Submitted:
23 October 2023
Posted:
24 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1 Main Properties of Biodegradable and Biomedical Implants:
1.2 Mechanical Properties:
2. Corrosion properties
3. Magnesium alloys for biomedical implants
4. Surface modification used for Mg alloys
- Surface coating preparation:
- Chemical conversion coatings:
- Biomimetic deposition
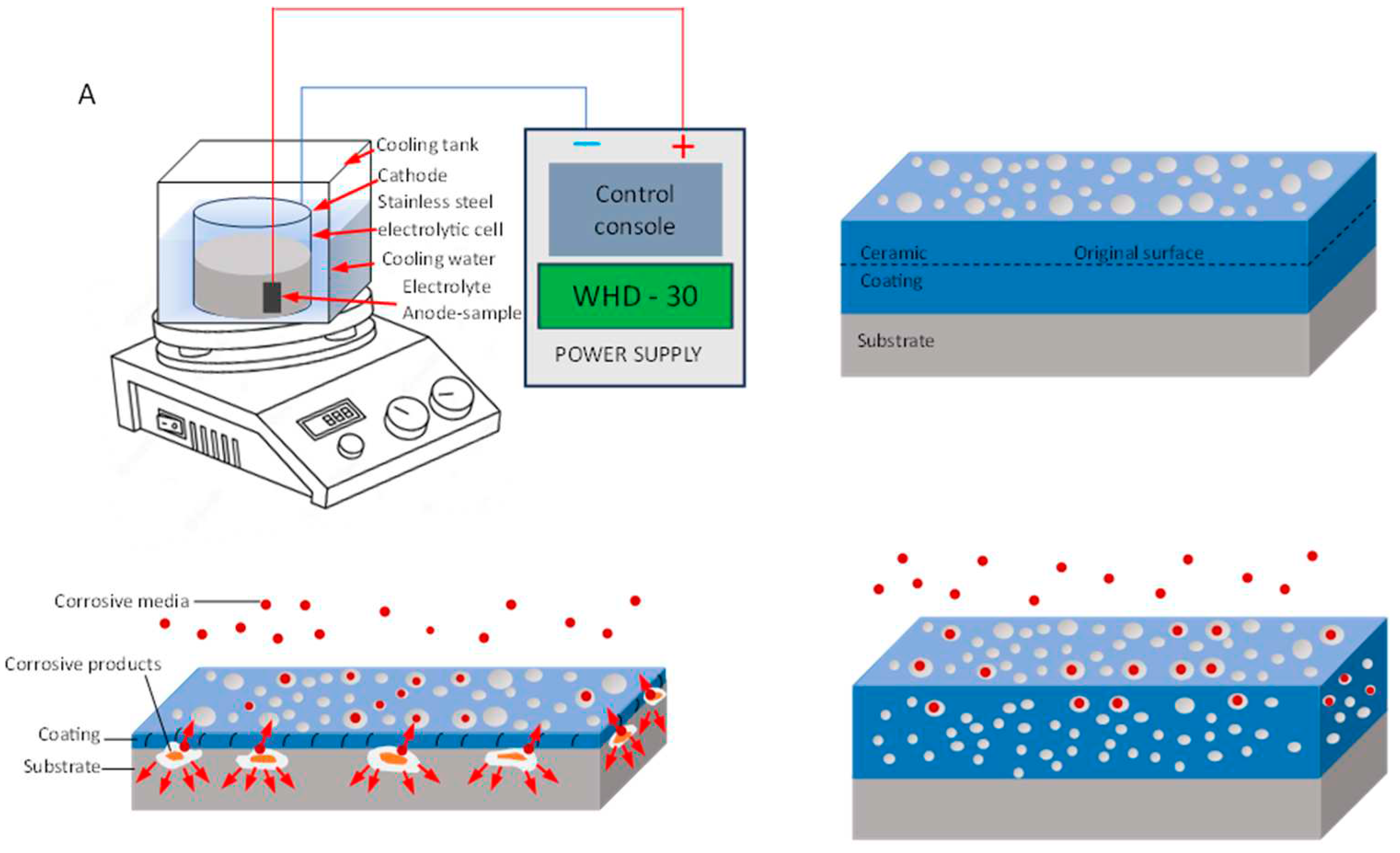
- Micro-arc oxidation coating
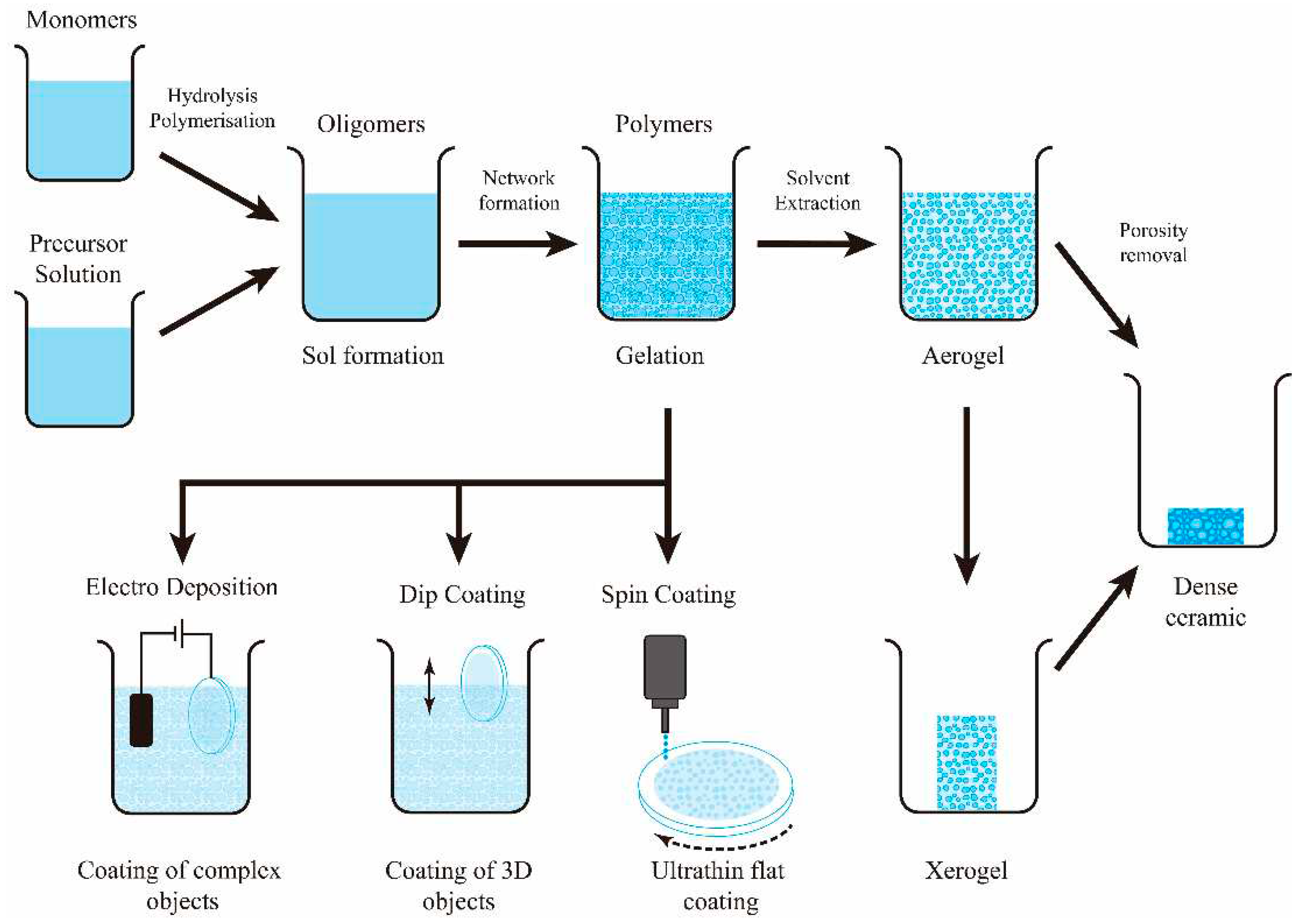
- Sol-gel coating
- Ion implantation:
- Surface microstructural modification:
- Laser surface modification

- Friction stir processing
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopedic implants – A review. Prog Mater Sci 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepreel, M.A.-H.; Niinomi, M. Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzański, L.A.; Dobrzańska-Danikiewicz, A.D.; Dobrzański, L.B. Effect of Biomedical Materials in the Implementation of a Long and Healthy Life Policy. Processes 2021, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Marquez, D.; Delmar, Y.; Sun, S.; Stewart, R.A. Exploring macroporosity of additively manufactured titanium metamaterials for bone regeneration with quality by design: A systematic literature review. Materials 2020, 13, 4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Xia, R.F.; Li, W.; Lu, D.; Jin, Z.M. 3D-Printed Ti6Al4V Scaffolds with Graded Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Structure for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 4993–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, D.; Alabort, E.; Reed, R. Synthetic bone: Design by additive manufacturing. Acta Biomater. 2019, 97, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.C.; Klemm, D.; Eckert, J.; Hao, Y.L.; Sercombe, T.B. Manufacture by selective laser melting and mechanical behavior of a biomedical Ti–24Nb–4Zr–8Sn alloy. Scr Mater 2011, 65, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J.A. Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Prakash, C. Current trends in biomaterials and bio-manufacturing. In Biomanufacturing; Springer, 2019; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Long, M.; Rack, H.J. Titanium alloys in total joint replacement—A materials science perspective. Biomaterials 1998, 19, 1621–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Dubey, A.; Lahiri, D. In Vitro Biodegradation and Biocompatibility of Mg–HA-Based Composites for Orthopaedic Applications: A Review. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2019, 99, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-C.; Chen, L.-Y. A review on biomedical titanium alloys: recent progress and prospect. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1801215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, K. Review on titanium and titanium based alloys as biomaterials for orthopaedic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 844–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.-W.; Fang, F.-Z. State of the art of bioimplants manufacturing: part I. Adv Manuf 2018, 6, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Vural, M.; Raja, S.; Shaikh, M.B.N. Finite element analysis of thermal behavior in maraging steel during SLM process. Optik 2020, 208, 164128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Hamdan, H.Y.; Azeem, M.; Hussain, P.B.; bin Salit, M.S.; Khan, R.; Arif, S.; Ansari, A.H. Modelling and optimisation of hardness behaviour of sintered Al/SiC composites using RSM and ANN: A comparative study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14036–14050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, N.; Evis, Z.; Kayhan, S.M.; Tahmasebifar, A.; Koç, M. Review of magnesium-based biomaterials and their applications. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2018, 6, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhu, M.; Chung, C.Y. Biomedical porous shape memory alloys for hard-tissue replacement materials. Materials 2018, 11, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, A.; Girdler, S.J.; Mikhail, C.M.; Ahn, A.; Cho, S.K. Biomaterials in spinal implants: A review. Neurospine 2020, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, M.B.N.; Aziz, T.; Arif, S.; Ansari, A.H.; Karagiannidis, P.G.; Uddin, M. Effect of sintering techniques on microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of Al-SiC composites. Surfaces and Interfaces 2020, 20, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Ya, H.H.; Yusuf, M.; Sivraj, R.; Mamat, O.B.; Sapuan, S.M.; Masood, F.; Parveez, B.; Sattar, M. Modeling, optimization and performance evaluation of TiC/graphite reinforced Al 7075 hybrid composites using response surface methodology. Materials 2021, 14, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. Tissue-biomaterial interactions. J. Mater. Sci. 1987, 22, 3421–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M. Mechanical properties of biomedical titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, K. A review on magnesium alloys for biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 953344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsson, O. Knee arthroplasty registers. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.F. Titanium in medicine. BIOMATERIALS-GUILDFORD- 2002, 23, 3913–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Vimala, K.; Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ramam, K. Nanotechnology Applications for Tissue Engineering; Elsevier Chennai: India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Neo, M.; Suzuki, J.; Kokubo, T.; Nakamura, T. Mechanical properties and osteoconductivity of porous bioactive titanium. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6014–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, M.; Verić, O.; Božić, Ž.; Sušić, A. Fracture analysis of a total hip prosthesis based on reverse engineering. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 215, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
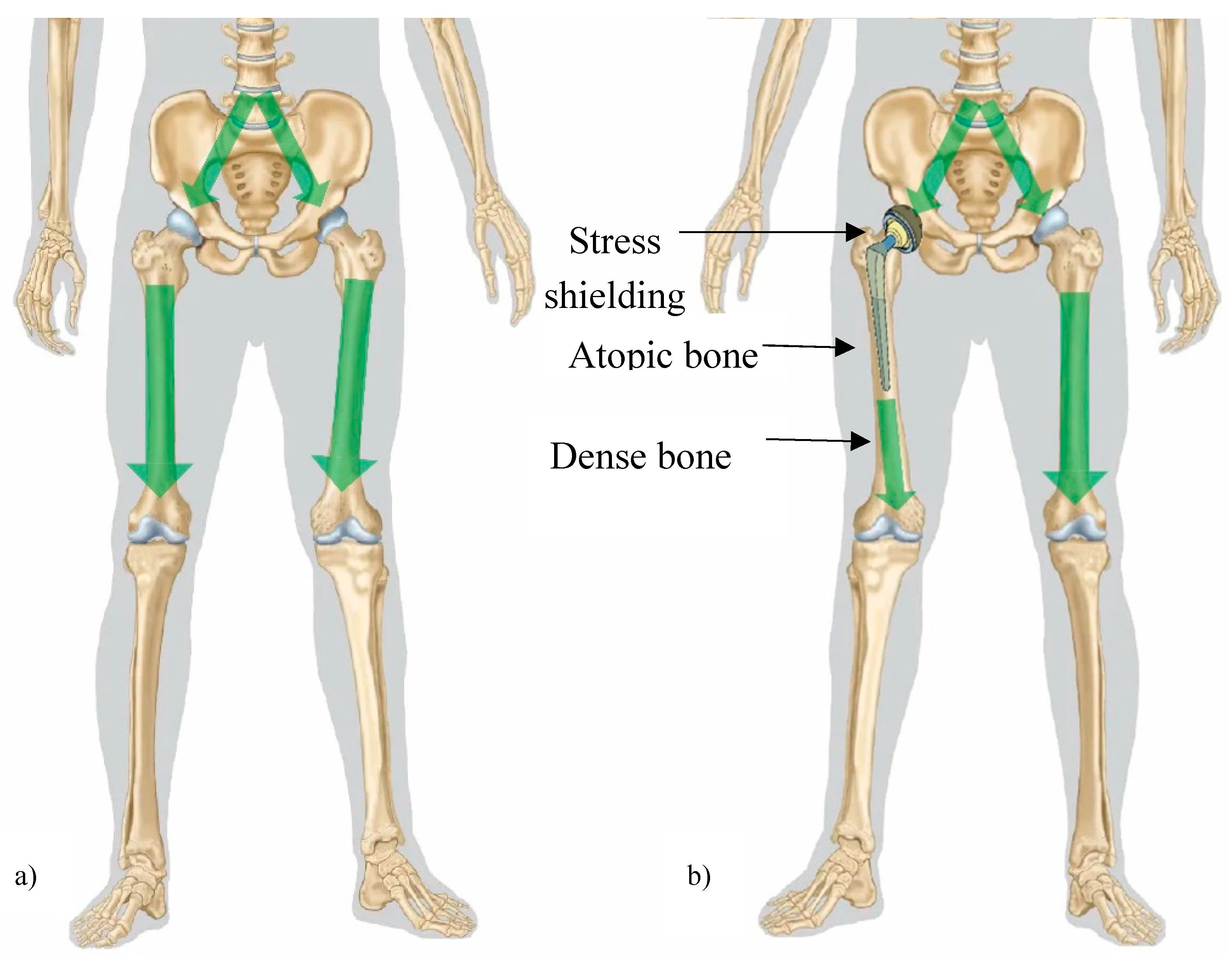
- Nagels, J.; Stokdijk, M.; Rozing, P.M. Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2003, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, D. Long-term implant fixation and stress-shielding in total hip replacement. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.G.; Advani, S.G.; Miller, F.; Santare, M.H. Analysis of a femoral hip prosthesis designed to reduce stress shielding. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savio, D.; Bagno, A. When the Total Hip Replacement Fails: A Review on the Stress-Shielding Effect. Processes 2022, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawan, H.; Dubé, D.; Mantovani, D. Developments in metallic biodegradable stents. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, F. The history of biodegradable magnesium implants: A review. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Hu, T.; Chu, P.K. Influence of test solutions on in vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, C238–C243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Dubey, A.; Lahiri, D. In Vitro Biodegradation and Biocompatibility of Mg–HA-Based Composites for Orthopaedic Applications: A Review. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2019, 99, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failure Mechanisms in Total-Joint and Dental Implants - Biomaterials for Osseointegration and Novel Engineering. Available online: http://danieli.wikidot.com/2-failure-mechanisms-in-total-joint-and-dental-implants (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Manivasagam, G.; Dhinasekaran, D.; Rajamanickam, A. Biomedical implants: Corrosion and its prevention-a review. Recent Patents Corros. Sci. 2010, 2, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksakal, B.; Yildirim, Ö.S.; Gul, H. Metallurgical failure analysis of various implant materials used in orthopedic applications. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention 2004, 4, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amel-Farzad, H.; Peivandi, M.; Yusof-Sani, S. In-body corrosion fatigue failure of a stainless steel orthopaedic implant with a rare collection of different damage mechanisms. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2007, 14, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, T. An overview of the corrosion aspect of dental implants (titanium and its alloys). Indian J. Dent. Res. 2009, 20, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, C.; Lou, T.; Chen, B.; Yi, R.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zuo, M.; Xu, H.; Han, P.; et al. Crevice corrosion – A newly observed mechanism of degradation in biomedical magnesium. Acta Biomater. 2019, 98, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, B.D.; Hoffman, A.S.; Schoen, F.J.; Lemons, J.E. Biomaterials science: an introduction to materials in medicine; San Diego, California, 2004; pp. 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, S.I. International dictionary of medicine and biology (In three volumes). 01 May 1986; (accessed on 1 May 2023). [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Rodriguez, A.; Chang, D.T. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratner, B.D. Host response to biomaterials; Elsvier Inc., 2015; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Oshida, Y.; Tuna, E.B.; Aktören, O.; Gençay, K. Dental implant systems. Int J Mol Sci 2010, 11, 1580–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rossen, I.; Braak, L.; de Putter, C.; de Groot, K. Stress-absorbing elements in dental implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1990, 64, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepreel, M.A.-H.; Niinomi, M. Biocompatibility of Ti-alloys for long-term implantation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orden, V.; Fraker, A.C.; Sung, P. The influence of small variations in composition on the corrosion of cobalt–chromium alloys. Proceedings of the Society for Biomaterials 1982, 5, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsden, J.; Allen, D.; Stephenson, D.; Alcock, J.; Peggs, G.; Fuller, G.; Goch, G. The design and manufacture of biomedical surfaces. CIRP Ann. 2007, 56, 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotman, I. Characteristics of Metals Used in Implants. J. Endourol. 1997, 11, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, K.A. Allergy to Surgical Implants. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 56, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallab, N.J.; Anderson, S.; Caicedo, M.; Brasher, A.; Mikecz, K.; Jacobs, J.J. Effects of soluble metals on human peri-implant cells. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A: An Official Journal of The Society for Biomaterials, The Japanese Society for Biomaterials, and The Australian Society for Biomaterials and the Korean Society for Biomaterials 2005, 74, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Curtin, J.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, S. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 68, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipan, N.; Pandey, A.; Mishra, P. MAGNESIUM BASED ALLOYS FOR BIODEGRADABLE IMPLANTS APPLICATIONS USING ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUE: A REVIEW. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, L.; Yu, X.; Etim, I.P.; Ibrahim, M.; Yang, K. Mechanical properties of magnesium alloys for medical application: A review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Lin, T.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Song, K.; Li, Q. Advances in Degradation Behavior of Biomedical Magnesium Alloys: A Review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 908, 164600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Lin, W.; Zhang, S. Magnesium Promotes the Regeneration of the Peripheral Nerve. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K.; Genuis, S.J. The importance of magnesium in clinical healthcare. Scientifica 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, I.; Perchy, D.; Liu, H. In vitro evaluation of the surface effects on magnesium-yttrium alloy degradation and mesenchymal stem cell adhesion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 100A, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Curtin, J.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, S. Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 68, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Hopkins, C.; Chow, D.H.; Qin, L. Biodegradable magnesium-based implants in orthopedics—a general review and perspectives. Advanced Science 2020, 7, 1902443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.C.; Al-Saadi, S.; Choudhary, L.; Harandi, S.E.; Singh, R. Magnesium implants: Prospects and challenges. Materials 2019, 12, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, O.; Porchetta, D.; Schroeder, M.-L.; Klein, M.; Wegner, N.; Walther, F.; Feyerabend, F.; Barbeck, M.; Kopp, A. In vivo simulation of magnesium degradability using a new fluid dynamic bench testing approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, P.Y.Y.; Cheok, Q.; Glowacz, A.; Caesarendra, W. A review of in-vivo and in-vitro real-time corrosion monitoring systems of biodegradable metal implants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Singh, R.A.; Gupta, M. The Potential of Magnesium-Based Materials for Engineering and Biomedical Applications. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2022, 102, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekguleryuz, M.O.; Kainer, K.U.; Kaya, A.A. Fundamentals of magnesium alloy metallurgy; Elsevier, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Dai, J.; Zhang, X. Improvement of corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys for biomedical applications. Corros. Rev. 2015, 33, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, W.; Tsuru, T.; Lobzenko, I.; Jiang, J.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, T.; Bae, J.W.; et al. Metalloid substitution elevates simultaneously the strength and ductility of face-centered-cubic high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 225, 117571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, K.; Lin, J.; Wen, C.; Wright, P.F.; Li, Y. Mechanical, corrosion, and biocompatibility properties of Mg-Zr-Sr-Sc alloys for biodegradable implant applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 102, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Jin, X.; Sun, J.; Han, X.; Zeng, M.; Qiu, Y.; Bian, W. Microalloying Design of Biodegradable Mg–2Zn–0.05Ca Promises Improved Bone-Implant Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ibrahim, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Tan, L.; Yang, K. Biofunctional Mg coating on PEEK for improving bioactivity. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-X.; Wang, S.-R.; Wang, G.-Q.; Yu, X.-C.; Liu, W.-T.; Chang, Z.-Q.; Wen, D.-S. Microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of magnesium alloy bone plate treated by high-energy shot peening. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-Z.; Qi, W.-C.; Zeng, R.-C.; Chen, X.-B.; Gu, C.-D.; Guan, S.-K.; Zheng, Y.-F. Advances in coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2020, 8, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, S.A.; Joseph, M.A.; Kumar, T.S.S.; T, H. Recent progress in surface modification of Mg alloys for biodegradable orthopedic applications. Front. Mater. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandelt, K. Encyclopedia of interfacial chemistry: surface science and electrochemistry; Elsevier, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pereda, M. D.; Alonso, C.; Gamero, M.; Del Valle, J. A.; De Mele M. F., L. Comparative study of fluoride conversion coatings formed on biodegradable powder metallurgy Mg: The effect of chlorides at physiological level. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nisbet, D.; Li, R.; Smith, P.; Abbott, T.; Easton, M.; Zhang, D.-H.; Birbilis, N. Controlling initial biodegradation of magnesium by a biocompatible strontium phosphate conversion coating. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willbold, E.; Gu, X.; Albert, D.; Kalla, K.; Bobe, K.; Brauneis, M.; Janning, C.; Nellesen, J.; Czayka, W.; Tillmann, W.; et al. Effect of the addition of low rare earth elements (lanthanum, neodymium, cerium) on the biodegradation and biocompatibility of magnesium. Acta Biomater. 2015, 11, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Yuan, G.; Niu, J.; Zong, Y.; Ding, W. In vitro degradation behavior and biocompatibility of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr alloy by hydrofluoric acid treatment. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Tan, L.; Zhang, B.; Yang, K. Fluoride Conversion Coating on Biodegradable AZ31B Magnesium Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; et al. Multifunctional MgF2/polydopamine coating on Mg alloy for vascular stent application. J Mater Sci Technol 2015, 31, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Lan, Z.; Kong, L.; Huang, Y.; Cui, H. Characterization of calcium-modified zinc phosphate conversion coatings and their influences on corrosion resistance of AZ31 alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2011, 205, 3347–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-B.; Yang, H.-Y.; Abbott, T.B.; Easton, M.A.; Birbilis, N. Corrosion protection of magnesium and its alloys by metal phosphate conversion coatings. Surf. Eng. 2014, 30, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
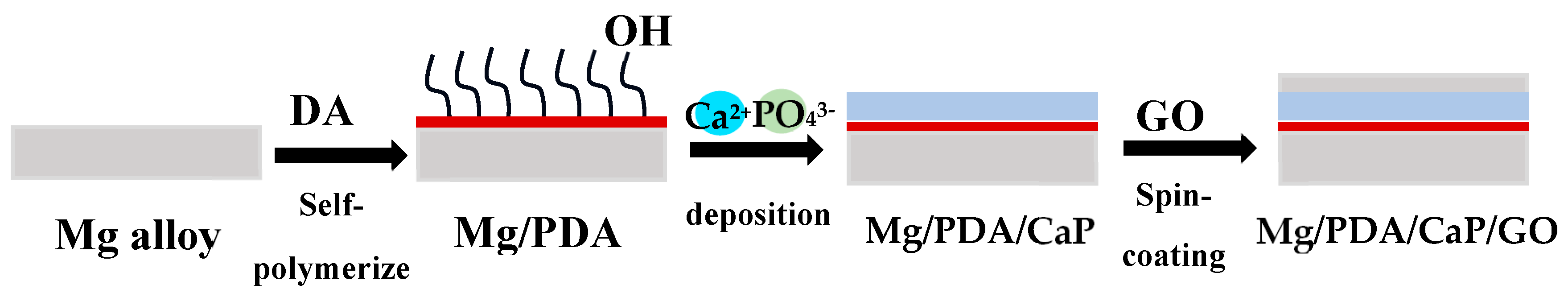
- Lin, B.; Zhong, M.; Zheng, C.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Cao, B. Preparation and characterization of dopamine-induced biomimetic hydroxyapatite coatings on the AZ31 magnesium alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2015, 281, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Lian, J. A polydopamine-based calcium phosphate/graphene oxide composite coating on magnesium alloy to improve corrosion resistance and biocompatibility for biomedical applications. Materialia 2022, 21, 101315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mohedano, M.; Blawert, C.; Matykina, E.; Arrabal, R.; Kainer, K.U.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings with particle additions – A review. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2016, 307, 1165–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Niu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Bi, X.; Liang, J. Micro-arc oxidation behavior of fly ash cenospheres/magnesium alloy degradable composite and corrosion resistance of coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 391, 125693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, L. Surface modification of biomedical titanium alloy: micromorphology, microstructure evolution and biomedical applications. Coatings 2019, 9, no 4, p 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R.B.; Fontinha, I.R.; Silva, C.J.R.; Pereira, E.V. Hybrid Sol-Gel Coatings: Smart and Green Materials for Corrosion Mitigation. Coatings 2016, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, G.J.; Singh, R.K.; Foroutan, F.; Alqaysi, M.; Han, C.-M.; Mahapatra, C.; Kim, H.-W.; Knowles, J.C. Sol–gel based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 77, 1–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R.B. Hybrid Sol–gel Coatings for Corrosion Mitigation: A Critical Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamesh, M.I.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, W.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.; Chu, P.K. Effects of zirconium and nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of Mg–Y–RE alloy in simulated body fluid and cell culture medium. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; et al. Corrosion resistance improvement of Mg alloy AZ31 by combining bilayer amorphous DLC: H/SiNx film with N+ ions implantation. J Alloys Compd 2018, 762, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, S.; Ionescu, M.; Mathan, B.K. Ion implantation of calcium and zinc in magnesium for biodegradable implant applications. Metals 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y. Improved cytocompatibility of Mg-1Ca alloy modified by Zn ion implantation and deposition. Mater. Lett. 2017, 205, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.-Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.-M.; Lee, I.-S. Advances in the surface modification techniques of bone-related implants for last 10 years. Regen. Biomater. 2014, 1, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.-Z.; Qi, W.-C.; Zeng, R.-C.; Chen, X.-B.; Gu, C.-D.; Guan, S.-K.; Zheng, Y.-F. Advances in coatings on biodegradable magnesium alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2020, 8, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, Y.; Fu, D.; Jin, B.; Lu, J. Effect of surface mechanical attrition treatment on tribological behavior of the AZ31 alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowron, K.; Dryzek, E.; Wróbel, M.; Nowak, P.; Marciszko-Wiąckowska, M.; Le Joncour, L.; François, M.; Panicaud, B.; Baczmański, A. Gradient microstructure induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) in magnesium studied using positron annihilation spectroscopy and complementary methods. Materials 2020, 13, 4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y. Effect of surface mechanical attrition treatment on biodegradable Mg–1Ca alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 35, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacı, H.; Bozkurt, Y.; Yetim, A.; Aslan, M.; Çelik, A. The effect of surface plastic deformation produced by shot peening on corrosion behavior of a low-alloy steel. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2019, 360, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhaede, M.; Pastorek, F.; Hadzima, B. Influence of shot peening on corrosion properties of biocompatible magnesium alloy AZ31 coated by dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCPD). Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 39, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peral, L.; Zafra, A.; Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M.; Fernández-Pariente, I. Effect of warm shot peening treatments on surface properties and corrosion behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2020, 401, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, N.; Wei, D.; Xie, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Kato, H.; Lu, W.; Zhang, L.-C.; Wang, L. Evolution of microstructural complex transitions in low-modulus β-type Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr alloy manufactured by laser powder bed fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 48, 102376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Han, S.; Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.-C. Strengthening mechanism and micropillar analysis of high-strength NiTi–Nb eutectic-type alloy prepared by laser powder bed fusion. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2020, 200, 108358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, S.; Guan, W.; Xie, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Excellent thermal shock resistance of NiCrAlY coatings on copper substrate via laser cladding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 130, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, U.; Vadali, M. A steady-state semi-analytical approximation of melt pool evolution in pulsed laser surface melting. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 74, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cristino, V.; Tam, L.; Lo, K.; Kwok, C. Laser surface alloying of copper with Cr/Ti/CNT for enhancing surface properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Khan, A.N.; Mahmud, T.B.; Khan, T.I.; Ajmal, M. Effect of laser melting on plasma sprayed WC-12wt. %Co coatings. Surf Coat Technol 2015, 266, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Shi, Q.; Liu, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, G. Fabrication of in situ carbon fiber/aluminum composites via friction stir processing: Evaluation of microstructural, mechanical and tribological behaviors. Compos B Eng 2018, 139, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.-C.; Lu, W. Tensile and superelastic behaviors of Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr with gradient structure. Mater. Des. 2020, 194, 108961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; et al. Microstructure evolution and electrochemical properties of TiO2/Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr micro/nano-composites fabricated by friction stir processing. Mater Des 2019, 169, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xie, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.C.; Chen, L.-Y.; Meng, Q.; Qu, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, W. Microstructure evolution and superelastic behavior in Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr alloy processed by friction stir processing. Acta Mater. 2017, 131, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Chen, L.-Y.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qin, J.; Zhang, D.; Lu, W. Investigation of Deformation Mechanisms in β-Type Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr Alloy via FSP Leading to Surface Strengthening. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 4813–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mechanical performance | |
|---|---|
| Biomaterial | Mechanical Characteristics |
| Hip prosthesis | Strong and rigid |
| Tendon material | Strong and flexible |
| Heart valve leaflet | Flexible and tough |
| Articular cartilage | Soft and elastomeric |
| Mechanical performance | |
|---|---|
| Biomaterial | Durability |
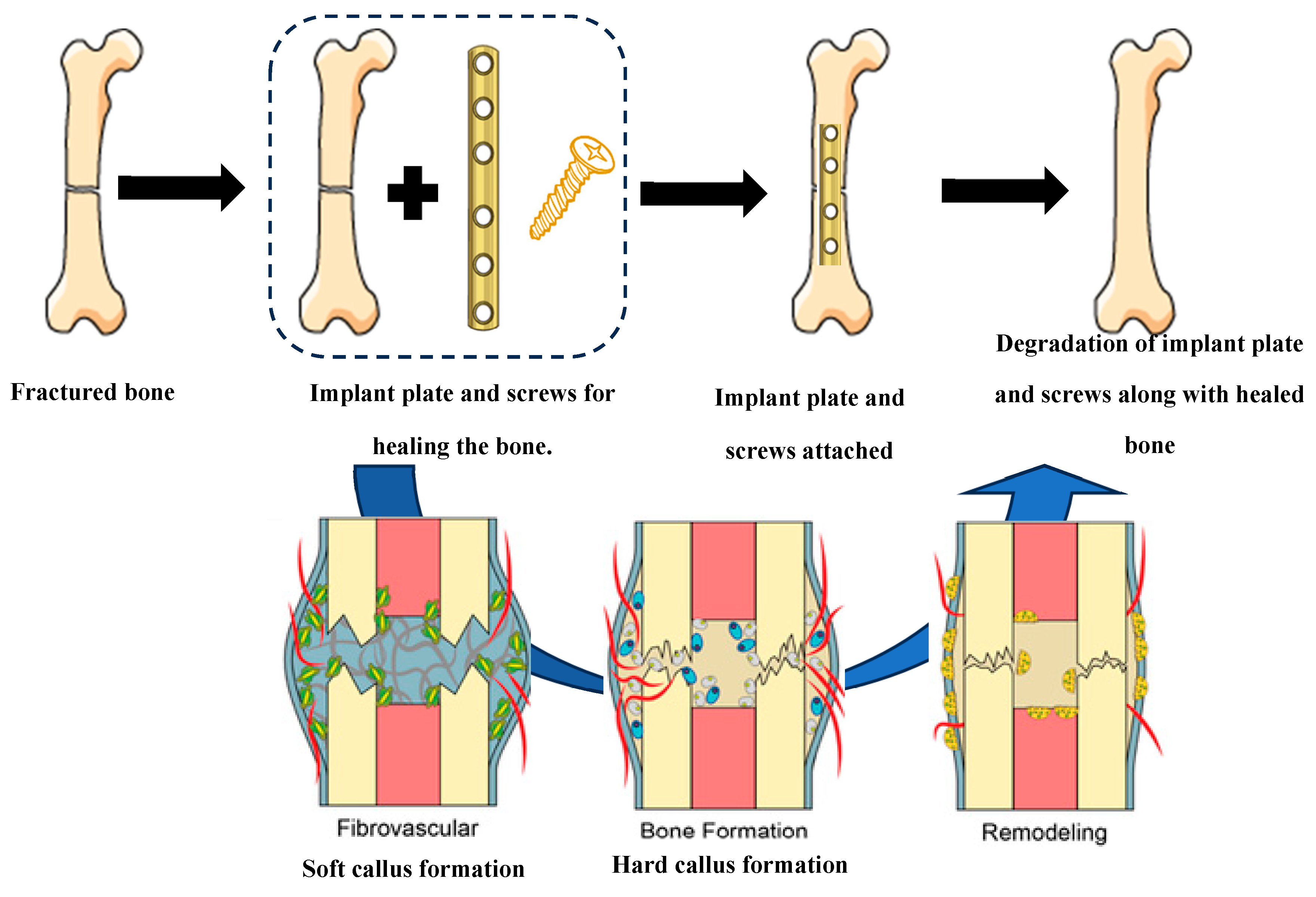
| Bone plate | Six months or longer |
| Hip joint | Ten years or longer under heavy loads |
| Heart valve leaflet | Able to fully flex 60 times/min without undergoing failure for several decades |
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced density and elastic stiffness | Density and elastic stiffness are like human bone. |
| Higher specific strength | Strength to weight ratio is roughly 35-260 KNm/kg. |
| Machinability | Mg has good machining capability, achieving accurate dimensions and processing into complex shapes. |
| Stress shielding effect | The elastic stiffness of Mg is very close to bone. |
| Biocompatibility | Mg is shown to have osteogenic functions. |
| Degradability | Mg naturally degrades in the body, which is favorable to the patients. |
| Disadvantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Low mechanical properties | Implants must be able to endure specific loads and deformation. It is difficult for Mg to meet medical demands in strength and plasticity. |
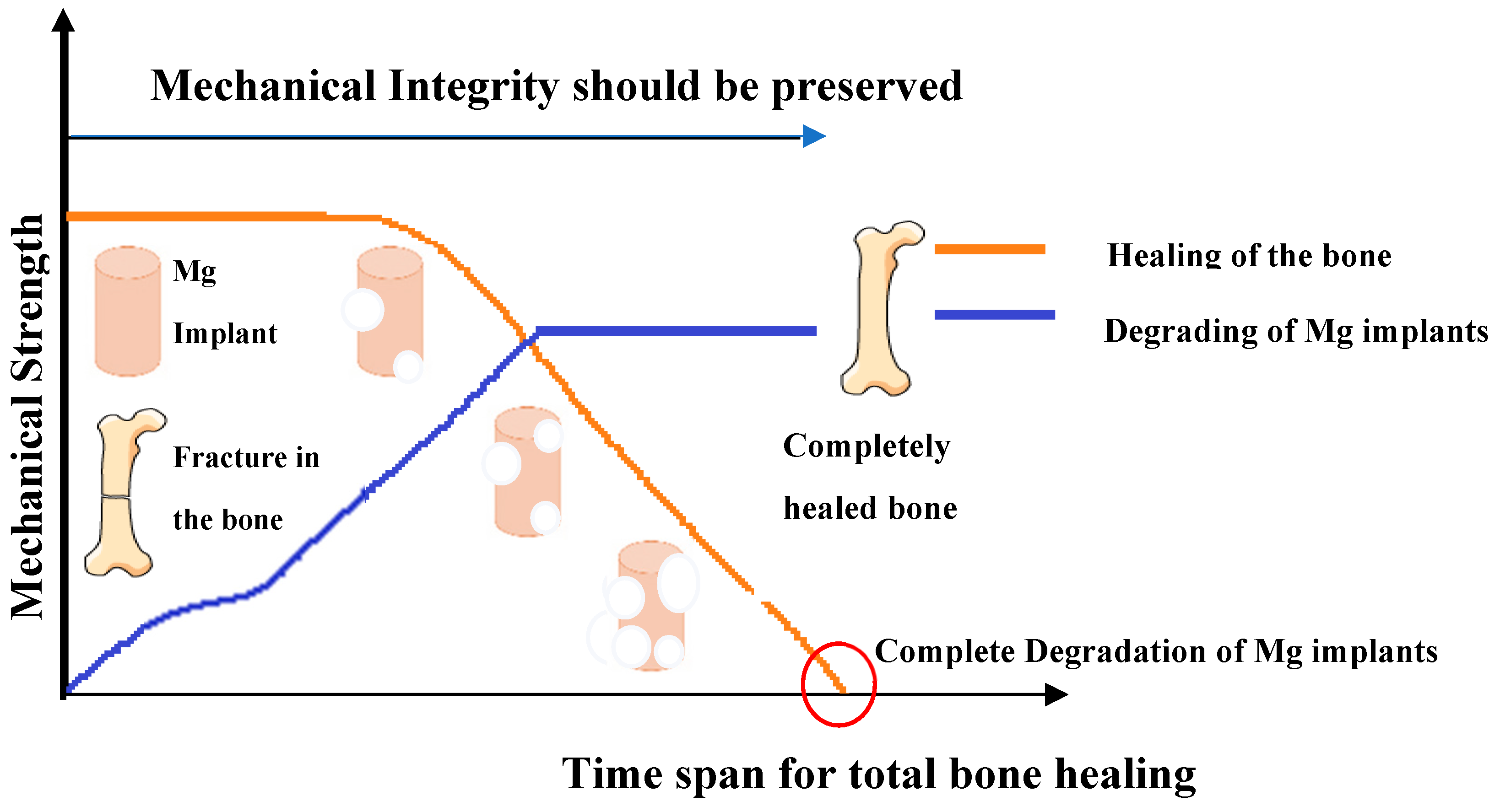
| High degradation rate | It leads to premature loss of mechanical integrity and implant supports. |
| Hydrogen generation | Hydrogen release creates air bubbles in the surrounding tissues. |
| Alloying elements | Biocompatibility | Corrosion resistance | Mechanical performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Al is neurotoxic. It can cause Alzheimer's disease and damage muscle fibers. | It is beneficial in providing corrosion resistance. | Increases strength and plasticity. |
| Zn | Non-cytotoxic and good biocompatibility. | Corrosion resistance decreases with higher Zn content. | Zn participates in solid solution strengthening, increasing strength with increasing Zn content. |
| Mn | Cytotoxic and neurotoxic | Provide good corrosion resistance. | It gives higher yield strength and reduces tensile strength and ductility. |
| Ca | An essential component of human bone | Corrosion resistance decreases with increasing Ca content | With increasing Ca content, strength increases, and plasticity decreases. |
| Sr | Sr is a vital component of human bone. It also aids in bone formation | Corrosion resistance of Mg alloy drops with increasing Sr content | The strength of the alloy increases with increasing Sr content |
| Zr | Good biocompatibility and bone-bonding ability | Corrosion resistance decreases with increasing Zr content | Grains undergo refinement, increasing strength and plasticity |
| Nd | Cytotoxic at high concentrations but has good biosafety at low concentrations. | Improves corrosion resistance | Forms new phases, grain refinement, and improvement in mechanical performance |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





