Submitted:
25 October 2023
Posted:
26 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods

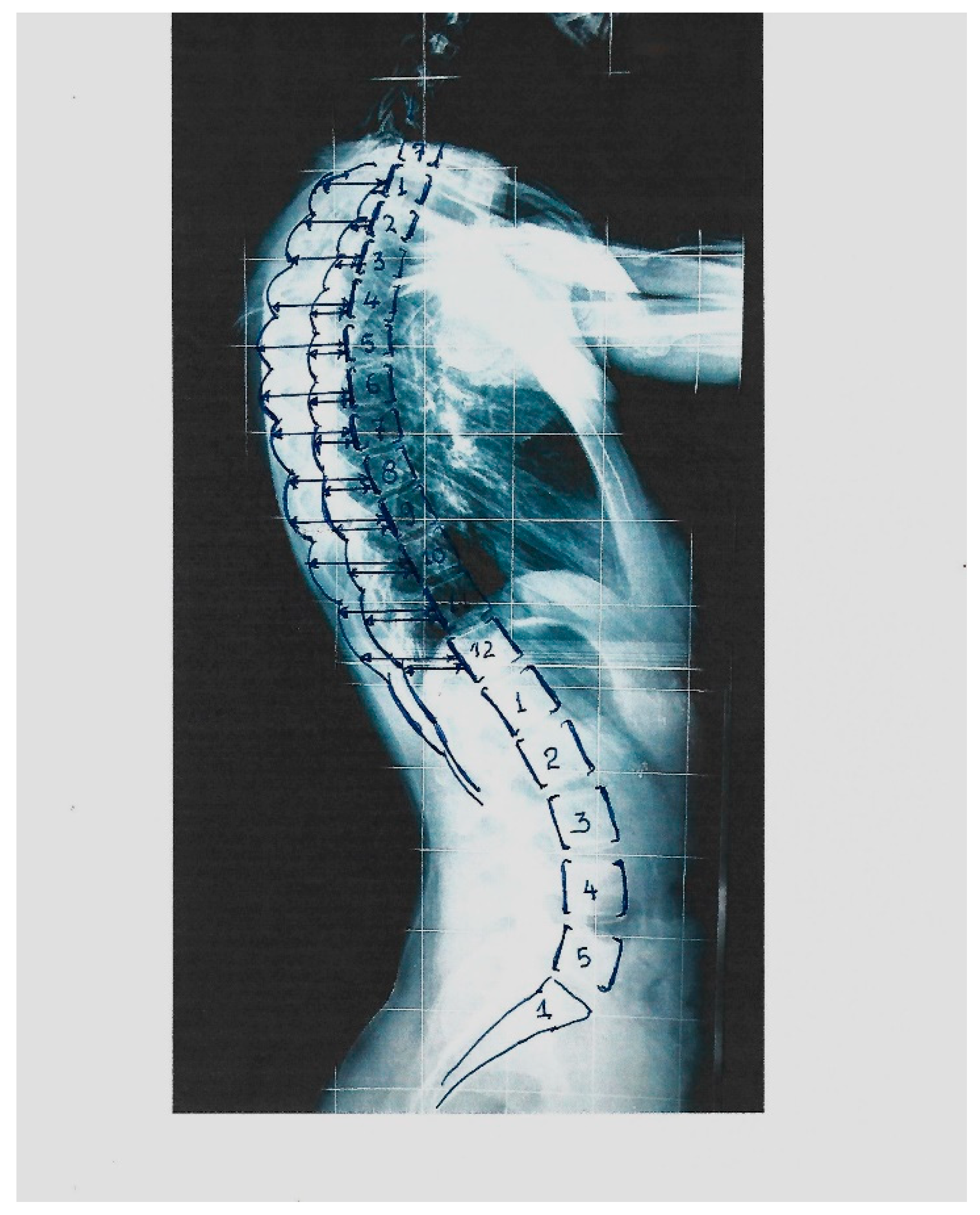
3. Results
| Total | Female | Male | p value | |
| N | 83 | 63 (75,9%) | 20 (24.1%) | |
| Age (years) | 12.3 ± 2.7 | 12.5 ± 2.5 | 11.5 ± 3.5 | 0.241a |
| Risser stage | 2 (4) | 2 (4) | 0 (2.8) | 0.023b |
| Cobb angle | 26.3±10.8 | 27.7±11.2 | 22.7±7.8 | 0.068a |
| ATR | 7.6±4.3 | 8.0±4.4 | 7.3±4.6 | 0.514a |
| Gender | Curve type | n | Mean ± SD |
| Male | Thoracic | 6 (7.2%) | 25.4 ± 8.1 |
| Thoracolumbar | 6 (7.2%) | 22.0 ± 10.4 | |
| Lumbar | 8 (9.6%) | 21.1 ± 5.6 | |
| Female | Thoracic | 19 (22.9%) | 29.0 ± 12.2 |
| Thoracolumbar | 26 (31.3%) | 27.7 ± 9.8 | |
| Lumbar | 18 (21.7%) | 26.2 ± 12.5 |
| n=83 | Pearson correlation | p value |
|---|---|---|
| T6 | 0.292 | 0.007* |
| T7 | 0.220 | 0.046* |
| T8 | 0.240 | 0.029* |
| n=25 | Pearson correlation | p value |
|---|---|---|
| T6 | 0.432 | 0.031* |
| T7 | 0.419 | 0.037* |
| T8 | 0.520 | 0.008* |
| T9 | 0.424 | 0.034* |
| T10 | 0.491 | 0.013* |
| T11 | 0.556 | 0.004* |
| T12 | 0.485 | 0.014* |
Segmental Rib Index and Cobb angle correlations
| Female |
Thoracic n=19 |
Thoracolumbar n=26 |
Lumbar n=18 |
p value |
| T1 | 1.30 (0.48) | 1.20 (0.43) | 1.15 (0.50) | 0.444a |
| T2 | 1.40 (0.54) | 1.67 (0.72) | 1.24 (0.71) | 0.310a |
| T3 | 1.51 (0.51) | 1.57 (0.59) | 1.38 (0.64) | 0.233a |
| T4 | 1.59 (0.58) | 1.57 (0.40) | 1.38 (0.51) | 0.201a |
| T5 | 1.67 (0.95) | 1.46 (0.35) | 1.45 (0.48) | 0.404a |
| T6 | 1.60 (0.60) | 1.42 (0.40) | 1.40 (0.42) | 0.322a |
| T7 | 1.54 (0.51) | 1.40 (0.29) | 1.39 (0.47) | 0.133a |
| T8 | 1.60 (0.50) | 1.39 (0.30) | 1.34 (0.45) | 0.054a |
| T9 | 1.73 (0.52)TL | 1.38 (0.33) | 1.42 (0.41) | 0.018a |
| T10 | 1.75 (0.57) | 1.42 (0.55) | 1.20 (0.66) | 0.052a |
| T11 | 1.43 (0.70) | 1.49 (0.50) | 1.20 (0.54) | 0.091a |
| T12 | 1.22 (0.67) | 1.41 (0.50)L | 1.11 (0.32) | 0.021a |
| female | Thoracic vs thoracolumbar |
Thoracic vs lumbar |
Thoracolumbar vs lumbar | |
| T9 | 0.011* | - | - | |
| T12 | - | - | 0.005* |
| Male | Thoracic (n=6) |
TL (n=6) |
Lumbar (n=8) |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 1.11 (0.20) | 1.18 (0.39) | 1.21 (0.49) | 0.487a |
| T2 | 1.13 (0.51) | 1.29 (0.42) | 1.32 (0.63) | 0.768a |
| T3 | 1.26 (0.58) | 1.52 (1.17) | 1.36 (0.47) | 0.691a |
| T4 | 1.26 (0.66) | 1.50 (1.13) | 1.44 (0.51) | 0.372a |
| T5 | 1.22 (0.88) | 1.50 (1.02) | 1.36 (0.62) | 0.215a |
| T6 | 1.52 (0.59) | 1.39 (0.88) | 1.26 (0.58) | 0.352a |
| T7 | 1.43 (0.35) | 1.58 (0.82) | 1.32 (0.60) | 0.331a |
| T8 | 1.47 (0.28) | 1.61 (1.01) | 1.39 (0.66) | 0.411a |
| T9 | 1.50 (0.17) | 1.61 (0.97) | 1.40 (0.59) | 0.371a |
| T10 | 1.53 (0.41) | 1.70 (0.95) | 1.41 (0.34) | 0.300a |
| T11 | 1.43 (0.66) | 1.59 (0.54) | 1.29 (0.33) | 0.219a |
| T12 | 1.19 (0.38) | 1.63 (0.90) | 1.38 (0.43) | 0.274a |
| All patients | Age<13 | Age>13 | Age<14 | Age>14 | |
| r (p value) | r (p value) | r (p value) | r (p value) | r (p value) | |
| Thoracic curve | n=25 | n=13 | n=12 | n=14 | n=11 |
| T8 | - | - | - | - | 0.703 (0.016) |
| T9 | - | - | - | - | 0.679 (0.022) |
| T10 | 0.462 (0.020) | - | - | - | 0.703 (0.016) |
| T11 | 0.465 (0.019) | - | 0.587 (0.045) | - | 0.745 (0.009) |
| T12 | 0.547 (0.005) | - | 0.591 (0.043) | - | - |
| Thoracolumbar curve | n=32 | n=15 | n=17 | n=19 | n=10 |
| T1 | - | - | - | - | 0.642 (0.046) |
| T4 | -0.388 (0.031) | -0.571 (0.026) | - | -0.623 (0.004) | - |
| T6 | - | - | -0.503 (0.039) | - | - |
| T7 | - | - | -0.527 (0.030) | - | - |
| T8 | - | - | -0.582 (0.014) | - | - |
| T9 | - | - | -0.561 (0.019) | - | - |
| Lumbar curve | n=26 | n=10 | n=16 | n=10 | n=16 |
| T1 | - | -0.835 (0.010) | - | - | - |
| T2 | - | -0.938 (0.001) | - | - | - |
| T8 | - | - | 0.527 (0.036) | 0.613 (0.020) | - |
| T9 | 0.394 (0.046) | - | 0.662 (0.005) | - | - |
| T11 | - | - | 0.507 (0.045) | - | - |
4. Discussion and conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nissinen M, Heliovaara M, Tallroth K, Poussa M. Trunk asymmetry and scoliosis. Anthropometric measurements in prepubertal school children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989, 78, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivas, T.B. Thorax and the idiopathic Scoliosis. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 11, 1252–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle H, Richards SB, De Kleuver M, Grivas TB, Luk KD, Wong HK, Thometz J, Beauséjour M, Turgeon I, Fong DY. Screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: an information statement by the scoliosis research society international task force. Scoliosis. 2013, 8:17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivas TB. Rib index. Scoliosis. 2014, 9: 20. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, A., Lebel, V. Rib index, an objective measure to document changes of the rib hump deformity in a Risser 4 progressive AIS patient treated with the Schroth method. Scoliosis 9 (Suppl 1), O18, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Grivas TB. Radiological appraisal of thoracic deformity - improvement or deterioration using the convex/concave rib-hump index (‘double rib contour sign’) in curves Lenke Type 1, 3, 5 and 6. In book: Scoliosis Research Society. Half-Day Courses, Chapter: Radiological appraisal of thoracic deformity - improvement or deterioration using the convex/concave rib-hump index (‘double rib contour sign’) in curves Lenke Type 1, 3, 5 and 6., Publisher: Scoliosis Research Society, Editors: SRS 2012-2013 Education Committee, 2013, 29-30.
- Haber LL, Adams TM, Briski DC, Celestre PC, Robbins DJ, Waldron SR. Long-term Results of Spine Stapling for AIS to Skeletal Maturity and Beyond J Pediatr Orthop. 2020, 40(1): e37-e41. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsirikos AI and McMillan TE. All Pedicle Screw versus Hybrid Hook–Screw Instrumentation in the Treatment of Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS): A Prospective Comparative Cohort Study Healthcare 2022, 10, 1455. [CrossRef]
- Sevastik J., Burwell R. G., Dangerfield P. H. A new concept for the etiopathogenesis of the thoracospinal deformity of idiopathic scoliosis: summary of an electronic focus group debate of the IBSE. Eur Spine J (2003) 12: 440–450. [CrossRef]
- Burwell RG, Dangerfield PH, Moulton A, Grivas TB, Cheng JC. Whither the etiopathogenesis (and scoliogeny) of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis? Incorporating presentations on scoliogeny at the 2012 IRSSD and SRS meetings. Scoliosis. 2013 Feb 28;8(1) :4. [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J. Outline for the study of scoliosis. Instr Course Lect. 1948, 5, 261–275. [Google Scholar]
- Grivas TB, Vasiliadis ES, Kouropoulos G, Segos D, Triantafyllopoulos G, Mouzakis V. 2006. Study of trunk asymmetry in normal children and adolescents. Scoliosis. 2006, 1:19. [CrossRef]
- Cheung M-C, Yip J, Lai JSK. Biofeedback Posture Training for Adolescents with Mild Scoliosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Monticone M, Ambrosini E, Cazzaniga D, Rocca B, Ferrante S. Active self-correction and task-oriented exercises reduce spinal deformity and improve quality of life in subjects with mild adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Results of a randomized controlled trial. Eur. Spine J. 2014, 23, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, Czaprowski D, Schreiber S, De Mauroy JC, Diers H, Grivas TB, Knott P, Kotwicki T, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: Orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein SL, Dolan LA, Wright JG, Dobbs MB. Effects of bracing in adolescents with idiopathic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1512–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznia AL, Hernandez AK. Lee LU. Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Common Questions and Answers. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 101, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Courvoisier A, Drevelle X, Dubousset J, Skalli W. Transverse plane 3D analysis of mild scoliosis. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 2427–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijs JE, W Keessen, R van der Meer, J C van Wieringen, M A Hageman. School screening for scoliosis: methodologic considerations. Part 1: External measurements Spine. 1992, 17, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Pruijs JE, W Keessen, R van der Meer, J C van Wieringen. School screening for scoliosis: the value of quantitative measurement. Eur Spine J. 1995. 4(4):226-30. [CrossRef]
- Nissinen M, Heliovaara M, Tallroth K, Poussa M. Trunk asymmetry and scoliosis. Anthropometric measurements in prepubertal school children. Acta Paediatr Scand 1989, 78, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissinen M, Heliovaara M, Seltsamo J, Poussa M. Trunk Asymmetry, Posture, Growth, and Risk of Scoliosis. A Three-Year Follow-Up of Finnish Prepubertal School Children. Spine 1993, 18, 1, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Sevastik JA, Aaro S, Normelli H. Scoliosis. Experimental and clinical studies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984, 191, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Normelli H, Sevastik J, Wallberg H. The thermal emission from the skin and the vascularity of the breasts in normal and scoliotic girls. Spine 1986, 11(5):405-8. [CrossRef]
- Sevastik JA, Aaro S, Lindholm ST, Dalhborn M. Experimental scoliosis in growing rabbits by operations on the rib cage. Clinical Orthopaedics. 1987, 136, 282–86. [Google Scholar]
- Agadir M, Sevastik B, Sevastik JA, Persson A, Isberg B. Induction of scoliosis in the growing rabbit by unilateral rib-growth stimulation. Spine. 1988, 13, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normelli H, Sevastik JA, Ljung, G, Jönsson-Söderström AM. The symmetry of the breasts in normal and scoliotic girls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1986, 11(7):749-52. [CrossRef]
- Sevastik J, Agadir M, Sevastik B 1990. Effects of rib elongation on the spine: I. Distortion of the vertebral alignment in the rabbit. Spine. 1990, 15: 822-825. [CrossRef]
- Sevastik J, Agadir M, Sevastik B. 1990. Effects of rib elongation on the spine: II. Correction of scoliosis in the rabbit. Spine. 1990, 15: 826-829. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agadir M, Sevastik B, Reinholt FP, Perbeck L, Sevastik J. Vascular Changes in the Chest Wall After Unilateral Resection of the Intercostal Nerves in the Growing Rabbit. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 1990, 8, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastik B, Xiong B, Lundberg A, Sevastik JA. In vitro opto-electronic analysis of 3-D segmental vertebral movements during gradual rib lengthening in the pig. Acta Orthop Belg. 1995, 61, 218–25 PMID: 8525819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gréalou L, Aubin CE, Sevastik JA, Labelle H Simulations of rib cage surgery for the management of scoliotic deformities. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002, 88, 345–9 PMID: 15456059. [PubMed]
- Sevastik JA Dysfunction of the autonomic nerve system (ANS) in the aetiopathogenesis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002, 88, 20–3 PMID: 15455999. [PubMed]
- Sevastik JA, Burwell RG, Dangerfild PH. A new concept for the etiopathogenesis of the thoracospinal deformity of idiopathic scoliosis: summary of an electronic focus group debate of the IBSE. Eur Spine J. 2003. 12: 440–450. [CrossRef]
- Sevastik, JA. Right convex thoracic female adolescent scoliosis in the light of the thoracospinal concept. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2006, 123, 552–8 PMID: 17108486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiong B, Sevastik JA. A physiological approach to surgical treatment of progressive early idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 1998, 7(6):505-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Βurwell RG, Cole AA, Cook TA, Grivas TB, Kiel AW, Moulton A, Thirlwall AS, Upadhyay SS, Webb JK, Wemyss-Holden SA, Whitwell DJ, Wojcik AS, Wythers DJ. 1991-1992. Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Scoliosis. The Nottingham Concept. Acta Orthop Belgica 1992, 58 Suppl. 1, 33–58.
- Dansereau J, Stokes IAF. Measurements of three-dimensional shape of the rib cage. J Biomech 1988, 21, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierholzer E, Hackenberg L. Three-dimensional shape analysis of the scoliotic spine using MR tomography and rasterstereography. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2002, 91, 184–9, PMID: 15457720. [PubMed]
- Sangole AP, Aubin CE, Labelle H, Stokes IA, Lenke LG, Jackson R, Newton P. Three-dimensional classification of thoracic scoliotic curves. Spine 2009, 1;34(1):91-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donzelli S, Poma S, Balzarini L, Borboni A, Respizzi S, Villafane JH, Zaina F, Negrini S. State of the art of current 3-D scoliosis classifications: a systematic review from a clinical perspective. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2015, 16; 12:91. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dansereau J, Stokes IAF, Moreland MS. Radiographic reconstruction of 3D human rib cage. In Surface Topography and Spinal Deformity Edited by: Stokes IAF, Pekelsky JR, Moreland MS. Stuttgart: Gustav Fischer 33, 67–76.
- Grivas, T.B.; Jevtic, N.; Ljubojevic, D.; Pjanic, P.; Golic, F.; Vasiliadis, E. Segmental Rib Index and Spinal Deformity: Aetiological Implications to Idiopathic Scoliosis. 2023. Međunarodni Kongres, se Održava na Zlatiboru u Kongresnom Centru “Hotel Mona” od 21–24 Septembra 2023, Godine Pod Nazivom: “Nove Perspektive u Razvoju Fizikalne i Rehabilitation Medicine”. Available online: https://fizijatri.org/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Barrett DS, MacLean JGB, Bettany J, Ransford AO, Edgar MA. Costoplasty in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Objective results in 55 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1993, 75, 881–885.
- Harvey Jr. CJ, Betz RR, Clements DH, Huss GK, Clancy M. Are there indications for partial rib resection in patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treated with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation? Spine 1593, 18, 1593–1598.
- Shufflebarger HL, Smiley K, Roth HJ. Internal thoracoplasties. A new procedure. Spine 1994, 19, 840–842. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, HH. Rib resection and spine fusion in correction of convex deformity in scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1983, 65, 920–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkula G, Sponseller PD, Kiter AE. Rib deformity in scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2003, 12(3):281-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





