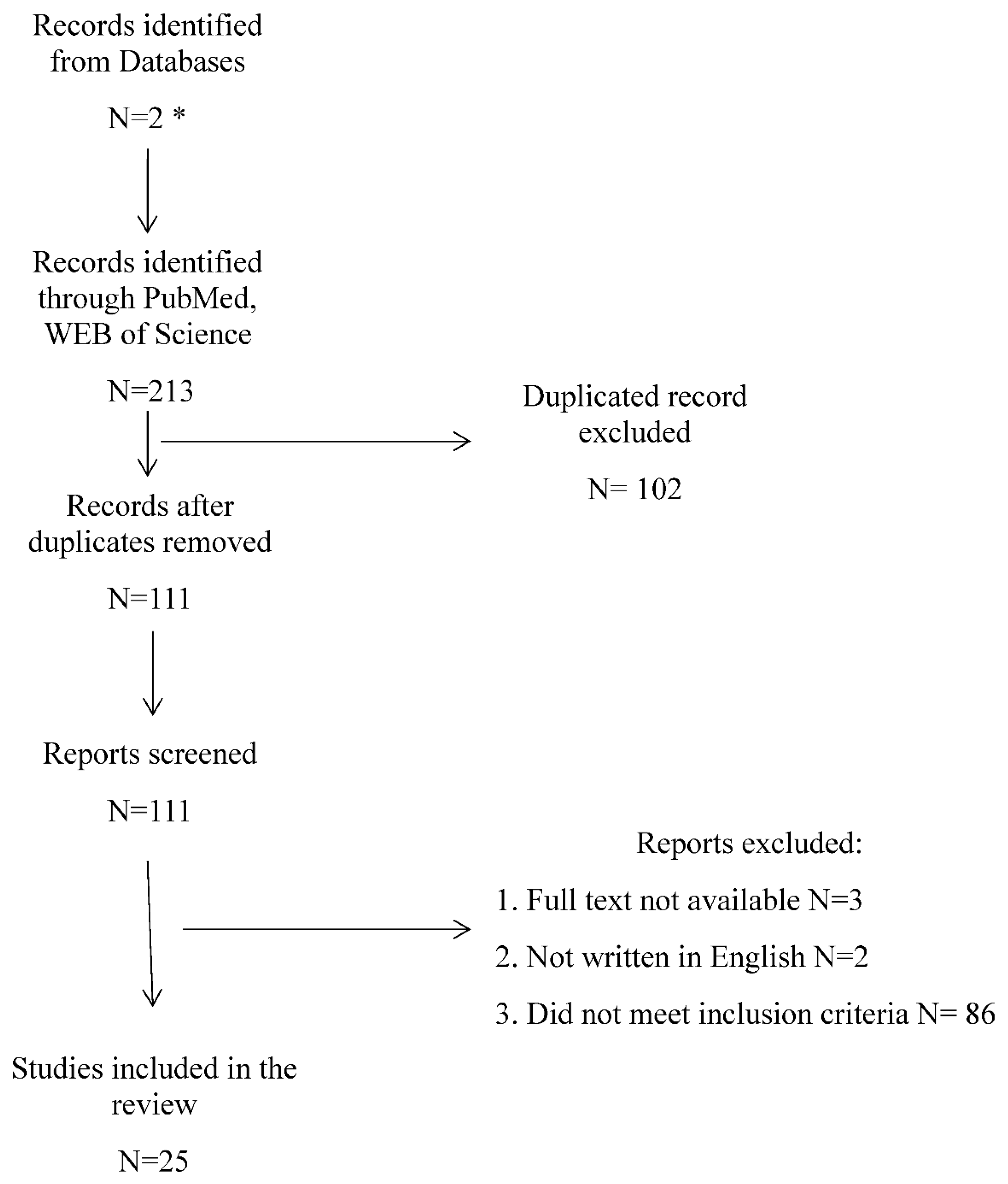
Submitted:
02 October 2023
Posted:
11 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute Kidney Injury |
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| CaOx | Calcium Oxalate |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| HN | Hydronephrosis |
| hs-CRP | Highly sensitive C-reactive protein |
| IL | Interleukin |
| KIM-1 | Kidney Injury Molecule – 1 |
| L-FABP | Liver-type Fatty Acid-Binding Protein |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein – 1 |
| MET | Medical expulsion therapy |
| MGP | Matrix Gla protein |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| NAG | N-Acetyl-β-d-amino Glycosidase |
| NC | Nephrocalcin |
| NGAL | Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PCNL | Nephrolithotripsy |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone |
| RIRS | Retrograde intrarenal surgery |
| SSP | Spontaneous stone passage |
| UPTF-1 | Urinary prothrombin fragment -1 |
| URS | Ureterorenoscopy |
| THP | Tamm – Horsfall Protein |
| TNF – α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
References
- Issler, N.; Dufek, S.; Kleta, R.; Bockenhauer, D.; Smeulders, N.; van‘t Hoff, W. Epidemiology of Paediatric Renal Stone Disease: A 22-Year Single Centre Experience in the UK. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasian, G.E.; Ross, M.E.; Song, L.; Sas, D.J.; Keren, R.; Denburg, M.R.; Chu, D.I.; Copelovitch, L.; Saigal, C.S.; Furth, S.L. Annual Incidence of Nephrolithiasis among Children and Adults in South Carolina from 1997 to 2012. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2016, 11, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Bayne, D.; Wiener, S.; Ahn, J.; Stoller, M.; Chi, T. Stone Formation in Patients Less than 20 Years of Age Is Associated with Higher Rates of Stone Recurrence: Results from the Registry for Stones of the Kidney and Ureter (ReSKU). J. Pediatr. Urol. 2020, 16, 373.e1–373.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, M.; Goldfarb, D.S.; Nazzal, L. The Role of the Microbiome in Kidney Stone Formation. Int. J. Surg. Lond. Engl. 2016, 36, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Filler, G. Epidemiology of Pediatric Urolithiasis. Indian J. Urol. 2010, 26, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edvardsson, V. Urolithiasis in Children. In Pediatric Nephrology; Avner, E.D., Harmon, W.E., Niaudet, P., Yoshikawa, N., Emma, F., Goldstein, S., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 1–52. ISBN 978-3-642-27843-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alpay, H.; Ozen, A.; Gokce, I.; Biyikli, N. Clinical and Metabolic Features of Urolithiasis and Microlithiasis in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. Berl. Ger. 2009, 24, 2203–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobs, K.; Rakowska, M.; Paturej, A. Urolithiasis in The Pediatric Population − Current Opinion on Epidemiology, Patophysiology, Diagnostic Evaluation and Treatment. Dev. Period Med. 2018, 22, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penido, M.G.M.G.; Tavares, M. de S. Pediatric Primary Urolithiasis: Symptoms, Medical Management and Prevention Strategies. World J. Nephrol. 2015, 4, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaro, G.; Croppi, E.; Coe, F.; Lingeman, J.; Moe, O.; Worcester, E.; Buchholz, N.; Bushinsky, D.; Curhan, G.C.; Ferraro, P.M.; et al. Metabolic Diagnosis and Medical Prevention of Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Its Systemic Manifestations: A Consensus Statement. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandur, Y.; Gonen, S.; Fidan, K.; Soylemezoglu, O. Evaluation of Urinary KIM-1, NGAL, and IL-18 Levels in Determining Early Renal Injury in Pediatric Cases with Hypercalciuria and/or Renal Calculi. Clin. Nephrol. 2016, 86, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, E.; Pishgar, F.; Hojjat, A.; Soleimani, M.; Asgari, M.A.; Kajbafzadeh, A.-M. The Role of Serum and Urinary Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 in Predicting Renal Injury Associated with Ureteral Stone. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, S.; Chakkarai, K.; Arulvijayavani, S.; Senthilkumar, G.; Manikandan, R.; Kalyaperumal, M. Association between Vitamin D, Parathyroid Hormone and Inflammatory Markers in Urolithiasis Patients. J. Ren. Inj. Prev. 2017, 6, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşdemir, M.; Fuçucuoğlu, D.; Küçük, S.H.; Erol, M.; Yiğit, Ö.; Bilge, I. Urinary Biomarkers in the Early Detection and Follow-up of Tubular Injury in Childhood Urolithiasis. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icer, M.A.; Gezmen-Karadag, M.; Sozen, S. Can Urine Osteopontin Levels, Which May Be Correlated with Nutrition Intake and Body Composition, Be Used as a New Biomarker in the Diagnosis of Nephrolithiasis? Clin. Biochem. 2018, 60, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobs, K.; Jung, A.; Lewicki, S.; Murawski, P.; Pączek, L.; Zdanowski, R. Assessment of Cross-Correlations Between Selected Macromolecules in Urine of Children with Idiopathic Hypercalciuria. Urol. J. 2018, 15, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirackal, R.S.; Jayachandran, M.; Wang, X.; Edeh, S.; Haskic, Z.; Perinpam, M.; Halling, T.M.; Mehta, R.; Rivera, M.E.; Lieske, J.C. Urinary Extracellular Vesicle-Associated MCP-1 and NGAL Derived from Specific Nephron Segments Differ between Calcium Oxalate Stone Formers and Controls. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F1475–F1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.T.; Gao, C.; Peters, M.; Manning, T.; Cashman, S.; Nambiar, A.; Cumberbatch, M.; Lamb, B.; Peacock, A.; Van Son, M.J.; et al. Factors Associated with Spontaneous Stone Passage in a Contemporary Cohort of Patients Presenting with Acute Ureteric Colic: Results from the Multi-Centre Cohort Study Evaluating the Role of Inflammatory Markers In Patients Presenting with Acute Ureteric Colic (MIMIC) Study. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, A.; Ando, R.; Taguchi, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Unno, R.; Sugino, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Tozawa, K.; Kohri, K.; et al. Identification of New Urinary Risk Markers for Urinary Stones Using a Logistic Model and Multinomial Logit Model. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2019, 23, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, K.; Ketz, J.; Saxena, V.; Spencer, J.D.; Safadi, F.; Schwaderer, A. Adolescents with Urinary Stones Have Elevated Urine Levels of Inflammatory Mediators. Urolithiasis 2019, 47, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bhutani, G.; Vaughan, L.E.; Enders, F.T.; Haskic, Z.; Milliner, D.; Lieske, J.C.; Assimos, D.; Baum, M.; Somers, M.; et al. Urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 Associated with Calcium Oxalate Crystallization in Patients with Primary Hyperoxaluria. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.F.; Moyes, A.J.; Lamb, R.M.; Ella-Tongwiis, P.; Bell, C.; Moussa, A.; Shergill, I. The Role of Specific Biomarkers, as Predictors of Post-Operative Complications Following Flexible Ureterorenoscopy (FURS), for the Treatment of Kidney Stones: A Single-Centre Observational Clinical Pilot-Study in 37 Patients. BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, V.; Pottel, H.; Lieske, J.C.; Lukas, P.; Cavalier, E.; Delanaye, P.; Rule, A.D. Evaluation of Inactive Matrix-Gla-Protein (MGP) as a Biomarker for Incident and Recurrent Kidney Stones. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.F.; Jones, N.; Thomas-Wright, S.J.; Banwell, J.; Moyes, A.J.; Shergill, I. Shock Wave Lithotripsy, for the Treatment of Kidney Stones, Results in Changes to Routine Blood Tests and Novel Biomarkers: A Prospective Clinical Pilot-Study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2020, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilesiz, N.C.; Ozkan, A.; Kalkanli, A.; Eroglu, A.; Gezmis, C.T.; Simsek, B.; Arslan, B. Can Serum Procalcitonin Levels Be Useful in Predicting Spontaneous Ureteral Stone Passage? BMC Urol. 2020, 20, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, L.; Lu, H.; Kovacevic, N.; Thomas, R.; Lakshmanan, Y. Cystatin C, Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin, and Lysozyme C: Urinary Biomarkers for Detection of Early Kidney Dysfunction in Children With Urolithiasis. Urology 2020, 143, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Lai, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, X. The Predictive and Diagnostic Ability of IL-6 for Postoperative Urosepsis in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, V.; Aarthy, P.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, A.P.S. Role of Inflammatory Markers and Their Trends in Predicting the Outcome of Medical Expulsive Therapy for Distal Ureteric Calculus. Urol. Ann. 2022, 14, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milišić, E.; Alić, J.; Zvizdić, Z.; Lepara, O.; Jonuzi, A.; Milišić, L.; Fajkić, A. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Level as a Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury Following Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2021, 74, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymer, K.M.; Sharma, V.; Manka, M.; Agarwal, D.; Dodge, N.; Gettman, M.; Rivera, M. A Serum C-Reactive Protein and Procalcitonin-Based Risk Score to Predict Urinary Infection in Patients with Obstructive Urolithiasis Undergoing Decompression. J. Endourol. 2021, 35, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Ye, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Heng, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wei, S.; Xuehe, Z.; Sun, Y.; Cui, R.; et al. Metabolic Differences between Unilateral and Bilateral Renal Stones and Their Association with Markers of Kidney Injury. J. Urol. 2022, 207, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonin, C.; Peerapen, P.; Yoodee, S.; Kapincharanon, C.; Kanlaya, R.; Thongboonkerd, V. Systematic Analysis of Modulating Activities of Native Human Urinary Tamm-Horsfall Protein on Calcium Oxalate Crystallization, Growth, Aggregation, Crystal-Cell Adhesion and Invasion through Extracellular Matrix. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 357, 109879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, L.; Kovacevic, N.; Lakshmanan, Y. Proteomic Analysis of Inhibitory Protein Profiles in the Urine of Children with Nephrolithiasis: Implication for Disease Prevention. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2783–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memmos, D.; Sarafidis, P.; Alexandrou, M.E.; Theodorakopoulou, M.; Anastasiadis, A.; Mykoniatis, I.; Dimitriadis, G.; Dimitrios, H. The Effect of Standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy, Miniaturized Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy and Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery on Biomarkers of Renal Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Clin. Kidney J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savin, Z.; Mintz, I.; Lifshitz, K.; Achiam, L.; Aviram, G.; Bar-Yosef, Y.; Yossepowitch, O.; Sofer, M. The Role of Serum and Urinary Markers in Predicting Obstructing Ureteral Stones and Reducing Unjustified Non-Contrast Computerized Tomographic Scans in Emergency Departments. Emerg. Radiol. 2023, 30, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R.; Hackett, R.L. Hyperoxaluria, Enzymuria and Nephrolithiasis. Contrib. Nephrol. 1993, 101, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R.; Finlayson, B.; Hackett, R.L. Histologic Study of the Early Events in Oxalate Induced Intranephronic Calculosis. Invest. Urol. 1979, 17, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R. Experimental Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis and the Formation of Human Urinary Stones. Scanning Microsc. 1995, 9, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wiessner, J.H.; Hasegawa, A.T.; Hung, L.Y.; Mandel, G.S.; Mandel, N.S. Mechanisms of Calcium Oxalate Crystal Attachment to Injured Renal Collecting Duct Cells. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, J.F.; Doust, J.; Tett, S.E.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Cystatin C Compared to Serum Creatinine for the Estimation of Renal Dysfunction in Adults and Children--a Meta-Analysis. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onopiuk, A.; Tokarzewicz, A.; Gorodkiewicz, E. Cystatin C: A Kidney Function Biomarker. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 68, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, J.; Gomes, K.; Fernandes, A.; Domingueti, C. Cystatin C: A Promising Biomarker to Evaluate Renal Function. Rev. Bras. Análises Clínicas 2016, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, H.V.; Ritchie, J.P.; Pagano, S.; Middleton, R.J.; Pruijm, M.; Vuilleumier, N.; Kalra, P.A. The Associations of Blood Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin with Progression from CKD to ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2016, 11, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarajan, P. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin—an Emerging Troponin for Kidney Injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 3737–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.; Desai, P.B.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Hull, V.V.; Math, A.A.K.; Vernekar, S.N. Markers of Renal Function Tests. North Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010, 2, 170–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, M.A.; Waikar, S.S. Established and Emerging Markers of Kidney Function. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mårtensson, J.; Xu, S.; Bell, M.; Martling, C.-R.; Venge, P. Immunoassays Distinguishing between HNL/NGAL Released in Urine from Kidney Epithelial Cells and Neutrophils. Clin. Chim. Acta 2012, 413, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, H.I.; Mueller, M.; Rutherford, C.; Passo, M.H.; Witte, D.; Grom, A.; Mishra, J.; Devarajan, P. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker of Nephritis in Childhood-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2577–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgeri, M.; Whiting, D.; Reche, A.; Manghat, P.; Sriprasad, S. Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin (NGAL) as a Biomarker of Renal Injury in Patients with Ureteric Stones: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Urol. 2020, 14, 205141582094756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, G.-C.; Che, J.-P.; Xu, Y.-F.; Peng, B.; Zheng, J.-H. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin, a Biomarker for Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome in Patients with Nephrolithiasis. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 187, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wang, N. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 in Kidney Disease. Ren. Fail. 2016, 38, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.K.; Bailly, V.; Abichandani, R.; Thadhani, R.; Bonventre, J.V. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): A Novel Biomarker for Human Renal Proximal Tubule Injury. Kidney Int. 2002, 62, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Posada, D.; Dayarathna, T.; Dion, M.; Alenezi, H.; Sener, A.; Denstedt, J.D.; Pautler, S.E.; Razvi, H. KIM-1 Is a Potential Urinary Biomarker of Obstruction: Results from a Prospective Cohort Study. J. Endourol. 2017, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Xue, W.; Shao, X.; Che, X.; Xu, W.; Ni, Z.; Mou, S. Analysis of a Urinary Biomarker Panel for Obstructive Nephropathy and Clinical Outcomes. PloS One 2014, 9, e112865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, N.; Sener, A.; Sabbisetti, V.; Nott, L.; Lang, R.M.; Welk, B.K.; Méndez-Probst, C.E.; MacPhee, R.A.; VanEerdewijk, S.; Cadieux, P.A.; et al. Urinary Expression of Novel Tissue Markers of Kidney Injury After Ureteroscopy, Shockwave Lithotripsy, and in Normal Healthy Controls. J. Endourol. 2013, 27, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbschat, A.; Gauer, S.; Paulus, P.; Reissig, M.; Weipert, C.; Ramos-Lopez, E.; Hofmann, R.; Hadji, P.; Geiger, H.; Obermüller, N. Serum and Urinary NGAL but Not KIM-1 Raises in Human Postrenal AKI. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 44, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilis-Pstrusinska, K.; Szajerka, U.; Zwolinska, D. Unspecific Increase of Tumor Markers in a Girl with Nephrotic Syndrome and Ovarian Teratoma. Ren. Fail. 2013, 35, 654–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, B.F.; Ernst, C.S.; Herlyn, M.; Steplewski, Z.; Sears, H.F.; Koprowski, H. Gastrointestinal Cancer-Associated Antigen in Immunoperoxidase Assay. Cancer Res. 1982, 42, 4820–4823. [Google Scholar]
- Malaguarnera, G.; Giordano, M.; Paladina, I.; Rando, A.; Uccello, M.; Basile, F.; Biondi, A.; Carnazzo, S.; Alessandria, I.; Mazzarino, C. Markers of Bile Duct Tumors. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2011, 3, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybek, H.; Aybek, Z.; Sinik, Z.; Demir, S.; Sancak, B.; Tuncay, L. Elevation of Serum and Urinary Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 in Benign Hydronephrosis. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2006, 13, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.I.; Dénes, F.T.; Bartolamei, M.G.; Reis, S.; Sanches, T.R.; Leite, K.R.; Srougi, M.; Seguro, A.C. Serum and Urinary Values of CA 19-9 and TGFß1 in a Rat Model of Partial or Complete Ureteral Obstruction. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. Off. J. Austrian Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. Al Z. Kinderchir. 2015, 25, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. Elevation of Serum and Urinary Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 in Benign Hydronephrosis. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2007, 14, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Muraishi, O.; Tokue, A. The Correlation of Serum Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 with Benign Hydronephrosis. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenstad, O.; Roald, A.B.; Grubb, A.; Aukland, K. Renal Handling of Radiolabelled Human Cystatin C in the Rat. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 1996, 56, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febbraio, M.A.; Pedersen, B.K. Contraction-Induced Myokine Production and Release: Is Skeletal Muscle an Endocrine Organ? Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2005, 33, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastard, J.P.; Jardel, C.; Delattre, J.; Hainque, B.; Bruckert, E.; Oberlin, F. Evidence for a Link between Adipose Tissue Interleukin-6 Content and Serum C-Reactive Protein Concentrations in Obese Subjects. Circulation 1999, 99, 2221–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.; Seneff, M.; Nelson, D.; Williams, M.; Levy, H.; Kimmel, P.; Macias, W. Elevated Plasma Concentrations of IL-6 and Elevated APACHE II Score Predict Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Severe Sepsis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. CJASN 2007, 2, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Molitoris, B.A.; Pescovitz, M.; Kelly, K.J. Urinary Actin, Interleukin-6, and Interleukin-8 May Predict Sustained ARF after Ischemic Injury in Renal Allografts. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2003, 41, 1074–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, W.H.; Evans, G.S.; Finn, A. The Significance of Interleukin 8 in Urine. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 85, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Wen, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z. The Expression of Tristetraprolin and Its Relationship with Urinary Proteins in Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Shikata, K.; Hiramatsu, M.; Nakatou, T.; Kitamura, T.; Wada, J.; Itoshima, T.; Makino, H. Serum Interleukin-18 Levels Are Associated with Nephropathy and Atherosclerosis in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lamki, R.S.; Mayadas, T.N. TNF Receptors: Signaling Pathways and Contribution to Renal Dysfunction. Kidney Int. 2015, 87, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Tam, F.W.K. Urinary Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Renal Disease. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2011, 412, 2022–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybi Szumińska, A.; Wasilewska, A.; Kamianowska, M. Protein Biomarkers in Chronic Kidney Disease in Children—What Do We Know So Far? J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umekawa, T.; Chegini, N.; Khan, S.R. Increased Expression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) by Renal Epithelial Cells in Culture on Exposure to Calcium Oxalate, Phosphate and Uric Acid Crystals. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. Off. Publ. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Assoc. - Eur. Ren. Assoc. 2003, 18, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Baltz, M.L. Acute Phase Proteins with Special Reference to C-Reactive Protein and Related Proteins (Pentaxins) and Serum Amyloid A Protein. Adv. Immunol. 1983, 34, 141–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, A.R.; Byrne, J.C.; Vaughan, E.D.; Marion, D.N. The Effect of Acute Obstruction on Ureteral Function. J. Urol. 1990, 143, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Türk, C.; Knoll, T.; Seitz, C.; Skolarikos, A.; Chapple, C.; McClinton, S. ; European Association of Urology Medical Expulsive Therapy for Ureterolithiasis: The EAU Recommendations in 2016. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, C.; Aydoğdu, O.; Senocak, C.; Damar, E.; Eraslan, A.; Oztuna, D.; Bozkurt, O.F. Predictive Factors for Spontaneous Stone Passage and the Potential Role of Serum C-Reactive Protein in Patients with 4 to 10 Mm Distal Ureteral Stones: A Prospective Clinical Study. J. Urol. 2015, 194, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Park, C.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, D.; Park, C.; Kim, C. 2078 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN NATURAL PASSAGE RATE OF LESS THAN 8MM URETER STONE AND C-REACTIVE PROTEIN AND NEUTROPHIL PERCENTAGE. J. Urol. 2012, 187, e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaqadossi, H.A. Stone Expulsion Rate of Small Distal Ureteric Calculi Could Be Predicted with Plasma C-Reactive Protein. Urolithiasis 2013, 41, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Crown, S.E.; Handel, T.M. Chemokine: Receptor Structure, Interactions, and Antagonism. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 787–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinholt, F.P.; Hultenby, K.; Oldberg, A.; Heinegård, D. Osteopontin--a Possible Anchor of Osteoclasts to Bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1990, 87, 4473–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.R.; Garvin, M.R.; Stewart, D.K.; Hinohara, T.; Simpson, J.B.; Schwartz, S.M.; Giachelli, C.M. Osteopontin Is Synthesized by Macrophage, Smooth Muscle, and Endothelial Cells in Primary and Restenotic Human Coronary Atherosclerotic Plaques. Arterioscler. Thromb. J. Vasc. Biol. 1994, 14, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Huang, S.-P.; Tsai, L.-Y.; Wu, W.-J.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Chou, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Wu, M.-T. The Impact of Osteopontin Promoter Polymorphisms on the Risk of Calcium Urolithiasis. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2010, 411, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaman, F. Üriner sistem taş hastalığı etiyopatogenezinde fetuin-a ve osteopontin [Specialist Thesis]. Fetuin-a and osteopontin in the etiopathogenesis of nephrolithiasis [Specialist Thesis]. 2011.
- Hamamoto, S.; Yasui, T.; Okada, A.; Hirose, M.; Matsui, Y.; Kon, S.; Sakai, F.; Kojima, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tozawa, K.; et al. Crucial Role of the Cryptic Epitope SLAYGLR within Osteopontin in Renal Crystal Formation of Mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 2967–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, M.; Tozawa, K.; Okada, A.; Hamamoto, S.; Higashibata, Y.; Gao, B.; Hayashi, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Kubota, Y.; Yasui, T.; et al. Role of Osteopontin in Early Phase of Renal Crystal Formation: Immunohistochemical and Microstructural Comparisons with Osteopontin Knock-out Mice. Urol. Res. 2012, 40, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Kaiser, E.T.; Coe, F.L. Isolation and Characterization of Calcium Oxalate Crystal Growth Inhibitors from Human Urine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 84, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Margolis, H.C.; Yokoyama, S.; Kézdy, F.J.; Kaiser, E.T.; Coe, F.L. Purification and Characterization of a Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystal Growth Inhibitor from Human Kidney Tissue Culture Medium. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 3936–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Abram, V.; Kézdy, F.J.; Kaiser, E.T.; Coe, F.L. Purification and Characterization of the Principal Inhibitor of Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystal Growth in Human Urine. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 12594–12600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Parks, J.H.; Kézdy, F.J.; Coe, F.L. Molecular Abnormality of Urinary Glycoprotein Crystal Growth Inhibitor in Calcium Nephrolithiasis. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 1985, 98, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- COE, F.; HC, M.; LH, D.; AL, S. URINARY MACROMOLECULAR CRYSTAL GROWTH INHIBITORS IN CALCIUM NEPHROLITHIASIS. Urin. Macromol. Cryst. GROWTH Inhib. CALCIUM NEPHROLITHIASIS 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Y, N. Immunohistochemical Localization of Nephrocalcin (NC) to Proximal Tubule and Thick Ascending Limb of Henle’s Loop (TALH) of Human and Mouse Kidney. Kidney Int 1990, 37, 474. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Ahmed, M.; Hall, S.L.; Deganello, S.; Coe, F.L. Isolation from Human Calcium Oxalate Renal Stones of Nephrocalcin, a Glycoprotein Inhibitor of Calcium Oxalate Crystal Growth. Evidence That Nephrocalcin from Patients with Calcium Oxalate Nephrolithiasis Is Deficient in Gamma-Carboxyglutamic Acid. J. Clin. Invest. 1987, 79, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurutz, J.; Carvalho, M.; Nakagawa, Y. Nephrocalcin Isoforms Coat Crystal Surfaces and Differentially Affect Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate Crystal Morphology, Growth, and Aggregation. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 255, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyan, A.; Yaşar, H.; Bayazit, A.K.; Anarat, R.; Bayazit, Y.; Anarat, A. Urinary Nephrocalcin Excretion in Children with Urolithiasis. Nephron Physiol. 2003, 94, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuyama, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yachiku, S. Identification of Bikunin Isolated from Human Urine Inhibits Calcium Oxalate Crystal Growth and Its Localization in the Kidneys. Int. J. Urol. Off. J. Jpn. Urol. Assoc. 2003, 10, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmani, F.; Khan, S.R. Role of Urinary Bikunin in the Inhibition of Calcium Oxalate Crystallization. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 1999, 10 (Suppl. 14), S385–S388. [Google Scholar]
- De Yoreo, J.J.; Qiu, S.R.; Hoyer, J.R. Molecular Modulation of Calcium Oxalate Crystallization. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 291, F1123–F1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsland, K.J.; Kelly, J.K.; Coe, B.J.; Coe, F.L. Urine Protein Markers Distinguish Stone-Forming from Non-Stone-Forming Relatives of Calcium Stone Formers. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 291, F530–F536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Médétognon-Benissan, J.; Tardivel, S.; Hennequin, C.; Daudon, M.; Drüeke, T.; Lacour, B. Inhibitory Effect of Bikunin on Calcium Oxalate Crystallization in Vitro and Urinary Bikunin Decrease in Renal Stone Formers. Urol. Res. 1999, 27, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foell, D.; Wittkowski, H.; Roth, J. Mechanisms of Disease: A “DAMP” View of Inflammatory Arthritis. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Roth, J.; Oppenheim, J.J.; Tracey, K.J.; Vogl, T.; Feldmann, M.; Horwood, N.; Nanchahal, J. Alarmins: Awaiting a Clinical Response. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgeworth, J.; Gorman, M.; Bennett, R.; Freemont, P.; Hogg, N. Identification of P8,14 as a Highly Abundant Heterodimeric Calcium Binding Protein Complex of Myeloid Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 7706–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, S.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Naqvi, Z.A.; Rattani, A.; Talati, J.; Palmberg, C.; Shafqat, J. Identification of Myeloperoxidase, Alpha-Defensin and Calgranulin in Calcium Oxalate Renal Stones. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2007, 384, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momohara, C.; Tsujihata, M.; Yoshioka, I.; Tsujimura, A.; Nonomura, N.; Okuyama, A. Mechanism Underlying the Low Prevalence of Pediatric Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Ducy, P.; McKee, M.D.; Pinero, G.J.; Loyer, E.; Behringer, R.R.; Karsenty, G. Spontaneous Calcification of Arteries and Cartilage in Mice Lacking Matrix GLA Protein. Nature 1997, 386, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, J.A.; Glenton, P.A.; Khan, S.R. Characterization of Tamm-Horsfall Protein in a Rat Nephrolithiasis Model. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikri, K.L.; Foster, C.L.; MacHugh, N.; Marshall, R.D. Localization of Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein in the Human Kidney Using Immuno-Fluorescence and Immuno-Electron Microscopical Techniques. J. Anat. 1981, 132, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serafini-Cessi, F.; Malagolini, N.; Cavallone, D. Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein: Biology and Clinical Relevance. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2003, 42, 658–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryall, R.L.; Harnett, R.M.; Hibberd, C.M.; Edyvane, K.A.; Marshall, V.R. Effects of Chondroitin Sulphate, Human Serum Albumin and Tamm-Horsfall Mucoprotein on Calcium Oxalate Crystallization in Undiluted Human Urine. Urol. Res. 1991, 19, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, W.G.; Scurr, D.S.; Bridge, C.M. Factors Influencing the Crystallisation of Calcium Oxalate in Urine - Critique. J. Cryst. Growth 1981, 53, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellström, B.; Danielson, B.G.; Ljunghall, S.; Wikström, B. Crystal Inhibition: The Effects of Polyanions on Calcium Oxalate Crystal Growth. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1986, 158, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, P.K.; Marshall, V.R.; Ryall, R.L. Tamm-Horsfall Mucoprotein Reduces Promotion of Calcium Oxalate Crystal Aggregation Induced by Urate in Human Urine in Vitro. Clin. Sci. Lond. Engl. 1979 1994, 87, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, G.A.; Sulaiman, S. Tamm-Horsfall Mucoproteins Promote Calcium Oxalate Crystal Formation in Urine: Quantitative Studies. J. Urol. 1982, 127, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T.; Koide, T.; Utsunomiya, M.; Itatani, H.; Oka, T.; Sonoda, T. Possible Role of Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein in Calcium Oxalate Crystallisation. Br. J. Urol. 1989, 64, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.K.; Ryall, R.L.; Marshall, V.R. Does Tamm-Horsfall Mucoprotein Inhibit or Promote Calcium Oxalate Crystallization in Human Urine? Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1990, 190, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.R.; Atmani, F.; Glenton, P.; Hou, Z.; Talham, D.R.; Khurshid, M. Lipids and Membranes in the Organic Matrix of Urinary Calcific Crystals and Stones. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1996, 59, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R. Role of Renal Epithelial Cells in the Initiation of Calcium Oxalate Stones. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2004, 98, e55–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, I.R.; Ryall, R.L.; Marshall, V.R. Inclusion of Proteins into Calcium Oxalate Crystals Precipitated from Human Urine: A Highly Selective Phenomenon. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, D.; Rodgers, A.L.; Sturrock, E.D. Synergism between Urinary Prothrombin Fragment 1 and Urine: A Comparison of Inhibitory Activities in Stone-Prone and Stone-Free Population Groups. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, X.; Ward, M.D.; Wesson, J.A. Adhesion between Molecules and Calcium Oxalate Crystals: Critical Interactions in Kidney Stone Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 2854–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year of publication | Author and title | Study design | Results |
| 2016 |
Kandur Y. et al.[12] Evaluation of urinary KIM-1, NGAL, and IL-18 levels in determining early renal injury in pediatric cases with hypercalciuria and/or renal calculi. |
40 children with nephrolithiasis (NL), 23 patients with hypercalciuria (HC) and 20 healthy controls were included to measure Urinary concentrations of NGAL, KIM-1 and IL-18. | In regard to the urinary NGAL/cr ratio (p < 0.001), a statistically significant difference was found between the patient groups (NL and HC) and the control group. No significant differences between patient groups and healthy children in terms of urinary IL-18/cr and KIM-1/cr ratio. |
| 2016 |
Amini E. et al. [13] The role of serum and urinary carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in predicting renal injury associated with ureteral stone. |
This study was designed to evaluate the role of urinary and serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (uCA19-9 and sCA19-9) as a biomarker in the assessment of patients with ureteral stone. A total of 38 patients with ureteral stone and hydronephrosis who underwent transurethral lithotripsy (TUL) (Group A) and 24 age-matched healthy peers (Group B) were evaluated in this study. Urinary and serum CA19-9 concentrations were measured in group A before TUL and 4 and then 8 weeks following the operation; sCA-19-9 and uCA19-9 concentrations were also measured in group B participants. | Median concentration of uCA19-9 and sCA19-9 was 34.0 and 15.0 kU/L in group A patients and 16.1 and 5.3 kU/L in group B, respectively (p < 0.001). Medians of CA19-9 concentration in urine and serum reduced to 12.5 and 4.5 kU/L 8 weeks after TUL (p < 0.001). Following successful TUL and hydronephrosis resolution, a significant decline was detected in serum and urinary CA19-9. The duration of ureteral obstruction was associated with serum and urinary CA19-9 concentrations, suggesting the potential role of this marker in predicting renal damage associated with urinary tract obstruction and determining the timing of interventions. |
| 2017 |
Venkatesan, S et al. [14] Association between vitamin D, parathyroid hormone and inflammatory markers in urolithiasis patients |
It was a cross-sectional study. About 41 confirmed renal calculi patients and 41 age and sex matched controls were recruited. Patients with malignancies, hyperparathyroidism, chronic disease, and patients taking vitamin D supplementations were excluded. Serum levels of 25(OH) vitamin D, i-PTH, hs-CRP, IL-6, calcium and phosphorous, 24 hours urine levels of calcium and phosphorus were estimated. | There was a significant difference in the serum levels of 25(OH) vitamin D (12.26 vs 19.61 ng/mL), i-PTH (75.5 vs. 33.5 pg/mL), hsCRP (5117.05 vs. 1721.87 ng/mL), IL-6 (13.49 vs. 1.47 pg/mL) calcium (11.5 vs. 9.4 mg/dL) and urinary calcium (370.5 vs. 342 mg/d) and phosphorous levels (1172 vs. 1432 mg/d) between the cases and the control. There was negative correlation between the levels of i-PTH and vitamin D (r = -0.765) and positive correlation between i-PTH and hsCRP, IL-6, Serum calcium and urine calcium (r = 0.353, 0.340, 0.522, 0.501 respectively) |
| 2018 |
Taşdemir M. et al. [15] Urinary biomarkers in the early detection and follow-up of tubular injury in childhood urolithiasis. |
Seventy children [36 girls, mean age: 7.3 ± 5.0 years (0.5-18.2)] with urolithiasis/microlithiasis were included. Anthropometric data, urinary symptoms, family history and diagnostic studies were recorded. Urine samples were analysed for metabolic risk factors (urinary calcium, uric acid, oxalate, citrate, cystine, magnesium, and creatinine excretion), and the urinary KIM-1 (uKIM-1), NAG (uNAG), and NGAL (uNGAL) levels were measured 3 times in 6-months intervals. |
UKIM-1/Cr, uNAG/Cr and uNGAL/Cr ratios were not significantly different between patients and controls. Furthermore, no significant changes in their excretion were shown during follow-up. Only uNAG/Cr and uNGAL/Cr ratios were significantly increased in patients with hydronephrosis (n = 6, p = 0.031 and 0.023, respectively). |
| 2018 |
Icer M. A. et al.[16] Can urine osteopontin levels, which may be correlated with nutrition intake and body composition, be used as a new biomarker in the diagnosis of nephrolithiasis? |
A total of 88 subjects participated in the study, including 44 affected patients with kidney stones, aged between 20 and 65 years and 44 healthy peers. Several serum parameters and urinary osteopontin (uOPN) levels were examined. In addition, anthropometric measurements were assessed, body mass index was calculated, 24-hour diet and water intake were registered, and participants completed an eating frequency questionnaire to assess their dietary status. | Among patients, uOPN levels (ng/ml) were significantly lower than in controls (p<0.05). A positive correlation (p<0.05) was also observed between uOPN levels in male patients and dietary intake of energy, carbohydrates, polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and n-6 fatty acids. In contrast, in female patients, there was a negative correlation between uOPN level (ng/ml) and serum creatinine concentration (mg/dl) (p<0.05). The uOPN level was positively correlated with body weight, waist circumference, hip circumference and muscle mass in healthy men (p<0.05). |
| 2018 |
Jung K. et al. [17] Assessment of cross-correlations between selected macromolecules in urine of children with idiopathic hypercalciuria. |
In the study, uromodulin, osteopontin, calgranulin and bicunin were measured in a fresh morning urine sample in a group of children diagnosed with nephrolithiasis in the course of idiopathic hypercalciuria. The study included 57 patients between the ages of 12 and 18 years; 33 healthy children were the control group. The study included 57 patients aged 12 months to 18 years; the control group consisted of 33 healthy peers. |
Significantly reduced excretion of osteopontin and significantly increased excretion of bicunin were found in the urine of people with urinary tract stones. A significant positive correlation between uromodulin and bicunin was found in both groups. Calgranulin was excreted in higher amounts but without statistical significance. |
| 2019 |
Chirackal R.S. et al. [18] Urinary extracellular vesicle-associated MCP-1 and NGAL derived from specific nephron segments differ between calcium oxalate stone formers and controls. |
The study was designed to test the hypothesis that extracellular vesicles (EV) containing potential biomarkers for inflammation (monocyte chemoattractant protein, MCP-1), kidney epithelium injury (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, NGAL) and abnormal calcification (osteopontin, OPN) might reflect intrarenal stone formation process. 64 calcium formers (CF) and 40 age- and sex- matched healthy peers were included. Urolithiasis participants were divided into 2 subgroups: with low (<5%) and high papillary surface area that reflect the respective amount of Randall plaques (precursors of crystallisation). EV carrying MCP-1, NGAL and OPN were assessed in the urine. | The number of EV carrying MCP-1 and NGAL were significantly lower in CF participants compared with healthy group but it did not differ between patients with low and high papillary surface area. The number of EV with OPN did not differ between any groups. |
| 2019 |
Shah T.T. et al. [19] Factors associated with spontaneous stone passage in a contemporary cohort of patients presenting with acute ureteric colic: results from the Multi-centre cohort study evaluating the role of Inflammatory Markers In patients presenting with acute ureteric Colic (MIMIC) study |
The research included 4170 patients with acute ureteral colic due to urolithiais. Presence of a single stone was showed in a CT scan. White blood cell (WBC) counts and other inflammatory indicators were studied, stone size and position were assessed as well as use of medical excretory therapy (MET), with spontaneous stone passage (SSP). The main goal of the study was to measure spontaneous stone passage (SSP), with no need of intervention to facilitate stone passage (SP). | The composite analysis did not detect that any of the measured parameters (WBC, neutrophil count, C-reactive protein (CRP)) did not predict SSP, with adjusted odds ratios (OR) of 0.97 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.91-1.04, P = 0.38), 1.06 (95% CI 0.99-1.13, P = 0.1) and 1.00 (95% CI 0.99-1.00, P = 0.17), respectively. |
| 2019 |
Okada A. et al. [20] Identification of new urinary risk markers for urinary stones using a logistic model and multinomial logit model |
The study included three groups of men (between 20 and 79 years of age): 48 healthy individuals without urolithiasis or history of renal colic, 22 individuals with calcium oxalate stones after one episode, 40 individuals also with calcium oxalate stones but with recurrent episodes of colic. The concentrations of 18 urinary proteins were measured in the urine samples using multiplex analysis on the MagPix (R) system. | The authors based on logistic regression models classifying control and first-time groups detected that interleukin (IL)-1a and IL-4 were independent factors, with significantly high areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (1.00 and 0.87, respectively, P < 0.01 for both). Multivariate models with IL-4 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) showed higher areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (0.93) compared with the univariate model with IL-4. In the classification of control, first-time and relapse groups, accuracy was highest for the multinomial logit model with IL-4, GM-CSF, IL-1b, IL-10 and urinary magnesium (concordance rate 82.6%). |
| 2019 |
Kusumi K. et al. [21] Adolescents with urinary stones have elevated urine levels of inflammatory mediators. |
The main objective of this study was to compare urinary inflammatory markers in stone forming children versus healthy matched controls. The urine samples were collected from 12 adolescents with urolithiasis and 15 controls. The levels of 30 urinary cytokines were assessed with the use of a Mesoscale 3-0-Plex Human Cytokine panel and normalized to urine creatinine. | Among others MIP1β and IL13 were significantly increased in affected participants. Interleukin 17A was elevated in the urine of controls. |
| 2020 |
Wang X. et al. [22] Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 associated with calcium oxalate crystallization in patients with primary hyperoxaluria. |
30 patients with primary hyperoxaluria and CaOx crystals and 47 healthy peers were included. In the urine samples of study participants a panel of biomarkers reflecting different nephron sites and potential mechanism of injury was assessed: clusterin, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), 8-isoprostane (8-IP), Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein -1 (MCP-1), Liver-fatty acid binding protein (L-FABP), heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) and osteopontin (OPN). | After adjustment for age-, sex-, and eGFR, a higher urinary MCP-1 concentration and MCP-1/creatinine ratio was positively correlated with CaOx supersaturation. Higher urinary NGAL and NGAL/creatinine as well as urinary OPN and OPN/creatinine, were related to higher eGFR. IT seems that higher urinary MCP-1 might reflect ongoing collecting tubule crystallisation, while greater urinary NGAL and OPN may reflect preservation of kidney mass and function. |
| 2020 |
Hughes S.F. et al. [23] The role of specific biomarkers, as predictors of post-operative complications following flexible ureterorenoscopy (FURS), for the treatment of kidney stones: a single-centre observational clinical pilot-study in 37 patients. |
37 patients (24 men, 13 women) participated in the research, after FURS because of nephrolithiasis. Venous blood samples were taken from all patients in time intervals: before intervention and then after 30 minutes, 2 hours and 4 hours post surgery. Changes in the quantities of specified molecules were assessed: NGAL, Cystatin-C, MPO, PCT with the use of ELISA method. | In the study, postoperative complications were observed in 4 patients (3 - URI with urinary retention, 1 - urosepsis). NGAL concentrations increased significantly after FURS (p = 0.034). In contrast, no significant differences were observed in cystatin C, MPO and PCT concentrations . It should be noted that the study involved a small group of subjects and a sampling interval. |
| 2020 | Castiglione V. et al. [24]Evaluation of inactive Matrix-Gla-Protein (MGP) as a biomarker for incident and recurrent kidney stones. | The study assessed serum dpucMGP levels in subjects with symptomatic urolithiasis and individuals without stones at the initial visit. Symptomatic recurrence of stones was assessed in stone-forming patients over a 5-year period. The association of dpucMGP with incident or recurrent kidney stones was evaluated with and without adjustment for clinical, blood and urine characteristics. | There was no statistically significant difference in levels of serum dpucMGP between 498 stone-formers and 395 non-stone-formers (510 vs 501 pmol/L; p = 0.66). The higher the MGP level, the lower the risk of stone formation (OR = 0.674, 95% CI 0.522-0.870). Recurrence of renal colic occurred in 21% (79) of subjects (375) observed for 5 years. When comparing patients with recurrent and non-recurrent stones, there was no difference in serum dpucMGP levels (482 vs 502 pmol/l; p = 0.26). There was a correlation between serum dpucMGP and cystatin C levels in subjects without lithiasis and in subjects with incident and recurrent lithiasis (r > 0.3, p < 0.0001). |
| 2020 |
Hughes S.F. et al.[25] Shock wave lithotripsy, for the treatment of kidney stones, results in changes to routine blood tests and novel biomarkers: a prospective clinical pilot-study. |
Patients with unilateral kidney stones after SWL (n=12) were collected for the study. Venous blood samples were collected from patients (8 men and 4 women) aged between 31 and 72 years (median 43 years) at different time intervals (preoperative-baseline, 30, 120 and 240 minutes postoperatively). A Sysmex XE-5000 and Beckman Coulter AU5800 and AU680 analyser were used. Concentrations of NGAL, IL-18, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10 and IL-8 were determined by ELISA. | After SWL surgery, a significant increase in NGAL concentration was observed at a maximum of 30 minutes after surgery (p = 0.033). IL-6 showed a significant increase from the preoperative period to 4 hours after surgery (p < 0.001), while TNF-α increased significantly, peaking at 30 min after SWL (p = 0.05). IL-18 increased, but not statistically significantly (p = 0.116). IL-10 and IL-8 concentrations did not change significantly after SWL (p > 0.05). |
| 2020 |
Cilesiz N.C. et al.[26] Can serum procalcitonin levels be useful in predicting spontaneous ureteral stone passage? 21 |
The study was carried out in patients with a single distal ureteral stone between 5 and 10 mm in diameter and without indications for interventional treatment and healthy subjects. Blood and urine samples were collected and analysed from all participants. Patients were followed up every 2 weeks for 1 month. Patients who did not pass stones at follow-up were considered to have complete stone passage [SP(+)] and failure [SP(-)] was defined if the patient did not pass stones by the end of the study. Levels of WBC (white blood cells), c-reactive protein (CRP), SED (sedimentation), MPV (mean platelet volume), NLR (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio) and serum procalcitonin (PCT) were analysed. All patients received diclofenac sodium 75 mg/day, tamsulosin 0.4 mg/day and at least 3 l of fluids daily. Patients were followed up for one month using a variety of imaging techniques: plain films of the kidney, ureter, bladder (KUB), ultrasonography (USG) and unenhanced abdominal CT during MET treatment. | The SP(+) and SP(-) groups were compared. PCT and leucocyturia levels were significantly higher in the SP(-) group than in the SP(+) group (p = 0.000; p = 0.004). Based on ROC curve analysis, 160 pg/ml (sensitivity 86.7%, specificity 70.8%, p < 0.001; AUC: 0.788 95% CI (0.658-0.917) was identified as the optimal cut-off value for PCT. In logistic regression analysis, significant efficacy was observed for PCT and leukocyturia in univariate analysis for spontaneous transition. In multivariate analysis, significant independent PCT activity was observed (p < 0.05). |
| 2020 |
Kovacevic L. et al.[27] Cystatin C, Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin, and Lysozyme C: Urinary Biomarkers for Detection of Early Kidney Dysfunction in Children With Urolithiasis. |
This was a prospective, controlled, pilot study where children with urolithiasis (RS) and a control group (HC) were assessed. Quantitative proteomic evaluation was the screening test for the RS and HC group liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry was used. |
Three promising proteins, cystatin C (CYTC), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and lysozyme C, were detected. These were significantly over-represented in the RS group compared with HC. Urinary CYTC and NGAL were significantly elevated and urinary lysozyme C levels were almost significantly elevated in the RS group (N = 24) compared with the control group (N = 13). In both hypercalciuria (N = 14) and hypocitraturia (N = 10), subgroup analysis showed significantly higher urinary CYTC levels compared to HC (P <0.05). |
| 2021 |
Taiguo Q. et al.[28] The predictive and diagnostic ability of IL-6 for postoperative urosepsis in patients undergoing percutaneous nephrolithotomy. |
The aim of this study was assessment of the predictive and diagnostic role of IL-6 for postoperative urosepsis in patients undergoing percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL). 90 patients undergoing PCNL between April 2019 and September 2019 were studied. 16 patients progressed to urosepsis (EXP1 group, n = 16) and 74 patients did not (CON group, n = 74); 25 patients who progressed to postoperative urosepsis without receiving the test of IL-6 between March 2018 and March 2019 were also enrolled (EXP2 group, n = 25); demographic and perioperative data were compared between all groups. | Compared with CON group, EXP1 group showed: higher serum levels of IL-6 (p < 0.001) and neutrophil (p < 0.001) at postoperative hour two; higher serum levels of IL-6 (p < 0.001), procalcitonin (PCT) (p < 0.05), white blood cell (WBC) (p < 0.05), and neutrophil (p < 0.001) on postoperative day one; higher serum levels of PCT (p < 0.05) and WBC (p < 0.05) on postoperative day three. ROC curves showed IL-6 (AUC = 1.000) at postoperative hour two and PCT (AUC = 0.954) on postoperative day three. Compared with EXP2 group, EXP1 group showed shorter time to intervene (p < 0.001), a shorter postoperative hospital stay (p < 0.001), and a lower incidence rate of severe urosepsis (p < 0.05). The main conclusion was the possible predictive values of IL6 as a early diagnostic marker for postoperative urosepsis in patients after PCNL at postoperative hour two and postoperative day one. |
| 2021 |
Ramasamy V. et al. [29] Role of inflammatory markers and their trends in predicting the outcome of medical expulsive therapy for distal ureteric calculus. |
The study assessed C-reactive protein (CRP), white blood cell (WBC) count and neutrophil percentage (NP) in relation to predicting the outcome of medical excretory therapy (MET). Nineteen hundred and two patients with distal ureteral stones >5 mm in size were included in the study. CRP, WBC and NP were measured on days: 1, 7, 14 MET and then analysed. | On days 1, 7, 14 stone size and mean CRP, WBC and NP values in patients who had not undergone stones were significantly higher compared to those who had undergone stones. ROC analysis showed an area under the curve of 0.798 (p=0.001) for CRP, and the cut-off value was 1.35 mg/dl. Multivariate analysis showed a significant association of higher CRP levels >1.35 mg/dl and stone size >7 mm with MET failure. A downward trend in CRP was observed in both groups, but values were higher in those who had not undergone stones. Only in those with stones did WBC and NP decrease. |
| 2021 |
Milisic E. et al.[30] Urinary neutrophil gelatinase – associated lipocalin level as a biomarker of acute kidney injury following extracorporeal shock lithotripsy. |
The aim of this research was to evaluate the severity of the kidney tissue response to extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) injury by measuring the urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) as an indicator of acute kidney injury (AKI) in the early phase. The study included 62 patients with nephrolithiasis undergoing single ESWL therapy. UNGAL level was measured before the procedure and 6 h and 12 h after it. |
The median uNGAL level increased by 126% 6 h post ESWL (p<0,001) with the further growth up to 583,7% after 12 h when compared to pre-treatment level. The median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) dropped by 15,3% 12 h post intervention but increased by 5 % in the period of 7 days to 3 months after. uNGAL level was significantly negatively correlated with eGFR 12 h, 7 days, and 3 months after ESWL. The sensitivity of uNGAL 12 h after ESWL was 60,6% and specifity 5% with a positive predictive value of 74% and negative predictive value of 61,7%. UNGAL had the highest predictive value of AKI 12 h after the ESWL treatment. |
| 2021 |
Wymer, KM et al. [31] A Serum C-Reactive Protein and Procalcitonin-Based Risk Score to Predict Urinary Infection in Patients with Obstructive Urolithiasis Undergoing Decompression |
Retrospectively, more than 30 clinical parameters were assessed in patients presenting to the emergency room after upper urinary tract decompression for fear of recurrent urolithiasis and a composite risk score was created. The aim was also to identify predictors of a true urinary tract infection (UTI). | There were 98 patients included in the study in which true UTI was identified in 50 (51%). The standard model of serum white blood cell count >15 or temperature >38 degrees C had an area under the curve (AUC) of only 0.67 to predict UTI. A multivariable regression-based 4-point risk score (1 point for each of the following: positive urine Gram stain, perinephric fatty bands on CT scan, serum CRP >21.95 and serum procalcitonin >0.36) had an AUC of 0.91 to predict UTI. Individually, these components had AUCs of 0.68, 0.68, 0.80 and 0.77, respectively. The chances of confirming ZUM were 8%, 11%, 68% and 100% for risk scores of 0, 1, 2 and 3 to 4, respectively (p < 0.001). |
| 2022 |
Xiaohong F. et al.[32] Metabolic Differences between Unilateral and Bilateral Renal Stones and Their Association with Markers of Kidney Injury. |
The study included 10,281 participants. All subjects had a renal ultrasound examination to detect urinary stones; stone-formers were divided into groups with unilateral or bilateral kidney stones based on ultrasound. CKD was defined according to reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, <60 ml/minute/1.73 m2) and/or albuminuria (albumin/creatinine ratio ≥30 mg/gm). Elevated urinary NAG and α1-MG levels were defined as their values above the 75th percentile of the sample distribution. | 4.9% (507) of participants had unilateral nephrolithiasis and 0.7% (75) had bilateral nephrolithiasis. The percentage of CKD in those without stones, with unilateral and bilateral kidney stones was 11.0%, 19.2% and 29.7%, respectively (p for trend <0.001). Those with bilateral nephrolithiasis had the highest proportion of metabolic components, such as elevated blood pressure and serum glucose levels. Bilateral nephrolithiasis was significantly associated with an increased risk of lower eGFR (OR 3.38; 95% CI 1.05-10.90), albuminuria (OR 3. 01; 95% CI 1.76-5.13), CKD (OR 3.18; 95% CI 1.88-5.36), increased urinary NAG/creatinine ratio (OR 1.95; 95% CI 1.21-3.16) and α1-MG/creatinine (OR 2.54; 95% CI 1.56-4.12) compared with no stones. |
| 2022 |
Noonin et al.[33] Systematic analysis of modulating activities of native human urinary Tamm-Horsfall protein on calcium oxalate crystallization, growth, aggregation, crystal-cell adhesion and invasion through extracellular matrix. |
This research was planned to clarify the roles of native urinary Tamm Horsfall Protein (THP) in CaOx monohydrate stones formation. In the study 24 h urine specimens from 10 male patients with idiopathic nephrolithiasis without no well-known metabolic risk factors were collected. At least 50% of stones were composed of CaOx. As controls 10 men and 10 women were assessed without personal or family history of kidney stones. THP was purified from the urine by adsorption methods and its effects on stone formation, crystal growth, aggregation, cell adhesion and further invasion through extracellular matrix were examined. |
Analyses revealed that THP concentration-dependently (0,4-40 µg/ml) reduced CaOx monohydrate crystals size but without effect on their mass during initial crystallization. What is more THP concentration-dependently inhibited CaOx crystals growth, aggregation and further adhesion but it did not prevent crystals invasion through the extracellular matrix. It occurred that THP has two large calcium binding domains and three small oxalate binding domains, however in immunofluorescence it appeared that THP binds only calcium ions with high affinity. |
| 2022 |
Kovacevic L. et al.[34] Proteomic analysis of inhibitory protein profiles in the urine of children with nephrolithiasis: implication for disease prevention. |
A prospective, controlled, pilot study in which urine collected from RS (N = 30, 24 women, mean age 12.95 ± 4.03 years) was examined and compared with HC using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Criteria for protein selection were: (1) patient/control ratio < 0.5; and (2) p-value ≤ 0.05 for Fisher's exact test. Results were confirmed by ELISA. | 67 proteins were decreased in the RS group and 17 were significantly different compared to the control group. 5 proteins ( 2 actin, annexin A5, keratin 6B and serpin B4) were completely absent in the urine of patients with lithiasis, but were present in the control group. The 12 other proteins were significantly less frequent in the urine of patients compared to the control group. Modelling of protein-protein interactions of significant proteins identified syndecan-1 as a key node, a protein associated with adhesion pathways. There was a statistically significant difference in urinary osteopontin excretion (5.1 ± 3.22 ng/mg creatinine vs. 14.1 ± 9.5 ng/mg creatinine, p = 0.046) between patients with hypocyturic stones and controls. A positive correlation was also detected between urinary osteopontin levels and urinary citrate excretion (r = 0.417, p = 0.03). |
| 2023 |
Memmos D. et al.[35] The effect of standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy, miniaturized percutaneous nephrolithotomy and retrograde intrarenal surgery on biomarkers of renal injury: a randomized clinical trial. |
The study was designed to compare the effect of standard percutaneous nephrolithotomy (sPCNL) with miniaturized PCNL (mPCNL) and retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) as a nephrolithiasis treatment and measure urinary ratios: NGAL/creatinine (uNGAL/cr), KIM-1/creatinine (uKIM-1/cr) and Interleukin-18/creatinine ( uIL-18/cr) at baseline and 2- , 6-, 24- and 48 h postoperatively. |
No significant differences were shown in uNGAL/cr changes between sPGNL and mPGNL and RIRS. Similarly no-between group changes were observed for urinary ratio KIM-1 and IL-18 at 2 h and all biomarkers at any time point post operatively. Within particular groups increases from baseline were noted only for uNGAL/cr, uKIM-1/cr and uIL-18/cr at 2 h and progressively lower rises from time zero were in all participants for uKIM-1/cr and uIL-18/cr at 6- , 24- and 48 h post procedure. No significant differences in these indicators were noticed in AKI or other complications. |
| 2023 |
Savin Z. et al. [36] The role of serum and urinary markers in predicting obstructing ureteral stones and reducing unjustified non-contrast computerized tomographic scans in emergency departments. |
The study evaluated all patients admitted to the ED between December 2019 and February 2020 with symptoms of renal colic (acute flank pain) and assessed by non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT). Serum white blood cell (WBC), C-reactive protein (CRP) and creatinine (Cr) levels and urine findings were measured. Rates of unreasonable NCCT scans were also calculated. | The NCCT method diagnosed obstructive urolithiasis (OU) in 108 of the 200 patients studied (54%). The median WBC, CRP and Cr values were 9 100/mu L, 4.3 mg/L and 1 mg/dL, respectively. The most accurate thresholds for predicting OU were WBC = 10 000/mu L and Cr = 0.95 mg/dL. Only WBC >= 10 000/mu L (OR = 3.7, 95% CI 1.6-8.3, p = 0.002) and Cr >= 0.95 mg/dL (OR = 5, 95% CI 2.3-11, p < 0.001) were associated with OU. The positive predictive value and specificity for detecting OU in patients with a total WBC count >= 10 000 and Cr >= 0.95 were 83% and 89%, respectively. Significantly more unsubstantiated NCCTs (p = 0.03) were performed in patients with negative serum marker criteria. The negative predictive value of serum criteria for a justified NCCT test was 81%. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





