Submitted:
19 October 2023
Posted:
20 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
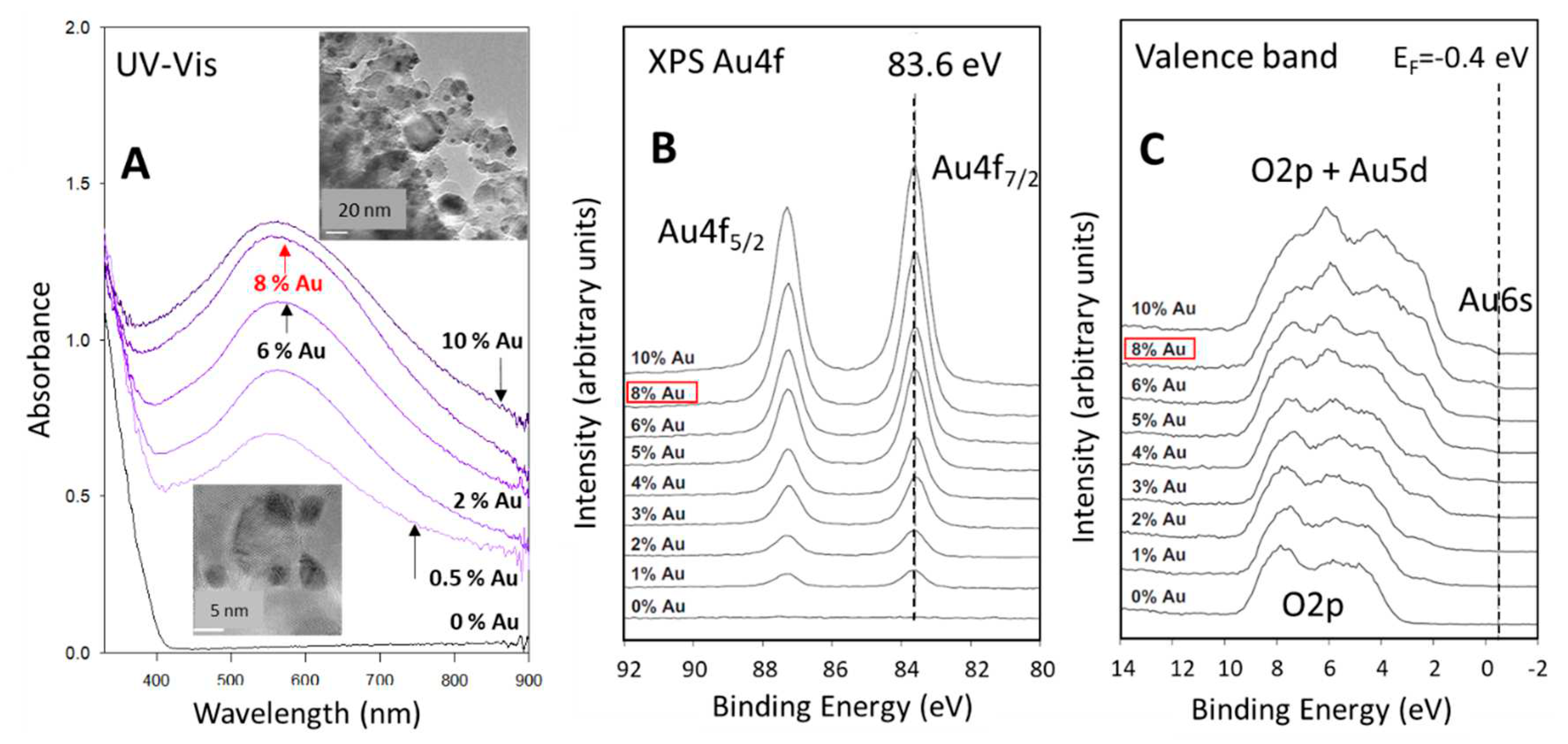
2.1. Preparation and characterization of 8 wt.% Au/ P25 TiO2
2.2. Photoreaction setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Photocatalytic water gas shift reaction at ≈ 25 °C (room temperature)
3.2. Thermal water gas shift reaction
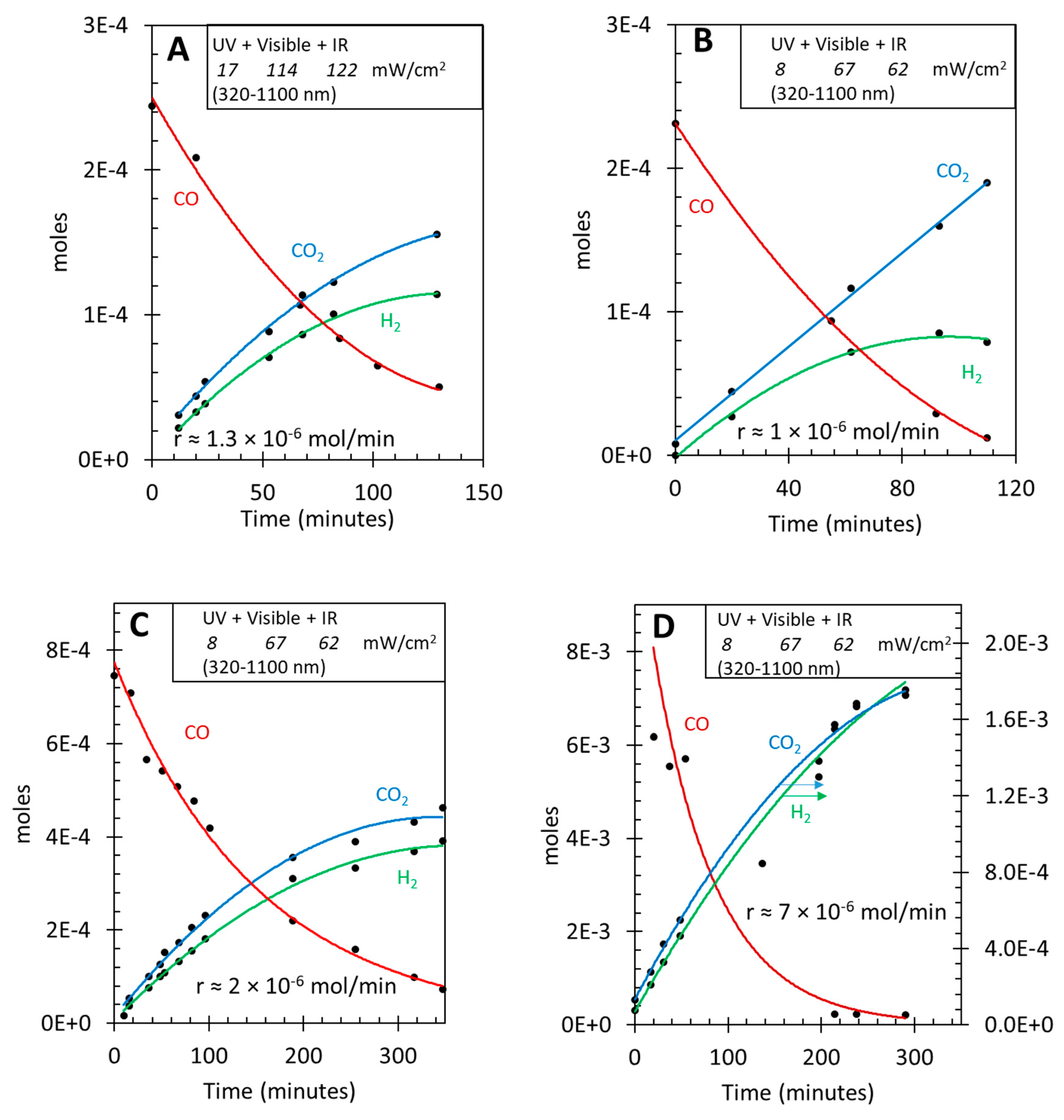
3.3. Photo-assisted water gas shift reaction at 85 oC; effect of CO concentration
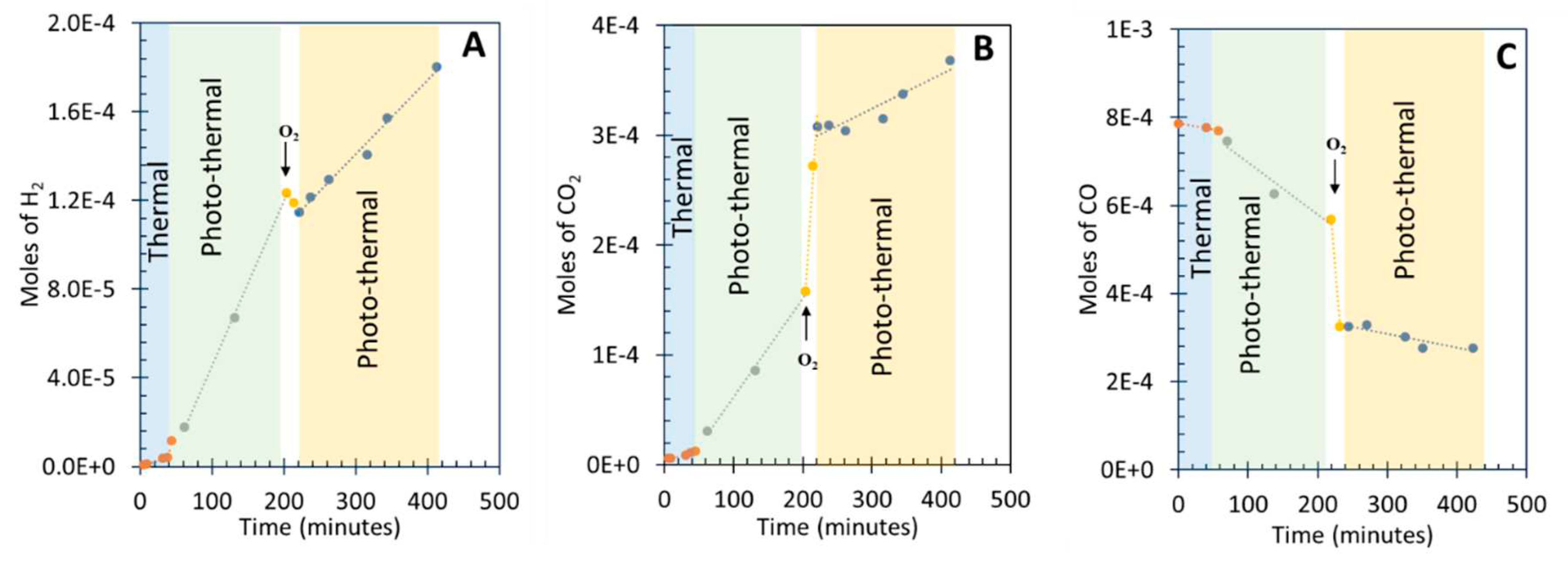
3.4. Photo-assisted water gas shift reaction at 85 oC; effect of O2 concentration
| [CO] | [H2O] | Ratio [H2O]/[CO] | Initial r(H2) mol/min | Initial r(CO2) mol/min | Ratio [H2]/[CO2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00022 | 0.0011 | 5.0 | 1.2 × 10-6 | 1.5 ×10-6 | 0.8 |
| 0.00067 | 0.0011 | 1.6 | 2 × 10-6 | 2.4 × 10-6 | 0.9 |
| 0.0058 | 0.0055 | ≈ 1 | 7 × 10-6 | 6 × 10-6 | 1.1 |
| Before r(H2) mol/min |
Before r(CO2) mol/min |
Before r(CO) mol/min |
During r(H2) mol/min | During r(CO2) mol/min |
During r(CO)mol/min |
After r(H2) mol/min |
After r(CO2) mol/min |
After r(CO)mol/min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.75 × 10-6 | 0.5 × 10-6 | -1.2 × 10-6 | -0.5 × 10-6 | 11 × 10-6 | -19 ×10-6 | 0.35 × 10-6 | 0.35 × 10-6 | -0.35 × 10-6 |
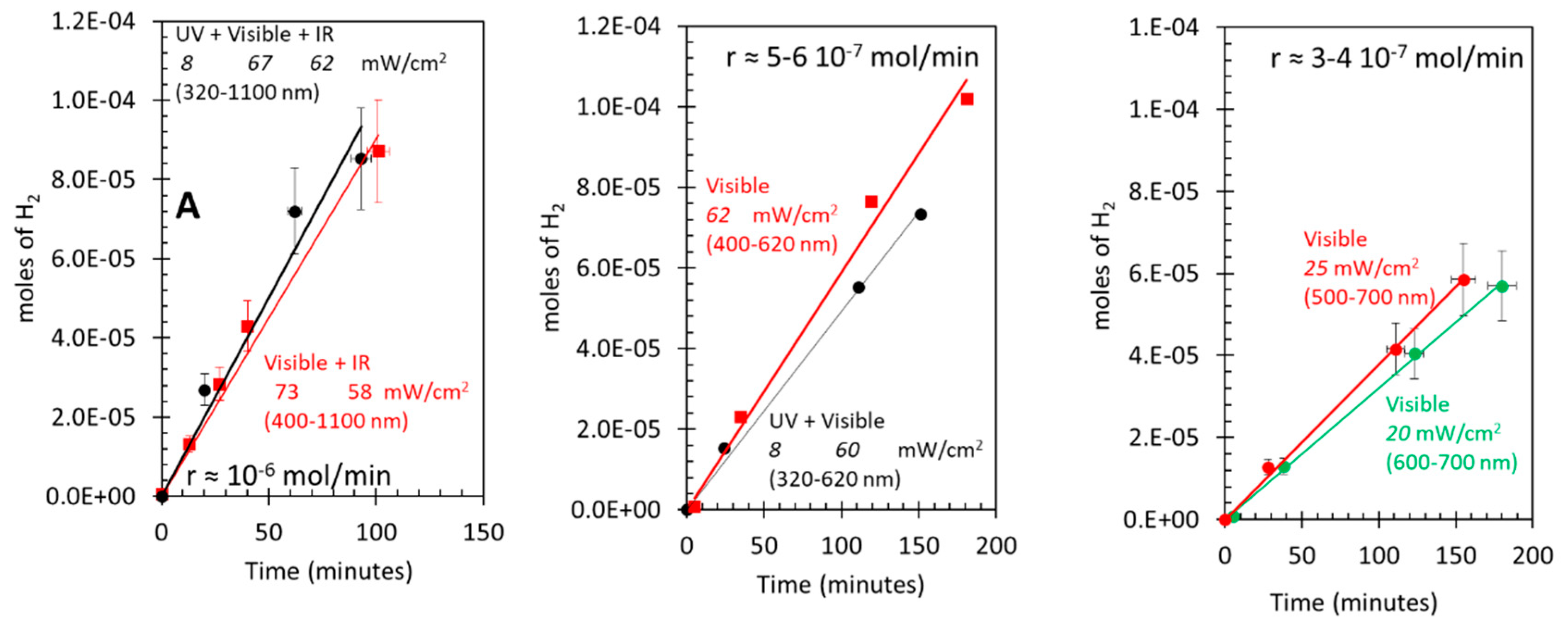
3.5. Photo-assisted water gas shift reaction at 85 oC; effect of light energy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- Ratnasamy, C.; Wagner, J.P. Water Gas Shift Catalysis. Catal. Rev. 2009, 51, 325–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai H, Ueda A, Kobayashi T, Haruta M. Low-temperature water–gas shift reaction over gold depositedon TiO2. Chemical Communications 1997, 271–2.
- Sandoval, A.; Gómez-Cortés, A.; Zanella, R.; Díaz, G.; Saniger, J.M. Gold nanoparticles: Support effects for the WGS reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2007, 278, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yixuan C, Zhaobin W, Yanxin C, Huaxin L, Zupei H, Huiqing L, et al. Metal-semiconductor catalyst: photocatalytic and electrochemical behavior of Pt-TiO2 for the water-gas shift reaction. Journal of Molecular Catalysis 1983, 21, 275–89.
- Tabakova, T. Recent Advances in Design of Gold-Based Catalysts for H2 Clean-Up Reactions. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-P.; Guo, L.-W.; Wang, W.-W.; Ma, C.; Jia, C.-J.; Wu, K.; Si, R.; Sun, L.-D.; Yan, C.-H. Direct Identification of Active Surface Species for the Water–Gas Shift Reaction on a Gold–Ceria Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shido, T.; Iwasawa, Y. Regulation of reaction intermediate by reactant in the water-gas shift reaction on CeO2, in relation to reactant-promoted mechanism. J. Catal. 1992, 136, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakova, T.; Boccuzzi, F.; Manzoli, M.; Sobczak, J.; Idakiev, V.; Andreeva, D. A comparative study of nanosized IB/ceria catalysts for low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2006, 298, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata JJ, Romero-Sarria F, Suárez JA, Márquez AM, Laguna ÓH, Odriozola JA, et al. Improving the activity of gold nanoparticles for the water-gas shift reaction using TiO 2–Y 2 O 3: an example of catalyst design. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2018, 20, 22076–83.
- Wang, J.; Kispersky, V.F.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H. Determination of the Au active site and surface active species via operando transmission FTIR and isotopic transient experiments on 2.3wt.% Au/TiO2 for the WGS reaction. J. Catal. 2012, 289, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.; Goguet, A.; Meunier, F.C. A critical analysis of the experimental evidence for and against a formate mechanism for high activity water-gas shift catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2011, 409-410, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun K, Kohyama M, Tanaka S, Takeda S. Reaction mechanism of the low-temperature water–gas shift reaction on Au/TiO2 catalysts. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2017, 121, 12178–87.
- ZHANG X, XUE J, Yue M, QIAN M, XIA S, NI Z. Reaction mechanism of water gas shift over Aun clusters: a density functional theory study. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology 2017, 45, 1473–80.
- Sastre, F.; Oteri, M.; Corma, A.; García, H. Photocatalytic water gas shift using visible or simulated solar light for the efficient, room-temperature hydrogen generation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2211–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; White, J.M. Photoassisted water-gas shift reaction over platinized titanium dioxide catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 7206–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, L.; Bowker, M. Photocatalytic water-gas shift reaction at ambient temperature. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2002, 148, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruta, M.; Tsubota, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kageyama, H.; Genet, M.J.; Delmon, B. Low-Temperature Oxidation of CO over Gold Supported on TiO2, α-Fe2O3, and Co3O4. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlexer P, Widmann D, Behm RJ, Pacchioni G. CO oxidation on a Au/TiO2 nanoparticle catalyst via the Au-assisted Mars–van Krevelen mechanism. Acs Catalysis 2018, 8, 6513–25.
- Green IX, Tang W, Neurock M, Yates Jr JT. Spectroscopic observation of dual catalytic sites during oxidation of CO on a Au/TiO2 catalyst. Science 2011, 333, 736–9.
- Saavedra, J.; Whittaker, T.; Chen, Z.; Pursell, C.J.; Rioux, R.M.; Chandler, B.D. Controlling activity and selectivity using water in the Au-catalysed preferential oxidation of CO in H2. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, J.; Doan, H.A.; Pursell, C.J.; Grabow, L.C.; Chandler, B.D. The critical role of water at the gold-titania interface in catalytic CO oxidation. Science 2014, 345, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha P, Chang L-H, Chen Y-W. Preferential oxidation of CO in H2 stream on Au/TiO2 catalysts: effect of preparation method. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2009, 48, 5666–70.
- Leal, G.B.; Ciotti, L.; Watacabe, B.N.; da Silva, D.C.L.; Antoniassi, R.M.; Silva, J.C.M.; Linardi, M.; Giudici, R.; Vaz, J.M.; Spinacé, E.V. Preparation of Au/TiO2 by a facile method at room temperature for the CO preferential oxidation reaction. Catal. Commun. 2018, 116, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartadi, Y.; Behm, R.J.; Widmann, D. Competition of CO and H2 for Active Oxygen Species during the Preferential CO Oxidation (PROX) on Au/TiO2 Catalysts. Catalysts 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bion, N.; Epron, F.; Moreno, M.; Mariño, F.; Duprez, D. Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide in the Presence of Hydrogen (PROX) over Noble Metals and Transition Metal Oxides: Advantages and Drawbacks. Top. Catal. 2008, 51, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida Y, Izumi Y. Recent advances in the preferential thermal-/photo-oxidation of carbon monoxide: Noble versus inexpensive metals and their reaction mechanisms. Catalysis Surveys from Asia 2016, 20, 141–66.
- Dai, W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Fu, X. The promoted effect of UV irradiation on preferential oxidation of CO in an H2-rich stream over Au/TiO2. J. Power Sources 2009, 188, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Aguado, E.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Talon, A.; Storaro, L.; León-Reina, L.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Moretti, E. Au nanoparticles supported on nanorod-like TiO2 as catalysts in the CO-PROX reaction under dark and light irradiation: Effect of acidic and alkaline synthesis conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 44, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar M, Wang J, Lee W-S, Williams WD, Kim SM, Stach EA, et al. Size and support effects for the water–gas shift catalysis over gold nanoparticles supported on model Al2O3 and TiO2. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2012, 134, 4700–8.
- Williams, W.D.; Shekhar, M.; Lee, W.-S.; Kispersky, V.; Delgass, W.N.; Ribeiro, F.H.; Kim, S.M.; Stach, E.A.; Miller, J.T.; Allard, L.F. Metallic Corner Atoms in Gold Clusters Supported on Rutile Are the Dominant Active Site during Water−Gas Shift Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14018–14020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Gold Atoms Stabilized on Various Supports Catalyze the Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Accounts Chem. Res. 2013, 47, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Flytzani-Stephanopoulos, M. Design of single-atom metal catalysts on various supports for the low-temperature water-gas shift reaction. Catal. Today 2017, 298, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Horváth, A.; Stefler, G.; Scurrell, M.S.; Guczi, L. Role of Preparation Techniques in the Activity of Au/TiO2 Nanostructures Stabilised on SiO2: CO and Preferential CO Oxidation. Top. Catal. 2009, 52, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma Z, Tao F, Gu X. Development of new gold catalysts for removing CO from H2. Heterogeneous Catalysis at Nanoscale for Energy Applications 2014, 217–38.
- Jovic, V.; Chen, W.-T.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Blackford, M.G.; Idriss, H.; Waterhouse, G.I. Effect of gold loading and TiO2 support composition on the activity of Au/TiO2 photocatalysts for H2 production from ethanol–water mixtures. J. Catal. 2013, 305, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, R.; Giorgio, S.; Shin, C.-H.; Henry, C.R.; Louis, C. Characterization and reactivity in CO oxidation of gold nanoparticles supported on TiO2 prepared by deposition-precipitation with NaOH and urea. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azri ZH, Chen W-T, Chan A, Jovic V, Ina T, Idriss H, et al. The roles of metal co-catalysts and reaction media in photocatalytic hydrogen production: Performance evaluation of M/TiO2 photocatalysts (M= Pd, Pt, Au) in different alcohol–water mixtures. Journal of Catalysis 2015, 329, 355–67.
- Jovic, V.; Smith, K.E.; Idriss, H.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Heterojunction Synergies in Titania-Supported Gold Photocatalysts: Implications for Solar Hydrogen Production. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiski, R.; Desponds, O.; Chang, Y.-F.; Somorjai, G. Kinetics of the water-gas shift reaction over several alkane activation and water-gas shift catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 1993, 101, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, O.B.J.; Katsiev, K.; Baek, B.; Harrison, G.; Thornton, G.; Idriss, H. Direct Visualization of a Gold Nanoparticle Electron Trapping Effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, C.-M.; Lamoureux, P.S.; Mellor, A.; Pang, C.L.; Idriss, H.; Pacchioni, G.; Thornton, G. Size and Shape Dependence of the Electronic Structure of Gold Nanoclusters on TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 8363–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiev K, Harrison G, Al-Salik Y, Thornton G, Idriss H. Gold cluster coverage effect on H2 production over rutile TiO2 (110). ACS Catalysis 2019, 9, 8294–305.
- Alsalik, Y.M.; Katsiev, K.; Idriss, H. Electron Transfer From a Semiconductor to a Metal and Its Implication on Photocatalysis for Hydrogen Production. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 15184–15190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziani, A.; Al-Taweel, S.; Nadeem, M.A.; Idriss, H. Effect of Gold Loading on Time-Resolved ps Photoluminescence of ZnO. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 16148–16157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, C.J.; Montemore, M.M. Mechanistic Insights into Plasmonic Catalysis by Dynamic Calculations: O2 and N2 on Au and Ag Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, A.; Ricart, J.M.; Illas, F. Origin of the size dependence of Au nanoparticles toward molecular oxygen dissociation. Theor. Chem. Accounts 2010, 128, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, A.; González, S.; Ricart, J.M.; Illas, F. Critical Size for O2 Dissociation by Au Nanoparticles. Chemphyschem 2009, 10, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.P.P.; Illas, F.; Gomes, J.R.B. Adsorption of CO on the rutile TiO2(110) surface: a dispersion-corrected density functional theory study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 19, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pursell, C.J.; Chandler, B.D.; Manzoli, M.; Boccuzzi, F. CO Adsorption on Supported Gold Nanoparticle Catalysts: Application of the Temkin Model. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11117–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phala, N.S.; Klatt, G.; van Steen, E. A DFT study of hydrogen and carbon monoxide chemisorption onto small gold clusters. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 395, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H. Oxygen vacancies role in thermally driven and photon driven catalytic reactions. Chem Catal. 2022, 2, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 |
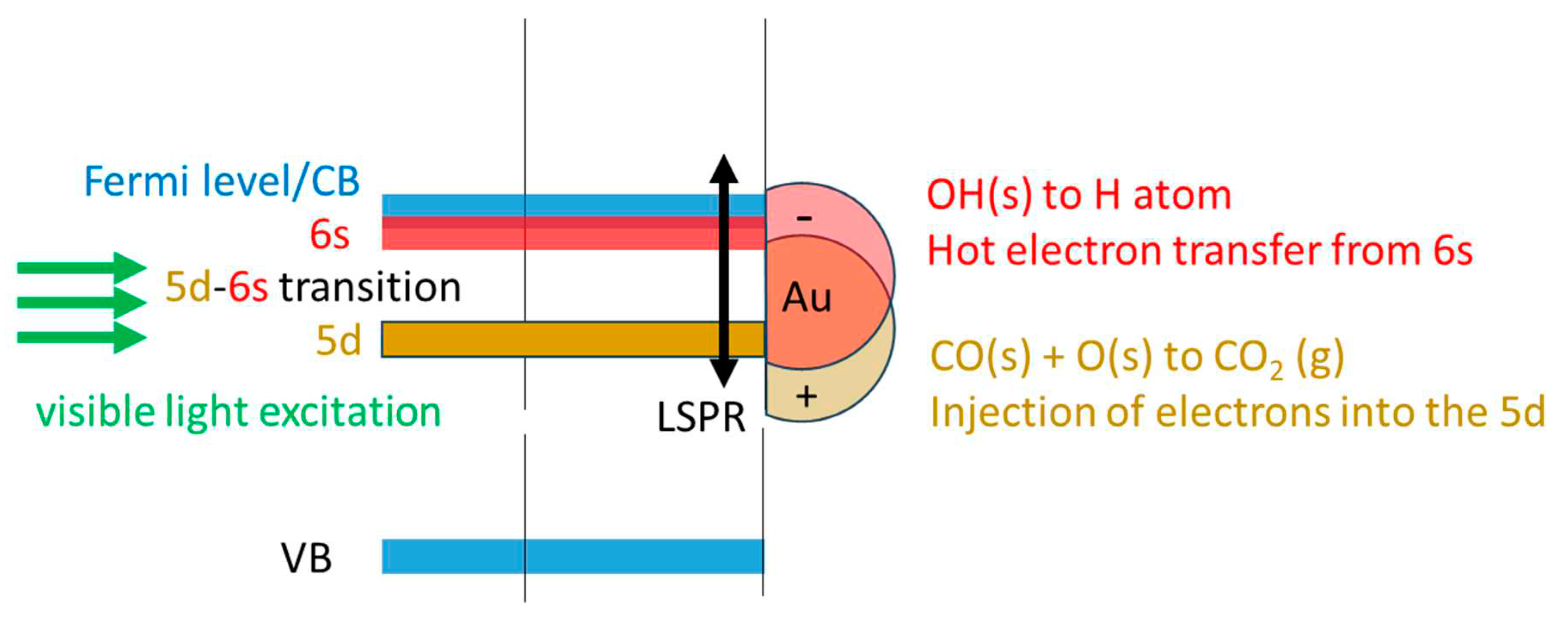
O2(g) + e(CB) → O2-. → O atom + O-.
(6)
The oxygen atom reacts with CO to give CO2, while the O-. may react with a proton of a surface OH group to give an OH radical. OH radicals are powerful oxidants. They then react with CO to give formates and inject an electron into the VB.
CO + O atom → CO2(g)
O-. + OH(s) → OH radical + O(s)
OH radical + CO(g) + h(VB) → HOCO(a)
The sum of the above equations is equation 10
2CO(g) + O2(g) + hν + OH(s) → CO2(g) + HOCO(a) + O(s)
Equations 7 and 9 may explain why the rate of disappearance of CO is twice that of the appearance of CO2, since largely only one oxygen atom of molecular oxygen has reacted to give the CO2 while the other gave a formate species (if the latter do not have a major role in the reaction at this temperature and light flux).
The other route is that related to Au particles and their plasmonic effect (LSP). O2 can dissociate on Au particles, yet this occurs on those with sizes below 2 nm or so [45,46,47].. Au particles of the catalyst used here are of mean particle size of 5 nm (about 3000 atoms), while defects on these and the possible presence of some much smaller particles (not identified by TEM) may still have activity for the dissociative adsorption of O2, their effect is neglected here. In particular, a recent time dependent DFT computational study of Au particles with different sizes has pointed out to two important observation that might be relevant to this work [45]. First, it seems that under light excitation particle size is not determinant and second, O2 dissociates largely because of the electric field effect and not by charge transfer. Based on these results, there are two distinct ways for O2 dissociation on Au/TiO2 either in the dark or under light excitation. 1. Dark dissociation seems to be on small Au particles (< 2nm or so). 2. Light induced dissociation can occur upon TiO2 excitation (UV) followed by charge transfer to Au particles and/or upon LSPR that directly excite Au particles (largely by electric field effect).
|
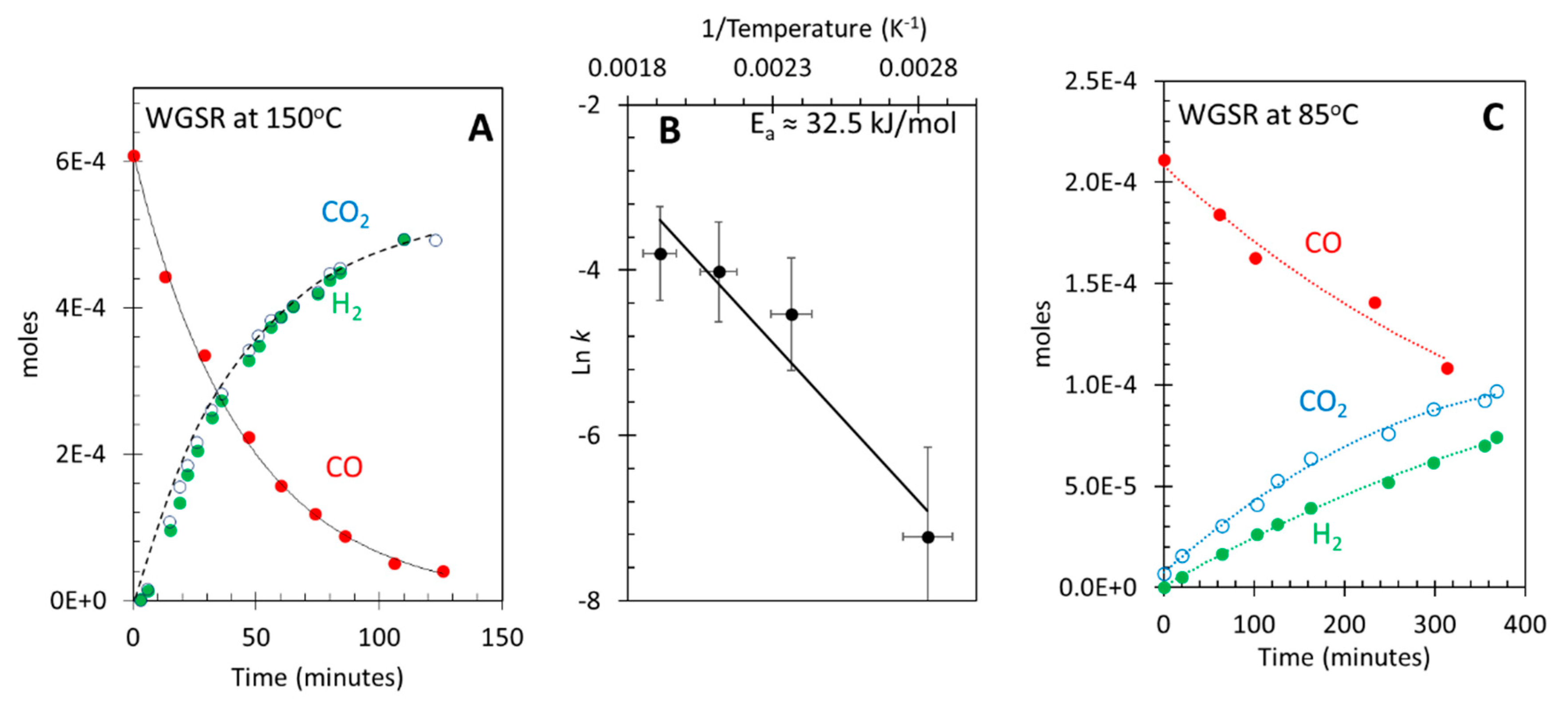
| T (oC) | T (K) | 1/T(K) | Rate (H2 moles/min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | 353 | 0.002832 | 4.87 × 10-7 |
| 150 | 423 | 0.002363 | 8.69 × 10-6 |
| 200 | 473 | 0.002113 | 9.00 × 10-6 |
| 250 | 523 | 0.001911 | 1.97 × 10-5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





