Submitted:
11 October 2023
Posted:
11 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Aetiology
CMT type I
CMT type II
1.2. Epidemiology
1.3. Clinical presentation
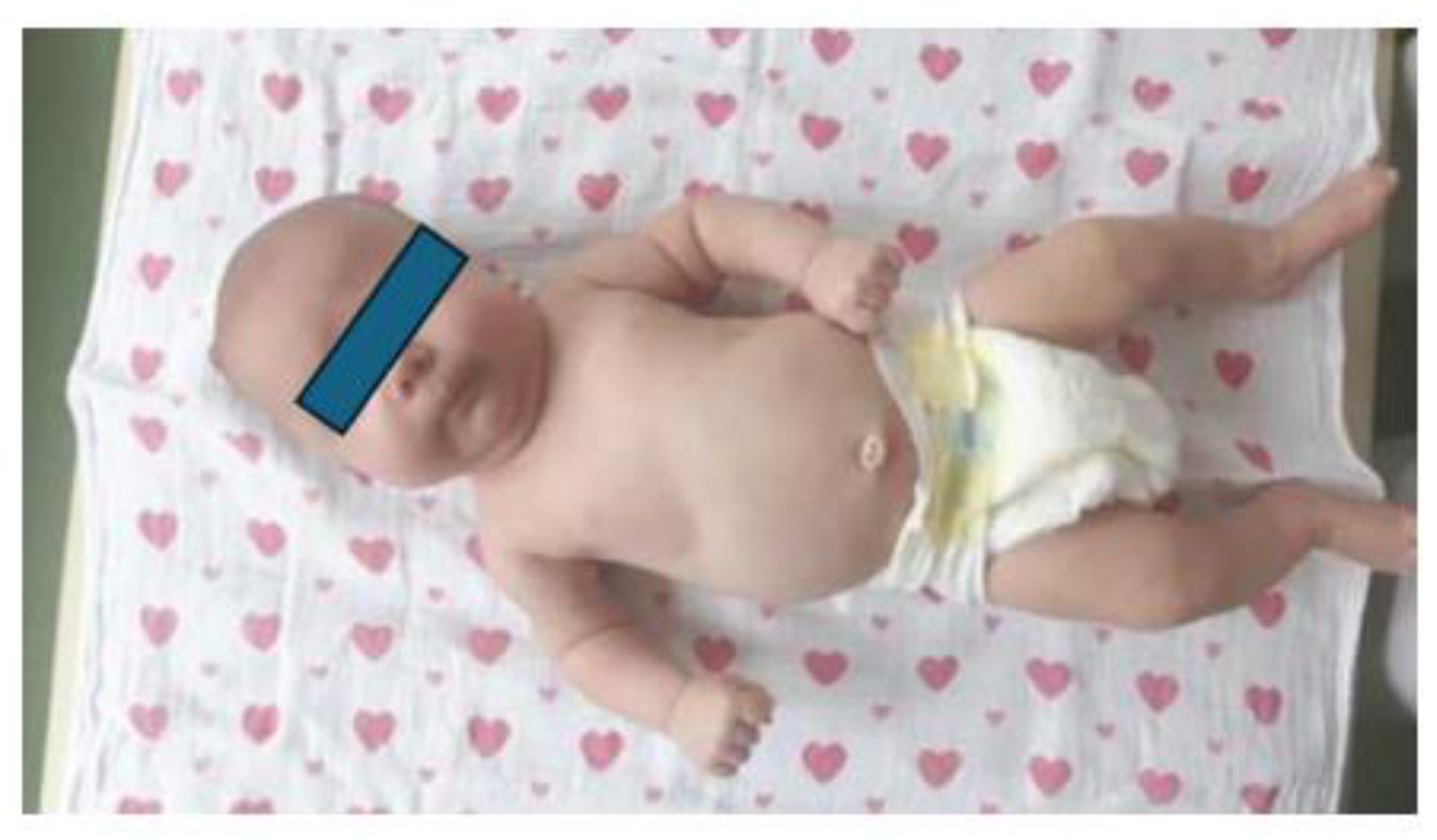
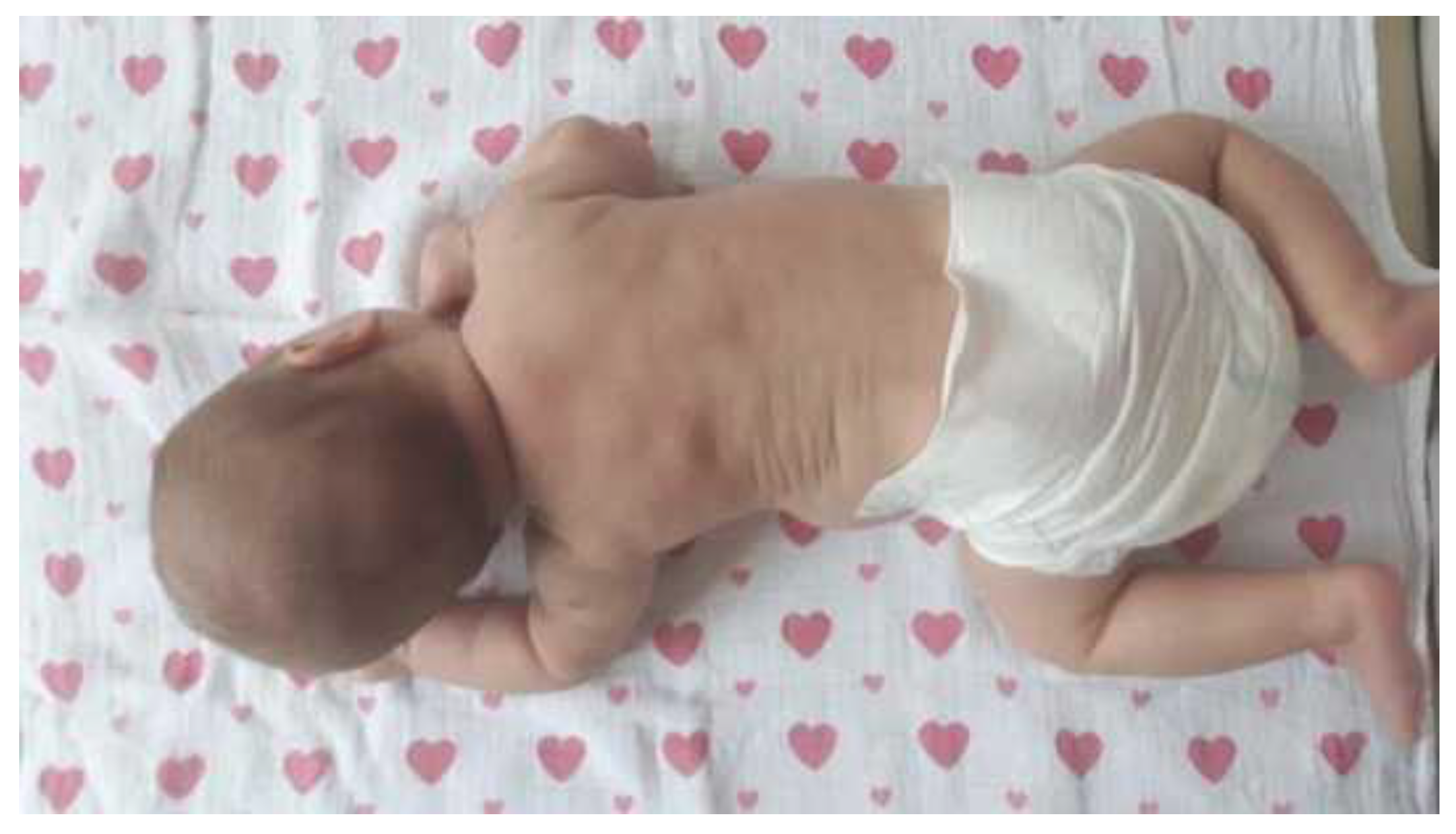
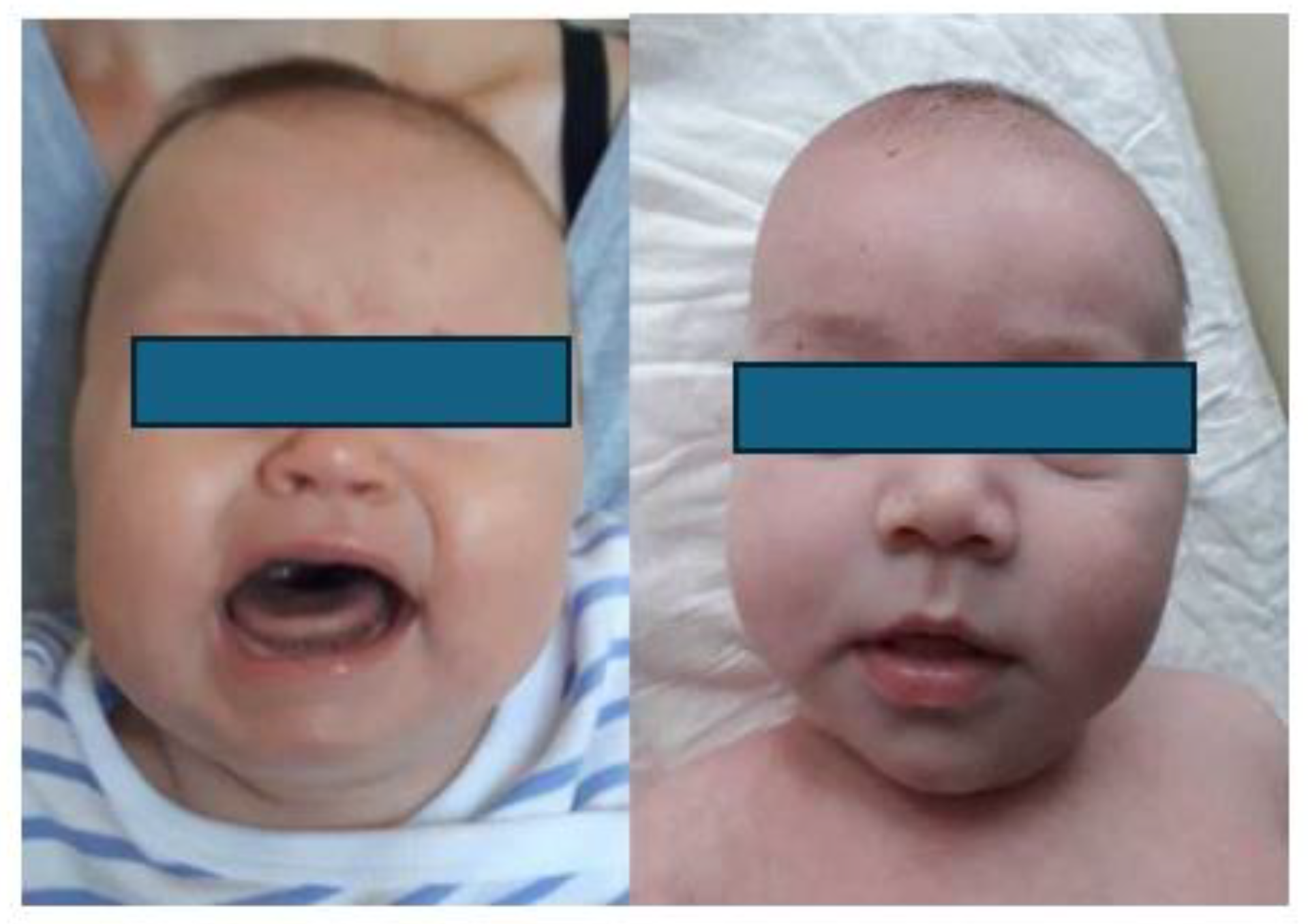
1.4. Radiological image
1.5. Treatment
Conservative treatment
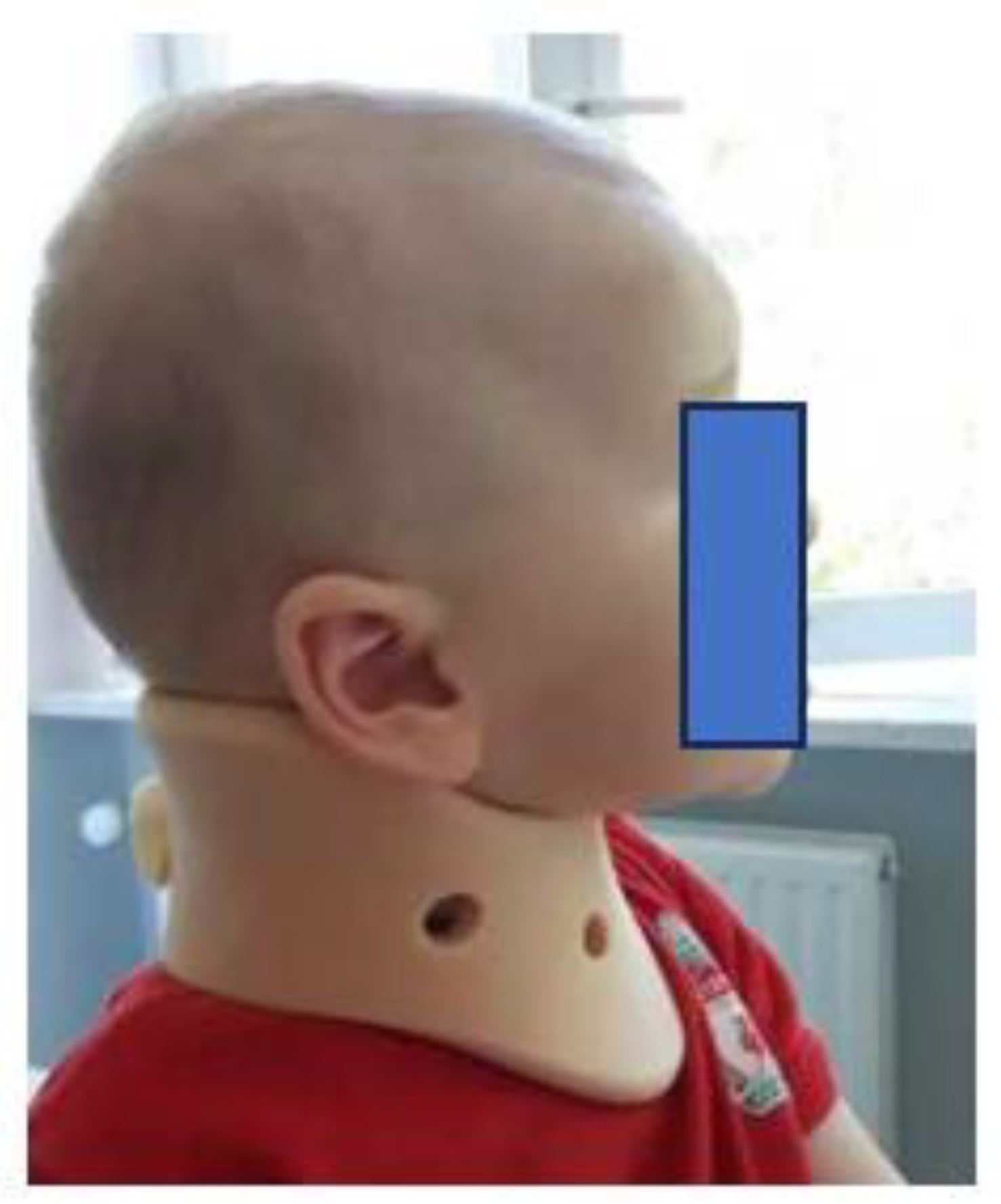
Botulinum toxin type A (BTX-A)
Surgical treatment
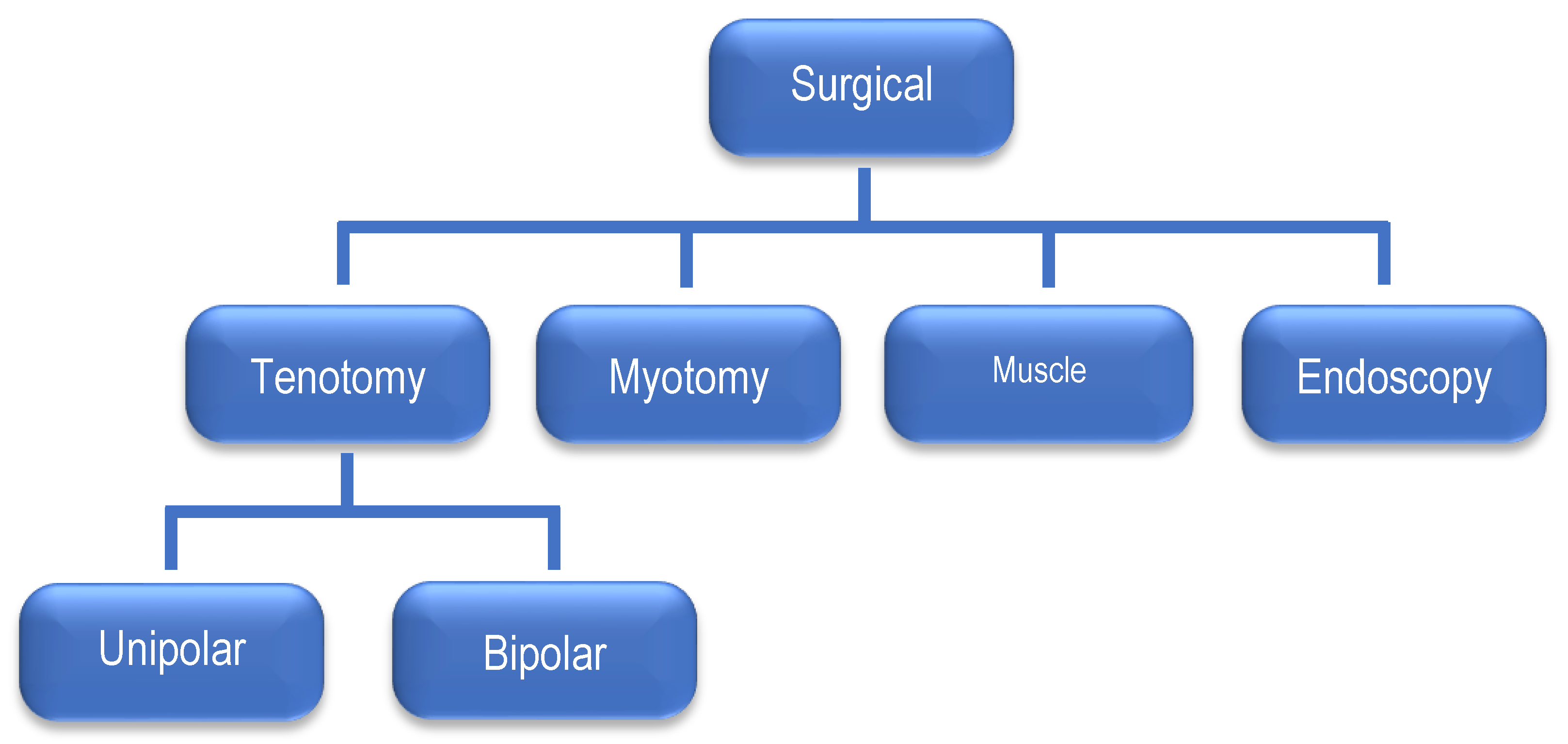
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study group
2.2. The inclusion criteria for the analysis were as follows:
2.3. The following relationships were analyzed:
2.4. Statistical analysis
2.5. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Relationship between the side of CMT location and the type of delivery
3.2. Relationship between the birth body weight and the location of CMT
3.3. Relationship between the extent of the SCM muscle thickening and the type of delivery (cc vs. natural)
| Natural delivery | Cesarian section | Mean body weight at birth | |
|---|---|---|---|
| L-sided torticollis | 91% | 9% | 3,674 |
| R-sided torticollis | 69% | 31% | 3,274 |
| Width of R-SCM [mm] | Width of L-SCM [mm] | Difference [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural birth | 8.30 | 13.99 | 6.07 |
| Cesarean section | 9.39 | 17.72 | 4.14 |
| 1st birth | 8.58 | 14.94 | 5.47 |
| Next birth | 8.30 | 14.00 | 6.35 |
| Boys | 8.40 | 14.56 | 5.86 |
| Girls | 8.67 | 14.92 | 5.44 |
| L-CMT | 4.93 | 10.69 | 5.76 |
| R-CMT | 11.22 | 5.61 | 5.61 |
3.4. Incidence of CMT depending on the order of delivery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davids, J.R.; Wenger, D.R.; Mubarak, S.J. Congenital muscular torticollis: A sequela of intrauterine or perinatal compartment syndrome. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1993, 13, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sanerkin, N.G. Birth injury to the sternomastoid muscle. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1966, 48, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, L.; Pietrzyk, D.; Kandzierski, G.; Wilczynski, M. Bilateral congenital torticollis: A case report with 25 years of follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2017, 26, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, M.K.; Lee, P.; Mahadev, A.; Lee, E.H. Congenital bilateral sternocleidomastoid contracture: A case report. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2009, 18, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ha, E.K.; Kim, J.H.; Jo, Y.H.; Rhie, S.; Han, M.Y.; Chae, K.Y. Neurodevelopmental outcomes and comorbidities of children with congenital muscular torticollis: Evaluation using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children database. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2022, 65, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, E.R.A.; Andras, L.M.; Skaggs, D.L. Screening for hip dysplasia in congenital muscular torticollis: Is physical exam enough? J Child Orthop 2014, 8, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenzio, G.; Carlisi, E.; Morani, I.; Tinelli, C.; Barak, M.; Bejor, M.; Dalla Toffola, E. Early rehabilitation treatment in newborns with congenital muscular torticollis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.C.; Wong, F.H.; Lo, L.J.; Chen, Y.R. Craniofacial deformity in patients with uncorrected congenital muscular torticollis: An assessment from three-dimensional computed tomography imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 113, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.Y.; Tang, S.P.; Chen, T.M.; Wong, M.W.; Wong, E.M. The clinical presentation and outcome of treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants - a study of 1,086 cases. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2000, 35, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardgrib, N. et al. Do obstetric risk factors truly influence the etiopathogenesis of congenital muscular torticollis? J. Orthop. Traumatol. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 18, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulbert, K.F. Congenital torticollis. J. Bone Joint Surg. 1950, 32, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D. Sternomastoid tumor and muscular torticollis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1969, 51, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanerkin, N.G. Birth injury to the sternomastoid muscle. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 1966, 48, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mukherji, S. Congenital muscular torticollis. Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery 2013, 3, 198. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.L.; Schwartz, K.M.; Weaver, A.L.; Orvidas, L.J. Pseudotumor of Infancy and Congenital Muscular Torticollis: 170 Cases. The Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.W.; Landenberger, M.; Jung, T.; Lindenthal, T.; Philippi, H. Vojta therapy and neurodevelopmental treatment in children with infantile postural asymmetry: A randomized controlled trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghelli, B.; Vitorino, N.G.D. Incidence of congenital muscular torticollis in babies from southern Portugal: Types, age of diagnosis and risk factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 2022, 19, 9133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.Y.; Au, A.W.Y. Infantile torticollis: A review of 624 cases. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1993, 14, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Chang, H.C.; Hsieh, C.F.; Yen, M.F.; Chen, T.H. Predictive Model for Congenital Muscular Torticollis: Analysis of 1021 Infants With Sonography. Arch Phys Med Rehabilit 2005, 86, 2199–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogi, J. Wrodzony mięśniowy kręcz szyi. In: Pizzutillo P.: Ortopedia dziecięca. Czelej. Lublin 1997, 341-342.
- Rao, R.; Morton, G.V.; Kushner, B.J. Ocular torticollis and facial asymmetry. Binocul. Vis. Strabismus Q. 1999, 14, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Koh, S.E.; Lee, I.S.; Jung, H.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.I.; Bang, H. The cervical range of motion as a factor affecting outcomes in patients with congenital muscular torticollis. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2013, 37, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.; Cheng, J.; Metreweli, C. Ultrasonography of congenital muscular torticollis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2005, 22, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.; Wong, W.M.; Tang, S.P.; Chen, T.M.; Shum, S.L.; Wong, E.M. Clinical determinants of the outcome of manual stretching in the treatment of congenital muscular torticollis in infants. A prospective study of eight hundred and twenty-one cases. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carenzio, G.; Carlisi, E.; Morani, I.; Tinelli, C.; Barak, M.; Bejor, M.; Toffola, E. Early rehabilitation treatment in newborns with congenital muscular torticollis. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 51, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, M.B.; de Chalain, T.M. Treatment of recalcitrant idiopathic muscular torticollis in infants with botulinum toxin type A. J. Craniofac Surg. 2005, 16, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.; Jankovic, J. Botulinum toxin injection for congenital muscular torticollis presenting in children and adults. Neurology. 2006, 67, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszek, J.L.; Chang, N.; Apkon, S.D.; Wilson, P.E. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of children with congenital muscular torticollis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 84, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P. The Transaxillary Subcutaneous Endoscopic Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Division as an Approach for the Surgical Treatment of Congenital Muscular Torticollis in Children. Indian. J. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2020, 72, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.T.; Yoon, K.; Kim, Y.B.; Chung, P.W.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Chung, S.H.; Cho, S.K.; Han, B.H. Clinical features and outcome of physiotherapy in early presenting congenital muscular torticollis with severe fibrosis on ultrasonography: A prospective study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.C.; Wong, F.H.; Lo, L.J.; Chen, Y.R. Craniofacial deformity in patients with uncorrected congenital muscular torticollis: An assessment from three-dimensional computed tomography imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2004, 113, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, K.; Türkyılmaz, Z.; Demiroğulları, B.; Özen, I.; Karabulut, R.; Bağbancı, B.; Başaklar, A.; Kale, N. Congenital Muscular Torticollis in Children. ORL, 2005, 67, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.S.; Jang, H.P. Operative treatment of congenital torticollis. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.Y.; Tang, S.P. Outcome of surgical treatment of congenital muscular torticollis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1999, 362, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Liu, Y. Endoscopic release of congenital muscular torticollis with radiofrequency in teenagers. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2018, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.T.; Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.W.; Tong, Q.S.; Cao, G.Q.; Li, S. Endoscopic transaxillary approach for congenital muscular torticollis. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2010, 45, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angoules, A.; Boutsikari, E.; Latanioti, E. Congenital Muscular Torticollis: An Overview. J. Gen. Pract. 2013, 1, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronic, I.; Brdar, R.; Cirovic, D.; Nikolic, D.; Lukac, M.; Janic, D.; Pavicevic, P.; Golubovic, Z.; Knezevic, T. Congenital muscular torticollis in children: Distribution, treatment duration and outcome. Eur. J. PhysRehabil Med. 2010, 46, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.O.; Kim, S.J. Results of the conservative management in congenital muscular torticollis. J. Korean Acad. Rehabil. Med. 1992, 16, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Leibovitch, L.; Kuint, J.; Rosenfeld, E.; Schushan-Eisen, I.; Weissemann-Brenner, A.; Maayan-Metzger, A. Short-term outcome among term singleton infants with intrapartum oligohydramnios. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachdjian, Mihrano, O. Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery. W.B. Saunders Co. Phila. 1990, 1, 112–124. [Google Scholar]
- Özkan, E.; Özkan, M.; Isik, I. Evaluation of the clinical role of strain elastography in patients diagnosed with congenital torticollis. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2021, 37, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcicki, K.; Krieger, R.; Berry, A.; Reuther, W. Fibromatosis colli spuriously presenting as a retropharyngeal mass on cervical spine radiographs. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 11, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N (%) | Left-sided CMT | Right-sided CMT | Mean birth weight | Birth | Term of birth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cc | natural | pre | on time | |||||
| Boys | 61 (54%) | 33 | 28 | 3632 | 10 | 51 | 1 | 60 |
| Girls | 50 (46%) | 24 | 26 | 3299 | 11 | 39 | 5 | 45 |
| Total | 111 (100%) | 57 | 54 | 21 | 90 | 6 | 105 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





