Submitted:
19 October 2023
Posted:
20 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Advanced Melanoma Treatments
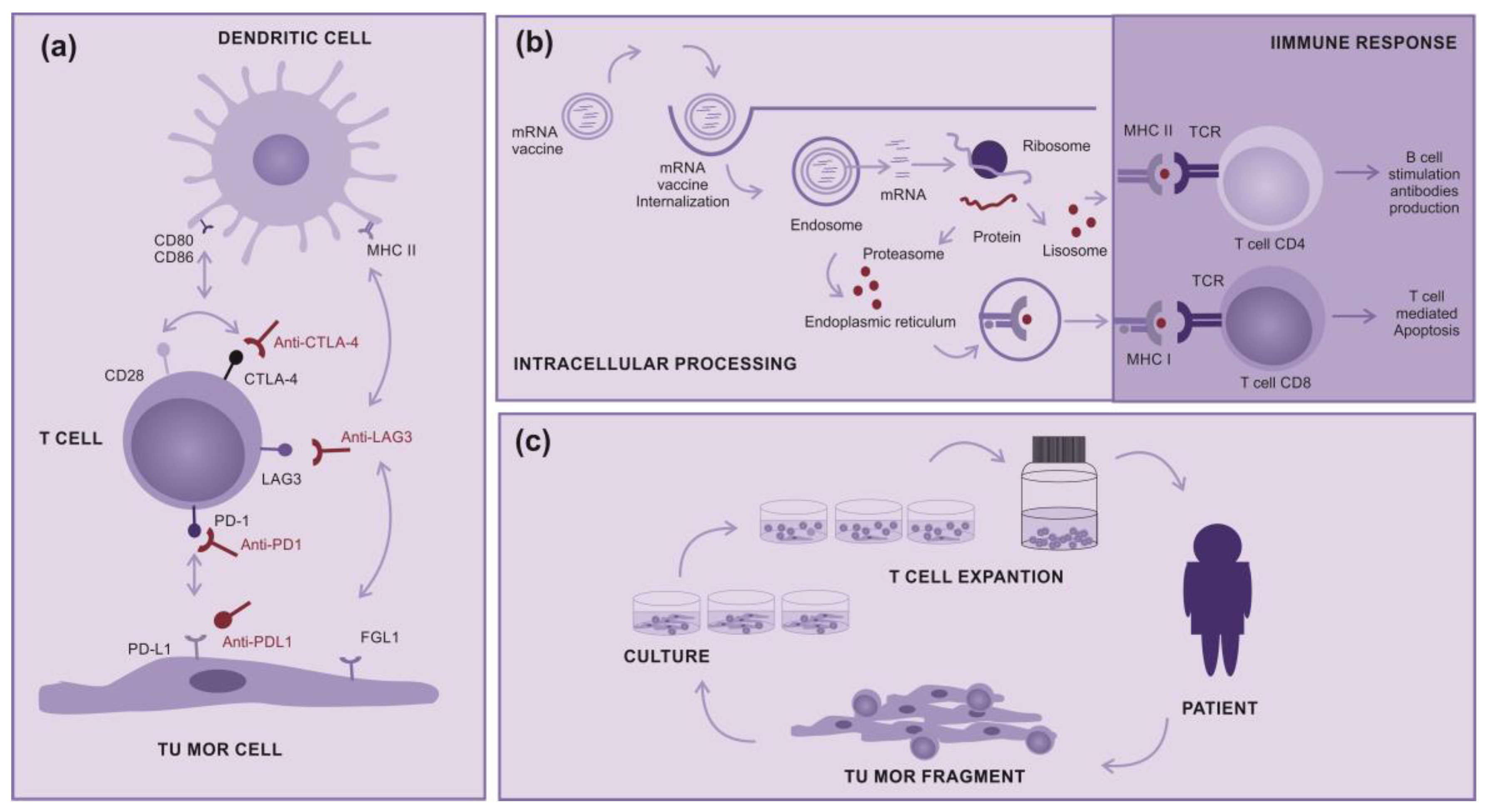
2.1. Immunotherapy
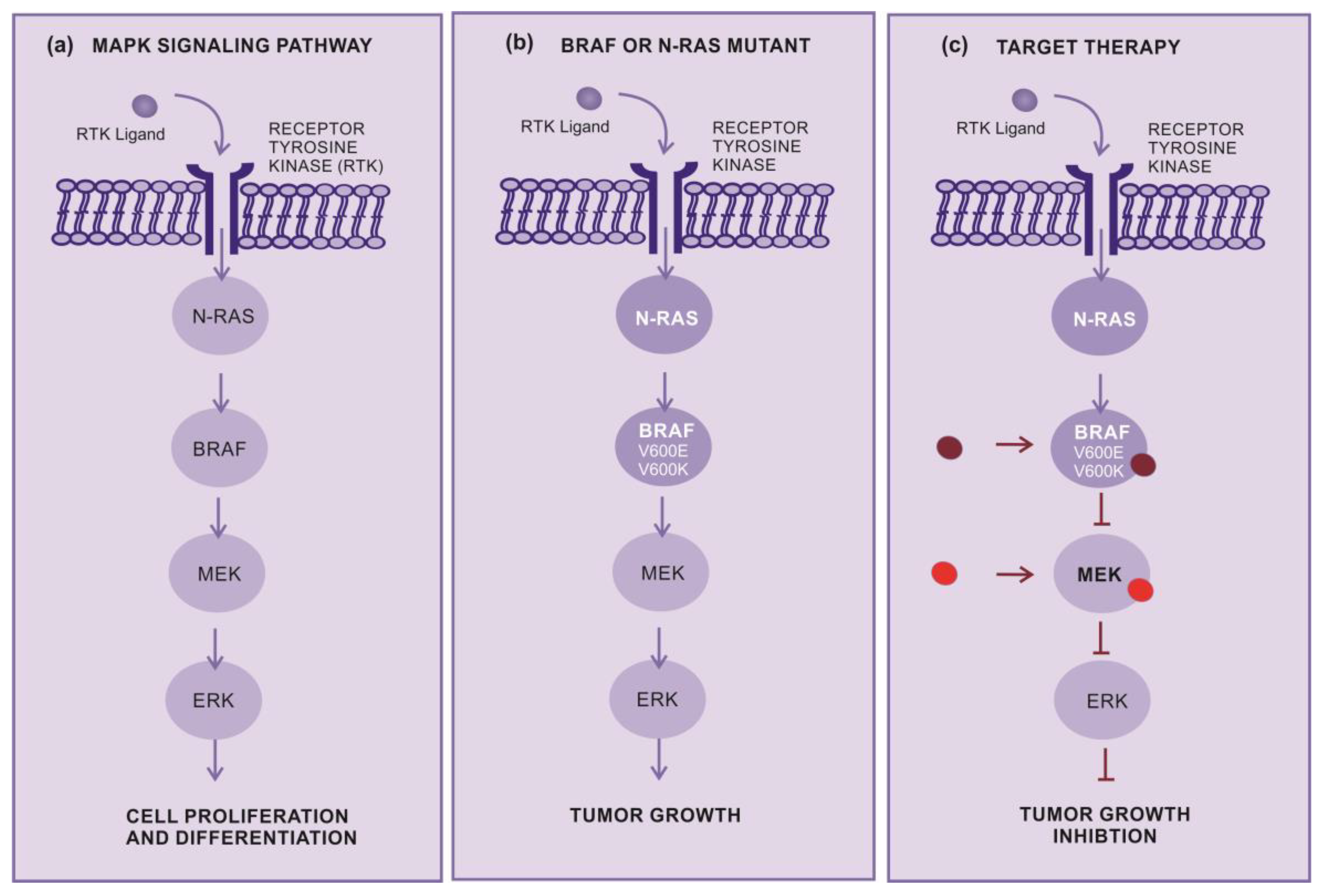
2.2. Target therapy
2.3. Lysine histone methyl transferase inhibitors
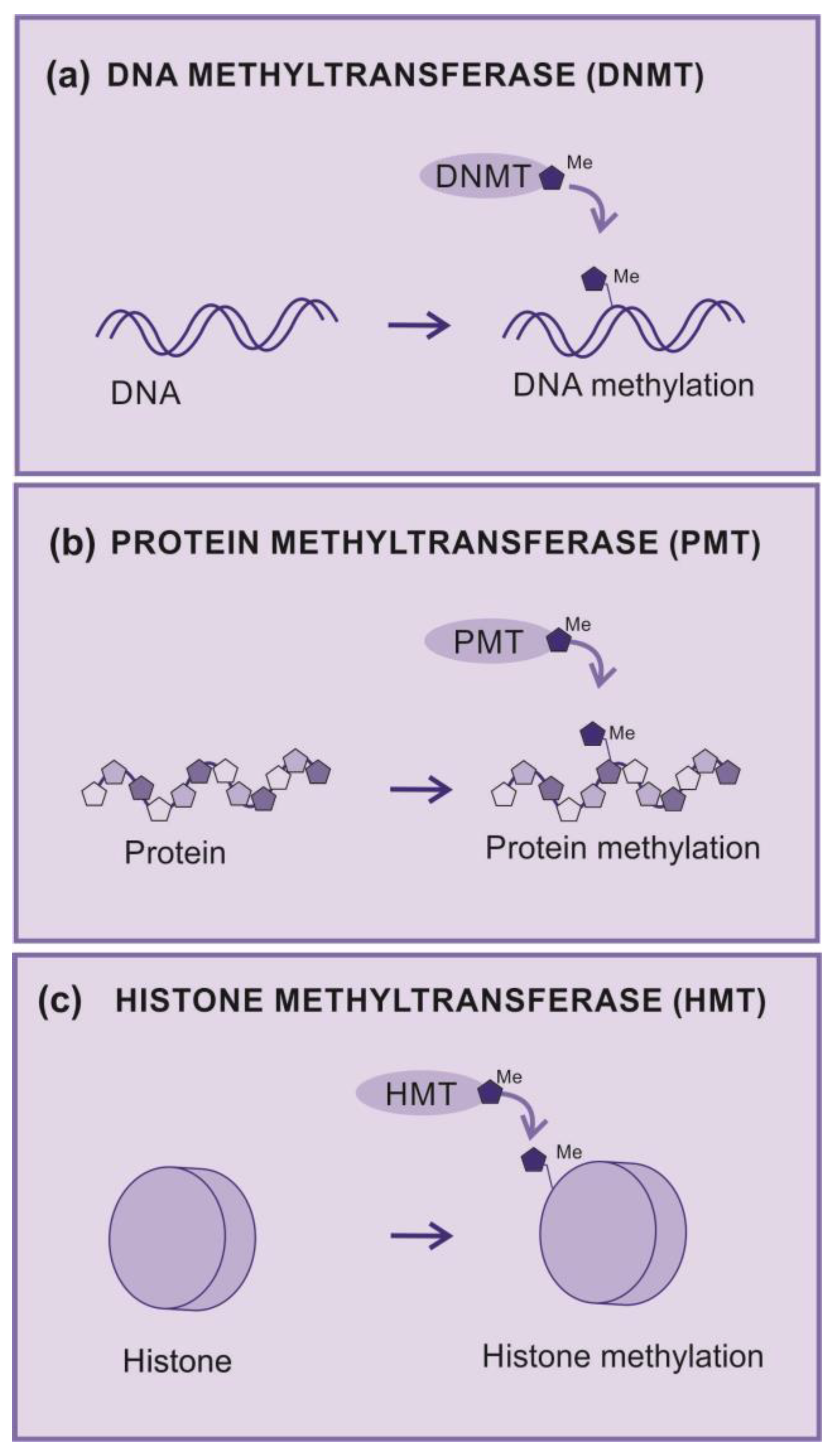
2.3.1. Methyltransferases
2.3.2. DNA methyltransferases
2.3.3. Protein methyltransferases
2.3.4. Histones and Histone methylation
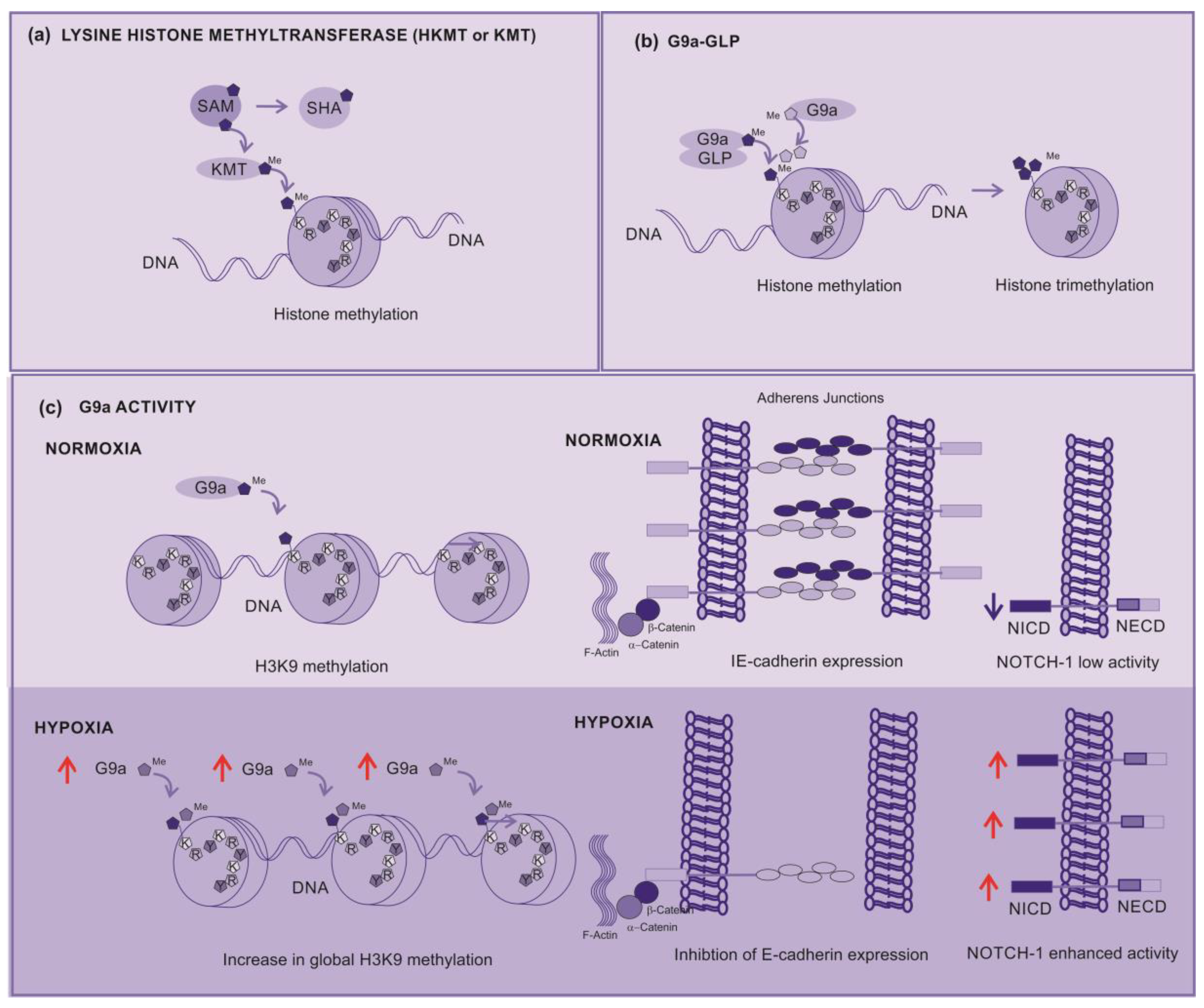
2.3.5. Histone Methyltransferases (HMT)
2.3.6. Lysine Histone Methyltransferases (KMT)
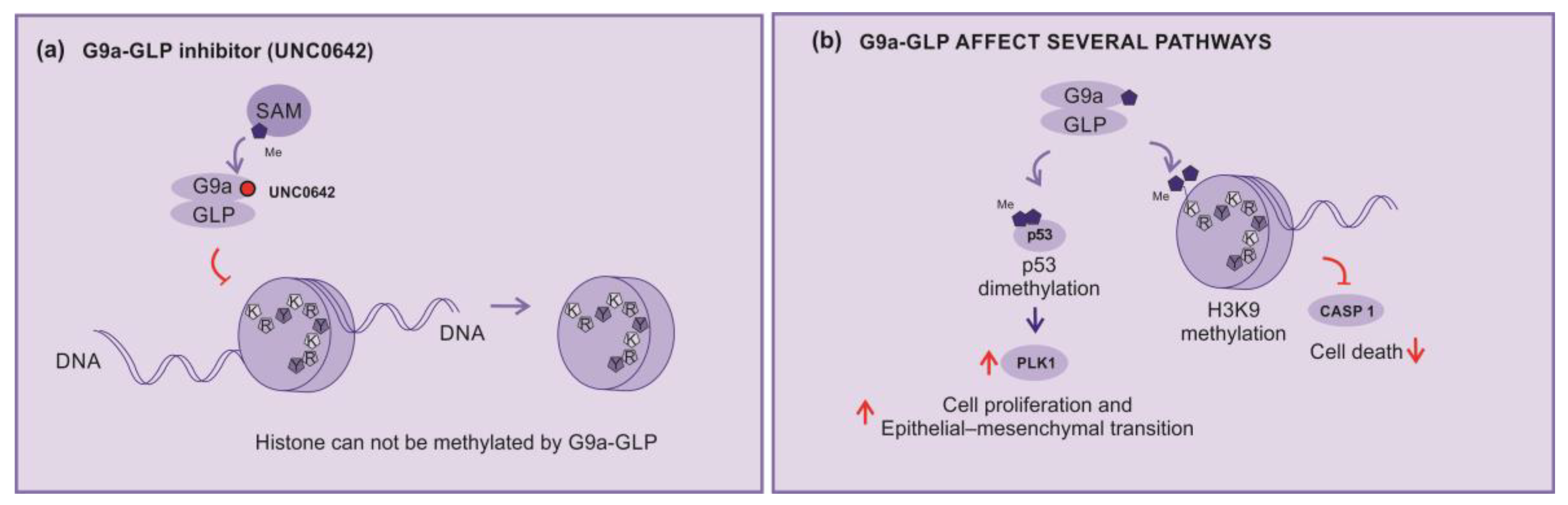
2.3.7. KMT inhibitors
2.3.8. Broad-spectrum inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shain AH, Bastian BC. From melanocytes to melanomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016; 16(6):345-58. [CrossRef]
- Potrony M, Badenas C, Aguilera P, Puig-Butille JA, Carrera C, Malvehy J, Puig S. Update in genetic susceptibility in melanoma. Ann Transl Med. 2015; 3(15):210. [CrossRef]
- Qin Z, Zheng M. Advances in targeted therapy and immunotherapy for melanoma (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2023; 13;26(3):416. [CrossRef]
- Hodi FS, O’Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW, Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel JC, Akerley W, van den Eertwegh AJ, Lutzky J, Lorigan P, Vaubel JM, Linette GP, Hogg D, Ottensmeier CH, Lebbé C, Peschel C, Quirt I, Clark JI, Wolchok JD, Weber JS, Tian J, Yellin MJ, Nichol GM, Hoos A, Urba WJ. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363(8):711-23. [CrossRef]
- Eggermont AM, Chiarion-Sileni V, Grob JJ, Dummer R, Wolchok JD, Schmidt H, Hamid O, Robert C, Ascierto PA, Richards JM, Lebbé C, Ferraresi V, Smylie M, Weber JS, Maio M, Bastholt L, Mortier L, Thomas L, Tahir S, Hauschild A, Hassel JC, Hodi FS, Taitt C, de Pril V, de Schaetzen G, Suciu S, Testori A. Prolonged Survival in Stage III Melanoma with Ipilimumab Adjuvant Therapy. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1845-1855. [CrossRef]
- Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, Gogas HJ, Arance AM, Cowey CL, Dalle S, Schenker M, Chiarion-Sileni V, Marquez-Rodas I, Grob JJ, Butler MO, Middleton MR, Maio M, Atkinson V, Queirolo P, Gonzalez R, Kudchadkar RR, Smylie M, Meyer N, Mortier L, Atkins MB, Long GV, Bhatia S, Lebbé C, Rutkowski P, Yokota K, Yamazaki N, Kim TM, de Pril V, Sabater J, Qureshi A, Larkin J, Ascierto PA; CheckMate 238 Collaborators. Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in Resected Stage III or IV Melanoma. [CrossRef]
- Tawbi HA, Schadendorf D, Lipson EJ, Ascierto PA, Matamala L, Castillo Gutiérrez E, Rutkowski P, Gogas HJ, Lao CD, De Menezes JJ, Dalle S, Arance A, Grob JJ, Srivastava S, Abaskharoun M, Hamilton M, Keidel S, Simonsen KL, Sobiesk AM, Li B, Hodi FS, Long GV; RELATIVITY-047 Investigators. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(1):24-34. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Kammula US, Hughes MS, Phan GQ, Citrin DE, Restifo NP, Robbins PF, Wunderlich JR, Morton KE, Laurencot CM, Steinberg SM, White DE, Dudley ME. Durable complete responses in heavily pretreated patients with metastatic melanoma using T-cell transfer immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(13):4550-7. [CrossRef]
- Sarnaik AA, Hamid O, Khushalani NI, Lewis KD, Medina T, Kluger HM, Thomas SS, Domingo-Musibay E, Pavlick AC, Whitman ED, Martin-Algarra S, Corrie P, Curti BD, Oláh J, Lutzky J, Weber JS, Larkin JMG, Shi W, Takamura T, Jagasia M, Qin H, Wu X, Chartier C, Graf Finckenstein F, Fardis M, Kirkwood JM, Chesney JA. Lifileucel, a Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Therapy, in Metastatic Melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021;39(24):2656-2666. [CrossRef]
- Seitter SJ, Sherry RM, Yang JC, Robbins PF, Shindorf ML, Copeland AR, McGowan CT, Epstein M, Shelton TE, Langhan MM, Franco Z, Danforth DN, White DE, Rosenberg SA, Goff SL. Impact of Prior Treatment on the Efficacy of Adoptive Transfer of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(19):5289-5298. [CrossRef]
- Qin S, Tang X, Chen Y, Chen K, Fan N, Xiao W, Zheng Q, Li G, Teng Y, Wu M, Song X. mRNA-based therapeutics: powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022; 7(1):166. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, Leitman S, Chang AE, Ettinghausen SE, Matory YL, Skibber JM, Shiloni E, Vetto JT, et al. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 1985;313(23):1485-92. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad S, Fan T, Hai Y, Gao Y, He J. Reigniting hope in cancer treatment: the promise and pitfalls of IL-2 and IL-2R targeting strategies. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):121. [CrossRef]
- Andtbacka RH, Colichio F, Harrington KJ et al. Final analyses of OPTiM: a randomized phase III trial of talimogene laherparepvec versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in unresectable stage III–IV melanoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2019; 7:145-56.
- Bai R, Chen N, Li L, Du N, Bai L, Lv Z, Tian H, Cui J. Mechanisms of Cancer Resistance to Immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2020 ;10:1290. . [CrossRef]
- Ribas A, Camacho LH, Lopez-Berestein G, Pavlov D, Bulanhagui CA, Millham R, Comin-Anduix B, Reuben JM, Seja E, Parker CA, Sharma A, Glaspy JA, Gomez-Navarro J. Antitumor activity in melanoma and anti-self responses in a phase I trial with the anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 monoclonal antibody CP-675,206. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(35):8968-77. [CrossRef]
- Liao B, Shroff S, Kamiya-Matsuoka C, Tummala S. Atypical neurological complications of ipilimumab therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014;16(4):589-93. [CrossRef]
- Bertrand A, Kostine M, Barnetche T, Truchetet ME, Schaeverbeke T. Immune related adverse events associated with anti-CTLA-4 antibodies: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2015; 13:211. [CrossRef]
- Chang L, Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001;410(6824):37-40. [CrossRef]
- Liebmann C. Regulation of MAP kinase activity by peptide receptor signalling pathway: paradigms of multiplicity. Cell Signal. 2001;13(11):777-85. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi AM, Simeone E, Ascierto PA. The role of MEK inhibitors in the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014;26(2):196-203. [CrossRef]
- Thompson N, Lyons J. Recent progress in targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway with inhibitors in cancer drug discovery. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5(4):350-6. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi AM, Simeone E, Festino L, Vanella V, Strudel M, Ascierto PA. MEK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma and Solid Tumors. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18(6):745-754. 7: Dermatol. 2017;18(6). [CrossRef]
- Lopes J, Rodrigues CMP, Gaspar MM et al. Melanoma Management: From Epidemiology to Treatment and Latest Advances. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(19): 4652-76. [CrossRef]
- Pham DDM, Guhan S, Tsao H. KIT and Melanoma: Biological Insights and Clinical Implications. Yonsei Med J. 2020;61(7):562-571. [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo Falconi VM, Torres-Arciga K, Matus-Ortega G, Díaz-Chávez J, Herrera LA. DNA Methyltransferases: From Evolution to Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 ;23(16):8994. [CrossRef]
- Kaniskan HÜ, Martini ML, Jin J. Inhibitors of Protein Methyltransferases and Demethylases. Chem Rev. 2018;118(3):989-1068. [CrossRef]
- Tachibana M, Matsumura Y, Fukuda M, Kimura H, Shinkai Y. G9a/GLP complexes independently mediate H3K9 and DNA methylation to silence transcription. EMBO J. 2008;27(20):2681-90. [CrossRef]
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129(4):823-37. [CrossRef]
- Black JC, Van Rechem C, Whetstine JR. Histone lysine methylation dynamics: establishment, regulation, and biological impact. Mol Cell. 2012;48(4):491-507. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Q, Rank G, Tan YT, Li H, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Cerruti L, Curtis DJ, Patel DJ, Allis CD, Cunningham JM, Jane SM. PRMT5-mediated methylation of histone H4R3 recruits DNMT3A, coupling histone and DNA methylation in gene silencing. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16(3):304-311. [CrossRef]
- Rea S, Eisenhaber F, O’Carroll D, Strahl BD, Sun ZW, Schmid M, Opravil S, Mechtler K, Ponting CP, Allis CD, Jenuwein T. Regulation of chromatin structure by site-specific histone H3 methyltransferases. Nature. 2000;406(6796):593-9. [CrossRef]
- Bates S. Epigenetic Therapies for Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021; 383:650-63. [CrossRef]
- Moran B, Silva R, Perry AS, Gallagher W. Epigenetics of malignant melanoma. Semin Cancer Biol 2021;51:80-88. [CrossRef]
- Harel T, Lupski JR. Genomic disorders 20 years on-mechanisms for clinical manifestations. Clin Genet 2021; 93:439-49. [CrossRef]
- Sang Y, Deng Y. Current insights into the epigenetic mechanisms of skin cancer. Dermatol Ther. 2019;32(4):e12964. [CrossRef]
- Nacev BA, Feng L, Bagert JD, Lemiesz AE, Gao J, Soshnev AA, Kundra R, Schultz N, Muir TW, Allis CD. The expanding landscape of ‘oncohistone’ mutations in human cancers. Nature. 2019;567(7749):473-478. [CrossRef]
- Husmann D, Gozani O. Histone lysine methyltransferases in biology and disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2019;26(10):880-889. [CrossRef]
- Karami Fath M, Azargoonjahromi A, Soofi A, Almasi F, Hosseinzadeh S, Khalili S, Sheikhi K, Ferdousmakan S, Owrangi S, Fahimi M, Zalpoor H, Nabi Afjadi M, Payandeh Z, Pourzardosht N. Current understanding of epigenetics role in melanoma treatment and resistance. Cancer Cell Int. 2022;22(1):313. [CrossRef]
- Casciello F, Windloch K, Gannon F, Lee JS. Functional Role of G9a Histone Methyltransferase in Cancer. Front Immunol. 2015; 6:487. [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian MD, Zhang K, Grunstein M. Histone H2B ubiquitylation controls processive methylation but not monomethylation by Dot1 and Set1. Mol Cell. 2005;19(2):271-7. [CrossRef]
- Tachibana M, Ueda J, Fukuda M, Takeda N, Ohta T, Iwanari H, Sakihama T, Kodama T, Hamakubo T, Shinkai Y. Histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP form heteromeric complexes and are both crucial for methylation of euchromatin at H3-K9. Genes Dev. 2005;19(7):815-26. [CrossRef]
- Fan J, Xing Y, Wen X, Jia R, Ni H, He J, Ding X, Pan H, Qian G, Ge S, Hoffman AR, Zhang H, Fan X. Long non-coding RNA ROR decoys gene-specific histone methylation to promote tumorigenesis. Genome Biol. 2015;16(1):139. [CrossRef]
- Liao Q, Yang J, Ge S, Chai P, Fan J, Jia R. Novel insights into histone lysine methyltransferases in cancer therapy: From epigenetic regulation to selective drugs. J Pharm Anal. 2023;13(2):127-141. [CrossRef]
- Dang NN, Jiao J, Meng X, An Y, Han C, Huang S. Abnormal overexpression of G9a in melanoma cells promotes cancer progression via upregulation of the Notch1 signaling pathway. Aging. 2020;12(3):2393-2407. [CrossRef]
- Filho RSO, Peixoto GR, Sangiuliano LDC, Oliveira DA. Notch receptors as a therapeutic target in melanoma: a narrative bibliographic review. Braz. J. Nat. Sci 2021; 4:614-28. [CrossRef]
- Ayaz F, Osborne BA. Non-canonical notch signaling in cancer and immunity. Front Oncol. 2014; 4:345. [CrossRef]
- Bedogni B. Notch signaling in melanoma: interacting pathways and stromal influences that enhance Notch targeting. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014;27(2):162-8. [CrossRef]
- Zhang K, Wong P, Salvaggio C, Salhi A, Osman I, Bedogni B. Synchronized Targeting of Notch and ERBB Signaling Suppresses Melanoma Tumor Growth through Inhibition of Notch1 and ERBB3. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(2):464-472. [CrossRef]
- Tang H, Xiao WR, Liao YY, Li L, Xiao X, Xu XP, Feng H. EGFL7 silencing inactivates the Notch signaling pathway; enhancing cell apoptosis and suppressing cell proliferation in human cutaneous melanoma. Neoplasma. 2019;66(2):187-196. [CrossRef]
- Bhat KP, Ümit Kaniskan H, Jin J, Gozani O. Epigenetics and beyond: targeting writers of protein lysine methylation to treat disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(4):265-286. [CrossRef]
- Rugo HS, Jacobs I, Sharma S, Scappaticci F, Paul TA, Jensen-Pergakes K, Malouf GG. The Promise for Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors for Epigenetic Therapy in Clinical Oncology: A Narrative Review. Adv Ther. 2020;37(7):3059-3082. [CrossRef]
- Link PA, Gangisetty O, James SR, Woloszynska-Read A, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y, Karpf AR. Distinct roles for histone methyltransferases G9a and GLP in cancer germ-line antigen gene regulation in human cancer cells and murine embryonic stem cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2009 ;7(6):851-62. [CrossRef]
- Sweis RF, Pliushchev M, Brown PJ, Guo J, Li F, Maag D, Petros AM, Soni NB, Tse C, Vedadi M, Michaelides MR, Chiang GG, Pappano WN. Discovery and development of potent and selective inhibitors of histone methyltransferase g9a. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014; 2;5(2):205-9. [CrossRef]
- Park KS, Xiong Y, Yim H, Velez J, Babault N, Kumar P, Liu J, Jin J. Discovery of the First-in-Class G9a/GLP Covalent Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2022;65(15):10506-10522. [CrossRef]
- Liu F, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Li F, Xiong Y, Korboukh V, Huang XP, Allali-Hassani A, Janzen WP, Roth BL, Frye SV, Arrowsmith CH, Brown PJ, Vedadi M, Jin J. Discovery of an in vivo chemical probe of the lysine methyltransferases G9a and GLP. J Med Chem. 2013; 56(21):8931-42. [CrossRef]
- Flesher JL, Fisher DE. G9a: An Emerging Epigenetic Target for Melanoma Therapy. Epigenomes. 2021;5(4):23. [CrossRef]
- Cao H, Li L, Yang D, Zeng L, Yewei X, Yu B, Liao G, Chen J. Recent progress in histone methyltransferase (G9a) inhibitors as anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;179:537-546. [CrossRef]
- Porcelli L, Mazzotta A, Garofoli M, Di Fonte R, Guida G, Guida M, Tommasi S, Azzariti A. Active notch protects MAPK activated melanoma cell lines from MEK inhibitor cobimetinib. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:111006. [CrossRef]
- Golan T, Levy C. Negative Regulatory Loop between Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF) and Notch Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 ;20(3):576. [CrossRef]
- Kato S, Weng QY, Insco ML, Chen KY, Muralidhar S, Pozniak J, Diaz JMS, Drier Y, Nguyen N, Lo JA, van Rooijen E, Kemeny LV, Zhan Y, Feng Y, Silkworth W, Powell CT, Liau BB, Xiong Y, Jin J, Newton-Bishop J, Zon LI, Bernstein BE, Fisher DE. Gain-of-Function Genetic Alterations of G9a Drive Oncogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2020;10(7):980-997. [CrossRef]
- Kelly GM, Al-Ejeh F, McCuaig R, Casciello F, Ahmad Kamal N, Ferguson B, Pritchard AL, Ali S, Silva IP, Wilmott JS, Long GV, Scolyer RA, Rao S, Hayward NK, Gannon F, Lee JS. G9a Inhibition Enhances Checkpoint Inhibitor Blockade Response in Melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(9):2624-2635. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




