Introduction: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most ancient illnesses known to human. Around 3000 years ago, it was first mentioned in an Egyptian text. In recent decades, there has been a significant surge in the global prevalence of diabetes and its associated metabolic complications. The difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes was established in 1936 [
1]. The frequency of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM), a chronic metabolic condition, has been continuously rising worldwide. According to the World Health Organization, the incidence of obesity worldwide nearly The global diabetic population is steadily rising, currently estimated at 422 million individuals [
2]. T2DM is characterized by dysregulation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism, which occurs from decreased insulin secretion, insulin resistance, or a combination of the two, usually occurs later in life and is frequently linked to lifestyle factors [
3]. Among the three main groups of diabetes, which include Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and gestational diabetes, Type 2 diabetes is the most prevalent form [
4]. The primary cause of T2DM is a gradual decline in insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells, typically occurring against a backdrop of pre-existing insulin resistance in skeletal muscle, liver, and adipose tissue [
5,
6]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes stands as a primary contributor to conditions such as blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputations [
7]. Diabetes is linked to both microvascular (diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy) and macrovascular (cardiovascular disease or CVD) complications [
8]. Individuals with diabetes face an elevated risk of CVD, encompassing conditions like coronary heart disease (CHD) [
9], hypertension, increased levels of low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL), and obesity [
5,
10]
Adiponectin, the most prevalent peptide released by adipocytes plays prominent role in the intricate connection between adiposity, insulin resistance, and inflammation [
11]. The levels of adiponectin are inversely correlated with adiposity, that means increase the body fat reduce the adiponectin and reduce the fat accumulation increase the adiponectin level [
12]. Adiponectin shows its biological action through several mechanisms such as enhancing insulin sensitivity in the peripheral cells [
13,
14,
15] anti-inflammatory actions by reducing the production of inflammatory molecules [
16], breakdown of fatty acids and inhibits the production of fatty acids in the liver [
17], maintain the health and flexibility of blood vessels [
18,
19] etc. It is also adiponectin also maintain a responsible role for appetite regulation and energy expenditure [
20,
21].
Till toady there are several treatment options for T2DM. However, treating T2DM is very challenging due to its complex nature and the diversity of factors involved. T2DM is a progressive disease as the production of insulin are reduced day by day irrespective of treatment of diabetes. Insulin resistance is another challenge to treat diabetes. Life style modifications including diet and exercise plays a crucial role for diabetes. However, sustaining these alterations can be arduous. Moreover, chronic conditions like T2DM have significant effects on emotional health.
Recent studies has shown that, A reduction in plasma adiponectin concentration is closely associated with the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obesity [
22,
23]. Both animal and experimental research have demonstrated that adiponectin enhances insulin sensitivity, suggesting it may serve as a preventive measure against the onset of T2DM [
24].
In the current review we will discuss recent advancements in studying the pathophysiological functions of adiponectin and its receptors in relation to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome.
Adiponectin: An Overview: Adiponectin, alternatively referred to as AdipoQ, APM1 or ACRP30, is a single-chain adipokine composed of 244 amino acids, possessing a molecular weight of around 26 kilodaltons (kDa) secreted by white adipose tissue. The Adiponectin protein is encoded by the AdipoQ gene located on the chromosome locus 3q27. Adiponectin consists of several distinct structural components. It includes an NH2-terminal hyper-variable region, a collagenous domain consisting of 22 Gly-XY repeats, and a COOH-terminal C1q-like globular domain. When it is secreted into the bloodstream, adiponectin forms three oligomeric complexes, which are a trimer, a hexamer, and a high molecular weight multimer [
25]. Adiponectin primarily binds to seven-transmembrane receptors known as AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, to regulate a range of physiological functions including whole-body energy balance, inflammatory responses, insulin sensitivity, and the process of fat metabolism [
26]. Unlike traditional G-protein coupled receptors, these receptors possess a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus and an extracellular COOH terminal domain. AdipoR1 is most abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle, whereas AdipoR2 is predominantly expressed in the liver [
27]. In humans and mice, AdipoR1 is situated on chromosome 1p36.13-q41, while AdipoR2 is found on chromosome 12p13.31 and 6 F1, respectively. The molecular structure of both forms of the receptor exhibits significant homology, featuring an internal N-terminus and an external C-terminus [
28]. AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 are adiponectin receptors that stimulate AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and PPAR activity, regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Adiponectin-induced complete AMPK activation requires both Ca2+/CaMKK and AMP/LKB1 [
29].
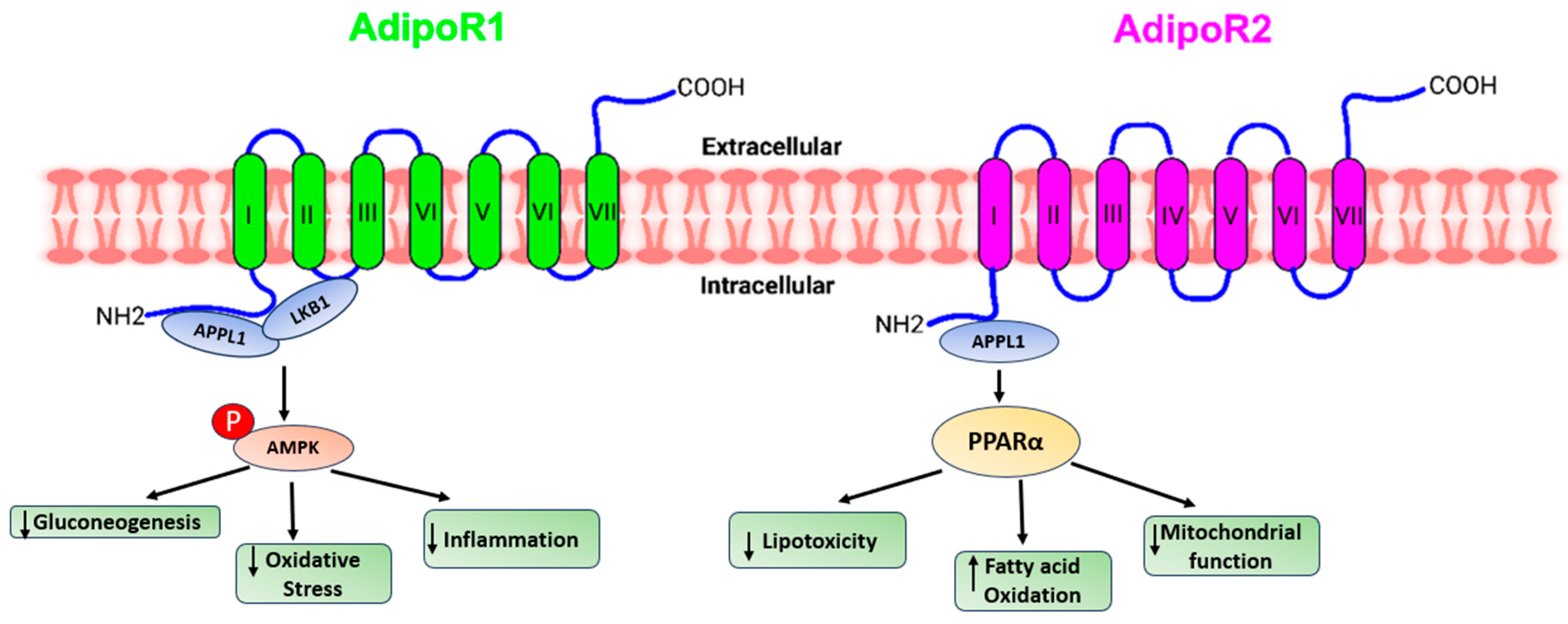
Figure 1.
A presentation demonstrating the diverse pathways through which adiponectin receptors exert their functions.
Figure 1.
A presentation demonstrating the diverse pathways through which adiponectin receptors exert their functions.
Adiponectin stimulates glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle after binding to AdipoR1, which is mediated by the recruitment of the adaptor protein with the pleckstrin homology domain, phosphotyrosine domain, and leucine zipper domain (APPL). APPL binding to the intracellular domain of AdipoR1 activates Rab5, a small GTPase that enhances GLUT4 membrane translocation and glucose absorption in muscle. APPL also binds to PI3 kinase and Akt, showing that adiponectin can boost insulin signaling as well [
30]. The interaction of APPL and AdipoR1 activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which inhibits acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and promotes fatty acid oxidation—adipoR-mediated activation of AMPK leads in higher fatty acid oxidation and decreased obesity. AMPK activation increases glucose absorption and lactate generation in muscle while suppressing gluconeogenesis. Together, the adiponectin signaling pathways underscore the relevance of adiponectin in glucose and lipid metabolism [
31].
Adiponectin activates and enhances the production of PPAR ligands via AdipoR2, as well as fatty acid combustion and energy consumption. This is accomplished in part by enhanced expression of the ACO and UCP genes, which include the peroxisome proliferator response element (PPRE) in their promoter regions [
32].
Adiponectin Pathway Regulation: Adiponectin regulation is a complicated combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. The adiponectin regulatory mechanism centers mostly around the expression and release of adiponectin from adipocytes.
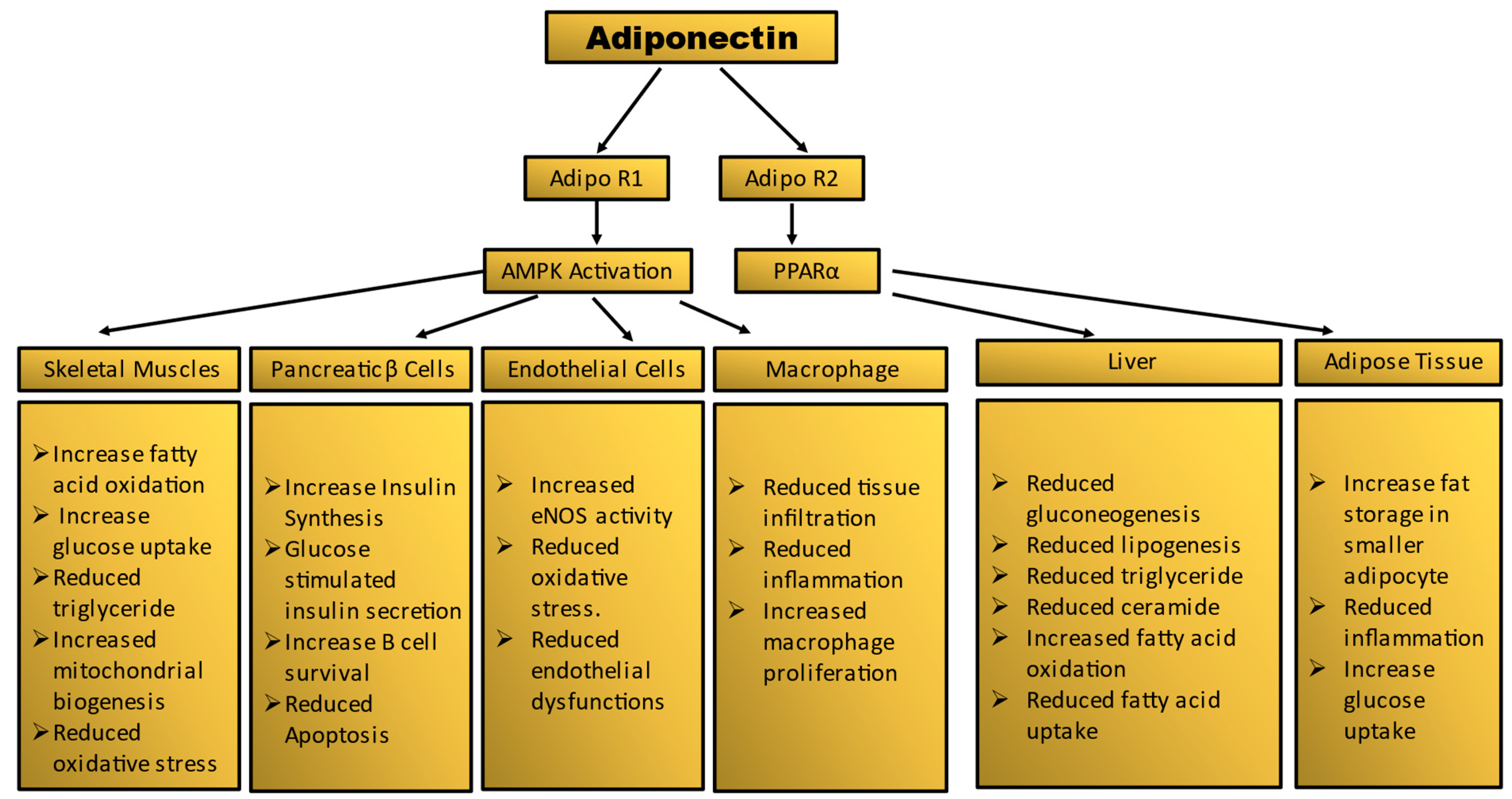
Figure 2.
Summary of tissue-specific functions of adiponectin. Mechanism of adiponectin actions in prevention of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Figure 2.
Summary of tissue-specific functions of adiponectin. Mechanism of adiponectin actions in prevention of insulin resistance and diabetes.
Genetic Factors: Adiponectin is mostly generated in white adipose tissue by mature adipocytes. Originally assumed to be expressed solely by adipose tissue, it is now widely documented that adiponectin is generated and released by a variety of cell types, including skeletal and cardiac muscles [
33,
34]. The normal range of adiponectin in human plasma is 2-20 ug/mL. Adiponectin levels can be influenced by genetic variations in the ADIPOQ gene, which encodes adiponectin. Some genetic polymorphisms are linked to increased or decreased adiponectin production [
35].
Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin sensitivity is one of most important determinant of adiponectin levels. Higher the insulin sensitivity higher the adiponectin secretion. On the other hand reduced insulin sensitivity in several diseases such as diabetes and obesity the adiponectin level also decreases [
36]. A team of researchers from the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden conducted a study involving 942 men. They found a robust correlation between insulin sensitivity and three ADIPOQ variants—namely, rs17300539, rs3774261, and rs6444175. In obese individuals, lower serum adiponectin levels were observed compared to those in normal, healthy individuals [
37].
Inflammatory State: The levels of Adiponectin in the bloodstream decline following an elevation in proinflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6, along with endothelial reticulum stress and adipocyte hypertrophy. This phenomenon is associated with conditions linked to expanded adipose tissue, including obesity, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome [
38].
Adipose Tissue Distribution: The adiponectin levels are influenced by the distribution of adipose tissue. Subcutaneous adipose tissue is associated with higher adiponectin levels compared to visceral fat [
39].
Diet and Nutritional Factors: Several dietary components such as omega-3 fatty acid, and polyphenols are influenced production of adiponectin [
40]. A group of researchers from Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil observed in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, 2-month clinical trial with 80 individuals that, supplementation of ω-3 fatty acid showed an increase in serum adiponectin [
41].
Physical Exercise: Regular physical exercise mainly aerobic exercises such as jogging or cycling, as well as resistance training, can increase adiponectin levels. Although exercise enhances the insulin sensitivity, which is linked to adiponectin secretions [
42].
Hormonal Regulation: Leptin, another hormone secreted by adipose tissue, can influence adiponectin levels by opposing effects on metabolic regulation [
43]. Insulin can stimulate adiponectin production and secretion. With improved insulin sensitivity, as seen with weight loss and exercise, can lead to increased adiponectin levels [
44].
Adiponectin Receptors: Adiponectin shows its effects after binding to specific receptors, AdipoR1 and AdipoR2. Various tissues, including skeletal muscle, liver, and the cardiovascular system shows expression of these receptors which can influence the secretion of adiponectin [
45].
Aging: As individuals age, there is a decrease in the activity of brown adipose tissue, a decline in sex hormone levels, and an expansion of abdominal adipose tissue. This is accompanied by a shift of lipids from the subcutaneous fat compartment to the visceral fat compartment. This ultimately results in reduced the production of adiponectin [
46].
Therapeutic Interventions: Certain medications and lifestyle interventions can influence adiponectin levels. Anti diabetic drug such as thiazolidinediones (TZDs), metformin can increase adiponectin levels [
47,
48].
Adiponectin and Diabetes: In 1995, a group of researchers from Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research, Cambridge, Massachusetts first discovered adiponectin [
12]. This was a significant discovery because at the time, adipose tissue was primarily viewed as a passive energy storage site. Following studies, it was shown that adiponectin plays an important role in modulating insulin sensitivity. Higher levels of adiponectin have been linked to better insulin sensitivity, whereas lower levels have been linked to insulin resistance [
49]. Several studies has shown a significant correlation between adiponectin levels and diabetes.
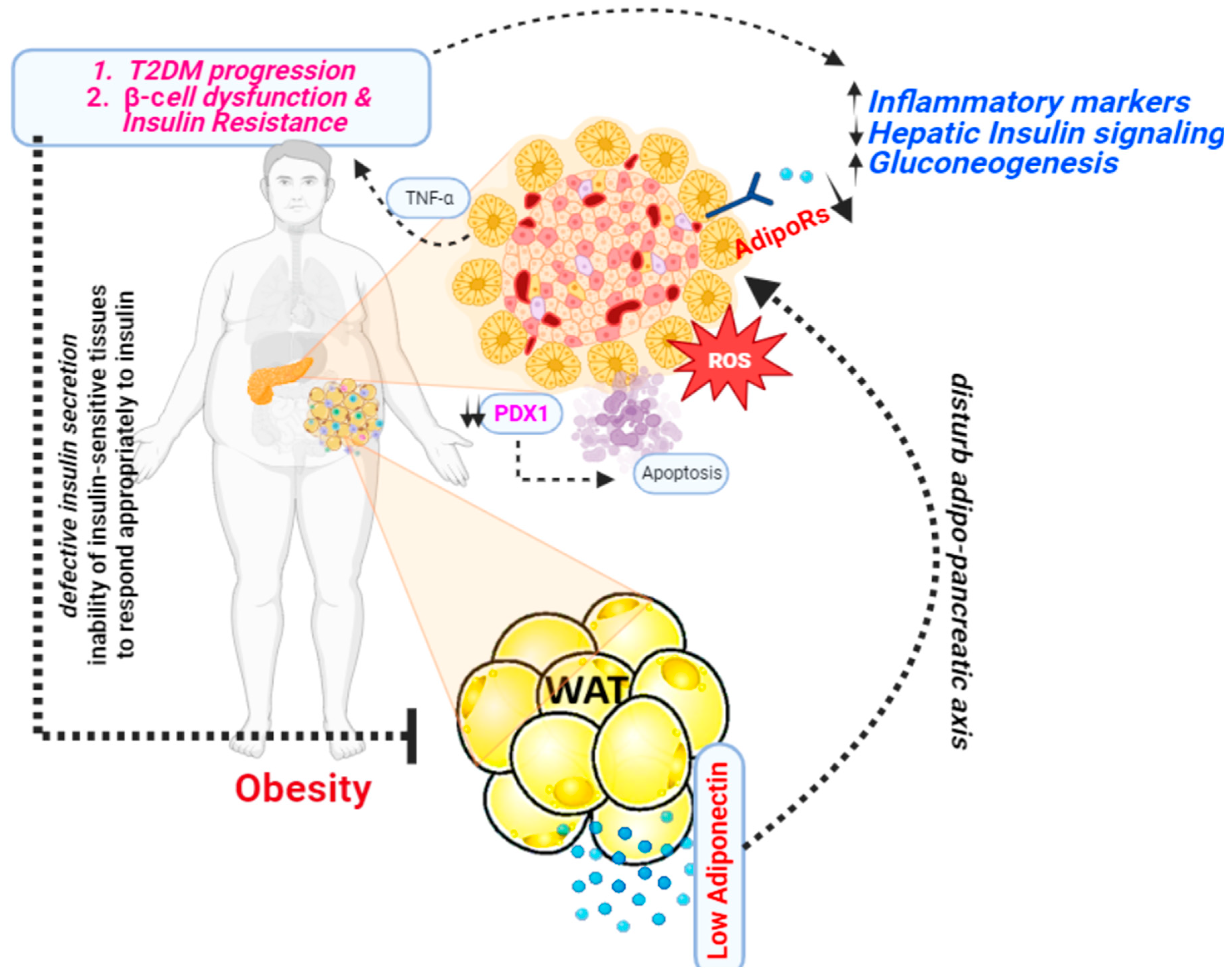
Figure 3.
A presentation illustrating the mechanism through which adiponectin functions as an antidiabetic agent.
Figure 3.
A presentation illustrating the mechanism through which adiponectin functions as an antidiabetic agent.
Insulin resistance and adiponectin: Insulin resistance has a hereditary component that is not fully understood and is frequently passed down through generations. Furthermore, obesity has a significant hereditary component that inevitably worsens insulin resistance. As a result, obesity and insulin resistance are often present for many years before additional alterations such as high blood pressure, dyslipidemia, T2DM, and cardiovascular disease develop [
19,
50]The discovery that, in both mice and humans, a loss of adipose tissue results in higher levels of circulating triglycerides and fatty acids and insulin resistance serves as more evidence of the critical role that adipose tissue plays in regulating whole-body metabolism by sequestering fat [
51,
52,
53]. Additionally, the appropriate release of adipokines like leptin and adiponectin, which improve insulin sensitivity, depends on the amount of adipose tissue. Lipodystrophies affect adipokine secretion in humans and mice.
The first study to show that adiponectin actively influences insulin sensitivity was reported in 2001. A C-terminal globular adiponectin fragment can lower plasma glucose levels by boosting fatty acid oxidation in muscle [
14,
54,
55]. Globular adiponectin appears to function in conjunction with AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (and later by inhibiting acetyl-CoA carboxylase) and PPAR- (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha) to create its metabolic action in the muscles. Ceramidase silencing can inhibit AMPK phosphorylation in C2C12 myotubes, indicating a function for sphingolipid metabolism with adiponectin signaling in this tissue. Adiponectin binding increases glucose uptake (through GLUT4 translocation) and non-oxidative glycolysis while decreasing intramyocellular triacylglycerol concentration and boosting fatty acid oxidation. Furthermore, adiponectin influences the quantity of mitochondria and the kind of oxidative fibers [
54].Adiponectin's actions on skeletal muscles are diminished in disease situations. Obese and insulin-resistant rats had poorer binding of globular and full-length adiponectin, which may be attributed to a lower density of adiponectin receptors. Human investigations, on the other hand, have not shown changed levels of Adipor1/Adipor2 RNAm related with insulin resistance states [
56].
Apoptosis and Adiponectin: Liu et al reported that, by stimulating the AdipoR1/AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signal pathway, adiponectin decreased early apoptotic cells and prevented the mitochondrial apoptosis process. Furthermore, PPAR linked to the ATF2 promoter area and suppressed ATF2 transcription. ATF2 transcriptional suppression was associated with adiponectin's ability to prevent apoptosis in adipocytes [
57]. Zuo et al. reported Adiponectin suppresses inflammation and reduces apoptosis caused by excessive hyperglycemia by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-B signaling pathway [
58]. The apoptotic-inducing influence of adiponectin is primarily facilitated by AdipoRs, which trigger the activation of caspase family members (caspase 3, 8, 9)[
59,
60].
Treatment of beta-cell line INS-1 cells with cytokine combination (IL-1b/IFN-c) or palmitic acid strongly promoted apoptosis, which could be greatly suppressed by gAPN via caspase-3 inhibition without altering NF-jB [
61]. Lin et al. reported Adiponectin cotreatment partially reversed high glucose-induced INS-1 cell death, malfunction, and decrease in insulin gene expression, which was mediated at least in part by transiently activating the AMPK signaling system [
59]. Adiponectin has also been identified to modulate several additional molecular pathways involved in apoptosis. This contains the Bcl-2 family of proteins, which are critical in managing the balance of pro-apoptotic (cell death-promoting) and anti-apoptotic (cell death-inhibiting) signals inside the cell. Adiponectin has the ability to modulate the expression and activity of the Bcl-2, Bax, and Bak proteins [
62].
Adiponectin may also have an effect on the tumor suppressor protein p53, which is important in starting apoptosis in response to cellular stress or injury. The action of adiponectin on p53 may contribute to its proapoptotic effects [
63,
64]Adiponectin has also been demonstrated to influence the iNOS/ROS/RNS pathways. All chemicals involved in cellular signaling and stress responses are iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase), ROS (reactive oxygen species), and RNS (reactive nitrogen species). The regulation of these pathways by adiponectin may contribute to its proapoptotic effects [
65].
β-cell function and Adiponectin: There have been a number of research looking at the direct impact of adiponectin on insulin secretion in β-cells. A group of researchers from University of Tokyo reported that, Adiponectin enhances insulin release from isolated mouse islets by promoting the exocytosis of insulin granules, with no discernible impact on ATP production, KATP channels, membrane potential, calcium influx, or activation of AMPK [
66]. An additional investigation demonstrated that adiponectin safeguards β-cells from apoptosis induced by prolonged serum deprivation and glucotoxicity. These outcomes are facilitated by the activation of both MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and PI3K-Akt pathways [
67]. James E P et al. reported that globular adiponectin induces a notable enhancement in cell viability, dependent on ERK1/2 signaling, along with a substantial rise in Pdx-1 expression in rat β-cell lines [
68]. Adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase (AMPK) is triggered by adiponectin, leading to the direct phosphorylation and subsequent inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity in β-cells [
69].
Adiponectin knockout mice exhibit compromised glucose tolerance, even in the presence of normal or lower-than-normal insulin levels [
70]. Transgenic ob/ob mice expressing the globular domain of adiponectin demonstrate heightened insulin sensitivity and elevated insulin secretion in comparison to nontransgenic mice[
32,
71,
72] In vivo experiments conducted in C57BL/6 mice reveal that intravenous administration of adiponectin leads to an augmentation in insulin secretion[
66] .
An observational study involving Asian children found that adiponectin levels exhibit an inverse relationship with body weight, body mass index, and proinsulin levels in both boys and girls. Moreover, in girls, there is an inverse association between adiponectin levels and insulin concentration as well as the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) [
73]. Studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between adiponectin levels and insulin sensitivity. Conversely, there is an inverse correlation between adiponectin levels and fasting proinsulin concentration, as well as the proinsulin-to-insulin ratio, which serves as a marker of β-cell failure [
74]. Furthermore, it has been suggested that the decrease in adiponectin levels is longitudinally linked with a reduced ability of β-cells to compensate for insulin resistance in women with a history of gestational diabetes [
75]. In overweight Hispanic adolescents, a cross-sectional study affirmed that both leptin and adiponectin are individually linked to insulin sensitivity, while they do not exhibit an association with insulin secretion [
76].
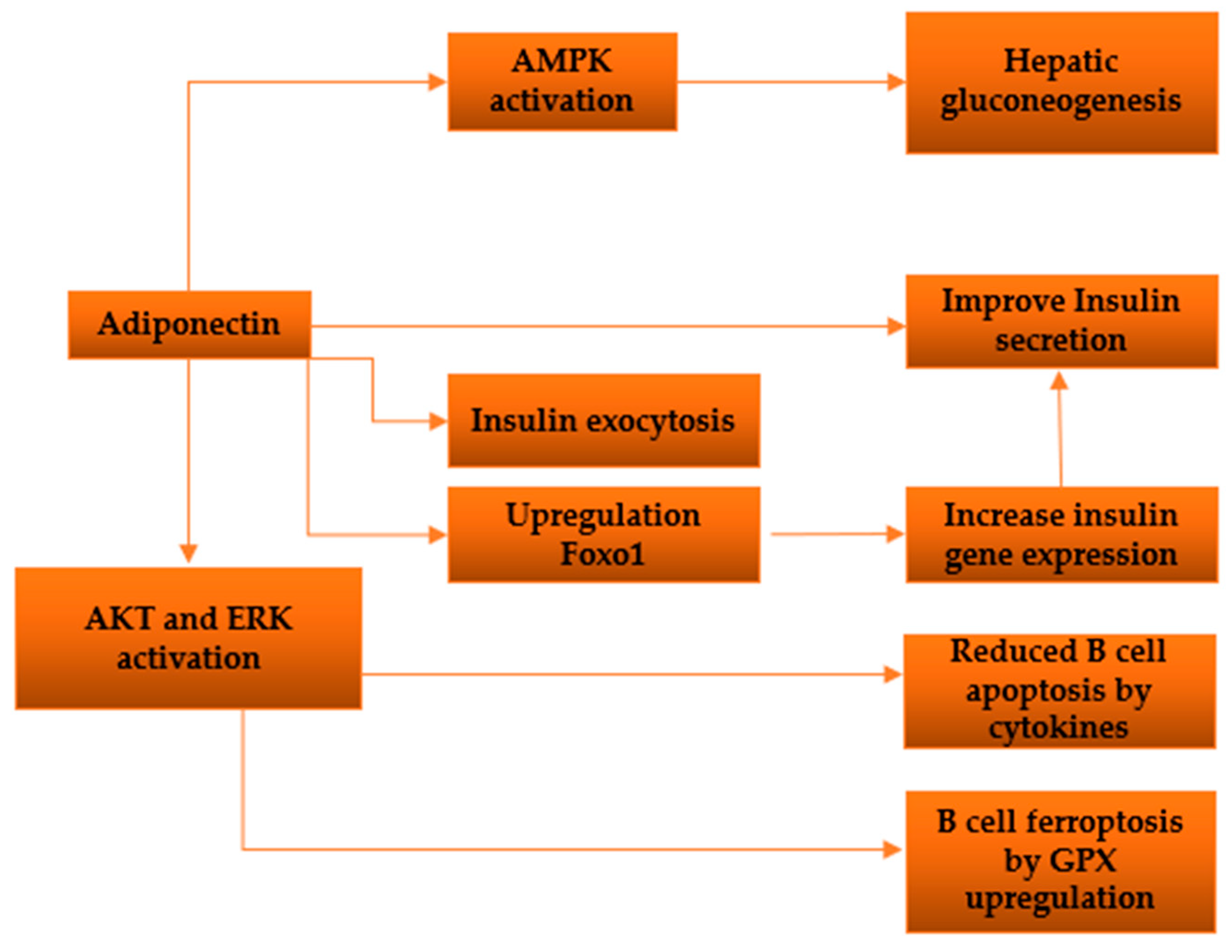
Figure 4.
Diagram depicting the investigated pathways illustrating the impacts of adiponectin on pancreatic β-cells.
Figure 4.
Diagram depicting the investigated pathways illustrating the impacts of adiponectin on pancreatic β-cells.
Oxidative stress and adiponectin: The production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) leads to oxidative stress, causing a range of cellular and molecular alterations, including dysfunction in mitochondria, which disrupts normal physiological processes in the body [
77,
78,
79,
80].While oxidative pathways are crucial in mitochondrial-mediated processes, the exact molecular mechanisms responsible are still unclear. The compromised mitochondrial function is evident in insulin resistance across different cell types. Furthermore, ongoing research is unraveling the roles of the master antioxidant pathway involving nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1), and antioxidant response elements (ARE) in elucidating various molecular pathways associated with diabetes.
Kadowaki and colleagues' findings revealed that oxidative stress was elevated in mice lacking AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, offering compelling evidence that the adiponectin-AdipoR pathway plays a pivotal role in reducing oxidative stress [
29]. In a mouse model of kidney disease, the absence of adiponectin resulted in heightened albuminuria and elevated expression of genes associated with oxidative stress [
81]. In experiments conducted on cultured murine pre-adipocytes (3T3-L1), it has been observed that oxidative stress leads to a reduction in the secretion of adiponectin [
82]. In 2006, Chen et al. conducted experiments using cultured pre-adipocytes (3T3-L1) and discovered that ROS decreased the expression of adiponectin mRNA. In a separate study, 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes were subjected to oxidative stress by introducing H2O2 or glucose oxidase into the incubation medium [
83]. In 2015, Pan et al. discovered that H2O2 decreased adiponectin production by 3T3-L1 adipocytes by a factor of 2, and led to a threefold increase in the synthesis of TNF-α and IL-6. The oxidative stress induced by the addition of H2O2 to the incubation medium of 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes resulted in elevated mRNA levels of leptin, IL-6, and MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein 1), along with increased secretion of these proteins by adipocytes. Notably, there was an almost threefold increase in the secretion of IL-6 [
84,
85].
In 2003, Talior and colleagues reported that a high-fat diet and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) both induce the activation of protein kinase Cδ (PKC-δ). They conducted experiments with 3T3-L1 adipocytes and found that H2O2 also triggers the activation of several kinases, including Akt (an anti-apoptotic kinase), JAKs (Janus kinases), and ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase) [
86].
Anti-inflammatory functions of adiponectin: Numerous metabolic strains that contribute to insulin resistance and T2DM also trigger the activation of inflammation- and stress-related enzymes, namely IκB kinase-β (IKKβ) and JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK). This implies that these kinases likely play pivotal roles in the development of these disorders [
87]. Specifically, IKKβ initiates the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and obesity leads to heightened expression of NF-κB-regulated genes, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines, in both the liver and adipose tissue [
88]. These cytokines, encompassing TNF, IL-6, and IL-1β, can potentially induce insulin resistance in the originating tissues like the liver and adipose tissue [
89]. Furthermore, they may be disseminated through the circulation, exerting their influence on more remote locations such as vessel walls, skeletal and cardiac muscle, the kidneys, and circulating leukocytes [
90]. The involvement of IL-6 signaling in insulin resistance has sparked controversy, displaying occasional paradoxical effects [
91]. Elevated levels of circulating IL-6 and CRP, which is stimulated by IL-6 in the liver, are observed in obesity and serve as predictive markers for Type 2 Diabetes in predisposed individuals [
92]. While hepatic and adipose tissue production of IL-6 is believed to contribute to insulin resistance, its generation in skeletal muscle, particularly during intense exercise, is considered advantageous [
93]. The examination of mice with specific deletion of the IL-6 receptor in hepatocytes has further fueled the debate, as these mice appear to be shielded from both local and systemic insulin resistance [
94].
A number of experimental studies with genetic loss-of-function manipulations indicate that ablation of adiponectin contributes to diet-induced insulin resistance, increased vascular remodeling in response to injury, and severe cardiac damage under ischemic conditions [
95]. A sequence of in vitro experiments has shown that adiponectin has the capacity to impede the production and influence of TNFα, which is a pivotal proinflammatory cytokine. This effect has been observed in different types of cells, including cardiac and vascular cells [
96]. Devaraj et al. provided evidence that adiponectin can inhibit the production of CRP induced by high glucose levels. This inhibition occurs through adiponectin's capacity to suppress the activation of nuclear factor-κ B (NF-κB). These findings align with earlier research that demonstrated adiponectin's ability to mitigate TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation in endothelial cells. This, in turn, leads to decreased expression of cell adhesion molecules and interleukin (IL)-8 [
97].
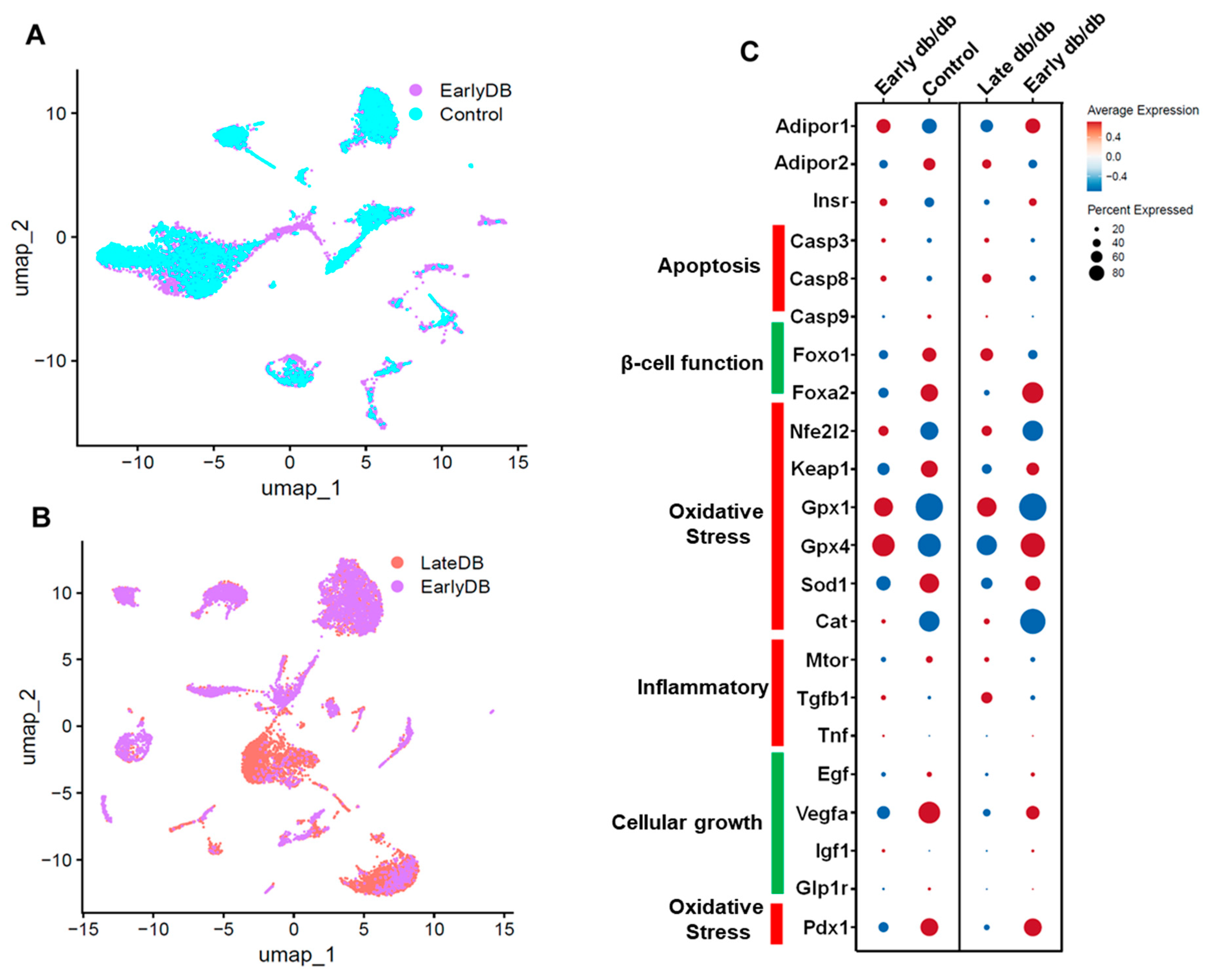
Figure 5.
Single-cell UMAP Visualization depicting the cellular landscape comparison of Early db/db vs Control (A), Late db/db vs Early db/db (B) of pancreatic islet cells. The differential expression of critical genes in Adiponectin signaling, Apoptosis, β-cell function, Oxidative stress, Inflammation and Cellular growth (C).
Figure 5.
Single-cell UMAP Visualization depicting the cellular landscape comparison of Early db/db vs Control (A), Late db/db vs Early db/db (B) of pancreatic islet cells. The differential expression of critical genes in Adiponectin signaling, Apoptosis, β-cell function, Oxidative stress, Inflammation and Cellular growth (C).
Single cell data from db/db mice pancreatic islet cells: We retrieved single-cell data of pancreatic islet cells from GEO (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) using the accession number GSE165267. Data was analyzed using the software, Seurat v4.1.1 implemented in R v4.2.1. In our observations, we noted a decrease in adiponectin receptor levels compared to the control group, coinciding with the progression of diabetes in the pancreatic islet cells of diabetic model mice. This reduction in adiponectin receptor was associated with an upregulation of apoptosis-related genes, specifically casp3 and casp9, and a downregulation of antioxidant genes such as gpx4, gpx1, and sod1. Additionally, there was an upregulation of inflammatory genes including Mtor, Tgfb1, and tnf. These findings align with our earlier hypotheses and support the proposed pathway involving the role of adiponectin [
98,
99,
100]
Future Directions and Challenges: A multimodal strategy is required for future developments in adiponectin-based diabetic therapy. Adiponectin receptor agonists are being developed by researchers in order to imitate the positive effects of adiponectin on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Gene treatments have the potential to increase adiponectin expression or activity in diabetics. The goal of pharmaceutical treatments is to find molecules that can increase adiponectin production from adipose tissue. Understanding how food and exercise affect adiponectin levels is also an important area of research. Combinatorial techniques, personalized medicine approaches, biomarker research, and rigorous clinical trials are all critical components in enhancing the promise of adiponectin-based therapeutics for improving metabolic health in diabetic patients. It is critical to understand that any new therapies will need to go through extensive testing and regulatory processes before they can be used in clinical trials. It is best to check contemporary scientific literature or healthcare practitioners with current understanding in the subject for the most up-to-date information.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the significance of adiponectin in diabetes management cannot be overstated. Its pivotal role in regulating glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity highlights its potential as a promising therapeutic target. As research in this sector advances, tapping the full potential of adiponectin may lead to novel and successful diabetic therapies. Further research, including clinical trials and in-depth molecular investigations, will be critical in achieving the full therapeutic potential of this unique hormone. With ongoing effort and scientific study, the road to improving diabetes management with adiponectin-based therapy holds enormous potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B and M.S.M.; methodology, M.C. and MBT; software, M.C. and M.B.; validation, S.A. (Shahida Arbee) and M.M.M.; resources, N.M., A.C. and P.S.; writing—original draft preparation; writing—review and editing, M.C., M.B., S.A. (Shahida Arbee); visualization, M.C. and M.M.M.; supervision, M.S.M.; project administration, M.C. and M.S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to acknowledge Svaksha Shukla, Jyothi, Arpita Barua, Amayah Mohiuddin, Vardaan Choubey, Lishant Tirumalasetty for their outstanding support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ahmed, A.M. History of diabetes mellitus. Saudi Med. J. 2002, 23, 373–378. [Google Scholar]
- CDC Global Health - Infographics - World Diabetes Day Available online:. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/globalhealth/infographics/diabetes/world-diabetes-day.html (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Olokoba, A.B.; Obateru, O.A.; Olokoba, L.B. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Current Trends. Oman Med. J. 2012, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E.; Groop, L.; Henry, R.R.; Herman, W.H.; Holst, J.J.; Hu, F.B.; Kahn, C.R.; Raz, I.; Shulman, G.I.; et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2015, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Choubey, M.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Minhaz, N.; Biswas, M.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Safeguarding Intimate Health: Decoding the Interplay of Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction 2023. [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; DeFronzo, R.A. Contributions of beta-cell dysfunction and insulin resistance to the pathogenesis of impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.S.; Himeno, T.; Inoue, R.; Miura-Yura, E.; Yamada, Y.; Nakai-Shimoda, H.; Asano, S.; Kato, M.; Motegi, M.; Kondo, M.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Protects Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons against Oxidative Insult. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 9426014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, M.S.; Himeno, T.; Yamada, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Kondo, M.; Tsunekawa, S.; Kato, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Kamiya, H. Glucagon Prevents Cytotoxicity Induced by Methylglyoxal in a Rat Neuronal Cell Line Model. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, S.; Choubey, M.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Minhaz, N.; Akhtar, A.; Bismee, N.N.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Exploring the Significance of Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health 2023. [CrossRef]
- Nur, M.I.; Al-Mamun, F.; Yasmin, F.; Mohiuddin, M.S.; Kaggwa, M.M.; Sikder, Md.T.; Mamun, M.A. Psychological benefits of the COVID-19 vaccination: A Bangladeshi comparative study. Health Sci. Rep. 2023, 6, e1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choubey, M.; Ranjan, A.; Bora, P.S.; Baltazar, F.; Krishna, A. Direct actions of adiponectin on changes in reproductive, metabolic, and anti-oxidative enzymes status in the testis of adult mice. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 279, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A Novel Serum Protein Similar to C1q, Produced Exclusively in Adipocytes (*). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Choubey, M.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Akhtar, A.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Mohiuddin, M.S. The Potent Potential of Green Tea In against Cardiac Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Discoveries 2023. [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Tasnim, S.; Barua, R.; Choubey, M.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Minhaz, N.; Choudhury, A.; Sarker, P.; Mohiuddin, M.S. The Effect of COVID-19 on Gut Microbiota: Exploring the Complex Interplay and Implications for Human Health. Gastrointest. Disord. 2023, 5, 340–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, M.; Ranjan, A.; Bora, P.S.; Krishna, A. Protective role of adiponectin against testicular impairment in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Biochimie 2020, 168, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, M.; Ranjan, A.; Krishna, A. Adiponectin/AdipoRs signaling as a key player in testicular aging and associated metabolic disorders. Vitam. Horm. 2021, 115, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin increases fatty acid oxidation in skeletal muscle cells by sequential activation of AMP-activated protein kinase, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raka, M.A.; Tisha, A.; Khan, S.; Paran, T.Z.; Ahmed, N.; Mohib, M.M.; Sagor, Md.A.T.; Mohiuddin, S. Inhibitory Role of Resveratrol in the Development of Profibrogenesis and Fibrosis Mechanisms. Immunol. Endocr. Metab. Agents - Med. Chem. Med. Chem. - Immunol. Endocr. Metab. Agents 2018, 18, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.A.; Ouchi, N.; Shibata, R.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin Actions in the Cardiovascular System. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Choubey, M.; Mohib, M.M.; Arbee, S.; Sagor, M.A.T.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Stem Cell Therapy in Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Recent Advancements and Future Directions. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Shao, J. Adiponectin and Energy Homeostasis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, S.; Auny, F.M.; Hassan, Y.; Yesmin, R.; Ara, I.; Mohiuddin, M.S.; Kaggwa, M.M.; Gozal, D.; Mamun, M.A. Antenatal depression among women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a pilot study. Reprod. Health 2022, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Md.M.; Mukheem, A.; Kamarul, T. The prevention and treatment of hypoadiponectinemia-associated human diseases by up-regulation of plasma adiponectin. Life Sci. 2015, 135, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, N.; Auger, K.; Rahimi, N.; Jialal, I. Biochemistry, Adiponectin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kadowaki, T. Adiponectin receptors: a review of their structure, function and how they work. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbe, A.; Bongrani, A.; Mellouk, N.; Estienne, A.; Kurowska, P.; Grandhaye, J.; Elfassy, Y.; Levy, R.; Rak, A.; Froment, P.; et al. Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action in Fertility: An Overview from Gametogenesis to Gestation in Humans and Animal Models in Normal and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Nio, Y.; Maki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Takazawa, T.; Iwabu, M.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Kawamoto, S.; Kubota, N.; Kubota, T.; et al. Targeted disruption of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 causes abrogation of adiponectin binding and metabolic actions. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APPLs: More than just adiponectin receptor binding proteins - PubMed Available online:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28108259/ (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Goldstein, B.J.; Scalia, R. Adiponectin: A novel adipokine linking adipocytes and vascular function. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Imai, Y.; Shimozawa, N.; Hioki, K.; Uchida, S.; Ito, Y.; Takakuwa, K.; Matsui, J.; et al. Globular Adiponectin Protected ob/ob Mice from Diabetes and ApoE-deficient Mice from Atherosclerosis*. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaigle, A.M.; Senou, M.; Guiot, Y.; Many, M.-C.; Brichard, S.M. Induction of adiponectin in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic mice: In vivo and in vitro studies. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.P.; Liu, Y.; Vu, V.; Chan, L.; Xu, A.; Riddell, M.C.; Sweeney, G.; Hawke, T.J. Adiponectin is expressed by skeletal muscle fibers and influences muscle phenotype and function. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2008, 295, C203–C212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xia, Z.; Yuen, V.G.; McNeill, J.H. Cardiac expression of adiponectin and its receptors in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.D. Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations Predict Insulin Sensitivity of Both Glucose and Lipid Metabolism | Diabetes | American Diabetes Association Available online:. Available online: https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/52/2/239/26695/Plasma-Adiponectin-Concentrations-Predict-Insulin (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Fantuzzi, G. Adiponectin and inflammation: Consensus and controversy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, M.; James, R.; Marks, J.; Zhao, S.; Szabo, A.; Kidambi, S. Adiposity distribution influences circulating adiponectin levels. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2014, 164, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, M.; Ramezani, A.-H.; Shishehbor, F.; Mansoori, A. The Effect of Omega-3 on Circulating Adiponectin in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, M.M. de A.L.; Melo, A.L.T.R. de; Damasceno, N.R.T. The benefits of ω-3 supplementation depend on adiponectin basal level and adiponectin increase after the supplementation: A randomized clinical trial. Nutr. Burbank Los Angel. Cty. Calif 2017, 34, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibalini, G.; Lucertini, F.; Agostini, D.; Vallorani, L.; Gioacchini, A.; Barbieri, E.; Guescini, M.; Casadei, L.; Passalia, A.; Del Sal, M.; et al. Concurrent Aerobic and Resistance Training Has Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Increases Both Plasma and Leukocyte Levels of IGF-1 in Late Middle-Aged Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 3937842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V.; Rodríguez, A.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J. Adiponectin-leptin ratio: A promising index to estimate adipose tissue dysfunction. Relation with obesity-associated cardiometabolic risk. Adipocyte 2017, 7, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemke, F.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin in insulin resistance: lessons from translational research1234. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 258S–261S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Christie, B.R.; van Praag, H.; Lin, K.; Siu, P.M.-F.; Xu, A.; So, K.-F.; Yau, S. AdipoRon Treatment Induces a Dose-Dependent Response in Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, P.; Bouchard, B. The Impact of Aging on Adipose Function and Adipokine Synthesis. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamia, N.; Virsaladze, D.; Charkviani, N.; Skhirtladze, M.; Khutsishvili, M. Effect of metformin therapy on plasma adiponectin and leptin levels in obese and insulin resistant postmenopausal females with type 2 diabetes. Georgian Med. News 2007, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Riera-Guardia, N.; Rothenbacher, D. The effect of thiazolidinediones on adiponectin serum level: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, K.; R, K.; Swaminathan, G.; Jupudi, S.; Dhama, K.; Barua, R.; Emran, T.; Osman, H.; Khandaker, M. A Critical Review on the Potency of Phytoconstituents in the Management of COVID-19. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 17, 1320–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, P.G.; Michael, M.D.; Crute, B.E.; Cohen, S.E.; Ueki, K.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Keller, S.R.; Lienhard, G.E.; Kahn, C.R. Lipoatrophic diabetes in Irs1(-/-)/Irs3(-/-) double knockout mice. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 3213–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søvik, O.; Vestergaard, H.; Trygstad, O.; Pedersen, O. Studies of insulin resistance in congenital generalized lipodystrophy. Acta Paediatr. Oslo Nor. 1992 Suppl. 1996, 413, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitra, J.; Mason, M.M.; Olive, M.; Krylov, D.; Gavrilova, O.; Marcus-Samuels, B.; Feigenbaum, L.; Lee, E.; Aoyama, T.; Eckhaus, M.; et al. Life without white fat: a transgenic mouse. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 3168–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavusoglu, E.; Ruwende, C.; Chopra, V.; Yanamadala, S.; Eng, C.; Clark, L.T.; Pinsky, D.J.; Marmur, J.D. Adiponectin is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality, cardiac mortality, and myocardial infarction in patients presenting with chest pain. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K. The link between obesity and albuminuria: adiponectin and podocyte dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2009, 76, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, R.; Mizuno, K.; Tashima, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Taguchi, A.; Okajima, T. Bioinformatics and Functional Analyses Implicate Potential Roles for EOGT and L-fringe in Pancreatic Cancers. Mol. Basel Switz. 2021, 26, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gan, L.; Wu, T.; Feng, F.; Luo, D.; Gu, H.; Liu, S.; Sun, C. Adiponectin reduces ER stress-induced apoptosis through PPARα transcriptional regulation of ATF2 in mouse adipose. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2487–e2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Xiao, T.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, N. Adiponectin reduces apoptosis of diabetic cardiomyocytes by regulating miR-711/TLR4 axis. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Yang, N.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hou, X. Adiponectin reduces glucotoxicity-induced apoptosis of INS-1 rat insulin-secreting cells on a microfluidic chip. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 217, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiponectin-induced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis - PubMed Available online:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14983034/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Rakatzi, I.; Mueller, H.; Ritzeler, O.; Tennagels, N.; Eckel, J. Adiponectin counteracts cytokine- and fatty acid-induced apoptosis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontiers | The role of BCL-2 family proteins in regulating apoptosis and cancer therapy Available online:. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2022.985363/full (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Momen, F.; Barua, R.; Kabir, Md.G. Comparative Analysis of in Vitro Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activity of Unripe and Ripe Fruits of Solanum sisymbriifolium. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Role of Adiponectin in Cancer: A Review of Current Evidence - PMC Available online:. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3410224/ (accessed on 9 October 2023).
- Cohen, K.E.; Katunaric, B.; Schulz, M.E.; SenthilKumar, G.; Young, M.S.; Mace, J.E.; Freed, J.K. Role of Adiponectin Receptor 1 in Promoting Nitric Oxide-Mediated Flow-Induced Dilation in the Human Microvasculature. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 875900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Ohara-Imaizumi, M.; Kubota, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Eto, K.; Kanno, T.; Kubota, T.; Wakui, M.; Nagai, R.; Noda, M.; et al. Adiponectin induces insulin secretion in vitro and in vivo at a low glucose concentration. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, N.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Suhail, A.; Sweeney, G.; Wheeler, M.B. Adiponectin-induced ERK and Akt phosphorylation protects against pancreatic beta cell apoptosis and increases insulin gene expression and secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33623–33631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.E.P.; Conner, A.C.; Digby, J.E.; Ward, K.L.; Ramanjaneya, M.; Randeva, H.S.; Dunmore, S.J. Regulation of beta-cell viability and gene expression by distinct agonist fragments of adiponectin. Peptides 2010, 31, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huypens, P.; Moens, K.; Heimberg, H.; Ling, Z.; Pipeleers, D.; Van de Casteele, M. Adiponectin-mediated stimulation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in pancreatic beta cells. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, T.; Moroi, M.; Matsui, J.; Eto, K.; Yamashita, T.; Kamon, J.; Satoh, H.; et al. Disruption of adiponectin causes insulin resistance and neointimal formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25863–25866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, Md.E.U.; Momen, F.; Barua, R.; Sultana, S.; Yesmin, F.; Islam, M.S.; Bhuiyan, R.H. In vitro Assessment of Cytotoxic Activity of Hybrid Variety of Momordica charantia (Bitter Gourd). J. Phytopharm. 2020, 9, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, R.; Talukder, M.E.U.; Islam, M.S.; Yesmin, F.; Chakma, K.; Kabir, M.G.; Bhuiyan, R.H. Nutritional analysis and phytochemical evaluation of Bitter Gourd (Momordica Charantia) from Bangladesh. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. ISSN 2321–1571 2020, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, Y.-J.; Chu, N.-F.; Wang, S.-C.; Hsieh, C.-H.; He, C.-T.; Lee, C.-H.; Fan, S.-C. Correlation of plasma leptin and adiponectin with insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in children - the Taipei Children Heart Study. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2006, 60, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, F.; Saad, R.; Gungor, N.; Arslanian, S.A. Adiponectin in youth: relationship to visceral adiposity, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, A.H.; Kawakubo, M.; Trigo, E.; Kjos, S.L.; Buchanan, T.A. Declining β-Cell Compensation for Insulin Resistance in Hispanic Women With Recent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koebnick, C.; Roberts, C.K.; Shaibi, G.Q.; Kelly, L.A.; Lane, C.J.; Toledo-Corral, C.M.; Davis, J.N.; Ventura, E.E.; Alexander, K.; Weigensberg, M.J.; et al. Adiponectin and leptin are independently associated with insulin sensitivity, but not with insulin secretion or beta-cell function in overweight Hispanic adolescents. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechselforschung Horm. Metab. 2008, 40, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najnin, R.A.; Shafrin, F.; Polash, A.H.; Zaman, A.; Hossain, A.; Taha, T.; Ahmed, R.; Tuli, J.F.; Barua, R.; Sajib, A.A.; et al. A diverse community of jute (Corchorus spp.) endophytes reveals mutualistic host–microbe interactions. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, R.; Sultana, S.; Talukder, M.E.U.; Chakma, K.; Monirul Hasan, C.M.; Islam, M.S. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of crude flavonoid fraction from the fruits of hybrid variety of Momordica charantia (Bitter gourd). Br. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 4, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, W.K.; Arbee, S.; Debnath, S.; Bin Zahur, S.M.; Akter, S.; Karim, A.K.M.R.; Mohabbulla Mohib, M.; Tisha, A.; Taher Sagor, M.A.; Mohiuddin, S. Potent Role of Antioxidant Molecules in Prevention and Management of Skin Cancer. J. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, M.; Himeno, T.; Nakai-Shimoda, H.; Inoue, R.; Ozeki, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Sasajima, S.; Mohiuddin, M.S.; Asano-Hayami, E.; Kato, M.; et al. Deficiency of glucagon gene-derived peptides induces peripheral polyneuropathy in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 532, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, K.; Iwatani, H.; Kihara, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Komura, N.; Fujita, K.; Maeda, N.; Nishida, M.; Katsube, F.; Shimomura, I.; et al. Exacerbation of albuminuria and renal fibrosis in subtotal renal ablation model of adiponectin-knockout mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1910–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.F.; Guichardant, M.; Cozzone, D.; Bernoud-Hubac, N.; Bouzaïdi-Tiali, N.; Lagarde, M.; Géloën, A. Effects of oxidative stress on adiponectin secretion and lactate production in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Lam, M.C.; Shen, J.; Wong, L.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, A. Hypoxia dysregulates the production of adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 independent of reactive oxygen species in adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, K.; Olejnik, A. Cranberries (Oxycoccus quadripetalus) inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Qiao, Q.Y.; Pan, L.H.; Zhou, D.C.; Hu, C.; Gu, H.F.; Fu, S.K.; Liu, X.L.; Jin, H.M. Losartan reduces insulin resistance by inhibiting oxidative stress and enhancing insulin signaling transduction. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Off. J. Ger. Soc. Endocrinol. Ger. Diabetes Assoc. 2015, 123, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wei, J.; Wang, W.; Cui, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M.; Guo, W.; Yu, J. Identification of signaling pathways involved in aberrant production of adipokines in adipocytes undergoing oxidative stress. Arch. Med. Res. 2009, 40, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkan, M.C.; Hevener, A.L.; Greten, F.R.; Maeda, S.; Li, Z.-W.; Long, J.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Poli, G.; Olefsky, J.; Karin, M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkan, M.C.; Hevener, A.L.; Greten, F.R.; Maeda, S.; Li, Z.-W.; Long, J.M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Poli, G.; Olefsky, J.; Karin, M. IKK-β links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance - PubMed Available online:. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17053832/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Cai, D.; Yuan, M.; Frantz, D.F.; Melendez, P.A.; Hansen, L.; Lee, J.; Shoelson, S.E. Local and systemic insulin resistance resulting from hepatic activation of IKK-beta and NF-kappaB. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvas, J.L.; Khaper, N.; Lees, S.J. The IL-6 Paradox: Context Dependent Interplay of SOCS3 and AMPK. J. Diabetes Metab. 4172; 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Point: Interleukin-6 does have a beneficial role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis. J. Appl. Physiol. Bethesda Md 1985 2007, 102, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.K.; Bunkin, D.A.; Greenberg, A.S. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, F.T.; Ströhle, P.; Könner, A.C.; Gruber, S.; Tovar, S.; Brönneke, H.S.; Juntti-Berggren, L.; Li, L.-S.; van Rooijen, N.; Libert, C.; et al. Interleukin-6 signaling in liver-parenchymal cells suppresses hepatic inflammation and improves systemic insulin action. Cell Metab. 2010, 12, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin as an anti-inflammatory factor. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2007, 380, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biolo, A.; Shibata, R.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Sonoda, M.; Walsh, K.; Sam, F. Determinants of Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Chronic Systolic Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraj, S.; Torok, N.; Dasu, M.R.; Samols, D.; Jialal, I. ADIPONECTIN DECREASES C-REACTIVE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS FROM ENDOTHELIAL CELLS: EVIDENCE FOR AN ADIPOSE TISSUE-VASCULAR LOOP. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Structure-Based Virtual Screening of Pseudomonas aeruginosa LpxA Inhibitors using Pharmacophore-Based Approach Available online:. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/2/266 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Nataraj Sekhar, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B.; Zubaidha, P.K.; Hashmi, A.M.; Kadam, T.A.; Anandareddy, L.; De Maeyer, M.; Praveen Kumar, K.; Vijaya Bhaskar, B.; Munichandrababu, T.; et al. Experimental validation and docking studies of flavone derivatives on aldose reductase involved in diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy. Med. Chem. Res. 2011, 20, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.V.; Mohan, A.R.; Babu, T.M.C.; Rajesh, S.S.; Bhuvaneswar, C.; Sivaraman, T.; Gunasekar, D.; Rajendra, W. Antibacterial efficacy of fractions and compounds from Indigofera barberi: Identification of DNA gyrase B inhibitors through pharmacophore based virtual screening. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).