Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Anesthetic Protocol
2.3. Electroacupuncture Protocol
2.4. Sampling and Analysis of Immune Function
2.5. Statistical Analysis
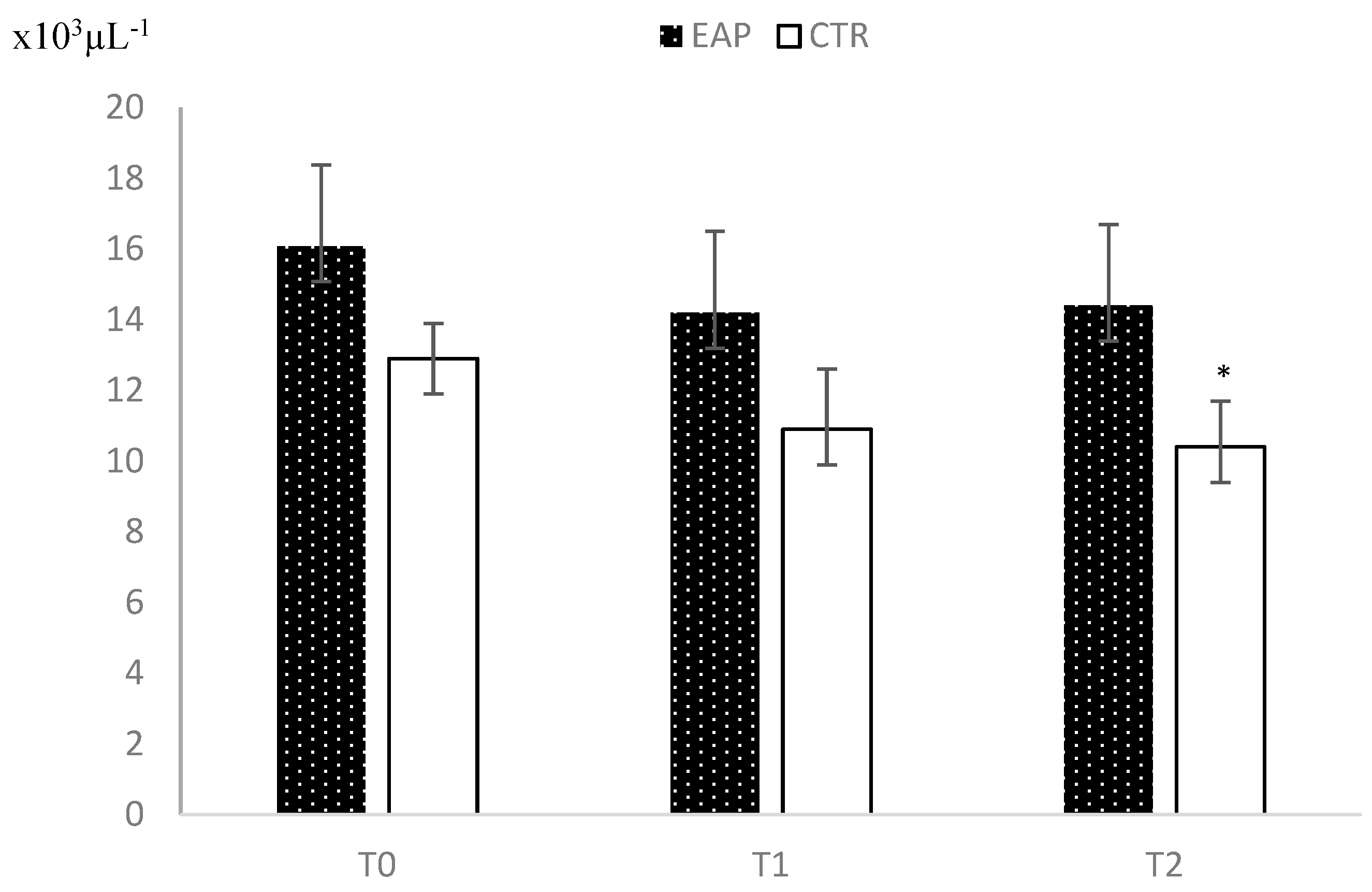
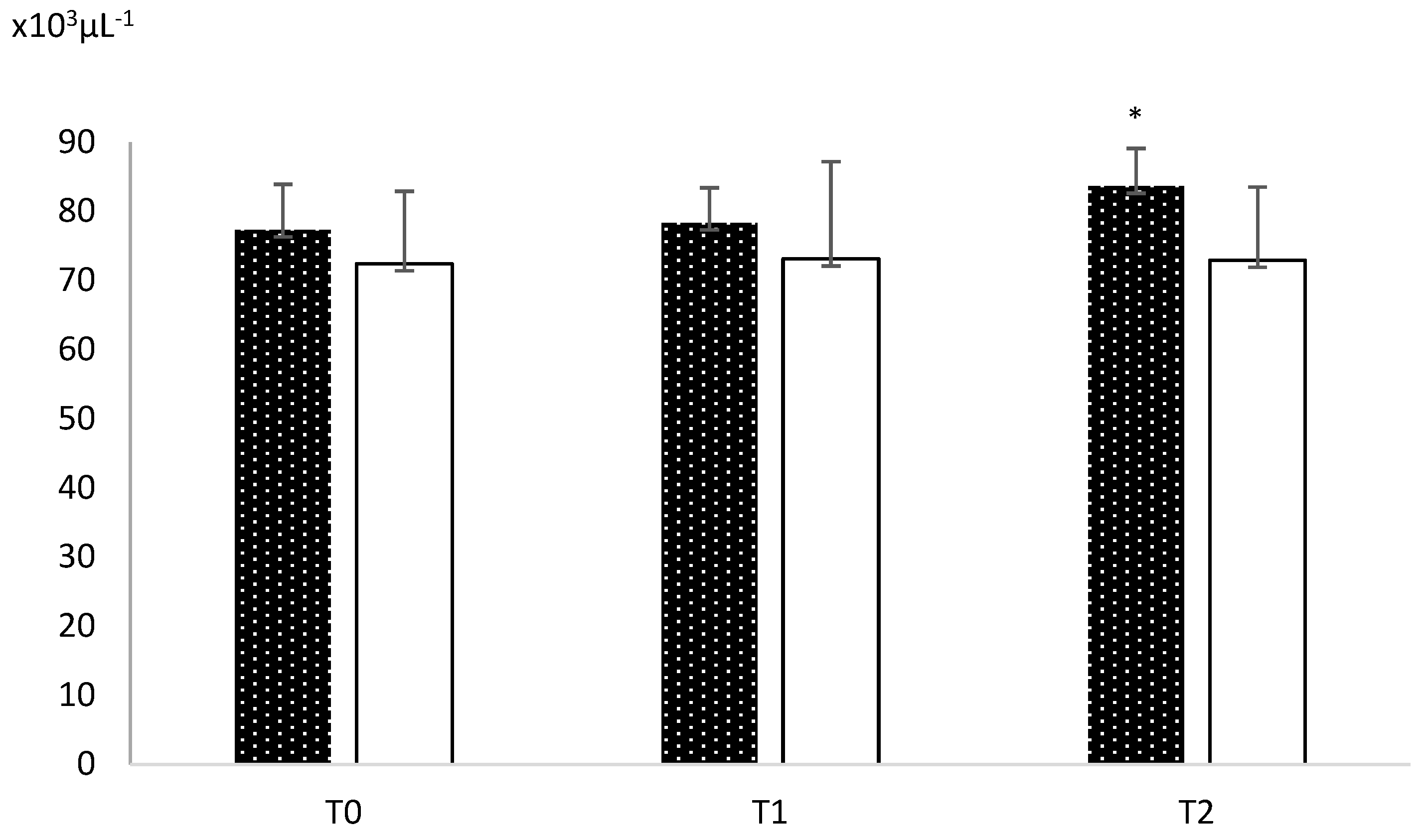
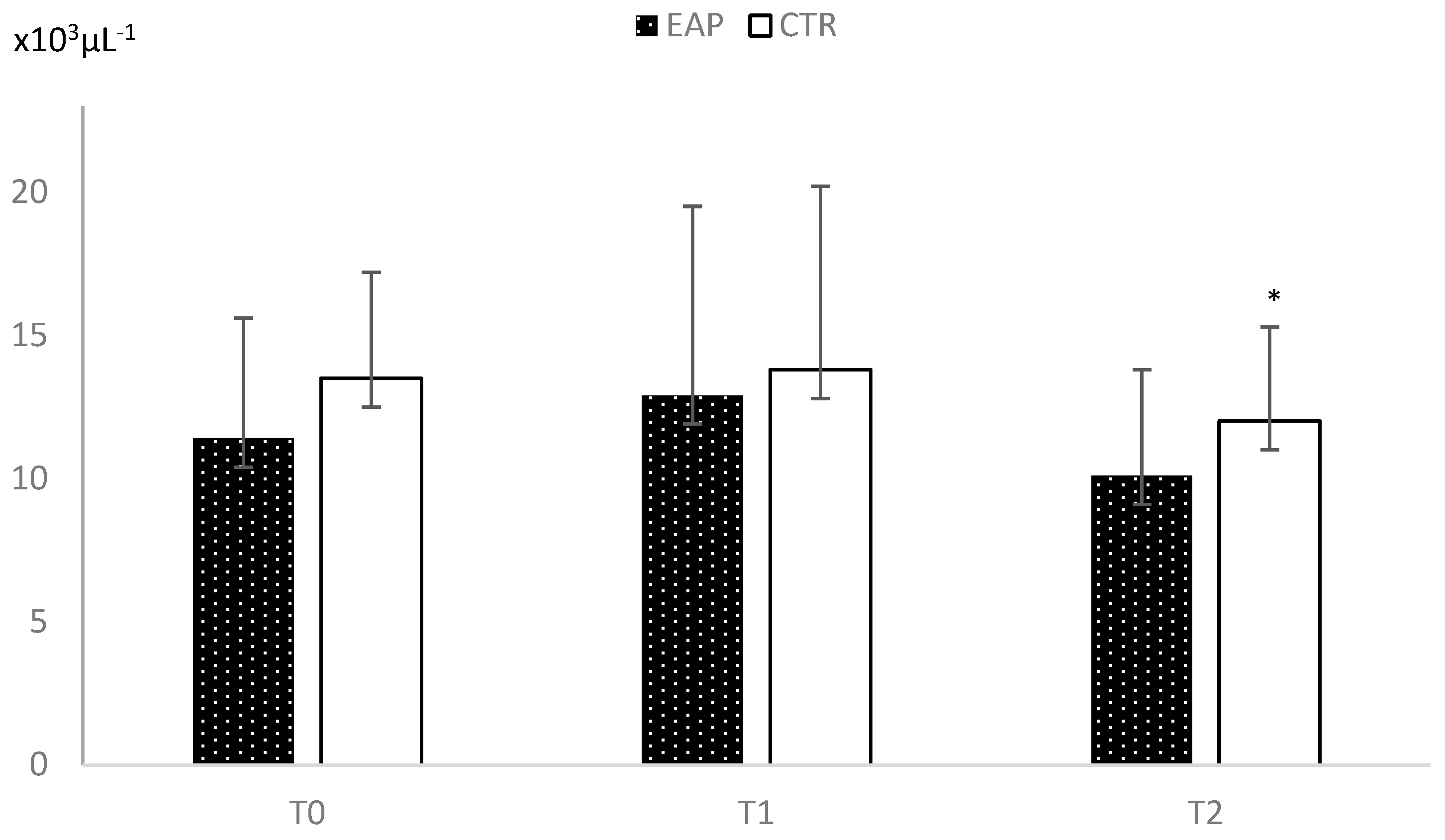
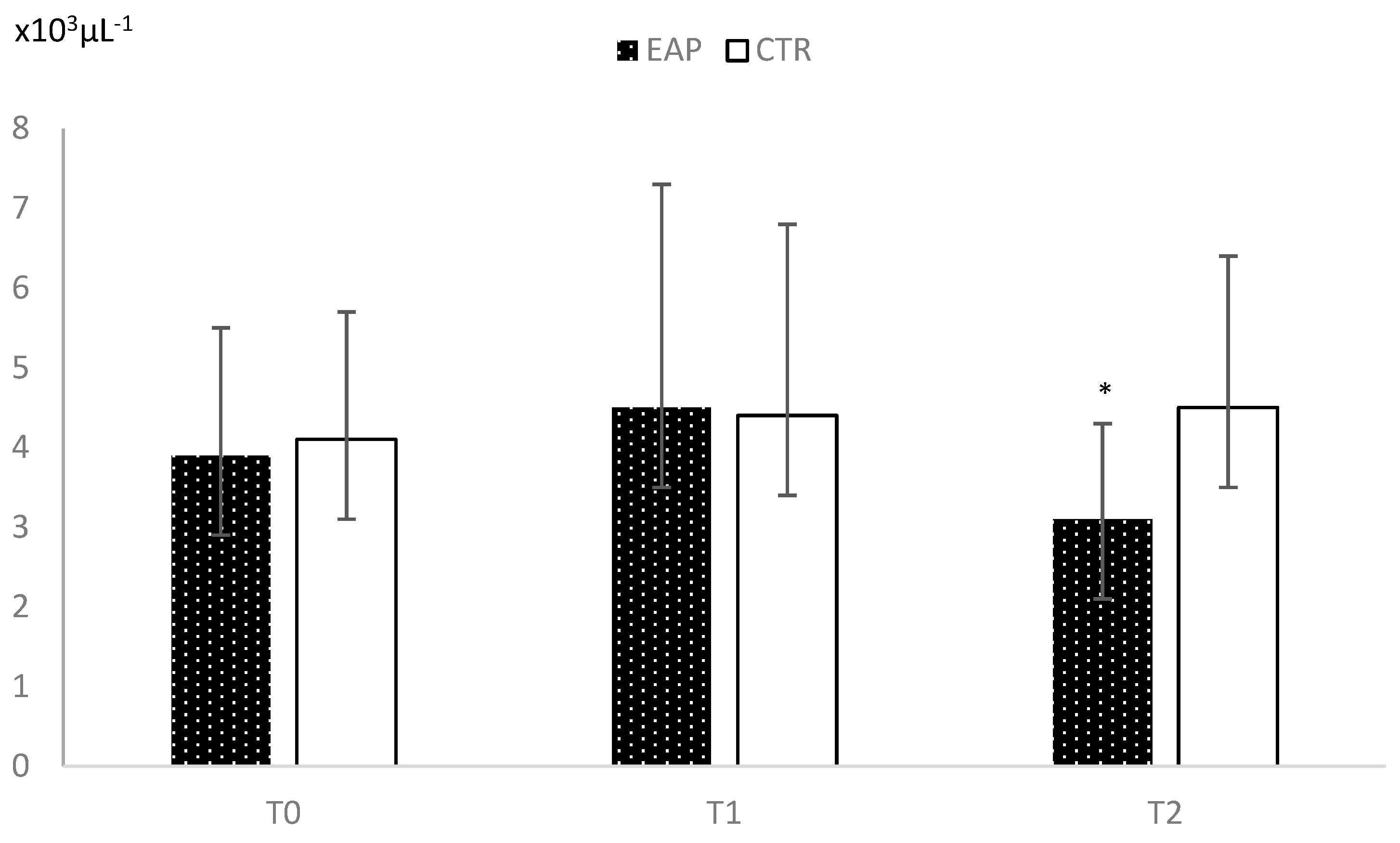
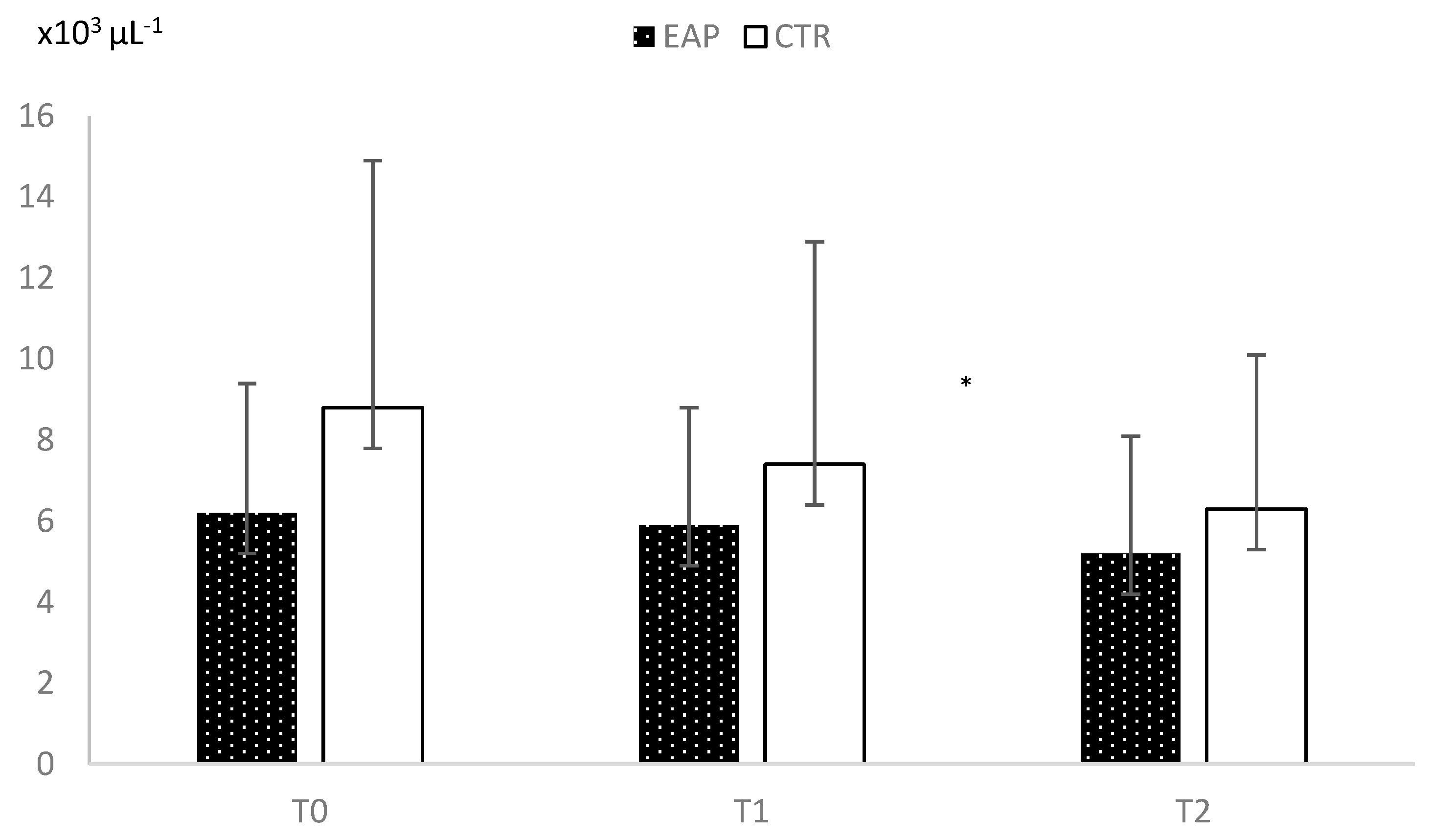
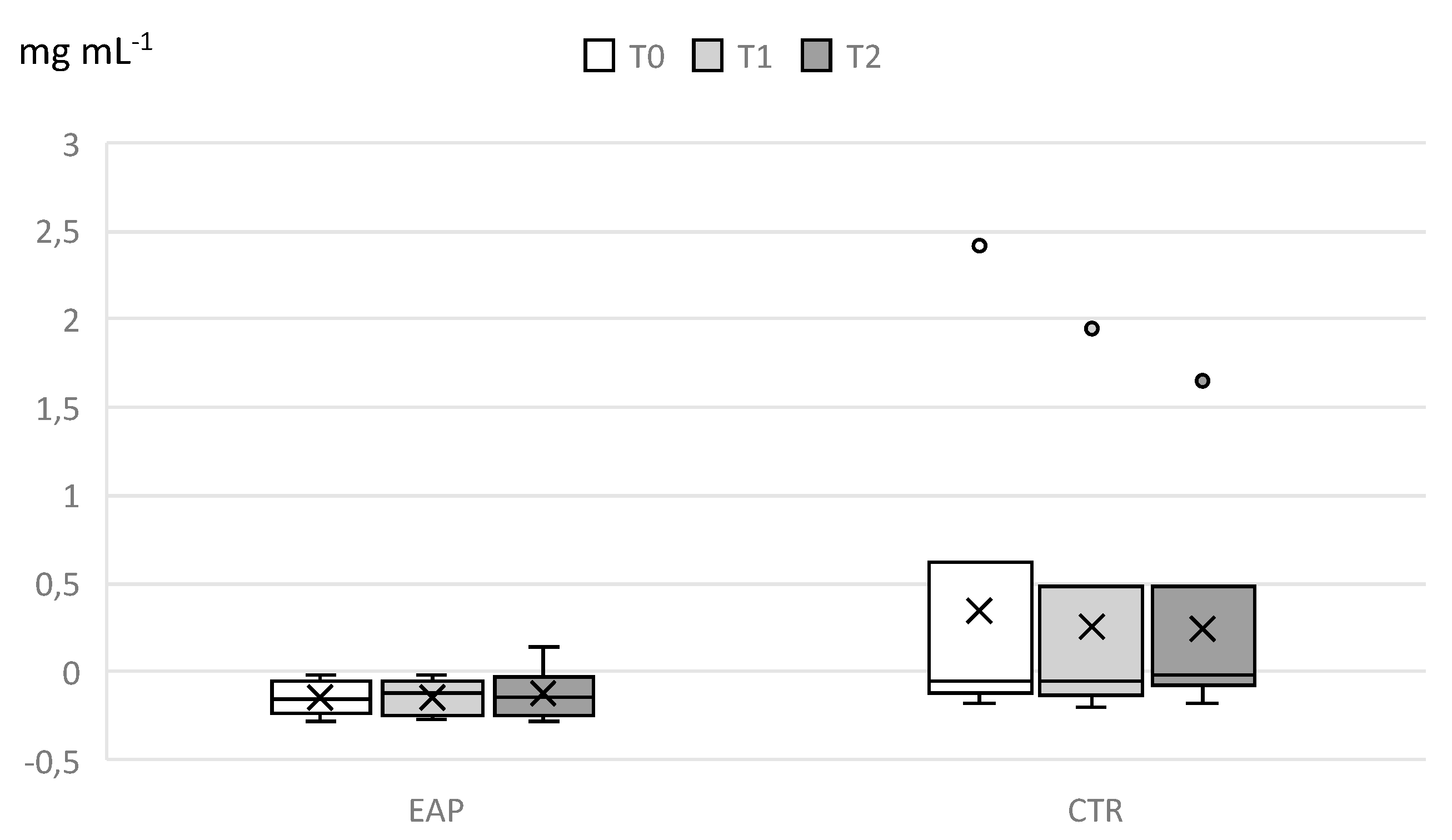
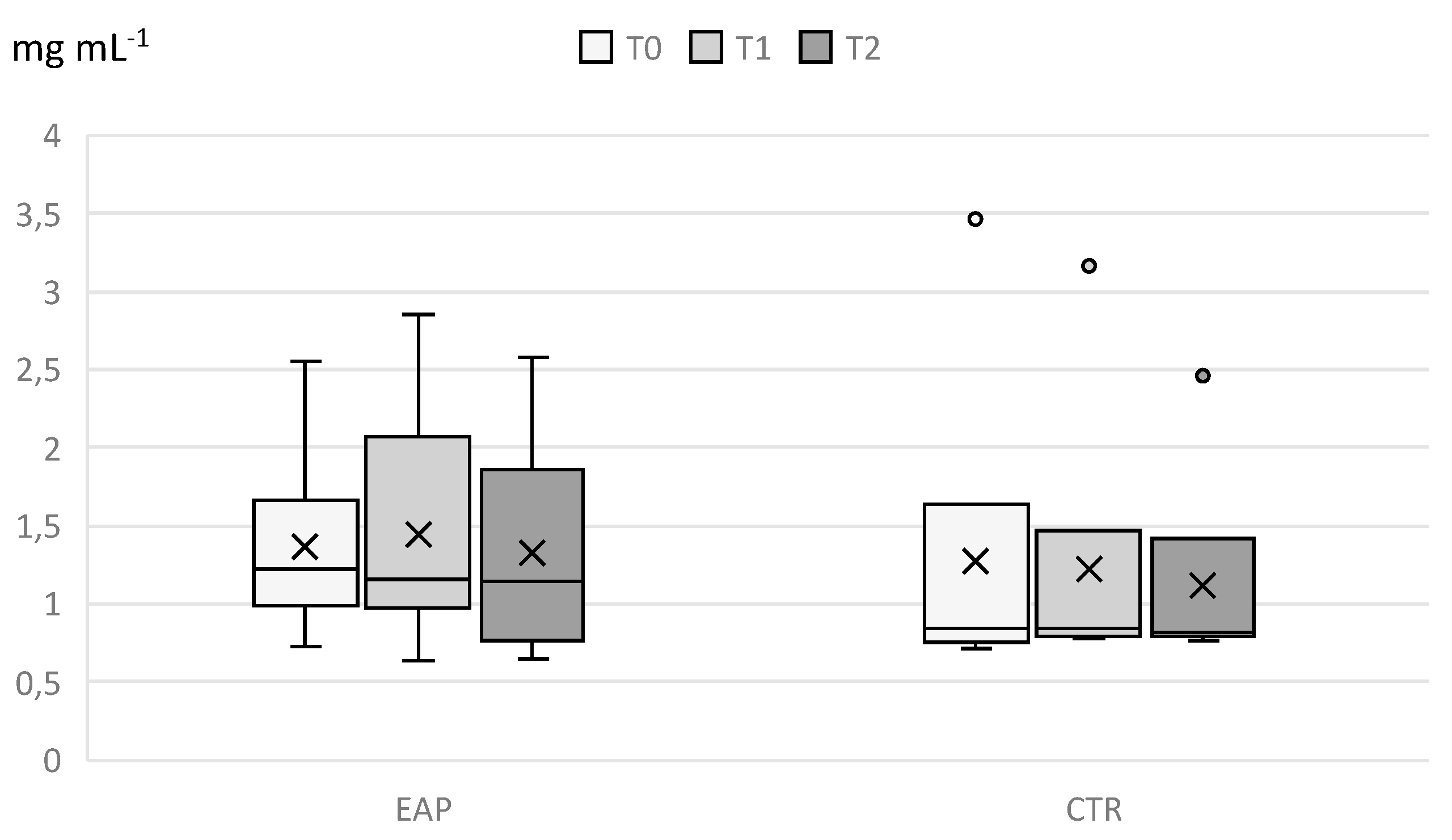
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Hematological Parameters in EAP and CTR Groups at Each Time Point
|
RBC x106µL-1 |
WBC x103µL-1 |
Hb g dL-1 |
Ht % |
PLT x103µL-1 |
MCH pg |
MCHC g dL-1 |
MCV µ3 |
RDW % |
MPV µ3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| ID. | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 | T0 | T1 | T2 |
| EAP1 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 14.8 | 10.4 | 18.5 | 12.9 | 14.2 | 15.2 | 37.6 | 41.9 | 44 | 385 | 243 | 372 | 22.1 | 22.2 | 22.2 | 34.3 | 33.9 | 34.5 | 64.3 | 65.4 | 64.2 | 16.9 | 18.4 | 18.7 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 10.1 |
| EAP 2 | 6.2 | 5.3 | 5.5 | 18.4 | 16.7 | 14.2 | 15.1 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 44.1 | 38.5 | 39.8 | 438 | 462 | 422 | 24.5 | 24.4 | 24.5 | 34.2 | 33.5 | 33.9 | 71.6 | 72.9 | 72.4 | 19 | 16.3 | 17.2 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 9.6 |
| EAP 3 | 7.5 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 13.5 | 13.7 | 12.6 | 18.3 | 14.8 | 15.7 | 50.6 | 44 | 45.6 | 213 | 236 | 233 | 24.4 | 24.1 | 24.1 | 36.2 | 33.6 | 34.4 | 67.4 | 71.8 | 70 | 20.3 | 17.9 | 18.5 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 12 |
| EAP 4 | 7.6 | 5.6 | 7 | 14.8 | 14.5 | 13.4 | 17.5 | 15.6 | 16.4 | 49.4 | 38.8 | 47.8 | 211 | 190 | 237 | 23 | 27.9 | 23.3 | 35.4 | 40.2 | 34.3 | 65 | 69.3 | 67.8 | 19.8 | 15.6 | 18.9 | 10.5 | 9.7 | 11.8 |
| EAP 5 | 7.2 | 6 | 6.1 | 19.5 | 16.2 | 15.2 | 16.4 | 14 | 14.1 | 46.1 | 41.6 | 41.7 | 201 | 192 | 184 | 22.9 | 23.2 | 23 | 35.6 | 33.7 | 33.8 | 64.4 | 68.9 | 68.1 | 20.2 | 18.2 | 18.1 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 11.6 |
| EAP 6 | 7.2 | 5.9 | 7.3 | 15.4 | 13.7 | 12.3 | 16.8 | 13.8 | 16.9 | 41.5 | 40.2 | 49.5 | 164 | 138 | 163 | 23.3 | 23.5 | 23.3 | 35.4 | 34.3 | 34.2 | 66 | 68.6 | 68.2 | 20.9 | 18.2 | 19.9 | 13.5 | 12.6 | 12.4 |
| CTR 1 | 7.9 | 6.9 | 7.7 | 13.1 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 19.6 | 16.9 | 18.8 | 53.5 | 47.9 | 52.4 | 311 | 172 | 278 | 24.6 | 24.6 | 24.5 | 36.6 | 35.3 | 35.9 | 67.1 | 69.7 | 67.3 | 20.1 | 18.7 | 20.1 | 11.3 | 11.9 | 11.3 |
| CTR 2 | 8 | 7 | 7.1 | 13.1 | 11.6 | 10.2 | 19.6 | 17.1 | 17.2 | 54.4 | 47.7 | 46.7 | 170 | 174 | 164 | 24.4 | 24.3 | 24.3 | 36 | 35.8 | 36.8 | 67.7 | 67.8 | 66 | 21.1 | 20.2 | 20.1 | 12.9 | 13 | 13.1 |
| CTR 3 | 6.7 | 5.4 | 5.7 | 11.4 | 8.2 | 8 | 16 | 13.1 | 13.2 | 47.9 | 39.4 | 40.1 | 230 | 212 | 139 | 23.8 | 24.1 | 23.3 | 33.4 | 33.2 | 32.9 | 71.2 | 72.6 | 70.7 | 19.1 | 16.3 | 17.8 | 12.3 | 12.6 | 12.3 |
| CTR 4 | 6.8 | 6.4 | 6.6 | 12.7 | 10.6 | 10.9 | 15.3 | 14.3 | 14.8 | 44 | 42.1 | 41.1 | 276 | 288 | 258 | 22.5 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 34.8 | 34 | 36 | 64.6 | 65.7 | 62 | 20 | 19.6 | 19.6 | 11.6 | 12 | 11.2 |
| CTR 5 | 7.7 | 6.8 | 6.7 | 12.7 | 13 | 10 | 18.3 | 16.2 | 16 | 52.7 | 45.9 | 45.6 | 193 | 192 | 199 | 23.7 | 23.9 | 23.7 | 34.7 | 35.3 | 35.1 | 68.4 | 67.6 | 67.7 | 19.9 | 18.8 | 18.3 | 12.8 | 13 | 13 |
| CTR 6 | 6.8 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 14.5 | 12.1 | 11.4 | 17.2 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 47.8 | 41.6 | 41.3 | 284 | 310 | 287 | 25.4 | 25.4 | 25.3 | 36 | 34.6 | 34.1 | 70.5 | 73.4 | 74.1 | 20.4 | 17.8 | 16.8 | 11.5 | 11.7 | 11.2 |
References
- Tizard, I.R. Veterinary immunology, 10th ed.; Elsevier: St Louis, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa, S.; Kato, M. Anesthetics, immune cells, and immune responses. J Anesth. 2008, 22, 263–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Malissen, B. Innate and adaptive immunity: specificities and signaling hierarchies revisited. Nature Immunology 2005, 6, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; An, L.; Wang, B. Electroacupuncture alleviates intraoperative immunosuppression in patients undergoing supratentorial craniotomy. Acupuncture Medicine 2013, 31, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, G.; Dall’Ara, P.; Martino, P.A.; Rosati, S. Microbiologia e immunologia veterinaria, 3rd ed.; EDRA: Milano, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, M.; Lozano, R.; Larrad, L.; Román, A.; Suarez, J.; Armijo, J. Variation in T helper cell/T cytotoxic-suppressor cell index during cardiac operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1988, 96, 962–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardinale, F.; Chinellato, I.; Caimmi, S.; Peroni, D.G.; Franceschini, F.; Miraglia Del Giudice, M.; Bernardini, R. Perioperative period: immunological modifications. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology 2011, 24, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, E.J.; Walsh, S.R.; Farooq, N.; Alberts, J.C.; Justin, T.A.; Keeling, NJ. Post-operative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts complications following colorectal surgery. Int J Surg. 2007, 5, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, B.V.; Peter, M.B.; Shenoy, H.G.; Horgan, K.; Hughes, T.A. Surgery induced immunosuppression. Surgeon 2011, 9, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Sumino, H.; Kanda, T.; Yamaguchi, N. Acupuncture modifies immune cells. J Exp Clin Med 2009, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Yang, S.B.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Koh, J.S.; Kwon, S.; Jung, W.S.; Moon, S.K.; Park, J.M.; Ko, C.N.; Park, S.U. Anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory effects of acupuncture after craniotomy: study protocol for a parallel-group randomized controlled trial. Trials 2017, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, J.; Cao, X.D.; Wu, G.C. Electroacupuncture suppresses surgical trauma stress-induced lymphocyte apoptosis in rats. Neuroscience Letters 2005, 383, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.D.; Wu, G.C.; He, Q.Z.; Cao, X.D. Effect of continued electroacupuncture on induction of interleukin-2 production of spleen lymphocytes from the injured rats. Acupunct Electrother Res 1997, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2022.868967/full.
- Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2022.868967/full.
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Di, J.; Su, X. Monitoring pre- and post-operative immune alterations in patients with locoregional colorectal cancer who underwent laparoscopy by single-cell mass cytometry. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 807539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Terachi, T.; Okada, Y.; Yoshida, O. Effect of surgical stress on immune function in patients with urologic cancer. Int J Urol 1996, 3, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, G.; von Haefen, C.; Kurth, J.; Yuerek, F.; Spies, C. Innate immunity recovers earlier than acquired immunity during severe postoperative immunosuppression. Int J Med Sci. 2018, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G. Acupuncture and innate immunity. Acupunct Res 2008, 33, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.M.; Liu, X.J.; Bai, S.S.; Mu, L.L.; Kong, Q.F.; Sun, B.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, J.H.; Shu, S.; Wang, G.Y.; Li, H.I. The effect of electroacupuncture on T cell responses in rats with experimental autoimmune encephalitis. J Neuroimmunol 2010, 220, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Tanimura, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Akimoto, T.; Kono, I. Effect of acupuncture on salivary immunoglobulin A after a bout of intense exercise. Acupunct Med 2010, 28, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.X.; Fan, A.Y.; Chen, S.; Alemi, S.F. Acupuncture modulates immunity in sepsis: Toward a science-based protocol. Auton Neurosci 2021, 232, 102793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabioğlu, M.T.; Cetin, B.E. Acupuncture and immunomodulation. Am J Chin Med 2008, 36, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Yang, C.H. Bidirectional role of acupuncture in the treatment of drug addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2021, 126, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.X. Bidirectional regulation of acupuncture and its plausible mechanisms. Acupunct Res 2019, 44, 843–853. [Google Scholar]
- Alazawi, W.; Pirmadjid, N.; Lahiri, R.; Bhattacharya, S. Inflammatory and immune responses to surgery and their clinical impact. Annals of Surgery 2016, 64, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Takahashi, T.; Sakuma, M.; Sugita, T.; Uchikawa, K.; Sakaihara, S.; Kanda, T.; Arai, M.; Kawakita, K. Acupuncture regulates leukocyte subpopulations in human peripheral blood. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2007, 4, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.M.; Shang, Y.Q.; Liang, H.; Yan, P.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; Wang, K. Research progress of effect of acupuncture therapy on T cell subsets. J Clin Acupunct 2018, 7, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Silvério-Lopes, S.; da Mota, M.P.G. Acupuncture in Modulation of Immunity. IntechOpen 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Ge, J.; Liu, S. The immunomodulatory mechanisms for acupuncture practice. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1147718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.B.; Koc, E.; Ahnc, C.; Choic, H.; Rhoc, S.; Shinc, M.K.; Hongc, M.C.; Minb, B.I.; Bae, H. Suppression of IgE production and modulation of Th1/Th2 cell response by electroacupuncture in DNP-KLH immunized mice. J Neuroimmunol 2004, 151, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Yu, Z.F.; Kang, F.H. Th1/Th2 balance on depression patients by acupuncture treatment combined with antidepressant. J Clin Acupunct Moxibustio 2014, 30, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, G. The effects of electroacupuncture on TH1/TH2 cytokine mRNA expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in the splenic T cells of traumatized rats. Anesth Analg 2009, 109, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.D. Involvement of orphanin FQ in electroacupuncture modulation on immunosuppression by trauma. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2001, 26, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Cabioğlu, M.T.; Ergene, N.; Surucu, H.S.; Çelik, H.H.; Findik, D. Serum IgG, IgA, IgM, and IgE levels after electroacupuncture and diet therapy in obese women. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine 2007, 35, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Wang, B.; An, L. The effect of electroacupuncture on postoperative immunoinflammatory response in patients undergoing supratentorial craniotomy. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 2013, 6, 699–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, C.; Ji, F.; Li, T. Opioid System Modulates the Immune Function: A Review. Transl Perioper Pain Med 2016, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





