1. Introduction
Replacement of harmful chemical pesticides by environmentally friendly biological means is a pressing need in present agriculture worldwide. Microbes, such as bacteria and fungi were proven as being promising candidates for development of efficient agents useful in sustainable agriculture. At present, endospore-forming
Bacillus spp., and gram-negative
Pseudomonas spp. are the most used constituents of bioformulations applied in biological plant protection. The main advantage of bioformulations based on
Bacillus endospores is their longevity, which makes their stability comparable with that of chemical fungicides [
1].
During a survey for plant-beneficial bacteria as part of the microbiome of healthy Vietnamese crop plants, a number of Gram-positive, endospore-forming bacteria, able to suppress common plant pathogens, have been isolated from healthy crop plants grown in fields infested with plant pathogens. Based on their draft genome sequences, the isolates were taxonomically assigned as being members of the
Bacillaceae-family, representing four main taxonomic groups:
Lysinibacillus spp.,
Brevibacillus spp., the
Bacillus subtilis species complex, and the
Bacillus cereus group [
2]. Our further studies revealed that by contrast to
Lysinibacillus sp., the plant-associated Brevibacilli harbored a multitude of interesting antimicrobial peptides with a strong potential to suppress phytopathogenic bacteria, fungi, and nematodes [
3]. The
Bacillus velezensis isolates TL7 and S1, members of the
B. subtilis species complex, were identified in large scale trials as being the most promising candidates for developing efficient biocontrol agents [
4]. In this study we focus on the plant-associated isolates belonging to the
B. cereus group in order to investigate their potential for biocontrol and plant growth promotion.
The
B. cereus group, also known as
B. cereus sensu lato (
s.l.), comprises a steadily increasing number of species [
5] including the human-pathogenic
B. anthracis, the entomopathogenic
B. thuringiensis, and the opportunistic pathogen
B. cereus sensu stricto (
s.s.)., The three species are able to cause human diseases with different severity [
6]. They are closely related, and harbor very similar genome sequences, which not necessarily justify their delineation in different species. Traditionally, they have been discriminated due to properties mainly encoded by extrachromosomal elements.
B. anthracis (risk group 3) has been identified in 1876 by the German physician Robert Koch as the causative agent of anthrax [
7], the first disease which has been linked to a microbe. Its virulence is based on the ability to form exotoxins and a capsule, which are encoded by the plasmids pXO1 and pXO2 [
8].
The plasmid encoded production of the highly toxic cereulide is restricted to rare emetic
B. cereus strains occurring in some foods, whilst production of the chromosomally encoded diarrheal-inducing enterotoxins (haemolysin BL, HBL; non-hemolytic enterotoxin, NHE; and cytotoxin K, CytK) is comm on in
B. cereus s.l. [
6]. Due to the extreme stability of the cyclic dodecadepsipeptide cereulide, which is withstanding current food processing techniques, their emetic
B. cereus producer strains are of particular concern for human health [
9].
B. thuringiensis (Bt), isolated 1901 by Ishikawa as “B. sotto” from silkworm, and some years later as
B. thuringiensis by Berliner from meal moth [
10], is an insect pathogen that is successfully used in agriculture as a biopesticide based on the production of diverse crystal toxins, also known as δ-endotoxins [
11].
However, the
B. cereus taxonomy solely based on presence of virulence plasmids with specific function becomes increasingly questionable in light of the recent phylogenomic data. Occurrence of
B. cereus strains containing pXO1-like plasmids [
12], and of crystal protein harboring
B. thuringiensis strains, which are phylogenetically related to
B. anthracis [
13], make the identification of these species to a difficult task. Moreover, occurrence of virulence genes in
B. cereus s.l. species cannot be excluded. Therefore,
B. cereus s.l. strains with potential for use in sustainable agriculture can be a risk for public health, and need to be carefully checked for their genomic content, also in case that their taxonomic delineation suggests to be a “safe” species.
In this study, we aimed to elucidate the potential of plant-associated members of the B. cereus species complex for biological plant protection. Genome based phylogenetic analyses revealed that most of the isolates were clustered within two subspecies of the B. cereus s.s. species. Interestingly, the isolate B. cereus TK1 harbored genes encoding two different crystal proteins, and one vegetative insectopathogenic toxin (Vip3). Genome mining for biosynthetic gene clusters probably involved in synthesis of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), and direct mass-spectrometric investigation of the synthesized AMPs, revealed that the isolates are promising candidates for use in sustainable agriculture. In this context, the lipopeptides kurstakin and thumolycin seem to be of special importance. A special highlight of our research was resolving the primary structure of the plasmid-encoded thumolycin pentapeptide by LIFT-MALDI-TOF/TOF fragment analysis. The inhibiting action of the B. cereus s.l. isolates against plant pathogens was corroborated in direct assays performed with pathogenic ooymycetes, fungi, and nematodes. Finally, plant growth promoting activity of some of the isolates was demonstrated. Regardless of these promising results, we have to consider the risk for public health due to the presence of virulence genes, when the B. cereus s.l. isolates are applied as biological means in agriculture.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain isolation and cultivation
Isolation from Vietnamese healthy crop plants, and purification of the strains was performed as described previously [
4]. Cultivation of the bacterial strains on standard media and DNA isolation have been previously described [
14]. The
B. cereus group strains were cultivated on Cereus Ident agar and Cereus selective agar as described in
Section 2.4.
2.2. Reconstruction of complete genomes
The genome sequences of
Bacillus cereus A22,
B. cereus A24,
B. cereus HD1.4B, and
B. cereus HD2.4 were reconstructed using a combined approach of two sequencing technologies which generated short paired-end reads and long reads. The resulted sequences were then used for hybrid assembly [
14]. Long read sequencing was done in house with the Oxford Nanopore MinION with the flowcell (R9.4.1) as described previously [
3]. The quality of assemblies was assessed by determining the ratio of falsely trimmed protein by using Ideel (
https://github.com/phiweger/ideel). Genome coverage of the obtained contigs was 50 x in average. Genome annotation and visualization was performed as described previously [
3].
2.3. Screening of the virulence genes
The screening of virulence genes in WGS and complete genomes was performed by using a combined analysis of the PATRIC annotation system [
15] and tblastN in the 17 genomes. The most characteristic genes from
B. anthracis Vollum, including four genes of the pXO1 plasmid (
cya,
lef,
pagA and
repX) and six genes of the pXO2 plasmid (
capA,
capB,
capC,
capD,
capE and
repS), were used as the reference sequences. The tblastN threshold for both similarity and coverage was >30%, and all BLAST results were cross-checked against the PATRIC annotation, available at the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center, BV-BRC,
https://www.bv-brc.org/.
The criteria for the presence of virulence plasmids were established as described by Liu et al. [
16]. Sequences representing the different types of δ-endotoxins (
Suppl. Table S1) were extracted from the NCBI data bank. Searches for presence of genes encoding crystal proteins, and toxins in the 17 plant-associated
B. cereus genome sequences were performed with tblastN using the respective protein sequences as query.
2.4. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of isolate B. cereus CD3-1a
In addition to the
B. anthracis virulence genes mentioned above, the genome of strain
B. cereus CD3-1a was also screened for presence of the four
B. anthracis-specific prophage regions (dhp) described by Radnedge et al. [
17]. These in silico analyses were complemented by real-time PCR assays targeting
pagA,
capB,
rpoB and dhp61.183. Colony morphology was examined on Columbia blood agar, blood trimethoprim agar, Cereus Ident agar and Cereus selective agar [
18].
2.5. Taxonomical phylogeny assessment
Species and subspecies delineation were performed using the Type (Strain) Genome Server (TYGS) platform [
4]. Information on nomenclature was provided by the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN, available at
https://lpsn.dsmz.de [
19]. The EDGAR3.0 pipeline [
20] was used for elucidating taxonomic relationships as described previously [
4].
2.6. Genome mining
In silico prediction of gene clusters involved in secondary metabolite synthesis was performed using the antiSMASH pipeline version 6 [
21], the bioinformatic tool described by Bachmann and Ravel [
22], and BAGEL4 [
23].
2.7. Sample preparation and mass-spectrometric detection of the bioactive peptides
Bioactive compounds of the investigated
B. cereus s.l. strains were detected and identified by MALDI-TOF MS, as outlined previously [
24,
25]. A Bruker Autoflex Speed TOF/TOF mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics; Bremen, Germany) was used with Smartbeam laser technology applying a 1 kHz frequency-triple Nd-YAG-laser (λ
ex = 355 nm). Samples (2 µl) of surface extracts and culture supernatants were mixed with 2 µl matrix solution (a saturated solution of α-hydroxy-cinnamic acid in 50% aqueous ACN containing 0.1 % TFA) spotted on the target, air dried and measured. Mass spectra were obtained by positive-ion detection in reflector mode. Monoisotopic masses were observed. Parent ions were detected with a resolution of 10.000. Sequence analysis of peptide products was performed by MALDI-LIFT-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry in laser induction decay (LID) mode [
26]. The product ions in the LIFT-TOF/TOF fragment spectra were obtained with a resolution of 1000.
2.8. Antibacterial, antifungal, nematocidal, and plant growth-promoting activity assays
Assays for activity against plant pathogens (oomycetes, fungi, neatodes) were performed as previously described [
4]. The root-knot nematode
Meloidogyne sp. was isolated from roots of infested pepper plants according to Hooper et al. [
27]. Tomato plantlets were grown in pots with natural soil under controlled conditions in greenhouse. Test bacteria and second stage juveniles (J2) nematodes were added to the pots two weeks after transplanting. Ten weeks after infesting with the nematodes the number of knots in tomato plants was estimated [
28].
Plant growth promotion assays were performed with
Arabidopsis thaliana seedlings as described previously [
29].
2.9. Data analysis
The data obtained from biocontrol and plant growth promotion experiments were analyzed using one-factorial analysis of variance (ANOVA). Mean values were calculated from the results of the replicates (n≥3). The Fisher´s least significant difference (LSD) test was conducted as
post-hoc test for estimating significant differences (p≤ 0.05) between the mean values as described previously [
4].
2.10. Gene bank accession numbers of complete genome sequences
Bacillus cereus A22 chromosome: CP085498.1, Bacillus cereus A22 plasmid P1: CP085499.1, Bacillus cereus A22 plasmid P2: CP085500.1, Bacillus cereus A24 chromosome: CP085501.1, Bacillus cereus A24 plasmid P1: CP085502.1, Bacillus cereus A24 plasmid P2: CP085503.1, Bacillus cereus HD1.4B chromosome: CP0855510.1, Bacillus cereus HD1.4B plasmid P1: CP085511.1, Bacillus cereus HD1.4B plasmid P2: CP085512.1, Bacillus cereus HD1.4B plasmid P3: CP085513.1, Bacillus cereus HD2.4 chromosome: CP0855506.1, Bacillus cereus HD2.4 plasmid P1: CP085507.1, Bacillus cereus HD2.4 plasmid P2: CP085508.1, Bacillus cereus HD2.4 plasmid P3: CP085509.1.
3. Results and Discussion
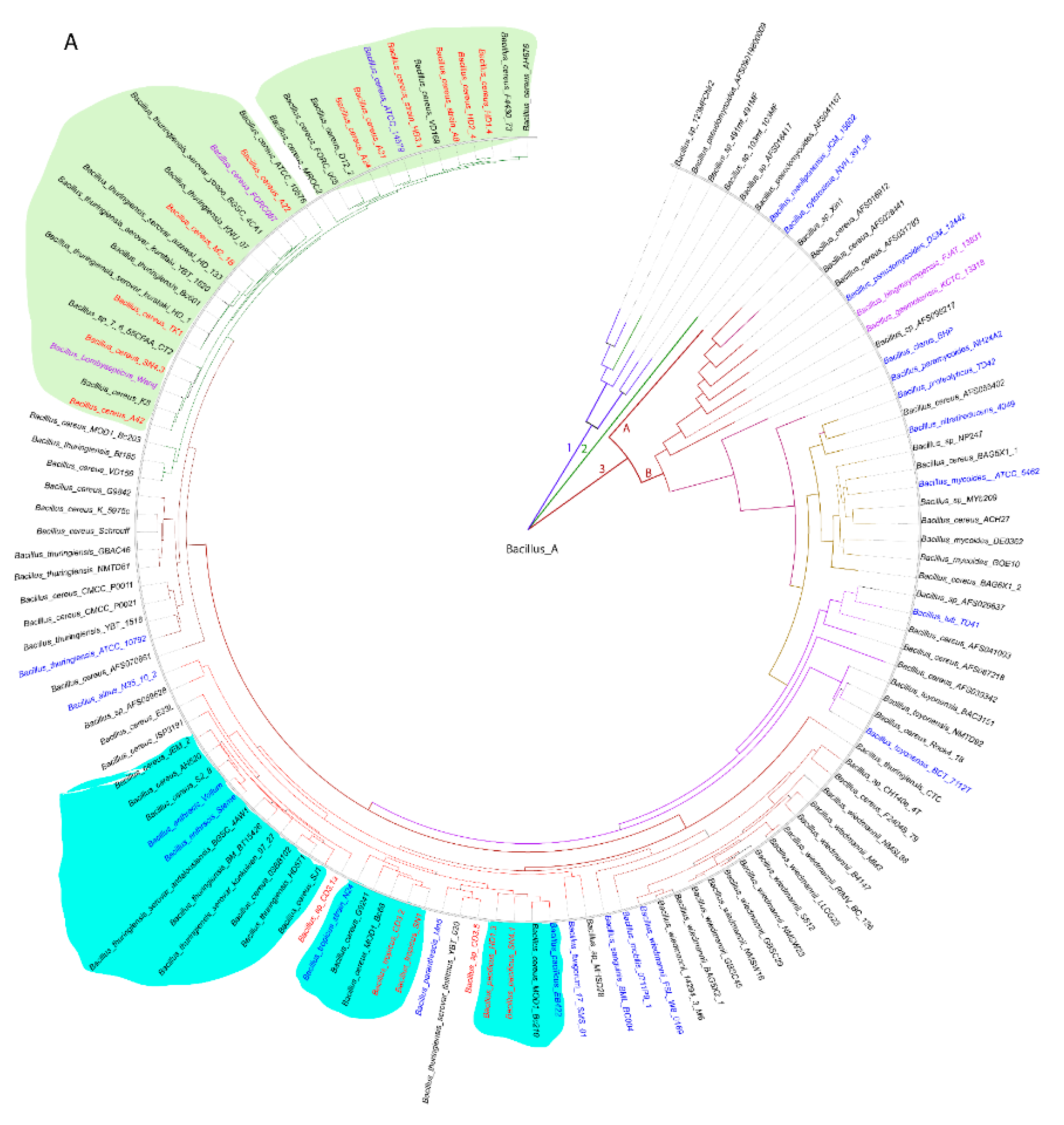
3.1. Comparative genome analysis of the isolates from Vietnamese crop plants representing the Bacillus cereus s.l. complex
3.1.1. Genome-based species and subspecies delineation of the plant-associated isolates belonging to the B. cereus group
Seventeen of the endospore-forming bacterial strains, isolated from Vietnamese crop plants have been previously assigned to the
Bacillus cereus sensu lato group [
2]. All isolates displayed the typical features of
B. cereus: they developed phospholipase C and hemolytic activity. The phylogenetic tree obtained from the 16S rRNA sequences supported their previous taxonomic assignment as members of the
B. cereus s.l. group, but possessed an average branch support of only 28.5 % (
Suppl. Figure S1), which is not sufficient for robust species delineation.
We used a whole-genome based approach for robust delineating of the taxonomic position of the plant-associated
B. cereus s.l. isolates. The phylogenomic tree containing a total of 128
B. cereus s.l. genomes, mainly extracted from the NCBI data bank, yielded three main branches (1,2,3). Branch 3 was subdivided into the clusters 3A and 3B. All of our isolates were distributed within the cluster 3B, and found related to the clusters formed by the type strains of
B. cereus,
B. anthracis,
B. tropicus, and
B. pacificus (
Figure 1A).
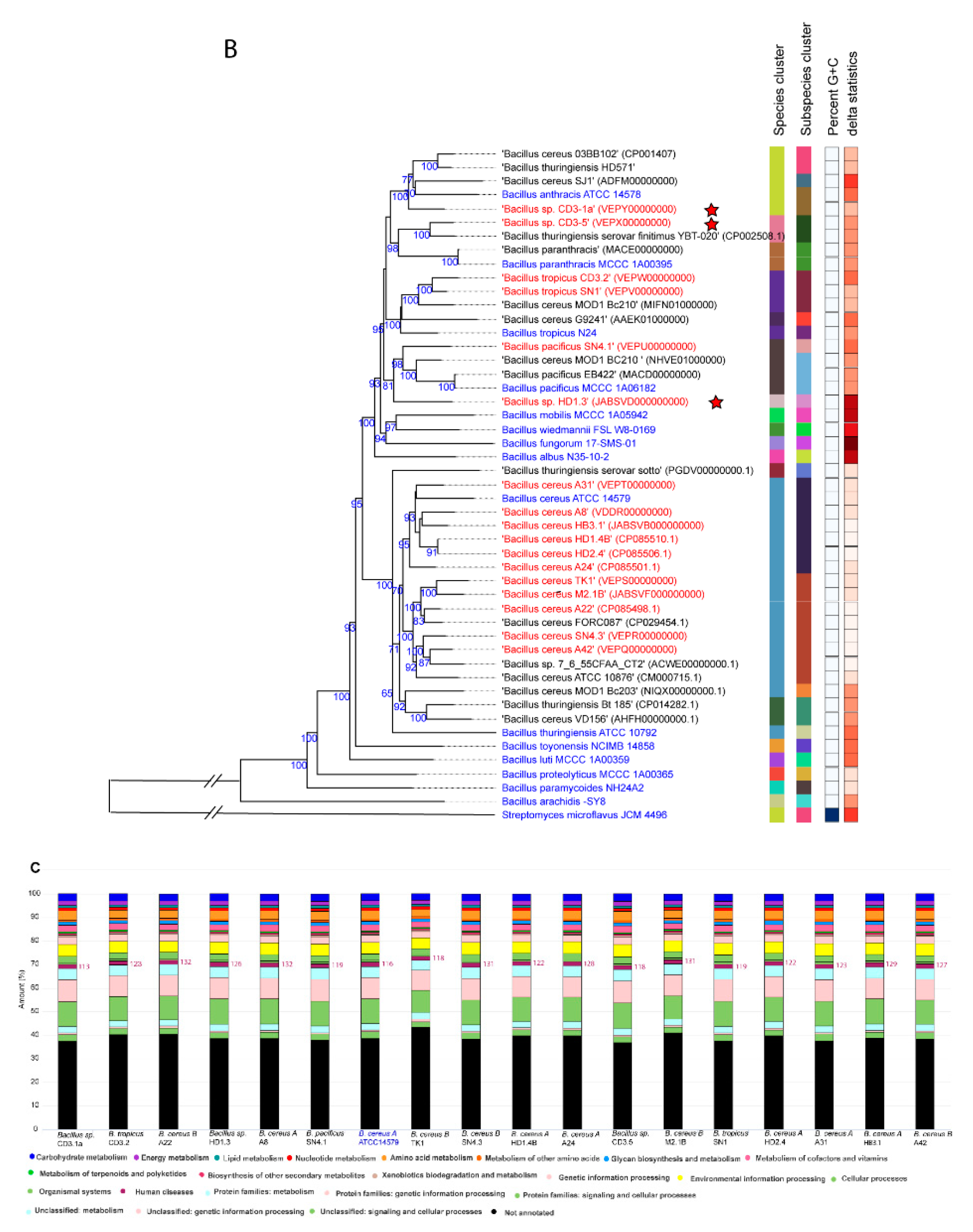
Similar, but more detailed results were obtained when using the Type (Strain) Genome server TYGS [
30]. Our survey resulted in assigning of six species and seven subspecies clusters (
Figure 1B,
Suppl. Figure S2). 15 of the isolates were assigned to four valid species,
B. cereus (11),
Bacillus pacificus (1),
Bacillus tropicus (2), and
Bacillus anthracis (1). In case of
B. cereus, the dDDH values obtained after comparison of 11 isolates with the type strain ATCC14579 exceeded the species cut off (>70%,
Suppl. Table S2). On the genomic level, two subclusters were distinguished: Six isolates, yielding dDDH values above the subspecies cutoff (>79%), represented the subspecies ´A´ (
B. cereus subsp.
cereus), whilst five isolates showed dDDH values ranging from 72% to 74%, when compared with ATCC14579. The latter cluster formed together with
B. cereus FORC087.1 a second subcluster ´B´, which was clearly distinguished from subcluster ´A´ (
Suppl. Table S2). When the genomes of the members of the
B. cereus subcluster ´B´ were compared with the genome of
Bacillus bombysepticus Wang [
31], their dDDH values exceeded the subspecies cutoff (>79%,
Suppl. Table S2). The direct comparison of FORC087 with
B. bombysepticus Wang yielded a dDDH value of 87.8%, suggesting their close relationship. In the Genome Taxonomy Database, GTDB [
32], the genomospecies
Bacillus_A bombysepticus harbored 667 members, whilst the
B. cereus genomospecies represented by
B. cereus ATCC 14579 harbored only 310 genomes (GTDB release 08-RS214, 28
th April 2023).
Although
B. bombysepticus is still not listed as valid species in the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature, LPSN [
33], we propose to designate the
B. cereus subcluster ´B´ as genomosubspecies
B. cereus subsp.
bombysepticus, taking into account that the members of the ´
bombysepticus group` shared dDDH values above the species cutoff with
B. cereus ATCC 14579.
The genomes of two other isolates, SN1 and CD3-2, were assigned, according to their dDDH and Fast ANI values, to
Bacillus tropicus. However, when compared with the
B. tropicus type strain N24, their dDDH and ANI values were below the subspecies cutoff indicating that these isolates form together with
B. cereus MOD1 Bc210 the subcluster ´B´, distinct from the
B. tropicus type strain (
Figure 1B,
Suppl. Table S2).
The isolate Bacillus sp. CD3-1a clustered together with the B. anthracis type strains. However, this species delineation appeared to be questionable, since we did not detect the B. anthracis virulence plasmids pXO1 and pXO2 in the draft genome of CD3-1a (see next section).
Two isolates,
Bacillus sp. CD3-5, and
Bacillus sp. HD1.3, although distantly related to
B. tropicus and
B. pacificus, could not be assigned to any species present in the TYGS database (17-04-2023), and might represent novel genomospecies (
Figure 1B).
3.1.2. Occurrence of virulence genes might restrict application of B. cereus s.l. isolates
Functional KEGG analysis revealed presence of genes possibly involved in human disease in the genomes of all plant-associated
B. cereus s.l. isolates (
Figure 1C).
Within the
B. cereus group, occurrence of virulence factors, which are closely linked to disease symptoms [
35,
36], and of entomopathogenic Cry toxins [
37] have been reported. In past, these elements have been widely applied to assign
B. anthracis,
B. cereus and
B. thuringiensis.
Since the genome sequence of the isolate CD3-1a formed a cluster together with the
B. anthracis type strain ATCC 14578 (
Figure 1), we checked the CD3-1a draft genome for the presence of sequences of the characteristic anthrax toxin plasmids pXO1 and pXO2. No sequences similar to the genes encoding the Rep proteins RepX (pXO1) and RepS (pXO2) were detected in CD3-1a. Moreover, no sequences exhibiting significant similarity with the anthrax genes of pXO1 (
cya,
pagA,
lef) and pXO2 (
capABCDE) were found in CD3-1a, and in the other plant-associated
B. cereus s.l. isolates, excluding their taxonomic delineation as representative of the human-pathogenic
B. anthracis species (
Suppl. Table S3).
To distinguish “true”
B. anthracis isolates from non-anthrax-causing representatives of the
B. cereus group, detecting of the dhp chromosomal marker sequences, which are indicating the presence of
B. anthracis specific prophages was proposed [
17]. None of the
B. anthracis specific dhp fragments could be detected in the CD3-1a genome. In addition, real-time PCR amplification of the protective antigen
pagA gene, the capsule
capB gene and the dhp61.183 gene (one of the prophage regions) using CD3-1a DNA was not achieved. A delayed amplification signal was oserved for the for the
B. anthracis specific
rpoB gene, which is known for non-anthrax strains of the
B. cereus group [
38]. By contrast to
B. anthracis, but similar to the other isolates, CD3-1a was hemolytic when cultivated on Columbia blood agar or blood trimethoprim agar, and the genes encoding the haemolysin BL (HBL) toxin were present on the chromosome (
Suppl. Table S3). The isolate also displayed phospholipase C and lecithinase activity like typical strains of the
B. cereus group.
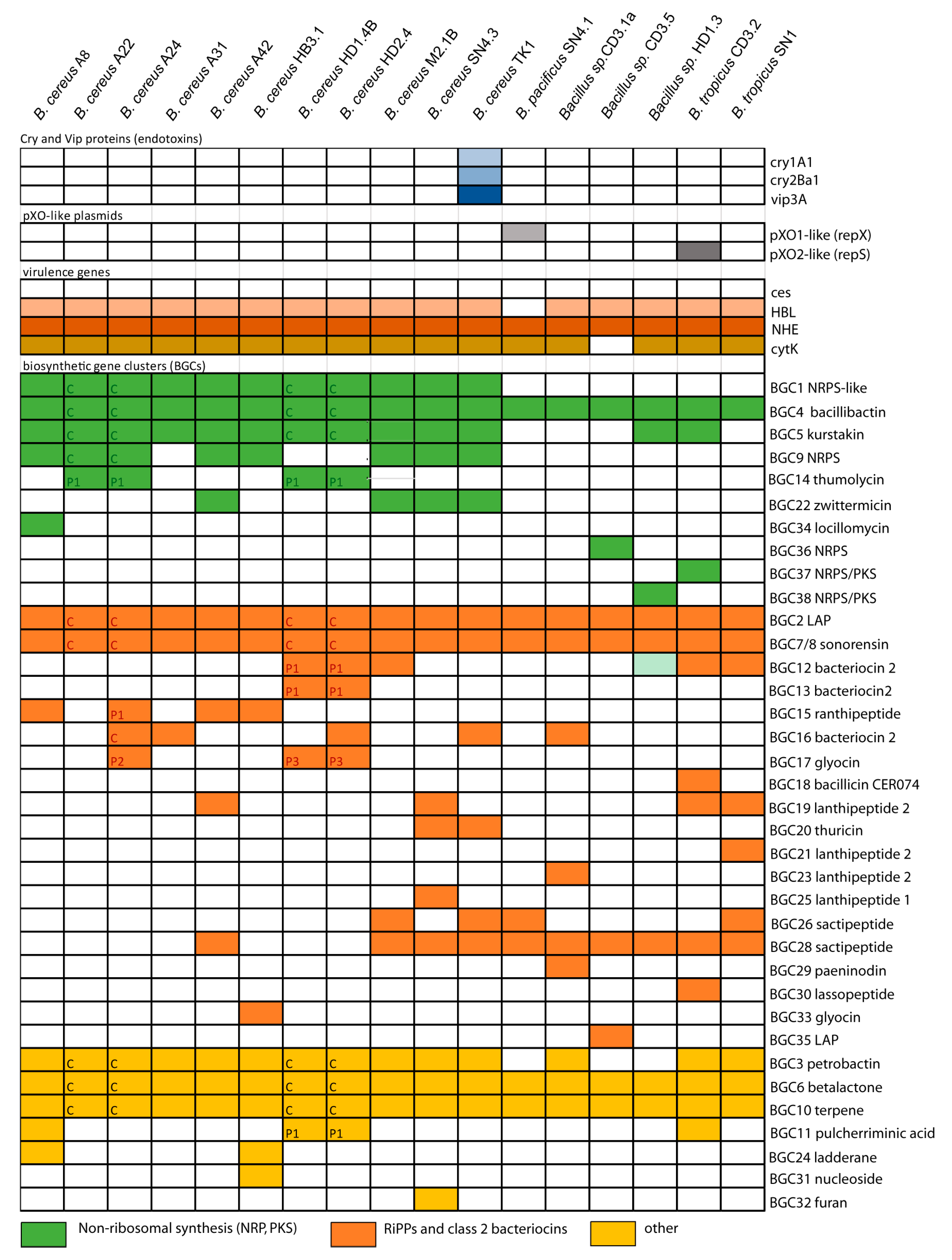
Interestingly, the isolate
B. pacificus SN4.1 harbored a pXO1-like
repX gene, and the isolate
B. tropicus CD3.2 harbored a sequence resembling to the pXO2-like
repS gene, in their draft genomes (
Figure 2,
Suppl. Table S3) suggesting that the
rep genes characteristic for the pXO plasmids can occur in other members of the
B. cereus s.l. species complex. This is in line with previous findings of Liu et al. [
16].
Next, we proved the
B. cereus s.l. isolates for the presence of other virulence genes involved in production of toxins responsible for foodborne diseases of human beings. Cereulide, the causative agent of the emetic syndrome [
39], is known to be non-ribosomally synthesized by giant peptide synthetases encoded by the
ces gene cluster. None of our isolates harbored this gene cluster (
Figure 2), suggesting that the plant-associated isolates did not represent emetic
B. cereus strains.
By contrast, the HBL/NHE enterotoxin operons encoding the non-hemolytic enterotoxin A (NHE), and the haemolysin component BL (HBL) [
40], occurred in nearly all isolates with one exception.
B. pacificus SN4.1 harbored the genes responsible for synthesis of the NHE enterotoxin, but not the genes for haemolysin synthesis (
Suppl. Table S3). HBL and NHE are the causative agents of the diarrhoeal syndrome in human beings, which is caused by ingestion of vegetative cells and spores that produce enterotoxins in the small intestine [
41].
Due to these findings, we can not exclude that the plant-associated B. cereus s.l. isolates can cause the diarrhoeal syndrome in human beings. Application of plant-associated B. cereus s.l. strains in crop protection agents represents a possible risk for public health and should be considered with care.
3.1.3. Genes encoding insecticidal proteins in B. cereus subsp. bombysepticus TK1
Furthermore, we proved the occurrence of
cry genes encoding entomocidal proteins (δ-endotoxins). Sequences completely matching with the crystal proteins Cry1A1 and Cry2Ba1 were detected in
B. cereus subsp.
bombysepticus TK1 (
Figure 2). Synthesis of δ-endotoxins is considered as a typical feature of
B. thuringiensis [
42] However, in line with our results, Liu et al. [
16] found, that the ability to synthesize δ-endotoxins is widespreaded in different members of the
B. cereus species complex. Thus, the presence or absence of
cry genes cannot be used to discriminate between the
B. cereus and
B. thuringiensis species.
In addition to Cry proteins, TK1 harbored a gene for synthesis of the vegetative insecticidal protein, Vip3. Vip proteins are referred as second-generation insecticidal proteins. Vip3 proteins have insecticidal activity against Lepidopteran pests [
43], and can be used for the management of various detrimental pests.
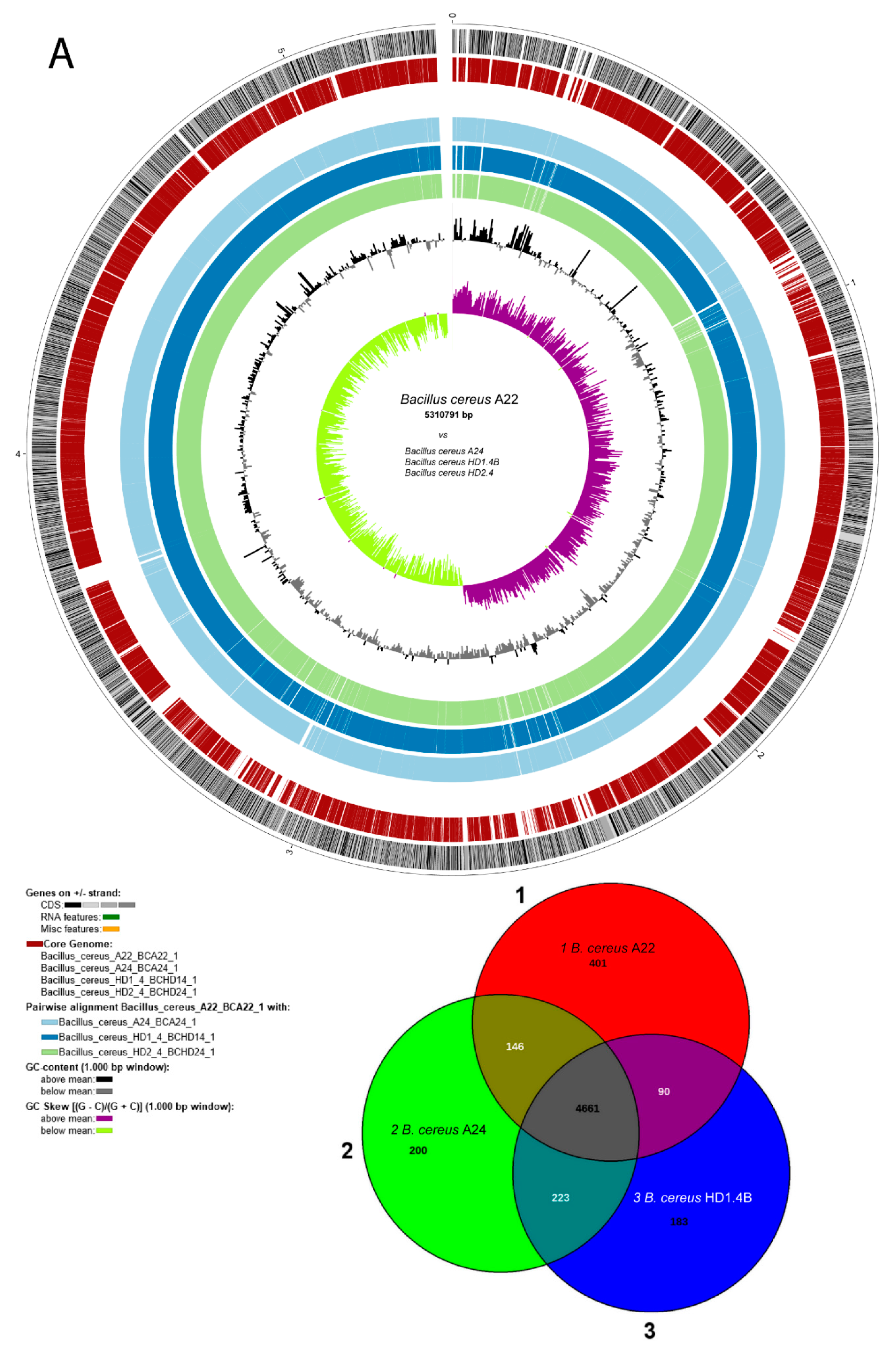
3.1.4. Plasmid-encoded virulence genes and biosynthetic gene clusters in B. cereus isolates A22, A24, HD1.4B and HD2.4
A first survey of the draft genome sequences for the presence of gene clusters encoding lipopeptides revealed that
B. cereus ssp. bombysepticus A22
, and the
B. cereus ssp. cereus strains A24
, HD1.4B
, and HD2.4 harbored gene clusters similar to the thumolycin gene cluster, previously detected in
B. thuringiensis BMB171 [
44]. This finding prompted us to sequence completely the four strains using the nanopore sequencing technology (see Materials and Methods). The complete genomes consisted of one single chromosomal DNA molecule and extrachromosomal DNA elements, bearing the features of plasmid DNA (
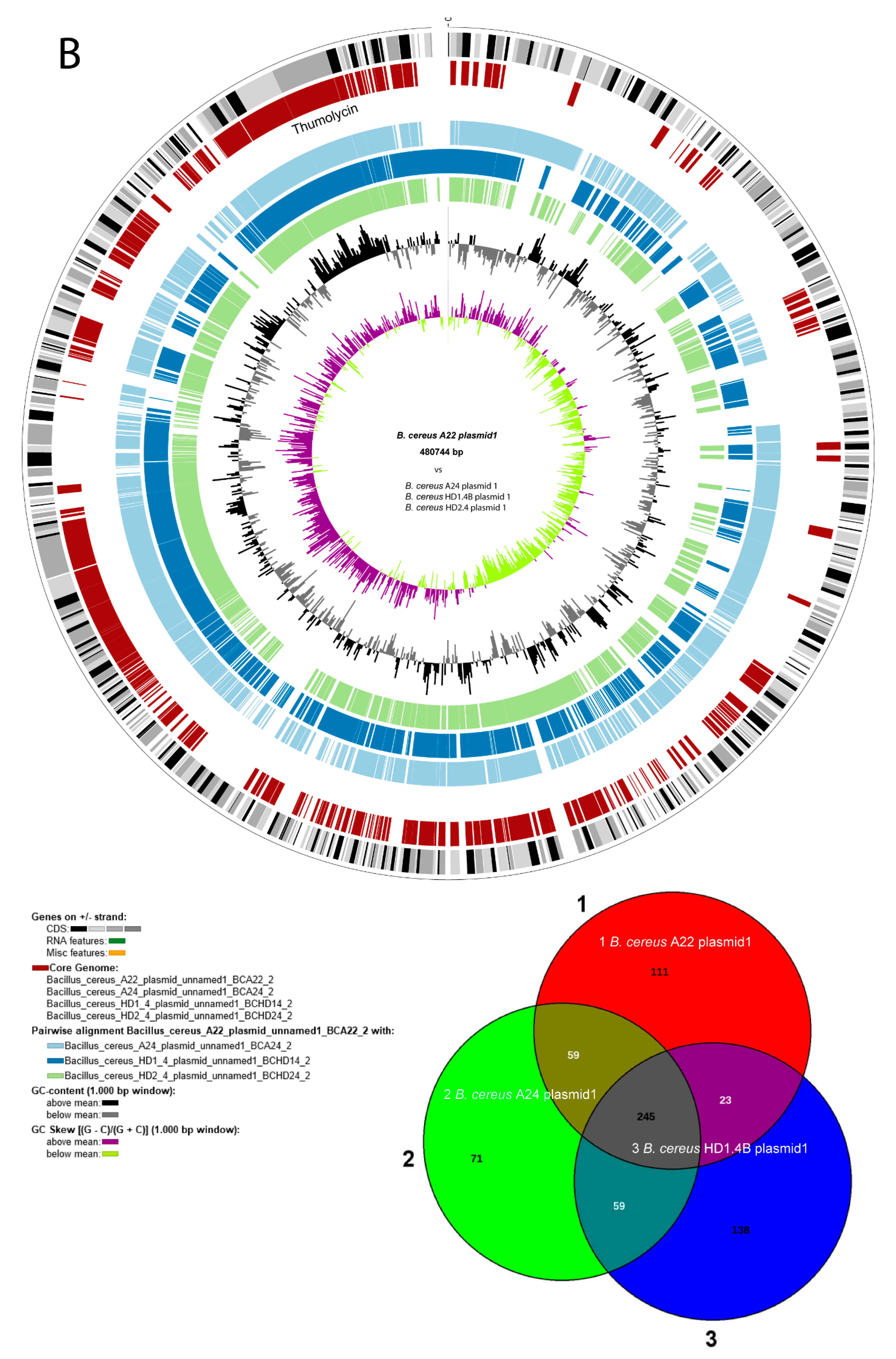
Figure 3). The chromosomes of all four isolates contained more than 5,000 kb. The large P1 plasmids of A22 and A24 contained 480,744 bps, and 471,669 bps, respectively
. The smaller P2 plasmid of A22 contained 93,778 bps. Small plasmids, not exceeding 12 kb were detected in A24 (P2), HD1.4B (P3), and HD2.4 (P3). The DNA elements found in HD1.4B and HD2.4 were nearly identical suggesting that both isolates represented clones of the same strain. Both, harbored one chromosome and three plasmids of nearly identical size and gene content (
Suppl. Table S4). The presence of plasmid-specific Rep proteins in all extrachromosomal elements was corroborated by using the SEED and the RAST annotation system [
45] (
Suppl. Figure S4).
Comparing B. cereus ssp. cereus A22 with the representatives of the B. cereus bombysepticus clade (B. bombysepticus Wang, FORC087, ATCC10876, A42, M2.1B, SN4.3, and TK1) yielded 113 singletons including two catalases, 5-methylcytosine-specificic restriction enzyme A and other restriction enzymes. Comparing B. cereus ssp. bombysepticus A24 with the representatives of the B. cereus cereus clade (ATCC14579, A22, HD1.4B, HD2.4, A8, HB3.1, and A31) revealed 367 singletons including proteins involved in conjugative transfer, the AlwI family type II restriction endonuclease, and urease subunits and associated proteins.
The potential virulence factor, phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC), a characteristic marker of the
B. cereus group [
40], was encoded by the large P1 plasmids of A22, A24, HD1.4B and HD2.4. PI-PLCs catalyze the cleavage of the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol (PI), or its phosphorylated derivatives, to produce diacylglycerol (DAG) and the water-soluble head group, phosphorylated
myo-inositol [
46].
Annotation of the chromosomal elements detected in A22, A24, HD1.4B and HD2.4 is summarized in
Suppl. Table S4. Surprisingly, the plasmid P1 sequences from HD1.4B, and HD2.4 harbored three genes with similarity to the NHE/ HBL enterotoxin operons. These genes are known to be located on the chromosome. In fact, the chromosomes of the four isolates including HB1.4, and HD2.4B harbored the complete NHE/HBL gene set (
Suppl. Figure S5).
Many metabolic features were found encoded by the large P1 plasmids harboring more than 500 coding genes. Besides the thumolycin gene cluster, present in the large plasmids of all four isolates, two other BGCs encoding pulcheriminic acid, and the bacteriocin cerein 7B precursor were found located in the large plasmids of HD1.4B and HD2.4.
Interestingly, in addition to the chromosomal encoded type 1 restriction modification systems (RM) [
47], type 1 RM gene clusters encoding the subunits M, S, and R were present in the 481 kb plasmid P1 of A24, and in the 94 kb plasmid P2 of A22. A fragmentary type III RM system consisting of RMIII helicase and the methylation subunit flanked by UvrD helicase and a transposase was detected onto the P1 plasmid of HD2.4
A gene cluster detected in plasmid P1 of the
B. cereus strains was similar to the anthrose BGC, previously described in
B. anthracis Sterne [
48]. The anthrose containing oligosaccharide attached at the surface of the exosporium, might contributes to enhanced survival rates under multiple stress conditions. Our results are in line with previous results of Dong et al. [
49] demonstrating that the presence of anthrose-containing exosporia is not restricted to
B. anthracis.
The complete operon for
myo-inositol catabolism was detected in the large plasmids of all the four
B. cereus isolates. The gene cluster was found harboring the genes encoding the same enzymes as the
myo-inositol operon previously detected in the chromosome of
B. subtilis [
50]. Presence of repeats and mobile elements in the flanking regions suggested that the operon might be acquired by horizontal gene transfer (
Suppl. Figure S6).
3.2. Genome mining for biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) encoding secondary metabolites
Antimicrobial compounds belong to structurally diverse groups of molecules, such as nonribosomal peptides (NRP) and polyketides (PK), ribosomal synthesized and posttranslationally modified (RiPPs) and unmodified (class 2 bacteriocins) peptides [51, 52]. Genome mining using the software pipelines of antiSMASH6.0 [
20], PKS/NRPS Analysis [
21], and BAGEL4 [
22] was performed with the genomes of all the Vietnamese isolates of the
B. cereus sensu lato complex. The results were subsequently compared against the MIBiG database [
53] in order to distinguish between characterized and uncharacterized BGCs. Our survey yielded a total of 209 BGCs representing 36 different gene clusters involved in biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. Only few, such as the siderophores petrobactin (BGC0000942) and bacillibactin (BGC0000309), zwittermicin (BGC0001059), locillomycin (BGC0001005) and pulcherrimic acid (BGC0002103) were found listed in the MIBiG data bank. Two BGCs, kurstakin, and thumolycin, although not listed in the MIBiG repository, could be identified due to their similarity to genes already deposited in the NCBI data bank. Most of the BGCs exhibited no or only low similarity to known BGCs present in the MIBiG data bank. Five BGCs encoding bacillibactin, RiPPs (2), betalactone (1), and terpene (1) were found conserved in all
B. cereus s.l. isolates (
Figure 2). An overview about the BGC species detected in the plant-associated
B. cereus isolates is presented in
Suppl. Table S5.
3.2.1. Non-ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides (NRP) and polyketides (PK)
NRPs are secondary metabolites, which are synthesized through giant multi-modular peptide synthetases [
54]. The complete
krs gene cluster (BGC5) encoding the cyclic lipoheptapeptide kurstakin [
55] was found widely distributed, and occurred in the genomes of most
B. cereus sensu lato isolates, except
B. pacificus SN4.1,
B. tropicus SN1, and
Bacillus sp. CD3-1a and CD3.5. Kurstakin is responsible for biofilm formation [
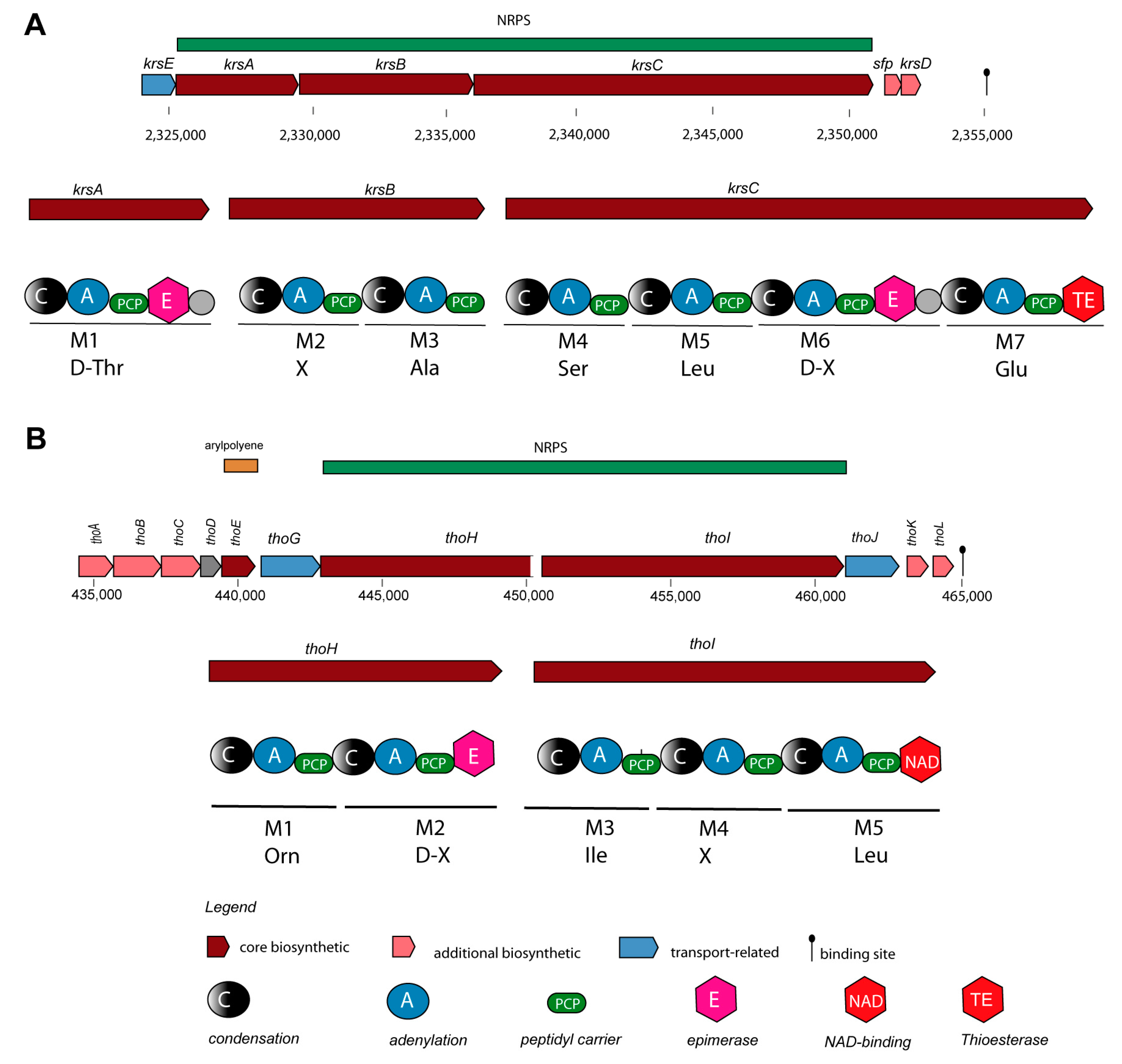
56]. Although, that kurstakin was present in the majority of the investigated isolates (13/17 strains), the kurstakin gene cluster, containing the genes
krsE, krsA, krsB, krsC, sfp, and
krsD (
Figure 4A), is not listed in the MIBiG data bank.
The lipopeptide thumolycin, recently detected in
B. thuringiensis BMB171, enabled the bacterium to develop a broad spectrum of antimicrobial and nematocidal activities [
44]. Unfortunately, the structure of the lipopeptide is still not resolved. We detected the thumolycin (
tho) gene cluster (BGC14) in plasmids of the
B. cereus strains A22, A24, HD1.4B, and HD2.4. The genes of the
tho cluster were spanning around 30 kb. Two multimodular non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (ThoH and ThoI) synthesized a putative pentapeptide Orn-D-X-Leu/Ile-XS-Leu (
Figure 4B). The
thoC,
thoD, and
thoE encoded proteins are probably involved in synthesis of the fatty acid chain [
44].
Fragments of the locillomycin gene cluster [
57] (BGC34) were detected in
B. cereus A8 (
Suppl. Table S5). To the best of our knowledge, until now the locillomycin gene cluster has been detected only in members of the
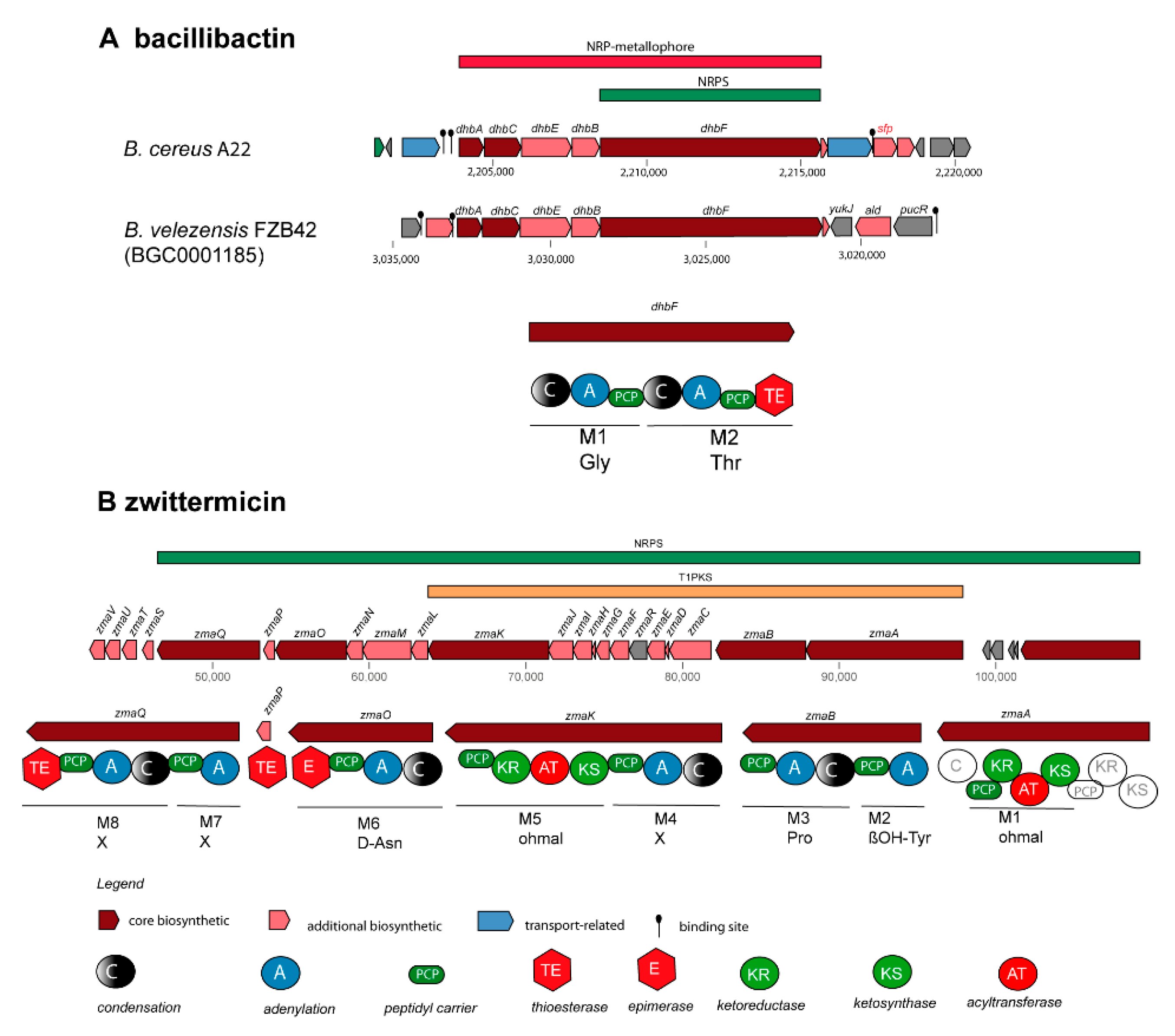
B.subtilis species complex. The gene cluster for synthesis of the catecholic iron siderophore bacillibactin, 2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl-Gly-Thr trimeric ester, has been previously reported in the genomes of
B. subtilis [
58] (BGC0000309), and
B. velezensis FZB42 [
59] (BGC0001185). Its non-ribosomal synthesis was found dependent on Sfp (phosphopantetheinyl transferase, [
60]. BGCs with similar structure as in BGC0000309, and BGC0001185 were detected in all 17
B. cereus sensu lato isolates investigated in this study. Whilst the core structure of the bacillibactin transcription unit was well conserved, a
sfp gene in the flanking region was identified as unique feature for the
B. cereus bacillibactin operon (
Figure 5A). This is in contrast to the operon structure in the
B. subtilis species complex, where the
sfp gene is located fare remote, downstream flanking the surfactin operon [
60].
The gene cluster for synthesis of the aminopolyol antibiotic zwittermicin was detected in four
B. cereus genomes. The highly polar zwittermicin A (ZmA) possesses antiprotist and antibacterial activities, and consists of numerous ethanolamine and glycolyl moieties flanked by N-terminal D-serine, and an unusual amide generated from ß-ureidoalanine. The aminopolyol structure of the final product results from different processing events of the NRPS/PK hybrid precursor molecule (
Figure 5B) in which a multitude of gene products of the
zma gene cluster is involved [
61].
In addition, numerous uncharacterized NRPs, PKS, and NRP/PKS hybrids were found (
Suppl. Tables S5 and S6). A unique gene in
B. tropicus CD3.2, located downstream of an uncharacterized NRP+PK cluster (BGC37,
Suppl. Figure S7), encoded a putative necrose inducing protein (NPP1 family) [
62].
3.2.2. Gene clusters representing RiPPs, and bacteriocins
By contrast to polyketides and peptides which are synthesized independent from ribosomes, numerous peptides with antimicrobial activity (bacteriocins) are synthesized by a ribosome-dependent mechanism. According to Zhao and Kuipers [
51] several groups of ribosomally synthesized peptides (RPs) are distinguished:
Class I: post-translationally modified peptides smaller than 10 kDa
Class II: small (<10 Da), unmodified peptides with or without leader sequence.
Class III: peptides larger than 10 kDa.
RiPPs, such as lanthipeptides (class1 and class2), linear azol(in)e-containing peptides (LAPs), lassopeptides, sactipeptides, thiopeptides, and representatives of the class II unmodified bacteriocins, such as UviB peptides (holin-like proteins), were detected in the
B. cereus group isolates applying the antiSMASH and BAGEL4 toolkits (
Suppl. Figures S8 and S9). Many RiPP biosynthetic proteins recognize and bind their cognate precursor peptide through a domain known as RiPP recognition element (RRE) [
63]. Detection of RRE domains by using antiSMASH supported genome mining was helpful in identifying BGCs involved in synthesis of RiPPs, which did not contain known core peptide encoding sequences [
64].
A total of 19 different BGCs encoding RiPPs and unmodified class 2 bacteriocins were detected. Only six encoded precursor peptides with apparent similarity to known RiPPs: BGC20 (Thuricin), BGC17 and BGC18 (sublancin/CER074), BGC29 (paeninodin), BGC26: thurincin H) (
Suppl. Tables S5 and S7).
Antimicrobial lanthipeptides (lantibiotics) are post-translationally highly modified, and contain the thioether amino acid lanthionine as well as several other modified amino acids [
65]. LanA precursor peptides consist of an N-terminal leader peptide and a C-terminal core region. The first step in posttranslational modification is the activation and elimination of water from the Ser and Thr residues forming dehydroalanine (DhA) and dehydrobutyrine (DhB), respectively. Then, ß-thioether cross-links are generated between DhA, DhB and the Cys residues. The modifying enzymes involved in formation of the thioether link in class AI lanthipeptides are the dehydratase LanB and the cyclase LanC. Modification of A2 lanthipeptides is accomplished by LanM, containing the dehydratase and the cyclase domain in one protein. Class A3 and A4 lanthipeptides are modified by LanKC and LanL, respectively [
66]. We detected a BGC encoding a representative of the A1 lanthipeptides in
B. cereus SN4.3 (BGC25). Four genes encoding precursor peptides similar to paenibacillin and subtilomycin were identified within BGC25. BGCs encoding A2 lantibiotics similar to plantaricin (BGC19), thuricin (BGC20), lichenicidin (BGC21), salivaricin (BGC23), and paenibacillin (BGC25) occurred in several
B. cereus isolates (
Suppl. Tables S5 and S7).
Gene clusters encoding LAPS were found widely distributed in
B. cereus and related species. LAPS are characterized by posttranslational modification of the precursor peptide yielding thiazol(in)e and (methyl)oxazol(in)e heterocycles. Modifying enzymes are the FMN-dependent dehydrogenase (SagB), and cyclodehdratase (SagC, YcaO) [
67]. BGC2 (Suppl.
Table S7) was identified as being member of the TOMM class (thiazole/oxazole-modified microcins) characterized by a gene cluster consisting of a cyclodehydratase gene, and associated genes encoding dehydrogenase and a maturation protein. The core region of the TOMM precursor leader peptide contained a region enriched with Cys residues (BGC7/8), which is typically for the hetero-cycloanthracin/sonorensin family [
68].
A glyocin encoding gene cluster (BGC17) was detected in plasmid P2 of
B. cereus A24. Glyocins are defined as post-translationally glycosylated RiPPs with antimicrobial activity [
69]. BGC17 resembled sublancin, which is an S-linked glycopeptide coding a SunS family peptide S-glcosyltransferase, and a bacillicin CER074 peptide (BGC0001863) containing a glucose attached to a cysteine residue [
70]. A second gene cluster (BGC33) harboring genes encoding a glycosyltransferase and a putative 75 aa precursor peptide was detected in
B. cereus HB3.1 (
Suppl. Table S5).
Lassopeptides are characterized by an N-terminal macrolactam ring threaded by the C-terminal tail. A cysteine protease B, and a lactam synthetase C are necessary for posttranslational modification of the precursor peptide [
71]. Two gene clusters, probably encoding lassopeptides, were identified. BGC29 harbored, besides a structural gene (
paeA) for synthesis of paeninodin lasso peptide [
72], the genes for synthesis of the essential components of posttranslational modification,
paeB1 (PQQD family protein),
paeB2 (cysteine protease), and
paeC (lactam ring closing cyclase). Four copies of the lasso precursor gene, and split B1 and B2 genes were detected in BGC30 (
Suppl. Table S7).
Two gene clusters (BGC26, BGC28), encoding the radical S-adenosylmethionine (rSAM) enzyme, necessary for posttranslational modification of sactipeptides, occurred in representatives of the
B. cereus group. A well-known representative of sactipeptides is subtilosin A (SboA) synthesized by
Bacillus subtilis. The rSAM enzyme (AlbA) catalyzes the linkage of a thiol with an α-carbon of a functional amino acid residue [
73]. BGC26 harbored genes involved in synthesis and rSAM-dependent modification of a thurincin H-like precursor peptide. A gene encoding a protein containing an N-terminal radical SAM domain (pfam04055) and a C-terminal pfam08756 domain with a CxCxxxxC motif (BmbF) was detected in BGC28. By contrast to
B. subtilis the YfkA and YfkB regions originally reported as separate ORFs in
B. subtilis were found fused in the
B. cereus gene cluster (
Suppl. Table S7).
Like the structurally related sactipeptides, the thioether linkage in ranthipeptides is generated via a radical-initiated mechanism. However, ranthipeptides do not contain α-carbon links, and were recently designated as non-α thioether peptides [
74]. The ranthipeptide gene cluster (BGC15) detected in four
B. cereus isolates harbored a gene encoding the rSAM protein belonging to the MoaA/NifB/PqqE/SkfB superfamily (
Suppl. Table S7).
A gene cluster (BGC7/8), involved in synthesis and modification of an 82 aa precursor thiopeptide belonging to the heterocycloanthracin/sonorensin family [
75], occurred in all
B. cereus group isolates. Its C-terminal region contained an extended repeat region with Cys at every third residue (
Suppl. Table S7).
Two different subclasses of bacteriocin class II peptides were detected: The holin-like BhlA encoding genes (BGC12 and BGC16), and a cluster (BGC13) harboring a gene encoding a cerein-like prepeptide belonging to the Blp family. Similar as in lanthipeptides, the Blp family prepeptides are characterized by a conserved GlyGly processing site between the N-terminal leader and the C-terminal core peptide region [
76]. The BhlA holin of
Bacillus pumilus causes bacterial death by cell membrane disruption [
77]. Besides the genes encoding leaderless BhlA peptides, the holin gene clusters harbored genes encoding muramidases (GH25 glycosyl hydrolases) that hydrolyze the peptidoglycan cell wall (
Suppl. Table S7, Suppl. Figures S8 and S9)).
3.2.3. Other antimicrobial secondary metabolites
Seven BGCs encoding other antimicrobial secondary metabolites were identified in the plant-associated
B. cereus isolates (
Suppl. Figure S7, Suppl. Table S8). Three of them, BGC3 (=BGC0000942, petrobactin), BGC11 (=BGCBGC0002103, pulcherriminic acid), and BGC32 (=BGC0000914, furan) were similar to known BGCs deposited in the MiBIG data bank.
The
asbABCDEF gene cluster is responsible for biosynthesis of petrobactin, a catecholate siderophore that functions in both, iron acquisition and virulence [
78]. We detected the petrobactin gene cluster in the genomes of 14 isolates. Only
B. pacificus SN4-1 and HD1-3, and
Bacillus sp. CD3.5 did not harbor the BGC0000942 cluster, which is common in most representatives of the
B. cereus group [
79].
Pulcherriminic acid is a cyclic dipeptide, able to chelate Fe
3+ [
80]. Due to its high affinity to Fe ions,
Bacillus strains producing pulcherriminic acid compete successfully with other microorganisms in low iron environments. A gene cluster similar to the pulcherriminic acid synthesis cluster in
B. subtilis (BGC0000914) was detected in the
B. cereus HD1.4B and HD2.4 plasmid sequences (
Suppl. Table S4), and in the draft genomes of
B. cereus A8 and
B. tropicus CD3-2.
Several genes of BGC32, possibly involved in synthesis of a furan-like metabolite, showed striking similarity to the methylenomycin A gene cluster in
Streptomyces coelicolor [
81].
Four BGCs did not show similarity to any characterized biosynthetic gene clusters. BGC6 possibly encoded a ß-lactone harbored genes with similarity to genes flanking the plipastatin BGC in B. subtilis. BGC24 contained several genes of the carbohydrate metabolism probably involved in synthesis of ladderane. BGC10 and BGC31 encoded enzymes for synthesis of terpene and nucleoside metabolites, respectively.
3.3. Detection of bioactive peptides by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry
The genome mining data summarized in
Figure 2 indicate the presence of BGCs on the genomic level. However, the real biosynthetic capacity of the investigated isolates can only be verified by isolation and structural analysis of the compounds actually produced. In
Figure 6 we demonstrate the production of the non-ribosomally formed secondary metabolites of strain A22 as a representative for
B. cereus detected by MALDI-TOF MS. As an overview,
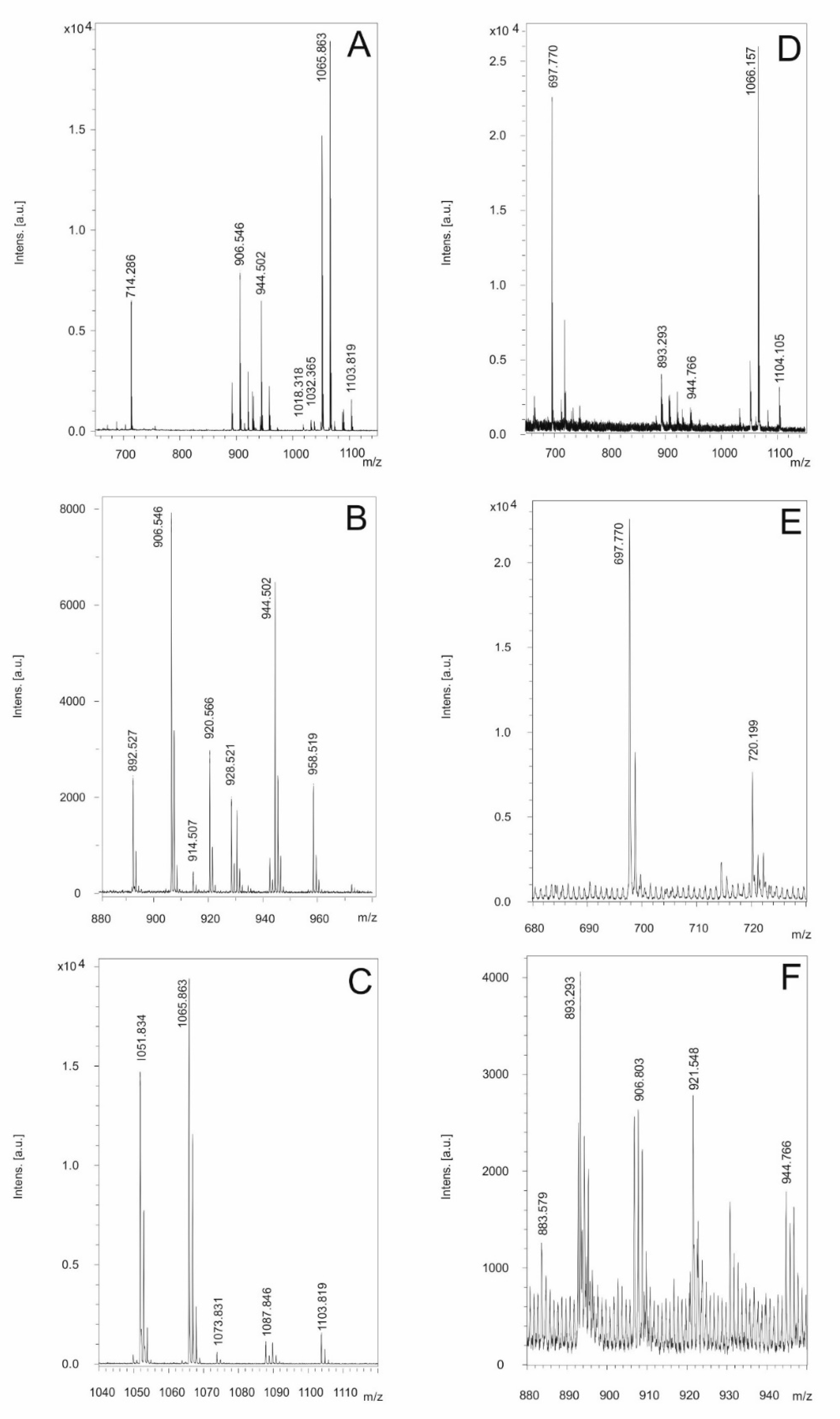
Figure 6A–C shows mass spectra for the compounds found in a surface extract of A22 taken from cell materials grown on agar plates in the Landy medium for 48 h. Two prominent products were observed.
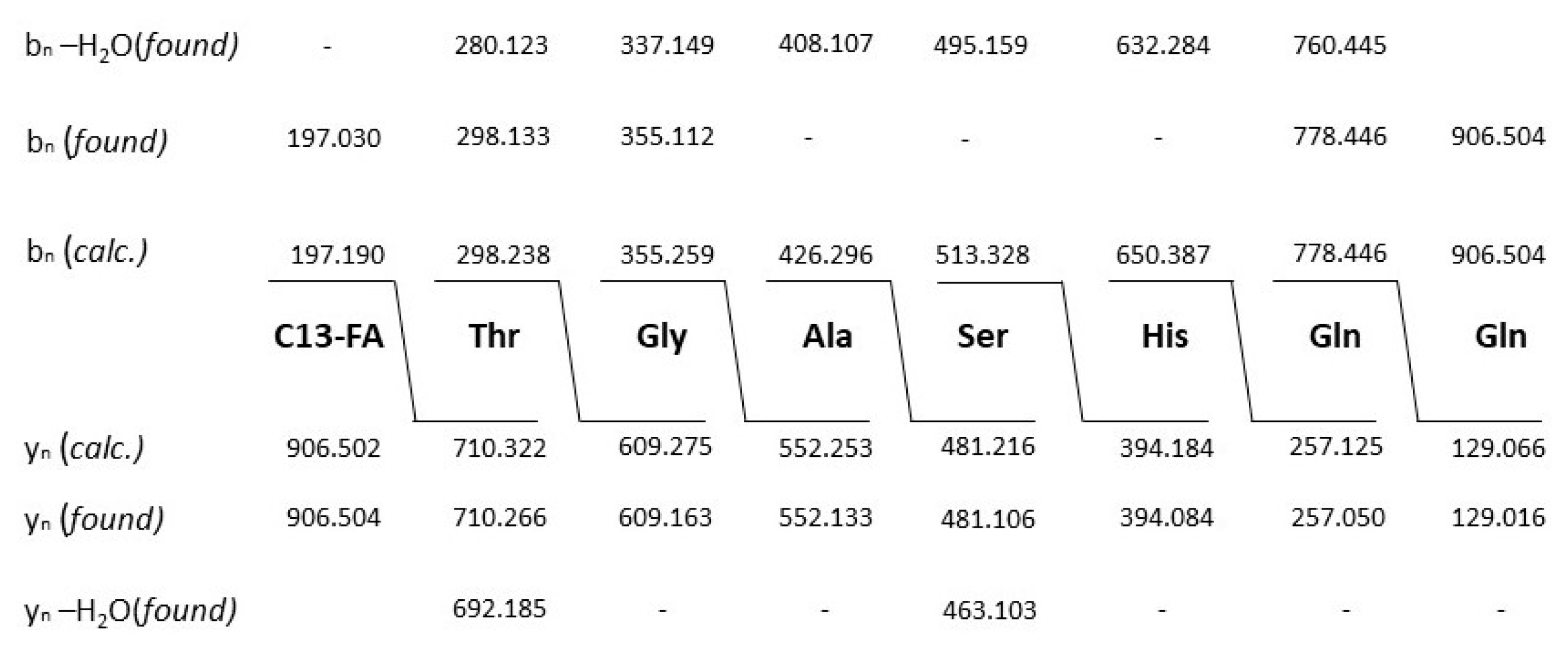
Figure 5B shows the mass peaks for two kurstakins with chain lengths of their fatty acid component of 12 and 13 carbon atoms, respectively. The following mass data were found: C12-kurstakins: [M + H,Na,K]
+ = 892,5/914,5/930.5 Da; C13-kurstakins: [M + H,Na,K]
+ = 906.5/928.5/944.5 Da. In addition, yet unknown compounds with mass numbers of 1051.8 and 1065.9 were found which dominate the MALDI-TOF mass spectrum of the surface extract in
Figure 6A. Presumably, there are two isomers which differ by a methylene group (
Figure 6C). This compound cannot be correlated to any of the BGCs of the antiSMASH-profile of strain A22.
Figures 6D–F show mass spectra of the products of A22 released into the culture broth on growth in liquid cultures for 48 in the Landy medium. Here the arylpolyene lipopeptide thumolycin and both siderophores bacillibactin and petrobactin were detected.
Figure 6E exhibits the mass peaks of thumolycin (m/z = 697.8) and petrobactin (m/z = 720.2). A relatively small part of the kurstakins is released into the culture filtrate, while the main part retains attached at the outer surface of A22. In
Figure 6F kurstakin mass peaks (
m/z = 906.8/930.8 and 944.8) overlap with those of the siderophore bacillibactin [M + H,Na,K]+ = 883.6/905.6/921 Da. These results demonstrate that kurstakins were predominantly foun
d attached to the outer surface of B. cereus cells, while thumolycin and both siderophores bacillibacin and petrobactin are released into the culture medium. Similar profiles have been obtained for strains A24, HD1.4B and HD2.4. All other investigated B, cereus isolates did not produce thumolycin.
The structure of both lipopeptide products of strain A22, kurstakin and thumolycin were investigated in detail by LIFT-MALDI-TOF/TOF fragment analysis [
26].
Figure 7 and
Table 1 show the sequence determination of a C13 kurstakin with a parent ion [M + H}+ = 906.504 Da derived from product ions obtained by LIFT-MALDI-TOF/TOF fragment ion spectra. In
Table 1 the structure of this compound is modelled from nearest neighbour-relationships using di-, tri- and tetrapeptide fragments.
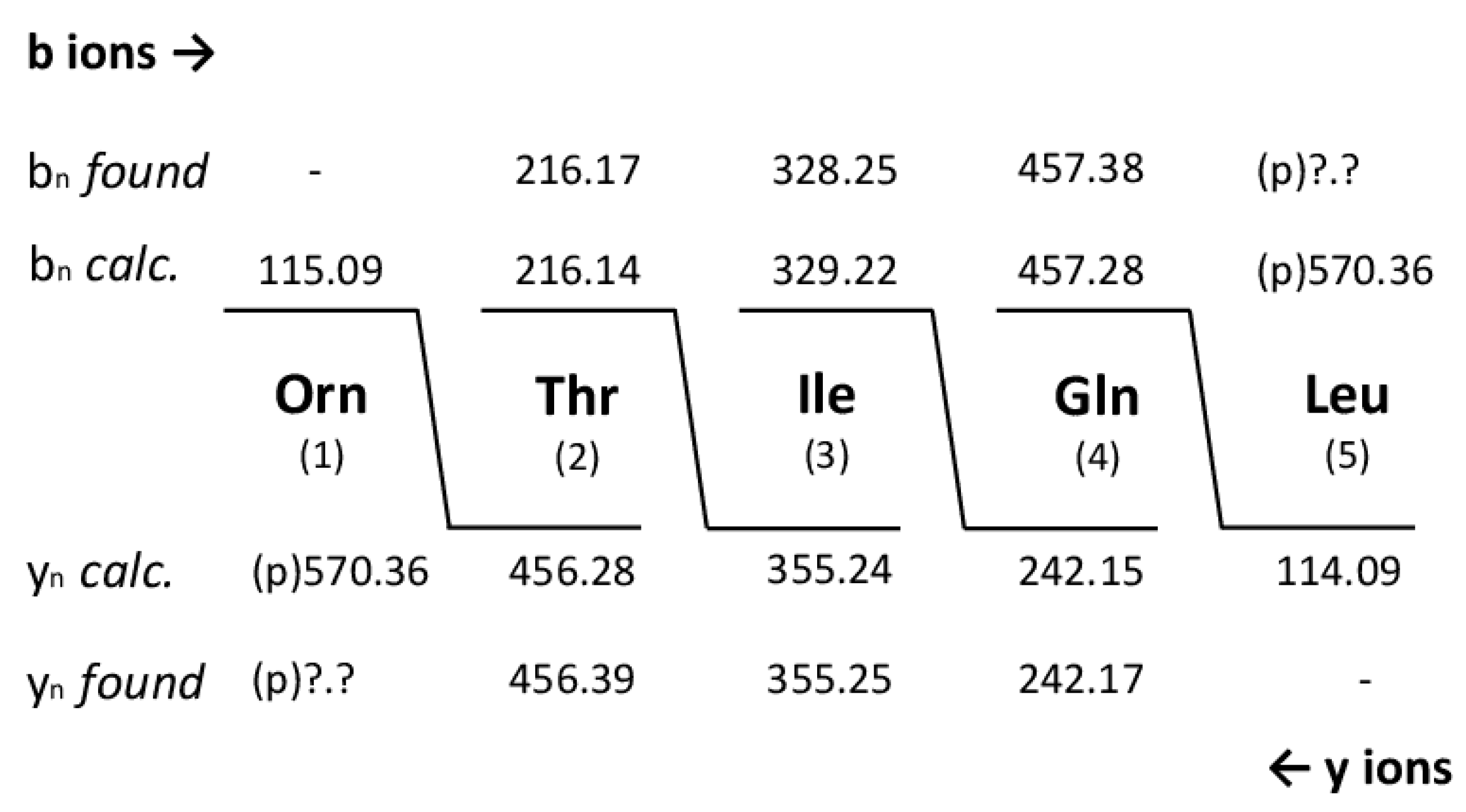
With the same technique we investigated thumolycin which is a combination of a pentapeptide attached to a yet unknown arylpolyene lipidic residue. By LIFT-MALDI-TOF/TOF fragment analysis we obtained the complete sequence of the pentapeptide part for the first time which is compatible with the initial results from Zheng et al. [
44], and the module organization of the corresponding BGC derived from antiSMASH 6.0 genome mining. The structure of this pentapeptide is shown in
Figure 8.
In summary, by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry we have detected all compounds produced by B. cereus strains non-ribosomally. Investigation of the RiPPs, such as lanthipeptides, sactipeptides and bacteriocins are in preparation.
3.4. B. cereus s. l. strains suppressed plant pathogens and promoted plant growth
3.4.1. Antifungal and nematocidal activity
Our
in vitro bioassays revealed, that only few of the
B. cereus group isolates inhibited efficiently phytopathogenic fungi, and nematodes. Antifungal activity was examined
in vitro using
Fusarium oxysporum known for causing fusarium wilt disease [
82], and
Phytophthora palmivora, one of the most detrimental plant pathogens in Vietnam [
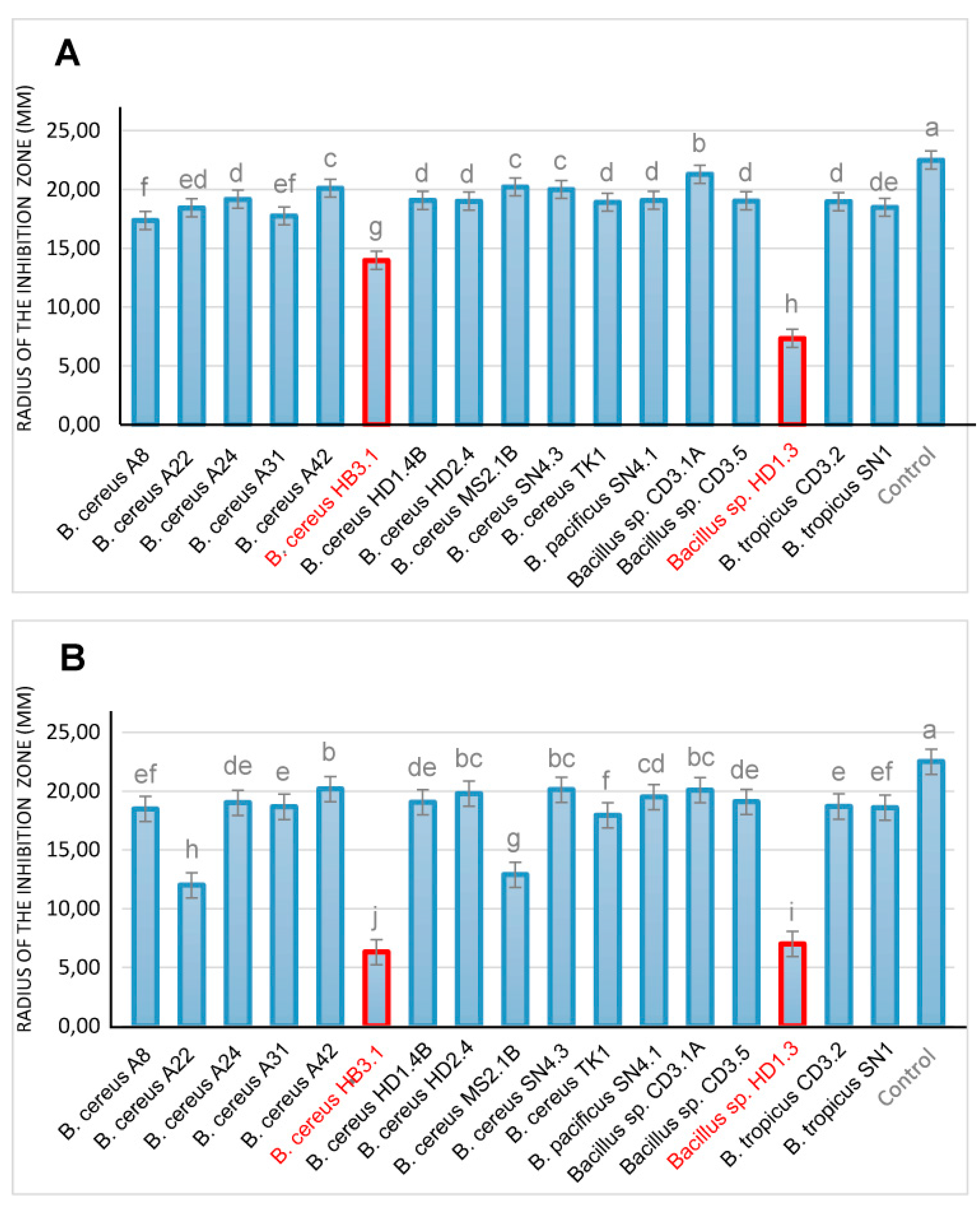
83]. Whilst most of the isolates did not significantly suppress growth of the pathogenic fungi, strong antifungal activity was exerted by
B. cereus HB3.1 and in
Bacillus sp. HD.3 (
Figure 9).
Root-knot nematodes, such as
Meloidogyne spp., are one of the most important plant pathogens in tropical and temperate agriculture, and are responsible for significant harvest losses of main Vietnamese crops, such as coffee and black pepper [
84]. In order to analyze antagonistic activity of the
B. cereus isolates, we tested at first their suppressing effect against the model nematode
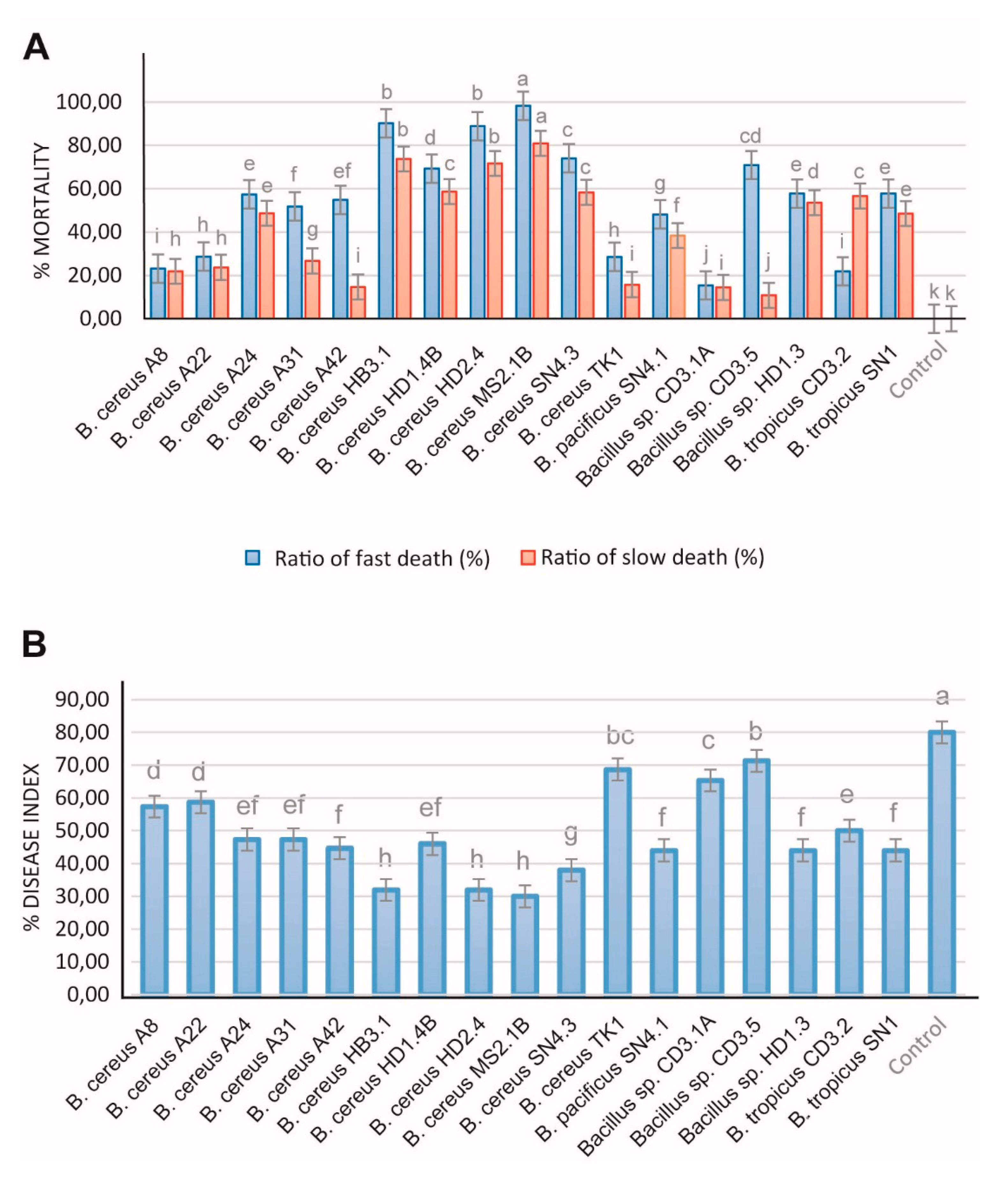
Caenorhabditis elegans. Fast and slow death rates were estimated in a bioassay under laboratory conditions. Most of the investigated
B. cereus isolates were able to kill considerable amounts of the nematodes as revealed in both test systems (
Figure 10A).
In order to examine inhibiting effects against phytopathogenic nematodes more directly, we isolated a representative strain of
Meloidogyne sp. from the galls of infested black pepper plant roots according to the hypochlorite procedure [
85]. The inhibiting effect exerted by the test bacteria on disease development was examined in a greenhouse experiment. Ten weeks after transplanting of the tomato plantlets in soil, formation of root knots was visually registered and used as measure for calculating the disease index according to Bridge and Page [
28]. All
B. cereus isolates were found efficient against nematodes. In presence of HB3.1, HD1.4B, HD2.4, MS2.1B, and SN4.3 the killing rates (estimated as slow and fast killing rates) of
Caenorhabditis elegans exceeded 60% (
Figure 10A). The
Melodoine sp. caused disease index of tomato plants was found reduced by more than 50% after application of
B. cereus HB3.1, HD2.4, MS2.1B, SN4.3 (
Figure 10B). Similar rates were previously detected in representatives of
B. velezensis [
4] and
Brevibacillus spp. [
3].
3.4.2. Plant growth promotion
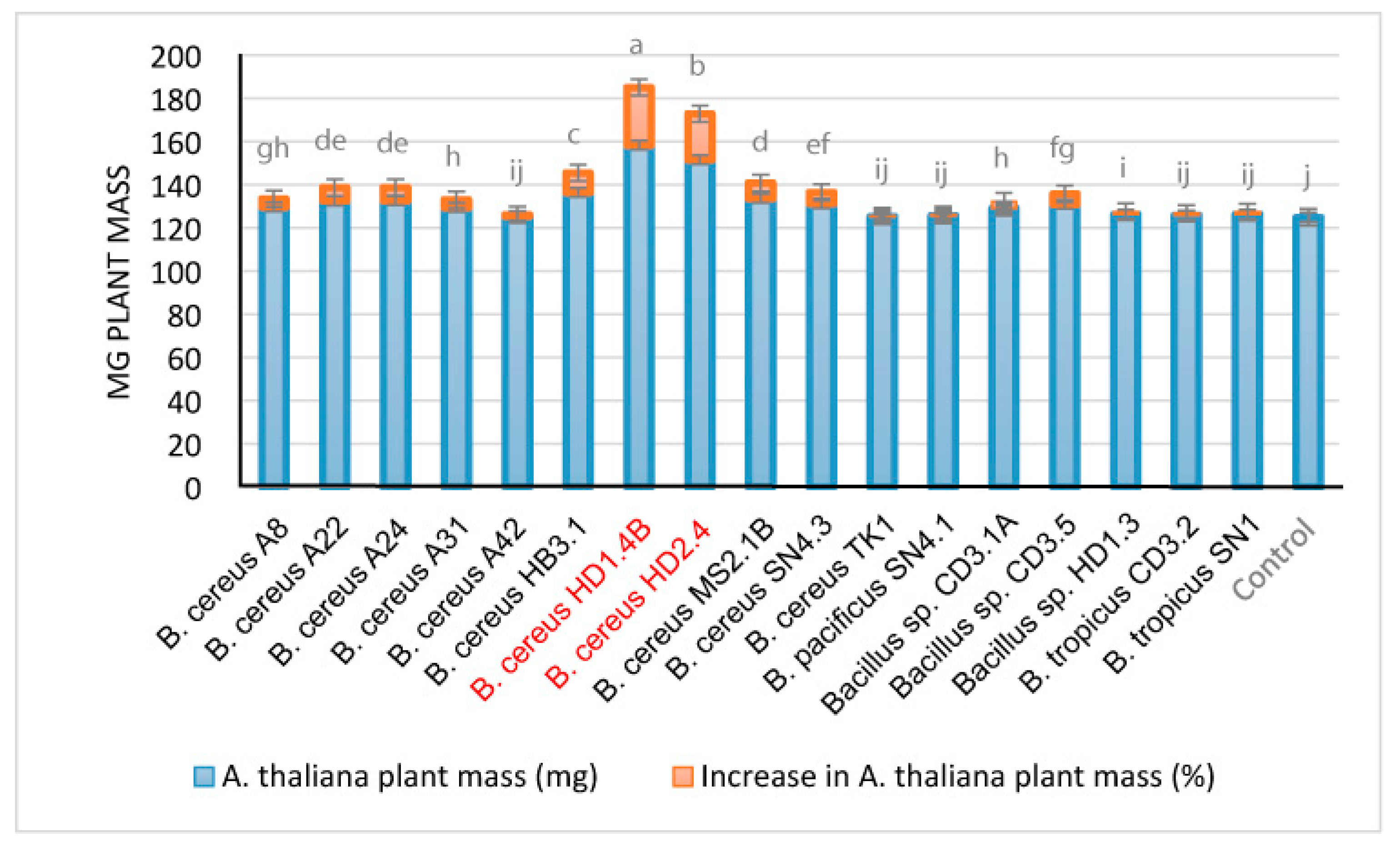
We examined the effect of the Vietnamese
B. cereus isolate
s in the
Arabidopsis thaliana biotest system [
29].
B. cereus HD1.4B and
B. cereus HD2.4 enhanced growth of the
Arabidopsis seedlings by more than 20% (
Figure 11). However, using the same biotest system, the increase rates observed for some plant-associated
Brevibacillus and
B. velezensis strains isolated during the same survey [
2] were higher and estimated to be in the range of 30 to 40 % [
3,
4].
4. Conclusions
In this study we have shown that plant-associated representatives of the B. cereus group were able to suppress important plant pathogens, such as fungi (Fusarium oxysporum), oomycetes (Phytophthora palmivora), and root-knot forming nematodes (Meloidogyne sp.) The plant-growth-promoting activity of some of the isolates could also be demonstrated.
Genome mining revealed that the members of the
B. cereus group are rich in gene clusters probably involved in synthesis of antimicrobial peptides efficient in inhibiting plant pathogens, and triggering plant induced systemic resistence [
86]. A total of 36 different biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs), many of them not listed in the MiBIG data bank, were detected in the 17 isolates obtained from Vietnames crop plants. Mass-spectrometric analysis revealed that in addition to some hitherto unknown compounds, several species of the antimicrobial lipopeptides kurstakin and thumolycin, and the siderophores bacillibactin and petrobactin were expressed in many of the isolates. The arylpolyene lipopeptide thumolycin was reported to possess interesting antimicrobial and nematocidal activities, but its primary structure was not resolved [
44]. Here, the primary structure of the pentapeptide part has been resolved, and the Orn residue was identified as being linked with the yet unknown arylpolyene lipid part.
Besides antimicrobial peptides, biocontrol of plant pathogens can be exerted by δ-endotoxins (parasporal inclusion proteins) traditionally known to be produced by B. thuringiensis, a close relative of B. cereus. cry genes encoding the entomocidal crystal proteins Cry1Aa1 and Cry2Ba1 were detected in the genome of B. cereus ssp. bombysepticus TK1. In the same strain another gene, encoding the vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3, was also detected suggesting that presence of insecticidal proteins is not restricted to B. thuringiensis. The encouraging results described above might cause to develop selected representatives of the B. cereus group as biocontrol agents. However, as known food poisoning organisms and members of risk group 2, the potential of the B. cereus group isolates to produce toxins needed to be carefully examined, before they can be applied in sustainable agriculture.
In this context we showed, that no gene clusters encoding B. anthracis pXO plasmid-related toxins were present in all the B. cereus s.l. genomes investigated here. Furthermore, we could rule out synthesis of the heat-stable cereulide toxin, the causative agent of the emetic syndrome. However, the regular appearance of chromosomally localized virulence genes, encoding the heat-labile enterotoxins HBL and NHE, might restrict the direct application of B. cereus s.l. strains in biological plant protection, although their presence commercial B. thuringiensis strains has not hindered their application as biocontrol agents.
In order to avoid such conflicts, utilization of interesting
B. cereus BGCs, and genes encoding entomocidal proteins can be achieved by their heterologous expression in safe plant-beneficial host strains, which has been already demonstrated with
B. velezensis FZB42 [
87,
88].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Tree inferred with FastMe 2.1.6.1 from GBDP distances calculated from 16S rDNA gene sequences.; Figure S2: GBDP tree (whole genome sequence based) inferred with FastMe 2.1.6.1 from GBDP distances calculated from genome sequences; Figure S3: Heat map of the FastANI values of 128
B. cereus group genomes calculated and drawn by the EDGAR software package; Figure S4: Figure S5: Localization of virulence genes and gene clusters on chromosomes and plasmids of B. cereus isolates. The cytK gene and the NHE/HBL gene clusters were chromosomally localized. The complete set of NHE and HBL genes was chromosomally localized in all four completely sequenced strains (A22, A24, HD1.4B, HD2.4). The P1 plasmid sequences of HD1.4B and HD2.4 harbored genes with similarity to the NHE/HBL enterotoxin family; Figure S6: Plasmid encoded catabolic operons, biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) and restriction/modification systems; Figure S7: BGCs in the
B. cereus group isolates encoding NRPS/PKS and other secondary metabolites; Figure S8: RiPP gene clusters detected by applying the BAGEL4 software (
http://bagel4.molgenrug.nl/) in the genomes of the Vietnamese
Bacillus cereus group genomes; Figure S9: RiPP gene clusters detected by applying the antiSMASH version 6 software in the Vietnamese
Bacillus cereus group genomes. Table S1: Types of entomocidal Cry toxins; Table S2: Species and subspecies delineation of the 17 Vietnamese
B. cereus sensu lato isolates according to their dDDH and Fast ANI values; Table S3: List of the 17
B. cereus group strains used inthis study with detailed annotation; Table S4: Genome annotation of the four completely sequenced B. cereus strains by RASTk; Table S5: Gene clusters (BGCs) of the Vietnamese Bacillus cereus group isolates; Table S6: Gene clusters (BGCs) of the Vietnamese Bacillus cereus group isolates involved in nonribosomal synthesis of antimicrobial pepttides (RiPPs and bacteriocins); Suppl. Table S7: Gene clusters (BGCs) of the Vietnamese Bacillus cereus group isolates involved in ribosomal synthesis of antimicrobial peptides (RiPPs and bacteriocins). Suppl. Table S8: Gene clusters (BGCs) of the Vietnamese Bacillus cereus group isolates involved in synthesis of other secondary metabolites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.B., L.T.T.T., T.S., P.L.; software, J.B.: investigation, J.V., J.J., S.H, L.T.T.T., A.S., P.T.L., L.T.T.P., S.R.K., R.B.; resources, T.S., P.L.; data curation, J.J. S.H., J.V., C.B.; writing, R.B., J.V., L.T.T.T.; review and editing, J.V., S.R.K., T.S., P.L., R.B.; project administration, R.B., T.S., P.L.; funding acquisition, R.B., T.S., P.L., L.T.T.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported through the project ENDOBICA by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) (grant no 031B0582A/031B0582B), the National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED); code no. 106.03-2017.28), and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) in Vietnam (code no. NDT.40.GER/18).
Data Availability Statement
Gene bank accession numbers of complete genome sequences available in the NCBI data bank are listed in section 2 Materials and Methods.
Acknowledgments
Mrs. Silke Becker and Petra Lochau is thanked for excellent technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- BORRISS; Rainer. Use of plant-associated Bacillus strains as biofertilizers and biocontrol agents in agriculture. In Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Growth Responses; Maheshwari, D.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 41–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, L.T.T.; Jähne, J.; Luong, P.T.; Thao, L.T.P.; Chung, L.T.K.; Schneider, A.; Blumenscheit, C.; Lasch, P.; Schweder, T.; Borriss, R. Draft Genome Sequences of 59 Endospore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacteria Associated with Crop Plants Grown in Vietnam. Genome Announc. 2020, 9, e01154-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähne, J.; Le Thi, T.T.; Blumenscheit, C.; Schneider, A.; Pham, T.L.; Le Thi, P.T.; Blom, J.; Vater, J.; Schweder, T.; Lasch, P.; et al. Novel Plant-Associated Brevibacillus and Lysinibacillus Genomospecies Harbor a Rich Biosynthetic Potential of Antimicrobial Compounds. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, L.T.T.; Jähne, J.; Luong, P.T.; Thao, L.T.P.; Nhat, L.M.; Blumenscheit, C.; Schneider, A.; Blom, J.; Chung, L.T.K.; Minh, P.L.A.; et al. Two plant-associated Bacillus velezensis strains selected after genome analysis, metabolite profiling, and with proved biocontrol potential, were enhancing harvest yield of coffee and black pepper in large field trials. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1194887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, L.M.; Cheng, R.A.; Wiedmann, M.; Kovac, J. Keeping up with the Bacillus cereus group: Taxonomy through the genomics era and beyond. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 7677–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus cereus Group: Bacillus Species with Pathogenic Potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R. Die Ätiologie der Milzbrand-Krankheit, begründet auf die Entwicklungsgeschichte des Bacillus Anthracis. Cohns Beiträge Zur Biol. Der Pflanz. 1876, 2, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Moayeri, M.; Leppla, S.H.; Vrentas, C.; Pomerantsev, A.P.; Liu, S. Anthrax Pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q. Cereulide and Emetic Bacillus cereus: Characterizations, Impacts and Public Precautions. Foods 2023, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berliner, E. Über die Schlafsucht der Mehlmottenraupe (Ephestia kühniella Zell) und ihren Erreger Bacillus thuringiensis n. sp. Zeitschrift für angewandte Entomologie, Berlin, 1915.
- Palma, L.; Muñoz, D.; Berry, C.; Murillo, J.; Caballero, P. Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins: An Overview of Their Biocidal Activity. Toxins 2014, 6, 3296–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, V.M. You Can’t B. cereus—A Review of Bacillus cereus Strains That Cause Anthrax-Like Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolstø, A.-B.; Tourasse, N.J.; Økstad, O.A. What Sets Bacillus anthracis Apart from Other Bacillus Species? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 451–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenscheit, C.; Jähne, J.; Schneider, A.; Blom, J.; Schweder, T.; Lasch, P.; Borriss, R. Genome sequence data of Bacillus velezensis BP1.2A and BT2.4. Data Brief 2022, 41, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A resource combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Q.; Göker, M.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z. Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radnedge, L.; Agron, P.G.; Hill, K.K.; Jackson, P.J.; Ticknor, L.O.; Keim, P.; Andersen, G.L. Genome Differences That Distinguish Bacillus anthracis from Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klee, S.R.; Özel, M.; Appel, B.; Boesch, C.; Ellerbrok, H.; Jacob, D.; Holland, G.; Leendertz, F.H.; Pauli, G.; Grunow, R.; et al. Characterization of Bacillus anthracis -Like Bacteria Isolated from Wild Great Apes from Côte d'Ivoire and Cameroon. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5333–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: A database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieckmann, M.A.; Beyvers, S.; Nkouamedjo-Fankep, R.C.; Hanel, P.H.G.; Jelonek, L.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A. EDGAR3.0: Comparative genomics and phylogenomics on a scalable infrastructure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W185–W192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, B.O.; Ravel, J. Chapter 8. Methods for in silico prediction of microbial polyketide and nonribosomal peptide biosynthetic pathways from DNA sequence data. Methods Enzymol. 2009, 458, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heel, A.J.; De Jong, A.; Song, C.; Viel, J.H.; Kok, J.; Kuipers, O.P. BAGEL4: A user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W278–W281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vater, J.; Herfort, S.; Doellinger, J.; Weydmann, M.; Borriss, R.; Lasch, P. Genome Mining of the Lipopeptide Biosynthesis of Paenibacillus polymyxa E681 in Combination with Mass Spectrometry: Discovery of the Lipoheptapeptide Paenilipoheptin. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mülner, P.; Schwarz, E.; Dietel, K.; Junge, H.; Herfort, S.; Weydmann, M.; Lasch, P.; Cernava, T.; Berg, G.; Vater, J. Profiling for Bioactive Peptides and Volatiles of Plant Growth Promoting Strains of the Bacillus subtilis Complex of Industrial Relevance. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suckau, D.; Resemann, A.; Schuerenberg, M.; Hufnagel, P.; Franzen, J.; Holle, A. A novel MALDI LIFT-TOF/TOF mass spectrometer for proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.J.; Hallmann, J.; Subbotin, S.A. Methods for extraction, processing and detection of plant and soil nematodes. In Plant Parasitic Nematodes in Subtropical and Tropical Agriculture; Luc, M., Sikora, R., Bridge, J., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2005; pp. 53–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.; Page, S.L.J. Estimation of Root-knot Nematode Infestation Levels on Roots Using a Rating Chart. Trop. Pest Manag. 1980, 26, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiharjo, A.; Chowdhury, S.P.; Dietel, K.; Beator, B.; Dolgova, O.; Fan, B.; Bleiss, W.; Ziegler, J.; Schmid, M.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Transposon Mutagenesis of the Plant-Associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ssp. plantarum FZB42 Revealed That the nfrA and RBAM17410 Genes Are Involved in Plant-Microbe-Interactions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O. FastME 2.0: A Comprehensive, Accurate, and Fast Distance-Based Phylogeny Inference Program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 2798–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lin, P.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Fu, B.; Long, R.; Liu, D.; Guo, Y.; Peng, L.; Xia, Q. Complete Genome Sequence of Bacillus bombysepticus , a Pathogen Leading to Bombyx mori Black Chest Septicemia. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00312-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, D.H.; Chuvochina, M.; Rinke, C.; Mussig, A.J.; Chaumeil, P.-A.; Hugenholtz, P. GTDB: An ongoing census of bacterial and archaeal diversity through a phylogenetically consistent, rank normalized and complete genome-based taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, D785–D794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parte, A.C.; Sardà Carbasse, J.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agata, N.; Ohta, M.; Mori, M. Production of an emetic toxin, cereulide, is associated with a specific class of Bacillus cereus. Curr Microbiol 1996, 33, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, L.; Read, T.D. Bacillus anthracis, a bug with attitude! Curr Opin Microbiol 2001, 4, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Porta, H.; García-Gómez, B.I.; Rodriguez-Almazan, C.; Pardo, L.; Soberón, M. Evolution of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry toxins insecticidal activity. Microb. Biotechnol. 2013, 6, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellerbrok, H.; Nattermann, H.; Ãzel, M.; Beutin, L.; Appel, B.; Pauli, G. Rapid and sensitive identification of pathogenic and apathogenicBacillus anthracisby real-time PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 214, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q. Cereulide and Emetic Bacillus cereus: Characterizations, Impacts and Public Precautions. Foods 2023, 12, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A.C.L. Cooperative, synergistic and antagonistic haemolytic interactions between haemolysin BL, phosphatidylcholine phospholipase C and sphingomyelinase from Bacillus cereus. Microbiology 2000, 146, 3033–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, R.; Jessberger, N.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Märtlbauer, E.; Granum, P.E. The Food Poisoning Toxins of Bacillus cereus. Toxins 2021, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanahuja, G.; Banakar, R.; Twyman, R.M.; Capell, T.; Christou, P. Bacillus thuringiensis: A century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Kumar, H.; Kaur, S. Vegetative Insecticidal Protein (Vip): A Potential Contender From Bacillus thuringiensis for Efficient Management of Various Detrimental Agricultural Pests. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 659736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, B.; Deng, Y.; Sun, M.; Tang, Y.-J.; Ruan, L. Bacillus thuringiensis produces the lipopeptide thumolycin to antagonize microbes and nematodes. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 215, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, R.; Olson, R.; Pusch, G.D.; Olsen, G.J.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Parrello, B.; Shukla, M.; et al. The SEED and the Rapid Annotation of microbial genomes using Subsystems Technology (RAST). Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D206–D214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.; Ryan, M. Bacterial phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C: Structure, function, and interaction with lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1999, 1441, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhu, J.; Feng, H.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Yan, X.-X.; Zhang, X.; Gao, P. Structural insights into assembly, operation and inhibition of a type I restriction–modification system. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; McPherson, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Turnbough, C.L.; Pritchard, D.G. Characterization of the Enzymes Encoded by the Anthrose Biosynthetic Operon of Bacillus anthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 5053–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; McPherson, S.A.; Tan, L.; Chesnokova, O.N.; Turnbough, C.L.; Pritchard, D.G. Anthrose Biosynthetic Operon of Bacillus anthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.-I.; Yamaguchi, M.; Morinaga, T.; Kinehara, M.; Ikeuchi, M.; Ashida, H.; Fujita, Y. myo-Inositol Catabolism in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10415–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Kuipers, O.P. Identification and classification of known and putative antimicrobial compounds produced by a wide variety of Bacillales species. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracanna, V.; de Jong, A.; Medema, M.H.; Kuipers, O.P. Mining prokaryotes for antimicrobial compounds: From diversity to function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terlouw, B.R.; Blin, K.; Navarro-Muñoz, J.C.; Avalon, N.E.; Chevrette, M.G.; Egbert, S.; Lee, S.; Meijer, D.; Recchia, M.J.J.; Reitz, Z.L.; et al. MIBiG 3.0: A community-driven effort to annotate experimentally validated biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D603–D610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finking, R.; Marahiel, M.A. Biosynthesis of Nonribosomal Peptides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 453–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béchet, M.; Caradec, T.; Hussein, W.; Abderrahmani, A.; Chollet, M.; Leclère, V.; Dubois, T.; Lereclus, D.; Pupin, M.; Jacques, P. Structure, biosynthesis, and properties of kurstakins, nonribosomal lipopeptides from Bacillus spp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 95, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, T.-X.; Tang, S.-Y.; Jin, Y.; Mi, D.-D.; Zheng, Y.; Niu, D.-D.; Guo, J.-H.; et al. Kurstakin Triggers Multicellular Behaviors in Bacillus cereus AR156 and Enhances Disease Control Efficacy Against Rice Sheath Blight. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, J.; Truong, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. Unusual Biosynthesis and Structure of Locillomycins from Bacillus subtilis 916. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6601–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.J.; Wendrich, T.M.; Marahiel, M.A. The dhb Operon of Bacillus subtilisEncodes the Biosynthetic Template for the Catecholic Siderophore 2,3-Dihydroxybenzoate-Glycine-Threonine Trimeric Ester Bacillibactin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7209–7217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-H.; Koumoutsi, A.; Scholz, R.; Borriss, R. More than Anticipated–Production of Antibiotics and Other Secondary Metabolites by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008, 16, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.H.; Koumoutsi, A.; Scholz, R.; Eisenreich, A.; Schneider, K.; Heinemeyer, I.; Morgenstern, B.; Voss, B.; Hess, W.R.; Reva, O.; et al. Comparative analysis of the complete genome sequence of the plant growth–promoting bacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevany, B.M.; Rasko, D.A.; Thomas, M.G. Characterization of the Complete Zwittermicin A Biosynthesis Gene Cluster fromBacillus cereus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellbrich, G.; Romanski, A.; Varet, A.; Blume, B.; Brunner, F.; Engelhardt, S.; Felix, G.; Kemmerling, B.; Krzymowska, M.; Nürnberger, T. NPP1, a Phytophthora-associated trigger of plant defense in parsley and Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2002, 32, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhart, B.J.; Hudson, G.A.; Dunbar, K.L.; Mitchell, D. A A prevalent peptide-binding domain guides ribosomal natural product biosynthesis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, A.M.; Shelton, K.E.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Mitchell, D.A. RRE-Finder: A Genome-Mining Tool for Class-Independent RiPP Discovery. mSystems 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahl, H.-G.; Jack, R.W.; Bierbaum, G. Biosynthesis and Biological Activities of Lantibiotics with Unique Post-Translational Modifications. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 230, 827–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Ge, X.; Zhang, J.; Teng, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, J. Bovicin HJ50-Like Lantibiotics, a Novel Subgroup of Lantibiotics Featured by an Indispensable Disulfide Bridge. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.C.; Eslami, S.M.; Hetrick, K.J.; Ackenhusen, S.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; van der Donk, W.A. Precursor peptide-targeted mining of more than one hundred thousand genomes expands the lanthipeptide natural product family. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnison, P.G.; Bibb, M.J.; Bierbaum, G.; Bowers, A.A.; Bugni, T.S.; Bulaj, G.; Camarero, J.A.; Campopiano, D.J.; Challis, G.L.; Clardy, J.; et al. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: Overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 108–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Biswas, S.; Ho, S.; van der Donk, W.A.; Zhao, H. Rapid Discovery of Glycocins through Pathway Refactoring in Escherichia coli. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2966–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oman, T.J.; Boettcher, J.M.; Wang, H.; Okalibe, X.N.; van der Donk, W.A. Sublancin is not a lantibiotic but an S-linked glycopeptide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Lasso Peptides: An Intriguing Class of Bacterial Natural Products. Accounts Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Hegemann, J.D.; Fage, C.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. Insights into the Unique Phosphorylation of the Lasso Peptide Paeninodin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 13662–13678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flühe, L.; Knappe, T.A.; Gattner, M.J.; Schäfer, A.; Burghaus, O.; Linne, U.; Marahiel, M.A. The radical SAM enzyme AlbA catalyzes thioether bond formation in subtilosin A. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, G.A.; Burkhart, B.J.; DiCaprio, A.J.; Schwalen, C.J.; Kille, B.; Pogorelov, T.V.; Mitchell, D.A. Bioinformatic Mapping of Radical S-Adenosylmethionine-Dependent Ribosomally Synthesized and Post-Translationally Modified Peptides Identifies New Cα, Cβ, and Cγ-Linked Thioether-Containing Peptides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8228–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, L.; Singh, G.; Choudhary, V.; Sahoo, D.K. Sonorensin: An Antimicrobial Peptide, Belonging to the Heterocycloanthracin Subfamily of Bacteriocins, from a New Marine Isolate, Bacillus sonorensis MT93. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, C.M.A.P.; Van Belkum, M.J.; Holzapfel, W.H.; Abriouel, H.; Gálvez, A. Diversity of enterococcal bacteriocins and their grouping in a new classification scheme. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunpad, R.; Panbangred, W. Evidence for Two Putative Holin-Like Peptides Encoding Genes of Bacillus pumilus Strain WAPB4. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 64, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Janes, B.K.; Passalacqua, K.D.; Pfleger, B.F.; Bergman, N.H.; Liu, H.; Håkansson, K.; Somu, R.V.; Aldrich, C.C.; Cendrowski, S.; et al. Biosynthetic Analysis of the Petrobactin Siderophore Pathway from Bacillusanthracis. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppisch, A.T.; Dhungana, S.; Hill, K.K.; Boukhalfa, H.; Heine, H.S.; Colip, L.A.; Romero, R.B.; Shou, Y.; Ticknor, L.O.; Marrone, B.L.; et al. Petrobactin is produced by both pathogenic and non-pathogenic isolates of the Bacillus cereus group of bacteria. BioMetals 2008, 21, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Yong, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Research Progress of the Biosynthesis of Natural Bio-Antibacterial Agent Pulcherriminic Acid in Bacillus. Molecules 2020, 25, 5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corre, C.; Song, L.; O'Rourke, S.; Chater, K.F.; Challis, G.L. 2-Alkyl-4-hydroxymethylfuran-3-carboxylic acids, antibiotic production inducers discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17510–17515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arie, T. Fusarium diseases of cultivated plants, control, diagnosis, and molecular and genetic studies. J. Pestic. Sci. 2019, 44, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, N.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Nam, H.B.; Quang, D.Q.; Phong, L.V.; Van, N.D.; Trang, T.T.; Kien, T.T.; Tam, T.T.T.; Dell, B. Management of Phytophthora palmivora disease in Citrus reticulata with chemical fungicides. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2020, 86, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenback, J.D.; Triantaphyllou, H.H. Root-knot nematodes: Meloidogyne species and races. In Manual of Agricultural Nematology; Nickle, W.R., Ed.; Marcell Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 191–274. [Google Scholar]
- Hussey, P.S.; Barker, K.R. A comparison of methods of collecting inocula of Meloidogyne spp., including a new technique. Plant Disease Reporter. 1973, 57, 1025–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.P.; Hartmann, A.; Gao, X.; Borriss, R. Biocontrol mechanism by root-associated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42—A review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.-Q.; Wu, H.-J.; Huo, R.; Gao, X.-W.; Borriss, R. Stimulation of plant growth and biocontrol by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum FZB42 engineered for improved action. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2014, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, H.-J.; Qiao, J.; Gao, X.; Borriss, R. Novel Routes for Improving Biocontrol Activity of Bacillus Based Bioinoculants. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).