Submitted:
11 October 2023
Posted:
12 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Treatment Regimens
2.3. Efficacy Assessment
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
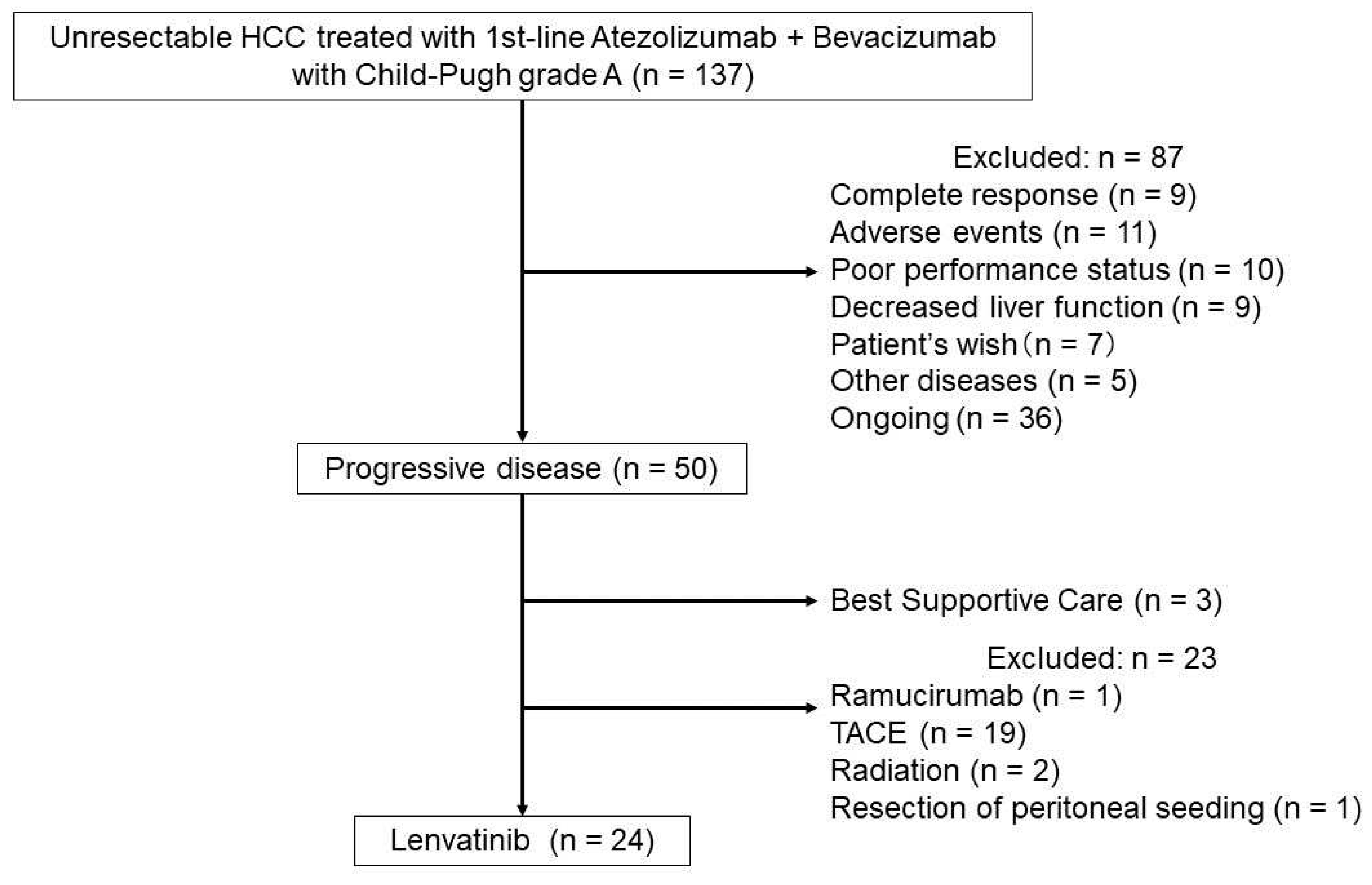
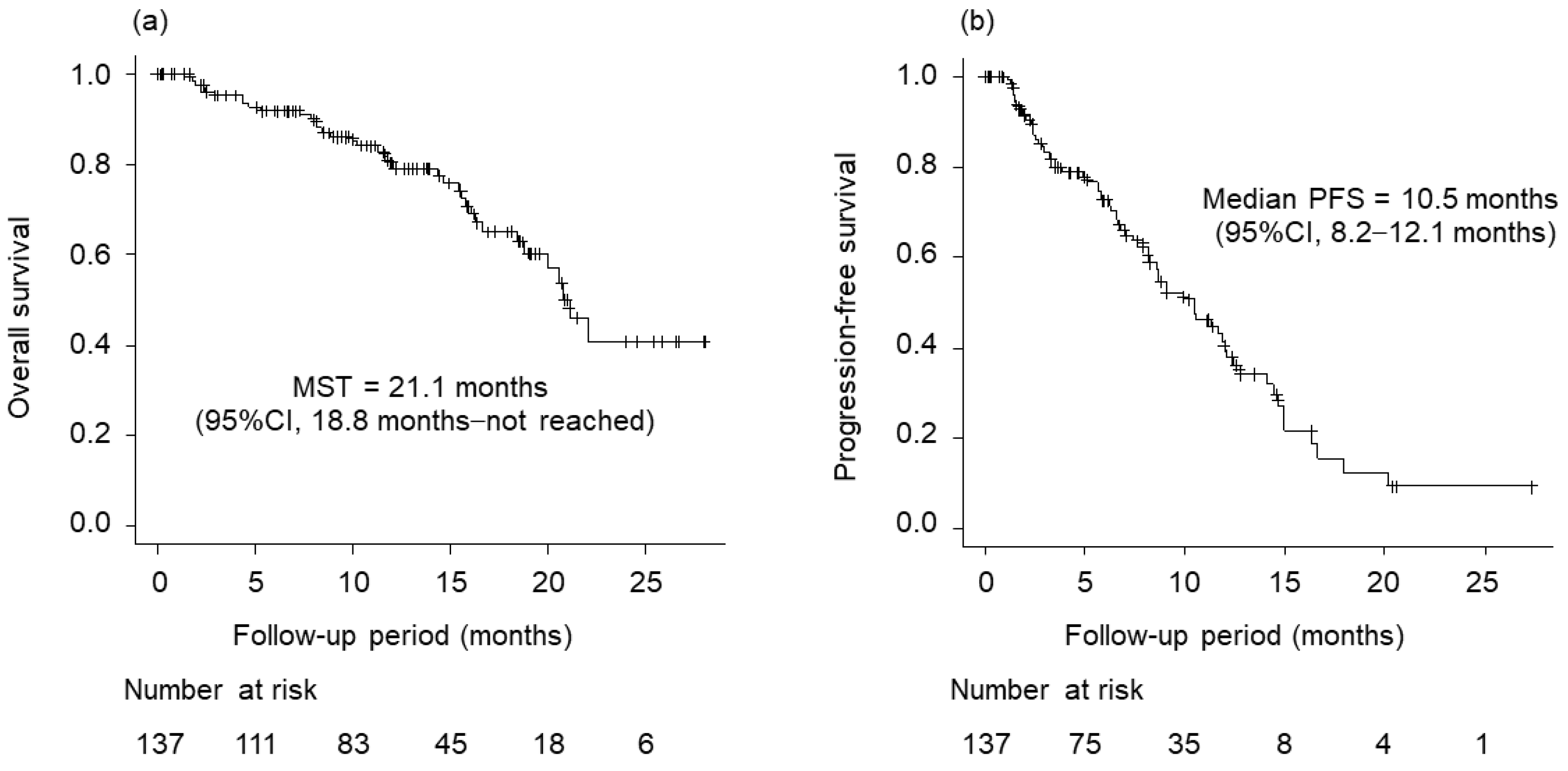
3.1. Patients’ Background Characteristics and Outcomes from the Beginning of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab
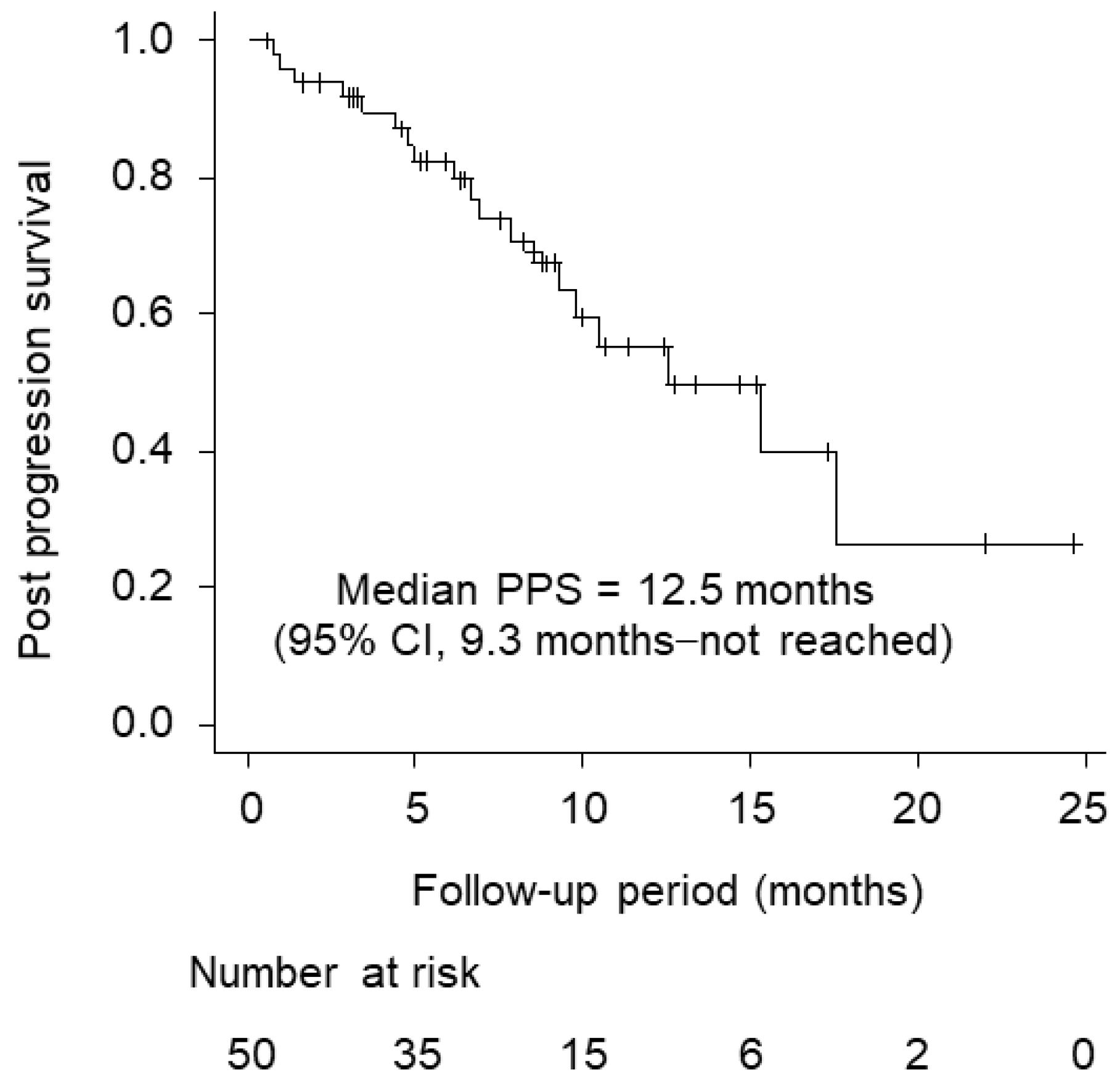
3.2. Patients’ Background Characteristics and Outcomes after Progression on Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab
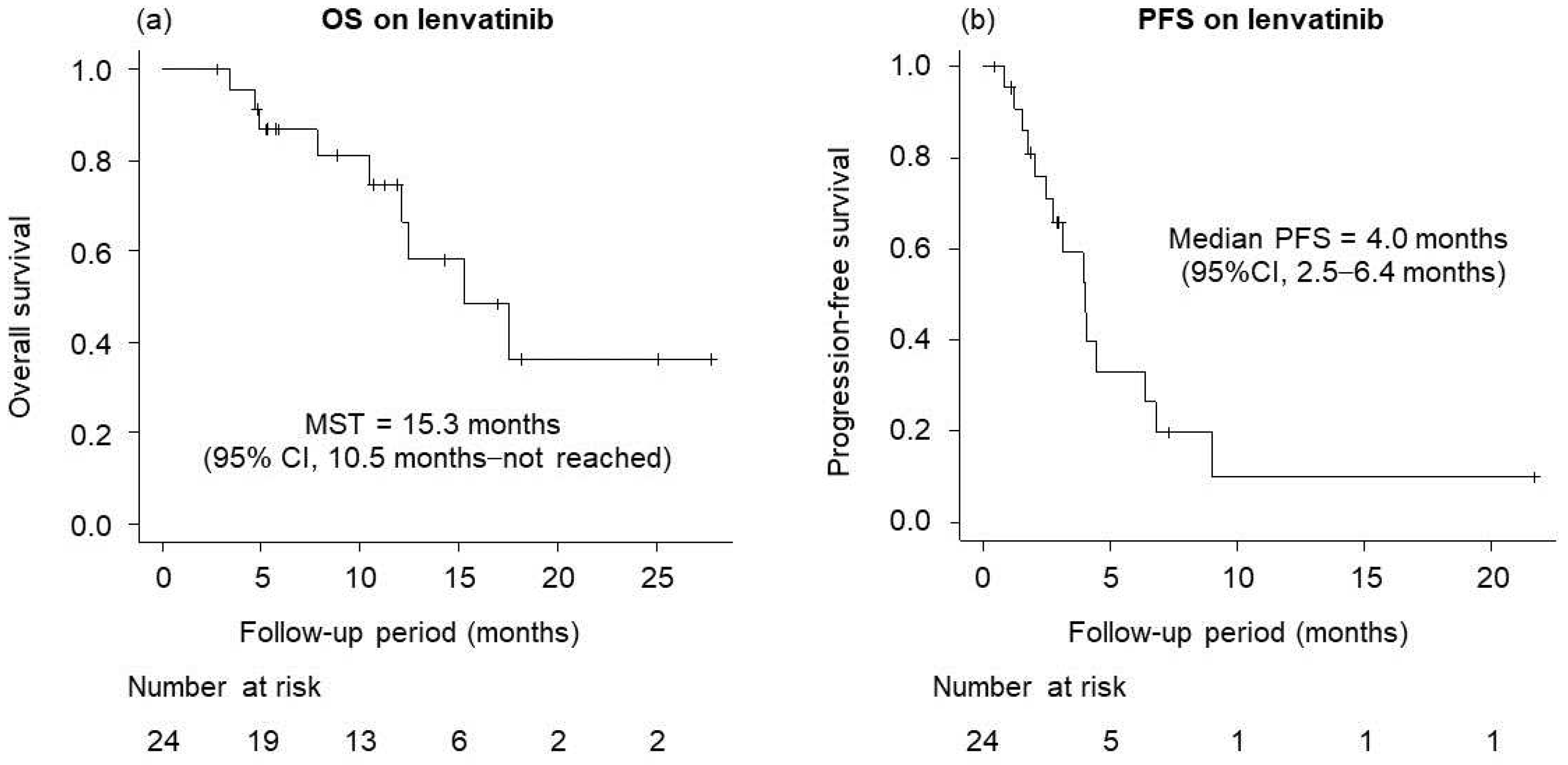
3.3. Antitumor Response to Lenvatinib Administration Following Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab.
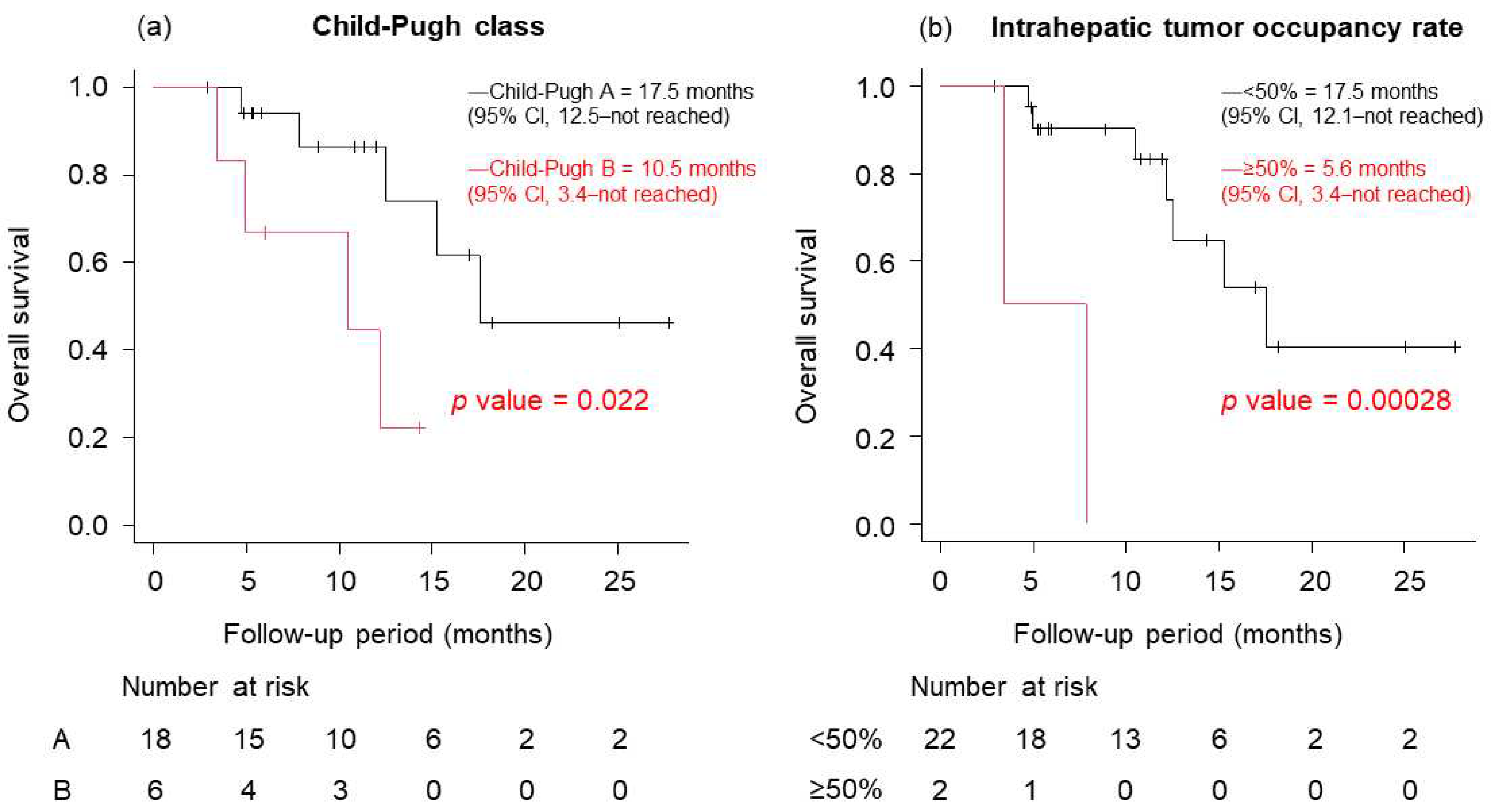
3.4. Prognostic Factors for OS and PFS on Lenvatinib
3.5. Treatment-Related Toxicities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R. L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209-249.
- Llovet, J. M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J. F.; de Oliveira, A. C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J. L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2008, 359, 378-390.
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R. S.; Qin, S.; Han, K. H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J. W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163-1173.
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y. H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56-66.
- Abou-Alfa, G. K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A. L.; El-Khoueiry, A. B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B. Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J. W.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2018, 379, 54-63.
- Zhu, A. X.; Kang, Y. K.; Yen, C. J.; Finn, R. S.; Galle, P. R.; Llovet, J. M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H. Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2019, 20, 282-296.
- Finn, R. S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P. R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T. Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A. O.; et al., Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 1894-1905.
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J. M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 2010, 30, 52-60.
- Gordan, J. D.; Kennedy, E. B.; Abou-Alfa, G. K.; Beg, M. S.; Brower, S. T.; Gade, T. P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Harris, W. P.; et al. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 4317-4345.
- Vogel, A.; Martinelli, E., Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann Oncol 2021, 32, 801-805.
- Llovet, J. M.; Villanueva, A.; Marrero, J. A.; Schwartz, M.; Meyer, T.; Galle, P. R.; Lencioni, R.; Greten, T. F.; Kudo, M.; Mandrekar, S. J.; et al. Trial design and endpoints in hepatocellular carcinoma: AASLD Consensus Conference. Hepatology 2021, 73 Suppl 1, 158-191.
- Sonbol, M. B.; Riaz, I. B.; Naqvi, S. A. A.; Almquist, D. R.; Mina, S.; Almasri, J.; Shah, S.; Almader-Douglas, D.; Uson Junior, P. L. S.; Mahipal, A.; et al. Systemic therapy and sequencing options in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2020, 6, e204930.
- Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Lin, J.; Bai, Y.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Seery, S.; Zhao, H. Comparing the efficacy and safety of second-line therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a network meta-analysis of phase III trials. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2020, 13, 1756284820932483.
- Yao, D. F.; Wu, X. H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, G. S.; Dong, Z. Z.; Yao, D. B.; Wu, W.; Qiu, L. W.; Meng, X. Y. Quantitative analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular density and their clinicopathologic features in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2005, 4, 220-226.
- Morais, C., Sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma. J Kidney Cancer VHL 2014, 1, 1-11.
- Teng, M. W.; Ngiow, S. F.; Ribas, A.; Smyth, M. J. Classifying cancers based on T-cell infiltration and PD-L1. Cancer Res 2015, 75, 2139-2145.
- Matsui, J.; Funahashi, Y.; Uenaka, T.; Watanabe, T.; Tsuruoka, A.; Asada, M. Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R) 2 and VEGF-R3 kinase. Clin Cancer Res 2008, 14, 5459-5465.
- Matsui, J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Funahashi, Y.; Tsuruoka, A.; Watanabe, T.; Wakabayashi, T.; Uenaka, T.; Asada, M. E7080, a novel inhibitor that targets multiple kinases, has potent antitumor activities against stem cell factor producing human small cell lung cancer H146, based on angiogenesis inhibition. Int J Cancer 2008, 122, 664-671.
- Yamada, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Yamada, Y.; Nokihara, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hirata, T.; Koizumi, F.; Nishio, K.; Koyama, N.; Tamura, T. Phase I dose-escalation study and biomarker analysis of E7080 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2011, 17, 2528-2537.
- Boss, D. S.; Glen, H.; Beijnen, J. H.; Keesen, M.; Morrison, R.; Tait, B.; Copalu, W.; Mazur, A.; Wanders, J.; O'Brien, J. P.; et al. A phase I study of E7080, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer 2012, 106, 1598-1604.
- Osa, A.; Uenami, T.; Koyama, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Okuzaki, D.; Takimoto, T.; Hirata, H.; Yano, Y.; Yokota, S.; Kinehara, Y.; et al. Clinical implications of monitoring nivolumab immunokinetics in non-small cell lung cancer patients. JCI Insight 2018, 3 (19), e59125.
- Harding, J. J.; Nandakumar, S.; Armenia, J.; Khalil, D. N.; Albano, M.; Ly, M.; Shia, J.; Hechtman, J. F.; Kundra, R.; El Dika, I.; et al. Prospective genotyping of hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical implications of next-generation sequencing for matching patients to targeted and immune therapies. Clin Cancer Res 2019, 25, 2116-2126.
- Yamauchi, M.; Ono, A.; Ishikawa, A.; Kodama, K.; Uchikawa, S.; Hatooka, H.; Zhang, P.; Teraoka, Y.; Morio, K.; Fujino, H.; et al. Tumor fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 level predicts the efficacy of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 2020, 11, e00179.
- Tohyama, O.; Matsui, J.; Kodama, K.; Hata-Sugi, N.; Kimura, T.; Okamoto, K.; Minoshima, Y.; Iwata, M.; Funahashi, Y. Antitumor activity of lenvatinib (e7080): an angiogenesis inhibitor that targets multiple receptor tyrosine kinases in preclinical human thyroid cancer models. J Thyroid Res 2014, 2014, 638747.
- Johira, Y.; Kawaoka, T.; Kosaka, M.; Shirane, Y.; Miura, R.; Murakami, S.; Yano, S.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; Ando, Y.; et al. Pathological complete response to lenvatinib after failure of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2022, 11, 174-177.
- Yano, S.; Kawaoka, T.; Johira, Y.; Miura, R.; Kosaka, M.; Shirane, Y.; Murakami, S.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; Ando, Y.; et al. Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with response to lenvatinib after atezolizumab plus bevacizumab. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021, 100, e27576.
- Lu, L. C.; Hsu, C.; Shao, Y. Y.; Chao, Y.; Yen, C. J.; Shih, I. L.; Hung, Y. P.; Chang, C. J.; Shen, Y. C.; Guo, J. C.; et al. Differential organ-specific tumor response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 480-490.
- Müller, P.; Rothschild, S. I.; Arnold, W.; Hirschmann, P.; Horvath, L.; Bubendorf, L.; Savic, S.; Zippelius, A. Metastatic spread in patients with non-small cell lung cancer is associated with a reduced density of tumor-infiltrating T cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2016, 65, 1-11.
- Ando, Y.; Kawaoka, T.; Kosaka, M.; Shirane, Y.; Johira, Y.; Miura, R.; Murakami, S.; Yano, S.; Amioka, K.; Naruto, K.; et al. Early tumor response and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in real-world practice. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13, 3958.
- Abou-Alfa, G. K.; Chan, S. L.; Kudo, M.; Lau, G.; Kelley, R. K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.-K.; Dao, T. V.; Toni, E. N. D.; et al. Phase 3 randomized, open-label, multicenter study of tremelimumab (T) and durvalumab (D) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40 (4_suppl), 379-379.
- Pal, S. K.; Albiges, L.; Tomczak, P.; Suárez, C.; Voss, M. H.; de Velasco, G.; Chahoud, J.; Mochalova, A.; Procopio, G.; Mahammedi, H.; et al. Atezolizumab plus cabozantinib versus cabozantinib monotherapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma after progression with previous immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment (CONTACT-03): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 185-195.
| All (n = 137) | |
|---|---|
| Age, range, y | 75 (47–92) |
| Sex (male/female), n | 107/30 |
| Performance status (0/1/2), n | 113/18/6 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/HBV+HCV/NBNC), n | 15/48/2/72 |
| Child–Pugh score (5/6), n | 84/53 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b), n | 52/45/40 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50%/≥50%), n | 130/7 |
| Size of main tumor, range, mm | 28 (0–220) |
| Microvascular invasion (absent/present), n | 112/25 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (absent/present), n | 93/44 |
| HCC stage (II/III/IVa/IVb), n | 33/50/22/32 |
| BCLC stage (A/B/C), n | 8/63/66 |
| Serum alpha-fetoprotein, range, ng/ml | 18.1 (1.2–63642) |
| Serum des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, range, mAU/ml | 236 (11–197680) |
| Observation period, range, months | 11.7 (1–28) |
| n = 50 | |
|---|---|
| Sex (male/female), n | 41/9 |
| Performance status (0/1/2), n | 32/12/5 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/NBNC), n | 7/19/24 |
| Child–Pugh grade (A/B/C), n | 34/14/2 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b/3), n | 12/10/23/5 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50%/≥50%), n | 45/5 |
| Size of main tumor, range, mm | 33 (0–170) |
| Microvascular invasion (absent/present), n | 35/15 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (absent/present), n | 27/23 |
| HCC stage (II/III/IVa/IVb), n | 6/16/9/19 |
| BCLC stage (A/B/C), n | 3/15/32 |
| Serum alpha-fetoprotein, range, ng/ml | 105.3 (0.8–64620) |
| Serum des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, range, mAU/ml | 2842.5 (22–247805) |
| Systemic therapy after atezolizumab plus bevacizumab | 25 (LEN 24, RAM 1) |
| n = 24 | |
|---|---|
| Sex (male/female), n | 20/4/ |
| Performance status (0/1/2), n | 19/4/1 |
| Etiology (HBV/HCV/NBNC), n | 5/11/8 |
| Child–Pugh grade (A/B/C), n | 34/14/2 |
| mALBI grade (1/2a/2b/3), n | 8/6/7/3 |
| Relative tumor volume (<50%/≥50%), n | 22/2 |
| Size of main tumor, range, mm | 30 (0–120) |
| Microvascular invasion (absent/present), n | 16/8 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (absent/present), n | 13/11 |
| HCC stage (II/III/IVa/IVb), n | 2/9/3/10 |
| BCLC stage (A/B/C), n | 8/16 |
| Serum alpha-fetoprotein, range, ng/ml | 140.5 (1.5–64620) |
| Serum des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin, range, mAU/ml | 2614 (25–214866) |
| Time to LEN administration after Atez+Bev, days | 17 (4–63) |
| %(n) | RECIST 1.1 | mRECIST |
|---|---|---|
| CR | 0.0 (0) | 4.2 (1) |
| PR | 33.3 (8) | 50.0 (12) |
| SD | 41.7 (10) | 25.0 (6) |
| PD | 20.1 (5) | 16.7 (4) |
| N.E | 4.2 (1) | 4.2 (1) |
| ORR | 33.3 (8) | 54.2 (13) |
| DCR | 75.0 (18) | 79.2 (19) |
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | ||
| Sex | Male | 0.13 | |||
| Etiology | Viral infection | 0.72 | |||
| Child–Pugh grade | A | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.02 0.76 | 0.02 |
| Microvascular invasion | Absent | 0.63 | |||
| Extrahepatic metastasis | Absent | 0.37 | |||
| Relative tumor volume | <50% | <0.01 | 0.03 | 0.003 0.35 | <0.01 |
| Serum alpha-fetoprotein | <400 ng/ml | 0.40 | |||
| TACE/TAI combination | yes | 0.13 | |||
| Event %(n) | All Patients (n = 24) | |
|---|---|---|
| Any Grade | Grade 3 or 4 | |
| Hypertension | 62.5 (15) | 16.7 (4) |
| Fatigue | 58.3 (14) | 25.0 (6) |
| Anorexia | 45.8 (11) | 12.5 (3) |
| Diarrhea | 41.7 (10) | 4.2 (1) |
| Proteinuria | 29.2 (7) | 20.8 (5) |
| Hand-foot syndrome | 29.2 (7) | 0.0 (0) |
| Hypothyroidism | 20.8 (5) | 0.0 (0) |
| Renal dysfunction | 12.5 (3) | 4.2 (1) |
| Increased AST or ALT | 8.3 (2) | 0.0 (0) |
| Hoarseness | 8.3 (2) | 0.0 (0) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 8.3 (2) | 4.2 (1) |
| Interstitial pneumonia | 4.2 (1) | 0.0 (0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





