1. Introduction
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) is a non-invasive procedure commonly used by physicians and health professionals to examine the aerobic capacity and dynamic interplay between exercise and integrated physiological systems of individuals [
1,
2]. Cardiovascular, ventilatory and gas exchange variables are collected during the test, usually performed in clinical or research settings to identify exercise intolerance and cardiovascular or cardiopulmonary diseases amplified or only present during exercise [
3,
4]. Moreover, not only is CPET relevant for assessing pre- and postsurgical complication risk, early detection of cardiopulmonary diseases, and guiding and monitoring individual physical training in rehabilitation [
5,
6,
7].
Although the Douglas Bag (DB) method has traditionally stood as the gold standard for assessing gas exchange during exercise [
8], its use has been discouraged as it is time-consuming, requires a laboured process to determine oxygen production (VO
2) and carbon dioxide production (VCO
2), and bag’s size may limit the duration of exercise assessment. Alternatively, computerized metabolic carts (MCs) have emerged as the new gold standard, surpassing the DB method while avoiding its cumbersome limitations. These devices are typically highly reliable and valid metabolic devices that can measure gas exchange by breath-by-breath mode during CPET by analysing exhaled air content [
9]. While validity and reliability studies are often conducted by trade names, comparative studies examining measurement differences between two different computerised MCs are scarce [
10,
11,
12,
13]. For instance, when multicentre studies are performed, combining two or more different devices, or even when these become obsolete and are replaced by newer versions.
In addition, the use of antibacterial filters during CPET in instances involving suspected or confirmed infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, introduces an additional possibility of measurement variation. Antibacterial filters during CPET have been of upmost importance in the context of aerosol-borne infectious diseases, and since minute ventilation and expiratory flow rates are increased up to 10-fold during intense exercise [
14], the risk of infection may increase disproportionately. When using facemasks attached to a filter, manufacturers have reported that antibacterial filters resistance to air flow vary around 0 to -0.5 cmH2O·(l/s)-1 at different ventilation rates up to 200 L·min-1 [
15], which represents an unnoticeable impact on the exercise test outcomes. In accordance with that, present evidence may suggest that bacterial filters have little impact on CPET measurements [
16,
17].
In this regard, the Jaeger Oxycon Pro and Quark RMR are two commonly used devices in the laboratory use. Both have been shown to be accurate devices for the measurement of gas exchange variables [
10,
12,
13] in the mixing chamber and breath-by-breath mode. However, they have never been compared to each other when antibacterial filters have been implemented. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to compare both devices using an antibacterial filter when measuring gas exchange variables during CPET. This will provide insight into whether the use of these metabolic carts could be interchangeable or combined when a single device cannot be used for CPET assessment.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted at the University of Castilla-La Mancha (Toledo, Spain). It was approved by the Ethics Committee of Clinical Research of the Toledo Hospital (C.E.I.C. nº591) and performed according to the Helsinki Declaration. All participants signed a written informed consent after a thorough explanation of the experimental procedures was provided to each participant.
2.1. Participants
A total sample of 42 participants was selected for this study. Sample size calculated using G*Power 3.1 [
18] suggested the inclusion of at least 39 participants to achieve a 95% statistical power (α = 0.05; and a moderate effect size = 0.6) for primary outcomes. The only inclusion criterion was being over 18 years old whereas the exclusion criteria included having any cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, such as angina pectoris or uncontrolled arrhythmias or suffering from infectious-contagious disease. Furthermore, the recruitment process was meticulously conducted with the aim of obtaining the most heterogeneous sample possible in terms of both age and body composition.
2.2. Experimental design
Participants were required to perform two maximal graded exercise tests (GXT) on two non-consecutive days, and using the Jaeger Oxycon Pro (Erich Jaeger GmbH, Hoechberg, Germany) and the COSMED Quark RMR (COSMED, Rome, Italy), in a counterbalance fashion. The use of each of the gas analysers was randomized before the first session. In order to minimize interference among both tests, each assessment was carried out 1 week apart. Similarly, the same measurement time and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, and cyclo-ergometer metrics) as on the first measurement day were replicated for the second day. In addition, each subject recorded a diary for physical activity, meals, and sleep one week prior to the first test. Then, they were asked to keep the same food intake, schedule and activity level between tests. As for the attendance conditions for each test, subjects were required to arrive at the laboratory: (i) rested, without having performed vigorous physical activity nor exercise 24 hours prior to the test; (ii) with an optimum hydration state; and (iii) in fasted conditions for ≥ 3 hours before the test and restrained from alcohol and stimulant substances (e.g., caffeine) ingestion.
2.3. Metabolic devices
For the Oxycon Pro (Erich Jaeger GmbH, Hoechberg, Germany), cardiopulmonary data was recorded in breath-by-breath mode together with a facemask (Hans Rudolph, Inc., Kansas City, USA) and a COVID antibacterial filter attached Before testing, this device went through a warm-up period of at least 4 hours, followed by a calibration phase. This calibration phase was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions: (i) calibration of room conditions (temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure); (ii) calibration of the flowmeter sensor (Triple V, Enrich Jaeger GmbH, Hoechberg, Germany) using a 3L volume certified syringe (CareFusion, San Diego, California, USA); and (iii) calibration of the O2 and CO2 analyser cells according to a certified gas sample (5.85% CO2, 15.00% O2, and balanced N2, Riessner-Gase GmbH, Lichtenfels, Germany). Both volume and gas calibration were repeated until the difference between consecutive calibrations was less than 1%.
For the COSMED Quark RMR (COSMED, Rome, Italy) gas exchange during exercise was assessed using the breath-by-breath mode together with a facemask (Hans Rudolph, Inc., Kansas City, USA) attached. However, no antibacterial filter was used with the COSMED device. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, a warm-up period of at least 45 minutes was performed before testing followed by a calibration phase: (i) calibration of the flowmeter using a 3L volume certified syringe (COSMED, Rome, Italy); and (ii) a metabolic calibration (ERGO) using a known reference gas (5.00% CO2, 16.00% O2, and balanced N2, Airgas Specialty Gases, LLC, PA, USA). Volume calibration was repeated until the difference between consecutive calibrations was less than 2%.
2.4. Maximal graded exercise test
Cardiopulmonary and related parameters were assessed by a GXT and a supramaximal constant-load verification test (VerT) on an electromagnetically braked cycle-ergometer (800S, Ergoline, Bitz, Germany). Seat and handlebar adjustments were fit to the subjects’ specifications and remained unchanged during all bouts. Gas exchange and related cardiorespiratory parameters were assessed using both Jaeger Oxycon Pro and COSMED Quark RMR and electrical activity of the myocardium and heart rate were continuously recorded and synchronized using a standard 12-lead ECG (Cardiosoft 12SL-ECG, GE Healthcare, Finland). Subjects performed two identical mutually exclusive GXT protocols according to age and sex:
(i) a 5-min resting phase to record baseline parameters;
(ii) a 5-min warm-up either at 15 (protocol 1), 30 (protocol 2), or 50 W (protocol 3) followed by (iii) a work-rate increment of 3, 4, or 5 W every 12s for protocols 1 to 3, respectively, until volitional exhaustion while receiving intense verbal encouragement (
Supplementary Table S1). Pedaling cadence was chosen by participants yet was required to be maintained constant between 60-90 rpm. The stage increments in work rate were chosen to bring the subject to exhaustion in ~8min [
19,
20]. At exhaustion, work rate was reduced to the warm-up stage and the subject cooled down actively for 2 minutes. After 10 minutes of seated rest with rehydration allowed, participants performed a two-step VerT:
(i) 1-min warm-up at 50% of the peak work rate (W
peak), followed by
(ii) as long as possible stage at 110% of W
peak. The test was terminated when pedaling cadence was dropped below 60 rpm for ten consecutive seconds despite strong verbal encouragement.
2.5. Anthropometrics and clinical information
Body mass (kg) and height (cm) were assessed to the nearest 0.1, using a stadiometer Seca 711 (Hamburg, Germany). Body Mass Index (BMI) was calculated as body mass divided by squared height (kg/m2). Besides, an individualized interview was conducted to record sex, age, clinical history, and cardiovascular disease risk factors or any other pathology.
2.6. Data analysis
Before analysis, mechanical (i.e, Wpeak) and ventilatory parameters (i.e., VO2) were averaged every 12 s and 20 s and graphically displayed. Peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) was expressed as the highest 20s-averaged segment in VO2 achieved during GXT and maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) was defined as the highest 20s-averaged segment VO2 value achieved either in GXT or VerT. Then, 12s-averaged submaximal-to-maximal segments of incremental loading phase were individually matched by load (W) between metabolic devices.
2.7. Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Normal distribution of the data was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Ventilatory outcomes were tested for differences between devices, correlation and agreement both at maximal effort and for the whole test. Differences in maximal physiological CPET outcomes, and throughout the entire incremental loading phase, were assessed using a generalized linear model with sex as between-subjects factor and metabolic device as within-subject factor. These differences were tested in the whole sample and divided by sex. When differences were found, Bonferroni’s post hoc test was also performed. The relative variability among devices was assessed using the coefficient of variation (CV) and mean±SD throughout the full exercise test. Pearson’s correlation coefficient (r) and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) were performed to examine the correlation and agreement, respectively. Moreover, Lin’s concordance correlation coefficient (Lin’s CCC) and Bland-Altman plots [
21] were also calculated to explore agreement among devices individually during the exercise. Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS version 23.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and the level of significance was set at α ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
A detailed description of the participant’s characteristics is shown in
Table 1. A total of 42 participants were included in the analyses, of which, 22 were men (33.0±11.0 years) and 20 were women (33.6±10.4 years).
Maximal effort was comparable between tests. On average between both devices, the maximal heart rate in the graded exercise test was 177.1 ± 13.3 beat·min
-1, occurring at a W
peak of 256.0 ± 81.6 W. In general, ventilatory variables at maximal effort were similar between gas analysers (
Table 2). Within the whole sample, no significant differences were found between metabolic devices in primary outcomes: VO
2 (mean difference: 57.7 ± 31.2 ml·min
-1) and VCO
2 (mean difference: 110.1 ± 59.4 ml·min
-1) and V
Emax (mean difference: 0.78 ± 2.17 L). However, Work-VO
2 slope was lower when using the Quark RMR device (mean difference: -0.69 ± 0.20 W·ml
-1·min
-1co).
Differences between Quark RMR and Oxycon Pro with an antibacterial filter along the whole incremental exercise were also analyzed by matching 12 s load stages (
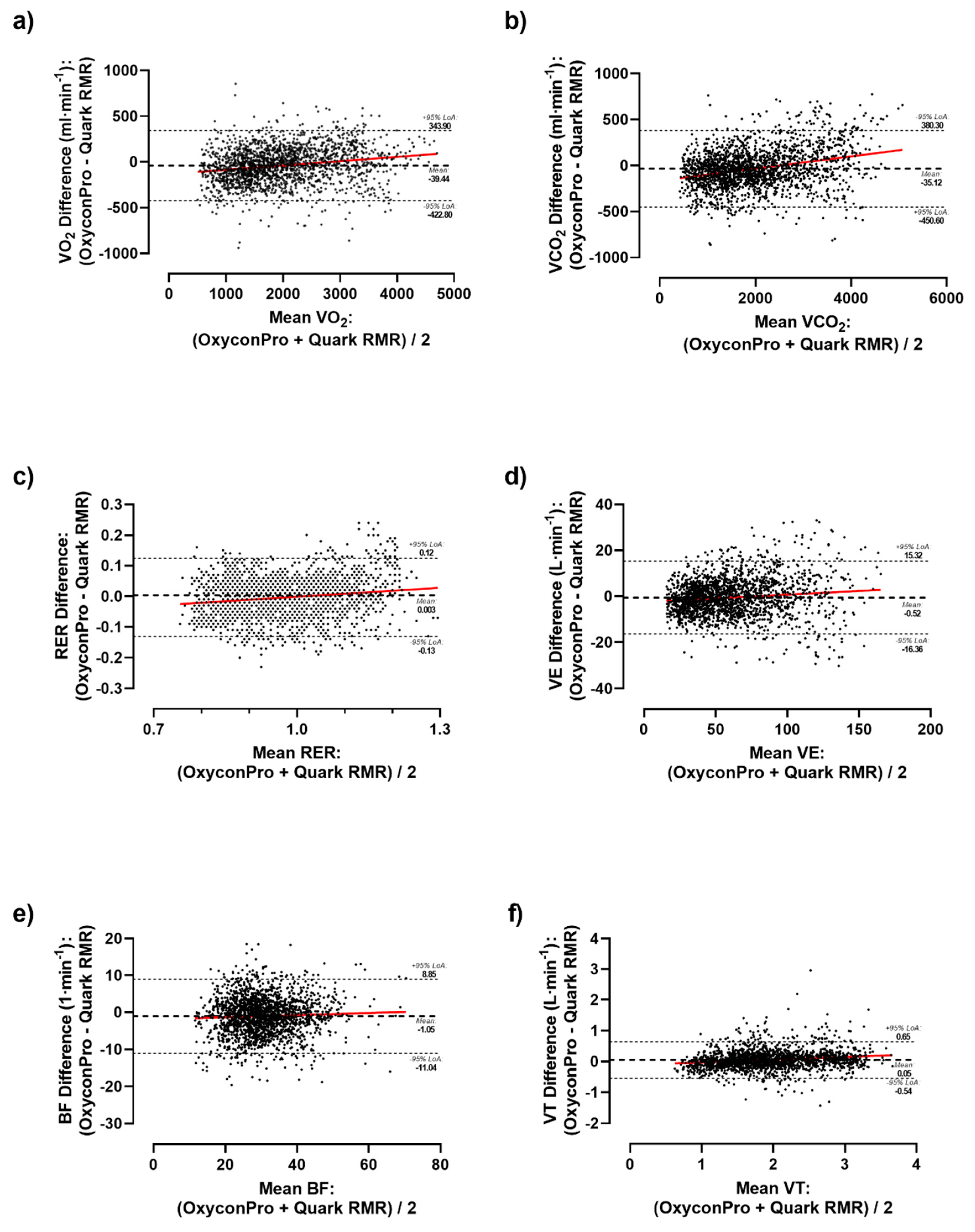
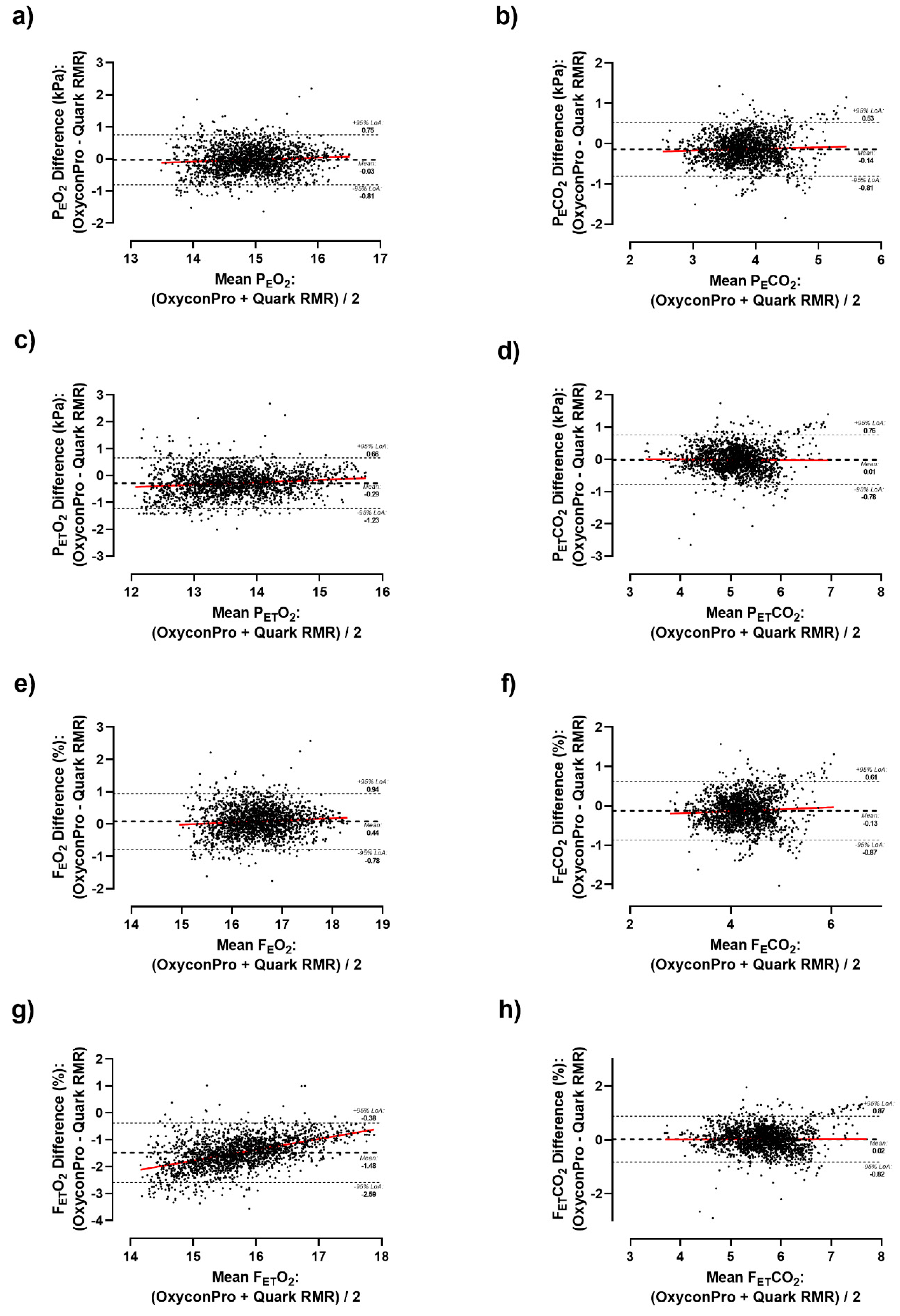
Supplementary Table S2). As a result, significant differences were detected in the vast majority of the measured ventilatory parameters both considering the whole sample and by sex. Likewise, differences were graphically depicted by Bland-Altman plots (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). Primary outcomes of VO
2 showed a mean bias of -39.44 ml·min
-1 (LoA: 343.90 to -422.80 ml·min
-1) (
Figure 1A), -35.12 ml·min
-1 (LoA: 380.30 to -450.60 ml·min
-1) for VCO
2 (
Figure 1B), and -0.003 (LoA: 0.12 to -0.13) for RER (
Figure 1C) during the whole test. As a result, a subtle but consistent overestimation of Oxycon Pro relative to Quark RMR was observed as airflow volume increased in all ventilatory parameters except for F
ETO
2 which has shown a higher mean bias of -1.48 % (LoA: -0.38 to -2.59 %) (
Figure 2G).
Regarding the reliability among devices (
Table 3), a within-devices mean coefficient of variation of 6.73% and 7.19% for VO
2 and VCO
2 was respectively obtained (range for other variables: CV 1.48-10.11%). Moreover, correlation analysis indicated significant relationships between respiratory measures from the two devices for the main ventilatory parameters of VO
2 (r=0.974, ICC=0.985; Lin’s CCC=0.971) and VCO
2 (r=0.977, ICC=0.987, Lin’s CCC=0.974) and in most of the remaining parameters (V
T, V
E, BF, ICC range: 0.902-0.981; and O
2 & CO
2 – P
E, P
ET, F
E and F
ET, ICC range: 0.811-0.857) except for F
ETO
2 (r= 0.764, ICC=0.390, Lin’s CCC=0.242).
4. Discussion
This study found consistently similar results for the evaluation of cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) between Quark RMR and Oxycon Pro, using an antibacterial filter with the latter. High concordance was found between metabolic devices in determining maximal ventilatory parameters which reveal little disparity between the two devices using an antibacterial filter only in one device. Additionally, there was an important level of agreement between main ventilatory outcomes recorded across the entire range at submaximal intensities.
One of the main findings within our research is the comparison of maximal physiological results obtained during exercise. Given the high level of reproducibility observed in maximal CPET outcomes among healthy individuals and those with some type of pathology [
22,
23,
24,
25], our results between both metabolic carts may suggest that both systems and methodology can be effectively used to compare CPET maximal values. Nevertheless, a slight tendency towards the overestimation of the Oxycon Pro over the Quark RMR device for VO
2 and VCO
2 could be observed (
Figure 1). To a lesser extent, this trend can also be observed in other variables (such as RER, VT, BF and VE). This could be of multi-factorial nature, namely, the type of measurement cell technology, maintenance status and different wear of cells could have potentially influenced the measurements. Besides, the use of antibacterial filters only with Oxycon Pro might have increased air flow resistance at higher ventilation rates, due to its wetting, which could have cause higher metabolic demands. Even so, our results have not shown any significant differences among devices.
However, maximal physiological response during exercise might not provide enough relevant information for diagnostic purposes [
26]. Thus, it was of utmost importance to determine the degree of agreement between both devices through the whole range of submaximal intensities during the incremental exercise test. Due to the initial experimental design i.e., ramp protocol, we were inclined to match results by 12-s load stages (W) increments, notwithstanding significant differences may appear when comparing smaller ventilation stages [
27]. Albeit, our results show a neutral mean difference close to zero for ventilatory parameters, these 12-s load stages differences tend to decrease percentage-wise as ventilatory flow increases (
Figure 1 and
Figure 2). These differences might be attributed to device variation, human biovariation, and data processing.
Computerized MC can determine CRF with CVs between 4% to 9% due to several sources of variation, such as environmental conditions, biological variability, and technical characteristics of the metabolic cart [
9]. Human physiological variation might account for between 5% to 10% of differences during cycling at moderate intensity under steady-state conditions [
28,
29]. In addition, given the fluctuation of breath-by-breath data, its processing may also contribute to variation in ventilatory parameters outcomes at submaximal intensities. As averaging strategy is diminished, variability could increase up to 7% between different measures [
30]. Besides, the presence of antibacterial filters while CPET measurements performed with Oxycon Pro may have had an impact on the final outcomes. And lastly, at the time of testing, whilst Oxycon Pro was an outdated 21-year-old device, Quark RMR was a brand-new gas analyser. Consequently, exhaustive maintenance of both devices before starting the trial and a thorough calibration process prior to each test was performed. Taking that into account, our results might be within the attainable range of biological variation and appliance error.
On the other hand, the strong correlation and concordance shown for VO
2 and VCO
2 indicate a substantial degree of agreement between both measurements. However, those statistical parameters decrease when considering pressures and fractions of expired air both in O
2 and CO
2. Notably, FETO2 showed the lowest concordance among all ventilatory parameters. At this juncture, MC “black box” [
9] comes into play. The user does not namely know the algorithm used by MC that determines the values of VO
2 consumption and VCO
2 production [
31]. In consideration of all the aforementioned factors, no adjustment between measurements has been deemed appropriate to fit the results obtained from the obsolete device.
Some limitations and strengths should also be acknowledged. First, the recordings were not performed simultaneously on both devices since the flowmeter turbine had to be attached to the face mask, which could trigger a time bias. For this reason, a strict counterbalancing protocol was followed and formal data processing criteria were applied. In addition, the use of biological systems may introduce biases linked to the inherent physiological fluctuations of the human being. However, strict attendance conditions were required (refraining from exercise 24 hours prior to the test, optimum hydration state, fasting, and abstention from stimulating substances ≥ 3 hours), keeping the same schedule one week prior to each test and providing environmental conditions as consistently uniform as possible. Moreover, an attempt was made to gather an age and physical condition heterogeneous sample to be able to detect possible measurements disagreement at different airflow ranges. Apart from that, it is crucial to highlight the implementation of an anti-bacterial filter attached to the flowmeter turbine only during Oxycon Pro recordings. Therefore, this limitation must be carefully considered for the general interpretation of the results since the influence on CPET has not firmly been demonstrated [
16,
17,
32]. Even so, the degree of agreement between both metabolic carts was remarkable.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate the agreement degree between Oxycon Pro Jaeger and COSMED Quark RMR when assessing aerobic capacity and gas exchange variables during CPET in the context of an aerosol-borne infectious disease. This study demonstrated high correlation and agreement between the COSMED Quark RMR and the Oxycon Pro Jaeger during CPETs. These results have not only been verified for maximal outcomes but also during submaximal intensity exercise. Therefore, this study provides consistency to CPET data comparisons between both devices when using an antibacterial filter only in one.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org. The following supporting information can be found: Supplementary Table S1. Cycle-ergometer graded exercise protocols. Supplementary Table S2. Differences in ventilatory parameters during CPET, matched by 12-s load stages (W) across the entire range by sex.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Miguel Muñoz-Muñoz, Javier Leal-Martín and Ivan Baltasar-Fernandez; Formal analysis, Miguel Muñoz-Muñoz, Javier Leal-Martín and José Losa-Reyna; Funding acquisition, Luis M. Alegre and Ignacio Ara; Investigation, Miguel Muñoz-Muñoz; Methodology, Miguel Muñoz-Muñoz and Javier Leal-Martín; Project administration, Julian Alcazar; Supervision, Ivan Baltasar-Fernandez, Luis M. Alegre, José Losa-Reyna and Ignacio Ara; Writing – original draft, Miguel Muñoz-Muñoz; Writing – review & editing, Javier Leal-Martín, Ivan Baltasar-Fernandez, Julian Alcazar, Luis M. Alegre, José Losa-Reyna and Ignacio Ara. All authors will be informed about each step of manuscript processing including submission, revision, revision reminder, etc. via emails from our system or assigned Assistant Editor.
Funding
This study was funded by the Carlos III Health Institute (PI18/00972). MMM received a grant from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación y Universidades (Grant FPU19/01276). JLM received a PhD grant from the Universidad de Castilla- La Mancha, Spain (2019- PREDUCLM- 11385). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of Clinical Research of the Toledo Complex Hospital (C.E.I.C nº591) and performed according to the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent Statement
All participants signed a written informed consent after a thorough explanation of the experimental procedures was provided to each participant. Experimental procedures were described in detail to each participant in advance.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to institutional restrictions but can be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Beltz, N.M.; Gibson, A.L.; Janot, J.M.; Kravitz, L.; Mermier, C.M.; Dalleck, L.C. Graded Exercise Testing Protocols for the Determination of VO2max: Historical Perspectives, Progress, and Future Considerations. Journal of Sports Medicine 2016, 2016, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albouaini, K.; Egred, M.; Alahmar, A.; Wright, D.J. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing and its application. Postgraduate Medical Journal 2007, 83, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, D.; Normandin, E.; ZuWallack, R. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the assessment of exertional dyspnea. Ann Thorac Med 2015, 10, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sietsema, K.E.; Stringer, W.W.; Sue, D.Y.; Ward, S. Wasserman & Whipp’s: principles of exercise testing and interpretation: including pathophysiology and clinical applications; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: 2020.
- Glaab, T.; Taube, C. Practical guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults. Respiratory Research 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guazzi, M.; Arena, R.; Halle, M.; Piepoli, M.F.; Myers, J.; Lavie, C.J. 2016 focused update: clinical recommendations for cardiopulmonary exercise testing data assessment in specific patient populations. European Heart Journal 2018, 39, 1144–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, R.; Blair, S.N.; Arena, R.; Church, T.S.; Després, J.-P.; Franklin, B.A.; Haskell, W.L.; Kaminsky, L.A.; Levine, B.D.; Lavie, C.J.; et al. Importance of Assessing Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Clinical Practice: A Case for Fitness as a Clinical Vital Sign: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, 653–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shephard, R.J. Open-circuit respirometry: a brief historical review of the use of Douglas bags and chemical analyzers. European Journal of Applied Physiology 2017, 117, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, D.J. Automated Metabolic Gas Analysis Systems. Sports Medicine 2001, 31, 841–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Austin, M.D.; Dew, D.; Utter, A.C. Validity of COSMED’s quark CPET mixing chamber system in evaluating energy metabolism during aerobic exercise in healthy male adults. Res Sports Med 2013, 21, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, L.D.; Brodie, D.A.; Bromley, P.D. Validity and reliability of selected commercially available metabolic analyzer systems. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2005, 15, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietjens, G.J.; Kuipers, H.; Kester, A.D.; Keizer, H.A. Validation of a computerized metabolic measurement system (Oxycon-Pro) during low and high intensity exercise. Int J Sports Med 2001, 22, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hooren, B.; Souren, T.; Bongers, B.C. Accuracy of respiratory gas variables, substrate, and energy use from 15 CPET systems during simulated and human exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, K.; Whipp, B.J. Excercise physiology in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 1975, 112, 219–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COSMED. Product Guide: Antiviral/Antibacterial filters. The most effective, safe and affordable solution to prevent viral and bacterial cross-contamination. 2021.
- Stacey, B.S.; Rose, G.A.; Davies, R.A.; Lewis, W.G.; Bailey, D.M. Effect of a novel viral filter on cardiopulmonary exercise testing during the COVID-19 pandemic. Anaesthesia 2021, 76, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faghy, M.A.; Sylvester, K.P.; Cooper, B.G.; Hull, J.H. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the COVID-19 endemic phase. Br J Anaesth 2020, 125, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfuhrer, M.J.; Hansen, J.E.; Robinson, T.E.; Sue, D.Y.; Wasserman, K.; Whipp, B.J. Optimizing the exercise protocol for cardiopulmonary assessment. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1983, 55, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.K.; Kravitz, L.; Robergs, R. VO2max, protocol duration, and the VO2 plateau. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2007, 39, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem Med (Zagreb) 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Westbrook, S.; Schwaibold, M.; Hajric, R.; Peters, K.; Roskamm, H. Short-term reproducibility of cardiopulmonary measurements during exercise testing in patients with severe chronic heart failure. Am Heart J 1997, 134, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saynor, Z.L.; Barker, A.R.; Oades, P.J.; Williams, C.A. Reproducibility of maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing for young cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 2013, 12, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, F.B.; Dalgas, U.; Brincks, J.; Langeskov-Christensen, M. Validity and reliability of VO2max testing in persons with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2023, 109, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decato, T.W.; Bradley, S.M.; Wilson, E.L.; Hegewald, M.J. Repeatability and Meaningful Change of CPET Parameters in Healthy Subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2018, 50, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrà, U.; Agostoni, P.G.; Anker, S.D.; Coats, A.J.S.; Crespo Leiro, M.G.; De Boer, R.A.; Harjola, V.-P.; Hill, L.; Lainscak, M.; Lund, L.H.; et al. Role of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in clinical stratification in heart failure. A position paper from the Committee on Exercise Physiology and Training of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. European Journal of Heart Failure 2018, 20, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robergs, R.A.; Dwyer, D.; Astorino, T. Recommendations for Improved Data Processing from Expired Gas Analysis Indirect Calorimetry. Sports Medicine 2010, 40, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCato, T.W.; Haverkamp, H.C.; Gooding, T.; Collingridge, D.S.; Hegewald, M.J. Variability in Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Biologic Controls. Respir Care 2023, 68, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porszasz, J.; Blonshine, S.; Cao, R.; Paden, H.A.; Casaburi, R.; Rossiter, H.B. Biological quality control for cardiopulmonary exercise testing in multicenter clinical trials. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Rincon, M.; Gonzalez-Henriquez, J.J.; Losa-Reyna, J.; Perez-Suarez, I.; Ponce-Gonzalez, J.G.; de La Calle-Herrero, J.; Perez-Valera, M.; Perez-Lopez, A.; Curtelin, D.; Cherouveim, E.D.; et al. Impact of data averaging strategies on O2max assessment: Mathematical modeling and reliability. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2019, 29, 1473–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Alvarez, J.J.; Lorenzo-Capella, I.; Calderon-Montero, F.J. Disadvantages of Automated Respiratory Gas Exchange Analyzers. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, M.S.; Fonseca, A.; Lima, R.; Ladeira, I.; Gomes, J.; Guimaraes, M. Effect of a viral filter on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Pulmonology 2022, 28, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).