Submitted:
13 October 2023
Posted:
17 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
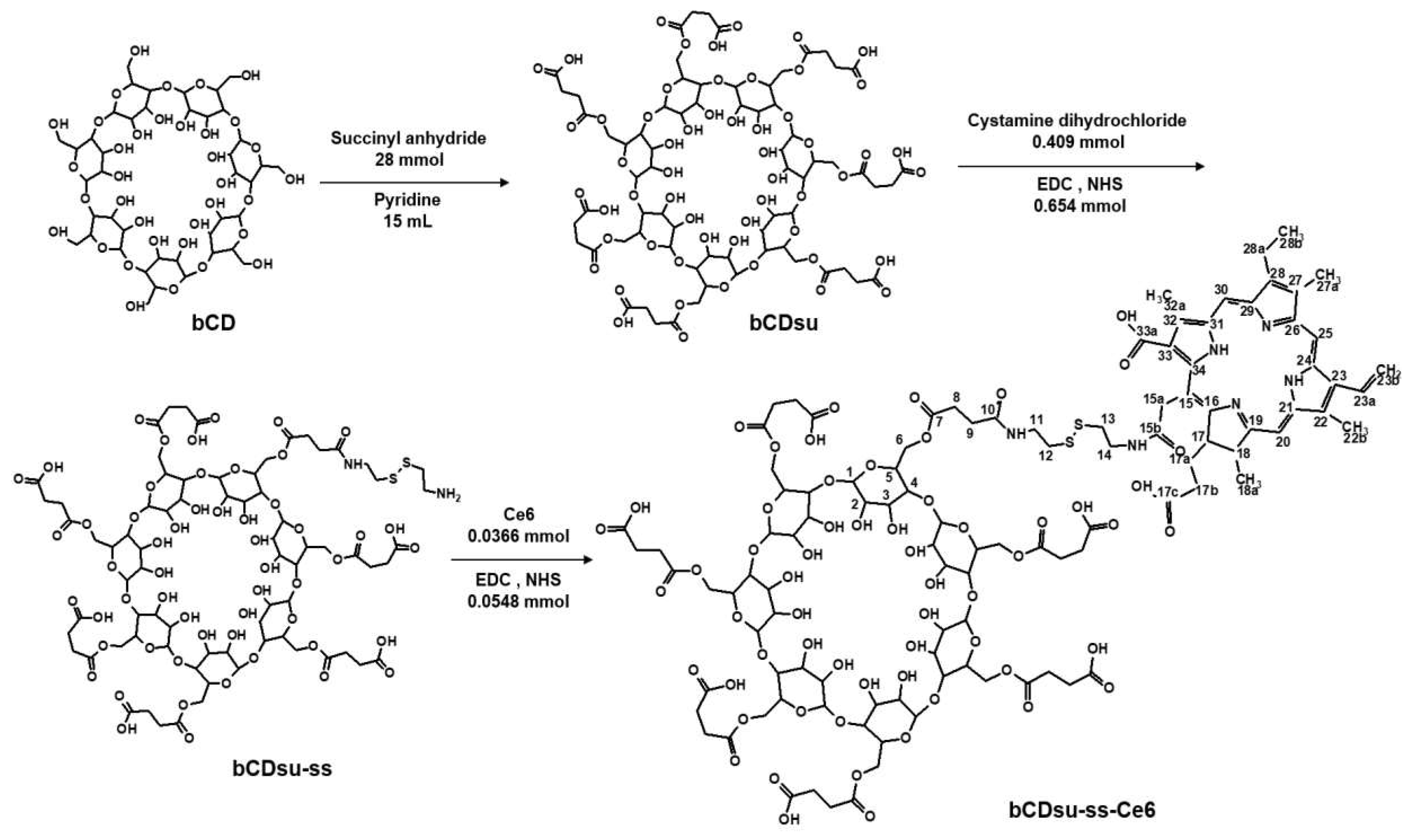
2.1. Synthesis of bCDsu-ss-Ce6 Conjugates
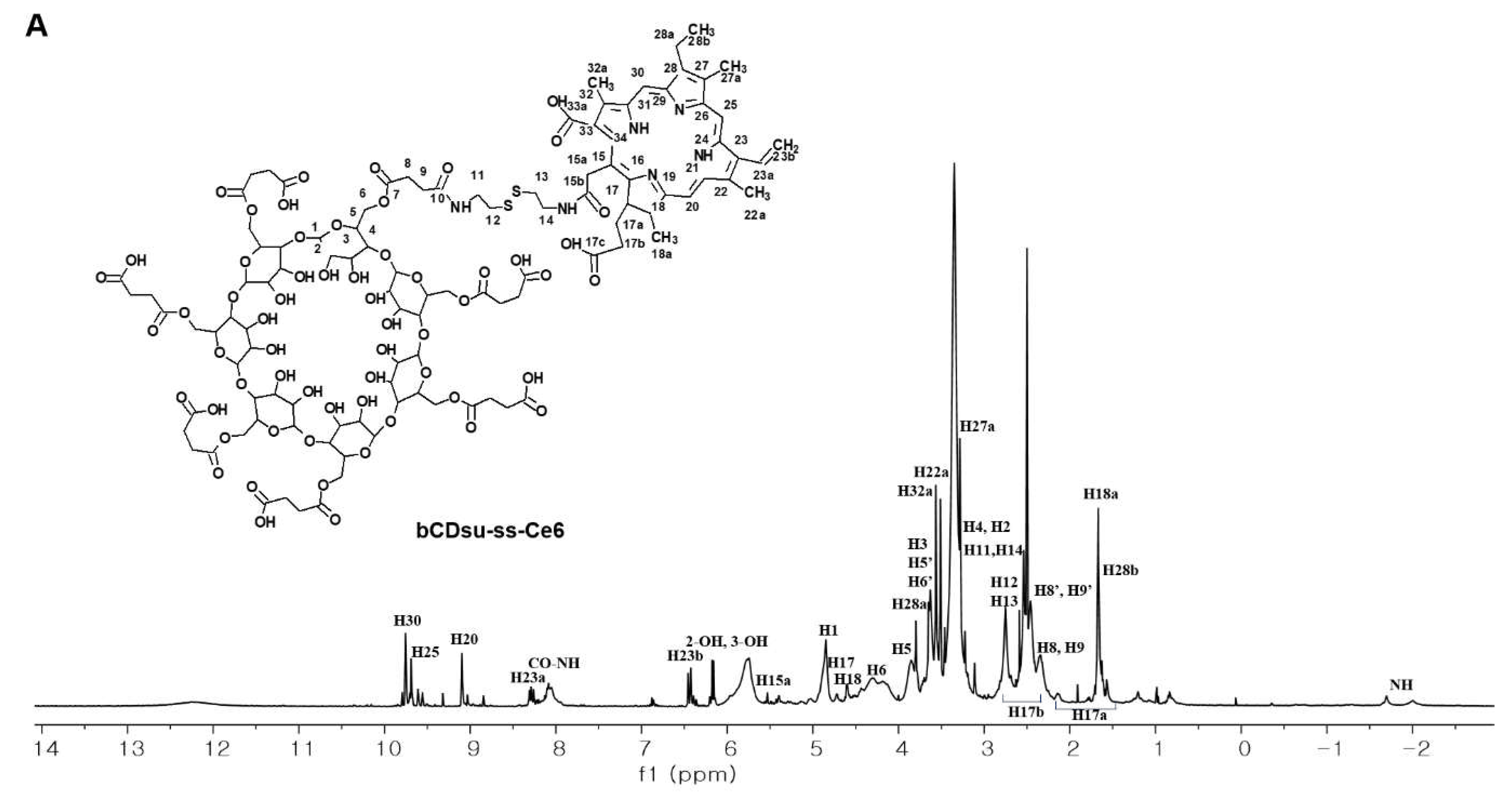
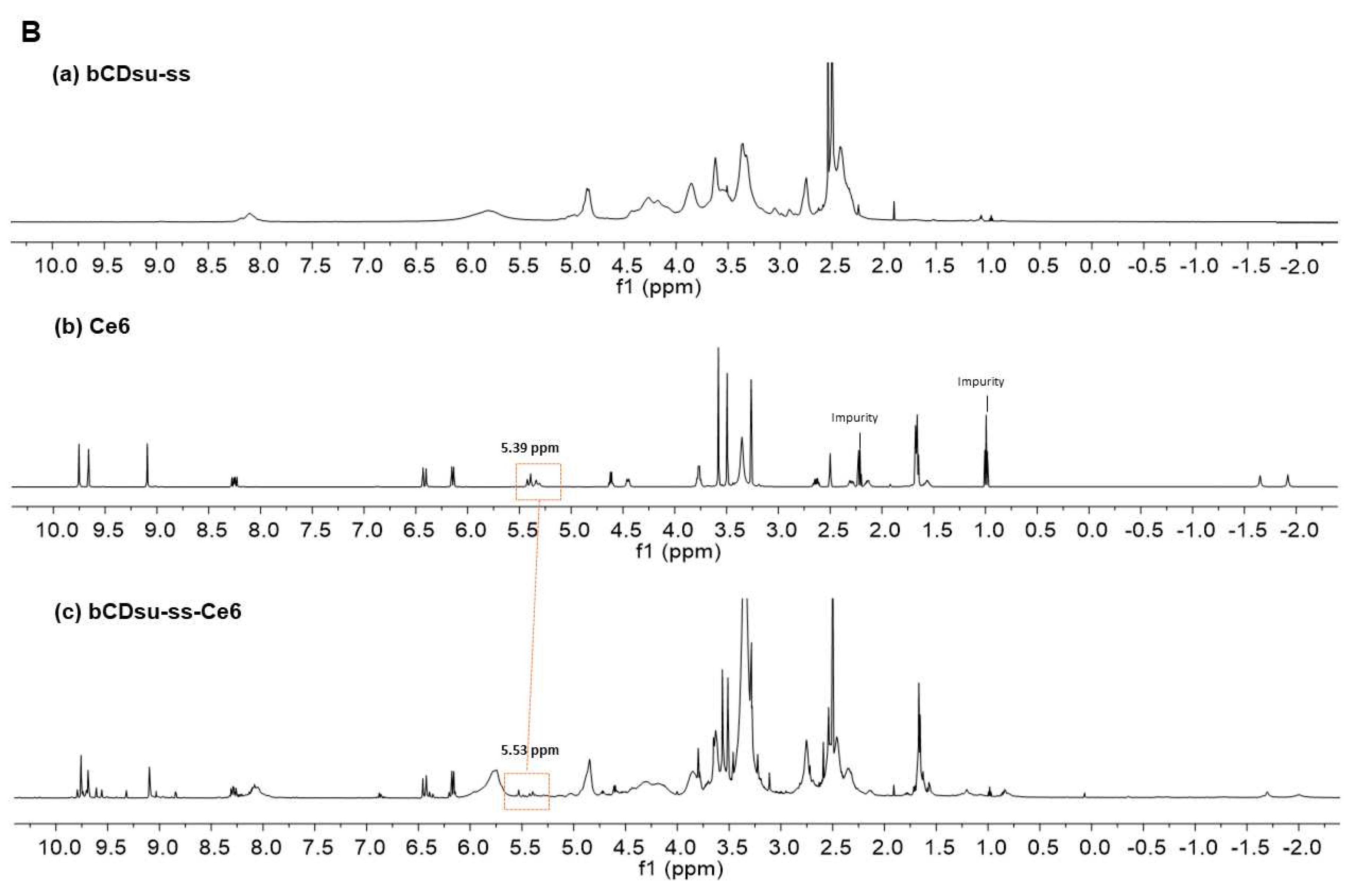
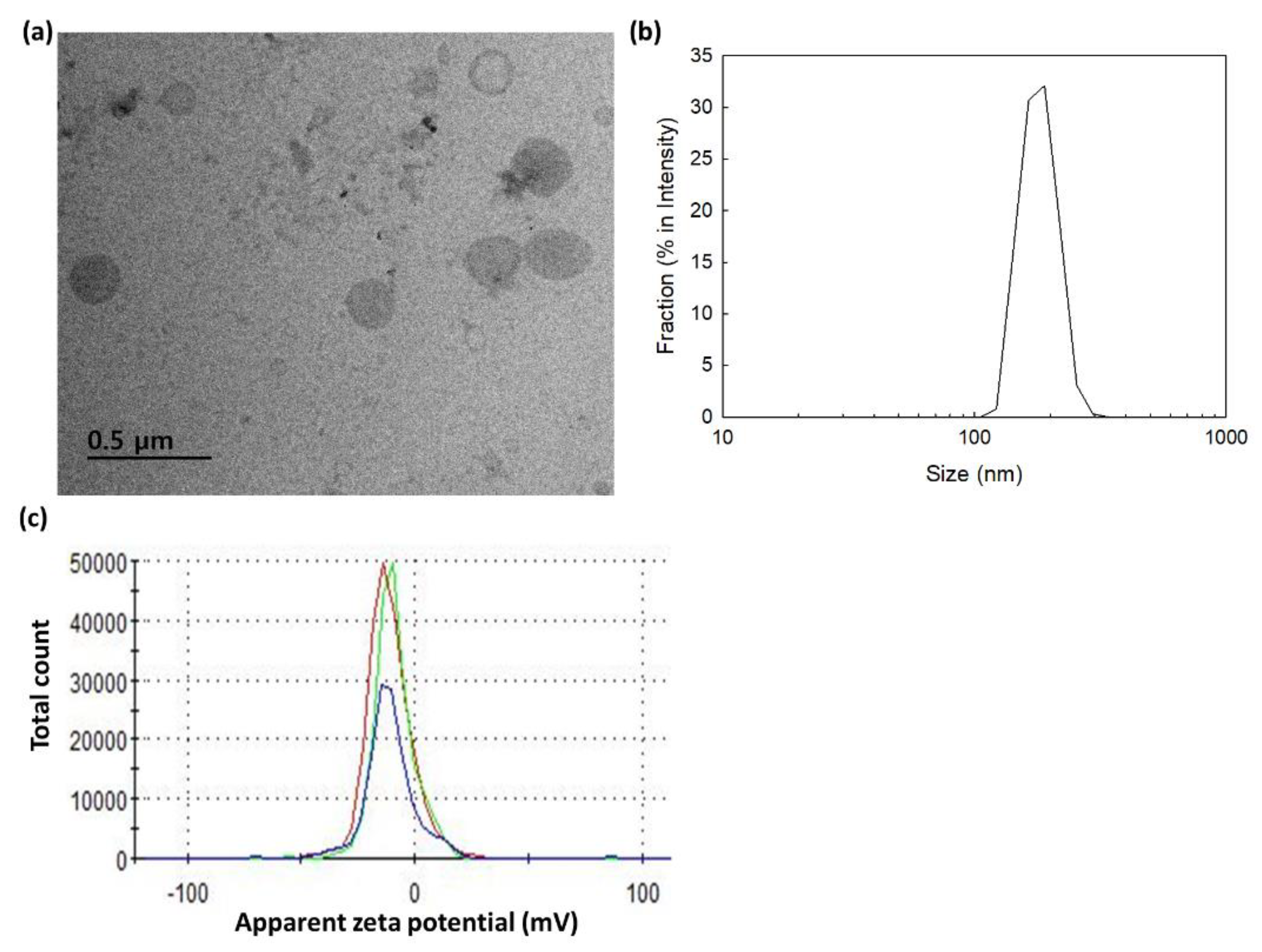
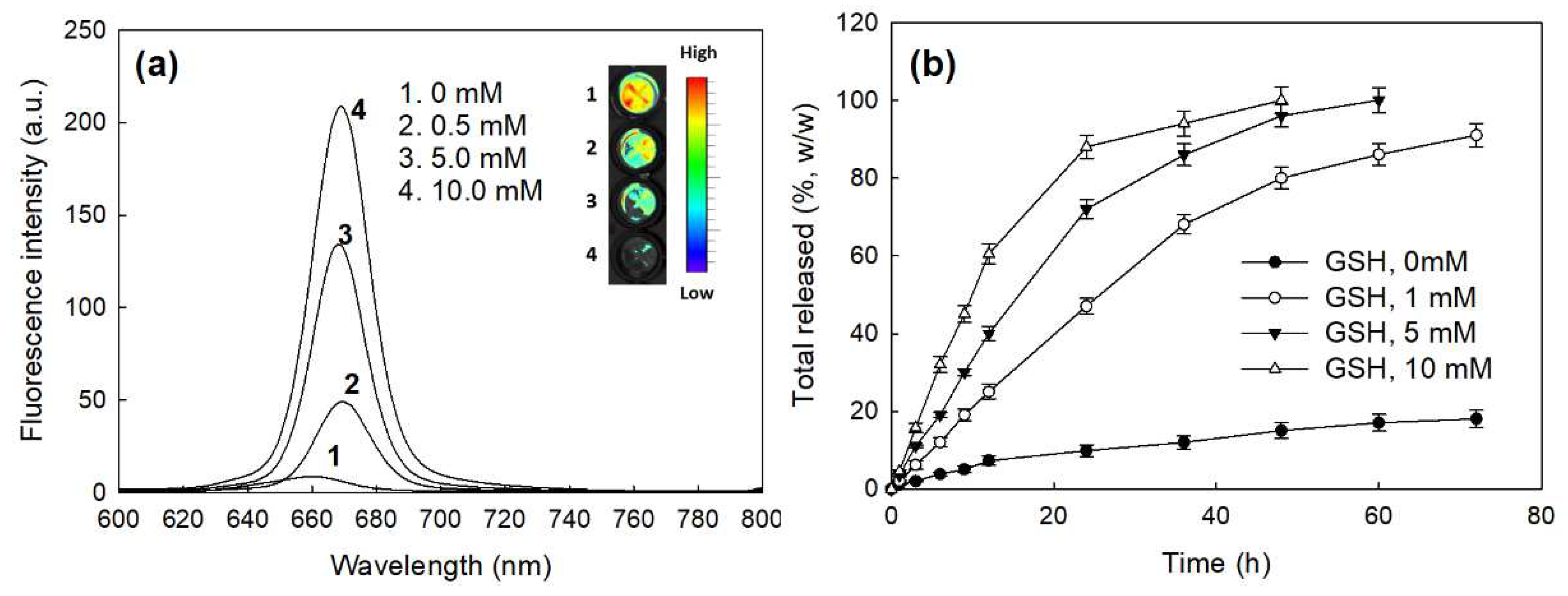
2.2. Characterization of bCDsu-ss-Ce6 Nanophotosensitizers
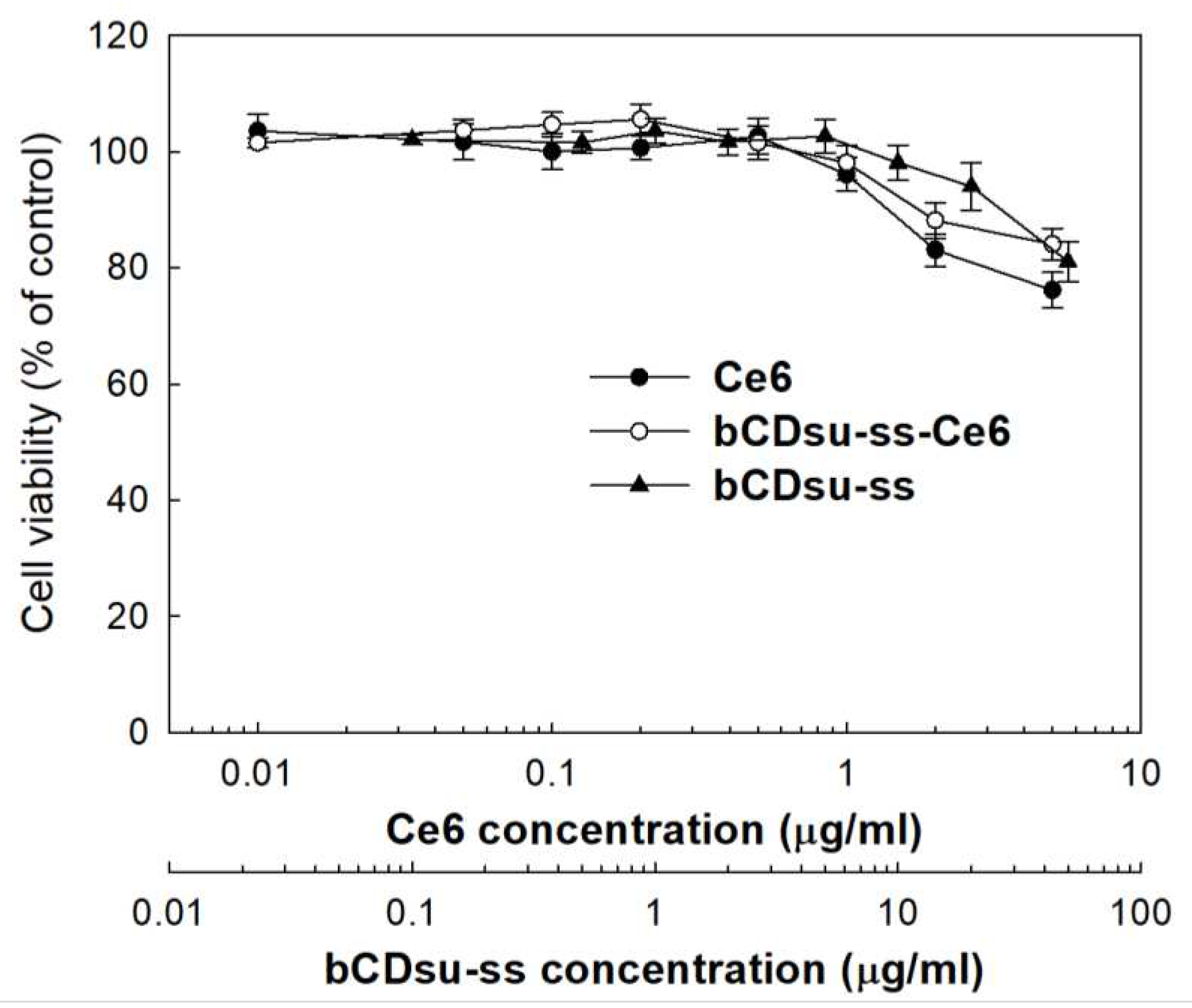
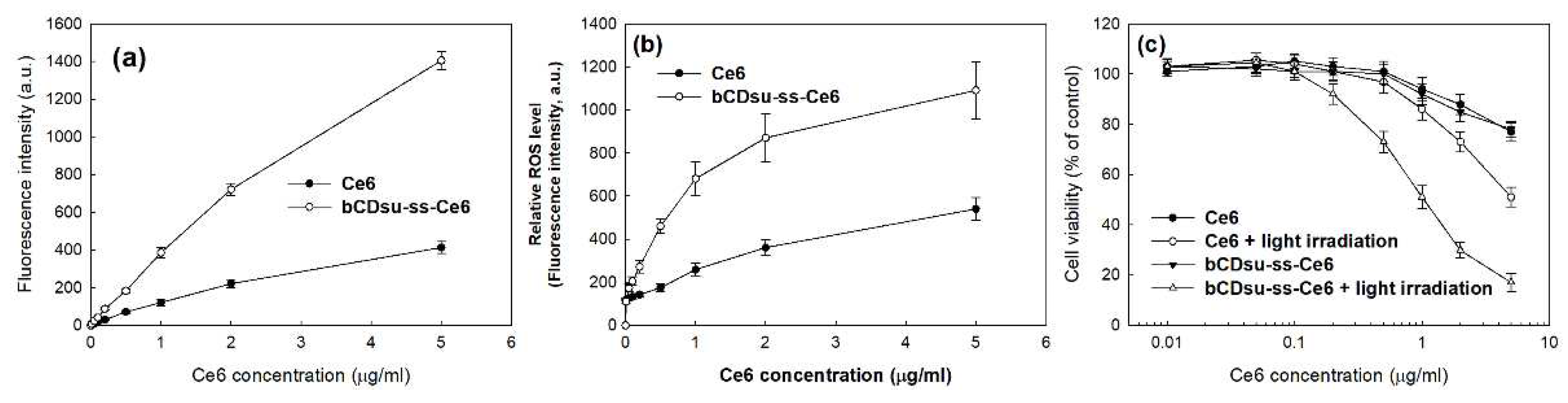
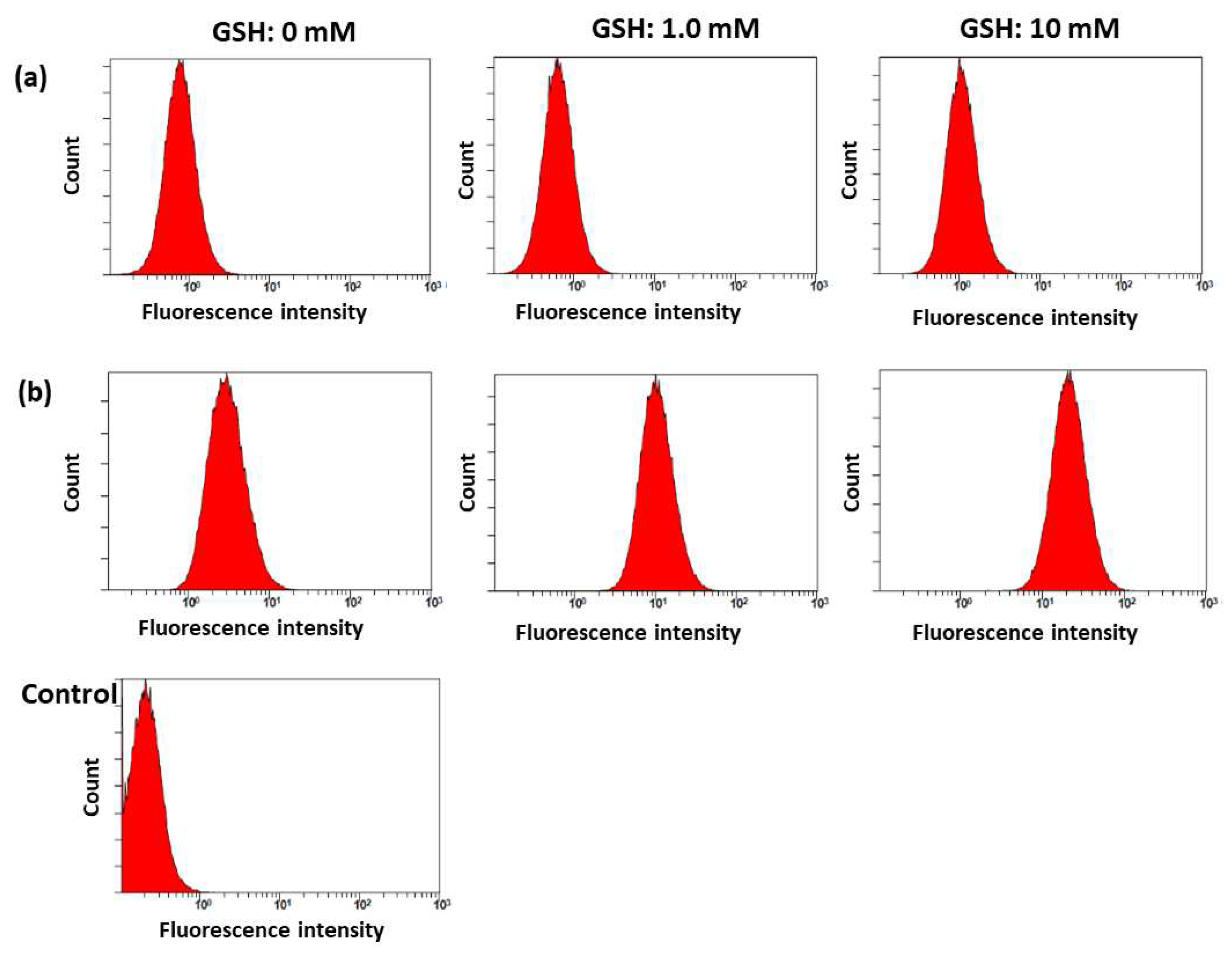
2.3. In Vitro Cell Culture Study
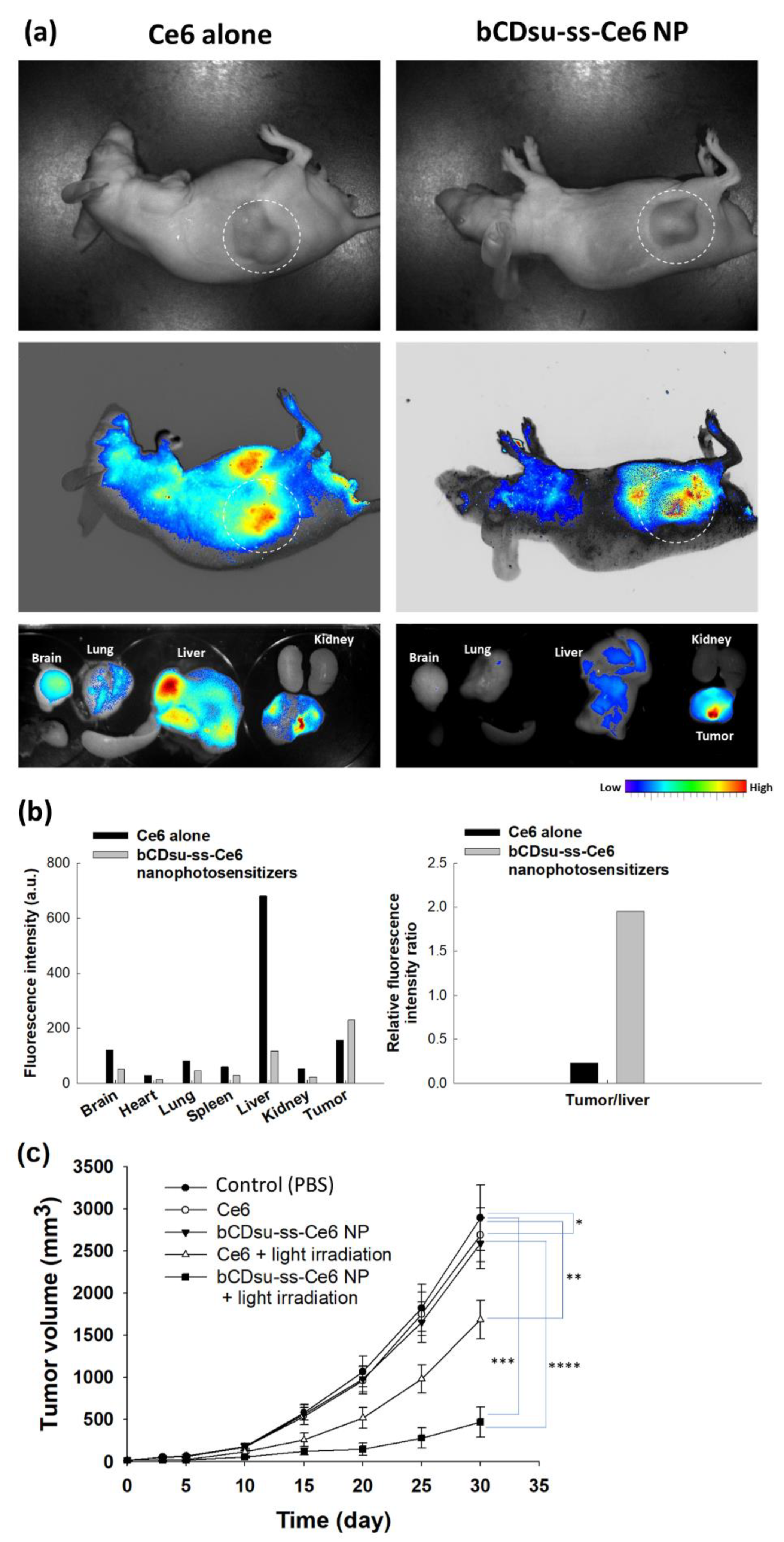
2.4. In Vivo Animal Tumor Xenograft Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instruments
4.3. Synthesis of bCDssCe6 Conjugates
4.4. Fabrication of bCDsu-ss-Ce6 Nanophotosensitizers
4.5. Fluorescence Spectra
4.6. Drug Release Study
4.7. Cell Culture Study
4.8. Animal Tumor Imaging Using HeLa tumor Xenograft Model In Vivo
4.9. PDT of HeLa Tumor Xenograft Model In Vivo
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanovsky, R.L.; Bartenstein, D.W.; Rogers, G.S.; Isakoff, S.J.; Chen, S.T. Photodynamic therapy for solid tumors: A review of the literature. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I. Photodynamic therapy in oncology: mechanisms and clinical use. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawczyk-Krupka, A.; Bugaj, A.M.; Latos, W.; Zaremba, K.; Wawrzyniec, K.; Siero ´n, A. Photodynamic therapy in colorectal cancer treatment: The state of the art in clinical trials. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2015, 12, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Furukawa, K.; Sato, M.; Okunaka, T.; Kusunoki, Y.; Kawahara, M.; Fukuoka, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Yana, T.; Matsui, K.; et al. Phase II clinical study of photodynamic therapy using mono-L-aspartyl chlorin e6 and diode laser for early superficial squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2003, 42, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, K.M.; Bisby, R.H.; Botchway, S.W.; Parker, A.W. New approaches to photodynamic therapy from types I, II and III to type IV using one or more photons. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallidi, S.; Anbil, S.; Bulin, A.L.; Obaid, G.; Ichikawa, M.; Hasan, T. Beyond the barriers of light penetration: Strategies, per-spectives and possibilities for photodynamic therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 2458–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inglut, C.T.; Gaitan, B.; Najafali, D.; Lopez, I.A.; Connolly, N.P.; Orsila, S.; Perttilä, R.; Woodworth, G.F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.C. Predictors and limitations of the penetration depth of photodynamic effects in the rodent brain. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringasci, M.D.; Fortunato, T.C.; Moriyama, L.T.; Filho, J.D.V.; Bagnato, V.S.; Kurachi, C. Interstitial PDT using diffuser fiber investigation in phantom and in vivo models. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjosé, S. The epidemiology of human papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Dis. Markers 2007, 23, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis, K.S.; Lai Yau, T.H.; Sideris, M. Chemoradiotherapy in cancer treatment: Rationale and clinical applications. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Warloe, T.; Berg, K.; Moan, J.; Kongshaug, M.; Giercksky, K.E.; Nesland, J.M. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy. Clinical research and future challenges. Cancer. 1997, 79, 2282–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popken, G.; Schultze-Seemann, W.; Seiler, K.U.; Birkel, M.; Wetterauer, U. Intravesical administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA). Safety and pharmacokinetics of 5-ALA and its metabolite protoporphyrin IX. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 56, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissonnette, R.; Nigen, S.; Bolduc, C.; Méry, S.; Nocera, T. Protection afforded by sunscreens containing inorganic sunscreening agents against blue light sensitivity induced by aminolevulinic acid. Dermatol. Surg. 2008, 34, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosin, F.C.P.; Teixeira, M.G.; Pelissari, C.; Corrêa, L. Resistance of oral cancer cells to 5-ALA-mediated photodynamic therapy. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 3554–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosin, F.C.P.; Teixeira, M.G.; Pelissari, C.; Corrêa, L. Photodynamic therapy mediated by 5-aminolevulinic acid promotes the upregulation and modifies the intracellular expression of surveillance proteins in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Photochem. Photobiol. 2019, 95, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X. Photodynamic treatment of colorectal cancer using chlorin e6-loaded poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-based nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 1939–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhiyentayev, T.; Xuan, Y.; Azhibek, D.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic inactivation of bacteria using polyethylenimine-chlorin(e6) conjugates: Effect of polymer molecular weight, substitution ratio of chlorin(e6) and pH. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, L.; Dong, Z.; Xin, X.; Yang, Z.; Deng, D.; Wagner, E.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Protein-drug conjugate programmed by pH-reversible linker for tumor hypoxia relief and enhanced cancer combination therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilho, M.L.; Jesus, V.P.S.; Vieira, P.F.A.; Hewitt, K.C.; Raniero, L. Chlorin e6-EGF conjugated gold nanoparticles as a nanomedicine based therapeutic agent for triple negative breast cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 33, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Heng, P.W.; Chan, L.W. pH-dependent complexation of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin with chlorin e6: effect on solubility and aggregation in relation to photodynamic efficacy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Ramsey, J.D.; Kabanov, A.V. Polymeric micelles for the delivery of poorly soluble drugs: From nanoformulation to clinical approval. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 156, 80–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Wu, H. Stimuli-responsive polymeric micelles for drug delivery and cancer therapy. Int. J Nanomedicine. 2018, 13, 2921–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, K.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Layered and orthogonal assembly of hydrophilic drugs and hydrophobic photosensitizers for enhanced cancer therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, F.; Zeng, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z.; Gao, M. Light-enhanced O2-evolving nanoparticles boost photodynamic therapy to elicit antitumor immunity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019, 11, 16367–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, E.Y.; Shi, W.J.; Fong, W.P.; Ng, D.K.P. Targeted delivery and site-specific activation of β-cyclodextrin-conjugated photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy through a supramolecular bio-orthogonal approach. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15461–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Simon, M.C. Glutathione metabolism in cancer progression and treatment resistance. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 2291–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Ahmed, R.; Mehta, M.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Recent advances in nanoparticle-based cancer drug and gene delivery. Adv. Cancer Res. 2018, 137, 115–170. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Polymeric micelles in cancer therapy: State of the art. J. Control. Release. 2021, 332, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Prakash Jain, J.; Domb, A.J.; Kumar, N. Exploiting EPR in polymer drug conjugate delivery for tumor targeting. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4785–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, M.; Dey, R.; Chen, Y. Nanomaterials for cancer therapy: current progress and perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawara, K.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Un, K.; Araki, T.; Kimura, T.; Higaki, K. Nanoparticle-based passive drug targeting to tumors: considerations and implications for optimization. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Feng, S.S. A strategy for precision engineering of nanoparticles of biodegradable copolymers for quantitative control of targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2010, 31, 9145–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Huang, D.; Deng, Y.; Yu, W.; Jin, Q.; Ji, J.; Fu, G. Chlorin e6 (Ce6)-loaded supramolecular polypeptide micelles with enhanced photodynamic therapy effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Iglesias, A.; Grzelczak, M.; Altantzis, T.; Goris, B.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Bals, S.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Donaldson, S.H. Jr; Chmelka, B.F.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Hydrophobic interactions modulate self-assembly of nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2012, 6, 11059–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.I.; Cheon, J.B.; Kim, S.H.; Nah, J.W.; Lee, Y.M.; Sung, Y.K.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.S. Clonazepam release from core-shell type nanoparticles in vitro. J. Control. Release. 1998, 51, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Wheate, N.J. Macrocycles as drug-enhancing excipients in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 100, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uekama, K.; Hirayama, F.; Irie, T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2045–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, T.M.; Kumar, P.V. A new approach for β-cyclodextrin conjugated drug delivery system in cancer therapy. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 266–300. [Google Scholar]
- Becket, G.; Schep, L.J.; Tan, M.Y. Improvement of the in vitro dissolution of praziquantel by complexation with alpha-, beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 179, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Heng, P.W.; Chan, L.W. pH-dependent complexation of hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin with chlorin e6: effect on solubility and aggregation in relation to photodynamic efficacy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, K.; Liu, Z.; Shi, M.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Layered and orthogonal assembly of hydrophilic drugs and hydrophobic photosensitizers for enhanced cancer therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Tao, W.; Hamaly, M.A.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Dreaden, E.C.; Brown, D.; Alkilany, A.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: journey inside the cell. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, N.S.; Mandal, N.; Patel, G.; Kirar, S.; Reddy, Y.N.; Kushwah, V.; Jain, S.; Kalia, Y.N.; Bhaumik, J.; Banerjee, U.C. Co-administration of zinc phthalocyanine and quercetin via hybrid nanoparticles for augmented photodynamic therapy. Nanomedicine. 2021, 33, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsjärvi, S.; Passirani, C.; Benoit, J.P. Passive and active tumor targeting with nanocarriers. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danhier, F.; Feron, O.; Préat, V. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Passive and active tumor targeting of nanocarriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Xu, C.; Sun, X.; Chen, X. Nanoparticle design strategies for enhanced anticancer therapy by exploiting the tumor microenvironment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3830–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, V.; Moliné, T.; Somoza, R.; Paciucci, R.; Kondoh, H.; LLeonart, M.E. Oxidative stress and cancer: An overview. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welters, M.J.; Fichtinger-Schepman, A.M.; Baan, R.A.; Flens, M.J.; Scheper, R.J.; Braakhuis, B.J. Role of glutathione, glutathione S-transferases and multidrug resistance-related proteins in cisplatin sensitivity of head and neck cancer cell lines. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.C.; Serpa, J. Glutathione in ovarian cancer: A double-edged sword. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhats, M.V.; Galievskii, V.A.; Zharnikova, E.S.; Knyukshto, V.N.; Lepeshkevich, S.V.; Stashevskii, A.S.; Trukhacheva, T.V.; Dzhagarov, B. M. Dynamics of photosensitized singlet oxygen generation and photophysical characteristics of chlorin e 6 in photolon ointment. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Chung, C.W.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kwak, T.W.; Jeong, Y.I.; Kang, D.H. Defensive mechanism in cholangiocarcinoma cells against oxidative stress induced by chlorin e6-based photodynamic therapy. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2014, 8, 1451–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García, A. .; Leonardi, D.; Lamas, M. Promising applications in drug delivery systems of a novel β-cyclodextrin derivative obtained by green synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ce6 contents (%, w/w) a | Particle size distribution (nm) | Polydispersity | Zeta potential (mV) |
|||
| NMR | UV | Int. ave. | Vol. ave. | Num. ave. | ||
| 17.23 | 17.3 | 162.9±24.4 | 152.0±23.2 | 142.7±20.2 | 0.202 | -10.4 |
| IC50 (mg/L) 1 | |
| Ce6 Ce6 + light irradiation bCDsu-ss-Ce6 NP bCDsu-ss-Ce6 NP + light irradiation |
n.d. 2 5.16 n.d. 1.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




