1. Introduction
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is an inherited hemoglobinopathy characterized by the presence of abnormal hemoglobin resulting in the formation of hard and sticky C-shaped red cells [
1]. This is caused by a single base-pair point mutation in the 6th position of the beta globin chain leading to substitution of the amino acid glutamic acid to valine (GAG to GTG). SCD encompasses homozygous mutations (S/S) as well as combined hemoglobinopathies, which may have a similar clinical presentation, such as the heterozygous mutation with a β0-thalassemia (S/β0) or other mutations (e.g., HbSC) [
2,
3]. SCD results in the formation of abnormal hemoglobin polymers when deoxygenated, with decreased deformability and the typical sickle form of the erythrocytes. The clinical manifestations of SCD are varied and due to the short life span of sickled red blood cells and their tendency to get stuck in the blood vessels [
4]. In fact, sickled erythrocytes possess many unfavorable physiologic properties and induce vascular changes that promote vaso-occlusion, infarction, hemolysis, and inflammation. Clinical manifestations of SCD are vaso-occlusive (VOC) crisis, acute pain syndrome, organ infarction, and hemolytic anemia. Relapsing vaso-occlusive crises can affect multiple organ systems, and SCD patients have an increased risk of stroke, renal dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, retinal illness, and avascular necrosis [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5].
Currently, the availability of proper care and appropriate treatment strategies, including the wide use of hydroxyurea as inducer of fetal hemoglobin synthesis, regular transfusions, and iron chelation therapy, have resulted in increased life expectancy and quality of life in patients suffering SCD [
6,
7]. The prolonged life span also increases the possibility that SCD patients face pregnancy. Pregnancy in SCD is a high-risk situation, especially during the third trimester of gestation, and in the post-partum period, due to chronic hypoxia and vaso-occlusive phenomena in the maternal-fetal microcirculation [
8]. Of note, it is reported an increased incidence of abortion, such as increased risk of pre-eclampsia, preterm delivery, caesarean section, and pulmonary embolism. In addition, fetal complications, such as intra-uterine growth restriction, prematurity, or fetal loss are more frequent in SCD pregnancies [
9]. Hydroxyurea, commonly used in symptomatic patients, is contraindicated in pregnancy due to concerns for the fetus health. Indeed, transfusion therapy is the mainstay to relief SCD symptoms. Nonetheless, the transfusion management of pregnancy in SCD patients remains controversial; although there is a consensus on the need for a strict and multidisciplinary follow-up within specialized structures, the benefit of prophylactic management, either by simple transfusions or by automated red blood cell exchange (aRBCX), is not unanimously recognized [
10,
11,
12].
In this study, we illustrate the cases of three SCD pregnant patients who underwent aRBCX procedures in different clinical situations. Moreover, we reviewed current literature to investigate the management of pregnancy in SCD, particularly regarding the practice of aRBCX.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, treatment and procedures
Three case reports are reported of aRBCX performed either for prophylactic or therapeutic indications. Data were anonymously recorded, and patients’ informed consent was obtained. As per the centre's routine procedure, all SCD patients were serologically typed for ABO, Rh (C, D, E, c, e), Kell, Duffy (Fya, Fyb), Kidd (Jka, Jkb), and MNS (S, s, M, N) blood group antigens. In addition, extended RBC antigen typing was determined and confirmed by molecular biology techniques using Human Erythrocyte Antigen (HEA) BeadChip (BioArray Solutions Ltd., Warren, NJ) [
13]. Before transfusion, the irregular antibody screening was performed and red blood cell (RBC) units were selected according to the broadest possible donor-recipient match. Prestorage leukoreduced RBCs with a Hct of approximatively 60% were used. Transfusion therapy was administered with a Hb target not exceeding 10 g/dl. RBC units were transfused with or without concomitant phlebotomy, depending on the pre-transfusion hematocrit (Hct) value: for Hct <30%, no phlebotomy was carried out, whereas for Hct ≥30%, patients usually received infusion of saline solution, isovolemic phlebotomy and then RBC unit transfusion. The aRBCX was performed using the cell separator Optia (Optia Spectra Apheresis System; Terumo BCT, Lakewood, CO). Pre- and post-RBCX complete blood count and HbS percentage (HPLC, BIO-RAD, Hercules, Ca, USA) were regularly determined. The exchange volumes was estimated according to patient gender, age, body weight, height, pre-procedure Hct and HbS level, and average Hct of blood products. The fraction of residual RBCs (FCR) and the volume to be replaced were estimated to achieve a target HbS of <30% and a final Hct of 30 ± 3% to avoid hyperviscosity [
14,
15]. Peripheral venous accesses were used whenever possible; otherwise, a temporary central vascular catheter (CVC) was placed. Data about single aRBCX procedure in pregnancy (venous access, blood volume substituted, HbS target and desirable FCR) were collected.
2.2. Systematic review
We conducted a systematic review on red blood cell exchange in the management of SCD in pregnancy. The reporting of this systematic review was guided by the standards of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement, when applicable. We performed a systematic search on the PubMed database using the following queries: “Pregnancy "[Mesh] AND “Anemia, Sickle Cell "[Mesh] AND “Blood Component Removal "[Mesh]. No additional search filters were applied. CGV, CP, SC, and LT independently controlled all references, including case reports, case series, and reviews. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved together. Papers not reporting procedures of erythrocytapheresis in pregnant homozygous HbS women, communications at congresses, duplicated studies, case reports, narrative reviews and papers with an abstract not in English were excluded. Up to August 2023, 11 total references were identified. We additionally screened the reference lists and the first 20 ‘similar articles’ in PubMed of included studies for additional eligible studies. In the end, seven papers were included and discussed in the review (
Figure 1). Collected data included study type, patient characteristics, erythrocytapheresis schedule and indications, procedure’s technical details, maternal and fetal outcomes.
3. Results
In the
Table 1 we report the main features of SCD patients described as follows, and the technical details of apheresis procedures performed in pregnancies.
3.1. Clinical reports
Case 1
A 37 years old patient was affected by sickle cell anemia combined with the 3.7 deletion of the hemoglobin alpha gene. She irregularly presented at hematological controls and was not on a regular transfusion program. The co-inheritance of SCD with α 3.7 deletion is associated to a less severe SCD phenotype and it could explain her stable baseline Hb level, decreasing the tendency of HbS to polymerize and reducing the rate of hemolysis [
16]. She had received transfusions only in occasion of previous three pregnancies in 2016 and 2017, all exited in miscarriages at gestational age of 10, 14 and 15 weeks, respectively. She also had subjected two aRBCX courses in emergency: in 2018 for a VOC with severe hemolysis and in 2019 for a painful crisis due to gallbladder stones. In 2021, she resumed hematological controls since she was at 14 weeks of the fourth gestation. Patient history was silent for recent painful crisis, VOCs or thromboembolic events. Antithrombotic prophylaxis was promptly set up with cardio aspirin 100 mg/die and a transfusion support every three weeks was resumed, in association with phlebotomy to maintain Hct within 30%. Obstetric echo tomography on the second and third trimesters were unremarkable. The HbS level during pregnancy ranged between 60% and 70. Patient was completely asymptomatic until week 36, when she presented at our emergency department with fever and pain diffused to the entire vertebral region, poorly responsive to the antalgic therapy. The search for Sars-Cov-2 infection was positive. An aRBCX was performed, reducing HbS level from 65% to 29%. Clinical conditions progressively improved and patient was discharged (
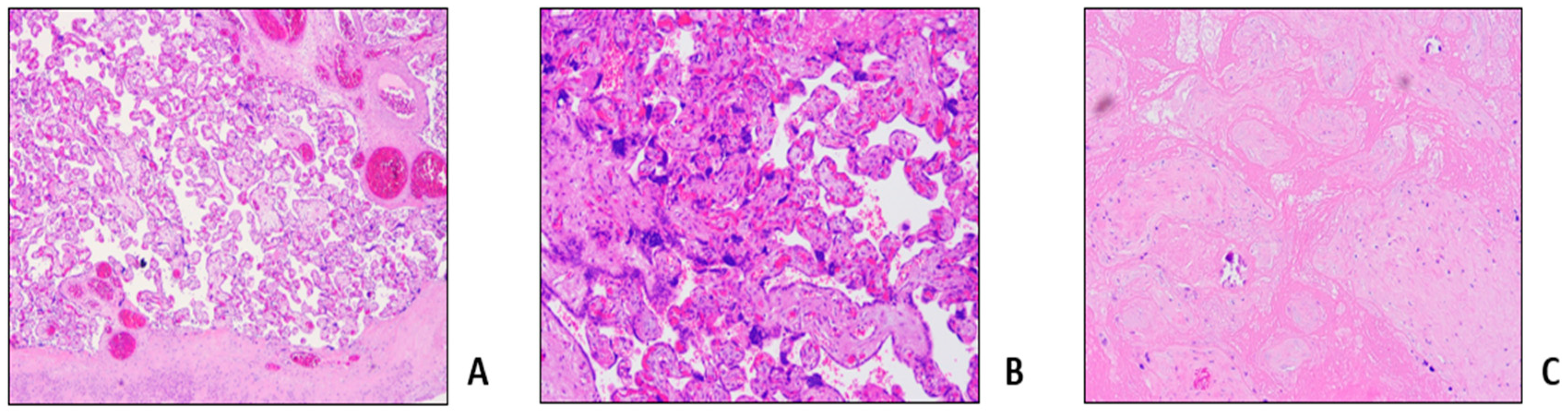
Table 1, Procedure 1A). Pregnancy ended 2 weeks later with a caesarean section for non-response to birth induction, with no maternal or fetal complications. Histological examination of placenta and fetal annexes showed maternal vascular malperfusion, and intravillar thrombosis (
Figure 2).
Case 2
Patient diagnosis dates to 1994 when she was 12 years old, with the onset of thrombophlebitis of the left leg, and since then she had been on a regular blood transfusion regimen at a different hospitals. The patient was lately referred to our Hematology Department in 2011, at the age of 23, during her first pregnancy; a silent medical history was collected at that time, with the exception of 2 previous surgeries (ovarian cysts removal in 2008, and tonsillectomy in 2010) performed without complications. She was initially treated with monthly simple transfusion to maintain Hb levels between 9 and 10 gr/dl. During the second trimester of pregnancy, the patient experienced widespread lumbar pain and dyspnea, because of a severe hemolytic crisis, requiring the first aRBCX procedure with rapid clinical beneficial (
Table 1, Procedure 2A). The patient continued transfusion support; at week 35 a urgent caesarean section was performed for amnionitis: no adverse maternal or fetal outcomes were recorded. During the following months, the patient experienced recurrent VOCs, so she stopped breast-feeding and started therapy with hydroxyurea, discontinued in 2015 for intolerance and occurrence of skin ulcers; patient then maintained transfusion support on a monthly basis. In 2016 and 2018 she experienced other two pregnancies, both resulting in miscarriage at approximatively 8 weeks; no antithrombotic prophylaxis or RBC exchange schedule were implemented due to the early occurrence of the adverse obstetric events. In 2019 patient had her fourth pregnancy: antithrombotic prophylaxis with enoxaparin was promptly started and transfusion regimen was intensified, in association with phlebotomies to maintain an average Hb value between 9 and 10 gr/dl and a Hct inferior to 30%. The patient frequently complained of discomfort for phlebotomies. In addition, she referred occasional painful episodes, responsive to anti-inflammatory oral therapy. To limit the antalgic therapy requirement, an initial aRBCX procedure was performed at week 16 of gestation, lowering HbS values from 46% to 19% (
Table 1, procedure 2B). A second aRBCX was prophylactically performed at week 28, with a HbS reduction from 40% to 25% (
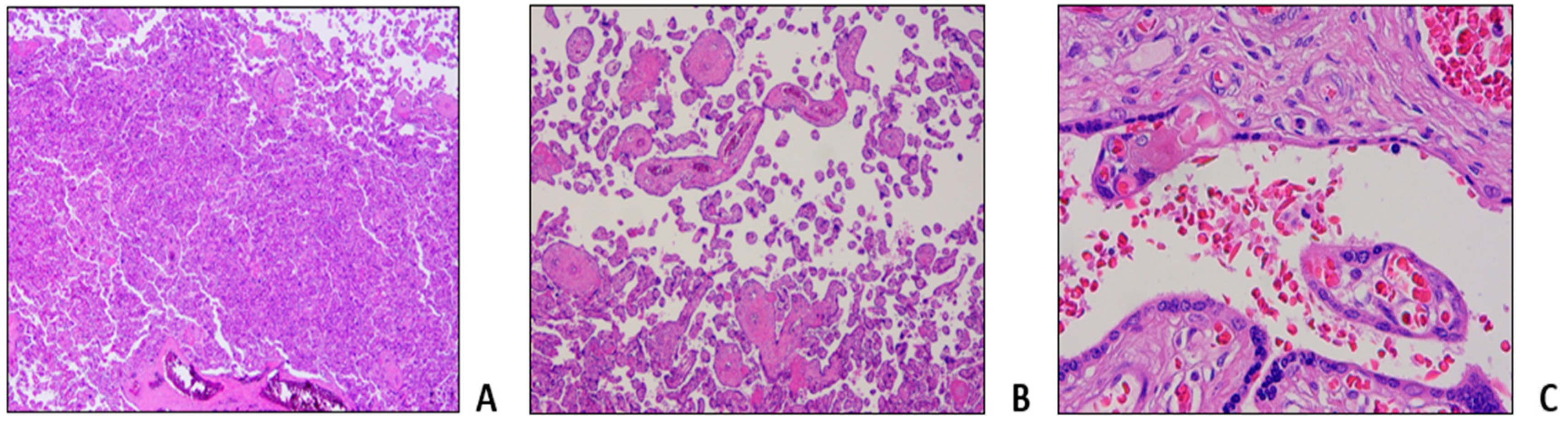
Table 1, Procedure 2C). Pregnancy evolved without fetal distress or intrauterine growth retardation as documented by serial echotomography assessment, that only evidenced a slight increase of pulsatility index (PI) of the uterine arteries at week 20, not further confirmed at subsequent controls. Patient delivered at week 36+4 with an elective caesarean section without gynecological and fetal complications. Histological examination of placenta and fetal annexes was performed, with the findings of maternal vascular malperfusion, perivillar fibrin deposits, and evidence of drepanocytes in the intervillous spaces (
Figure 3).
Case 3
Patient was diagnosed with drepanocytosis at the age of 6. She was first evaluated at our center in 2014, at the age of 34, during her first pregnancy: since then she had been scarcely symptomatic, and she seldom received transfusions. She was at the 8th week of gestation: antiplatelet prophylaxis with low dose molecular heparin was settled, patient remained asymptomatic without need for transfusions and pregnancy regularly progressed for the first two trimesters. At week 24 of gestation, a prophylactic aRBCX was performed (
Table 1, Procedure 3A). At week 38, patient underwent a planned caesarean section and delivered a healthy newborn Patient returned to our observation in 2021 for a new initial pregnancy (week 7). She reported two abortion episosed at 11 and 10 weeks of gestation, respectively, both occurring under antiplatelet therapy. Considering the HbS value of 90% and the previous obstetrical history, antithrombotic prophylaxis with enoxaparin was started, and an aRBCX was promptly performed (week 8 of gestation,
Table 1, Procedure 3B). HbS level reduced to 21%: a regular transfusion support every three weeks was then started, with occasional phlebotomies depending on the Hct level. Due to the progressive raise of HbS (76%) a new aRBCX was performed on week 34 of gestation, resulting in the HbS decrease to 31% (
Table 1, Procedure 3C). Then, patient underwent an elective caesarean section at week 39; no gynecological or fetal complications were recorded.
3.2. Literature revision
In total eleven studies were retrieved from literature search. Seven articles were excluded after abstract and full text screening. Three additional papers were identified and included after checking reference lists and the first 20 ‘similar articles’ in PubMed of the already included studies. Overall, seven papers were finally discussed in the review. Results are summarized in
Table 2 [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
4. Discussion
Appropriate transfusion support for patients with SCD are still a matter of debate and the use of erythrocytapheresis rather than simple transfusions during pregnancy remains controversial [
8]. From the revision of literature, it emerges that therapeutical approaches are very different among specialist centers. All the studies included in the review investigated the feasibility and the safety of aRBCX in pregnancy, exploiting the association between erythrocytapheresis-based approaches and maternal and fetal outcome [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. However, it is difficult to achieve definitive clinical indication, because of the eterogenity of apheresis schedule, the timing of RBCX procedures, and the different clinical outcome evaluated.
The American Society for Hematology and British Society of Hematology guidelines for management of SCD in pregnancy do not recommend to routinely start a program of prophylactic transfusion, but to consider the indication on a case-by-case basis, especially in women with a history of severe SCD-related complications before current pregnancy [
10,
11]. RBC transfusion should be considered a standard of care treatment, if and when clinically indicated on the basis of hemoglobin value and HbS level [
12,
24], while ASFA guidelines for therapeutic apheresis recommend aRBCX as a second-line treatment in pregnant patients (Category II, Grade 2B) [
25].
The most frequent therapeutic indication for RBCX is acute stroke, while it is indicated as prophylactic measure to prevent the recurrence of cerebrovascular accidents and before extensive surgery [
24,
25]; likewise, only few papers, mostly retrospectively studies [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23] or sporadic cases reports [
26,
27], deal with the use of RBCX in pregnancy, without reaching reliable conclusions. The first description of erythrocytapheresis for sickle cell disease during pregnancy dates to 1980, when Key et al. reported outcomes on eight pregnant women: all pregnancies were carried to term, with the delivery of healthy infants. There was no fetal or neonatal morbidity, except for a case of puerperal endometritis [
17]. Later on, Lee et al. in 1991 investigated possible RBCX-induced hemodynamic modifications occurring either in the mother or in the fetus: they observed only a slight tendency for reduced post-RBCX cardiac output in the mother, while no alterations were detected in the fetus. The authors concluded that changes in maternal hemodynamic and metabolic function were negligible [
18].
Among cases above described, the aRBCX was adopted as a “prophylactic approach” to prevent obstetric complications in all the three patients. Notably, all of them had undergone periodic ultrasound monitoring of fetal growth with uterine and cerebral Doppler velocimetry, not showing fetal distress or intrauterine growth retardation as documented by serial echotomography assessment. Nevertheless, we documented microcirculation obstructions at placental histopathologic findings with the presence of perivillar fibrin deposits, villar hypoplasia and parenchymal infarctions, all signs of maternal vascular malperfusion. Of note a patient experienced aRBCX early, at week 8 of gestation. Maternal vascular malperfusion is the predominant lesion in placentas of women with SCD and is strongly associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes, mainly small for gestational age infants, preterm birth, and stillbirth [
28]. The same histologic findings were documented by Vianello et al. that conducted a retrospective study enrolling 18 SCD women in a program of early prophylactic erytrocytoapheresis in association to LMWH [
22]: aRBCX was carried out every 3 or 4 weeks during pregnancy starting from a mean of 10.7 weeks of gestation until delivery, for a total of 160 procedures. Authors reported a positive impact on maternal outcomes (no episodes of severe VOCs, acute chest syndrome, and eclampsia were observed) and an improvement in newborn birthweight compared with previous studies. However, the 6.5% of pregnancies resulted in stillbirth, and placental histopathological examination showed signs of maternal vascular malperfusion and erythroblastosis in cord blood, compatible with fatal hypoxia due to vascular insufficiency [
22].
The effects of prophylactic aRBCX procedures on a considerable group of patients were first reported by Morrison et al., that described 131 pregnant women who received apheresis during pregnancy, while the control group received simple transfusion support [
19]. Patients on regular aRBCX regimen had a lower incidence of pregnancy-related complications (prenatal death, low birthweight infants and preterm deliveries) and a decreased hospital stay when compared to the control group. Two patients developed post-transfusion hepatitis and five had post-transfusion reactions [
19]. Similarly, a lower risk of intrauterine growth restriction and oligohydramnios in pregnant treated with aRBCX was reported also by other authors, that investigated the effects of prophylactic transfusion by means of erythrocytapheresis at the beginning of the third trimester of pregnancy, suggesting a potential improvement in fetal morbidity [
20]. Asma et al. retrospectively evaluated the complications of SCD in 37 pregnant patients: 24 patients received 43 prophylactic exchange procedures at variable time points, and they were compared with a control group of 13 patients [
21]. There was a significant difference in maternal mortality and incidence of VOCs between the study and control groups; however, due to study limitations, no difference in fetal complications’ incidence was stated [
21]. In a subsequent study performed at the same institution, higher rate of painful crises, preeclampsia, and preterm birth in control vs prophylactic aRBCX group were reported [
23].
A meta-analysis performed by Malinowski et al. in 2015 assessed the effects of prophylactic compared with on-demand red blood cell transfusions on maternal outcomes in pregnant SCD women [
29]; three studies involved prophylactic RBCX were also included. The authors concluded that this approach may positively affect maternal complications and reduce perinatal mortality, but these results were weakened by the paucity and the low quality of available evidences [
29].
No other studies have been afterwards published comparing prophylactic aRBCX to other treatment modality in SCD patients. Currently a multicenter feasibility trial to evaluate serial prophylactic exchange blood transfusion in pregnant women with SCD (TAPS-2, NCT03975894) is ongoing in UK [
30].
5. Conclusions
Our experience demonstrates that women with SCD with multi-abortion history can carry a pregnancy to term performing aRBCX at early pregnancy, allowing an efficacious and rapid HbS reduction. In our clinical practice prophylactic aRBCX in pregnancy is a feasible and safe procedure, however this strategy requires specialized equipment and an experienced apheresis team. Further research, with appropriately powered prospective trials about the transfusion modalities in this high-risk group of pregnant women, will be desirable to confirm our approach.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Caterina Giovanna Valentini and Luciana Teofili; Data curation, Caterina Giovanna Valentini, Claudio Pellegrino, Sara Ceglie, Vincenzo Arena, Patrizia Chiusolo and Luciana Teofili; Methodology, Caterina Giovanna Valentini, Claudio Pellegrino and Luciana Teofili; Resources, Caterina Giovanna Valentini, Claudio Pellegrino, Sara Ceglie, Vincenzo Arena, Francesca Di Landro, Patrizia Chiusolo and Luciana Teofili; Supervision, Caterina Giovanna Valentini and Luciana Teofili; Validation, Caterina Giovanna Valentini and Luciana Teofili; Visualization, Caterina Giovanna Valentini and Luciana Teofili; Writing – original draft, Caterina Giovanna Valentini, Claudio Pellegrino, Sara Ceglie and Luciana Teofili; Writing – review & editing, Caterina Giovanna Valentini and Luciana Teofili. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to reason that it concerns a literature revision, and as for the descriptions of the clinical reports, written informed consent was requested directly to the patients.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for their anonymized information to be published in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Because of the confidentiality agreements, the data analyzed for this study are only available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are in debt to all members of the medical and nursing staff of the apheresis unit.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
References
- Piel FB, Steinberg MH, Rees DC. Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017, 376, 1561–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serjeant, GR. Sickle-cell disease. Lancet. 1997, 350, 725–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart MJ, Nagel RL. Sickle-cell disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1343–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Eaton, W.; Hofrichter, J. Hemoglobin S gelation and sickle cell disease. 1987, 70, 1245–66.
- Paintsil, V.; Ally, M.; Isa, H.; Anie, K.A.; Mgaya, J.; Nkanyemka, M.; Nembaware, V.; Oppong-Mensah, Y.G.; Ndobho, F.; Chirande, L.; et al. Development of multi-level standards of care recommendations for sickle cell disease: Experience from SickleInAfrica. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1052179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manwani, D.; Frenette, P.S. Vaso-occlusion in sickle cell disease: pathophysiology and novel targeted therapies. Blood 2013, 122, 3892–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Early, M.L.; Eke, A.C.; Gemmill, A.; Lanzkron, S.; Pecker, L.H. Comparisons of Severe Maternal Morbidity and Other Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Pregnant People With Sickle Cell Disease vs Anemia. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2254545–e2254545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Ellsworth, P.; Key, N.S. Pregnancy in sickle cell trait: what we do and don’t know. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.K.; Boulet, S.L.D.; Cotsonis, G.M.; Geary, F.; Jamieson, D.J.; Lindsay, M. Association of Sickle Cell Disease With Severe Maternal Morbidity. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2022, 141, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.T.; Alsawas, M.; Fasano, R.M.; Field, J.J.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Howard, J.; Kameka, M.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; Pirenne, F.; Shi, P.A.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: transfusion support. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteng-Ntim E, Pavord S, Howard R, Robinson S, Oakley L, Mackillop L, Pancham S, Howard J; British Society for Haematology Guideline. Management of sickle cell disease in pregnancy. A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2021, 194, 980–995.
- Davis, B.A.; Allard, S.; Qureshi, A.; Porter, J.B.; Pancham, S.; Win, N.; Cho, G.; Ryan, K.; Haematology, T.B.S.F. Guidelines on red cell transfusion in sickle cell disease Part II: indications for transfusion. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 176, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzulu, R.; Piccirillo, N.; Orlando, N.; Massini, G.; Maresca, M.; Scavone, F.; Ricerca, B.M.; Zini, G. The role of molecular typing and perfect match transfusion in sickle cell disease and thalassaemia: An innovative transfusion strategy. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2017, 56, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stussi G, Buser A, Holbro A. Red Blood Cells: Exchange, Transfuse, or Deplete. Transfus Med Hemother. 2019, 46, 407–416.
- Biller, E.; Zhao, Y.; Berg, M.; Boggio, L.; Capocelli, K.E.; Fang, D.C.; Koepsell, S.; Music-Aplenc, L.; Pham, H.P.; Treml, A.; et al. Red blood cell exchange in patients with sickle cell disease—indications and management: a review and consensus report by the therapeutic apheresis subsection of the AABB. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.C.; Brousse, V.A.; Brewin, J.N. Determinants of severity in sickle cell disease. Blood Rev. 2022, 56, 100983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, T.C.; Horger, E.O.; Walker, E.M.; Mitchum, E.N. Automated erythrocytopheresis for sickle cell anemia during pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1980, 138, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Werch, J.; Rokey, R.; Pivarnik, J.; Miller, J. Physiologic observations of pregnant women undergoing prophylactic erythrocytapheresis for sickle cell disease. Transfusion 1991, 31, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.C.; Morrison, F.S.; Floyd, R.C.; Roberts, W.E.; Hess, L.W.; Wiser, W.L. Use of continuous flow erythrocytapheresis in pregnant patients with sickle cell disease. J. Clin. Apher. 1991, 6, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilli, S.; De Paula, E.; Biscaro, F.; Marques, J.; Costa, F.; Saad, S. Third-trimester erythrocytapheresis in pregnant patients with sickle cell disease. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2007, 96, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asma, S.; Kozanoglu, I.; Tarım, E.; Sarıturk, C.; Gereklioglu, C.; Akdeniz, A.; Kasar, M.; Turgut, N.H.; Yeral, M.; Kandemir, F.; et al. Prophylactic red blood cell exchange may be beneficial in the management of sickle cell disease in pregnancy. Transfusion 2014, 55, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vianello, A.; Vencato, E.; Cantini, M.; Zanconato, G.; Manfrin, E.; Zamo, A.; Zorzi, F.; Mazzi, F.; Martinelli, N.; Cavaliere, E.; et al. Improvement of maternal and fetal outcomes in women with sickle cell disease treated with early prophylactic erythrocytapheresis. Transfusion 2018, 58, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz Baran Ş, Kozanoğlu İ, Korur A, Doğan Durdağ G, Kalaycı H, Alemdaroğlu S, Asma S, Kılıçdağ EB, Boğa C. Role of prophylactic and therapeutic red blood cell exchange in pregnancy with sickle cell disease: Maternal and perinatal outcomes. J Clin Apher. 2021, 36, 283–290.
- Davis, B.A.; Allard, S.; Qureshi, A.; Porter, J.B.; Pancham, S.; Win, N.; Cho, G.; Ryan, K.; the British Committee for Standards in Haematology Guidelines on red cell transfusion in sickle cell disease. Part I: principles and laboratory aspects. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 176, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly-Smith, L.; Alquist, C.R.; Aqui, N.A.; Hofmann, J.C.; Klingel, R.; Onwuemene, O.A.; Patriquin, C.J.; Pham, H.P.; Sanchez, A.P.; Schneiderman, J.; et al. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice – Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Ninth Special Issue. J. Clin. Apher. 2023, 38, 77–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, S.; Perseghin, P.; Consonni, S.; Regalia, A.L.; Masera, N. A Case Report of a Successful Monochorionic Diamniotic Twin Pregnancy in a Patient Affected by Sickle Cell Disease Treated With Erythrocytapheresis. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2010, 14, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehly S, Diemunsch P, Waller C, Renaud R, Gros H. Utilisation de l'échange érythrocytaire chez une femme enceinte atteinte de drépanocytose [Use of erythrocytapheresis in a pregnant woman with sickle cell anemia]. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 1989, 8, 67–9.
- Malinowski, A.K.; Dziegielewski, C.; Keating, S.; Parks, T.; Kingdom, J.; Shehata, N.; Rizov, E.; D'Souza, R. Placental histopathology in sickle cell disease: A descriptive and hypothesis-generating study. Placenta 2020, 95, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowski, A.K.; Shehata, N.; D’souza, R.; Kuo, K.H.M.; Ward, R.; Shah, P.S.; Murphy, K. Prophylactic transfusion for pregnant women with sickle cell disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood 2015, 126, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, L.L.; Awogbade, M.; Brien, S.; Briley, A.; Chorozoglou, M.; Drasar, E.; Johns, J.; Rhodes, E.; Robinson, V.; Seed, P.; et al. Serial prophylactic exchange blood transfusion in pregnant women with sickle cell disease (TAPS-2): study protocol for a randomised controlled feasibility trial. Trials 2020, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).