Submitted:
11 October 2023
Posted:
12 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
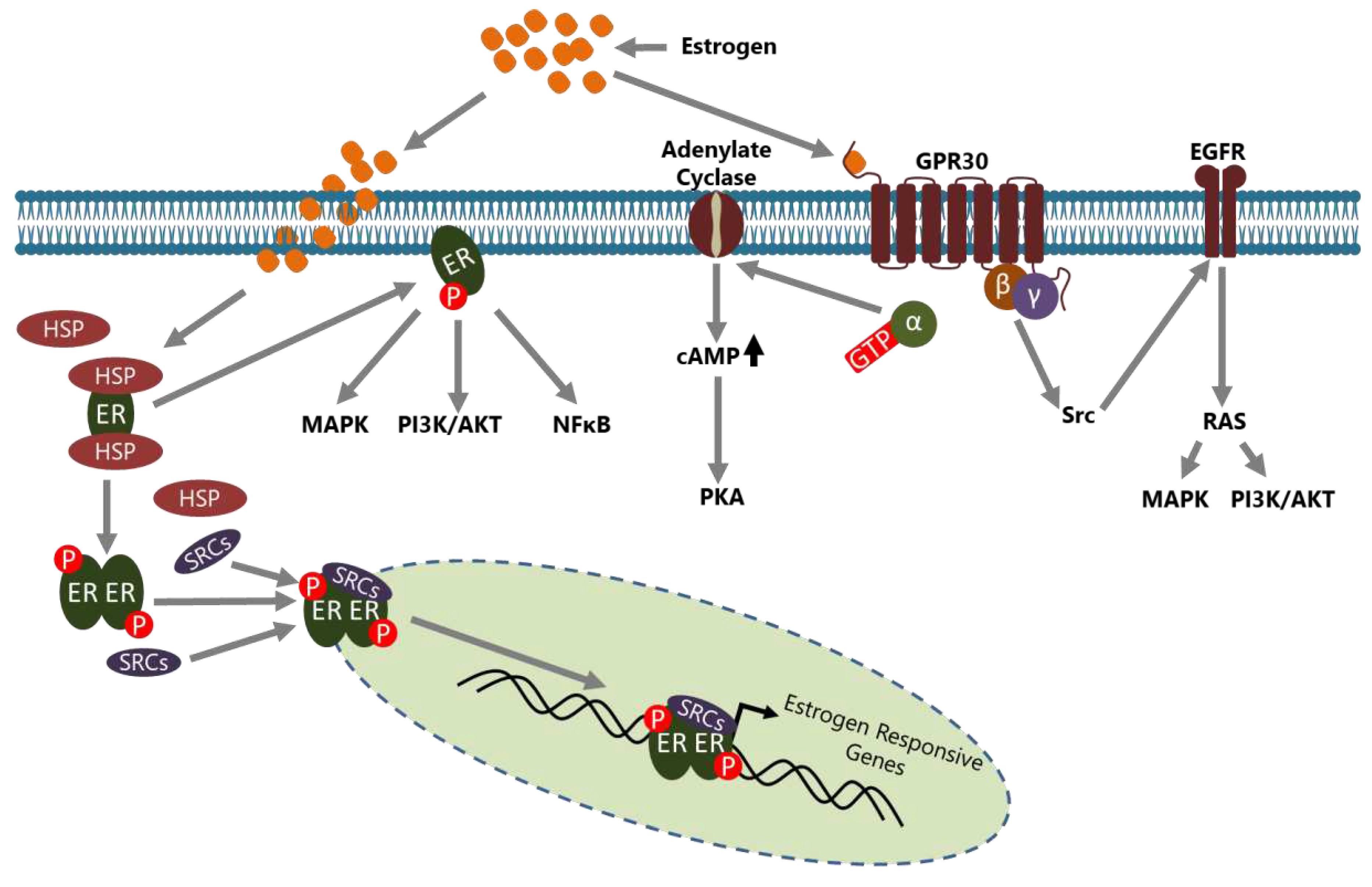
2. BCa and Estrogen Action
3. BCa Tumor Microenvironment
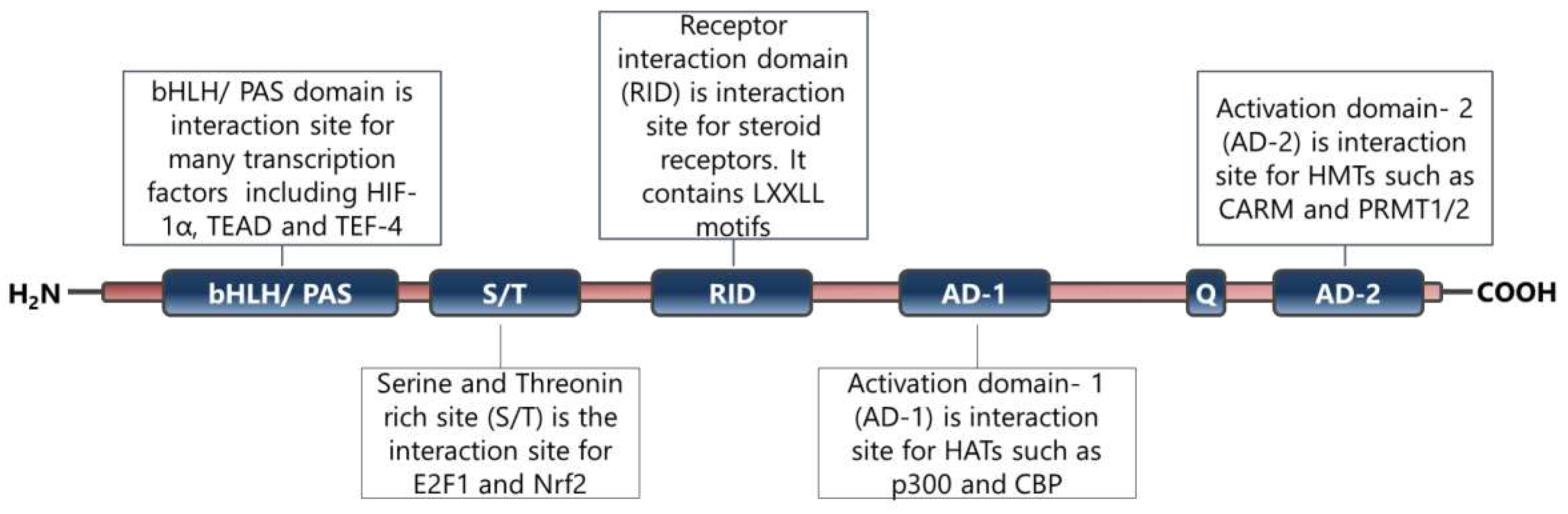
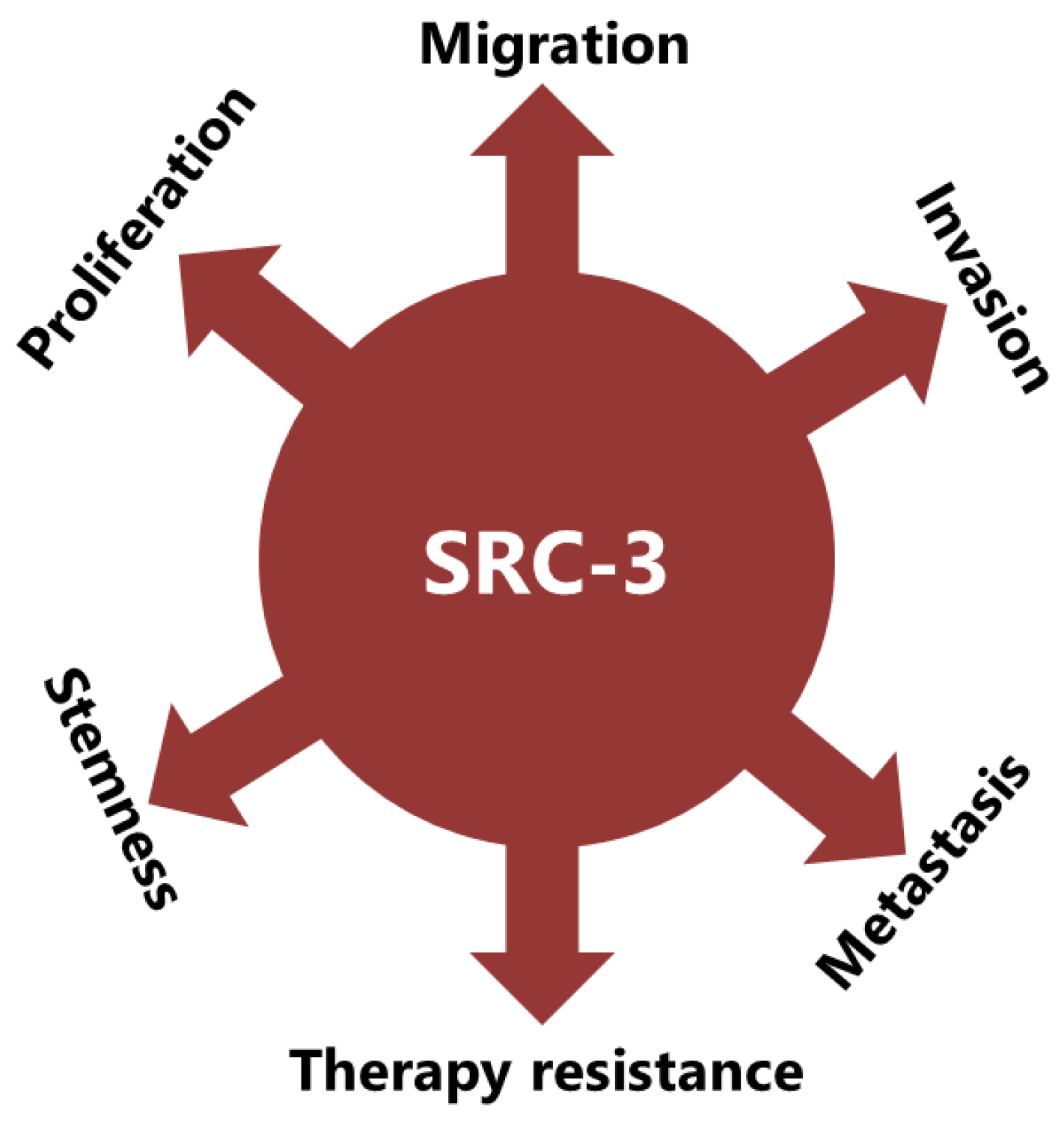
4. SRC-3 Has Multiple Roles in BCa Pathogenesis
4.1. SRC-3 Affects the Tumor Microenvironment and Promotes Stemness
4.2. SRC-3 Promotes Malignant Behaviors of Tumor Cells
5. SRC-3 May Contribute to Therapy Resistance in Multiple Ways in BCa
5.1. SRC-3 May Contributes to Hormone Therapy Resistance
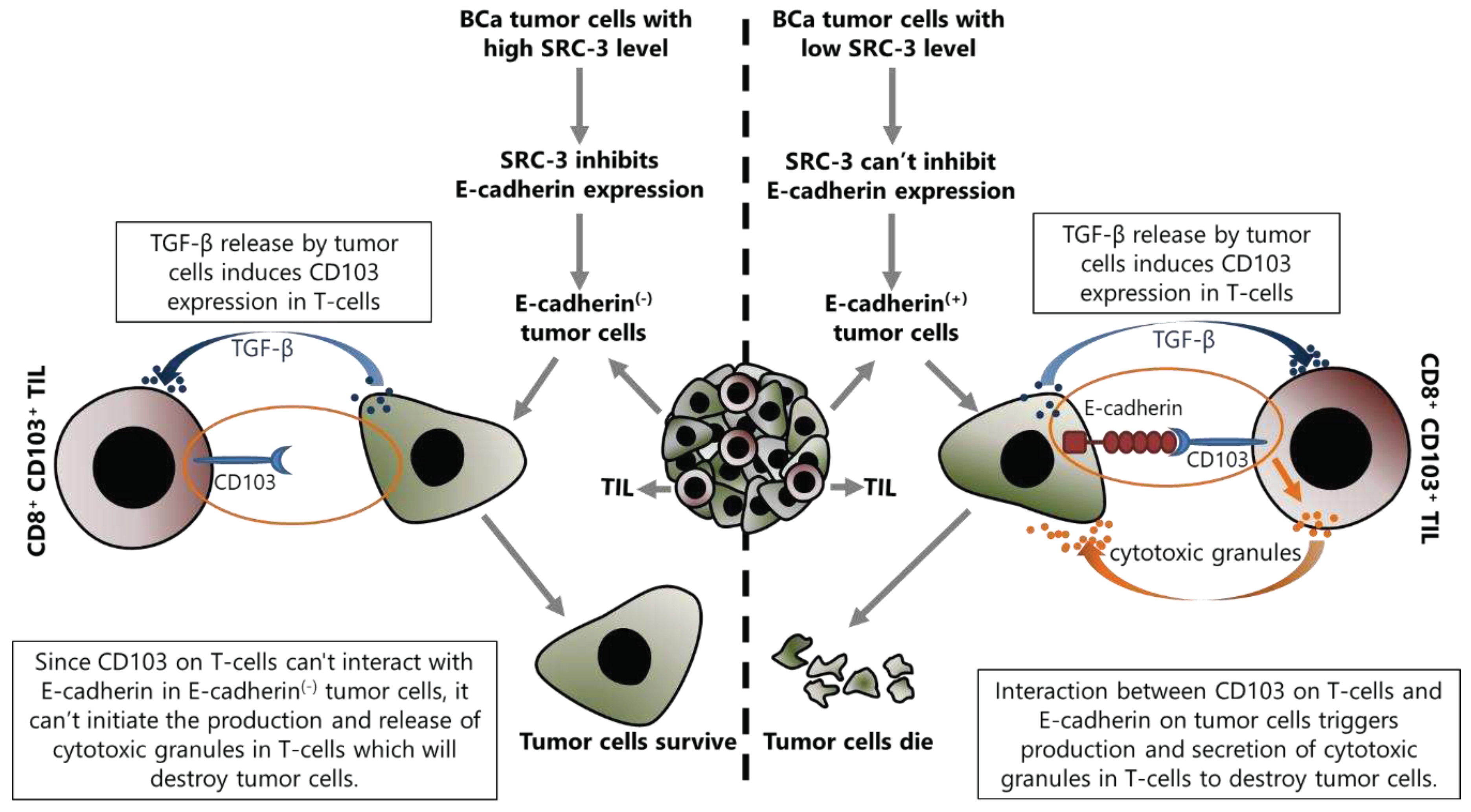
5.2. SRC-3 May Contribute to Immunotherapy Resistance
6. SRC-3 Is a Promising Target to Overcome Therapy Resistance in BCa
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023, 73, 17-48. [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 209-249. [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nunez, P.; Acuna-Aguilar, L.E.; Gomez-Valles, F.O.; Ramirez-Valdespino, C.A. Subtypes of Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer, Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Brisbane (AU), 2022.
- Yersal, O.; Barutca, S. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J Clin Oncol 2014, 5, 412-424. [CrossRef]
- Zattarin, E.; Leporati, R.; Ligorio, F.; Lobefaro, R.; Vingiani, A.; Pruneri, G.; Vernieri, C. Hormone Receptor Loss in Breast Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Settings, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Faltas, C.L.; LeBron, K.A.; Holz, M.K. Unconventional Estrogen Signaling in Health and Disease. Endocrinology 2020, 161. [CrossRef]
- Clusan, L.; Ferriere, F.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F. A Basic Review on Estrogen Receptor Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, N.; Silveyra, P. Estrogen receptor signaling mechanisms. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2019, 116, 135-170. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, R.C.; O'Malley, B.W. Normal and cancer-related functions of the p160 steroid receptor co-activator (SRC) family. Nat Rev Cancer 2009, 9, 615-630. [CrossRef]
- Stashi, E.; York, B.; O'Malley, B.W. Steroid receptor coactivators: servants and masters for control of systems metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2014, 25, 337-347. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, L.; Ning, G.; Yoshida-Komiya, H.; Deng, C.; O'Malley, B.W. The steroid receptor coactivator SRC-3 (p/CIP/RAC3/AIB1/ACTR/TRAM-1) is required for normal growth, puberty, female reproductive function, and mammary gland development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 6379-6384. [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.C.; Qin, J.; Yi, P.; Wong, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O'Malley, B.W. Selective phosphorylations of the SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator integrate genomic reponses to multiple cellular signaling pathways. Mol Cell 2004, 15, 937-949. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.F.; Wu, R.C.; Smith, C.L.; O'Malley, B.W. Rapid estrogen-induced phosphorylation of the SRC-3 coactivator occurs in an extranuclear complex containing estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol 2005, 25, 8273-8284. [CrossRef]
- Anzick, S.L.; Kononen, J.; Walker, R.L.; Azorsa, D.O.; Tanner, M.M.; Guan, X.Y.; Sauter, G.; Kallioniemi, O.P.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S. AIB1, a steroid receptor coactivator amplified in breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1997, 277, 965-968. [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.Y.; Xu, J.; Anzick, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S. Hybrid selection of transcribed sequences from microdissected DNA: isolation of genes within amplified region at 20q11-q13.2 in breast cancer. Cancer Res 1996, 56, 3446-3450.
- Gojis, O.; Rudraraju, B.; Gudi, M.; Hogben, K.; Sousha, S.; Coombes, R.C.; Cleator, S.; Palmieri, C. The role of SRC-3 in human breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2010, 7, 83-89. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Deng, C.X.; Chen, Q. SRC-3, a Steroid Receptor Coactivator: Implication in Cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Nikolai, B.C.; Jain, P.; Cardenas, D.L.; York, B.; Feng, Q.; McKenna, N.J.; Dasgupta, S.; Lonard, D.M.; O'Malley, B.W. Steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3/AIB1) is enriched and functional in mouse and human Tregs. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 3441. [CrossRef]
- Rohira, A.D.; Yan, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Lu, A.; Yu, Y.; Xu, J.; Lonard, D.M.; O'Malley, B.W. Targeting SRC Coactivators Blocks the Tumor-Initiating Capacity of Cancer Stem-like Cells. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 4293-4304. [CrossRef]
- Kiliti, A.J.; Sharif, G.M.; Martin, M.B.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. AIB1/SRC-3/NCOA3 function in estrogen receptor alpha positive breast cancer. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2023, 14. [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019, 5, 66. [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, H.; McArthur, H.; Olivotto, I.A.; Speers, C.; Bajdik, C.; Chia, S.K.; Ellard, S.; Norris, B.; Hayes, M.; Barnett, J.; et al. Risk of early recurrence among postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer treated with adjuvant tamoxifen. Cancer 2008, 112, 1437-1444. [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, H.F.; Olivotto, I.A.; Speers, C.; Norris, B.; Chia, S.K.; Bryce, C.; Gelmon, K.A. Late risk of relapse and mortality among postmenopausal women with estrogen responsive early breast cancer after 5 years of tamoxifen. Ann Oncol 2007, 18, 45-51. [CrossRef]
- Kennecke, H.; Yerushalmi, R.; Woods, R.; Cheang, M.C.; Voduc, D.; Speers, C.H.; Nielsen, T.O.; Gelmon, K. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 3271-3277. [CrossRef]
- Auchus, M.L.; Auchus, R.J. Human steroid biosynthesis for the oncologist. J Investig Med 2012, 60, 495-503. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.V.; Jacobson, H.I.; Walf, A.A.; Frye, C.A. Estrogen action: a historic perspective on the implications of considering alternative approaches. Physiol Behav 2010, 99, 151-162. [CrossRef]
- Yasar, P.; Ayaz, G.; User, S.D.; Gupur, G.; Muyan, M. Molecular mechanism of estrogen-estrogen receptor signaling. Reprod Med Biol 2017, 16, 4-20. [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, P.C.; Picard, D. Molecular chaperones, essential partners of steroid hormone receptors for activity and mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010, 1803, 641-649. [CrossRef]
- Marino, M.; Galluzzo, P.; Ascenzi, P. Estrogen signaling multiple pathways to impact gene transcription. Curr Genomics 2006, 7, 497-508. [CrossRef]
- Klinge, C.M. Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res 2001, 29, 2905-2919. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Briggs, M.R.; Ahlborn, T.E.; Kraemer, F.B.; Liu, J. Requirement of Sp1 and estrogen receptor alpha interaction in 17beta-estradiol-mediated transcriptional activation of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene expression. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 1546-1553. [CrossRef]
- Safe, S. Transcriptional activation of genes by 17 beta-estradiol through estrogen receptor-Sp1 interactions. Vitam Horm 2001, 62, 231-252. [CrossRef]
- Stossi, F.; Likhite, V.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Estrogen-occupied estrogen receptor represses cyclin G2 gene expression and recruits a repressor complex at the cyclin G2 promoter. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 16272-16278. [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 2000, 14, 121-141.
- McKenna, N.J.; O'Malley, B.W. Combinatorial control of gene expression by nuclear receptors and coregulators. Cell 2002, 108, 465-474. [CrossRef]
- Rae, J.M.; Johnson, M.D. What does an orphan G-protein-coupled receptor have to do with estrogen? Breast Cancer Res 2005, 7, 243-244. [CrossRef]
- Revankar, C.M.; Cimino, D.F.; Sklar, L.A.; Arterburn, J.B.; Prossnitz, E.R. A transmembrane intracellular estrogen receptor mediates rapid cell signaling. Science 2005, 307, 1625-1630. [CrossRef]
- Filardo, E.J.; Thomas, P. Minireview: G protein-coupled estrogen receptor-1, GPER-1: its mechanism of action and role in female reproductive cancer, renal and vascular physiology. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2953-2962. [CrossRef]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Barton, M. Estrogen biology: new insights into GPER function and clinical opportunities. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2014, 389, 71-83. [CrossRef]
- Paterni, I.; Granchi, C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Minutolo, F. Estrogen receptors alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta): subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids 2014, 90, 13-29. [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015, 29, 557-568. [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.T.; Jordan, V.C. The biological role of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2004, 50, 3-22. [CrossRef]
- Bakas, P.; Liapis, A.; Vlahopoulos, S.; Giner, M.; Logotheti, S.; Creatsas, G.; Meligova, A.K.; Alexis, M.N.; Zoumpourlis, V. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in uterine fibroids: a basis for altered estrogen responsiveness. Fertil Steril 2008, 90, 1878-1885. [CrossRef]
- Logotheti, S.; Papaevangeliou, D.; Michalopoulos, I.; Sideridou, M.; Tsimaratou, K.; Christodoulou, I.; Pyrillou, K.; Gorgoulis, V.; Vlahopoulos, S.; Zoumpourlis, V. Progression of mouse skin carcinogenesis is associated with increased ERalpha levels and is repressed by a dominant negative form of ERalpha. PLoS One 2012, 7, e41957. [CrossRef]
- Welboren, W.J.; Sweep, F.C.; Span, P.N.; Stunnenberg, H.G. Genomic actions of estrogen receptor alpha: what are the targets and how are they regulated? Endocr Relat Cancer 2009, 16, 1073-1089. [CrossRef]
- Dubik, D.; Dembinski, T.C.; Shiu, R.P. Stimulation of c-myc oncogene expression associated with estrogen-induced proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 1987, 47, 6517-6521.
- Millour, J.; Constantinidou, D.; Stavropoulou, A.V.; Wilson, M.S.; Myatt, S.S.; Kwok, J.M.; Sivanandan, K.; Coombes, R.C.; Medema, R.H.; Hartman, J.; et al. FOXM1 is a transcriptional target of ERalpha and has a critical role in breast cancer endocrine sensitivity and resistance. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2983-2995. [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, M.; Courilleau, D.; Mester, J.; Redeuilh, G. Estrogen induction of the cyclin D1 promoter: involvement of a cAMP response-like element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999, 96, 11217-11222. [CrossRef]
- Oesterreich, S.; Deng, W.; Jiang, S.; Cui, X.; Ivanova, M.; Schiff, R.; Kang, K.; Hadsell, D.L.; Behrens, J.; Lee, A.V. Estrogen-mediated down-regulation of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2003, 63, 5203-5208.
- Fujita, N.; Jaye, D.L.; Kajita, M.; Geigerman, C.; Moreno, C.S.; Wade, P.A. MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell 2003, 113, 207-219. [CrossRef]
- Vareslija, D.; Ward, E.; Purcell, S.P.; Cosgrove, N.S.; Cocchiglia, S.; O'Halloran, P.J.; Charmsaz, S.; Bane, F.T.; Brett, F.M.; Farrell, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of the AIB1 interactome in breast cancer reveals MTA2 as a repressive partner which silences E-Cadherin to promote EMT and associates with a pro-metastatic phenotype. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1318-1331. [CrossRef]
- Lauritsen, K.J.; List, H.J.; Reiter, R.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. A role for TGF-beta in estrogen and retinoid mediated regulation of the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2002, 21, 7147-7155. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; et al. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J Cancer 2017, 8, 761-773. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr Biol 2020, 30, R921-R925. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Baruch, A. Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: inflammatory cells, cytokines and chemokines in breast cancer progression: reciprocal tumor-microenvironment interactions. Breast Cancer Res 2003, 5, 31-36. [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Min, L.; Zhu, S. Cellular and Extracellular Components in Tumor Microenvironment and Their Application in Early Diagnosis of Cancers. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst) 2020, 2020, 6283796. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Tsang, J.Y.; Tse, G.M. Tumor Microenvironment in Breast Cancer-Updates on Therapeutic Implications and Pathologic Assessment. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- De Guillebon, E.; Dardenne, A.; Saldmann, A.; Seguier, S.; Tran, T.; Paolini, L.; Lebbe, C.; Tartour, E. Beyond the concept of cold and hot tumors for the development of novel predictive biomarkers and the rational design of immunotherapy combination. Int J Cancer 2020, 147, 1509-1518. [CrossRef]
- Farc, O.; Cristea, V. An overview of the tumor microenvironment, from cells to complex networks (Review). Exp Ther Med 2021, 21, 96. [CrossRef]
- Dannenfelser, R.; Nome, M.; Tahiri, A.; Ursini-Siegel, J.; Vollan, H.K.M.; Haakensen, V.D.; Helland, A.; Naume, B.; Caldas, C.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Data-driven analysis of immune infiltrate in a large cohort of breast cancer and its association with disease progression, ER activity, and genomic complexity. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 57121-57133. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.; Gilkeson, G. Estrogen receptors in immunity and autoimmunity. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2011, 40, 66-73. [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.; Ansar Ahmed, S. The Immune System Is a Natural Target for Estrogen Action: Opposing Effects of Estrogen in Two Prototypical Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol 2015, 6, 635. [CrossRef]
- Okasha, S.A.; Ryu, S.; Do, Y.; McKallip, R.J.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Evidence for estradiol-induced apoptosis and dysregulated T cell maturation in the thymus. Toxicology 2001, 163, 49-62. [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, M.J.; Carson, B.D.; Subramanian, S.; Afentoulis, M.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Ziegler, S.F.; Offner, H. Cutting edge: estrogen drives expansion of the CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell compartment. J Immunol 2004, 173, 2227-2230. [CrossRef]
- Staples, J.E.; Gasiewicz, T.A.; Fiore, N.C.; Lubahn, D.B.; Korach, K.S.; Silverstone, A.E. Estrogen receptor alpha is necessary in thymic development and estradiol-induced thymic alterations. J Immunol 1999, 163, 4168-4174.
- Svoronos, N.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Allegrezza, M.J.; Rutkowski, M.R.; Payne, K.K.; Tesone, A.J.; Nguyen, J.M.; Curiel, T.J.; Cadungog, M.G.; Singhal, S.; et al. Tumor Cell-Independent Estrogen Signaling Drives Disease Progression through Mobilization of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Cancer Discov 2017, 7, 72-85. [CrossRef]
- McMurray, R.W.; Ndebele, K.; Hardy, K.J.; Jenkins, J.K. 17-beta-estradiol suppresses IL-2 and IL-2 receptor. Cytokine 2001, 14, 324-333. [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, A.; Rothenberger, N.J.; Stabile, L.P. The Impact of Estrogen in the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1277, 33-52. [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, T.F.; Meng, Y.; Harlin, H. Immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunother 2006, 29, 233-240. [CrossRef]
- Polanczyk, M.J.; Hopke, C.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Offner, H. Treg suppressive activity involves estrogen-dependent expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1). Int Immunol 2007, 19, 337-343. [CrossRef]
- Prieto, G.A.; Rosenstein, Y. Oestradiol potentiates the suppressive function of human CD4 CD25 regulatory T cells by promoting their proliferation. Immunology 2006, 118, 58-65. [CrossRef]
- Tai, P.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Song, X.; Yan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Induction of regulatory T cells by physiological level estrogen. J Cell Physiol 2008, 214, 456-464. [CrossRef]
- Askenasy, N.; Kaminitz, A.; Yarkoni, S. Mechanisms of T regulatory cell function. Autoimmun Rev 2008, 7, 370-375. [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Li, D.J. Estrogen enhances the functions of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells that suppress osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro. Cell Mol Immunol 2011, 8, 50-58. [CrossRef]
- Adurthi, S.; Kumar, M.M.; Vinodkumar, H.S.; Mukherjee, G.; Krishnamurthy, H.; Acharya, K.K.; Bafna, U.D.; Uma, D.K.; Abhishekh, B.; Krishna, S.; et al. Oestrogen Receptor-alpha binds the FOXP3 promoter and modulates regulatory T-cell function in human cervical cancer. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 17289. [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, K.; Irie, T.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T-cell development in the tumor microenvironment. Eur J Immunol 2022, 52, 1216-1227. [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Kim, K.M.; Bae, J.S.; Park, H.S.; Lee, H.; Chung, M.J.; Moon, W.S.; Lee, D.G.; Jang, K.Y. Tumor-infiltrating PD1-Positive Lymphocytes and FoxP3-Positive Regulatory T Cells Predict Distant Metastatic Relapse and Survival of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Transl Oncol 2013, 6, 282-289. [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kusnadi, A.; Lee, E.J.; Kim, W.W.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, I.J.; Seong, J.; Ha, S.J. Tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells delineated by upregulation of PD-1 and inhibitory receptors. Cell Immunol 2012, 278, 76-83. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, H.J.; Son, J.; Lee, J.G.; Chung, K.Y.; Cho, N.H.; Shim, H.S.; Park, S.; Kim, G.; In Yoon, H.; et al. Tumor microenvironment dictates regulatory T cell phenotype: Upregulated immune checkpoints reinforce suppressive function. J Immunother Cancer 2019, 7, 339. [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Shitara, K.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression - implications for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019, 16, 356-371. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, D.; Nishikawa, H.; Maeda, Y.; Nishioka, M.; Tanemura, A.; Katayama, I.; Ezoe, S.; Kanakura, Y.; Sato, E.; Fukumori, Y.; et al. Anti-CCR4 mAb selectively depletes effector-type FoxP3+CD4+ regulatory T cells, evoking antitumor immune responses in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 17945-17950. [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massague, J. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924-940. [CrossRef]
- Cinier, J.; Hubert, M.; Besson, L.; Di Roio, A.; Rodriguez, C.; Lombardi, V.; Caux, C.; Menetrier-Caux, C. Recruitment and Expansion of Tregs Cells in the Tumor Environment-How to Target Them? Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Pacheco, I.; Madrigal, A.; Saudemont, A. Interaction between natural killer cells and regulatory T cells: perspectives for immunotherapy. Cell Mol Immunol 2013, 10, 222-229. [CrossRef]
- Sawant, D.V.; Yano, H.; Chikina, M.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, M.; Liu, C.; Callahan, D.J.; Sun, Z.; Sun, T.; Tabib, T.; et al. Adaptive plasticity of IL-10(+) and IL-35(+) T(reg) cells cooperatively promotes tumor T cell exhaustion. Nat Immunol 2019, 20, 724-735. [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; O'Garra, A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2010, 10, 170-181. [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Xu, H.; Wu, D.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Wu, F.; Zhou, H. TGF-beta signaling in the tumor metabolic microenvironment and targeted therapies. J Hematol Oncol 2022, 15, 135. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Jin, W.; Hardegen, N.; Lei, K.J.; Li, L.; Marinos, N.; McGrady, G.; Wahl, S.M. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25- naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med 2003, 198, 1875-1886. [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Cai, S.F.; Fehniger, T.A.; Song, J.; Collins, L.I.; Piwnica-Worms, D.R.; Ley, T.J. Granzyme B and perforin are important for regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of tumor clearance. Immunity 2007, 27, 635-646. [CrossRef]
- Deaglio, S.; Dwyer, K.M.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Usheva, A.; Erat, A.; Chen, J.F.; Enjyoji, K.; Linden, J.; Oukka, M.; et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J Exp Med 2007, 204, 1257-1265. [CrossRef]
- Stockis, J.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Halim, T.Y.F. Regulation of regulatory T cells in cancer. Immunology 2019, 157, 219-231. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liang, Y.Y.; Feng, X.H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O'Malley, B.W. Essential phosphatases and a phospho-degron are critical for regulation of SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator function and turnover. Mol Cell 2008, 31, 835-849. [CrossRef]
- York, B.; Yu, C.; Sagen, J.V.; Liu, Z.; Nikolai, B.C.; Wu, R.C.; Finegold, M.; Xu, J.; O'Malley, B.W. Reprogramming the posttranslational code of SRC-3 confers a switch in mammalian systems biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 11122-11127. [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Kuang, S.Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gonzalez, S.M.; O'Malley, B.W.; Xu, J. Molecular structure and biological function of the cancer-amplified nuclear receptor coactivator SRC-3/AIB1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2002, 83, 3-14. [CrossRef]
- Louet, J.F.; Coste, A.; Amazit, L.; Tannour-Louet, M.; Wu, R.C.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Auwerx, J.; O'Malley, B.W. Oncogenic steroid receptor coactivator-3 is a key regulator of the white adipogenic program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 17868-17873. [CrossRef]
- Coste, A.; Louet, J.F.; Lagouge, M.; Lerin, C.; Antal, M.C.; Meziane, H.; Schoonjans, K.; Puigserver, P.; O'Malley, B.W.; Auwerx, J. The genetic ablation of SRC-3 protects against obesity and improves insulin sensitivity by reducing the acetylation of PGC-1alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 17187-17192. [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.A.; Hall, J.A.; Sun, C.M.; Cai, Q.; Ghyselinck, N.; Chambon, P.; Belkaid, Y.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Retinoic acid enhances Foxp3 induction indirectly by relieving inhibition from CD4+CD44hi Cells. Immunity 2008, 29, 758-770. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Jin, H.; Korn, T.; Liu, S.M.; Oukka, M.; Lim, B.; Kuchroo, V.K. Retinoic acid increases Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and inhibits development of Th17 cells by enhancing TGF-beta-driven Smad3 signaling and inhibiting IL-6 and IL-23 receptor expression. J Immunol 2008, 181, 2277-2284. [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.V.; Rubio, M.F.; Fernandez Larrosa, P.N.; Panelo, L.C.; Azurmendi, P.J.; Ruiz Grecco, M.; Martinez-Noel, G.A.; Costas, M.A. The levels of RAC3 expression are up regulated by TNF in the inflammatory response. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 450-457. [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Park, S.G.; Strickland, I.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Nuclear factor-kappaB modulates regulatory T cell development by directly regulating expression of Foxp3 transcription factor. Immunity 2009, 31, 921-931. [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Q.; Kameswaran, V.; Tone, Y.; Li, L.; Liou, H.C.; Greene, M.I.; Tone, M.; Chen, Y.H. Development of Foxp3(+) regulatory t cells is driven by the c-Rel enhanceosome. Immunity 2009, 31, 932-940. [CrossRef]
- Grinberg-Bleyer, Y.; Caron, R.; Seeley, J.J.; De Silva, N.S.; Schindler, C.W.; Hayden, M.S.; Klein, U.; Ghosh, S. The Alternative NF-kappaB Pathway in Regulatory T Cell Homeostasis and Suppressive Function. J Immunol 2018, 200, 2362-2371. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Shan, N.; Xu, P.; Ge, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wen, L.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, L.; et al. Hypoxia-induced Downregulation of SRC-3 Suppresses Trophoblastic Invasion and Migration Through Inhibition of the AKT/mTOR Pathway: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10349. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhuo, M.; Lu, X.; Xia, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Yu, C. SRC-3 protects intestine from DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting inflammation and promoting goblet cell differentiation through enhancement of KLF4 expression. Int J Biol Sci 2018, 14, 2051-2064. [CrossRef]
- Mullany, L.K.; Rohira, A.D.; Leach, J.P.; Kim, J.H.; Monroe, T.O.; Ortiz, A.R.; Stork, B.; Gaber, M.W.; Sarkar, P.; Sikora, A.G.; et al. A steroid receptor coactivator stimulator (MCB-613) attenuates adverse remodeling after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2020, 117, 31353-31364. [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; York, B.; Wang, S.; Feng, Q.; Xu, J.; O'Malley, B.W. An essential function of the SRC-3 coactivator in suppression of cytokine mRNA translation and inflammatory response. Mol Cell 2007, 25, 765-778. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, T.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, C. Steroid receptor coactivator 3 is required for clearing bacteria and repressing inflammatory response in Escherichia coli-induced septic peritonitis. J Immunol 2010, 185, 5444-5452. [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Prieto, M.; Biarnes, X.; Vidossich, P.; Rovira, C. The molecular mechanism of the catalase reaction. J Am Chem Soc 2009, 131, 11751-11761. [CrossRef]
- Colo, G.P.; Rosato, R.R.; Grant, S.; Costas, M.A. RAC3 down-regulation sensitizes human chronic myeloid leukemia cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett 2007, 581, 5075-5081. [CrossRef]
- Colo, G.P.; Rubio, M.F.; Nojek, I.M.; Werbajh, S.E.; Echeverria, P.C.; Alvarado, C.V.; Nahmod, V.E.; Galigniana, M.D.; Costas, M.A. The p160 nuclear receptor co-activator RAC3 exerts an anti-apoptotic role through a cytoplasmatic action. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2430-2444. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lu, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Mo, P.; Tong, Z.; Wang, W.; Wan, W.; Su, G.; Xu, J.; et al. Steroid Receptor Coactivator 3 Contributes to Host Defense against Enteric Bacteria by Recruiting Neutrophils via Upregulation of CXCL2 Expression. J Immunol 2017, 198, 1606-1615. [CrossRef]
- Werbajh, S.; Nojek, I.; Lanz, R.; Costas, M.A. RAC-3 is a NF-kappa B coactivator. FEBS Lett 2000, 485, 195-199. [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.C.; Qin, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Wong, J.; Xu, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O'Malley, B.W. Regulation of SRC-3 (pCIP/ACTR/AIB-1/RAC-3/TRAM-1) Coactivator activity by I kappa B kinase. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 3549-3561. [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.; Hu, H.; Temiz, N.A.; Hagen, K.M.; Girard, B.J.; Brady, N.J.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; Lange, C.A.; Ostrander, J.H. Cancer Stem Cell Phenotypes in ER(+) Breast Cancer Models Are Promoted by PELP1/AIB1 Complexes. Mol Cancer Res 2018, 16, 707-719. [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.H.; Benner, E.A.; Hagen, K.M.; Temiz, N.A.; Kerkvliet, C.P.; Wang, Y.; Cortes-Sanchez, E.; Yang, C.H.; Trousdell, M.C.; Pengo, T.; et al. PELP1/SRC-3-dependent regulation of metabolic PFKFB kinases drives therapy resistant ER(+) breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4384-4397. [CrossRef]
- Panelo, L.C.; Machado, M.S.; Rubio, M.F.; Jaworski, F.; Alvarado, C.V.; Paz, L.A.; Urtreger, A.J.; Vazquez, E.; Costas, M.A. High RAC3 expression levels are required for induction and maintaining of cancer cell stemness. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5848-5860. [CrossRef]
- Dubrovska, A.; Hartung, A.; Bouchez, L.C.; Walker, J.R.; Reddy, V.A.; Cho, C.Y.; Schultz, P.G. CXCR4 activation maintains a stem cell population in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells through AhR signalling. Br J Cancer 2012, 107, 43-52. [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Shien, T.; Ogiya, A.; Ishida, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Horii, R.; Horimoto, Y.; Masuda, N.; Yasojima, H.; Inao, T.; et al. Differences in expression of the cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 among estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor type 2-negative breast cancer cases with early, late, and no recurrence. Breast Cancer Res 2016, 18, 73. [CrossRef]
- Dancik, G.M.; Voutsas, I.F.; Vlahopoulos, S. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Enzyme Functions in Acute Leukemia Stem Cells. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2022, 14, 8. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qiang, J.; Deng, Q.; Xia, J.; Deng, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; et al. ALDH1A1 Activity in Tumor-Initiating Cells Remodels Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells to Promote Breast Cancer Progression. Cancer Res 2021, 81, 5919-5934. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Guan, Q.; Kang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, L.; Li, J.; Wong, J. An acetylation-enhanced interaction between transcription factor Sox2 and the steroid receptor coactivators facilitates Sox2 transcriptional activity and function. J Biol Chem 2021, 297, 101389. [CrossRef]
- Domenici, G.; Aurrekoetxea-Rodriguez, I.; Simoes, B.M.; Rabano, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Millan, J.S.; Comaills, V.; Oliemuller, E.; Lopez-Ruiz, J.A.; Zabalza, I.; et al. A Sox2-Sox9 signalling axis maintains human breast luminal progenitor and breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3151-3169. [CrossRef]
- Leung, E.Y.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E.; Sarkar, D.; Ferraro-Peyret, C.; Joseph, W.R.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C. Endocrine Therapy of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer Cells: Early Differential Effects on Stem Cell Markers. Front Oncol 2017, 7, 184. [CrossRef]
- Percharde, M.; Azuara, V. Essential roles for the nuclear receptor coactivator Ncoa3 in pluripotency. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 195-196. [CrossRef]
- Percharde, M.; Lavial, F.; Ng, J.H.; Kumar, V.; Tomaz, R.A.; Martin, N.; Yeo, J.C.; Gil, J.; Prabhakar, S.; Ng, H.H.; et al. Ncoa3 functions as an essential Esrrb coactivator to sustain embryonic stem cell self-renewal and reprogramming. Genes Dev 2012, 26, 2286-2298. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L. Role of nuclear receptor coactivator 3 (Ncoa3) in pluripotency maintenance. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 38295-38304. [CrossRef]
- Chitilian, J.M.; Thillainadesan, G.; Manias, J.L.; Chang, W.Y.; Walker, E.; Isovic, M.; Stanford, W.L.; Torchia, J. Critical components of the pluripotency network are targets for the p300/CBP interacting protein (p/CIP) in embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 204-215. [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zeng, H.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, C.; Shen, M.; Chen, F.; et al. SRC-3 is involved in maintaining hematopoietic stem cell quiescence by regulation of mitochondrial metabolism in mice. Blood 2018, 132, 911-923. [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Ren, Y.; Wang, K.; He, J. SRC-3 has a role in cancer other than as a nuclear receptor coactivator. Int J Biol Sci 2011, 7, 664-672. [CrossRef]
- Torres-Arzayus, M.I.; Font de Mora, J.; Yuan, J.; Vazquez, F.; Bronson, R.; Rue, M.; Sellers, W.R.; Brown, M. High tumor incidence and activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in transgenic mice define AIB1 as an oncogene. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 263-274. [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.; Oh, A.S.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. Impact of the nuclear receptor coactivator AIB1 isoform AIB1-Delta3 on estrogenic ligands with different intrinsic activity. Oncogene 2004, 23, 403-409. [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. An isoform of the coactivator AIB1 that increases hormone and growth factor sensitivity is overexpressed in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 39736-39741. [CrossRef]
- Bautista, S.; Valles, H.; Walker, R.L.; Anzick, S.; Zeillinger, R.; Meltzer, P.; Theillet, C. In breast cancer, amplification of the steroid receptor coactivator gene AIB1 is correlated with estrogen and progesterone receptor positivity. Clin Cancer Res 1998, 4, 2925-2929.
- Hudelist, G.; Czerwenka, K.; Kubista, E.; Marton, E.; Pischinger, K.; Singer, C.F. Expression of sex steroid receptors and their co-factors in normal and malignant breast tissue: AIB1 is a carcinoma-specific co-activator. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2003, 78, 193-204. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, A.; Song, B.J.; Kang, C.S. Expression of AIB1 protein as a prognostic factor in breast cancer. World J Surg Oncol 2011, 9, 139. [CrossRef]
- Osborne, C.K.; Bardou, V.; Hopp, T.A.; Chamness, G.C.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Fuqua, S.A.; Wong, J.; Allred, D.C.; Clark, G.M.; Schiff, R. Role of the estrogen receptor coactivator AIB1 (SRC-3) and HER-2/neu in tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2003, 95, 353-361. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yasui, K.; Lee, C.J.; Kurioka, H.; Hosokawa, Y.; Oka, T.; Inazawa, J. Elevated expression levels of NCOA3, TOP1, and TFAP2C in breast tumors as predictors of poor prognosis. Cancer 2003, 98, 18-23. [CrossRef]
- Nakles, R.E.; Shiffert, M.T.; Diaz-Cruz, E.S.; Cabrera, M.C.; Alotaiby, M.; Miermont, A.M.; Riegel, A.T.; Furth, P.A. Altered AIB1 or AIB1Delta3 expression impacts ERalpha effects on mammary gland stromal and epithelial content. Mol Endocrinol 2011, 25, 549-563. [CrossRef]
- Tilli, M.T.; Reiter, R.; Oh, A.S.; Henke, R.T.; McDonnell, K.; Gallicano, G.I.; Furth, P.A.; Riegel, A.T. Overexpression of an N-terminally truncated isoform of the nuclear receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer 1 leads to altered proliferation of mammary epithelial cells in transgenic mice. Mol Endocrinol 2005, 19, 644-656. [CrossRef]
- Avivar, A.; Garcia-Macias, M.C.; Ascaso, E.; Herrera, G.; O'Connor, J.E.; Font de Mora, J. Moderate overexpression of AIB1 triggers pre-neoplastic changes in mammary epithelium. FEBS Lett 2006, 580, 5222-5226. [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.Q.; Liao, L.; Wang, S.; Medina, D.; O'Malley, B.W.; Xu, J. Mice lacking the amplified in breast cancer 1/steroid receptor coactivator-3 are resistant to chemical carcinogen-induced mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2005, 65, 7993-8002. [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.Q.; Liao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lee, A.V.; O'Malley, B.W.; Xu, J. AIB1/SRC-3 deficiency affects insulin-like growth factor I signaling pathway and suppresses v-Ha-ras-induced breast cancer initiation and progression in mice. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 1875-1885. [CrossRef]
- Planas-Silva, M.D.; Shang, Y.; Donaher, J.L.; Brown, M.; Weinberg, R.A. AIB1 enhances estrogen-dependent induction of cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 3858-3862.
- Suen, C.S.; Berrodin, T.J.; Mastroeni, R.; Cheskis, B.J.; Lyttle, C.R.; Frail, D.E. A transcriptional coactivator, steroid receptor coactivator-3, selectively augments steroid receptor transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 27645-27653. [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, M.K.; Carter, D.J.; Harris, A.M.; Le, H.M.; Azorsa, D.O.; Meltzer, P.S.; Murdoch, F.E. Endogenously expressed estrogen receptor and coactivator AIB1 interact in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 12536-12540. [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Chou, C.K.; Pintilie, G.D.; Shen, H.; Foulds, C.E.; Fan, G.; Serysheva, I.; Ludtke, S.J.; et al. Structural and Functional Impacts of ER Coactivator Sequential Recruitment. Mol Cell 2017, 67, 733-743 e734. [CrossRef]
- Fanning, S.W.; Mayne, C.G.; Dharmarajan, V.; Carlson, K.E.; Martin, T.A.; Novick, S.J.; Toy, W.; Green, B.; Panchamukhi, S.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; et al. Estrogen receptor alpha somatic mutations Y537S and D538G confer breast cancer endocrine resistance by stabilizing the activating function-2 binding conformation. Elife 2016, 5. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Laws, M.J.; Guillen, V.S.; Ziegler, Y.; Min, J.; Sharma, A.; Kim, S.H.; Chu, D.; Park, B.H.; Oesterreich, S.; et al. Structurally Novel Antiestrogens Elicit Differential Responses from Constitutively Active Mutant Estrogen Receptors in Breast Cancer Cells and Tumors. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 5602-5613. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Rose, D.W.; Hermanson, O.; Liu, F.; Herman, T.; Wu, W.; Szeto, D.; Gleiberman, A.; Krones, A.; Pratt, K.; et al. Regulation of somatic growth by the p160 coactivator p/CIP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 13549-13554. [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, T.; McGlynn, L.M.; Campbell, F.M.; Muller, S.; Tovey, S.M.; Dunne, B.; Nielsen, K.V.; Cooke, T.G.; Bartlett, J.M. Amplified in breast cancer 1 in human epidermal growth factor receptor - positive tumors of tamoxifen-treated breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13, 1405-1411. [CrossRef]
- Fereshteh, M.P.; Tilli, M.T.; Kim, S.E.; Xu, J.; O'Malley, B.W.; Wellstein, A.; Furth, P.A.; Riegel, A.T. The nuclear receptor coactivator amplified in breast cancer-1 is required for Neu (ErbB2/HER2) activation, signaling, and mammary tumorigenesis in mice. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 3697-3706. [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liao, L.; Redmond, A.; Young, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, H.; O'Malley, B.W.; Xu, J. The AIB1 oncogene promotes breast cancer metastasis by activation of PEA3-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and MMP9 expression. Mol Cell Biol 2008, 28, 5937-5950. [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Yi, P.; Amazit, L.; LaMarca, H.L.; Ashcroft, F.; Kumar, R.; Mancini, M.A.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O'Malley, B.W. SRC-3Delta4 mediates the interaction of EGFR with FAK to promote cell migration. Mol Cell 2010, 37, 321-332. [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Erdem, H.; Li, R.; Cai, Y.; Ayala, G.; Ittmann, M.; Yu-Lee, L.Y.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J. Steroid receptor coactivator-3/AIB1 promotes cell migration and invasiveness through focal adhesion turnover and matrix metalloproteinase expression. Cancer Res 2008, 68, 5460-5468. [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Pecina-Slaus, N. Tumor suppressor gene E-cadherin and its role in normal and malignant cells. Cancer Cell Int 2003, 3, 17. [CrossRef]
- Oda, H.; Takeichi, M. Evolution: structural and functional diversity of cadherin at the adherens junction. J Cell Biol 2011, 193, 1137-1146. [CrossRef]
- Kaszak, I.; Witkowska-Pilaszewicz, O.; Niewiadomska, Z.; Dworecka-Kaszak, B.; Ngosa Toka, F.; Jurka, P. Role of Cadherins in Cancer-A Review. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [CrossRef]
- Varisli, L.; Tolan, V. Increased ROS alters E-/N-cadherin levels and promotes migration in prostate cancer cells. Bratisl Lek Listy 2022, 123, 752-757. [CrossRef]
- Varisli, L.; Tolan, V.; Cen, J.H.; Vlahopoulos, S.; Cen, O. Dissecting the effects of androgen deprivation therapy on cadherin switching in advanced prostate cancer: A molecular perspective. Oncol Res 2022, 30, 137-155. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Almeida, C.; Oliveira, A.; Joao Ramos, M.; Fernandes, P.A.; Teixeira, N.; Amaral, C. Estrogen receptor-positive (ER(+)) breast cancer treatment: Are multi-target compounds the next promising approach? Biochem Pharmacol 2020, 177, 113989. [CrossRef]
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative, G. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet 2005, 365, 1687-1717. [CrossRef]
- Razavi, P.; Chang, M.T.; Xu, G.; Bandlamudi, C.; Ross, D.S.; Vasan, N.; Cai, Y.; Bielski, C.M.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; Jonsson, P.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Endocrine-Resistant Advanced Breast Cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 427-438 e426. [CrossRef]
- Dustin, D.; Gu, G.; Fuqua, S.A.W. ESR1 mutations in breast cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 3714-3728. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.R.; Wu, Y.M.; Vats, P.; Su, F.; Lonigro, R.J.; Cao, X.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Wang, R.; Ning, Y.; Hodges, L.; et al. Activating ESR1 mutations in hormone-resistant metastatic breast cancer. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 1446-1451. [CrossRef]
- Toy, W.; Shen, Y.; Won, H.; Green, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Will, M.; Li, Z.; Gala, K.; Fanning, S.; King, T.A.; et al. ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer. Nat Genet 2013, 45, 1439-1445. [CrossRef]
- Heck, S.; Rom, J.; Thewes, V.; Becker, N.; Blume, B.; Sinn, H.P.; Deuschle, U.; Sohn, C.; Schneeweiss, A.; Lichter, P. Estrogen-related receptor alpha expression and function is associated with the transcriptional coregulator AIB1 in breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 5186-5193. [CrossRef]
- Lumachi, F.; Santeufemia, D.A.; Basso, S.M. Current medical treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. World J Biol Chem 2015, 6, 231-239. [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, R.; Ozpolat, B. Molecular Mechanisms of Anti-Estrogen Therapy Resistance and Novel Targeted Therapies. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; O'Malley, B.W. Nuclear receptor modulation--role of coregulators in selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) actions. Steroids 2014, 90, 39-43. [CrossRef]
- Fawell, S.E.; White, R.; Hoare, S.; Sydenham, M.; Page, M.; Parker, M.G. Inhibition of estrogen receptor-DNA binding by the "pure" antiestrogen ICI 164,384 appears to be mediated by impaired receptor dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1990, 87, 6883-6887. [CrossRef]
- Wijayaratne, A.L.; Nagel, S.C.; Paige, L.A.; Christensen, D.J.; Norris, J.D.; Fowlkes, D.M.; McDonnell, D.P. Comparative analyses of mechanistic differences among antiestrogens. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 5828-5840. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.L.; Shioda, K.; Coser, K.R.; Rivizzigno, D.; McSweeney, K.R.; Shioda, T. Fulvestrant-induced cell death and proteasomal degradation of estrogen receptor alpha protein in MCF-7 cells require the CSK c-Src tyrosine kinase. PLoS One 2013, 8, e60889. [CrossRef]
- Boszkiewicz, K.; Piwowar, A.; Petryszyn, P. Aromatase Inhibitors and Risk of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Adverse Effects in Breast Cancer Patients-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [CrossRef]
- Lonard, D.M.; Tsai, S.Y.; O'Malley, B.W. Selective estrogen receptor modulators 4-hydroxytamoxifen and raloxifene impact the stability and function of SRC-1 and SRC-3 coactivator proteins. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 14-24. [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Hu, S.; Gao, H.; Ma, R.; Yang, Q.; Pan, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, F. Role of AIB1 for tamoxifen resistance in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Oncology 2008, 75, 159-168. [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Holmes, K.A.; Geistlinger, T.R.; Hutcheson, I.R.; Nicholson, R.I.; Brown, M.; Jiang, J.; Howat, W.J.; Ali, S.; Carroll, J.S. Regulation of ERBB2 by oestrogen receptor-PAX2 determines response to tamoxifen. Nature 2008, 456, 663-666. [CrossRef]
- Lebert, J.; Lilly, E.J. Developments in the Management of Metastatic HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Review. Curr Oncol 2022, 29, 2539-2549. [CrossRef]
- Bouras, T.; Southey, M.C.; Venter, D.J. Overexpression of the steroid receptor coactivator AIB1 in breast cancer correlates with the absence of estrogen and progesterone receptors and positivity for p53 and HER2/neu. Cancer Res 2001, 61, 903-907.
- Font de Mora, J.; Brown, M. AIB1 is a conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen receptor. Mol Cell Biol 2000, 20, 5041-5047. [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Massarweh, S.; Osborne, C.K.; Wakeling, A.E.; Ali, S.; Weiss, H.; Schiff, R. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004, 96, 926-935. [CrossRef]
- Lahusen, T.; Fereshteh, M.; Oh, A.; Wellstein, A.; Riegel, A.T. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine phosphorylation and signaling controlled by a nuclear receptor coactivator, amplified in breast cancer 1. Cancer Res 2007, 67, 7256-7265. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Jain, P.; Gilad, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sung, N.; Park, M.J.; Dean, A.M.; Lanz, R.B.; Xu, J.; Dacso, C.C.; et al. Steroid receptor coactivator 3 is a key modulator of regulatory T cell-mediated tumor evasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2023, 120, e2221707120. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Sung, N.; Wang, J.; O'Malley, B.W.; Lonard, D.M. Steroid receptor coactivator-3 inhibition generates breast cancer antitumor immune microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res 2022, 24, 73. [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.; Toksoy, A.; Goebeler, M.; Engelhardt, E.; Brocker, E.; Gillitzer, R. Strong expression of the lymphoattractant C-X-C chemokine Mig is associated with heavy infiltration of T cells in human malignant melanoma. J Pathol 1999, 189, 552-558. [CrossRef]
- Neo, S.Y.; Lundqvist, A. The Multifaceted Roles of CXCL9 Within the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1231, 45-51. [CrossRef]
- Ozga, A.J.; Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 859-874. [CrossRef]
- Walser, T.C.; Ma, X.; Kundu, N.; Dorsey, R.; Goloubeva, O.; Fulton, A.M. Immune-mediated modulation of breast cancer growth and metastasis by the chemokine Mig (CXCL9) in a murine model. J Immunother 2007, 30, 490-498. [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; Loibl, S.; Noske, A.; Roller, M.; Muller, B.M.; Komor, M.; Budczies, J.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Kronenwett, R.; Hanusch, C.; et al. Tumor-associated lymphocytes as an independent predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 105-113. [CrossRef]
- Specht, K.; Harbeck, N.; Smida, J.; Annecke, K.; Reich, U.; Naehrig, J.; Langer, R.; Mages, J.; Busch, R.; Kruse, E.; et al. Expression profiling identifies genes that predict recurrence of breast cancer after adjuvant CMF-based chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009, 118, 45-56. [CrossRef]
- Hardenberg, J.B.; Braun, A.; Schon, M.P. A Yin and Yang in Epithelial Immunology: The Roles of the alpha(E)(CD103)beta(7) Integrin in T Cells. J Invest Dermatol 2018, 138, 23-31. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.C.; Schon, M.P. Integrin alpha(E)(CD103)beta(7) in Epithelial Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [CrossRef]
- Mackay, L.K.; Rahimpour, A.; Ma, J.Z.; Collins, N.; Stock, A.T.; Hafon, M.L.; Vega-Ramos, J.; Lauzurica, P.; Mueller, S.N.; Stefanovic, T.; et al. The developmental pathway for CD103(+)CD8+ tissue-resident memory T cells of skin. Nat Immunol 2013, 14, 1294-1301. [CrossRef]
- Cepek, K.L.; Shaw, S.K.; Parker, C.M.; Russell, G.J.; Morrow, J.S.; Rimm, D.L.; Brenner, M.B. Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature 1994, 372, 190-193. [CrossRef]
- Karecla, P.I.; Bowden, S.J.; Green, S.J.; Kilshaw, P.J. Recognition of E-cadherin on epithelial cells by the mucosal T cell integrin alpha M290 beta 7 (alpha E beta 7). Eur J Immunol 1995, 25, 852-856. [CrossRef]
- Le Floc'h, A.; Jalil, A.; Vergnon, I.; Le Maux Chansac, B.; Lazar, V.; Bismuth, G.; Chouaib, S.; Mami-Chouaib, F. Alpha E beta 7 integrin interaction with E-cadherin promotes antitumor CTL activity by triggering lytic granule polarization and exocytosis. J Exp Med 2007, 204, 559-570. [CrossRef]
- Karecla, P.I.; Green, S.J.; Bowden, S.J.; Coadwell, J.; Kilshaw, P.J. Identification of a binding site for integrin alphaEbeta7 in the N-terminal domain of E-cadherin. J Biol Chem 1996, 271, 30909-30915. [CrossRef]
- Shields, B.D.; Koss, B.; Taylor, E.M.; Storey, A.J.; West, K.L.; Byrum, S.D.; Mackintosh, S.G.; Edmondson, R.; Mahmoud, F.; Shalin, S.C.; et al. Loss of E-Cadherin Inhibits CD103 Antitumor Activity and Reduces Checkpoint Blockade Responsiveness in Melanoma. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 1113-1123. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Z.; Dong, W.; He, W.; Chen, X.; Dong, X.; Zheng, L.; Lin, T.; et al. CD103+ Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes Predict a Favorable Prognosis in Urothelial Cell Carcinoma of the Bladder. J Urol 2015, 194, 556-562. [CrossRef]
- Austrup, F.; Rebstock, S.; Kilshaw, P.J.; Hamann, A. Transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced expression of the mucosa-related integrin alpha E on lymphocytes is not associated with mucosa-specific homing. Eur J Immunol 1995, 25, 1487-1491. [CrossRef]
- Pauls, K.; Schon, M.; Kubitza, R.C.; Homey, B.; Wiesenborn, A.; Lehmann, P.; Ruzicka, T.; Parker, C.M.; Schon, M.P. Role of integrin alphaE(CD103)beta7 for tissue-specific epidermal localization of CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Invest Dermatol 2001, 117, 569-575. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.W.; Green, S.J.; Carter, C.; Coadwell, J.; Kilshaw, P.J. Studies on transcriptional regulation of the mucosal T-cell integrin alphaEbeta7 (CD103). Immunology 2001, 103, 146-154. [CrossRef]
- Franciszkiewicz, K.; Le Floc'h, A.; Boutet, M.; Vergnon, I.; Schmitt, A.; Mami-Chouaib, F. CD103 or LFA-1 engagement at the immune synapse between cytotoxic T cells and tumor cells promotes maturation and regulates T-cell effector functions. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 617-628. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.A.; Massague, J. TGF-beta directly targets cytotoxic T cell functions during tumor evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 369-380. [CrossRef]
- Boutet, M.; Gauthier, L.; Leclerc, M.; Gros, G.; de Montpreville, V.; Theret, N.; Donnadieu, E.; Mami-Chouaib, F. TGFbeta Signaling Intersects with CD103 Integrin Signaling to Promote T-Lymphocyte Accumulation and Antitumor Activity in the Lung Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 1757-1769. [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, T.; Mackay, L.K. Local immunity by tissue-resident CD8(+) memory T cells. Front Immunol 2012, 3, 340. [CrossRef]
- Henson, S.M.; Akbar, A.N. KLRG1--more than a marker for T cell senescence. Age (Dordr) 2009, 31, 285-291. [CrossRef]
- Grundemann, C.; Bauer, M.; Schweier, O.; von Oppen, N.; Lassing, U.; Saudan, P.; Becker, K.F.; Karp, K.; Hanke, T.; Bachmann, M.F.; et al. Cutting edge: identification of E-cadherin as a ligand for the murine killer cell lectin-like receptor G1. J Immunol 2006, 176, 1311-1315. [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Maruyama, T.; Saito, N.; Koganei, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsumoto, N. Killer cell lectin-like receptor G1 binds three members of the classical cadherin family to inhibit NK cell cytotoxicity. J Exp Med 2006, 203, 289-295. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wan, S.; Tao, K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, E. KLRG1 restricts memory T cell antitumor immunity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61670-61678. [CrossRef]
- Martinet, L.; Smyth, M.J. Balancing natural killer cell activation through paired receptors. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15, 243-254. [CrossRef]
- Meinicke, H.; Bremser, A.; Brack, M.; Schrenk, K.; Pircher, H.; Izcue, A. KLRG1 impairs regulatory T-cell competitive fitness in the gut. Immunology 2017, 152, 65-73. [CrossRef]
- Tessmer, M.S.; Fugere, C.; Stevenaert, F.; Naidenko, O.V.; Chong, H.J.; Leclercq, G.; Brossay, L. KLRG1 binds cadherins and preferentially associates with SHIP-1. Int Immunol 2007, 19, 391-400. [CrossRef]
- Schwartzkopff, S.; Woyciechowski, S.; Aichele, U.; Flecken, T.; Zhang, N.; Thimme, R.; Pircher, H. TGF-beta downregulates KLRG1 expression in mouse and human CD8(+) T cells. Eur J Immunol 2015, 45, 2212-2217. [CrossRef]
- Attig, S.; Hennenlotter, J.; Pawelec, G.; Klein, G.; Koch, S.D.; Pircher, H.; Feyerabend, S.; Wernet, D.; Stenzl, A.; Rammensee, H.G.; et al. Simultaneous infiltration of polyfunctional effector and suppressor T cells into renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 8412-8419. [CrossRef]
- Baitsch, L.; Legat, A.; Barba, L.; Fuertes Marraco, S.A.; Rivals, J.P.; Baumgaertner, P.; Christiansen-Jucht, C.; Bouzourene, H.; Rimoldi, D.; Pircher, H.; et al. Extended co-expression of inhibitory receptors by human CD8 T-cells depending on differentiation, antigen-specificity and anatomical localization. PLoS One 2012, 7, e30852. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jing, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, L.; Hu, H.; Tang, C.; Liu, S.; Wei, Q.; Duan, R.; Guo, J.; et al. N-cadherin inhibitor creates a microenvironment that protect TILs from immune checkpoints and Treg cells. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Amarnath, S.; Mangus, C.W.; Wang, J.C.; Wei, F.; He, A.; Kapoor, V.; Foley, J.E.; Massey, P.R.; Felizardo, T.C.; Riley, J.L.; et al. The PDL1-PD1 axis converts human TH1 cells into regulatory T cells. Sci Transl Med 2011, 3, 111ra120. [CrossRef]
- Munn, D.H.; Sharma, M.D.; Baban, B.; Harding, H.P.; Zhang, Y.; Ron, D.; Mellor, A.L. GCN2 kinase in T cells mediates proliferative arrest and anergy induction in response to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Immunity 2005, 22, 633-642. [CrossRef]
- Kolijn, K.; Verhoef, E.I.; Smid, M.; Bottcher, R.; Jenster, G.W.; Debets, R.; van Leenders, G. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Prostate Cancer Demonstrates Enhanced Immune Evasion Marked by IDO1 Expression. Cancer Res 2018, 78, 4671-4679. [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ten Dijke, P. Harnessing epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity to boost cancer immunotherapy. Cell Mol Immunol 2023, 20, 318-340. [CrossRef]
- Raj, G.V.; Sareddy, G.R.; Ma, S.; Lee, T.K.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Li, R.; Liu, X.; Murakami, S.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, W.R.; et al. Estrogen receptor coregulator binding modulators (ERXs) effectively target estrogen receptor positive human breast cancers. Elife 2017, 6. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Lonard, D.M.; Chow, D.C.; Palzkill, T.; Xu, J.; O'Malley, B.W.; et al. Development of potent small-molecule inhibitors to drug the undruggable steroid receptor coactivator-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 4970-4975. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lonard, D.M.; Jung, S.Y.; Malovannaya, A.; Feng, Q.; Qin, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O'Malley, B.W. The SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator is degraded in a ubiquitin- and ATP-independent manner by the REGgamma proteasome. Cell 2006, 124, 381-392. [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.C.; Feng, Q.; Lonard, D.M.; O'Malley, B.W. SRC-3 coactivator functional lifetime is regulated by a phospho-dependent ubiquitin time clock. Cell 2007, 129, 1125-1140. [CrossRef]
- Ferry, C.; Gaouar, S.; Fischer, B.; Boeglin, M.; Paul, N.; Samarut, E.; Piskunov, A.; Pankotai-Bodo, G.; Brino, L.; Rochette-Egly, C. Cullin 3 mediates SRC-3 ubiquitination and degradation to control the retinoic acid response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 20603-20608. [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, L.; Jiao, X.; Hou, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, W.; et al. Thevebioside, the active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine, promotes ubiquitin-mediated SRC-3 degradation to induce NSCLC cells apoptosis. Cancer Lett 2020, 493, 167-177. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wen, L.; Yi, S.; Hu, J.; Ruan, J.; Zhao, F.; Cui, G.; Fang, J.; Chen, Y. Steroid receptor coactivator-3 is a pivotal target of gambogic acid in B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma and an inducer of histone H3 deacetylation. Eur J Pharmacol 2016, 789, 46-59. [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Yu, Y.; Chow, D.C.; Palzkill, T.; Madoux, F.; Hodder, P.; Chase, P.; Griffin, P.R.; O'Malley, B.W.; Lonard, D.M. Identification of verrucarin a as a potent and selective steroid receptor coactivator-3 small molecule inhibitor. PLoS One 2014, 9, e95243. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lonard, D.M.; Yu, Y.; Chow, D.C.; Palzkill, T.G.; O'Malley, B.W. Small molecule inhibition of the steroid receptor coactivators, SRC-3 and SRC-1. Mol Endocrinol 2011, 25, 2041-2053. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lonard, D.M.; Yu, Y.; Chow, D.C.; Palzkill, T.G.; Wang, J.; Qi, R.; Matzuk, A.J.; Song, X.; Madoux, F.; et al. Bufalin is a potent small-molecule inhibitor of the steroid receptor coactivators SRC-3 and SRC-1. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 1506-1517. [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.M.; Kim, K.B.; Kumagai, A.; Mercurio, F.; Crews, C.M.; Deshaies, R.J. Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001, 98, 8554-8559. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Ren, Y.; Cao, H.; Chen, J. Discovery of novel resorcinol diphenyl ether-based PROTAC-like molecules as dual inhibitors and degraders of PD-L1. Eur J Med Chem 2020, 199, 112377. [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Cao, C.; Ni, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, P.; Hao, S.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: great opportunities for academia and industry (an update from 2020 to 2021). Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 181. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, S.; Sun, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Yu, H.; Song, X.; et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) by a proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC). Bioorg Chem 2021, 111, 104833. [CrossRef]
- Han, S.J.; Jain, P.; Gilad, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sung, N.; Park, M.J.; Dean, A.M.; Lanz, R.B.; Xu, J.; Dacso, C.C.; et al. Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 is a Key Modulator of Regulatory T Cell-Mediated Tumor Evasion. bioRxiv 2023. [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, D.; Jain, P.; Yu, Y.; Cardenas, D.; Peng, X.; Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Development of improved SRC-3 inhibitors as breast cancer therapeutic agents. Endocr Relat Cancer 2021, 28, 657-670. [CrossRef]
- Manmuan, S.; Sakunrangsit, N.; Ketchart, W. Salinomycin overcomes acquired tamoxifen resistance through AIB1 and inhibits cancer cell invasion in endocrine resistant breast cancer. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2017, 44, 1042-1052. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cui, C.; Cai, F. Anticancer Mechanisms of Salinomycin in Breast Cancer and Its Clinical Applications. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 654428. [CrossRef]
- Hickson, I.; Zhao, Y.; Richardson, C.J.; Green, S.J.; Martin, N.M.; Orr, A.I.; Reaper, P.M.; Jackson, S.P.; Curtin, N.J.; Smith, G.C. Identification and characterization of a novel and specific inhibitor of the ataxia-telangiectasia mutated kinase ATM. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 9152-9159. [CrossRef]
- Varisli, L.; Cen, O.; Vlahopoulos, S. Dissecting pharmacological effects of chloroquine in cancer treatment: interference with inflammatory signaling pathways. Immunology 2020, 159, 257-278. [CrossRef]
- Stagni, V.; Kaminari, A.; Contadini, C.; Barila, D.; Sessa, R.L.; Sideratou, Z.; Vlahopoulos, S.A.; Tsiourvas, D. A Triphenylphosphonium-Functionalized Delivery System for an ATM Kinase Inhibitor That Ameliorates Doxorubicin Resistance in Breast Carcinoma Mammospheres. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [CrossRef]
- Stagni, V.; Kaminari, A.; Sideratou, Z.; Sakellis, E.; Vlahopoulos, S.A.; Tsiourvas, D. Targeting breast cancer stem-like cells using chloroquine encapsulated by a triphenylphosphonium-functionalized hyperbranched polymer. Int J Pharm 2020, 585, 119465. [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, B.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, M.; Yu, C.; Yang, C.J. Selection and Application of DNA Aptamer Against Oncogene Amplified in Breast Cancer 1. J Mol Evol 2015, 81, 179-185. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




