1. Introduction
As an important component of the world cultural heritage, bronzes, whose inscriptions, patterns and shapes show human activities in different historical periods, have high artistic value, historical value and scientific value, and are precious non-renewable resources. Under the influence of burial environment and other factors, various kinds of diseases have appeared in the unearthed bronzes, among which the mineralization problem is more prominent. The physical properties of mineralized bronzes have been destroyed, and the whole is loose and fragile, which is in urgent need of reinforcement and protection. As there are few researches on the application evaluation of mineralized bronze reinforcement materials, the selection of reinforcement materials is not targeted. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out systematic evaluation of mineralized bronze reinforcement materials and establish comprehensive evaluation of mineralized bronze reinforcement materials.
The main reinforcement methods for mineralized bronzes are penetration reinforcement, surface sealing reinforcement and bonding reinforcement. R.M.Organ [
1]. Several bronze ware reinforcing materials used in British Museum laboratory were summarized, such as Cosmolloid 80H, Bondafiller, Tensol, etc. Since the 1970s, various synthetic polymer materials have been applied to the protection of bronze cultural relics, such as acrylic resin [
2], epoxy resin [
3] and polyvinyl butyral resin [
4]. Since the 1980s, researchers have used 502 glue, white emulsion blue glue and trimethyl resin to strengthen and protect bronzes [
5]. The results showed that 502 glue was prone to "whitening" phenomenon, which affected the appearance, brittleness after curing, and poor water resistance and aging resistance. White latex is prone to moisture spalling and has limited effect on the structural strength of mineralized bronzes. Trimethyl resin has been widely used in the field of cultural relics protection in China, but its strengthening strength is not high, and it is easy to age and turn yellow [
6]. It is easy to cause changes in the appearance of cultural relics.
Since the 21st century, cultural relics protection workers have modified the existing reinforcement materials by compounding and other methods to achieve better reinforcement effects. The flexibility of epoxy resin was enhanced by toughening with nano-sio2 [
7]; The addition of anti-amine H-622, UV326 and other ultraviolet absorbent can improve the light stability of B72 and reduce the influence of aging and discoloration of B72 on cultural relics [
8]. Adding nano-silica to fluorocarbon materials and using composite coating method to protect outdoor iron cultural relics [
9]; According to the different degree of mineralization of copper, the reinforcement agent with fluororubber 2311 as the main body was prepared to protect a number of Nanjing Museum’s mineralized bronzes [
10]; A new complex was developed in Henan Province [
11] The stabilization treatment of mineralized bronzes also has a good effect.
Researchers conducted comparative experiments on a variety of polymer cultural relics protection materials, including epoxy resin, to analyze their changes before and after aging, and concluded that epoxy resin has good strengthening strength, but it is easy to cause color change due to ultraviolet light, and its comprehensive performance is not as good as B-72 [
12,
13,
14]. In addition, epoxy resin is a thermosetting resin, which can be treated poorly, and many cultural relics treated by epoxy resin have various problems due to the aging of materials [
15,
16,
17,
18].
In this paper, Paraliod B72, the most widely used reinforcement material for cultural relics protection, and AMC [
11], a self-developed osmotic reinforcement material, were respectively strengthened and protected for simulated corrosion sheet, and the surface stabilization and osmotic reinforcement effects of mineralized bronzes were evaluated and compared. The results showed that AMC was superior to B72 in terms of penetration, reinforcement strength and minimal appearance intervention.
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials and Instruments
Paraloid B-72 (Rohm & Haas), AMC (lab made), Tin dioxide: Analytical purity, Zhengzhou Yinfeng Chemical Reagent Factory. Basic copper carbonate: Analytical pure, Xilong Science Co., LTD. Basic Lead carbonate: Analytical pure, Xilong Science Co., LTD. Menthol: Analytically pure, Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co., LTD.
Electric tablet press: Tianjin Keji High-tech Company. BSA124S electronic balance: Beijing Sedolis Scientific Instrument Co., LTD. DZ-1BC vacuum drying oven: Tianjin Test Instrument Co., LTD. (1) Electronic balance: Germany Sartorius BSA124S precision electronic analysis balance: range 0g-120g, accuracy 0.1mg.) Electronic densitometer: Shenzhen DecA Precision Measuring Instrument Co., LTD DK-300A multi-function electronic densitometer: weighing range 0.01-300g, density display 0.001g/cm3. Universal material testing machine: 3345 universal material testing machine of American Instron Company; Measuring degree 0-5000N, load measurement accuracy ±0.5%. Vacuum drying oven: Tianjin Test Instrument Co., LTD DZ-1BC vacuum drying oven: temperature adjustable range 50-250°C. Uv aging test box: Guangdong Aipei Technology Co., LTD. Uv aging test box. Experimental conditions: UVB313, irradiation intensity 0.68W/m2. Microhardness tester: Shanghai Shang Material Company SCTMC digital microhardness tester. Experimental condition: F=0.098N.) Scanning electron microscope: QUANTA-650 environmental scanning electron microscope of FEI company. Experimental conditions: high vacuum mode; The operating voltage is 25 kV; Secondary electron image and backscatter image. Energy spectrometer: EDAX APOLIO-X type energy spectrometer. Experimental conditions: point scan, surface scan.X-ray diffraction analyzer: German Bruker D8 ADVANCE model. Experimental conditions: The radiation source is Cu/Kα, the wavelength is 15.4nm, the voltage is 40kV, the current is 40mA, and the diffraction measurement range is 10 ~ 70°. Color color meter: Japan Konica Minolta CR-400 color color meter. Experimental conditions: Measuring time 1s, measuring area 8mm, standard deviation AE< 0.07.
2.2. Preparation of highly mineralized bronze simulation samples(HMBS)
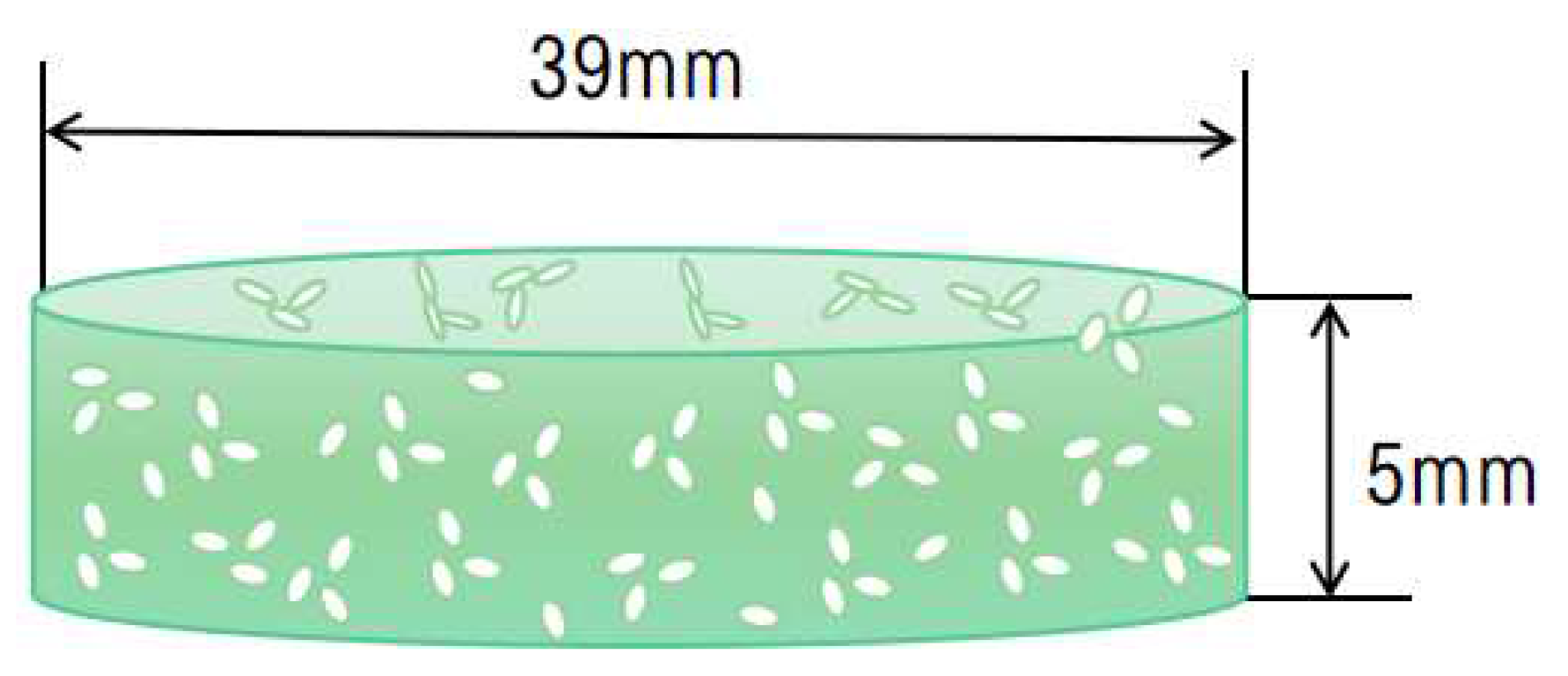
Using a measuring balance, 12.6g tin dioxide, 5.4g basic copper carbonate and 2g basic lead carbonate were prepared to produce a total of 20g of simulated sample materials. Place ingredients in an agate mortar and grind 15 turns clockwise and counterclockwise until well mixed. Place another 1.5g menthol in an agate mortar, mash and grind five times clockwise and five times counterclockwise. Mix the raw materials and menthol evenly and then fill the mold. The electric tablet press was used to press 39mm in diameter and 5mm in thickness into round sheet samples at 10Mpa pressure. The simulated sample was placed in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C for 6h, and then placed in a cool place for 48h after the menthol was fully volatilized.
Results and Discussion
3.1 Comparison of HMBS and natured mineralized layer of bronze arts
3.1.1. Microstructure of HMBS and authentic patina of bronze relics
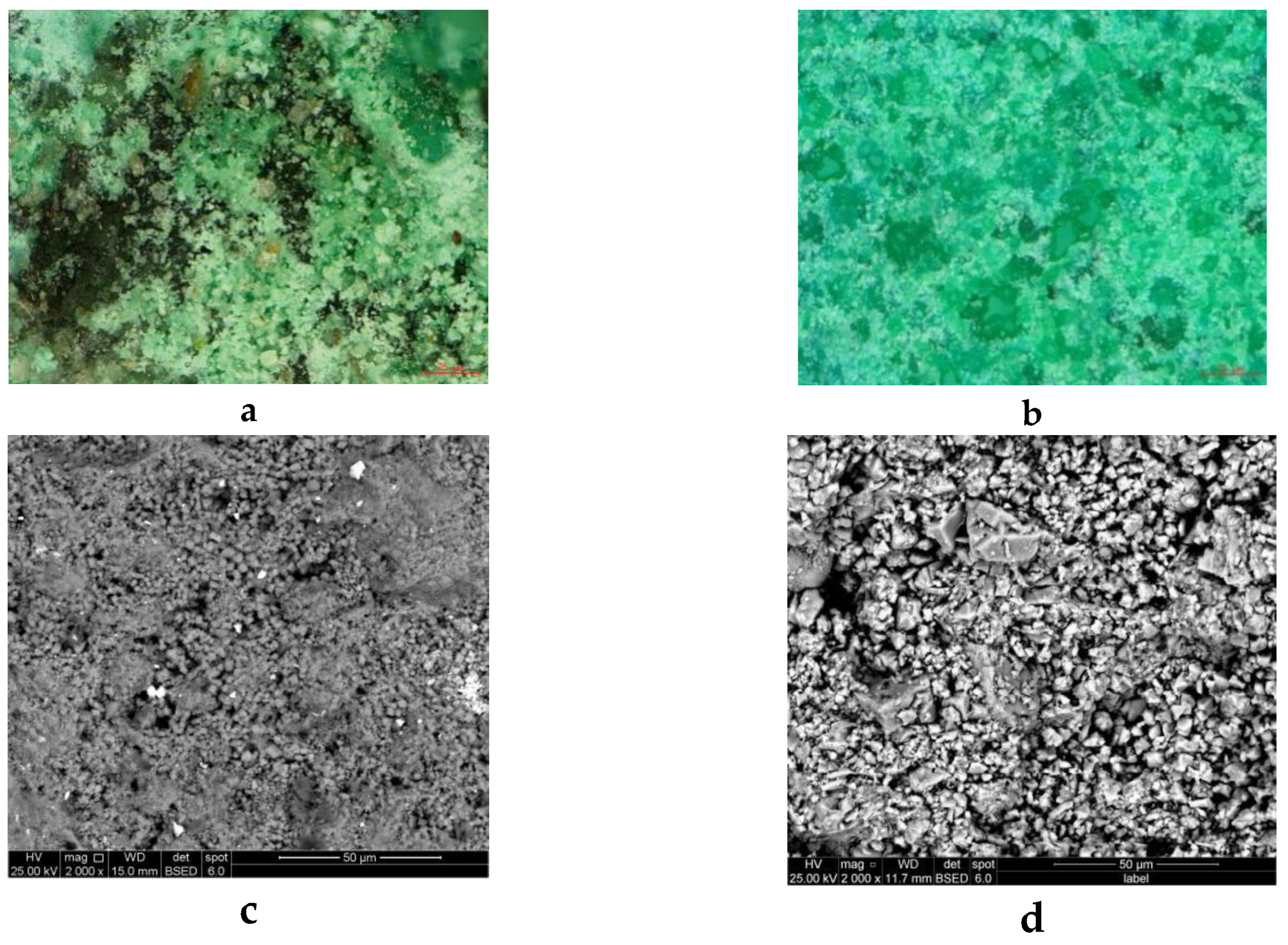
As shown in
Figure 1, HMBS and natured mineralized layer of bronze arts were observed by Optical Super Depth-of-Field Microscope(OSM) and scanning electronic Microscope(SEM).The authentic patina was observed to be granular in nature (
Figure 2a), exhibiting a predominantly light green color and containing some impurities.The structure of HMBS is observed to be similar to that of the authentic patina, presenting a granular morphology as well (
Figure 2b). However, HMBS exhibits a higher purity, larger particle size, and a deeper, more naturally grown coloration. The HMBS particles appear glass-like and exist in two distinct sizes.
The SEM images revealed that the similar granular microstructures of both samples. The surface particles of HMBS were observed to be larger (
Figure 2d), while the surface of the authentic sample appeared denser (
Figure 2c), which is consistent with the observations from OSM analysis.The results of the microscopic morphology analysis demonstrated that the prepared simulated pressed samples exhibited microstructures analogous to the authentic patina.
3.1.1. Phase analysis of HMBS and authentic patina of bronze relics
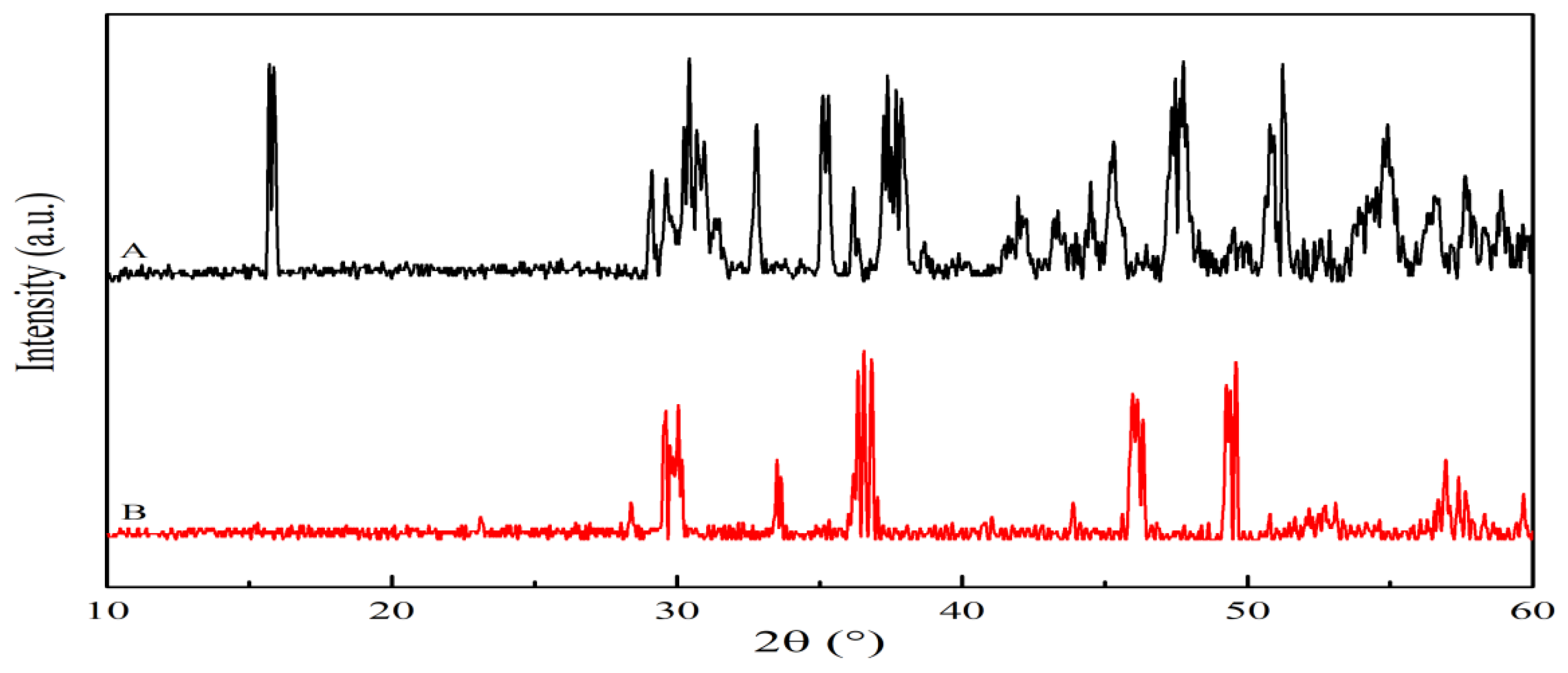
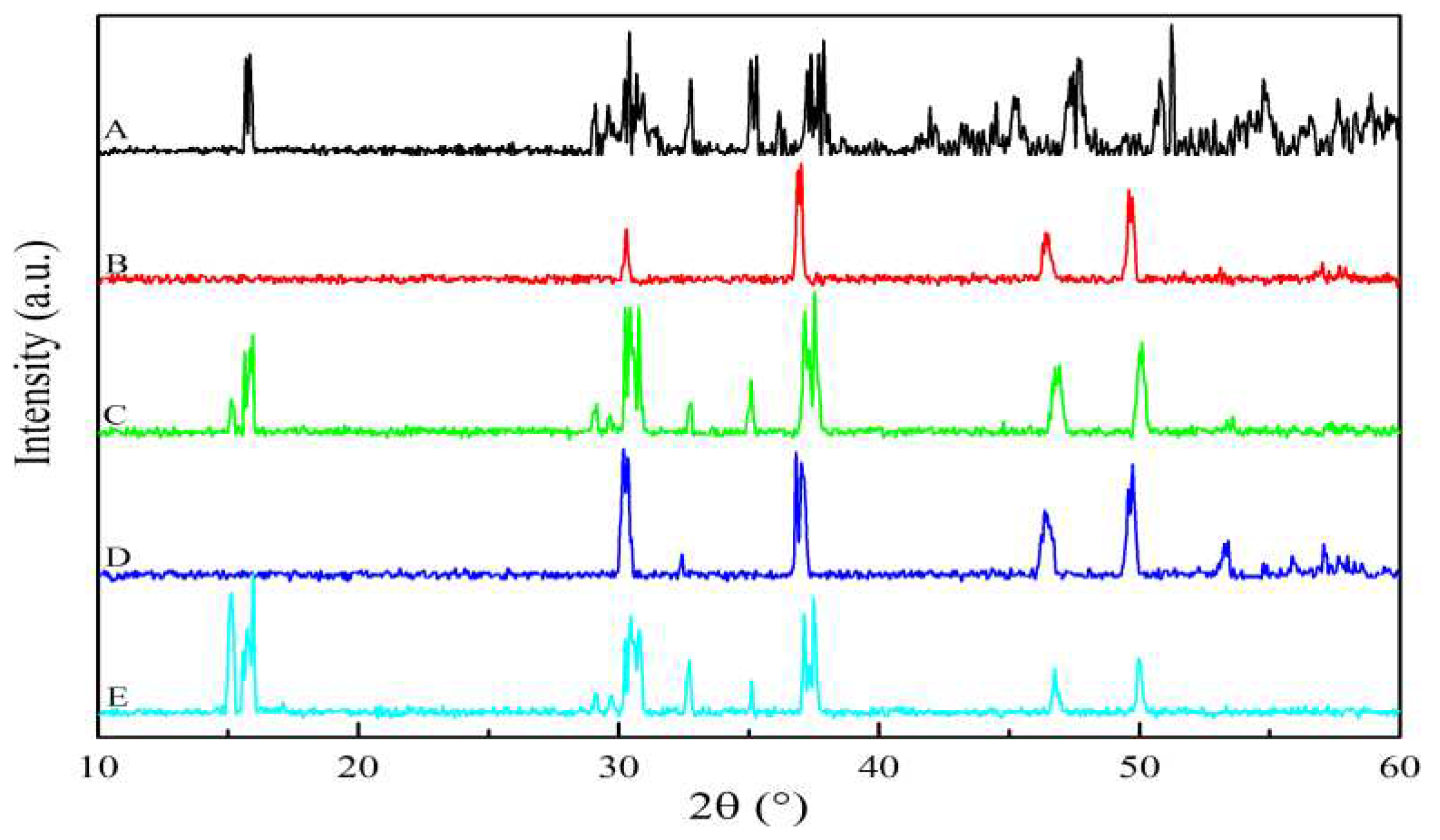
As shown in
Figure 3, The phase structures of HMBS and authentic patina were examined using an X-ray diffraction.The authentic patina primarily composed of copper chloride minerals, with the presence of other substances such as silicon dioxide. In contrast, the copper chloride minerals in HMBS closely resemble authentic patina.
3.2. Characterization of Reinforced material permeability
As shown in
Table 1 The permeability of cultural relics reinforcement material is one of the main criteria to determine the reinforcement effect. Good permeability can help strengthen the material to better enter the interior of the cultural relic matrix and improve the overall mechanical strength of the cultural relic. M1 is the mass before reinforcement, M2 is the mass after reinforcement, M3 is the mass after curing, and the permeability of the reinforced material can be calculated according to M3-M1/M1*100%. Comparing the permeability of powder rust samples before and after reinforcement, it can be seen that the actual permeability effect of these reinforcement materials is different with the evaporation of solvent. The average permeability of 1%B72 is 0.46%, that of 3%B72 is 0.83%, that of 5%B72 is 0.53%, and that of AMC is 2.33%. It can be seen that after solvent volatilization, there are obvious differences in actual permeability reinforcement materials. B72 is used as reinforcement material, and 3%B72 has the best permeability. The penetration rate of AMC is much higher than that of B72, reaching 2.33%.
3.3. Characterization of appearance and microstructure
3.3.1. Appearance and color change
There is a very important principle in the protection of cultural relics: "do not change the original appearance of cultural relics", pay attention to "repair the old as the old". The application of the two reinforcement materials should also apply this principle. The color change test of the reinforced sample was carried out by chromaticity colorimeter. The brightness value of the test sample was L*, representing the brightness value, a*, representing the ratio of red and green pairs, and b*, representing the ratio of yellow and blue pairs. In the test results, ΔL represents the brightness difference before and after reinforcement; Δa represents the contrast change of red and green before and after reinforcement; The color difference of L, a, and b can be expressed by the total color difference ΔE, calculated by the formula ΔE = √ΔL2+Δa2+Δb2. The same position is measured for three times respectively, and the average value is taken, and the obtained data is calculated and added to Table 4-4 using the formula.
As shown in
Table 3, after AMC and B72 reinforcement, the value of ΔL increases, and the color of B72 changes greatly. Because Paraloid B72 can form a transparent film on the surface of the sample, the brightness changes to a certain extent, resulting in the value of ΔL of B72 reinforcement sample is much higher than that of AMC. The acrylic complex gel-AMC has a good permeability effect. The reinforcement material penetrates into the specimen and the surface enrichment is small, so the ΔL value changes relatively little after AMC reinforcement. The values of Δa and Δb of the samples are changed, where Δa is positive, which means the treated sample is green, and Δb is positive, which means the treated sample is blue. The value of Δa is negative, which means that the processed sample is red, and the value of Δb is negative, which means that the processed sample is yellow. The smaller the value of E, the smaller the color change of the sample after reinforcement, and the more consistent with the principle of "not changing the original state of cultural relics".
For the reinforced sample of 1%B72, Δa is -1.39, indicating that the color is green after reinforcement, Δb is -0.22, indicating that the color is blue after reinforcement. For the reinforced sample 3%B72, Δa is *1.29, which means the color is green after reinforcement, Δb is -0.74, which means the color is blue. 5%B72 reinforced sample Δa is -2.11, representing the color after reinforcement, Δb is -0.09, representing the color of blue; For the reinforced AMC sample, Δa is -3.16, which means the color is green after reinforcement, and Δb is 2.30, which means the color is yellow after reinforcement. The value of ΔE after AMC reinforcement is the smallest, which indicates that compared with B72, AMC material changes the color of cultural relics the least.
3.3.2. Microstructure of samples before and after reinforcement
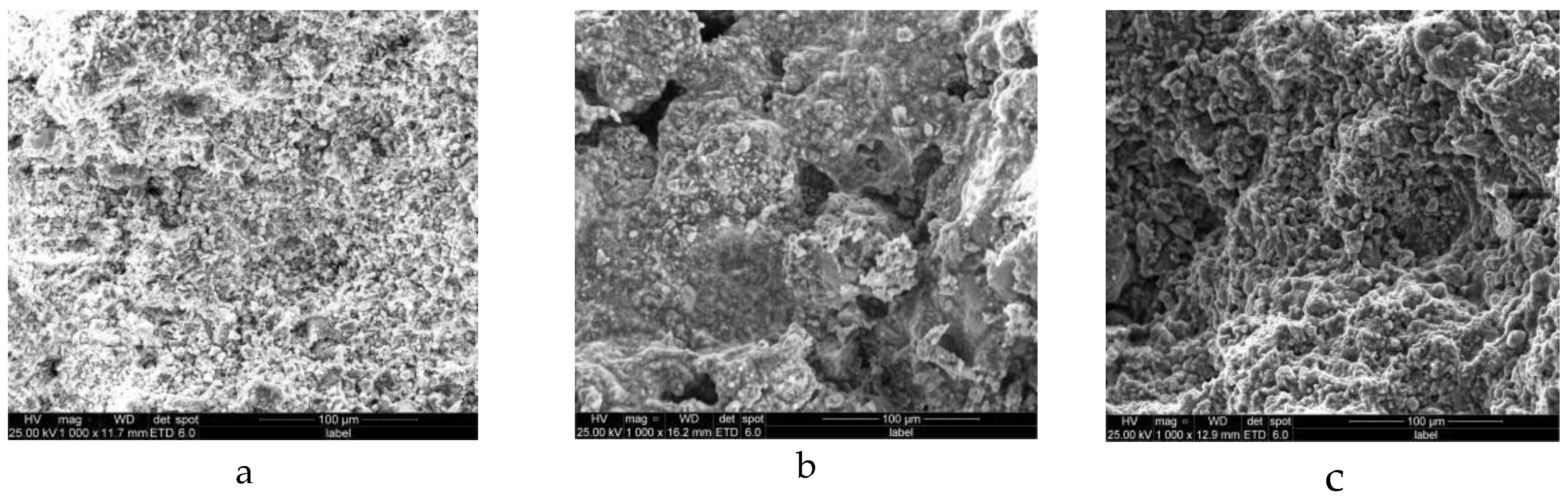
As shown in
Figure 4, Before reinforcement, the surface of the corroded sample was rough particle surface with irregular distribution of tiny cracks (
Figure 4a). After B72 treatment, the sample (
Figure 4b,c) had a film forming surface. After drying, the volume contraction of the film forming area led to obvious cracks inside the sample, indicating that B72 was filled with film on the surface of the sample and had poor compatibility with the sample. The surface of the sample reinforced by AMC showed rough particles close to that of the blank sample, and no obvious cracks were observed after drying, indicating that the AMC and the sample had strong interaction, realized microlevel compatibility, and had good osmotic bonding.
3.5. Phase Analysis of samples
X-ray diffraction analysis results (
Figure 5) show that there is no obvious phase change before and after B72 and AMC reinforcement, that is, no new crystal phase formation. However, after AMC and 3%B72 reinforcement, the peaks disappear when 2θ is 15, and the peak strength after reinforcement is significantly weakened, indicating that the crystal structure is not obvious after reinforcement, indicating that the reinforcement agent has an impact on the crystal structure, and the better the permeability of the protective material, the more obvious the impact on the crystal structure.
3.6. Aging resistance test
Traditional conservation materials primarily consist of polymers, which inevitably undergo aging and result in a decrease in both the strength and deterioration of the protected substrate. This phenomenon introduces new challenges to the preservation of cultural relics. Therefore, aging resistance is an important index to evaluate the excellent performance of reinforced materials.The protected bronze artifacts primarily stored indoors are most susceptible to the aging effects of ultraviolet (UV) light. In an UV aging test chamber, at a temperature of 35°C and an irradiance of 0.68W/m2 using UVB313 wavelength, two types of reinforcement materials underwent 50 hours of UV aging.
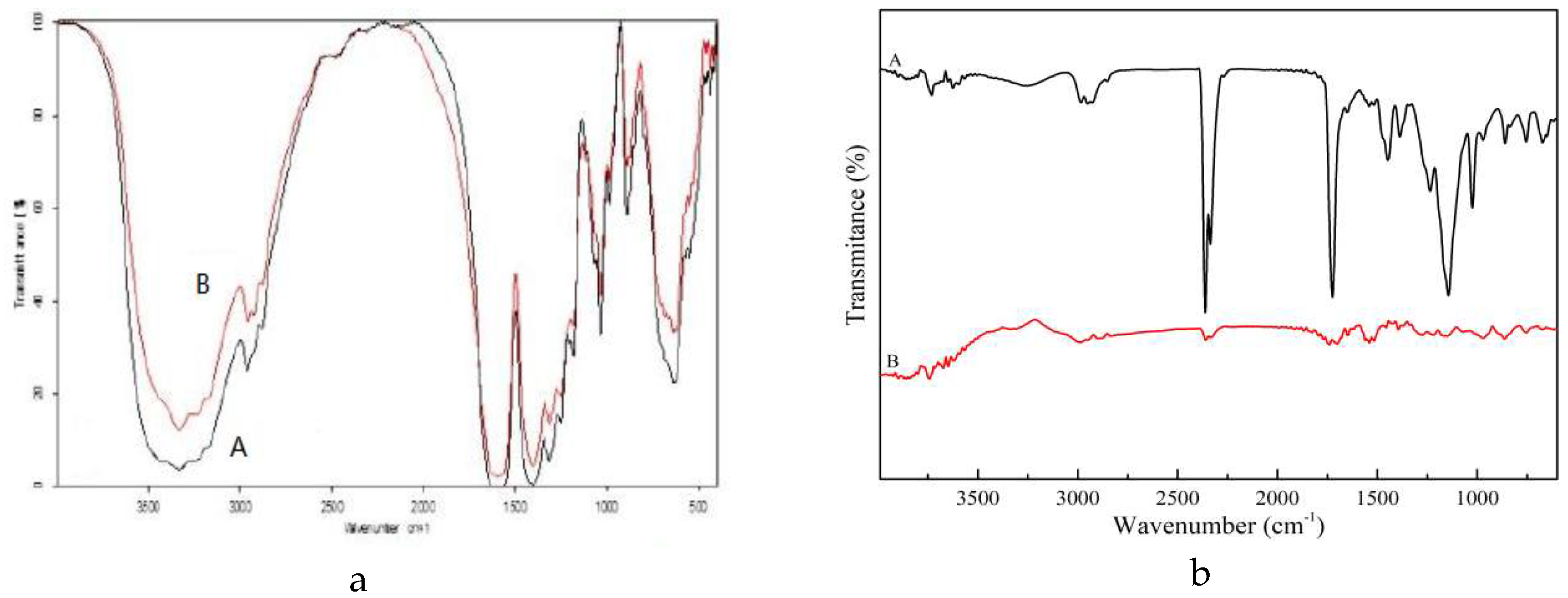
The FTIR (
Figure 6) of the aged reinforcement materials revealed that the internal structure of the AMC material remained largely unchanged, indicating its favorable resistance to UV aging. Conversely, significant reduction in the main absorption peaks of the B72 material after aging indicated its poor resistance to UV light.
4. Conclusion
This paper addresses common issues related to the reinforcement and protection of fragile bronze artifacts. It systematically analyzes the materials used for bronze artifact reinforcement and preservation over the past 50 years. In analyzing the widely used B72 material, a comparative evaluation was conducted with a novel complexing agent material called AMC, which was developed by the author. The results indicate that the reinforcement and protection provided by B72 primarily rely on encapsulation, resulting in poor penetration and compatibility with fragile bronze artifacts. In contrast, AMC mainly focuses on penetration reinforcement and exhibits better compatibility with the samples. Microscopic analysis and color comparison results both demonstrate that AMC outperforms B72. Furthermore, the results of aging resistance analysis before and after reinforcement show that AMC significantly outperforms B72 in terms of aging resistance. This paper validates that the novel reinforcement material, through high penetration and compatible strengthening, accomplishes minimal surface intervention for the protection of fragile bronze samples while achieving excellent reinforcement and aging resistance performance. The development of the AMC series materials provides new insights for the development of protective materials with broad application prospects in future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Chen Jiachang; methodology, Chen Jiachang ; validation, Mai yin,Chen Liwei , Zhang Liangshuai,Cui Xinzhan and Liu Xin; data curation, Chen.Jiachang,Mai.Yin.; writing—original draft preparation, Chen Jiachang.; funding acquisition, Chen.Jiachang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by The National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2020YFC1522000).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- R.M.Organ. "The consolidation of fragile metallic objects". Studies in Conservation,1961(6): 128-134.
- Gong Xin, Han Xiangna, Chen Kunlong: "Review of the application of atypical acrylic materials in cultural relics Protection", Science of Cultural Relics Protection and Archaeology, No. 3, 2021, pp. 108-117.
- S.Jeong, H.Ark. "Conservation of a Bronze Incense Burner from Chungung-dong, Hanam”. Conservation Science in Museum, 2015, 16: 32-45.
- A. Rison. "The effects of Butvar B-98 on bronze". ANAGPIC,2008,1.
- Hu Jiaxi, Ding Guorong: Strengthening and Repairing ancient bronzes after Corrosion ", Jianghan Archaeology, No.3, 1987, pp. 92-93.
- Zhao Dandan, Cheng Qian, Guo Hong: "Application of microemulsion in removing cultural relics failed protection materials - A case study of mural cleaning", Chinese Cultural Heritage, No. 4, 2020, pp. 83-88.
- Li Zhaoyang, Qiu Dajian, Xie Guoxian, Xiao Xiangding, Ni Xiaoxue: "Study on the toughening and modification of epoxy resin with Nano-sio2", Material Protection, No.4, 2008, pp. 21-23.
- Wang Liqin, Yang Lu, Dang Climax, ZHAO Jing, LIANG Guozheng: Research on light aging resistance of modified B72 cultural relics protection materials, Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), No.5, 2006, pp. 761-764.
- Ma Lizhi, Shen Dawa, Wang Yongsheng, Pan Lu, Ma Qinglin: Application of Fluorocarbon coatings in the sealing of iron cultural relics ", Cultural Relics Protection and Archaeology Science, 2 (2010), pp. 27-32.
- Wan Li: Introduction to the protection and restoration methods of Nanjing Museum's Bronzes, Cultural Relics Science and Technology Research Series IV, 2006, pp. 26-34.
- Chen Jiachang, Huang Xia, Chen Xiaolin, Liu Haiwang, Zhu Rusheng: "Study on the reinforcement and protection of acrylic acid complex Sol for unearthed fragile pottery relics", Materials Guide, 2015, No. S2, 479-482.
- Research on the stability of polymer coating materials for Cultural Relics Protection and Its Application in the Protection of Painted cultural Relics (Master's degree thesis), Northwest University, 2007.
- Kavur, Martina Blei , B. Kavur , and R. Starac . "Reflection of actions: The Late Bronze Age hoard from Moravika Sela, north-western Croatia." Archeologicke Rozhledy 72.3(2020):410-426.
- Podany, Jerry , et al. "Paraloid B-72 as a Structural Adhesive and as a Barrier within Structural Adhesive Bonds: Evaluations of Strength and Reversibility." Journal of the American Institute for Conservation (2001).
- Wang Sijia, Fang Shiqiang, Zhang Bingjian: "An explorative study on the aging process of typical epoxy-type binder materials", Cultural Relics Protection and Archaeological Science, Vol. 2, 2017, pp. 15-25.
- He, H. P. , J. J. Mei , and Y. Y. Hu . "Protective Effect of Resin on Efflorescent White Marble Cultural Relics." Corrosion and Protection 31.11(2010):886-888.
- Chen, X-QXie, L.Wang, F.Wu, Y.Zhang, B.Zhu, L. "Temporary consolidation and packaging of fragile cultural relics at underwater archaeological sites to maintain their original state during extraction." Archaeometry 62.Pta5(2020).
- Chenxi, et al. "A Brief Introduction of the Protective Agent for the Surface of Stone Cultural Relics." 2017.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).