1. Introduction
Maize is a cereal crop well adapted to many ecoregions, where a large proportion of people relies on it as their primary staple food. However, maize production and quality is often limited by fungal diseases, such as Gibberella ear rot (GER) caused by
Fusarium graminearum (Schwabe) [
1,
2]. Serious yield losses can be caused by the disease, especially in the high temperate and humid regions in the world [
3]. In Southwest China, severe occurrence of GER in maize growing areas causes yield loss [
4]. Agronomic and chemical practices preventing the disease are currently insufficient when climatic conditions are favorable for the pathogen. The preferred method for controlling GER disease is to breed and cultivate resistant maize genotypes [
5]. However, totally immune genotypes are not available and commercial hybrids always have less resistance to the GER [
6,
7,
8,
9]. So, it becomes urgent to select resistant maize germplasm resources and identify broad-resistant genes for improving GER resistance.
Fusarium graminearum (
F. graminearum) is a common fungal pathogen that infects many plant species including maize, wheat, rice [
10]. In maize, the spores of
F. graminearum could naturally infect maize upon conveyance through wind, rain splash or insect infestation. Infected kernels are observed with a reddish-pink mold starting at the tip of a rotten ear [
11]. Not only the
F. graminearum-caused disease can reduce yield, but also the fungal produces diverse mycotoxins in the grain including deoxynivalenol (DON) and zearalenone (ZEN), which threatening human and livestock health [
3,
5].
Accurate phenotypic assessment is the major bottleneck in identifying reistant genes and conducting genetics research on diseases [
12]. A precise and convenient phenotypic evaluation method for GER resistance is challenging, owing to multiple factors influencing disease resistance scoring: inoculation time, inoculation method, and environmental conditions [
13]. Under natural condition, the unstable disease symptoms make it difficult to distinguish resistance differences among genotypes [
14,
15,
16]. Therefore, development of a reliable phenotypic evaluation system is an essential step for improving breeding of maize resistance to
F. graminearum. Most previous studies concerning phenotypic performance of maize ear rot were focused on the field evaluation [
6–,
7,
8,
17,
18,
19,
20]
. Nevertheless, the field evaluation is time consuming, labor intensive, and influenced by numerous environmental factors. As an alternative method to precisely evaluate GER phenotypes, kernel bioassay is developed for testing GER severity in laboratory [
21,
22,
23]
. Herein, healthy mature seeds were incubated with a fungal suspension to survey seed rot caused by occurring pathogen. The assay can be completely controlled under laboratory conditions to achieve more accurate phenotypic results, which has been successfully applied in maize to evaluate the resistance to
Fusarium spp. [
24,
25]
. However, this method was based on heavy workload and patience for calculating numeration of spores, especially for large population [
21]
.
Previous efforts to characterize GER resistance indicated that the trait is generally considered as a quantitative inheritance with a complex genetic basis and influenced by various environmental factors [
5,
12]
. In recent years, much progress has been made in GER resistance, including the detection of quantitative trait loci (QTL), identification of resistant genes and characterization of defense responses [
6,
7,
8,
9,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]
. Although QTL mapping and omics research have identified a series of candidate regions or genes associated with disease resistance, the molecular mechanism of those genes underling GER resistance have only been identified in a few cases due to inconsistent results from different populations and environments. Recently, use of high-density single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) datasets in combination with genome-wide association study (GWAS) has emerged as a powerful alternative strategy to acquire target genes associated with desired traits [
31]. This efficient approach can rapidly detect valuable natural variations in trait-associated loci as well as allelic variations in genes underlying quantitative and complex traits [
32]. In maize ear rot, previous efforts were mainly focused on SNPs conferring resistance to
Fusarium verticillioides ear rot (FER) [
33,
34,
35,
36], whereas there are very few reports on GER [
5]. Until recently, a research conducted GWAS to detect SNPs involving in resistance to maize GER [
7]. However, no close association SNPs were obtained in their research. In another study, a GWAS was performed in an association panel consisting of 316 diverse inbred lines and 10 co-localized association SNPs linked to GER resistance including a peak SNP following ten candidate genes were obtained [
30].
In order to accurately estimate phenotypes of GER resistance, a maize association panel were evaluated for their resistance using the kernel bioassay. Then, we performed GWAS to identify SNPs and putative genes that may contribute to GER resistance. Moreover, we analyzed the alleles that can be potentially used to improve GER resistance for next breeding programs. To our knowledge, this is the first time to dissect genetic basis for maize GER resistance using large-scale kernel bioassay indoor.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Maize Germplasm
The association panel containing core maize breeding materials from China, International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and U.S.A., were evaluated for GER resistance using kernel bioassay in the laboratory. Detailed information regarding the plant materials has been reported in the previous study [
30]. Due to seed availability, a total of 303 inbred lines were used for the experiment.
2.2. Experimental Procedure for Kernel Bioassay
For each line, mature seeds with similar size, shape and without visible damage were selected for the experiment. To accurately evaluate the presence of contaminating fungal, the kernels of each line were surface-disinfested with 70% ethanol for 2 min and then 0.6% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min, and rinsed five times with sterile distilled water. To provide an infection court, the kernels were wounded by cutting the embryo side with a razor blade, and the cut depth of about 0.5 mm. Subsequently, the kernels were blotted dry and then placed in a 20-ml glass scintillation vial (Wheaton Science, Head Biotechnology CO., LTD., Beijing, China), and finally inoculated with 200 μl of a final concentration of approximately 1.0 × 10
6 ml
−1 spores suspension of
F. graminearum. Control seeds were received an equal amount of sterilized distilled water. For each line, four seeds were placed into a vial as one biological replicate, with three replicates per experiment. The vials were kept in a humidity chamber under controlled conditions (27 ± 1°C and 14: 10 light/dark photoperiod). In view of no robust standards for kernel bioassay at present, we chosen spore enumeration at different time pionts for the GER severity according to the described study [
21]. In current study, the vials were surveyed at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days after the
F. graminearum inoculation for spore enumeration. Finally, average number of spores across multiple time points were calculated to comprehensively evaluate the final GER severity of each line.
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis
Descriptive phenotypic analysis of the GER severity at different time points, including the range, mean, standard deviation (SD) and coefficient of variation (CV), were performed using the SPSS 21.0 software (
http://www.spss.com) (accessed on 29 September 2023). Due to strict controllable laboratory conditions, the effect of each line with environment interaction is absent, resulting to lack the analysis of the broad-sense heritability of GER.
2.4. GWAS Analysis
The association panels were genotyped and detailed information on the population structure, kinship matrix, principal component analysis (PCA) matrix and linkage disequilibrium (LD) decay distance have previously been described [
37]. A total of 43,735 SNPs were obtained with a minor allele frequency (MAF) less than 0.05 and a missing rate and heterozygosity greater than 20% for the present study. The average distance of LD decay was approximately 220 kb at
r2 = 0.2. The LD attenuation distance around each SNP was used to search for candidate genes according to significant SNPs in GWAS. To identify SNPs with robust associations with GER, three models: fixed and random model circulating probability unification model (FarmCPU), general linear model (GLM) and mixed linear model (MLM) were simultaneously applied in the GWAS analysis using the rMVP package in R software. Herein, the PCA and Kinship were added into the models for controlling false positive signals associated with traits [
38]. The phenotype variance explained (PVE) of SNPs were caculated as follow formula:
A Bonferroni test (0.05/N) was employed to select the SNPs significantly associated with GER, and a total of 24,535 (N) effective SNPs were ultimately obtained by the simpleM program in R [
39]. Considering that the GER was determined by multiple minor effective genes, a moderated stringency threshold of -log (0.5/24,535) = 2.04×10
-5 was chosen to determine the significant SNPs in FarmCPU and GLM. On the other side, a less stringent threshold of 1.0×10
-4 for MLM was reasonable according to previous reports [
33,
40]. Genes within the LD regions of significantly associated SNPs were considered as candidate genes governing GER resistance, and then captured and annotated according to the B73 reference genome (B73 RefGen_v4) in the MaizeGDB database.
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Evaluation of GER Severity
The association panel consisting of 303 diverse inbred lines were evaluated for GER severity at 7, 14, 21 and 28 days post-inoculation (dpi) using kernel bioassay. Mean of spore values among the panel was 0.71 (7 dpi, ranging from 0.00 to 14.40 × 10
6 ml
−1), 2.77 (14 dpi, ranging from 0.00 to 64.00 × 10
6 ml
−1), 4.67 (21 dpi, ranging from 0.00 to 108.96 × 10
6 ml
−1) and 7.25 (28 dpi, ranging from 0.00 to 84.70 × 10
6 ml
−1), respectively. The outcomes of spore enumeration revealed that the number of spores increased gradually with the extension of the time-course inoculation (
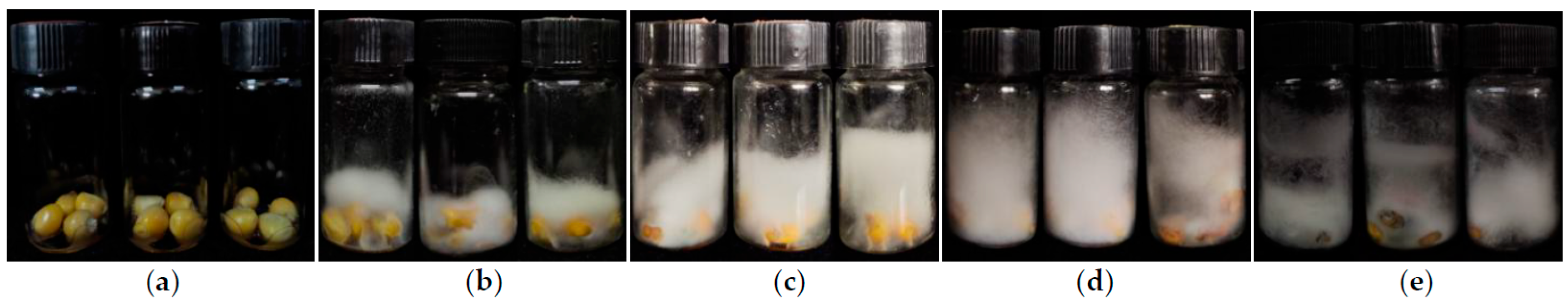
Table 1). Meanwhile, the vials was observed that the hyphae also grew gradually during the inoculation process (
Figure 1). Furthermore, their standard deviation (SD) and coefficient of variation (CV) were showed with high variation among the association panel (
Table 1), implying that a high proportion of the phenotypic variation was exhibited during the
F. graminearum infction. Overall, the spores number, hyphae growth and variation, were found with different types of response to
F. graminearum infction, displaying that the laboratory-inoculated kernel method was available for quantifying fungal growth and biomass, and evaluating phenotypic performance in GER severity. The description on GER severity using kernel bioassay
in large population is the first time.
Table 1.
Phenotypic description among the association panel using the kernel bioassay.
Table 1.
Phenotypic description among the association panel using the kernel bioassay.
| Days post-inoculation (dpi) |
Range (× 106 ml−1) a
|
Mean±SD(× 106 ml−1) b
|
CV (%)c
|
| 7 |
0.00-14.40 |
0.71±1.47 |
207 |
| 14 |
0.00-64.00 |
2.77±6.18 |
223 |
| 21 |
0.00-108.96 |
4.67±9.38 |
200.8 |
| 28 |
0.00-84.70 |
7.25±12.27 |
169 |
Figure 1.
Typical phenotypic performance of kernels during the F. graminearum inoculation via the kernel bioassay in the laboratory. (a) Inoculated kernerls at 0 day post-inoculation (dpi). (b) Inoculated kernerls at 7 dpi. (c) Inoculated kernerls at 14 dpi. (d) Inoculated kernerls at 21 dpi. (e) Inoculated kernerls at 28 dpi.
Figure 1.
Typical phenotypic performance of kernels during the F. graminearum inoculation via the kernel bioassay in the laboratory. (a) Inoculated kernerls at 0 day post-inoculation (dpi). (b) Inoculated kernerls at 7 dpi. (c) Inoculated kernerls at 14 dpi. (d) Inoculated kernerls at 21 dpi. (e) Inoculated kernerls at 28 dpi.
Considering the complexity of plant-pathogen interactions during F. graminearum infection, the final GER severity of each line was evaluted with an average number of spores across multiple time points. Based on the comprehensive evaluation, top ten lines were obtained from the association panel with low spore concentration, including SCML1950 (0.48 × 106 ml−1), Qi533 (0.52 × 106 ml−1), JD7275 (0.74× 106 ml−1), End28 (0.81× 106 ml−1), 5Gong (0.83× 106 ml−1), CG698C102 (1.19 × 106 ml−1), Su95-1 (1.28 × 106 ml−1), Lin-1 (1.34 × 106 ml−1), CLWN251 (1.41 × 106 ml−1) and BJ005 (1.45 × 106 ml−1). The identified germplasms can be potentially utilized in mazie disease-resistance breeding program for GER. In general, these outcomes suggested that the kernel assay may provide a new way to screen resistant germplasm sources or detect specific loci associated with resistance to GER in maize.
3.2. Association Analysis and SNPs Discovery
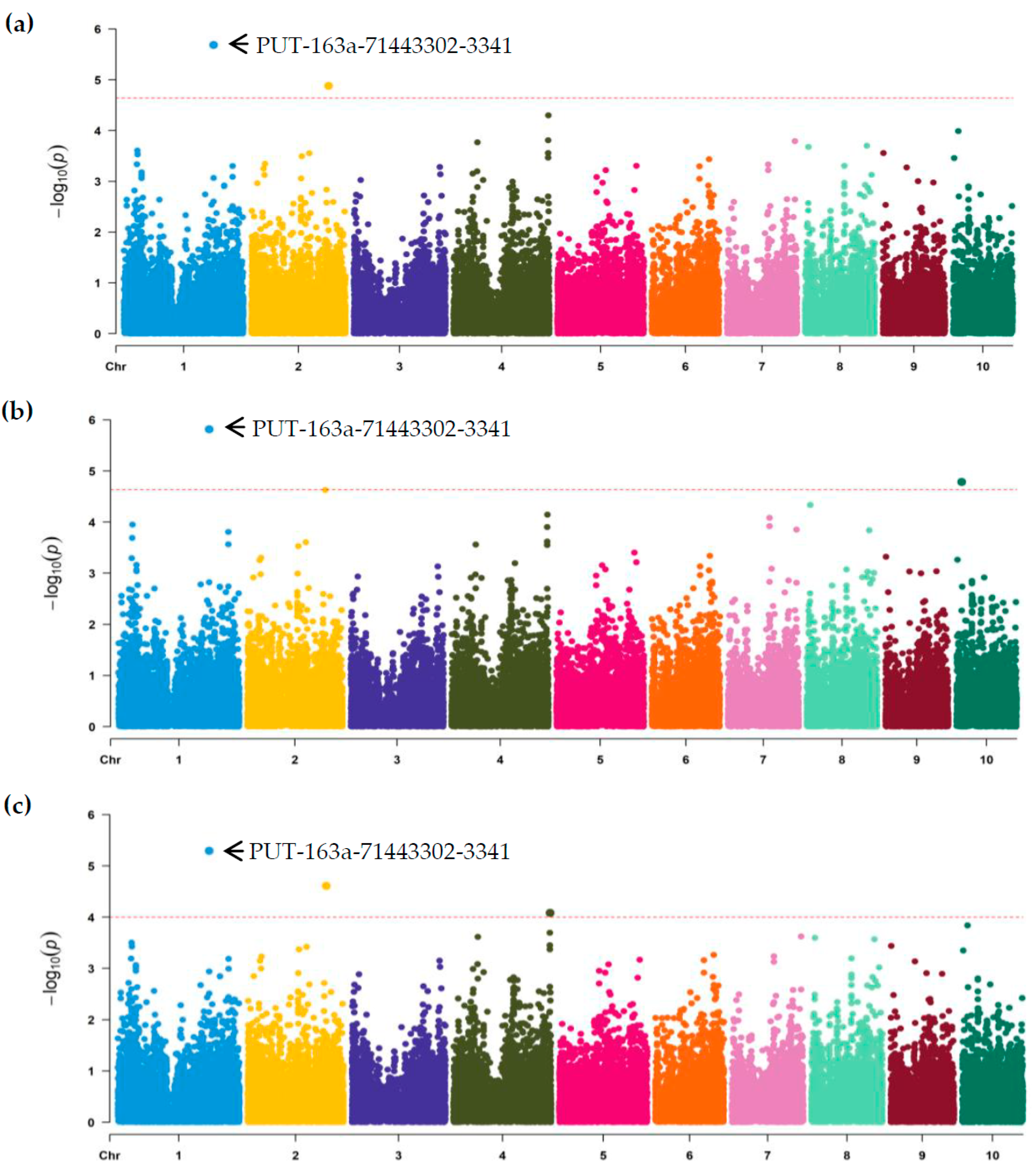
According to above comprehensive evaluation, the phenotypic data of 303 lines were ultimately obtained and further utilized to perform GWAS using the three models FarmCPU, GLM and MLM. In FarmCPU, only two significant association SNPs (PUT-163a-71443302-3341 and SYN9515) were identified with an adjusted threshold of 2.04 × 10
-5, distributing on the chromosomes 1 and 2, respectively (
Table 2,
Figure 2a). In GLM, two SNPs (PUT-163a-71443302-3341 and PZE-110014176) were also found with significant association and localized on the chromosomes 1 and 10, respectively (
Table 2,
Figure 2b). For MLM, three significant association SNPs (PUT-163a-71443302-3341, SYN9515 and PZE-104154469) were detected with the threshold of 1.0 × 10
-4, distributing on chromosomes 1, 2 and 4, respectively (
Table 2,
Figure 2c). The average PVE value of the identified SNPs was 5.6%, ranging from 3.51 to 6.42% (
Table 2). Among them, the association SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) had the greatest PVE value of 6.42%. A combination of the GWAS analysis from the three models revealed that only four significant SNPs were obtained associated with GER resistance. In details, the SNPs PUT-163a-71443302-3341 on chromosome 1 and SYN9515 on chromosome 2, were repeatedly detected in different models, indicating that the two loci were reliable. Interestingly, the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) with the greatest PVE value was detected in all models (
Figure 2), suggesting that the co-localized SNP was considered as a stable resistant locus. The peak region might contain important genetic components affecting GER resistance and the useful SNP should be concerned for discovering candidate resistant genes.
Table 2.
Significant association SNPs for GER resistance through GWAS with three models.
Table 2.
Significant association SNPs for GER resistance through GWAS with three models.
| Model a
|
SNP |
Chr. b
|
Position |
Allele |
MAFc
|
P value |
PVE (%)d
|
| FarmCPU |
PUT-163a-71443302-3341 |
1 |
226,136,399 |
G/A |
0.29 |
2.06E-06 |
6.42 |
| FarmCPU |
SYN9515 |
2 |
194,393,324 |
C/A |
0.36 |
1.32E-05 |
5.54 |
| GLM |
PUT-163a-71443302-3341 |
1 |
226,136,399 |
G/A |
0.29 |
1.53E-06 |
6.42 |
| GLM |
PZE-110014176 |
10 |
13,338,854 |
A/C |
0.43 |
1.65E-05 |
3.51 |
| MLM |
PUT-163a-71443302-3341 |
1 |
226,136,399 |
G/A |
0.29 |
5.12E-06 |
6.42 |
| MLM |
SYN9515 |
2 |
194,393,324 |
C/A |
0.36 |
2.46E-05 |
5.54 |
| MLM |
PZE-104154469 |
4 |
238,758,660 |
A/G |
0.49 |
8.28E-05 |
5.35 |
Figure 2.
Manhattan plot of genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) for GER resistance with three models. (a) GWAS analysis using a fixed and random model circulating probability unification model (FarmCPU). (b) GWAS analysis using a general linear model (GLM). (c) GWAS analysis using a mixed linear model (MLM). The Y-axis value corresponds to -log10 (p) of p-value scores, and the X-axis indicates chromosomes and physical positions of SNPs. The red dashed lines show genome-wide significance at the adjusted thresholds of 2.04 × 10-5 for FarmCPU and GLM, and 1.0 × 10-4 for MLM, respectively. The most significant association SNP PUT-163a-71443302-3341 was marked and co-localized by combined FarmCPU, GLM and MLM models.
Figure 2.
Manhattan plot of genome-wide association analysis (GWAS) for GER resistance with three models. (a) GWAS analysis using a fixed and random model circulating probability unification model (FarmCPU). (b) GWAS analysis using a general linear model (GLM). (c) GWAS analysis using a mixed linear model (MLM). The Y-axis value corresponds to -log10 (p) of p-value scores, and the X-axis indicates chromosomes and physical positions of SNPs. The red dashed lines show genome-wide significance at the adjusted thresholds of 2.04 × 10-5 for FarmCPU and GLM, and 1.0 × 10-4 for MLM, respectively. The most significant association SNP PUT-163a-71443302-3341 was marked and co-localized by combined FarmCPU, GLM and MLM models.
3.3. Genes Associated with GER Resistance
To identify genes with potential resistance to GER, candidate genes were explored within 220 kb upstream and downstream of the the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341). Finally, the focused SNP was adjacent to 12 putative genes according to the annotation information of the B73 reference genome (
Table 3). Of these candidate genes including the LRR-repeat protein and hydroxycinnamoyl transferase, several of them may have different roles in response to pathogen infection. Even though these genes were not described absolutely associated with GER resistance, the findings from this study suggest that the candidate SNP and linked genes should be taken in account and targeted to dissect funtions involving in diseases resistance.
Table 3.
The genomic regions of the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) and candidate genes associated with GER resistance a.
Table 3.
The genomic regions of the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) and candidate genes associated with GER resistance a.
| Physical position |
Candidate genes |
Annotation |
| 229515984-229517919 |
Zm00001d032527 |
hydroxycinnamoyltransferase13 |
| 229718687-229725690 |
Zm00001d032530 |
F-box/LRR-repeat protein |
| 229758635-229765316 |
Zm00001d032531 |
Membrane steroid-binding protein 1 |
| 229766139-229766442 |
ENSRNA049476973 |
Plant signal recognition particle RNA |
| 229816856-229817035 |
ENSRNA049476978 |
Plant signal recognition particle RNA |
| 229829797-229830137 |
Zm00001d032533 |
-- |
| 229830451-229831175 |
Zm00001d022929 |
-- |
| 229831273-229832169 |
Zm00001d032534 |
-- |
| 229847655-229849510 |
Zm00001d022930 |
-- |
| 229847655-229849510 |
Zm00001d032535 |
Tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-like superfamily protein |
| 229900429-229901097 |
Zm00001d032538 |
-- |
| 229992052-229992483 |
Zm00001d032542 |
plant/MXO21-9 protein |
3.4. Distribution of Favorable Alleles
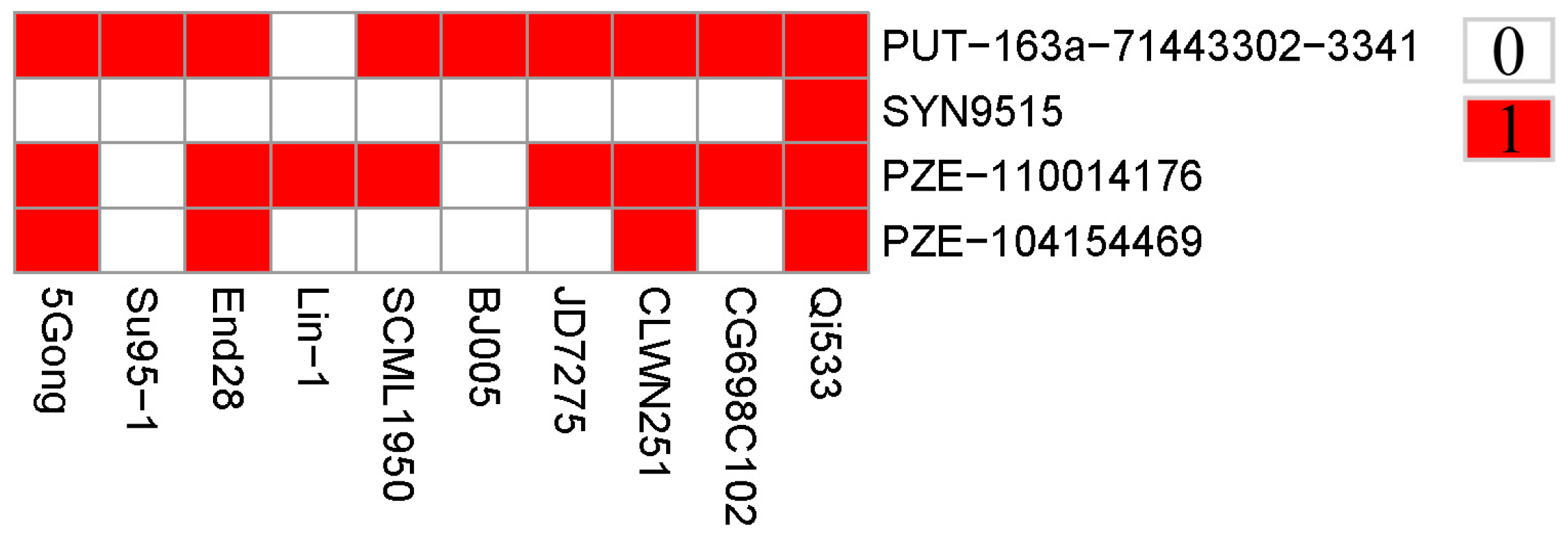
Since the ten elite resistant lines were obtained from the association panel via kernel bioassay evaluation, the favorable alleles of the association SNPs were estimated for further utilization. Herein, genotypes associated with lower level GER severity were defined as favorable alleles for GER resistance. The identified four association SNPs were distributed across the ten lines and the favorable alleles percentages of these SNPs ranged from 10.0% to 90.0%, with two SNPs (PUT-163a-71443302-3341 and PZE-104154469) containing more than 50% favorable alleles, wheareas the remaining two SNPs no less than 50% (
Figure 3). Moreover, each of the elite lines contained different favorable alleles, ranging from 1-4. In details, the seven lines (5Gong, End28, SCML1950, JD7275, CLWN251, CG698C102 and Qi533) contained at least two favorable alleles, wheareas the remaining three lines (Su95-1, Lin-1 and BJ005) contained only one favorable allele (
Figure 3). Notably, the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) contained the most 9 favorable alleles, suggesting that the significant SNP may have important effect on GER resistance.
Figure 3.
Distributions of favorable alleles among the ten elite lines. Red and white represent favorable and inferior alleles, respectively.
Figure 3.
Distributions of favorable alleles among the ten elite lines. Red and white represent favorable and inferior alleles, respectively.
4. Discussion
Disease severity caused by
F. graminearum, particularly for GER, is often influenced by environmental conditions, host genotypes and pathogenic races [
5,
12,
26]. The establishment of a precise and convenient phenotypic evaluation method for GER resistance, capable of accommodating large populations, is a prerequisite for conducting genetics research in future [
5,
8]. Given the genotype and enviroment interactions, field phenotypes of pathogen-caused diseases must be conducted in multiple environments over several years [
12]. Thus, a reliable way for evaluating GER resistance is urgently necessary for eliminate external environmental factors. To achieve this goal, the GER severity of the maize association panel were evaluated throught laboratory-inoculated in the present study. This is the first large-scale phenotypic evaluation for GER severity indoor. Thus far, previous efforts on evaluating GER resistance for large population were mainly on the field-inoculated test, and few efforts have been made indoor [
7,
26,
30]. Although the indoor assay has been applied to assess diseases severity for few samples, no much progress has been reported on large population due to the tedious process for spore enumeration at each inoculated time point [
22,
30,
41].
In order to accurately descript GER severity, spore enumeration were performed across multiple time points during the
F. graminearum infection. The results revealed a wide variation of GER severity among the lines (
Table 1,
Figure 1), suggesting that the indoor assay could effectively distinguish resistant variation for large population. It should be noted that their SDs and CVs were showed with a big variation range among the association panel, demonstrating that the amount of spores vary obviously at each time point. The most likely reason was that the assay was hard to control the seeds viability and nutrients, thus leading to the
F. graminearum cannot produce spores steadily [
13,
21]. Furthermore, given no previous reports on resistant rating scales or grades for kernel bioassay, we assumed that the final GER severity should be evaluated comprehensively during
F. graminearum infection. Indeedy, the spores at each time point is only a partial reflection of the final resistance [
13]. Thus, we considerated the average spores across multiple time points as the phenotypic data for the final GER severity in current study. However, this was just an initial tentative strategy in evaluating phenotypes of GER resistance for large population. Further prior approach on the phenotypic evaluation of GER severity through kernel bassay should be worthwhile. With the comprehensive evaluation, ten elite lines with low spore concentration were obtained from the association panel, indicating the kernel assay offered an alternative way to evaluate phenotypes of GER resistance, and also could be accelerate to obtain resistant germplasms for improving resistance of maize GER disease.
Plant resistance to pathogens is a complex interactions regulated by polygenic networks. In this study, GWAS was conducted by three models FarmCPU, GLM and MLM to identify the candidate genomic regions and SNPs conferring GER resistance. Only four individual significant association SNPs with a range of PVE were identified in GWAS (
Table 2,
Figure 2). The results different from previous similar studies [
7,
30], fewer loci were obtained in current study. The reason for this phenomenon was largely relying on the different phenotypic data between the field and indoor. As mentioned earlier, most of the previous researches concerning phenotypic performance of GER severity were focused on the field evaluation, and the field phenotypic data varied widely resulting in detecting more variation loci conferring resistance [
7,
30]. On the contrary, the kernel assay was strictly controlled under laboratory conditions, thus leading to the phenotypic data varied more gently with a smaller variation than that in the field [
21]. Despite few SNPs were obtained our GWAS, two of them were repeatedly detected in different models, indicating that the identified loci were reliable to help for understanding the complex genetic basis of GER resistance.
Furthermore, a combination analysis of GWAS results was performed to capture stable genomic region or key loci significantly associated with GER resistance. Interestingly, the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341) with the greatest PVE value of 6.42% was co-localized in all models. Then, the significant SNP hit 12 specific genes that several of them may involved in response to pathogen infection (
Table 3). For instance, a candidate gene
Zm00001d032530 was annotated as LRR-repeat protein, which was widely reported to be involved in plant immunity [
42]. Another candidate gene annotated as hydroxycinnamoyl transferase (
Zm00001d032527) was tightly associated with plant metabolim, playing important roles in the interaction between plants and pathogens [
43]. Overall, further investigation on these candidate regions and the significant association SNPs linked to candidate genes with potential resistance to GER in addition to the unknown genes is required. According to the distributions of the favorable alleles among the ten elite inbred lines, two SNPs were found containing more than 50% favorable alleles, suggesting that the SNPs should be emphasized in marker-assisted selection for GER breeding program (
Figure 3). Especially for the peak SNP (PUT-163a-71443302-3341), nine favorable alleles were observed accross the ten lines. These findings implied that the detected alleles might have important effect in reponse to GER resistance. In addition, the seven lines harboring more than two favorable alleles that exhibited low disease severity can be potentially utilized in a mazie disease-resistance breeding in the future.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we conducted a GWAS based on the laboratory-inoculated phenotypic evaluation to provide new and useful genetic information on maize GER resistance. We obtained four significant association SNPs through the GWAS, containing a peak significant SNP following 12 candidate genes. To our knowledge, this is the first large-scale GWAS focusing on the candidate regions and linked genes contributing to GER resistance by using kernel bioassay indoor. These findings will help to better understand the genetic complexity of GER resistance mechanisms in maize.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L. and G.Y.; methodology, J.Z., H.S. and Y.Y.; formal analysis, J.Z., H.S., Y.Y., C.Z. and Z.J.; investigation, C.Z., Z.J., T.M., M.W. and J.D.; data curation, T.M., M.W., J.D., N.H. and G.P.; writing-original draft preparation, J.Z. and G.Y.; supervision, N.H., G.P. and Z.L.; project administration, N.H.; funding acquisition, J.Z. and G.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Sichuan Science and Technology Support Project (Key Program for Maize Breeding), grant number 2021YFYZ0017, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32272177.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. S.B. Gao and Dr. X. Zhang (Sichuan Agricultural University, China) for providing the maize association panel and much technical assistance for this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Reid, L.M.; Nicol, R.W.; Ouellet, T.; Savard, M.; Miller, J.D.; Young, J.C.; Stewart, A.W.; Schaafsma, A.W. Interaction of Fusarium graminearum and F. moniliforme in maize ears: Disease progress, fungal biomass, and mycotoxin accumulation. Phytopathol. 1999, 89, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Balint-Kurtil, P.; Xu, M. Quantitative disease resistance: dissection and adoption in maize. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigier, B.; Reid, L. M.; Dwyer, L.M.; Stewart, D.W.; Sinha, R.C.; Arnason, J.T.; Butler, G. Maize resistance to Gibberella ear rot: symptoms, deoxynivalenol, and yield. Can. J. Plant. Pathol. 2001, 23, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.X.; Qin, Z.H.; Yang, Z.H.; Li, W.X.; Sun, S.L.; Zhu, Z.D.; Wang, X.M. Identification of pathogenic Fusarium spp. causing maize ear rot and potential mycotoxin production in China. Toxins 2016, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikpa, D.; Miedaner, T. Genomics-assisted breeding for ear rot resistances and reduced mycotoxin contamination in maize: methods, advances and prospects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giomi, G.M.; Kreff, E.D.; Iglesias, J.; Fauguel, C.M.; Fernandez, M.; Oviedo, M.S.; Presello, D.A. Quantitative trait loci for Fusarium and Gibberella ear rot resistance in Argentinian maize germplasm. Euphytica. 2016, 211, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Miedaner, T.; Utz, H.F.; Schipprack, W.; Schrag, T.A.; Melchinger, A.E. Genomic prediction and GWAS of Gibberella ear rot resistance traits in dent and flint lines of a public maize breeding program. Euphytica. 2018, 214, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, A.Z.; Woldemariam, T.; Reid, L.M.; Harris, L.J. Quantitative trait loci mapping for Gibberella ear rot resistance and associated agronomic traits using genotyping-by-sequencing in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Miedaner, T.; Dhillon, B.S.; Ufermann, U.; Kessel, B.; Ouzunova, M.; Schipprack, W.; Melchinger, A.E. Colocalization of QTL for Gibberella ear rot resistance and low mycotoxin contamination in early European maize. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkvold, G.P. Fusarium species and their associated mycotoxins. Methods Mol. Bio. 2017, 1542, 51–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.L.; Taylor, J.H.; Jie, L.; Sun, G.; William, M.; Kasha, K.J.; Reid, L.M.; Pauls, K.P. Molecular mapping of QTLs for resistance to Gibberella ear rot, in corn, caused by Fusarium graminearum. Genome 2005, 48, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesterházy, A.; Lemmens, M.; Reid, L.M. Breeding for resistance to ear rots caused by Fusarium spp. in maize-a review, Plant Breed. 2012, 131, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerbass, F.R.; Casa, R.T.; Kuhnem, P.R.; Vieira Jr, J.L.; Valente, J.B. Field evaluation of maize for Gibberella ear rot resistance using silk channel and kernel inoculation with Fusarium meridionale. Trop. plant pathol. 2015, 40, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerbass, F.R.; Casa, R.T.; Kuhnem, P.R.; Bogo, A.; Sangoi, L.; Fingstag, M.D.; Vieira, J.J.; Stoltz, J.C. Evaluation of Fusarium graminearum inoculation methods in maize ears and hybrid reaction to Gibberella ear rot under southern Brazilian environmental conditions. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, L.M.; Hamilton, R.L. Effects of inoculation position, timing, macroconidial concentration, and irrigation on resistance of maize to Fusarium graminearum infection through kernels. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 1996, 18, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, L.M.; Woldemariam, T.; Zhu, X.; Stewart, D.W.; Schaafsma, A.W. Effect of inoculation time and point of entry on disease severity in Fusarium graminearum, Fusarium verticillioides, or Fusarium subglutinans inoculated maize ears. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2002, 24, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, J.N.; DeClerck, G.; Greenberg, A.; Clark, R.; McCouch, S. Next-generation phenotyping: requirements and strategies for enhancing our understanding of genotype-phenotype relationships and its relevance to crop improvement. Theor. Appl.Genet. 2013, 126, 867–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butrón, A.; Reid, L.M.; Santiago, R.; Cao, A.; Malvar, R.A. Inheritance of maize resistance to Gibberella and Fusarium ear rots and kernel contamination with deoxynivalenol and fumonisins. Plant Pathol. 2015, 64, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuska, M.T.; Mahlein, A.K. Aiming at decision making in plant disease protection and phenotyping by the use of optical sensors. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2018, 152, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutka, A.M.; Bart, R.S. Image-based phenotyping of plant disease symptoms. Front Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.; Borrego, E.; Shim, W.B.; Isakeit, T.; Kolomiets, M. Quantification of fungal colonization, sporogenesis, and production of mycotoxins using kernel bioassays. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 62, e3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Shim, W.B.; Göbel, C.; Kunze, S.; Feussner, I.; Meeley, R.; Balint-Kurti, P.; Kolomiets, M. Disruption of a maize 9-lipoxygenase results in increased resistance to fungal pathogens and reduced levels of contamination with mycotoxin fumonisin. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 922–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, F.; Jiang, F.; Sun, Y.; Ruan, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X.; Gao, X. Mapping and validation of a stable quantitative trait locus conferring maize resistance to Gibberella ear rot. Plant Dis. 2021, 7, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Li, H.; Liu, E.; He, K.; Song, Y.; Dong, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H. Evaluation and identification of resistance lines and QTLs of maize to seedborne Fusarium verticillioides. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, M.; Zhou, Z.; Mu, C.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Dissecting the genetic architecture of Fusarium verticillioides seed rot resistance in maize by combining QTL mapping and genome-wide association analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miedaner, T.; Boeven, A.L.G.; Gaikpa, D.S.; Kistner, M.B.; Grote, C.P. Genomics-assisted breeding for quantitative disease resistances in small-grain cereals and maize. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; He, X.; Li, H.; Xiang, K.; Liu, L.; Zou, C.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, G. Transcriptomic responses in resistant and susceptible maize infected with Fusarium graminearum. Crop J. 2020, 8, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Chen, B.; Peng, H.; Zheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Xiang, K.; Liu, L.; Zou, C.; Lin, H.; Ding, H.; et al. QTL mapping for resistance to ear rot caused by Fusarium graminearum using an IBM Syn10 DH population in maize. Mol. Breed. 2020, 40, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Li, Y.; He, D.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Zou, C.; Ma, L.; Pan, G.; Shen, Y. A combination of QTL mapping and GradedPool-Seq to dissect genetic complexity for Gibberella ear rot resistance in maize using an IBM Syn10 DH population. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; He, D.; Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Zou, C.; Ma, L.; Gao, S.; Pan, G.; Shen, Y. Genome-wide association study discovers novel germplasm resources and genetic loci with resistance to Gibberella ear rot caused by Fusarium graminearum. Phytopathology, 2023, 113, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Buckler, E.S. Genetic association mapping and genome organization of maize. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2006, 17, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikha, K.; Shahi, J.P.; Vinayan, M.T.; Zaidi, P.H.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, B. Genome-wide association mapping in maize: status and prospects. 3 Biotech. 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zou, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Jeffers, D.; Fan, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y. Complex genetic system involved in Fusarium ear rot resistance in maize as revealed by GWAS, bulked sample analysis, and genomic prediction. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1725–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shrestha, R.; Ding, J.; Zheng, H.; Mu, C.; Wu, J.; Mahuku, G. Genome-wide association study and QTL mapping reveal genomic loci associated with Fusarium ear rot resistance in tropical maize germplasm. G3-Genes·Genom.·Genet. 2016, 6, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, A.; Loladze, A.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Olsen, M.; Vicent, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study and genomic prediction of Fusarium ear rot resistance in tropical maize germplasm. Crop J. 2021, 2, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zila, C.; Samayoa, L.F.; Santiago, R.; Butrón, A.; Holland, J.B. A genome-wide association study reveals genes associated with Fusarium ear rot resistance in a maize core diversity panel. G3-Genes·Genom.·Genet. 2013, 3, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Lan, H.; Ren, Z.; Liu, D.; Wu, L.; Jaqueth, J.; Li, B.; Pan, G.; Gao, S. Characterizing the population structure and genetic diversity of maize breeding germplasm in southwest China using genome-wide SNP markers. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X. rMVP: A memory-efficient, visualization-enhanced, and parallel-accelerated tool for genome-wide association study. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2021, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S.; Christensen, R.B.; Singmann, H.; Dai, B.; Grothendieck, G. Package ‘lme4′. Convergence 12. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Manolio, T.A.; Pasquale, L.R.; Boerwinkle, E.; Caporaso, N.; Cunningham, J.M.; deAndrade, M.; Feenstra, B.; Feingold, E.; Hayes, M.G.; et al. Genome partitioning of genetic variation for complex traits using common SNPs. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Brodhagen, M.; Isakeit, T.; Brown, S.H.; Göbel, C.; Betran, J.; Feussner, I.; Keller, N.P.; Kolomiets, M.V. Inactivation of thelipoxygenase ZmLOX3 increases susceptibility of maize to Aspergillus spp. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborski, J.; Krasileva, K.V. Evolution of plant NLR: From natural history to precise modification. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 355–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.; Shen, S.; He, F.; Tao, H.; Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; et al. Function of hydroxycinnamoyl transferases for the biosynthesis of phenolamides in rice resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae. J. Genet. Genom. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 776e786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).