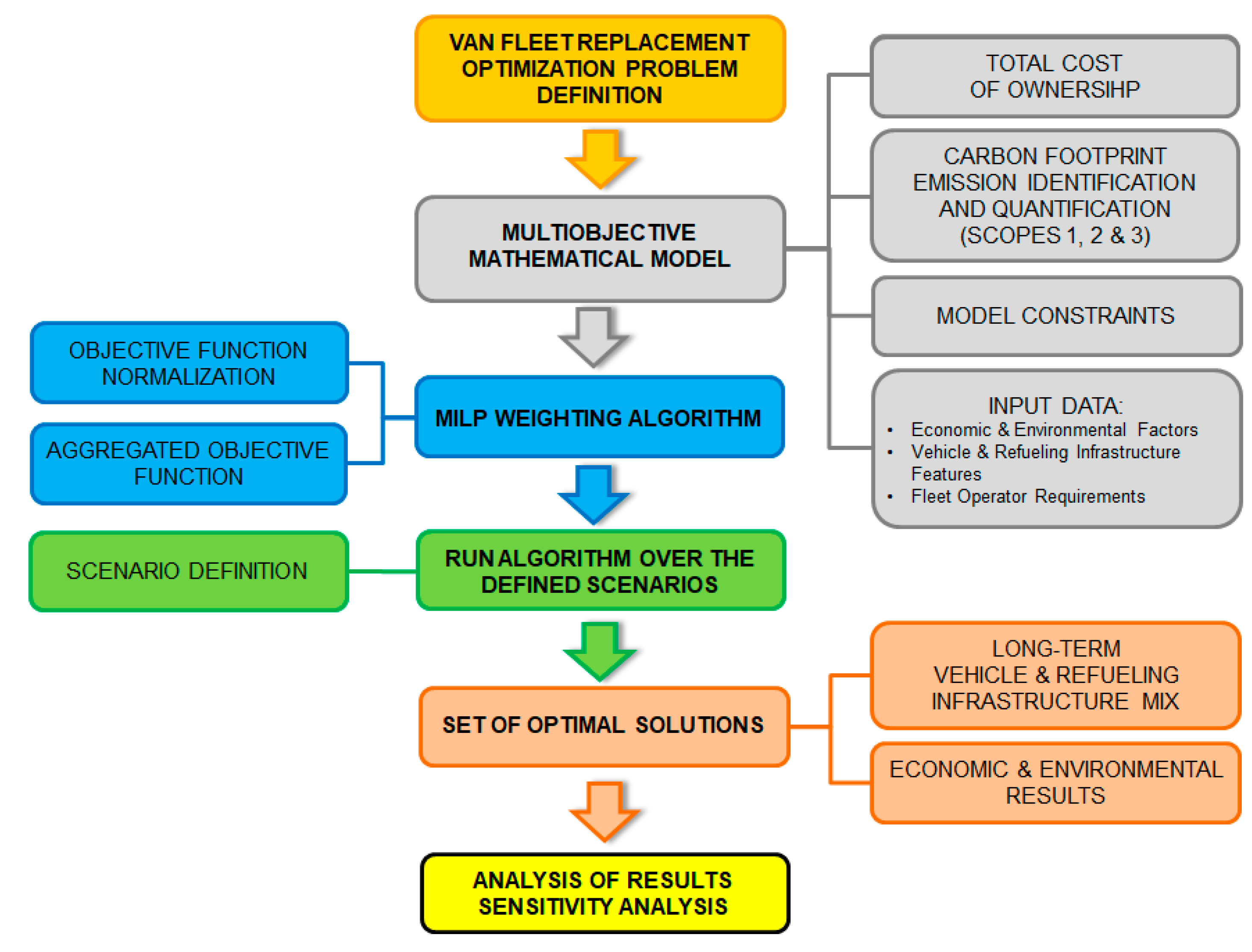
Figure 1 shows the approaching method used to fix the problem of optimal van fleet renewal. Both objective functions are combined using the weighted sum method forming one aggregate objective function (AOF), hence the initial MO problem has been changed into an SO optimization problem. This approach is the simplest and most widely used to solve MO engineering problems (Marler and Arora, 2004; Gunantara, 2018).
Afterward, it is performed comprehensive optimizations over different study scenarios in Spain to find effective fleet renewal strategies and critical factors that impact the fleet's competitiveness. Additionally, the long-term optimized fleet mix is compared with a fleet composed only of CNG vans. In this sense, the fleet operator managers could analyze the effect of tailored fleet operator requirements, such as the annual mileage demand, the van ownership period, fleet size, the corporate emission report scopes, and the on-site van energy supply pathway. Furthermore, to assess the robustness of the optimized strategies and to reduce the model parameters uncertainty, it is conducted a sensitivity scenario analysis of the critical fleet factors.
For each solution, the model's outcome comprises the fleet composition every year of the planning horizon (number of vans and energy supply infrastructure assets in use, purchased or retired), a set of economic results (per kilometer cost and the cost breakdown) and environmental results (per kilometer emissions and the emissions breakdown per scope).
This section has been split into three parts. The initial subsection is focused on establishing the model and providing the mathematical framework for the linear optimization algorithm. Afterward, it is exposed the scenario settings where it will be executed the optimization algorithm. Finally, the model input data is outlined and described.
3.1. Model definition and mathematical formulation
The model developed for the optimization of the fleet renewal challenge relies on deterministic linear programming. Moreover, it is considered that the fleet size is enough to meet transport demand and there is a budget limit.
The mathematical expression of the optimization problem is based on the algorithm developed by Figliozzi (Figliozzi et al., 2011). The novelty relies on the incorporation of the corporate carbon footprint quantification objective function split in scopes. Thus the original SO changed to an MO optimization problem. For a better understanding, the model’s indices, parameters and decision variables are explained in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4.
The mathematical expression of the MO algorithm is shown in Equation (1), where the objective function is a weighted combination of the economic aspects (
) calculated using the TDCO method and the expected monetary burdens for carbon emissions (
). Since the objective functions have different scales, it is necessary to standardize them into a non-dimensional format. This process is commonly known as normalization.
Where:
are the weighting coefficients where: and 0 ≤ ws ≤ 1
represents the scalarization factor for the objective function . It is computed as the highest value of the within the context of the examined current scenario.
represents the scalarization factor for the objective function . It is computed as the highest value of the within the context of the examined current scenario.
In this approach, the weights (
) represent the fleet operator's pre-established preferences. To find an approximation of the Pareto frontier, the optimization algorithm varies the weighting coefficients in the range of 0 to 1 and solves successive problems. Nevertheless, the appropriate choice of these weights can prove to be a considerable challenge. For this purpose, the authors have used the proposed method by Shahriari (Shahriari et al., 2011) to find the suitable weights as explained in Equation (2).
Where:
is the evaluation of the objective function
at its optimal solution
and it is defined as:
is the evaluation of the objective function at the optimal solution of the objective function () and it is defined as:
is the evaluation of the objective function at its optimal solution and it is defined as:
is the evaluation of the objective function at the optimal solution of the objective function () and it is defined as:
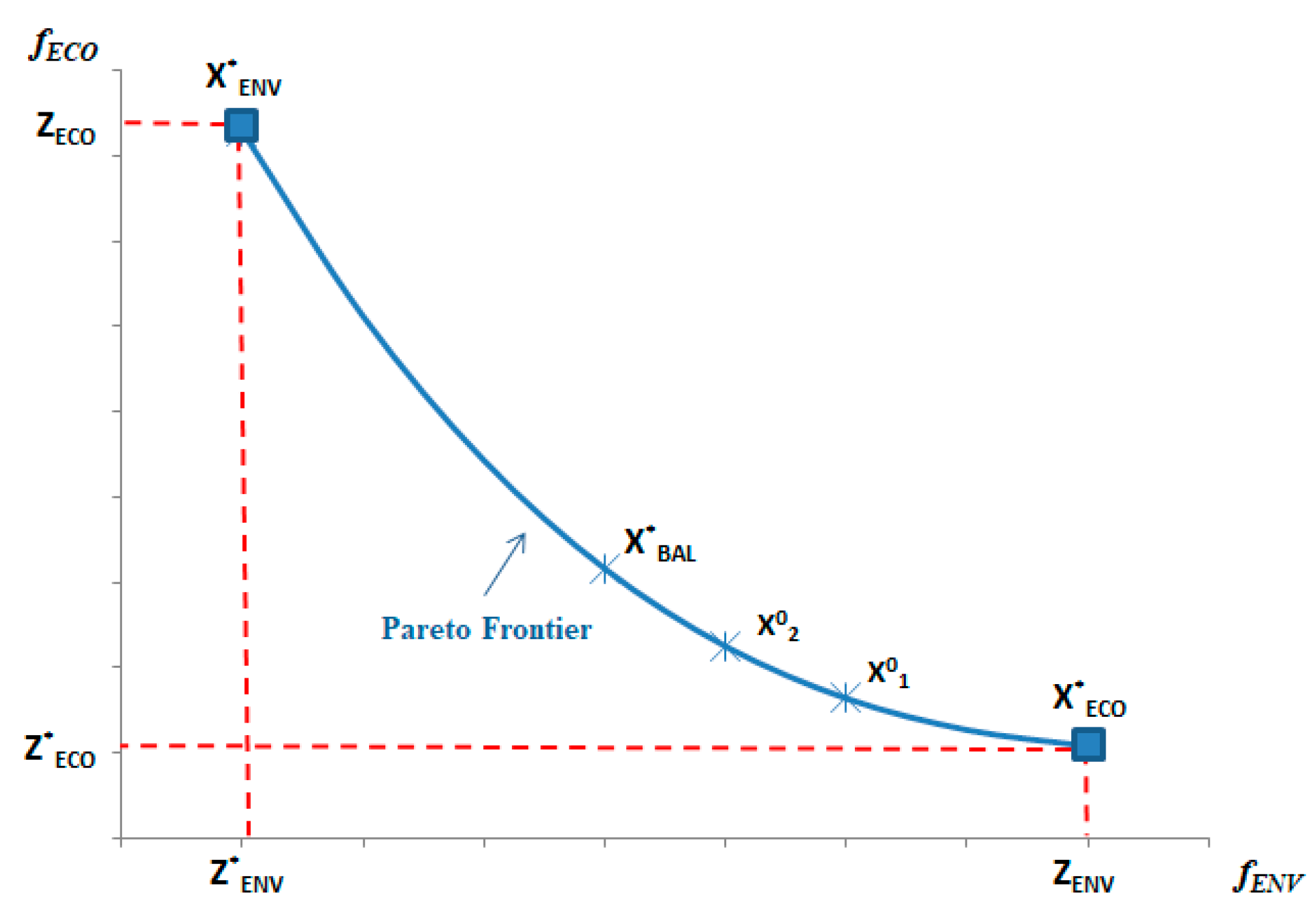
In this sense, it is possible to highlight three key solutions over the Pareto frontier (
Figure 2): economic (ECON -
), environmental (ENV -
) and balanced (BAL -
). The ECON solution provides the highest cost reductions (
, but the ENV solution shows the highest emission savings (
. However, the BAL solution is calculated considering the highest emissions savings are achieved with the lowest cost increase (
and
). The
value is obtained iteratively from
until a predefined percentage for reduction in costs is achieved.
The aggregated cost-objective function defined in Equation (1) is governed by the constraints expressed in Equation (3) to Equation (30). Every year, the fleet vans have to travel the distance specified by the fleet operator, Equation (3). Equation (4) and Equation (5) ensure that the quantity of acquired type "k" vans aligns with the new registrations of type "k" van entries. Equation (6) determines that the initial number of type "k" vans is calculated by the sum of vans of type "k" in operation and vans disposed of by the conclusion of the initial period. Equation (7) ensures the balance of van numbers year-on-year. Every van must be disposed of by the end of the final year, Equation (8). Upon the completion of its ownership duration, a van is obligated to be disposed of, Equation (9), and a newer van cannot be sold until it reaches the ownership duration, Equation (10) and Equation (11). Equation (12) and Equation (13) dictate the substitution of aging vehicles with new counterparts. There is a yearly budget limit for purchasing new vans, Equation (14). Equation (15) and Equation (16) express that there are sufficient charging points to recharge every day all the electric vans in the fleet, while the HRS must possess the capability to refuel the entire fleet of hydrogen-powered vans stationed at the depot daily, Equation (17) and Equation (18). Whenever hydrogen vans are present, there should be a minimum of one dispenser accessible, Equation (19). Equation (20) indicates that there is an annual budget for acquiring new energy supply infrastructure assets. The number of newly purchased infrastructures of type "r" must match the infrastructures of type "r" in use each year, Equations (21) and Equation (22). The energy supply infrastructure assets are in operation throughout the entire analysis period, Equation (23) and Equation (24). The energy supply infrastructure assets should be decommissioned when reaching their service life, Equation (25), or the last year of the planning horizon, Equation (26). Infrastructures can not be scratched before reaching their service life, Equation (27) and Equation (28). Equation (29) and Equation (30) show that variables are integer or binary numbers.
1.1.1. Total cost of ownership calculation
TDCO encompasses the complete ownership expenses of the asset, whether it's a vehicle or infrastructure, computed annually and expressed in present value terms, incorporating adjustments for discount rates and inflation. The cumulative yearly expenditures of the fleet are established through the aggregation of vehicle costs and the associated refueling infrastructure as expressed in Equation (31). Among the latter, variable costs include energy, maintenance and repair (M&R) expenses, while fixed costs cover circulation taxes and fees for insurance. Concerning infrastructure costs, it is considered the acquisition and scrapping values and M&R costs.
Where:
VRV are the revenues due to the vehicle resale at the end of the ownership period. It is defined as:
VOP are the vehicle operating costs (fixed and variable) due to the energy consumed, M&R activities, circulation taxes and fees for insurance. It is defined as:
API refers to the acquisition cost of energy supply infrastructure. It is defined as:
ISV represents the revenue attributed to the residual value of the infrastructure upon completion of the service life. It is defined as:
IOP are the infrastructure operating costs due to M&R activities, defined as:
1.1.1. Evaluation of corporate carbon footprint
To assess the carbon footprint, the authors have taken into account the guidelines outlined by the GHG Protocol (GreenHouse Gas Protocol, 2011; GreenHouse Gas Protocol and Carbon Trust, 2013) because it is one of the most widely used tools for assessing emissions inventories in companies (Schmied et al., 2012). The first step for corporate carbon footprint quantification is to delimit the scope of emissions according to organizational boundaries, followed by the emissions inventory data collection. In this research, the organizational boundaries are specified under the operational control approach, and in this case, it is focused on transport activities. Hence, for calculating the corporate footprint it is considered GHG emissions derived from (i) transport realized by the company’s vehicles (Scopes 1 and 2), (ii) cradle-to-gate emissions stemming from the company's acquisition of fuels and energy, and the corresponding transport and distribution losses of purchased electricity (Scope 3 – Category 3
rd), and finally, (iii) cradle-to-gate emissions of the vehicles purchased by the company (Scope 3 – Category 2
nd). In addition, the investigation considers the energy supply facilities acquired to fulfill van operational requirements. In this sense, these assets are in category 1
st of Scope 3. Nevertheless, in this study due to the power magnitude of the infrastructure means and the long lifetime considered, it is supposed that the emissions intensity of the acquired energy supply components is negligible compared to the emissions due to electricity production considered in Scope 2 (Wulf and Kaltschmitt, 2018; Bareiß et al., 2019; E4tech, 2019). Furthermore, the investigation scope considers on-road operation emissions from energy consumption, therefore maintenance and repairing related emissions are overlooked. The cost-objective function for the carbon footprint quantification (
) is shown in Equation (32)
, this variable is binary, assuming a value of one when Scope 3 emissions are taken into consideration
EQS3 quantifies the emissions encompassed within Scope 3. It is defined as:
The calculations used for the GHG accounting in each scope are explained in the following paragraphs. Additionally, for the GHG emissions quantification, it is used an emission factor (EF) (IPCC, 2007) measured in kg CO2e per activity unit.
1.1.1.1. Direct emissions: Scope 1.
This category accounts for emissions arising from the fuel usage of the company's van fleet. Equation (33) quantifies the GHG emission based on the yearly van CNG consumption.
Where:
is the EF associated with CNG (
Table 7)
1.1.1.1. Indirect emissions: Scope 2
This category comprises emissions linked to the purchased electricity utilized for van operations. In this study there are three cases of electricity consumption depending on the type of electric van:
BEV: the electricity power consumption comes from recharging the battery.
FCEREV: the electric power consumption is derived from both battery recharging and hydrogen supply.
FCEV: the electricity is used for hydrogen supply.
The electricity consumption for hydrogen supply depends on the hydrogen pathway used. In the case of purchasing the hydrogen in 20 MPa pressurized tanks, the electricity consumption comes from raising the pressure to 90 MPa and pre-cooling before dispensing the hydrogen into the vehicle. Conversely, should hydrogen production occur on-site through electrolysis it is necessary to add the electrolyzer consumption and the compressor consumption to raise the pressure from the electrolyzer outlet to 90 MPa. Equation (34) expresses the emission quantification based on the yearly electricity consumption.
Where:
is the EF associated with the Spanish electricity production mix (
Table 7)
1.1.1.1. Other indirect emissions: Scope 3
This category encompasses emissions attributed to van manufacturing as well as those related to the value chain of the energy consumed.
Electricity indirect GHG emission included in this scope comes from transmission losses of the purchased electricity reported in Scope 2. Equation (35) calculates the emissions based on the yearly electricity consumption and a grid loss factor (GLF). The GLF quantifies the grid losses and depends on the transmission distance. Usually, the GLF can be rated as 3 to 14% of the energy transmitted (Ministerio de Industria y Energía, 2014). A 6% value is used in the study according to International Energy Agency recommendations (IEA, 2020).
Furthermore, in the hydrogen purchased case, it is considered the emissions from hydrogen production, conditioning and distribution. If hydrogen production is made using renewable energy sources it is counted as zero emissions. The distribution mode considered is employing trailers with diesel trucks. The trailer hydrogen mass transportation capacity (
is 700 kg at 20 MPa (DOE, 2015) per trailer with a distance separating the hydrogen generation location and the end-user (
at most of 300 km. The energy spent in the compression of hydrogen is between adiabatic and isothermal ideal-gas compression values, and it is considered an electricity consumption for hydrogen pressurization up to 20 MPa (
) of 1,8 kWh/kg (Ligen et al., 2018). The EF associated with hydrogen pressurization and truck transportation is calculated in Equation (36). The evaluation of this expression results in 1,2 kg/CO
2e per kilogram of hydrogen transported, this value is more conservative than others used in related studies (Ramsden et al., 2013; Wulf and Kaltschmitt, 2018), which considers less than 1 kg/CO
2e.
Where:
Equation (37) expresses the emission quantification based on yearly van hydrogen consumption. Although in this research work the main concern is the utilization of hydrogen derived from sustainable sources, for sensitivity analysis purposes it is considered the scenario where the hydrogen supplied to fuel the fleet is blended with 40% of hydrogen obtained via steam methane reforming (SMR) to take into account the effect of using blended hydrogen option. These emissions are allocated in Scope 3 – Category 1
st.
Where:
The emission associated with the acquisition of vans is assigned to Scope 3 – Category 2
nd and it is calculated according to Equation (38). In this scope, it is considered the emissions related to the manufacturing stage, not contemplating the end-of-life emissions because the vans will be sold in the second-hand market. For the manufacturing emission analysis, it has been designed a simplified vehicle model, which is composed of a body and an engine unit, and includes not only the vehicle’s manufacture emissions but also the raw materials exploitation (Buberger et al., 2022). It is supposed that the EF associated with van body manufacturing is the same for all the van types analyzed. However, this is not the case for the engine unit which is different for each technology. The results obtained with Equation (38) are consistent with the literature values (Buberger et al., 2022).
Where:
is the k-type van body mass (
Table 8)
are the cradle-to-gate GHG emissions related to vehicle chassis manufacture (
Table 9)
is the i
th powertrain component characteristic of the k-type van: electric motor, traction battery, fuel cell system, hydrogen tank, CNG tank and ICE powertrain (
Table 8)
are the cradle-to-gate GHG emissions associated with the i
th powertrain component (
Table 9)
3.2. Scenario definition
A scenario reflects a probable situation of the vehicle fleet in the Spanish market (Castillo Campo and Álvarez Fernández, 2023). The design of the scenarios revolves around three key fleet operator variables, two emission reporting modes (with or without Scope 3 emissions), and two hydrogen supply pathways. The fleet operator variables are the yearly distance to be covered by each van in the fleet, the van’s ownership duration and the size of the fleet. By the way, the hydrogen supply pathway for the hydrogen refueling station (HRS) located at the depot could be acquired from a supplier (P scenarios), or generated on-site using an electrolyzer (G scenarios).
Table 5 summarizes the variable values for the different scenarios. The baseline scenario is configured according to the business-as-usual behavior of Spanish fleets.
3.3. Model data
The data input required for the optimization algorithm, expressed in Equation (1), is quite extensive. Additionally, the model considers the following assumptions: (i) The planning horizon time frame is 25 years (2025 to 2050), (ii) at the beginning of the planning horizon, the fleet company has a specific quantity of CNG vans evenly distributed across various ages, spanning from 0 to the duration of ownership period, and thus there are no energy supply infrastructures for electric vans, and finally (iii) the budgetary limit for acquiring vehicles and infrastructure assets is high enough to facilitate the replacement of older vans with the highest-cost electric van.
Data for cost objective function (
), such as initial fleet conditions, fleet manager requirements, van and energy supply infrastructure technical features, and the economic parameters are compiled from Castillo (Castillo Campo and Álvarez Fernández, 2023).
Table 6 compiles the basic economic parameters needed for the optimization simulations.
Furthermore, the compilation of environmental data for the economic quantification of the carbon footprint (
) have uncertainty due to the diversity of data sources, collecting methodologies and locations considered, but it is representative of the European area.
Table 7 compiled the GHG EF for the carbon footprint quantification referred to van energy consumption. Additionally,
Table 8 and
Table 9 show the van powertrain characteristics and the respective GHG EF needed for the evaluation of the emissions accounted for in Scope 3 related to vehicle manufacturing.
Finally, the carbon pricing forecast for the complete planning horizon is based on the data shown in the Carbon Pricing Dashboard of The World Bank (The World Bank, 2021). In this report, the carbon pricing in Spain is 18 €/tonCO2e and the maximum value is 137 €/tonCO2e, reached in Sweden. The average value is 77,5 €/tonCO2e, and it is used as the reference for this investigation.
4. Results and discussion
The optimization algorithm is executed over the scenarios described in the preceding paragraph. In each scenario, it is analyzed the economic (ECON), environmental (ENV) and balanced (BAL) solutions from the Pareto frontier. However, the BAL solution ensures a balance between the competing objectives of cost savings and emission reductions and it will be considered the optimal solution for further discussions in this section. Furthermore, optimal solutions are compared with a reference solution, where the van considered for replacing the old ones is always the CNG type.
The optimization algorithm provides a set of results that comprise:
Fleet mix: distribution of fleet vehicles (type and age) every year within the planning horizon and the evolution of the infrastructure required to service the van fleet. These results are post-processed and translated into the fleet share, it shows the average share of each type of electric van in the fleet, and the replacement rate, it expresses the percentage of time when the electric vans in the fleet are the majority (over 90%).
Economic results: average cost per kilometer of the fleet and cost breakdown.
Environmental results: average emissions per kilometer of the fleet and emissions broken down into Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
Finally, for the baseline scenario and BAL solution, it is conducted a sensitivity analysis over different combinations of the model parameters to calibrate their effect on the fleet mix, the cost and emissions rate per kilometer. The parameter sensitivity is evaluated with the expression shown in Equation (39).
Where:
Afterward, it is evaluated the robustness of the solutions using the worst-case scenarios analysis. The outcomes derived from the sensitivity assessment make it possible to fix the key parameters used to build up the worst-case scenarios.
4.1. Fleet mix
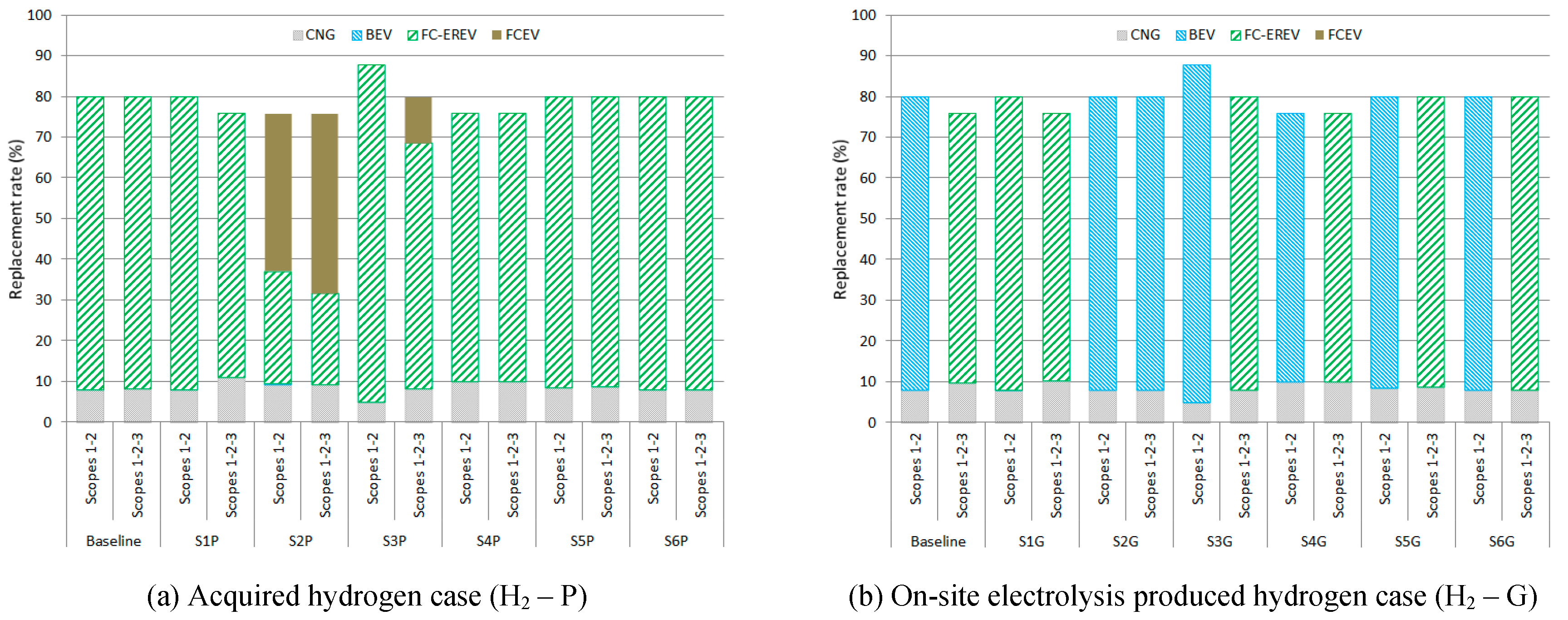
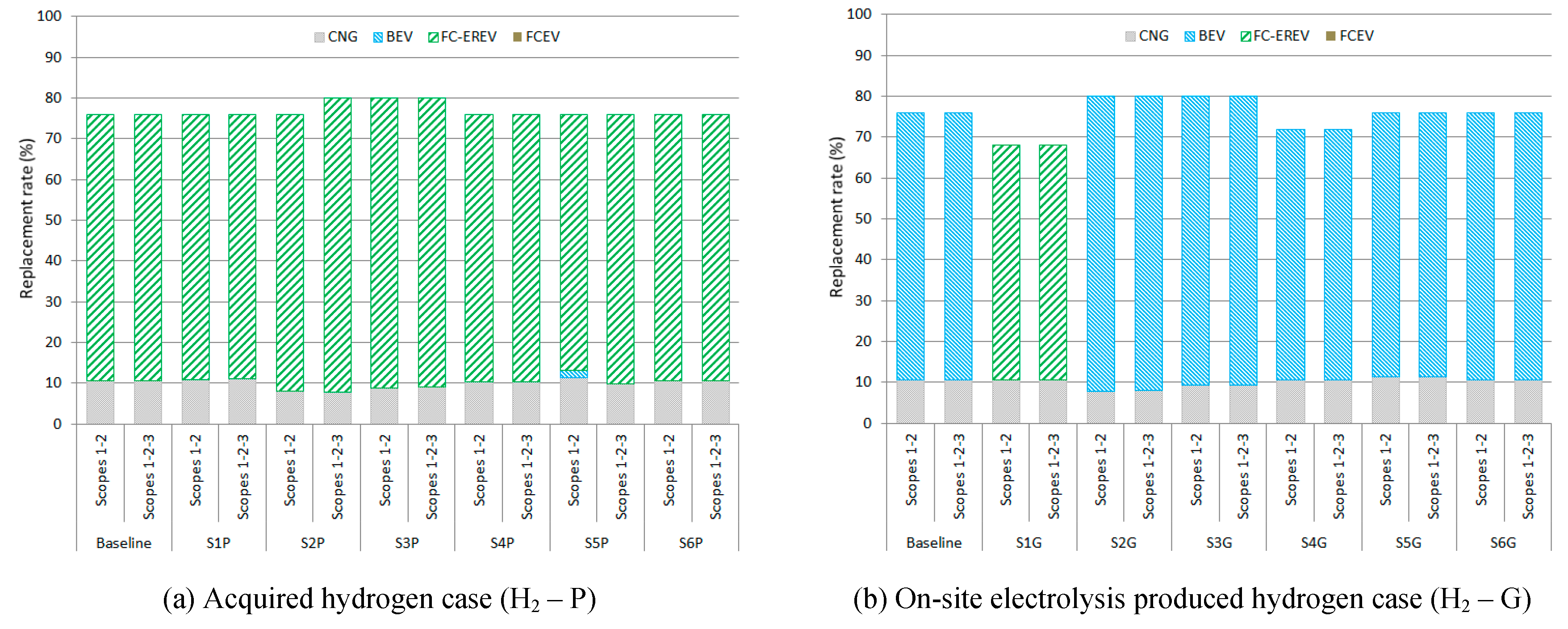
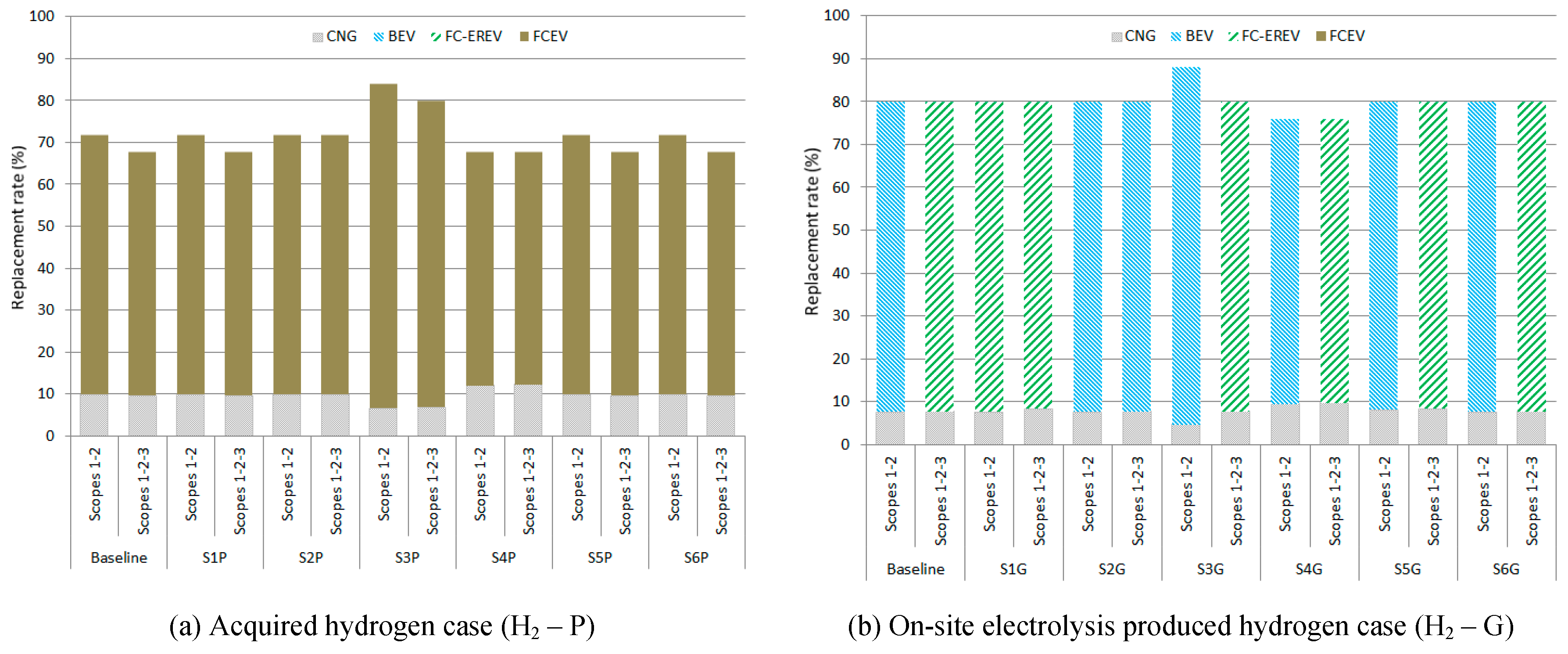
Figure 3 to
Figure 5 show the fleet share and the replacement rate for all the solutions and scenarios analyzed. Concerning fleet mix, the FCEREV van is the type of van most frequently used for the BAL and ECON solutions in H2P scenarios (
Figure 3a and
Figure 4a) regardless of the emission reporting scope. However, the FCEV van is the best option for the ENV solution (
Figure 5a). This type of van also has a chance in the BAL solution for higher annual mileage (S2-P) and shorter ownership periods with Scope 3 emissions reporting (S3-P) (
Figure 3a), for the following reasons: (i) the lower impact of hydrogen distribution and conditioning compared to the electricity production mix and transmission losses, considering the hydrogen production emissions to be null since it is green hydrogen, and (ii) the low manufacturing emissions of FCEV vans. On the other hand, in the H2G scenarios (
Figure 3b,
Figure 4b and
Figure 5b) the selected van types are BEV and FCEREV depending on the scenario parameters and emission reporting scopes. The selected van type is FCEREV in all the scenarios for the BAL and ENV solutions when Scope 3 emissions are accounted for (
Figure 3b and
Figure 5b), except in the scenario with higher annual distances traveled (S2-G), where BEV is the best option. The FCEREV van is also selected in low annual mileage scenarios (S1-G), it benefits from low hydrogen consumption due to the electric autonomy and the lower consumption.
Other conclusions that can be deducted from the data contained in
Figure 3 to
Figure 5 are:
As expected, the EV replacement rate is better for ENV solutions than ECON solutions, except for H2P scenarios due to the highest purchase price of FCEV vans compared to the FCEREV and the imposed budget limit.
For BAL solutions (
Figure 3a and
Figure 3b), the EV replacement rate depends mainly on the ownership period, the van purchase price and the emissions of Scope 3 accounting. The replacement rate with EV vans is lower in longer ownership periods (scenarios S4-P and S4-G). The higher purchase cost of FCEV vans limits the replacement rate in the scenarios where they are used (S2-P, S3-P and S4-P). If Scope 3 emissions are taken into account, especially in H2P scenarios, the EV replacement rate is lesser. This is due to the reduction in the difference in the emissions level between CNG and electrified vans. This effect is especially noteworthy in scenarios with lower mileage (S1-P), where the emissions caused by the use of CNG vans do not affect considerably, and shorter ownership periods (S3-P). Nevertheless, in shorter ownership periods the capacity to replace vans over time is higher, and the effect of manufacturing emissions of electrified vans has relevance.
4.2. Economic and environmental results
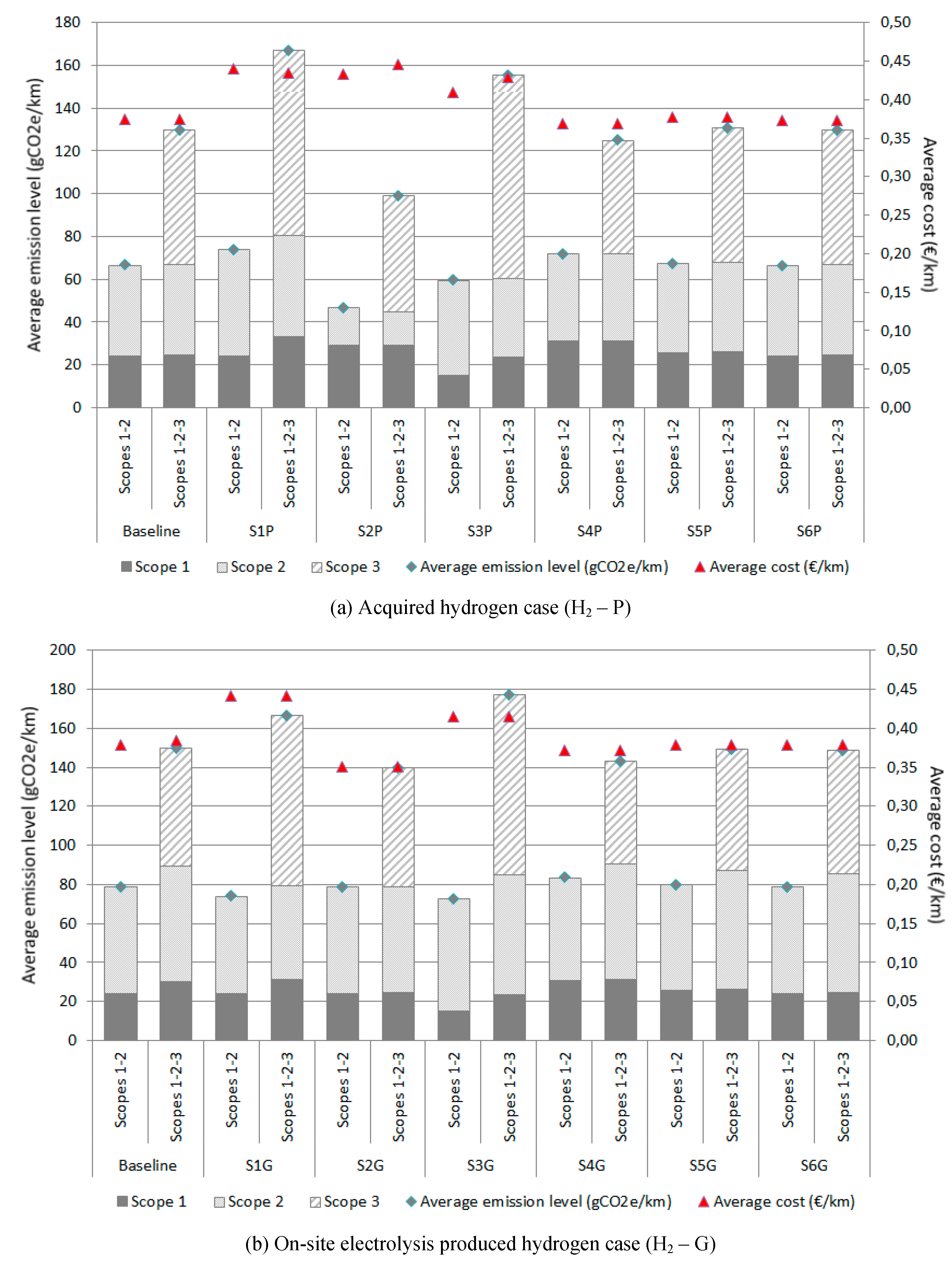
Figure 6 shows the emission breakdown per scope and the average cost and emissions per kilometer of the vehicles in each of the scenarios analyzed for the BAL solution. As can be observed, the average emissions and costs per kilometer depend mainly on the yearly mileage, the van’s ownership duration and the scopes included in the company emission report. In particular, the emissions are higher in H2G scenarios except for the scenarios with the lowest annual mileage (S1-P and S1-G), where H2P and H2G show a similar emissions level. On average, the difference is 20,7% if the emissions scopes reported are 1 and 2, and 16% when the emissions in Scope 3 are accounted for. The highest average emission level for H2P scenarios (
Figure 6a) is reached in the S1-P scenario regardless of the emissions scopes considered with a high share of CNG vans in the fleet. However, in H2G the maximum emissions, when only Scopes 1 and 2 are considered (
Figure 6b), is reached in the scenario with the largest ownership period (S4-G) and also with a high presence of CNG vans in the fleet, but when considering Scope 3 emissions the maximum is obtained in the opposite scenario with the shortest ownership period (S3-G) with a high replacement rate and it points out the importance of Scope 2 emissions due to the on-site hydrogen production using electricity from the grid. It is interesting to note that the S1-G scenario (
Figure 6b) gets a low level of emissions using FCEREV vans in the fleet.
Respecting the average costs per kilometer, considering an average price for hydrogen and electricity of 4,2 €/kg and 168 €/MWh respectively, the H2P and H2G scenarios, regardless of emission scopes, show a similar cost level except for the H2P scenario with higher annual mileages (S2-P) (
Figure 6a). In this scenario, there is a noteworthy presence of FCEV vans in the mix and the cost is significantly lower. Nevertheless, in the H2G case, the scenario with shorter annual mileages (S1-G) has the highest cost per kilometer and the lowest cost is reached in the opposite scenario (S2-G). Additionally, shorter ownership periods (S3) lead to higher costs per kilometer than longer periods (S4). As expected, these results point out the lower operating costs and higher acquisition costs of electric vans, especially the FCEV type, in comparison to CNG vans.
Concerning the distribution of emissions per scope it should be pointed out the following aspects:
The consideration of Scope 3 in the emissions report increases the level of accounted emissions by an average of over 71% in H2P and H2G scenarios.
The emissions reported in Scope 3 have approximately the same weight as the sum of the emissions accounted for in Scope 1 and 2, except for the S4 scenarios where it is performed the longest ownership period. Additionally, when the emissions in Scope 3 are considered, the emission level in Scope 1 grows, this is a result of the increased presence of CNG vans in the fleet mix.
The emissions reported in Scope 2 are always higher in H2G scenarios than in the H2P. The major and minor differences are shown in S2 and S1 scenarios with the largest and lowest annual mileages respectively. However, the emissions in Scope 3 are higher in H2P scenarios except for the scenario with the higher annual mileage (S2). These results highlight the importance of the electricity production mix and the hydrogen distribution in scenarios with high distances traveled per year.
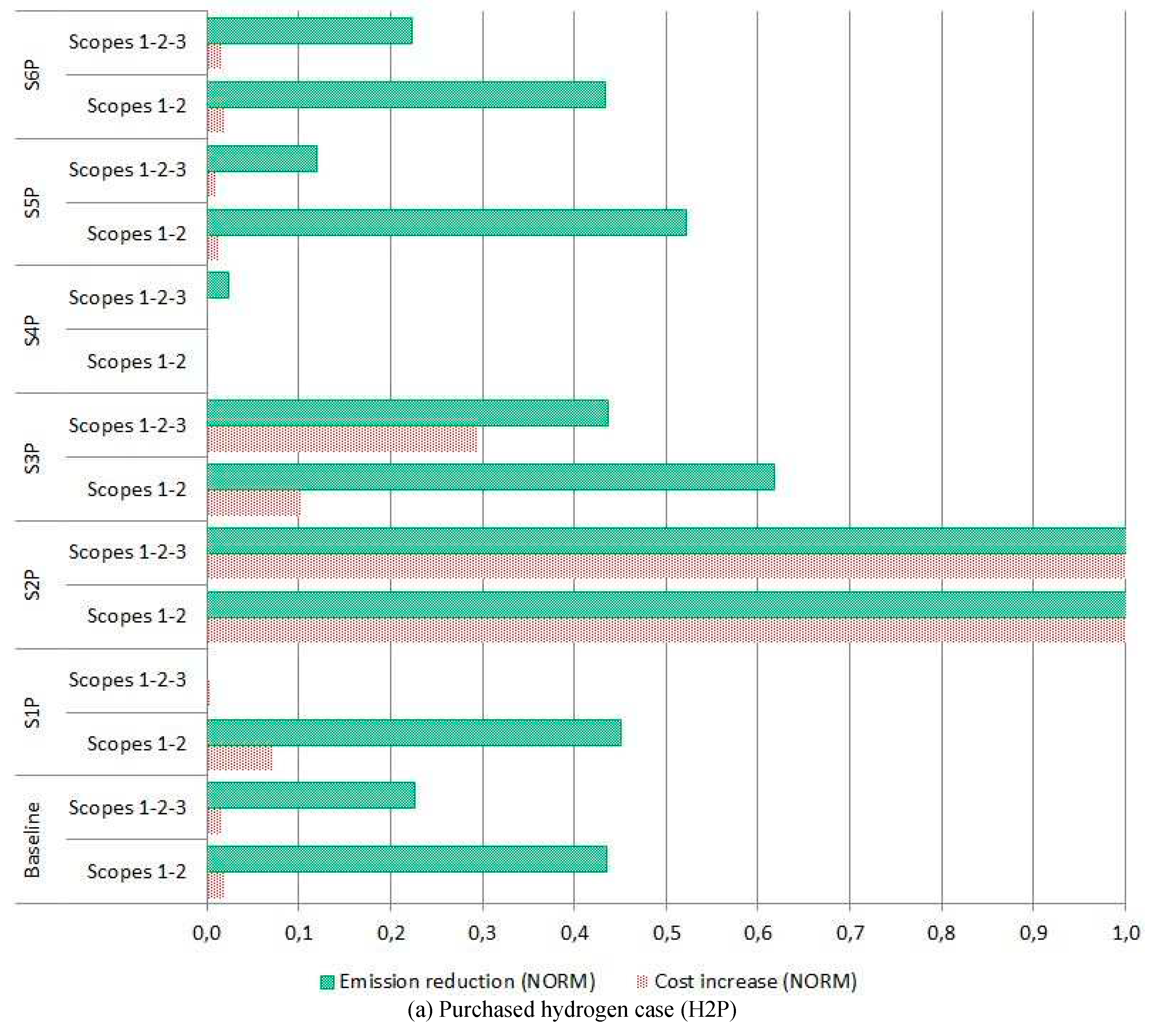
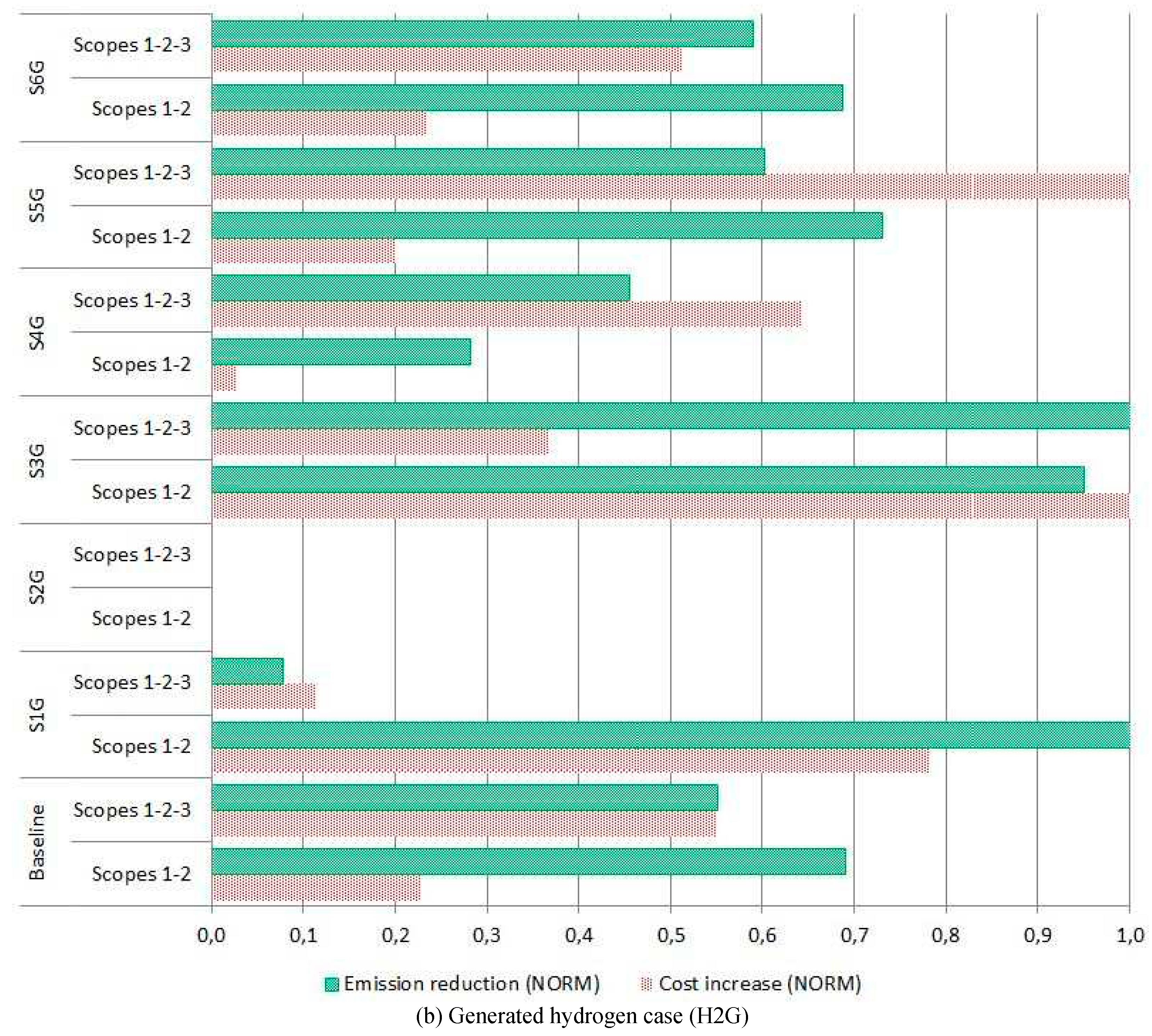
Figure 7 reflects the emission savings and cost increase of the BAL solutions compared to the ECON solutions on a standardized 0 – 1 scale. In general, a reduction in emissions results in an increase in costs, and mainly depends on the energy supply pathway and van type selected for the optimal solution.
Concerning the distance traveled per year, H2P scenarios are more sensitive to higher distances and H2G to lower distances. Additionally, reporting S3 emissions leads to BAL solutions close to ECON solutions.
Regarding the ownership period, shorter periods have more influence than larger ones. In particular, H2G scenarios with BEV vans in the fleet are more affected by short periods than H2P scenarios. Longer ownership periods result in approximately equivalent BAL and ECON solutions.
The fleet size has a significant cost effect due to the on-site energy supply infrastructure. The H2G scenarios are more affected than H2P, especially in small fleet size and S3 emissions reporting (S5G) because of the hydrogen supply assets needed to fuel the FCEREV vans.
4.3. Sensitivity and solution robustness analysis
The results obtained for the BAL solutions in the baseline scenario are summarized in
Table 10 for H2P scenarios, and
Table 11 for H2G scenarios. The fleet size change is excluded from the tables because it has no significant effect. The results show that the optimization solutions are sensitive to the electricity EF, the yearly mileage and the van’s ownership duration, followed by the purchase price of fuel-cell powered vans and the discount rate and inflation, whereas the fuel-cell powered van maintenance cost and the electricity price show a lower effect. Concerning related hydrogen parameters, such as price and EF, have influence only in H2P scenarios with Scope 3 emissions accounted and higher yearly mileages, over 30.000 km.
Additionally, from this analysis, it can be observed that modifying model parameters does not result in a shift in the selected van type except for in H2P scenarios with a high reduction in the electricity EF and higher annual mileages with Scope 3 emissions reporting. The reduction in electricity EF enables electric vans to participate in the fleet mix, while higher annual mileage opens up the opportunity for the FCEV vans.
The evaluation of the solution robustness has been carried out through a worst-case scenario analysis for the cases accounting for Scope 3 emissions that have shown higher sensitivity to the variation of certain model parameters. In the H2P case (
Table 12), the FCEREV van type is optimal for higher annual mileage (above 30.000 km) and any van’s ownership duration if the acquisition cost is equivalent to a BEV van. In this sense, the FCEV vans are more penalized by the increase in the discount and inflation rate due to their higher purchase price. Moreover, in the H2G case (
Table 13), the BEV van type is optimal for higher annual mileage (above 30.000 km) and any ownership period, and if the acquisition cost is cheaper than an FCEREV van (10%) is also convenient in lower annual mileage (20.000 km).
Nevertheless, the FCEREV van is not the optimal powertrain type for low annual mileage (20.000 km) when the price of electricity decreases (10%) and the purchase and maintenance cost of fuel-cell powered vans increases (10%) or the hydrogen is produced on-site using electricity from the grid. Additionally, an increase in discount and inflation rates in shorter ownership periods (5 years) makes it no longer efficient to use electric vans.
4.4. Research findings summary
The results obtained in the simulations conducted over the Spanish market scenarios reveal interesting information to support the fleet managers' action plan:
The replacement rate of CNG vehicles with electric vans primarily depends on the ownership period, the van purchase price and the emissions of Scope 3 accounting.
The results obtained for the fleet mix and EV replacement rate show that FCEREV vans get the right balance between emissions and the economy of use in a wide range of H2P and H2G scenarios. This type of van is suitable for moderate annual distances (up to 30.000 km) when S3 emissions are accounted for. Nevertheless, if S3 emissions are out of scope then the optimal distance is reduced up to 20.000 km. Meanwhile, the BEV vans are optimal for the H2G scenario for larger annual distances (over 40.000 km) when S3 emissions are reported and moderate distances (over 30.000 km) if only emissions in Scopes 1 and 2 are taken into account.
The average fleet emissions per kilometer are determined by yearly mileage, the van’s ownership duration, the electricity production mix and the hydrogen distribution and conditioning pathway. The emissions are higher in the H2G scenarios except for the scenarios with the lowest annual mileage. On average, the difference is 20,7% if the emissions scopes reported are 1 and 2, and 16% when the emissions in Scope 3 are accounted for. Therefore, from the emissions inventorying point of view, the purchased hydrogen scenario is the most favorable and it is not efficient to use grid electricity to produce hydrogen by on-site electrolysis.
The consideration of Scope 3 in the emissions report increases the level of accounted emissions by an average of over 71%. The emissions reported in Scope 3 have approximately the same weight as the sum of the emissions accounted for in Scope 1 and 2, except for the S4 scenarios where it is performed the longest ownership period. Additionally, when Scope 3 emissions are taken into account, the EV replacement rate is lesser. Both results point out the importance of the emissions generated during EV van manufacturing.
The average cost per kilometer is similar in the H2G and H2P scenarios, considering an average price for hydrogen and electricity of 4,2 €/kg and 168 €/MWh. The H2P solution gets up to 2,7% cost reduction compared to the H2G in cases with moderate annual mileages (below 30.000 km), long ownership periods (over 8 years) and a large number of vehicles in the fleet (over 200 vehicles), Nevertheless, higher annual mileages (over 40.000 km) give an advantage to the H2G solution with a cost reduction up to 21,4%. Additionally, the small fleet vans with on-site hydrogen production are more economically affected by the hydrogen supply infrastructure cost.
The investigation outcomes are aligned with previous research findings. Regardless of the higher purchase costs, when emissions are considered, EVs are the best option for commercial delivery vans with high utilization levels (Figliozzi et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2016; Li et al., 2016; Alp et al., 2022). However, the emissions from energy pathway production and vehicle manufacturing have important environmental implications that should be taken into account (Bauer et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2016; Alp et al., 2022). Additionally, it is shown that there is an emission–cost correlation and there is a cost increase for reducing fleet emissions (Zhao et al., 2016; Lemme et al., 2019; Desantes et al., 2021). Furthermore, the life cycle emissions structure is different for EV and CNG vans, while utilization emissions are high for CNG vans compared to production emissions values, in EVs is quite the opposite (Simons and Azimov, 2021; Buberger et al., 2022). Additionally, it is important to consider the energy supply infrastructure investments for using electrified vans in actual commercial fleets (Schiffer et al., 2021; Alp et al., 2022). Moreover, the investigation has shown that the FCEREV vans provide higher operation efficiencies, lower environmental impact and lower costs in a large range of scenarios (Ribau et al., 2014; Desantes et al., 2021; Lal et al., 2023).
5. Conclusions
These days, a sustainable logistics approach has become indispensable for any company aspiring to get cost savings and cultivate a favorable image. The first step for implementing a sustainable logistic strategy is to calculate the corporate emissions to identify the emissions hotspots and implement action plans accordingly. In this sense, collaborating with a transport provider with a sustainability commitment represents a major step that companies can take to cut down emissions throughout their supply chains. On this subject, transportation companies have set the target of electrifying their last-mile delivery vehicles. The adoption of electric vans for urban delivery activities requires an optimization approach for selecting the most favorable replacement strategy. The aim of this research work is just that. To reach this goal, the authors have innovated by combining in an MOLP the fleet parallel replacement problem with the corporate greenhouse gas emissions reporting following the GHG Protocol guidelines. This investigation brings the chance for fleet managers to evaluate the carbon footprint impact of the transport activity and analyze the cost-effective behavior of the van fleet. In this sense, the fleet operator could select the replacement calendar with the most suitable van type and refueling infrastructure characteristics fulfilling the economic and environmental corporation objectives.
The optimization model has been tested in a multi-scenario approach applied to the Spanish market for evaluating multiple electrified powertrain vans, including the necessary energy supply infrastructure. The research findings obtained confirm that BEV and FCEREV vans should have room to replace CNG vans to achieve higher corporate carbon footprint reductions in a cost-optimal way. However, the optimal van fleet mix is sensitive to the annual mileage and the van’s ownership duration, followed by the purchase price of fuel-cell powered vans. Meanwhile, the fuel-cell powered van maintenance cost and energy EF or price, electricity or hydrogen, have importance in cases of higher yearly mileages, (over 30.000 km). Additionally, the effect of these factors depends on the energy supply pathway (H2P or H2G) and the corporate emissions reporting scopes considered. In this sense, considering an average price for hydrogen and electricity of 4,2 €/kg and 168 €/MWh, the H2P energy pathway with FCEREV vans is the optimal solution with reductions in costs and emissions level up to 2,7% and 18,5% respectively compared to the H2G and BEV solution in cases with moderate annual mileages (below 30.000 km), long ownership periods (over 8 years) and a large number of vehicles in the fleet (over 200 vehicles). Nevertheless, higher annual mileage (over 40.000 km) gives an advantage to the H2G solution with a cost reduction of 21,4%, but with an emission increment of 41,4%. Concerning the corporate emissions reporting scope, the consideration of Scope 3 increases the level of accounted emissions by an average of over 71%. In this regard, the emissions resulting from van manufacturing and energy production, distribution and conditioning could represent a significant portion of the total corporate emissions and provide an overall view of emissions associated with the company’s activity. These findings imply that initiatives promoting the generation of hydrogen via water electrolysis and sustainable electricity sources have the potential to bolster the environmental attributes of hydrogen fuel-cell LCVs.
This new approach to solving vehicle replacement issues in urban delivery fleets can be applied to a wide range of van fleet typologies for transport agencies located in different countries. By using this optimization approach, fleet managers can detect significant factors in their fleets and make simulations to identify patterns and trends to make strategic decisions for planning future fleet mixes and refueling infrastructure needs. In conclusion, this methodology framework for assessing the emissions and economic feasibility of adopting EV vans in the fleet.
Limitations in this study lie basically in the values of the model parameters under consideration. Accordingly, due to the technological maturity of the vehicles and energy supply means used in this study, it is necessary to revise the model data to establish their effects in terms of environmental and economic performances over time. Moreover, the environmental parameters of the model should be updated depending on the location of the study. From this point of view, the developed model is sensitive to adjustments in the parameter values, the vehicle types and infrastructure assets, and fleet management requirements, such as budget, initial fleet conditions (the age and the number of vehicles and energy supply assets), daily distance demand and van’s ownership period.
Future research on this investigation can be oriented to identify in advance technological advancements in powertrain systems or refueling infrastructures that significantly impact the environmental and economic performance of vehicles, and thus, the fleet mix.
Therefore, the findings enable practical implications for building realizable fleet management action plans and selecting adequate corporate carbon footprint reporting methodology for logistic companies. To this effect, fleet operators should have consistent GHG emissions data for the vehicles and the energy supply chain from the suppliers, to ensure that the fleet gets a suitable carbon footprint performance. Additionally, opens up consequences on the corporate emissions inventory of the hydrogen supply pathway. These concerns are of interest not only to fleet managers but also to policymakers.
Abbreviations
| CNG |
Compressed natural gas |
LCA |
Life cycle assessment |
| EF |
Emission factor |
LCC |
Life cycle cost |
| EV |
Electric Vehicle |
LCV |
Light commercial vehicle |
| GLF |
Grid loss factor |
MILP |
Mixed Integer Linear Programming |
| BEV |
Battery electric vehicle |
MOLP |
Multi-Objective Linear Programming |
| FCEV |
Fuel cell electric vehicle |
M&R |
Maintaining and repairing |
| FCEREV |
Fuel cell extended range electric vehicle |
PHEV |
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicle |
| GHG |
Greenhouse gas |
PV |
Passenger vehicle |
| HEV |
Hybrid electric vehicle |
SMR |
Steam Methane Reforming |
| HRS |
Hydrogen refueling station |
TDCO |
Total Discounted Cost of Ownership |
| ICE |
Internal combustion engine |
|
|
References
- Aditjandra, P.T., Galatioto, F., Bell, M.C., Zunder, T.H., 2016. Evaluating the impacts of urban freight traffic: Application of micro-simulation at a large establishment. Eur. J. Transp. Infrastruct. Res. 16, 4–22. [CrossRef]
- Al-dal’ain, R., Celebi, D., 2021. Planning a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles for urban freight with routing and replacement considerations. Sustain. Cities Soc. 73. [CrossRef]
- Albitar, K., Al-Shaer, H., Liu, Y.S., 2023. Corporate commitment to climate change: The effect of eco-innovation and climate governance. Res. Policy 52, 104697. [CrossRef]
- Alp, O., Tan, T., Udenio, M., 2022. Transitioning to sustainable freight transportation by integrating fleet replacement and charging infrastructure decisions. Omega (United Kingdom) 109. [CrossRef]
- Bareiß, K., de la Rua, C., Möckl, M., Hamacher, T., 2019. Life cycle assessment of hydrogen from proton exchange membrane water electrolysis in future energy systems. Appl. Energy 237, 862–872. [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C., Hofer, J., Althaus, H.J., Del Duce, A., Simons, A., 2015. The environmental performance of current and future passenger vehicles: Life Cycle Assessment based on a novel scenario analysis framework. Appl. Energy 157, 871–883. [CrossRef]
- Bieker, G., 2021. A global comparison of the life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions of combustin engine and electric passenger cars.
- Buberger, J., Kersten, A., Kuder, M., Eckerle, R., Weyh, T., Thiringer, T., 2022. Total CO2-equivalent life-cycle emissions from commercially available passenger cars. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 159, 112158. [CrossRef]
- Castillo Campo, O., Álvarez Fernández, R., 2023. Economic optimization analysis of different electric powertrain technologies for vans applied to last mile delivery fleets. J. Clean. Prod. 385, 135677. [CrossRef]
- Desantes, J.M., Novella, R., Pla, B., Lopez-Juarez, M., 2021. Impact of fuel cell range extender powertrain design on greenhouse gases and NOX emissions in automotive applications. Appl. Energy 302, 117526. [CrossRef]
- Di Foggia, G., 2021. Drivers and challenges of electric vehicles integration in corporate fleet: An empirical survey. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. [CrossRef]
- DOE, 2015. Hydrogen Delivery, Fuel Cell Technologies; Office Multi-Year Research, Development and Demonstration Plant.
- E4tech, 2019. H2 Emission Potential Literature Review.
- EEA, 2022. Transport and environment report 2022. Digitalisation in the mobility system : challenges and opportunities.
- Ellram, L.M., 1995. Total cost of ownership; An analysis approach for purchasing. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 25, 4–23. [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, P., Colicchia, C., Creazza, A., 2017. Is environmental sustainability a strategic priority for logistics service providers? J. Environ. Manage. 198, 353–362. [CrossRef]
- Feng, W., Figliozzi, M., 2013. An economic and technological analysis of the key factors affecting the competitiveness of electric commercial vehicles: A case study from the USA market. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 26, 135–145. [CrossRef]
- Feng, W., Figliozzi, M., 2014. Vehicle technologies and bus fleet replacement optimization: Problem properties and sensitivity analysis utilizing real-world data. Public Transp. 6, 137–157. [CrossRef]
- Figliozzi, M.A., Boudart, J.A., Feng, W., 2011. Economic and environmental optimization of vehicle fleets. Transp. Res. Rec. [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A., Fischbeck, P., Matthews, H.S., 2018. Environmental and economic comparison of diesel and battery electric delivery vans to inform city logistics fleet replacement strategies. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 64, 216–229. [CrossRef]
- GreenHouse Gas Protocol, 2011. Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard.
- GreenHouse Gas Protocol, 2022. GHG Protocol - Calculation Tools [WWW Document]. URL https://ghgprotocol.org/calculation-tools (accessed 6.23.22).
- GreenHouse Gas Protocol and Carbon Trust, 2013. Technical Guidance for Calculating Scope 3 Emissions, World Resources Institute & World Business Council for Sustainable Development.
- Gunantara, N., 2018. A review of multi-objective optimization: Methods and its applications. Cogent Eng. 5, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- IEA, 2020. Emission Factors 2020 - Data base documentation.
- IPCC, 2007. Cimate Change 2007: Synthesis Report., Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
- Islam, A., Lownes, N., 2019. When to go electric? A parallel bus fleet replacement study. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 72, 299–311. [CrossRef]
- ISO, 2004. Environmental Management - Life Cycle Assessment - Principles and Framework (ISO 14040:2006), British Standard.
- Karaman, A.S., Kilic, M., Uyar, A., 2020. Green logistics performance and sustainability reporting practices of the logistics sector: The moderating effect of corporate governance. J. Clean. Prod. 258, 120718. [CrossRef]
- Lal, A., Renaldy, T., Breuning, L., Hamacher, T., You, F., 2023. Electrifying light commercial vehicles for last-mile deliveries: Environmental and economic perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 416, 137933. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y., Thomas, V.M., Brown, M.A., 2013. Electric urban delivery trucks: Energy use, greenhouse gas emissions, and cost-effectiveness. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 8022–8030. [CrossRef]
- Lemme, R.F.F., Arruda, E.F., Bahiense, L., 2019. Optimization model to assess electric vehicles as an alternative for fleet composition in station-based car sharing systems. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 67, 173–196. [CrossRef]
- Li, M., Zhang, X., Li, G., 2016. A comparative assessment of battery and fuel cell electric vehicles using a well-to-wheel analysis. Energy 94, 693–704. [CrossRef]
- Ligen, Y., Vrubel, H., Girault, H.H., 2018. Mobility from renewable electricity: Infrastructure comparison for battery and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 9. [CrossRef]
- Marler, R.T., Arora, J.S., 2004. Survey of multi-objective optimization methods for engineering. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 26, 369–395. [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Industria y Energía, 2014. Factores de emisión de CO2 y coeficientes de paso a energía primaria de diferentes fuentes de energía final en el sector de edificios en España.
- MITECO, 2022. Calculadora huella de carbono de una organización [WWW Document]. URL https://www.miteco.gob.es/es/cambio-climatico/temas/mitigacion-politicas-y-medidas/calculadoras.aspx (accessed 6.30.22).
- Onat, N.C., Abdella, G.M., Kucukvar, M., Kutty, A.A., Al-Nuaimi, M., Kumbaroğlu, G., Bulu, M., 2021. How eco-efficient are electric vehicles across Europe? A regionalized life cycle assessment-based eco-efficiency analysis. Sustain. Dev. 29, 941–956. [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Martínez, E., Marín-Hernández, S., Santos-Jaén, J.-M., 2022. Sustainability, corporate social responsibility, non-financial reporting and company performance: Relationships and mediating effects in Spanish small and medium sized enterprises. Sustain. Prod. Consum. [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q., Zhao, F., Liu, Z., Jiang, S., Hao, H., 2017. Comparative Study on Life Cycle CO2 Emissions from the Production of Electric and Conventional Vehicles in China, Energy Procedia. [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, T., Ruth, M., Diakov, V., 2013. Hydrogen Pathways: Cost, Well-to-Wheels Energy Use, and Emissions for the Current Technology Status of 10 Hydrogen Production, Delivery, and Distribution Scenarios. [CrossRef]
- Red Electrica de España, 2021. La eólica se convierte en la principal fuente de generación de energía eléctrica en España en 2021 [WWW Document]. URL https://www.ree.es/es/sala-de-prensa (accessed 7.18.22).
- Redmer, A., 2020. Strategic vehicle fleet management–a joint solution of make-or-buy, composition and replacement problems. J. Qual. Maint. Eng. [CrossRef]
- Ribau, J.P., Silva, C.M., Sousa, J.M.C., 2014. Efficiency, cost and life cycle CO2 optimization of fuel cell hybrid and plug-in hybrid urban buses. Appl. Energy 129, 320–335. [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, M., Klein, P.S., Laporte, G., Walther, G., 2021. Integrated planning for electric commercial vehicle fleets: A case study for retail mid-haul logistics networks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 291, 944–960. [CrossRef]
- Schmied, M., Knörr, W., Friedl, C., Hepburn, L., 2012. Calculating GHG emissions for freight forwarding and logistics services in accordance with EN 16258, European Association for Forwarding, Transport, Logistics and Customs Services (CLECAT).
- Seroka-Stolka, O., 2014. The Development of Green Logistics for Implementation Sustainable Development Strategy in Companies. Procedia - Soc. Behav. Sci. 151, 302–309. [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, M., Ehsanifar, M., Rokhsati, A., 2011. Selecting the Most Preferable Weights in Multi Objective Programming. Am. J. Sci. Res. 87–92.
- Simons, S., Azimov, U., 2021. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Propulsion Systems for Heavy-Duty Transport Applications. Energies 14, 3079. [CrossRef]
- The World Bank, 2021. State and Trends of Carbon Pricing 2021.
- Tsakalidis, A., Krause, J., Julea, A., Peduzzi, E., Pisoni, E., Thiel, C., 2020. Electric light commercial vehicles: Are they the sleeping giant of electromobility? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 86, 102421. [CrossRef]
- Usai, L., Hung, C.R., Vásquez, F., Windsheimer, M., Burheim, O.S., Strømman, A.H., 2021. Life cycle assessment of fuel cell systems for light duty vehicles, current state-of-the-art and future impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 280, 125086. [CrossRef]
- Wulf, C., Kaltschmitt, M., 2018. Hydrogen supply chains for mobility-Environmental and economic assessment. Sustain. 10, 1–26. [CrossRef]
- Yeow, L.W., Yan, Y., Cheah, L., 2022. Life cycle greenhouse gas emissions of alternative fuels and powertrains for medium-duty trucks: A Singapore case study. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 105, 103258. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y., Ercan, T., Tatari, O., 2016. Life cycle based multi-criteria optimization for optimal allocation of commercial delivery truck fleet in the United States. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 8, 18–31. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Research methodology scheme.
Figure 1.
Research methodology scheme.
Figure 2.
Example of Pareto frontier for the proposed bi-objective problem.
Figure 2.
Example of Pareto frontier for the proposed bi-objective problem.
Figure 3.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the BAL solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 3.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the BAL solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 4.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the ECON solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 4.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the ECON solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 5.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the ENV solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 5.
The replacement rate and fleet share for the ENV solution in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 6.
Average cost and emissions per kilometer, and the emissions per scope for the BAL solutions in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 6.
Average cost and emissions per kilometer, and the emissions per scope for the BAL solutions in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 7.
Emission savings and cost increase for the BAL solutions compared to the ECON solutions in all the scenarios analyzed.
Figure 7.
Emission savings and cost increase for the BAL solutions compared to the ECON solutions in all the scenarios analyzed.
Table 1.
Optimal fleet replacement with emissions concerns in literature.
Table 1.
Optimal fleet replacement with emissions concerns in literature.
| Ref. |
Method |
Economic evaluation |
GHG evaluation |
Scope of vehicle emissions analysis |
Vehicle type |
Powertrain |
| |
|
TDCO |
LCC |
Cost(CS)
|
Emissions (EM) |
OP |
LCA |
ECR |
|
BEV |
FCEV |
ICE |
Alternatives |
| (Figliozzi et al., 2011) |
LP-SO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
PV |
X |
|
X |
HEV |
| (Feng and Figliozzi, 2013) |
LP-SO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
LCV |
X |
|
X |
|
| (Feng and Figliozzi, 2014) |
LP-SO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
Bus |
|
|
X |
HEV |
| (Zhao et al., 2016) |
LP-MO |
|
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
LCV |
X |
|
X |
HEVCNG |
| (Lemme et al., 2019) |
LP-MO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
PV |
X |
|
X |
PHEV |
| (Islam and Lownes, 2019) |
LP-SO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
Bus |
X |
|
X |
|
| (Al-dal’ain and Celebi, 2021) |
LP-SO |
X |
|
X |
|
X |
|
|
LCV |
X |
|
X |
|
| Study contribution |
LP-MO |
X |
|
X |
|
|
|
X |
LCV |
X |
X |
X |
FCEREVCNG |
Table 2.
Indices used in the mathematical model.
Table 2.
Indices used in the mathematical model.
| Index |
Range |
Description |
Units |
| i |
0 to Nk
|
The age of the van |
Year |
| j |
0 to T |
The current year in the planning horizon |
Year |
| k |
k = 1 (van CNG); k = 2 (van BEV);
k = 3 (van FCEREV); k = 4 (van FCEV) |
The van’s powertrain type |
Dimensionless |
| m |
0 to Nr
|
The age of the energy supply infrastructure |
Year |
| r |
r = 1 (charging point for BEV);
r = 2 (charging point for FCEREV);
r = 3 (HRS for FCEREV bought or produced);
r = 4 (HRS for FCEV bought or produced);
r = 5 (FCEV and FCEREV hydrogen dispenser) |
The energy supply infrastructure type |
Dimensionless |
Table 3.
Parameters used in the mathematical model.
Table 3.
Parameters used in the mathematical model.
| Parameter |
Description |
Units |
| Nk
|
Van type “k” ownership period in the fleet. It is possible to set up different ownership durations for each van type (CNG, BEV, FCEREV and FCEV). |
Year |
| T |
Planning horizon analyzed |
Year |
| Nr
|
“r” type energy supply infrastructure asset service life. Each r-type energy supply device has a different service life |
Year |
| rif
|
Inflation index |
Dimensionless |
| rd
|
Discount rate (nominal value) |
Dimensionless |
| APVjk
|
The acquisition price in the year “j” of a van type “k” |
€/van |
| VDRik
|
Type “k” van “i” years old depreciation factor |
Dimensionless |
| FCijk
|
Fixed term of operating costs in the year “j” for a type “k” van “i” years old |
€/year |
| VECijk
|
Fueling costs during the year “j” for a type “k” van “i” years old |
€/km |
| MCVijk
|
Cost of van’s maintenance in the year “j” for a type “k” van “i” years old |
€/km |
| RCVijk
|
Cost of van’s repair in the year “j” for a type “k” van “i” years old |
€/km |
| AMijk
|
Annual mileage demand in the year “j” for a type “k” van “i” years old |
km/year |
| APIjr
|
“r” type energy supply infrastructure asset acquisition price in the year “j” |
€/infrastructure |
| ISRmr
|
“r” type energy supply infrastructure asset scrapping return value with “m” years of operation |
Dimensionless |
| MCImjr
|
“r” type energy supply infrastructure asset maintenance costs in the year “j” with “m” years of operation |
€/year |
| Parameter |
Description |
Units |
| RCImjr
|
“r” type energy supply infrastructure asset repairing costs in the year “j” with “m” years of operation |
€/year |
|
Scope 1 GHG emissions based on the CNG consumption |
kgCO2e
|
|
Emission tax in the year “j” |
€/kgCO2e
|
|
Yearly van CNG consumption |
kg |
|
Scope 2 GHG emissions associated with the purchased electricity |
kgCO2e
|
|
Yearly electricity consumption of each van of type “k”. There are only two plug-in vans: BEV (k = 2) and FCEREV (k = 3). |
kWh |
|
Scope 3 GHG emissions produced by the electricity acquired (reported in Scope 2) due to the transmission and distribution losses |
kgCO2e
|
|
Scope 3 GHG emissions based on the hydrogen purchased |
kgCO2e
|
|
Yearly hydrogen consumption of each van of type “k” n. There are only two vans powered by hydrogen: FCEREV (k = 3) and FCEV (k = 4). |
kg |
| NSIr
|
“r” type energy supply asset capacity for fueling vans per day |
van |
| PVbj
|
Budget for van purchasing during the year “j” |
€ |
| PIbj
|
The budgetary limit in the year “j” for purchasing an energy supply infrastructure asset |
€ |
Table 4.
Decision variables used in the mathematical model.
Table 4.
Decision variables used in the mathematical model.
| Variable |
Description |
| VOijk
|
Van “k” type “i” years old in operation during the year “j” |
| VSijk
|
Van “k” type “i” years old sold during the year “j” |
| VAjk
|
Van “k” type acquired during the year “j” |
| IOmjr
|
Energy supply infrastructure asset “r” type with “m” years in operation during the year “j” |
| ISmjr
|
Energy supply infrastructure asset “r” type with “m” years sold during the year “j” |
| IAjr
|
Energy supply infrastructure asset “r” type acquired during the year “j” |
Table 5.
Scenarios analyzed.
Table 5.
Scenarios analyzed.
| Modeling variables |
Units |
Scenario nomenclature |
| |
|
Baseline |
S1 (P/G) |
S2 (P/G) |
S3 (P/G) |
S4 (P/G) |
S5 (P/G) |
S6 (P/G) |
| Hydrogen supply pathway |
|
H2 acquired (P) or H2 on-site electrolysis produced (G) |
| Corporate emissions reporting option |
|
Scope 1 and 2 (S12) or Scope 1, 2 and 3 (S123) |
| Annual mileage |
km |
30.000 |
20.000 |
40.000 |
30.000 |
30.000 |
30.000 |
30.000 |
| Van’s ownership period |
years |
8 |
8 |
8 |
5 |
10 |
8 |
8 |
| Fleet size |
units |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
80 |
320 |
Table 6.
Economic data.
| |
|
CNG |
BEV |
FCEREV |
FCEV |
Comments |
| Discount rate |
% |
2,5 |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
| Inflation index |
% |
1,3 |
- |
- |
- |
(1) |
| Van acquisition cost |
€/van |
37.385 |
51.520 |
51.865 |
71.450 |
(2) |
| Maintenance cost (4)
|
€/km |
0,18 |
0,09 |
0,11 |
0,11 |
|
| Electricity cost (5)
|
€/MWh |
|
168 |
- |
- |
(3) |
| Hydrogen cost (5)
|
€/kg |
- |
- |
4,2 |
4,2 |
|
| CNG cost (5)
|
€/kg |
2,7 |
- |
- |
- |
|
Table 7.
Energy EF factors used for Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
Table 7.
Energy EF factors used for Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
| |
|
EF |
Comments |
References |
| CNG () |
kgCO2e / kg |
2,8 |
|
(a) (b) |
| Electricity ( |
kgCO2e / kWh |
0,25 |
(1) |
(c) |
| Diesel ( |
kgCO2e /l |
2,39 |
(2) |
(a) (b) |
| Hydrogen produced by SMR ( |
kgCO2e / kg |
11,8 |
|
(d) (e) (f) |
Table 8.
Van characteristics.
Table 8.
Van characteristics.
| |
|
CNG |
BEV |
FCEREV |
FCEV |
Comments |
| Van model |
|
Fiat Ducato L1H1 |
Peugeot e-Expert |
- |
- |
(1) |
| Powertrain power |
kW |
101,4 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
| Fuel-cell stack power |
kW |
- |
- |
30 |
100 |
|
| Storage capacity |
kg |
36 |
- |
1,5 |
3 |
|
| Battery capacity |
kWh |
- |
75 |
28 |
2 |
|
| Vehicle body weight |
kg |
1566 |
1576,4 |
1576,4 |
1576,4 |
|
| Powertrain weight |
kg |
135 |
28,6 |
28,6 |
28,6 |
|
| FC stack and peripheral components' weight |
kg |
- |
- |
25 |
60 |
|
| Fuel tank weight |
kg |
194 |
- |
26 |
53 |
|
| Battery pack weight |
kg |
- |
483 |
180 |
12 |
|
Table 9.
Manufacturing EF factors considered for vehicle components in Scope 3.
Table 9.
Manufacturing EF factors considered for vehicle components in Scope 3.
| |
|
EF |
Comments |
References |
| Vehicle chassis |
kgCO2e / kg |
4,5 |
|
(a) (b) (c) (g) |
| ICE motor |
kgCO2e / kg |
8 |
(1) |
(g) |
| Electric motor |
kgCO2e / kW |
17 |
|
(a) (h) |
| Traction battery |
kgCO2e / kWh |
158 |
|
(a) (b) (c) (d) (h) |
| Fuel cell system |
kgCO2e / kW |
57 |
|
(c) (d) (e) (h) |
| High-pressure hydrogen tank |
kgCO2e / kgH2 |
640 |
|
(c) (d) (e) (h) |
| CNG tank |
kgCO2e / kg |
8 |
(1) |
(h) |
Table 10.
Sensitivity analysis results in H2P scenarios for the BAL solutions.
Table 10.
Sensitivity analysis results in H2P scenarios for the BAL solutions.
| |
Parameters |
|
|
Baseline scenario
Scopes 1 - 2 |
Baseline scenario
Scopes 1 - 2 - 3 |
| |
Units |
Value in the baseline scenario |
Value for sensitivity analysis |
E (1)
|
SVO (2)
|
E |
SVO |
| Annual mileage |
km |
30.000 |
20.000 |
-0,26 |
FCEREV |
-0,26 |
FCEREV |
| km |
30.000 |
40.000 |
-0,51 |
FCEREV |
-0,86 |
MIX (6)
|
| Van’s ownership duration |
year |
8 |
5 |
0,49 |
FCEREV |
-0,39 |
FCEREV |
| year |
8 |
10 |
0,33 |
FCEREV |
-0,24 |
FCEREV |
| Discount rate |
% |
2,50 |
6 |
-0,37 |
FCEREV |
-0,36 |
FCEREV |
| Inflation index |
wf (3)
|
1 |
2,50 |
0,31 |
FCEREV |
0,31 |
FCEREV |
| Electricity price (4)
|
€/kWh |
0,17 |
0,15 |
0,04 |
FCEREV |
0,06 |
FCEREV |
| Hydrogen price (4)
|
€/kg |
4,20 |
4,61 |
0,01 |
FCEREV |
0,33 |
FCEREV |
| CNG price (4)
|
€/kg |
2,70 |
2,43 |
0,04 |
FCEREV |
0,05 |
FCEREV |
| FC (7) van purchase price |
wf |
1 |
1,10 |
0,45 |
FCEREV |
0,45 |
FCEREV |
| FC (7) van M&R cost |
wf |
1 |
1,10 |
0,17 |
FCEREV |
0,17 |
FCEREV |
| Carbon tax |
€/ton CO2e
|
77,5 |
155 |
0,00 |
FCEREV |
0,00 |
FCEREV |
| EF electricity |
kgCO2e/kWh |
0,25 |
0,10 |
0,56 |
MIX (5)
|
0,25 |
FCEREV |
| EF hydrogen |
kgCO2e/kg |
0 |
4,72 |
- |
- |
0,02 |
FCEREV |
Table 11.
Sensitivity analysis results in H2G scenarios for the BAL solutions.
Table 11.
Sensitivity analysis results in H2G scenarios for the BAL solutions.
| |
Parameters |
|
|
Baseline scenario
Scopes 1 - 2 |
Baseline scenario
Scopes 1 - 2 - 3 |
| |
Units |
Value in the baseline scenario |
Value for sensitivity analysis |
E (1)
|
SVO (2)
|
E |
SVO |
| Annual mileage |
km |
30.000 |
20.000 |
0,16 |
FCEREV |
0,16 |
FCEREV |
| km |
30.000 |
40.000 |
0,00 |
BEV |
-0,24 |
BEV |
| Van’s ownership duration |
year |
8 |
5 |
0,18 |
BEV |
-0,36 |
FCEREV |
| year |
8 |
10 |
0,26 |
BEV |
-0,21 |
FCEREV |
| Discount rate |
% |
2,50 |
6 |
-0,37 |
BEV |
-0,37 |
FCEREV |
| Inflation index |
wf (3)
|
1 |
2,5 |
0,31 |
BEV |
0,31 |
FCEREV |
| Electricity price (4)
|
€/kWh |
0,17 |
0,19 |
-0,07 |
BEV |
-0,11 |
FCEREV |
| CNG price (4)
|
€/kg |
2,670 |
2,43 |
0,04 |
BEV |
0,01 |
FCEREV |
| FC (5) van purchase price |
wf |
1 |
0,90 |
0,02 |
BEV |
-0,42 |
FCEREV |
| FC (5) van M&R cost |
wf |
1 |
0,90 |
0,00 |
BEV |
-0,13 |
FCEREV |
| Carbon tax |
€/ton CO2e
|
77,5 |
155 |
0,00 |
BEV |
-0,01 |
FCEREV |
| EF electricity |
kgCO2e/kWh |
0,25 |
0,10 |
0,61 |
BEV |
0,34 |
FCEREV |
Table 12.
Worst-case scenarios result in the H2P case for the BAL solutions considering Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
Table 12.
Worst-case scenarios result in the H2P case for the BAL solutions considering Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
| |
|
Worst-case scenarios and scenario values |
| Parameters |
Units |
S13-P |
S14-P |
S23-P |
S24-P |
S13DR-P |
S14VC-P |
| Annual mileage |
km |
20.000 |
20.000 |
40.000 |
40.000 |
20.000 |
20.000 |
| Van’s ownership duration |
year |
5 |
10 |
5 |
10 |
5 |
10 |
| Discount rate |
% |
6 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
2,5 |
6 |
| Inflation index |
wf (1)
|
2,50 |
2,50 |
2,50 |
2,50 |
1,00 |
2,50 |
| Electricity price (2)
|
€/kWh |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
0,15 |
| Hydrogen price (2)
|
€/kg |
4,61 |
4,61 |
4,61 |
4,61 |
4,61 |
4,61 |
| CNG price (2)
|
€/kg |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
| FC (3) van purchase price |
wf |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,00 |
| FC (3) van M&R cost |
wf |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
| Carbon tax |
€/ton CO2e
|
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
| EF electricity |
kgCO2e/kWh |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
| EF hydrogen |
kgCO2e/kg |
4,72 |
4,72 |
4,72 |
4,72 |
4,72 |
4,72 |
| PVO (4) |
CNG |
BEV |
FCEREV |
FCEREV |
BEV |
FCEREV |
Table 13.
Worst-case scenarios result in the H2G case for the BAL solutions considering Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
Table 13.
Worst-case scenarios result in the H2G case for the BAL solutions considering Scopes 1, 2 and 3.
| |
|
Worst-case scenarios and scenario values |
| Parameters |
Units |
S13-G |
S14-G |
S23-G |
S24-G |
S13DR-G |
S14VC-G |
| Annual mileage |
km |
20.000 |
20.000 |
40.000 |
40.000 |
20.000 |
20.000 |
| Van’s ownership duration |
year |
5 |
10 |
5 |
10 |
5 |
10 |
| Discount rate |
(%) |
6 |
6 |
6 |
6 |
2,5 |
6 |
| Inflation index |
wf (1)
|
2,50 |
2,50 |
2,50 |
2,50 |
1 |
2,50 |
| Electricity price (2)
|
(€/kWh) |
0,17 |
0,17 |
0,17 |
0,17 |
0,17 |
0,17 |
| CNG price (2)
|
(€/kg) |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
2,43 |
| FC (3) van purchase price |
wf |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,00 |
1,00 |
1,10 |
1,00 |
| FC (3) M&R cost |
wf |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
1,10 |
| Carbon tax |
€/ton CO2e
|
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
155 |
| EF electricity |
kgCO2e/kWh |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
0,25 |
| PVO (4) |
CNG |
BEV |
BEV |
BEV |
BEV |
FCEREV |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).