1. Introduction
Biofilms are intricate microbial ecosystems characterized by the coexistence of diverse bacterial species, living in close proximity within a matrix [
1,
2]. This matrix, often termed the "biofilm matrix," acts as the very foundation of this unique bacterial community, analogous to the shelter and infrastructure that supports human society [
3,
4,
5]. Comprising a complex network of proteins, polysaccharides, extracellular DNA, and lipids, the biofilm matrix plays an essential role in sustaining the structural integrity and functionality of these bacterial consortia [
6,
7,
8].
The biofilm matrix can be likened to the architectural framework of a city, providing stability and a habitat for its inhabitants, in this case, bacteria. It encapsulates a microcosm where bacteria collaborate, communicate, and adapt to their environment, forming complex structures on a variety of surfaces [
9,
10]. This symbiotic existence holds profound implications for a multitude of applications, spanning from health and industry to environmental science [
11,
12]. One of the most intriguing aspects of biofilm matrix is the duality they embody [
13,
14]. On one hand, they are harnessed for beneficial purposes, serving as powerful tools for a myriad of applications [
15,
16]. Engineered biofilm reactors, for instance, leverage the potential of biofilm matrix for water pollutant removal [
17,
18]. These innovative systems provide an eco-friendly and effective solution to the pressing global challenge of water purification [
19,
20]. By harnessing the remarkable capabilities of biofilm matrix, they facilitate the removal of pollutants and contaminants from water sources, resulting in cleaner and safer aquatic ecosystems [
21,
22,
23].
However, the story does not end here. The narrative of biofilm matrix extends beyond their constructive applications [
24,
25]. Some biofilm matrix harbours intrinsic risks to human health and environmental equilibrium [
26,
27,
28]. This sinister aspect of biofilm existence underscores the darker side of microbial communities and their matrix [
29]. The biofilm matrix can be responsible for detrimental effects on human health, including respiratory issues like lung infections, creating a stark contrast to their beneficial counterparts [
30,
31,
32]. With these divergent roles, it is imperative to recognize the significance of distinguishing between advantageous and harmful biofilm matrix [
33,
34]. Realizing the potential of biofilm matrix in enhancing human life and mitigating the adverse consequences of detrimental ones necessitates a comprehensive exploration of this intricate and multifaceted domain [
35]. Only through a systematic and in-depth investigation can we discern the nuances, characteristics, and functionalities of biofilm matrix, which will help us unlock their full potential for the betterment of human life and environmental conservation [
36].
In our quest to navigate the labyrinth of biofilm matrix, this study embarked on a comprehensive journey that employed an extensive dataset of the 1000 influential papers in the field. This exhaustive bibliographic review sought to provide a comprehensive snapshot of the current state of knowledge and developments in biofilm matrix research. This painstaking and thorough examination was a key step in unravelling the mysteries surrounding biofilm matrix, shedding light on the important aspects of their structure, functions, and applications. In doing so, this study not only contributes to a better understanding of biofilm matrix but also acts as a valuable resource, paving the way for future explorations and scientific inquiries in this dynamic and ever-evolving field.
The intricate interplay between beneficial and harmful biofilm matrix raises a myriad of questions and invites a wide array of investigations. Exploring the biofilm matrix landscape is not only a scientific endeavour but also a journey with profound implications for human health, the environment, and various industries. It is a field of study where the interconnectedness of biology, materials science, and engineering converges to offer innovative solutions for real-world problems. By peeling back the layers of biofilm matrix, we may uncover new strategies for water treatment, public health, and environmental conservation, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and harmonious world.
In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the landscape of biofilm matrix, delving into their structure, composition, and roles in both beneficial and harmful contexts. We will also examine how biofilm matrix can be harnessed for beneficial applications, especially in the context of engineered biofilm reactors for water pollutant removal. Additionally, we will explore the dark side of biofilm matrix, understanding the challenges they pose in terms of human health, with a particular focus on lung infections. As we navigate through this intricate and multifaceted domain, we hope to not only present a clear picture of the current state of biofilm matrix research but also to uncover the critical avenues for future exploration and innovation in this dynamic field. This paper is an essential resource for those interested in understanding the multifaceted nature of biofilm matrix and the complex interplay between their benefits and risks.
2. Material and methods
In this research, our methodology consisted of a systematic approach to gather and analyse the most influential papers related to biofilm matrix [
37]. We conducted an exhaustive search on Web of Science by Clarivate, a reputable source of academic publications [
38]. Our search query was "biofilm matrix," aimed at identifying a comprehensive dataset of scholarly works in this domain. We selected this dataset from a vast collection, specifically targeting influential papers that offer valuable insights into biofilm matrix. Once the dataset of 1000 papers were identified, we meticulously gathered bibliographic data from each of these papers. This data included various critical elements such as author information, affiliations, keywords, and citations. The purpose of this extensive data collection was to facilitate a comprehensive analysis of the existing body of knowledge regarding biofilm matrix.
Our subsequent step involved the utilization of VOSviewer 1.6.19, a widely recognized tool for creating bibliometric maps based on bibliographic data [
39,
40,
41]. With the 1000 selected papers as our foundation, we imported the entire dataset into VOSviewer in the Plain Text Format, ensuring that we had access to the full record of each publication. This step was pivotal in enabling us to conduct a thorough and in-depth analysis of the dataset. In the VOSviewer application, we conducted various types of analyses to gain valuable insights into the domain of biofilm matrix. These analyses focused on different aspects of the bibliographic data, allowing us to explore the key relationships and associations within this field. Specifically, we conducted three types of analyses:
(1) Co-occurrence Analysis: Keywords
In this analysis, we examined the co-occurrence of keywords within the dataset. We set a minimum threshold of 50 occurrences for a keyword to be considered significant. This analysis provided us with insights into the most prevalent and interconnected terms and concepts within biofilm matrix research.
(2) Co-authorship Analysis: Organizations
Our second type of analysis focused on the co-authorship relationships among organizations. We set a minimum requirement of 8 documents produced by an organization to establish a significant co-authorship relationship. This analysis enabled us to identify the key institutions and research bodies actively contributing to the field.
(3) Co-authorship Analysis: Countries
In the third analysis, we explored co-authorship relationships among countries. Here, we set a minimum threshold of 20 documents produced by a country to determine a significant co-authorship relationship. This analysis shed light on the global collaboration and distribution of research efforts related to biofilm matrix.
Based on the outcomes of these three distinct analyses, we constructed a comprehensive map within VOSviewer. This map visually represented the intricate web of associations, keywords, organizations, and countries in the field of biofilm matrix. The creation of this map served as a fundamental step in our research, providing us with a holistic perspective of the domain. By employing this rigorous and systematic methodology, we aimed to not only compile a comprehensive overview of the current state of biofilm matrix research but also to identify the key trends, relationships, and avenues for future exploration in this dynamic field. This methodological approach allowed us to navigate through the complexity of biofilm matrix and provided a solid foundation for our subsequent analyses and discussions.
3. Results
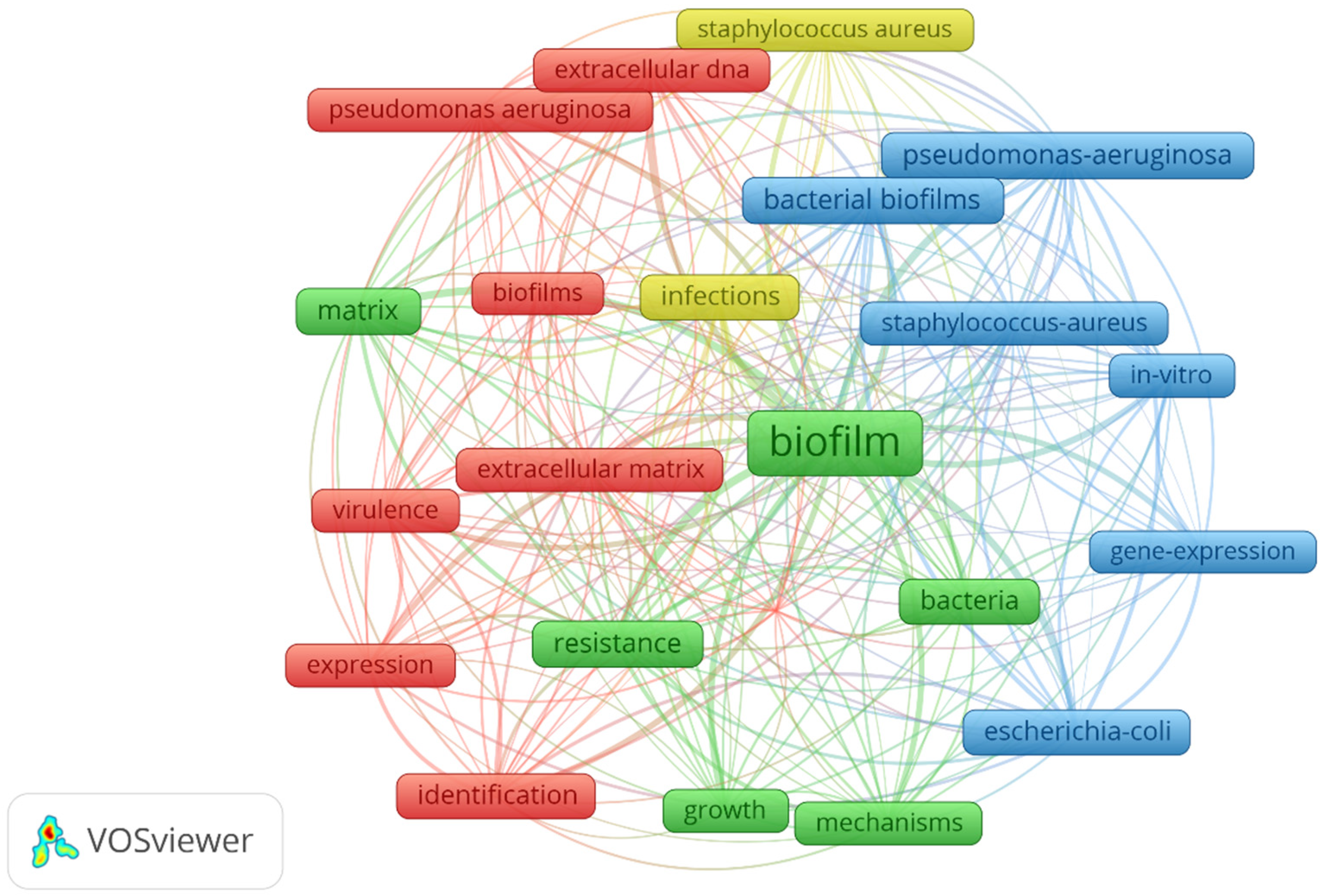
Figure 1 provided an illuminating visualization of the most important keywords associated with the term "biofilm matrix." This comprehensive keyword analysis yielded valuable insights into the field, shining a spotlight on prominent species names, including "
Pseudomonas aeruginosa," "
Staphylococcus aureus," and "
Escherichia coli." These species, widely recognized as the primary model organisms in biofilm matrix research, play a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of biofilm matrices. Furthermore, the analysis shed light on key process-related terms such as "gene expression," "expression," "growth," "infections," and "resistance," highlighting the fundamental processes intricately linked to biofilm matrices. Unravelling the significance of these species and processes is not only central to grasping the nuances of biofilm matrix studies but also critical for appreciating their far-reaching implications across diverse applications and industries. This understanding will pave the way for future research and innovation in this dynamic field.
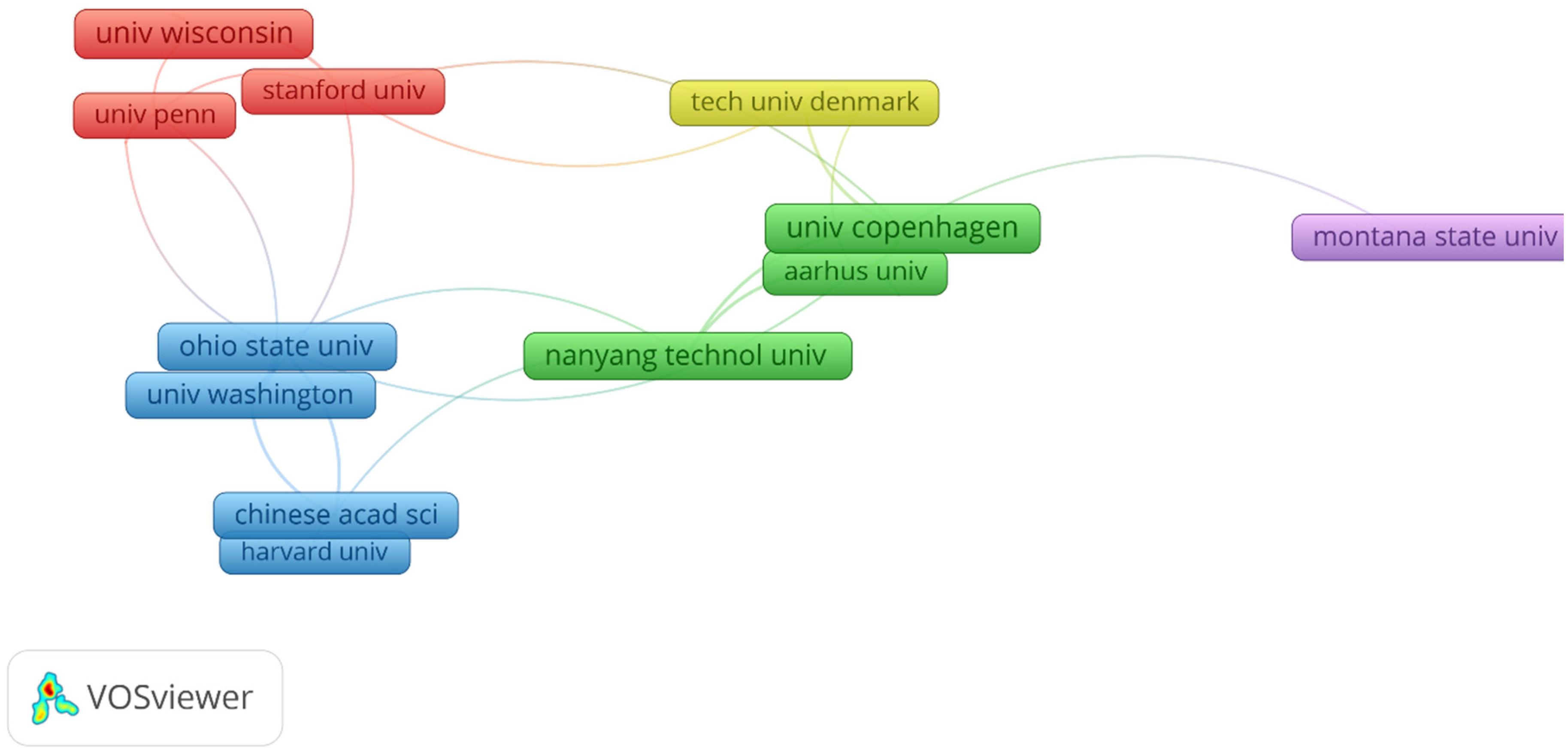
Figure 2 offers an informative and comprehensive portrayal of the primary institutions actively involved in the vibrant realm of "biofilm matrix" research. Within this diverse landscape, several key institutions have emerged as influential players, leaving an indelible mark on the progression of our knowledge about biofilm matrices. Notably, esteemed institutions such as Nanyang Technological University, Stanford University, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have made substantial and noteworthy contributions, significantly advancing our understanding of biofilm matrices. Moreover, it is essential to acknowledge the significant roles played by other institutions, including Montana State University, Aarhus University, University of Copenhagen, Technical University of Denmark, University of Pennsylvania, University of Wisconsin, Ohio State University, University of Washington, and Harvard University. These institutions have actively participated in the ongoing dialogue and collaborative efforts that define the dynamic landscape of research in the field of biofilm matrices. Recognizing the vital role of these institutions is central to appreciating the extensive cooperation and knowledge-sharing that underpin the continued evolution of this field. This acknowledgment underscores the diverse expertise and insights contributed by these institutions, collectively enriching our understanding of biofilm matrix research and its manifold applications.
Figure 1.
Keyword Clusters - VOSviewer identifies thematic clusters by analysing keyword co-occurrence. Colours denote distinct thematic groups of frequently associated keywords.
Figure 1.
Keyword Clusters - VOSviewer identifies thematic clusters by analysing keyword co-occurrence. Colours denote distinct thematic groups of frequently associated keywords.
Figure 2.
Collaboration Networks - Colours in these networks indicate varied collaborative clusters among connected institutions.
Figure 2.
Collaboration Networks - Colours in these networks indicate varied collaborative clusters among connected institutions.
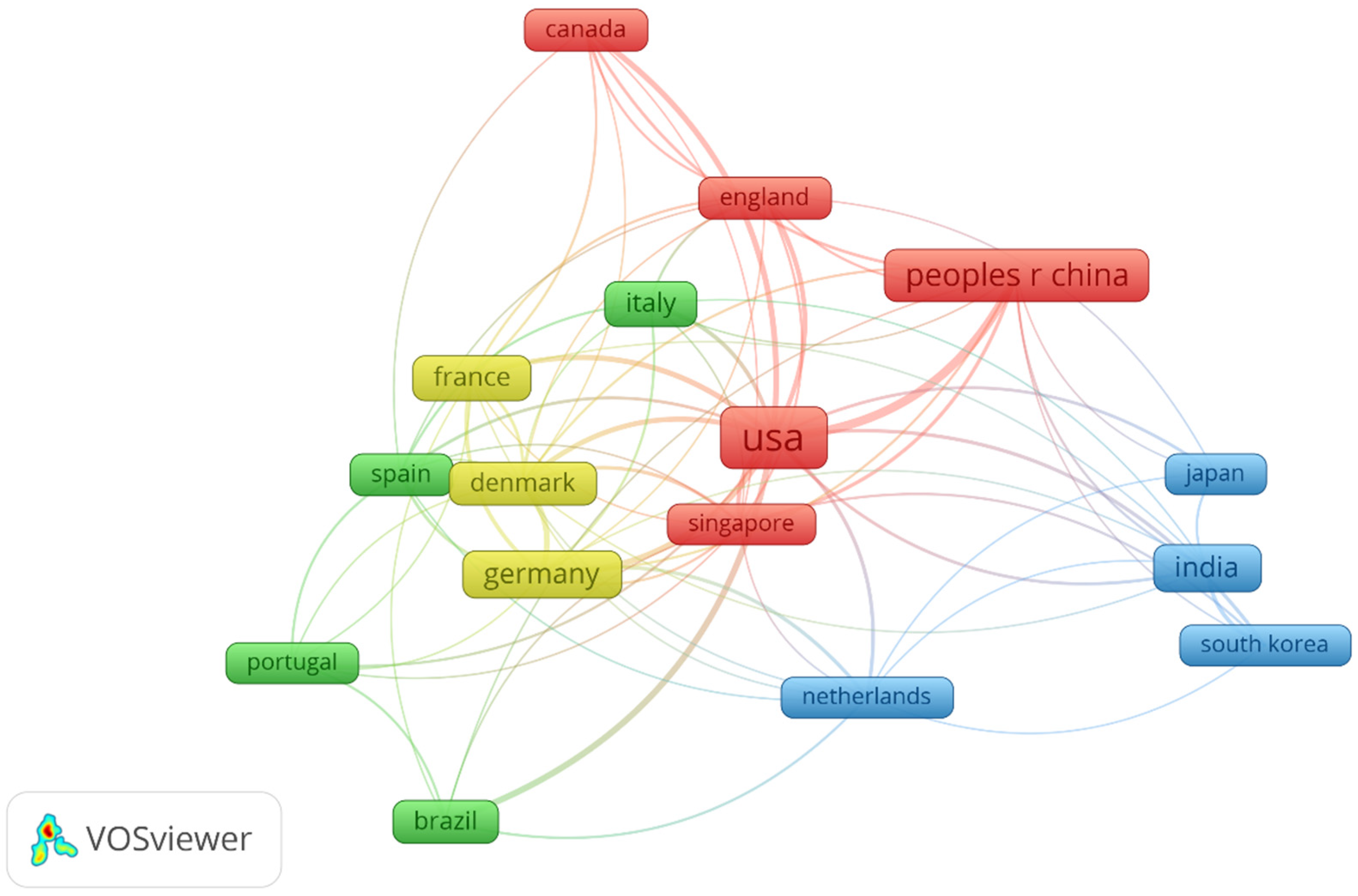
Figure 3 offers a compelling visual representation of the primary countries and regions actively engaged in the expansive domain of biofilm matrix research. This global perspective reveals the remarkable diversity of international contributions to this field. While certain regions have taken a prominent role, it is the collective effort of nations around the world that drives the continual expansion of knowledge in biofilm matrices. Notably, China, Singapore, the USA, and the UK have emerged as leaders in biofilm matrix research, making significant and influential contributions to the field. Their dedication to advancing our understanding of biofilm matrices serves as a testament to their commitment to scientific progress. Furthermore, it’s imperative to recognize the substantial contributions made by other countries and regions, such as Canada, Italy, France, Denmark, Spain, Germany, Portugal, Brazil, Netherlands, Japan, India, and South Korea. These nations have also played pivotal roles in enriching the body of knowledge related to biofilm matrices. The collaborative and diverse efforts of countries and regions worldwide underscore the international scope and significance of research endeavors in the realm of biofilm matrices. It is through this collective engagement and shared insights that our comprehension of biofilm matrices continues to evolve and expand, ultimately benefiting various industries and applications on a global scale.
Figure 3.
Collaboration Networks - Colours in these networks indicate varied collaborative clusters among connected countries/regions.
Figure 3.
Collaboration Networks - Colours in these networks indicate varied collaborative clusters among connected countries/regions.
4. Discussion
4.1. Biofilm matrix: A growing awareness in scientific research
The last 15 years have witnessed a remarkable surge in research papers dedicated to the multifaceted domain of biofilm matrix. This surge can be attributed to the growing awareness among scientists regarding the profound impact of biofilm matrix on various aspects of human daily life.
Table 1 thoughtfully compiles an assortment of pivotal research papers published over this time frame, shedding light on the substantial growth in this field.
A closer examination of
Table 1 reveals the diverse range of microorganisms employed by researchers to delve into the intricacies of biofilm matrix. These microorganisms include
Escherichia coli,
Shewanella oneidensis,
Comamonas testosterone,
Bacillus halodurans, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, underscoring the breadth of species harnessed in the pursuit of biofilm matrix knowledge. Furthermore, the research areas within biofilm matrix studies are as diverse as the microorganisms themselves.
In the engineering domain, biofilm matrix has emerged as a potent tool for addressing environmental challenges. Water sources are polluted by heavy metal in many developing countries [
42]. Biofilm matrix can be instrumental in the removal of pollutants and the purification of water sources [
43,
44,
45]. Simultaneously, they have found utility in the creation of microbial fuel cells that generate energy, opening new avenues for sustainable power generation [
46,
47,
48]. Biofilm matrix has also played a transformative role in the realm of civil engineering, contributing to the development of self-healing concrete, which promises to revolutionize infrastructure durability [
49,
50,
51].
Within the medical sphere, biofilm matrix has presented a unique challenge related to lung infections [
52,
53,
54]. The techniques for preventing and treating such infections have garnered intense research focus, given their critical importance to public health and well-being. Concurrently, the chemical characterization field has witnessed significant efforts aimed at unravelling the chemical mapping and obtaining higher-resolution fluorescence images of biofilm matrix [
55,
56,
57]. These endeavours have deepened our understanding of the intricate composition of biofilm matrix and their potential applications.
In essence, the burgeoning interest in biofilm matrix and their multifaceted roles underscores the pivotal position this field occupies in contemporary research, promising innovative solutions to some of the most pressing challenges in environmental engineering, healthcare, and materials science.
Table 1.
Prominent research in the biofilm matrix field over the past 15 years.
Table 1.
Prominent research in the biofilm matrix field over the past 15 years.
| Category |
Model species |
Main findings |
Reference |
| Engineering |
Shewanella sp. HRCR-1 |
U(VI) was immobilized by the Shewanella sp. HRCR-1 biofilms |
[43] |
| Engineering |
Shewanella oneidensis |
Cr(VI) was immobilized by the Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilm |
[44] |
| Engineering |
Comamonas testosteroni |
Biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline by Comamonas testosteroni biofilm and c-di-GMP |
[45] |
| Engineering |
Shewanella oneidensis / Escherichia coli
|
Electricity genernation and high-performance microbial fuel cells by biofilm matrix |
[46,47,48] |
| Engineering |
Bacillus halodurans |
Biofilm matrix enhanced the self-repairing process in concrete |
[49,50,51] |
| Medicine |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Biofilm matrix leaded to infection in a COVID-19 patient |
[52] |
| Medicine |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
Biofilm matrix leaded to chronic lung infection |
[53] |
| Medicine |
Staphylococcus aureus |
Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation causing infection can be reduced by linezolid or vancomycin |
[54] |
| Chemical characterization |
Shewanella oneidensis |
Molecular ion signal intensity for in situ biofilm matrix SIMS analysis was improved |
[55] |
| Chemical characterization |
Shewanella oneidensis |
In situ molecular imaging of the biofilm matrix was achieved by SIMS |
[56,57] |
| Chemical characterization |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
The biofilm matrix is identified by MALDI-TOF MS |
[58] |
4.2. Revolutionizing healthcare with innovative biofilm control
The imperative need for anti-bacterial and anti-biofilm strategies in biofilm research cannot be overstated due to the severe health risks associated with biofilm matrix-related infections [
52,
53]. As biofilm matrix are known to be a significant factor in infections that pose a direct threat to human lives, there has been a surge in research aimed at controlling biofilm development. A noteworthy example of this research is the incorporation of TiO
2 nanoparticles into cementitious materials [
59,
60], which has demonstrated remarkable antibacterial properties, effectively halting biofilm matrix development when exposed to light sources [
61,
62]. This technology holds great promise for application in hospital settings, where the control of hospital-acquired infections is of paramount concern. Implementation of such innovations in healthcare facilities could substantially enhance infection control measures, instilling greater confidence and safety among patients and visitors.
4.3. The promise of big data and machine learning in biofilm research
In the current era, various innovative technologies, such as big data and machine learning, have rapidly evolved and found applications across diverse fields, including psychological education policy [
63], ecological predictions [
64], and self-driving technology [
65,
66,
67]. Looking forward, envision a future where biofilm matrix data, including valuable information like chemical mapping data, can be systematically collected, and compiled from a multitude of studies, potentially amassing a database of more than a thousand records. This envisioned database would serve as a vast and comprehensive resource for scientists seeking to delve into the complexities of biofilm matrix. With such a substantial dataset at their disposal, scientists can harness the power of machine learning models to gain deeper insights into biofilm matrix. These insights, in turn, could significantly contribute to various aspects of medical decision-making, drug design, and infection control, ushering in a new era of knowledge-driven approaches to combat biofilm-related health threats.
References
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nature reviews microbiology 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiology and molecular biology reviews 2000, 64, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS matrix: the “house of biofilm cells”. Journal of bacteriology 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nature reviews microbiology 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, R. Biofilms: microbial cities of scientific significance. J Microbiol Exp 2014, 1, 00014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, C.; Peacock, C.L.; Sørensen, S.J.; Redmile-Gordon, M.A.; Xiao, K.-Q.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z. Cooperative microbial interactions drive spatial segregation in porous environments. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Genetic regulation, biosynthesis and applications of extracellular polysaccharides of the biofilm matrix of bacteria. Carbohydrate Polymers 2022, 291, 119536. [Google Scholar]
- Neu, T.R.; Lawrence, J.R. Extracellular polymeric substances in microbial biofilms. In Microbial glycobiology; Elsevier, 2010; pp. 733–758. [Google Scholar]
- Thormann, K.M.; Saville, R.M.; Shukla, S.; Pelletier, D.A.; Spormann, A.M. Initial phases of biofilm formation in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Journal of bacteriology 2004, 186, 8096–8104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thormann, K.M.; Duttler, S.; Saville, R.M.; Hyodo, M.; Shukla, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Spormann, A.M. Control of formation and cellular detachment from Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 biofilms by cyclic di-GMP. Journal of bacteriology 2006, 188, 2681–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, X.; Shi, L.; Cao, B. Electrochemically active biofilm-enabled biosensors: Current status and opportunities for biofilm engineering. Electrochimica Acta 2022, 428, 140917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.-E.; Chew, S.C.; Tan, S.Y.-Y.; Givskov, M.; Yang, L. Emerging frontiers in detection and control of bacterial biofilms. Current opinion in biotechnology 2014, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol-González, C.; Domingo-Calap, P. Phages for biofilm removal. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. The biofilm matrix: Multitasking in a shared space. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2023, 21, 70–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kassinger, S.J.; van Hoek, M.L. Biofilm architecture: An emerging synthetic biology target. Synthetic and systems biotechnology 2020, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J. Microbial model communities: To understand complexity, harness the power of simplicity. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2020, 18, 3987–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokoohi, R.; Asgari, G.; Leili, M.; Khiadani, M.; Foroughi, M.; Sedighi Hemmat, M. Modelling of moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) efficiency on hospital wastewater (HW) treatment: a comprehensive analysis on BOD and COD removal. International journal of environmental science and technology 2017, 14, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Xing, J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; Fan, F.; Ahmed, T.; Meng, F. Development of a flow-through biofilm reactor for anammox startup and operation: nitrogen removal and metacommunity. ACS ES&T Water 2021, 1, 573–583. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green-synthesized nanocatalysts and nanomaterials for water treatment: Current challenges and future perspectives. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2021, 401, 123401. [Google Scholar]
- Cámara, M.; Green, W.; MacPhee, C.E.; Rakowska, P.D.; Raval, R.; Richardson, M.C.; Slater-Jefferies, J.; Steventon, K.; Webb, J.S. Economic significance of biofilms: a multidisciplinary and cross-sectoral challenge. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes 2022, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lei, Q.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Biofilm-mediated bioremediation is a powerful tool for the removal of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Habimana, O. Biofilm research within irrigation water distribution systems: Trends, knowledge gaps, and future perspectives. Science of the total environment 2019, 673, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlapudi, A.P.; Venkateswarulu, T.C.; Tammineedi, J.; Kanumuri, L.; Ravuru, B.K.; Ramu Dirisala, V.; Kodali, V.P. Role of biosurfactants in bioremediation of oil pollution-a review. Petroleum 2018, 4, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Kokare, C.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Khopade, A.N.; Mahadik, K.R. Biofilm: importance and applications. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Harkins, D.M.; Torralba, M.; Gomez, A.; Highlander, S.K.; Jones, M.B.; Leong, P.; Saffery, R.; Bockmann, M.; Kuelbs, C. Supragingival plaque microbiome ecology and functional potential in the context of health and disease. MBio 2018, 9, e01631–01618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valm, A.M. The structure of dental plaque microbial communities in the transition from health to dental caries and periodontal disease. Journal of molecular biology 2019, 431, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römling, U.; Balsalobre, C. Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies. Journal of internal medicine 2012, 272, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, A.; Olsen, L.; Choffnes, E.R. Microbial Ecology in States of Health and Disease: Workshop Summary; National Academies Press, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zeibich, L.; Koebele, S.V.; Bernaud, V.E.; Ilhan, Z.E.; Dirks, B.; Northup-Smith, S.N.; Neeley, R.; Maldonado, J.; Nirmalkar, K.; Files, J.A. Surgical menopause and estrogen therapy modulate the gut microbiota, obesity markers, and spatial memory in rats. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 2021, 11, 702628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Gautam, P.K.; Misra, K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. A review on basic biology of bacterial biofilm infections and their treatments by nanotechnology-based approaches. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences 2020, 90, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Kolpen, M.; Qvist, T.; Aanæs, K.; Pressler, T.; Skov, M.; Ciofu, O. Diagnosis of biofilm infections in cystic fibrosis patients. Apmis 2017, 125, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chai, M.; Li, X.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J. Size and charge adaptive clustered nanoparticles targeting the biofilm microenvironment for chronic lung infection management. ACS nano 2020, 14, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, E.R.; Yasir, M.; Turner, A.K.; Wain, J.; Charles, I.G.; Webber, M.A. Massively parallel transposon mutagenesis identifies temporally essential genes for biofilm formation in Escherichia coli. Microbial Genomics 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, N.N.; Hlaing, M.M.; Ravensdale, J.T.; Coorey, R.; Chandry, P.S.; Dykes, G.A. Characterization of the biofilm matrix composition of psychrotrophic, meat spoilage pseudomonads. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 16457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, H.; Allan, R.N.; Howlin, R.P.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L. Targeting microbial biofilms: current and prospective therapeutic strategies. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2017, 15, 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allioui, H.; Mourdi, Y. Exploring the Full Potentials of IoT for Better Financial Growth and Stability: A Comprehensive Survey. Sensors 2023, 23, 8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, J. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of scientific publications on atlantoaxial spine surgery based on Web of Science and VOSviewer. World neurosurgery 2020, 137, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quantitative Science Studies 2020, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A bibliography study of Shewanella oneidensis biofilm. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 2023, fiad124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, W.; Altaf, M.T.; Barutçular, C.; Zayed, E.M.; Hussain, T. Drought and sorghum: a bibliometric analysis using VOS viewer. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Zha, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhu, C.; Chen, E. A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer of publications on COVID-19. Annals of translational medicine 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Heavy metal pollution and transboundary issues in ASEAN countries. Water Policy 2019, 21, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Ahmed, B.; Kennedy, D.W.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L.; Marshall, M.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Isern, N.G.; Majors, P.D.; Beyenal, H. Contribution of extracellular polymeric substances from Shewanella sp. HRCR-1 biofilms to U (VI) immobilization. Environmental science & technology 2011, 45, 5483–5490. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Peng, N.; Du, Y.; Ji, L.; Cao, B. Disruption of putrescine biosynthesis in Shewanella oneidensis enhances biofilm cohesiveness and performance in Cr (VI) immobilization. Applied and environmental microbiology 2014, 80, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cohen, Y.; Cao, B. Elevated level of the second messenger c-di-GMP in Comamonas testosteroni enhances biofilm formation and biofilm-based biodegradation of 3-chloroaniline. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2015, 99, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cao, B.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Song, H. Enhancing bidirectional electron transfer of Shewanella oneidensis by a synthetic flavin pathway. ACS synthetic biology 2015, 4, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.e.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Zhang, Y.; Kjelleberg, S.; Loo, J.S.C.; Cao, B.; Zhang, Q. Hybrid conducting biofilm with built-in bacteria for high-performance microbial fuel cells. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-e.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, V.B.; Bao, B.; Kjelleberg, S.; Cao, B.; Loo, S.C.J.; Wang, L.; Huang, W. Chemically functionalized conjugated oligoelectrolyte nanoparticles for enhancement of current generation in microbial fuel cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 14501–14505. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Weng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Use of genetically modified bacteria to repair cracks in concrete. Materials 2019, 12, 3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, S. Mechanical performance of strain-hardening cementitious composites (SHCC) with bacterial addition. Journal of Infrastructure Preservation and Resilience 2022, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Influence of bacterial incorporation on mechanical properties of engineered cementitious composites (ECC). Construction and Building Materials 2019, 196, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Duan, X.; Han, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuo, C. Persistent bacterial coinfection of a COVID-19 patient caused by a genetically adapted Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic colonizer. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 2021, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hengzhuang, W.; Wu, H.; Damkiær, S.; Jochumsen, N.; Song, Z.; Givskov, M.; Høiby, N.; Molin, S. Polysaccharides serve as scaffold of biofilms formed by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Immunology & Medical Microbiology 2012, 65, 366–376. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, R.A.G.; Afonina, I.; Kline, K.A. Eradicating biofilm infections: an update on current and prospective approaches. Current Opinion in Microbiology 2021, 63, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Ding, Y.; Yu, J.; Hua, X.; Evans, J.E.; Yu, X.; Lao, D.B.; Heldebrant, D.J.; Nune, S.K. Improving the molecular ion signal intensity for in situ liquid SIMS analysis. Journal of The American Society for Mass Spectrometry 2016, 27, 2006–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Szymanski, C.; Fredrickson, J.; Shi, L.; Cao, B.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. In situ molecular imaging of the biofilm and its matrix. Analytical chemistry 2016, 88, 11244–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, X.-Y. Molecular evidence of a toxic effect on a biofilm and its matrix. Analyst 2019, 144, 2498–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, E.; Kiel, A.; Kaltschmidt, B.P.; Wortmann, M.; Schmidt, N.; Hüsgen, B.; Hütten, A.; Knabbe, C.; Kaltschmidt, C.; Kaltschmidt, B. Identification of microorganisms from several surfaces by MALDI-TOF MS: P. aeruginosa is leading in biofilm formation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Graphene-Based TiO2 Cement Composites to Enhance the Antibacterial Effect of Self-Disinfecting Surfaces. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Visible light antibacterial potential of graphene-TiO2 cementitious composites for self-sterilization surface. Journal of Sustainable Cement-Based Materials 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Mechanical and antibacterial behavior of photocatalytic lightweight engineered cementitious composites. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering 2021, 33, 04021262. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdany, A.H.; Ding, Y.; Qian, S. Cementitious Composite Materials for Self-Sterilization Surfaces. ACI Materials Journal 2022, 119, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting Academic Performance in Pennsylvania’s Schools. Social Sciences 2023, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Machine Learning and Its Applications in Studying the Geographical Distribution of Ants. Diversity 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilgoe, J. Machine learning, social learning and the governance of self-driving cars. Social studies of science 2018, 48, 25–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, X. Development of the growth mindset scale: Evidence of structural validity, measurement model, direct and indirect effects in Chinese samples. Current Psychology 2023, 42, 1712–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, Y. Assessing the Psychometric Properties of STEAM Competence in Primary School Students: A Construct Measurement Study. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment 2023, 41, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).