Submitted:
20 October 2023
Posted:
23 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
- (1)
- Concept definition
- (2)
- Related research
4. Methods
4.1. Place name disambiguation
4.2. Area studied recognition
4.3. Automatic Generation of Massive Thematic Maps
5. Experiment
5.1. Data pre-processing
5.2. Evaluation index
5.3. Experimental results
5.3.1. Area studied feature recognition
5.3.2. Area studied extraction
5.3.3. Mapping results
6. Conclusion and Discussion
References
- Ma, X.; Xuan, Z.; Wu, J. A Topic Finding Method for Scientific and Technical Literature[C]. 2010.
- Yingjie, Hu. Geo-Text Data and Data-Driven Geospatial Semantics. Geography Compass 2018, e12404. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, C.; Wanzeng, W.; Hao, W.; et al. Basic issues and research agenda of geospatial knowledge service. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2019, 44, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mónica, M.; Julián, U.; Sonia, S.C.; et al. Named entity recognition: Fallacies, challenges and opportunities. Computer Standards & Interfaces 2013, 35, 482–489. [Google Scholar]
- Gritta, M.; Pilehvar, M.; Collier, N. A pragmatic guide to geoparsing evaluation. Lang Resour Eval 2020, 54, 683–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, W.A.; Church, K.W.; Yarowsky, D. One sense perdiscourse. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Speech andNatural Language, Harriman, NY, USA, 23–26 February 1992; pp. 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, B.; Manguinhas, H.; Borbinha, J.; et al. A geo-temporal information extraction service for processing descrip-tive metadata in digital libraries. E Perimetron 2009, 4, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Edwin, A.; Alejandro, M.; Ivan, L.; et al. Adaptive Geoparsing Method for place name Recognition and Resolution in Unstructured Text. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 3041. [Google Scholar]
- Buscaldi, D.; Rosso, P. A conceptual density-based approach forthe disambiguation of place names. International Journal of Geo-graphical Information Science 2008, 22, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Xingguang, W.; Min, C.; et al. A semantics-based method for extracting geographic scopes of texts. High technology letters 2012, 22, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Xuri, T.; Xiaohe, C.; Xueying, Z. Research on place name resolution in Chinese text. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2010, 35, 930–935, 982. [Google Scholar]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Pezanowski, S.; MacEachren, A.; et al. GeoTxt: A scalable geoparsing system for unstructured text geolocation. Trans. GIS 2019, 23, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xingguang, W.; Ruijie, Z.; Yi, Z. place name resolution based on Geo-relevance and D-S theory. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis 2017, 53, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, R.; Clough, P.; Jones, C.B.; Arampatzis, A.; Bucher, B.; Finch, D.; Fu, G.; Joho, H.; Syed, A.K.; Vaid, S.; et al. The design and implementation of SPIRIT: A spatially aware search engine for information retrieval on the Internet. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2007, 21, 717–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewandaru, A.; Widyantoro, D.H.; Akbar, S. Event Geoparser with Pseudo-Location Entity recognition and Numerical Argument Extraction Implementation and Evaluation in Indonesian News Domain. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2020, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LDC. ACE (Automatic Content Extraction) English Annotation Guidelines for Events V5.4.3 Linguistic Data Consortium. 2005. Available online: https://www.ldc.upenn.edu/collaborations/past-projects/ace (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- Imani, M.B.; Chandra, S.; Ma, S.; Khan, L.; Thuraisingham, B. Focus location extraction from political news reports with bias correction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), Boston, MA, USA, 11–14 December 2017; pp. 1956–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Liu, H.; Ward, M.D. Lost in Space: Geolocation in Event Data. Political Sci. Res. Methods 2019, 7, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halterman, Andrew, Linking Events and Locations in Political Text (1 September 2018). MIT Political Science Department Research Paper No. 2018–21.
- Halterman, A. Geolocating Political Events in Text. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Natural Language Processing and Computational Social Science, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 6 June 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL): Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- O'brien, R. Global financial integration: The end of geography. Royal Institute of International Affairs 1992, 68, 531–532. [Google Scholar]
- Cairncross, F. The Death of Distance: How the Communica- tions Revolution Will Change Our Lives; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 1–304. [Google Scholar]
- Dodge, M. The geographies of cyberspace: A research note. Communication Studies 1998, 12, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, B. From phenomena to essence:envisioning the nature of digital map generalisation. The Cartographic Journal 1995, 32, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Algorithmic Foundation of Multi-Scale Spatial Representation; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group): London, UK, 2007; p. 281. [Google Scholar]
- Raposo, P. Scale-specific automated line simplification by vertex clustering on a hexagonal tessellation. Cartography and Geographic Information Science 2013, 40, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ormeling, F.J. Cybermap: The map for cyberspace. The Cartographic Journal 1997, 34, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F. Cyberspace and cybermap. Map 1999, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- GAO, J. Cartographic tetrahedron: explanation of cartography in the digital era. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinca 2004, 33, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.D.; Guo, Q.Q.; Jiang, D.; et al. The theoretical basis and technical path of cyberspace geography. Acta Geo- graphica Sinica 2019, 74, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar]
- AI, T.H. Development of cartography driven by big data. Journal of Geomatics 2016, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern classification. John Wiley & Sons. 2012.
- Hang, Z. Research on Location-referenced Web Textual Information Extraction and Cartographic Visualization. Wuhan University: Wuhan, 2019.

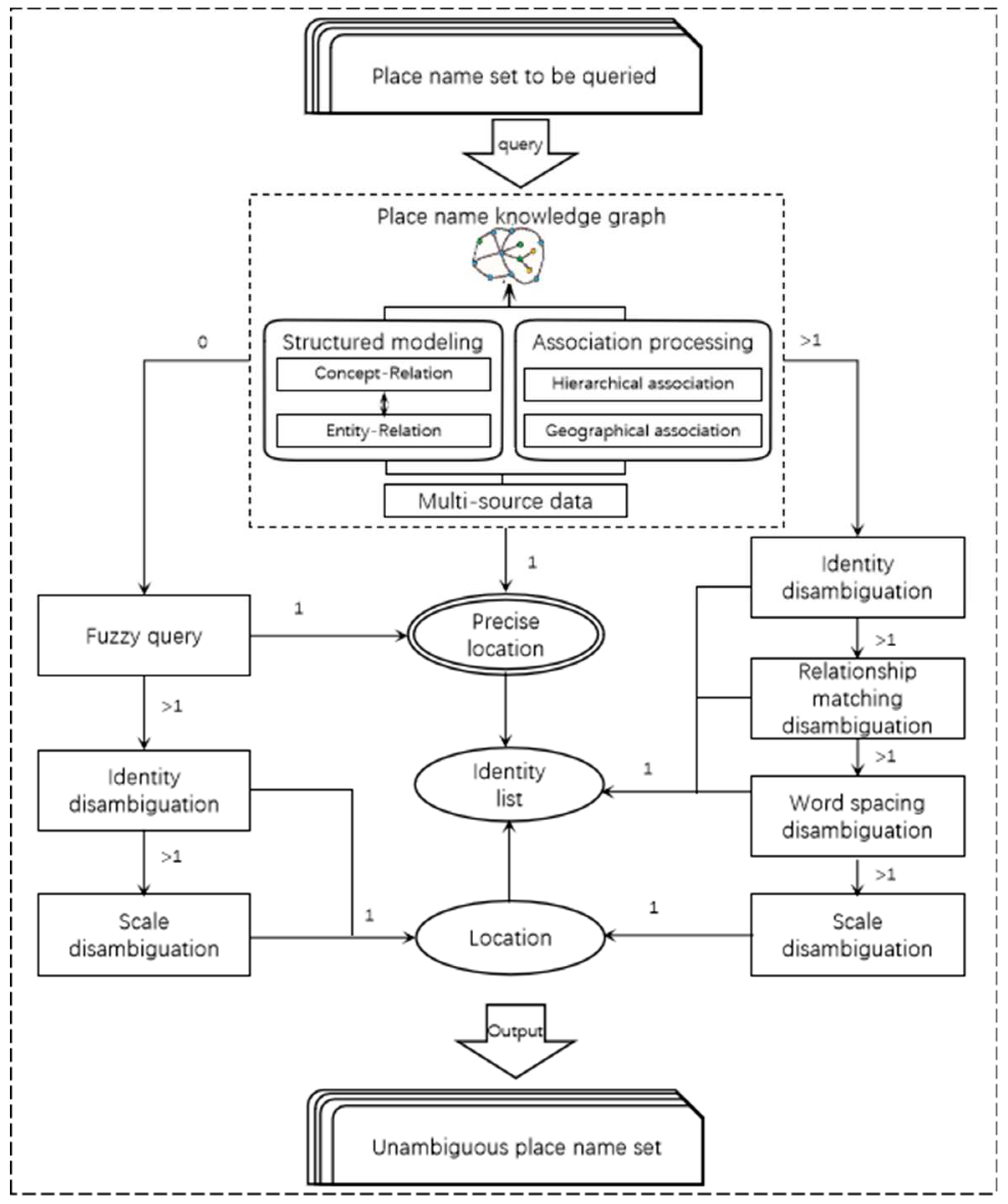
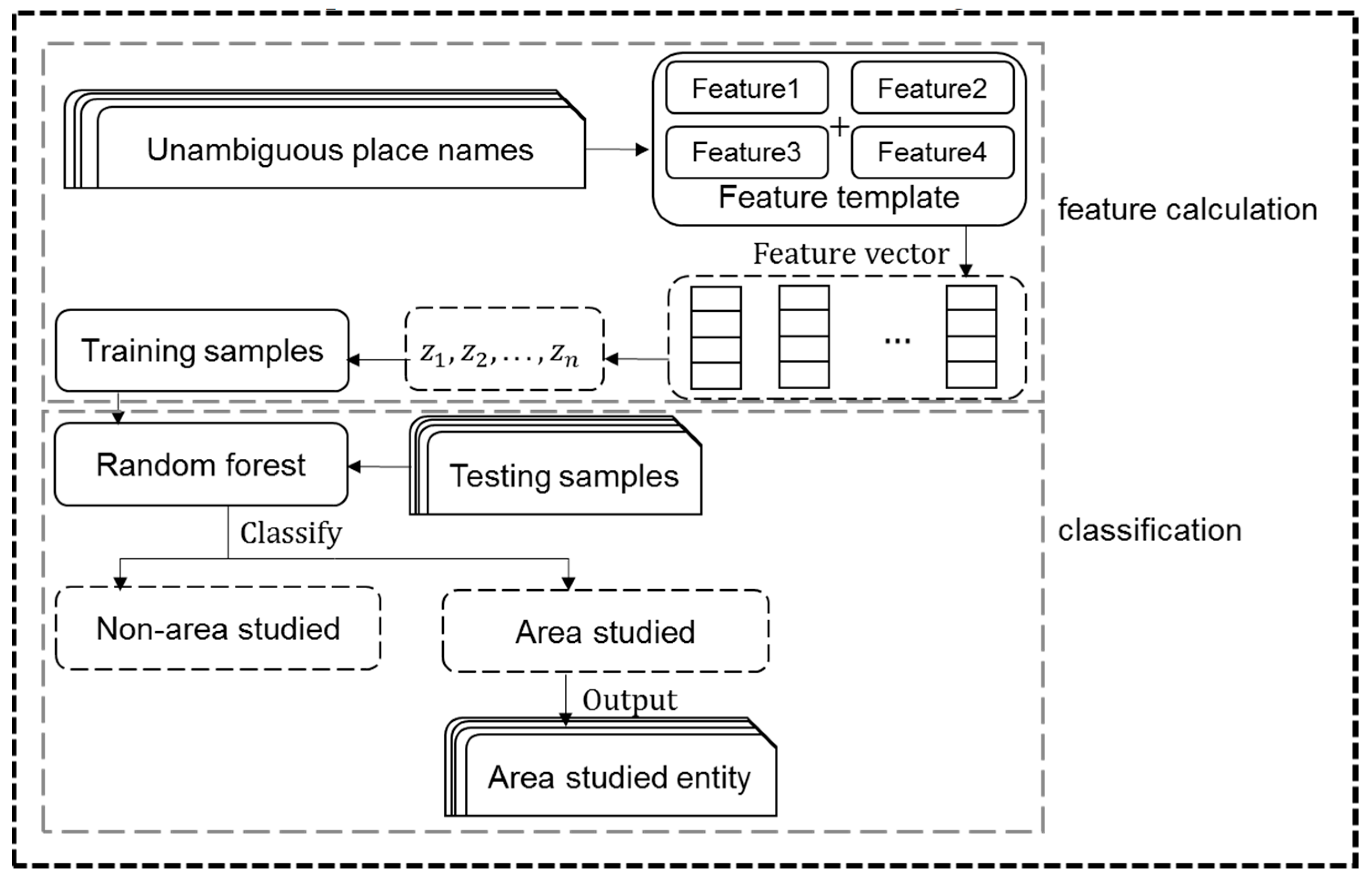
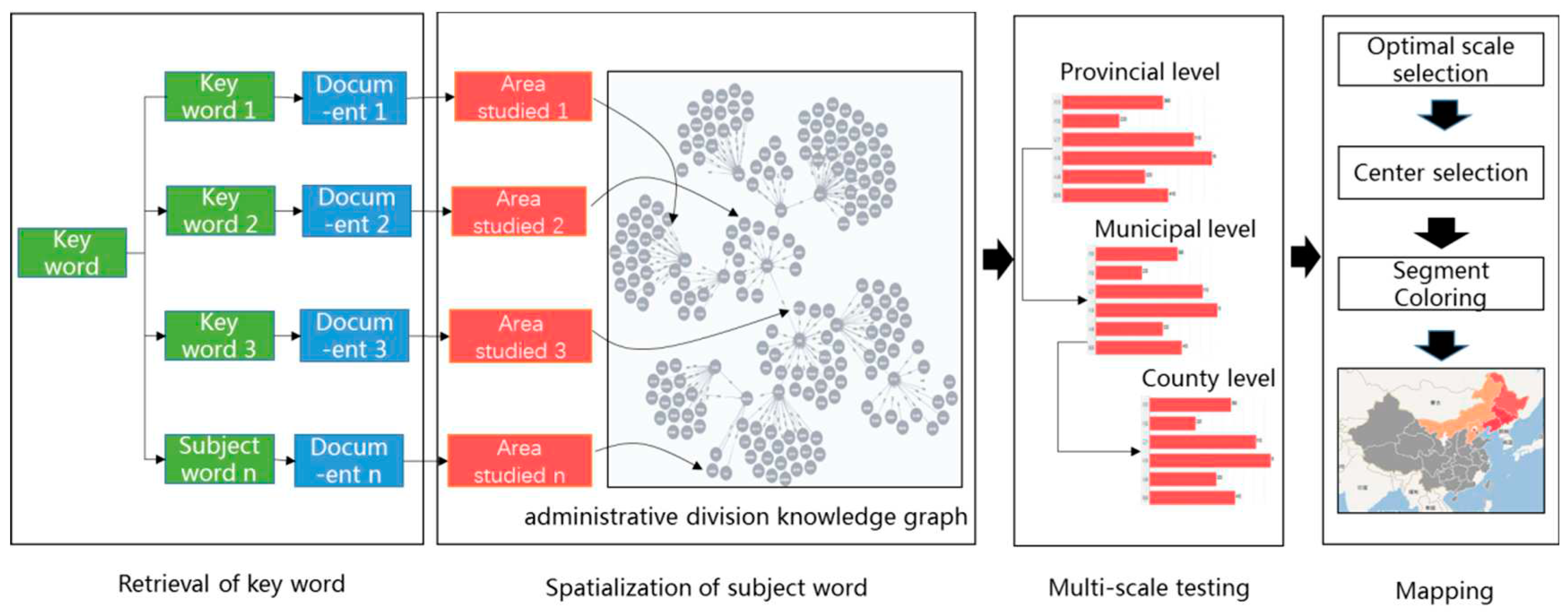
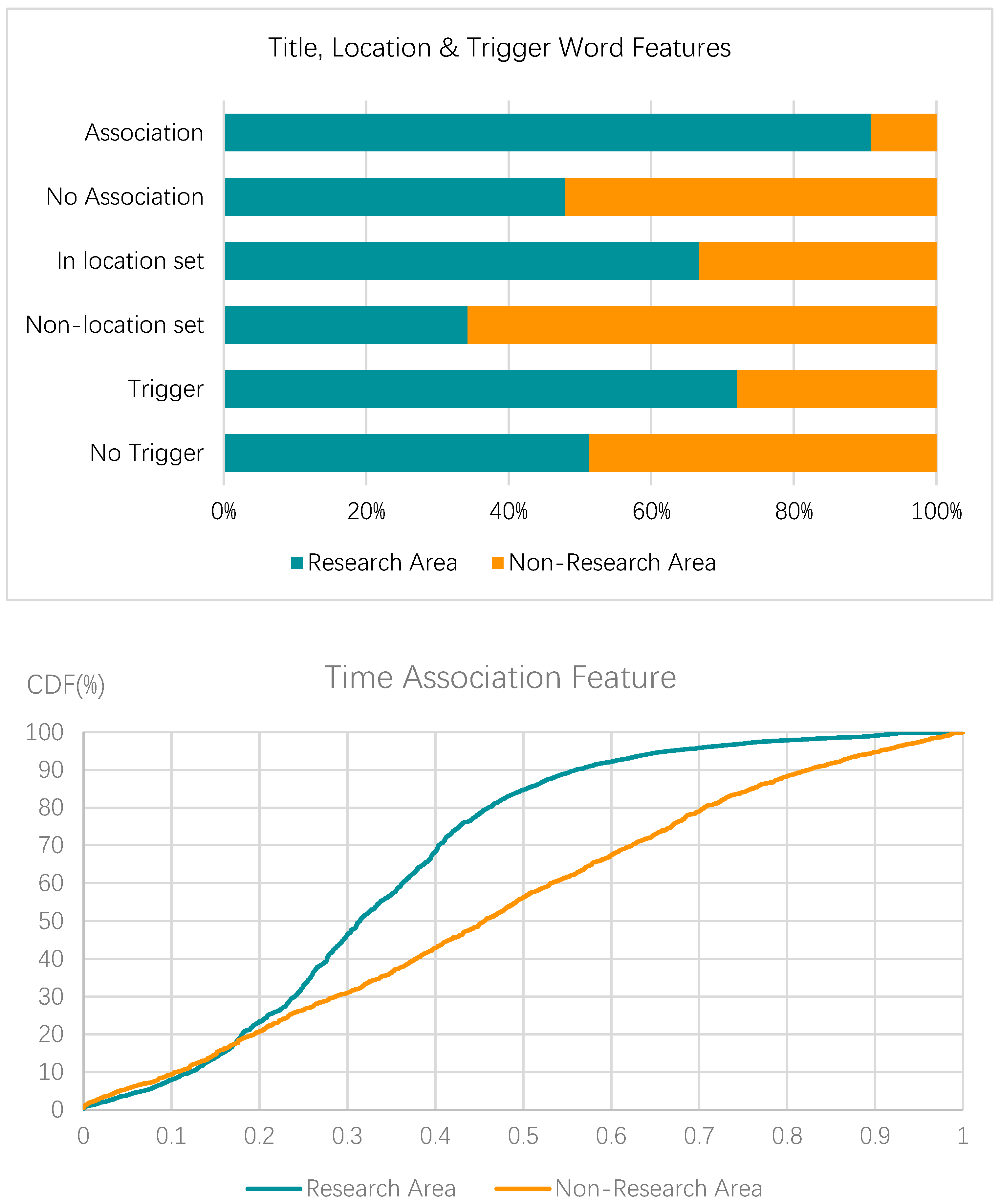
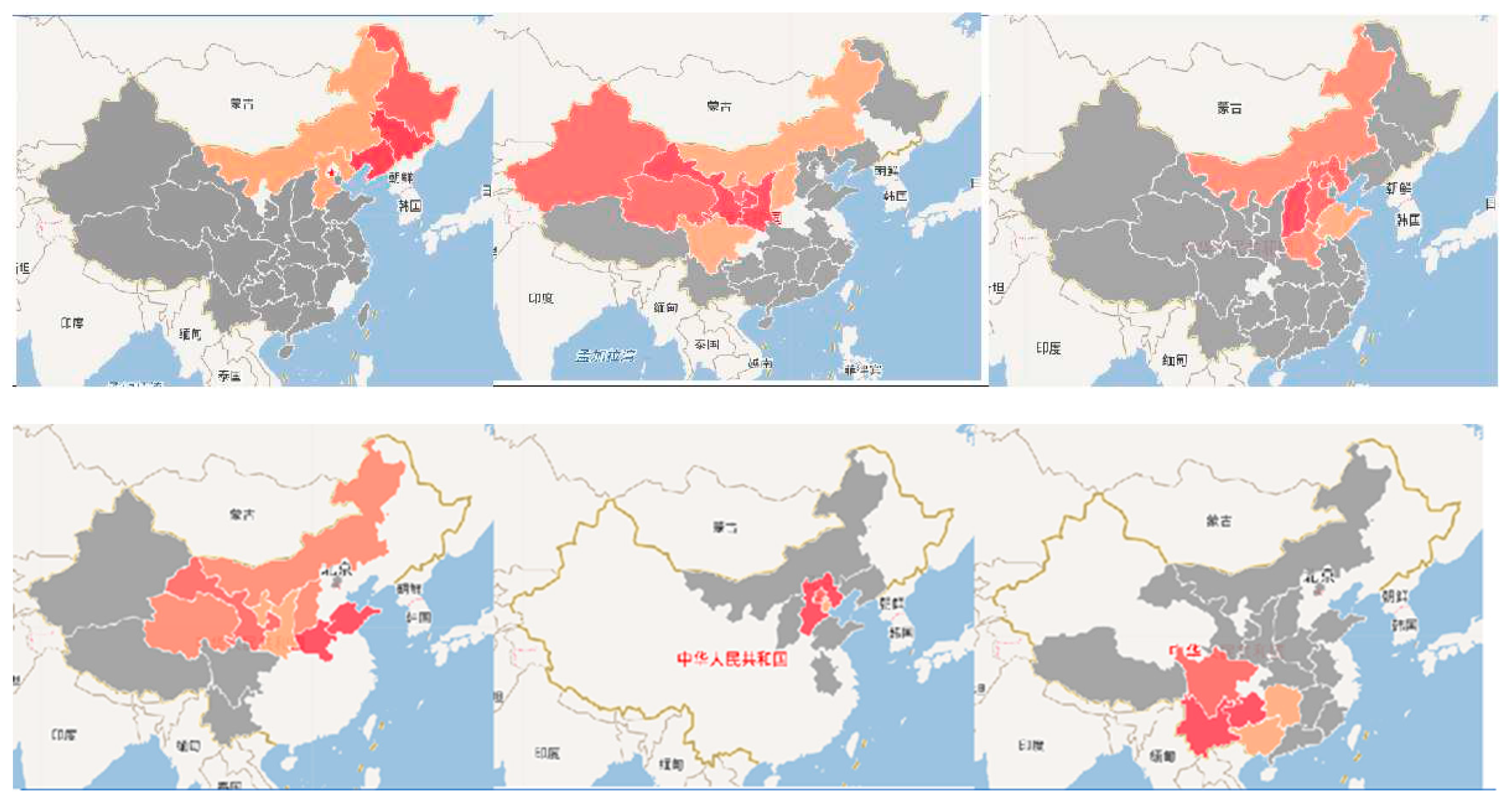
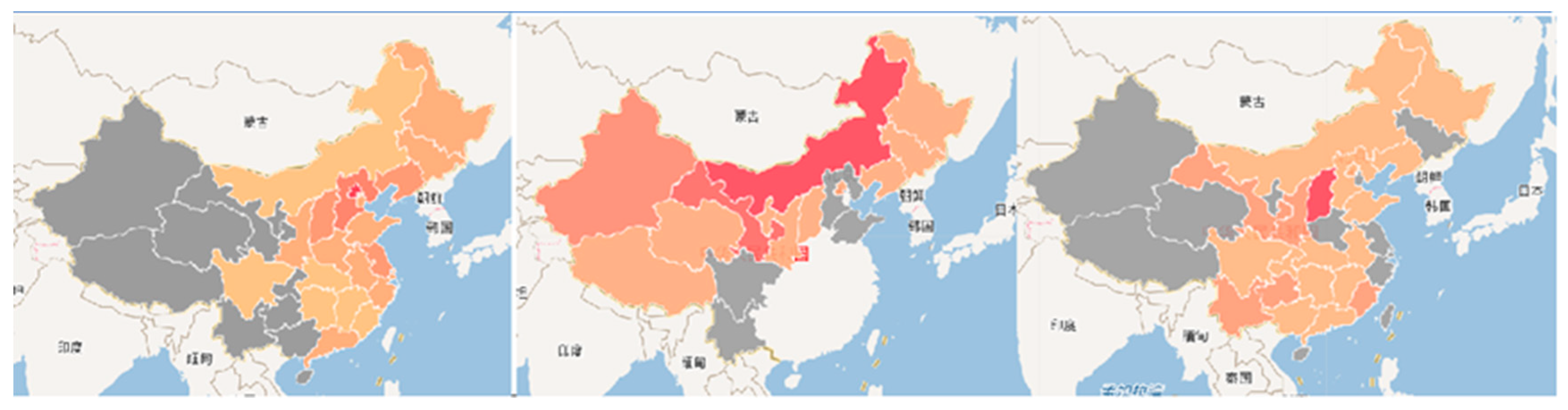
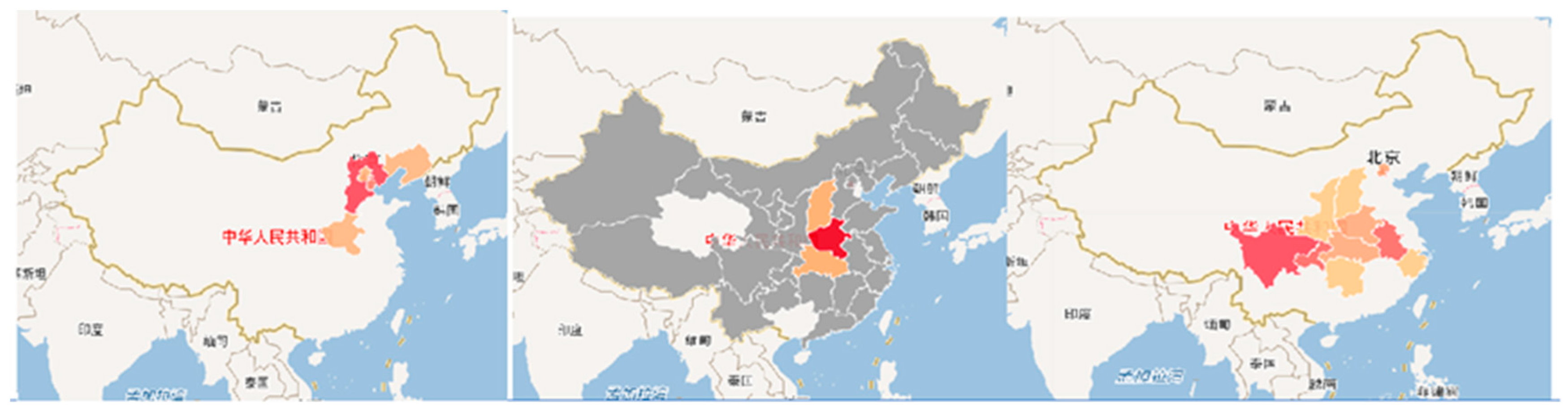
| Function | Algorithm Model |
|---|---|
| Place name recognition | BiLSTM-CRF |
| Place name disambiguation | Improved heuristic disambiguation method |
| area studied classification | Random Forest |
| Entity Number | w | y | Place name entities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [1,1,-0.993684, 0] | 1 | Altai |
| 2 | [0,1 ,-0.762557,1] | 0 | Anhui Province |
| 3 | [1,1, -0.858639,1] | 1 | Beijing |
| Algorithm. | Precision(%) | Recall(%) | F1-score(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GaussianNB(NaiveBayes) | 69 | 68 | 69 |
| BernoulliNB | 76 | 65 | 67 |
| LogisticRegression | 70 | 68 | 69 |
| SVM | 72 | 72 | 72 |
| GradientBoostingClassifier | 77 | 76 | 76 |
| KNeighborsClassifier | 79 | 77 | 78 |
| DecisionTreeClassifier | 93 | 96 | 94 |
| RandomForestClassifier | 97 | 96 | 96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




