Submitted:
09 October 2023
Posted:
10 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
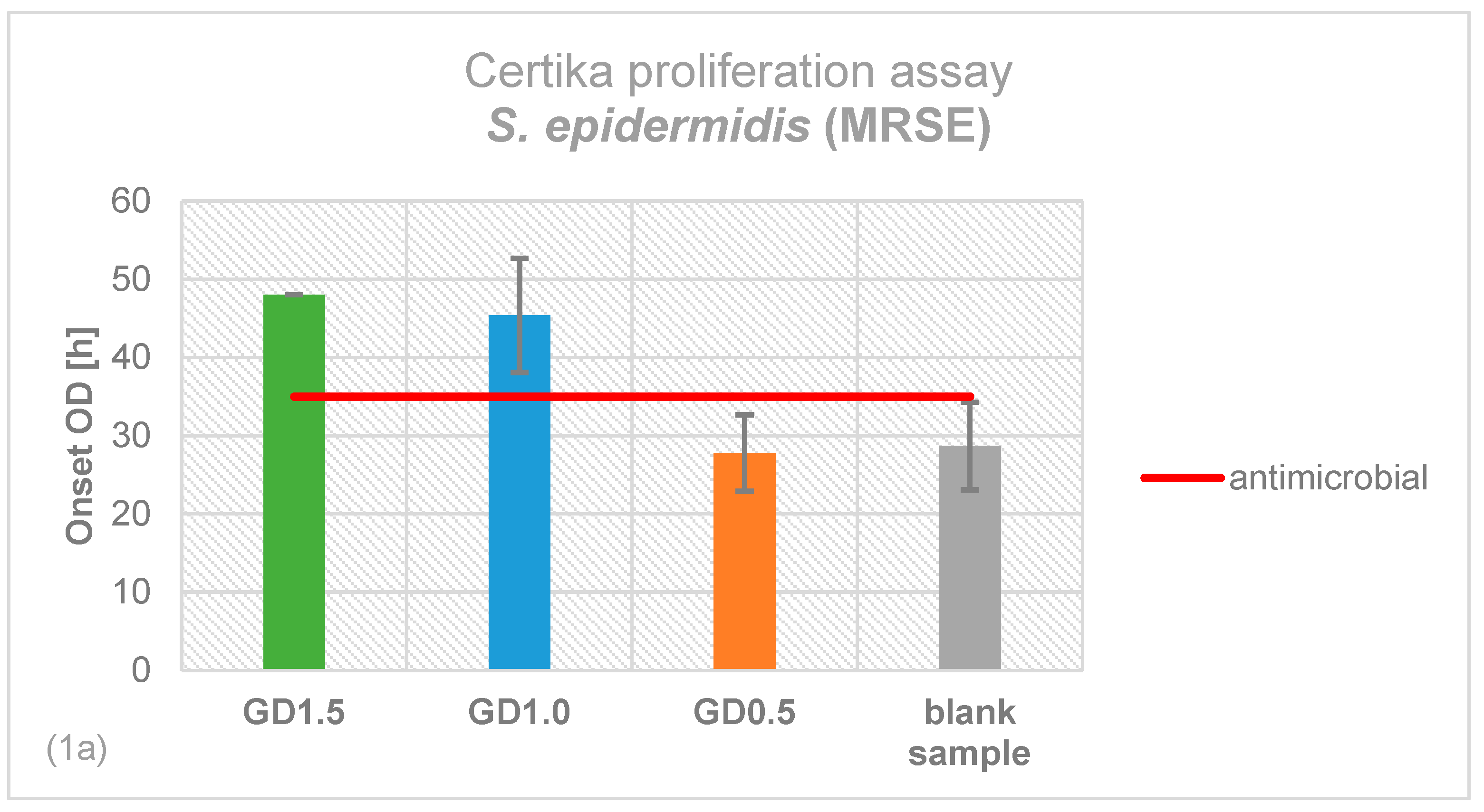
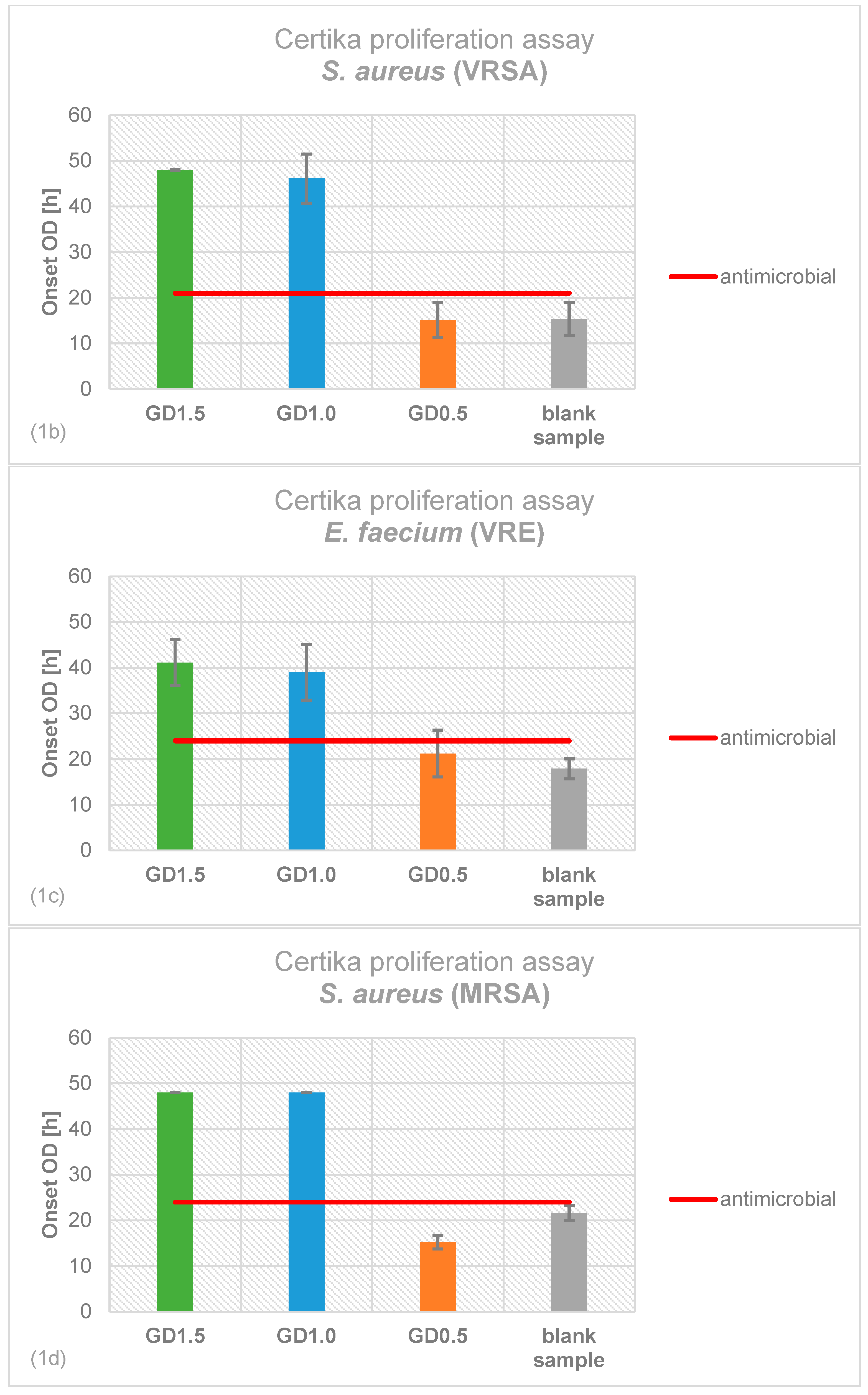
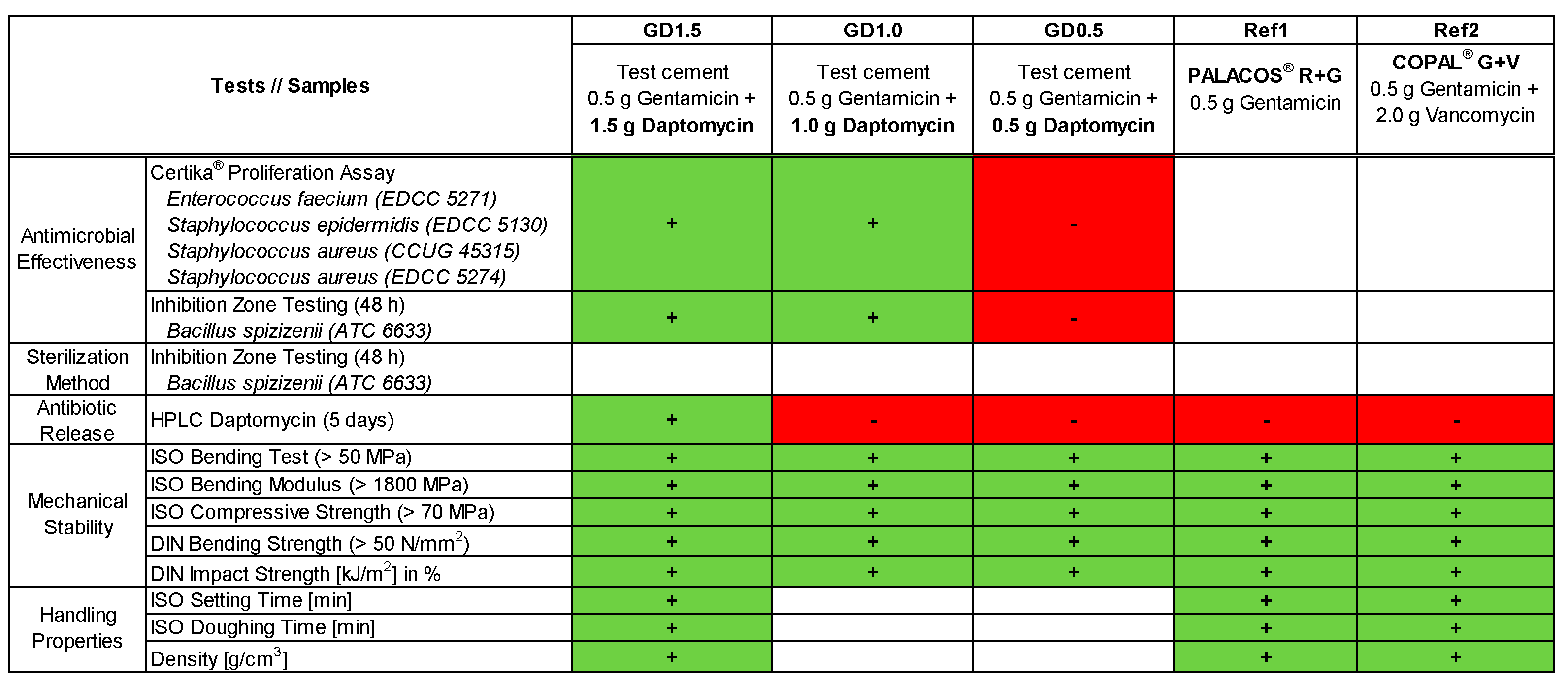
2.1. Antimicrobial Effectiveness determined by Proliferation Assay
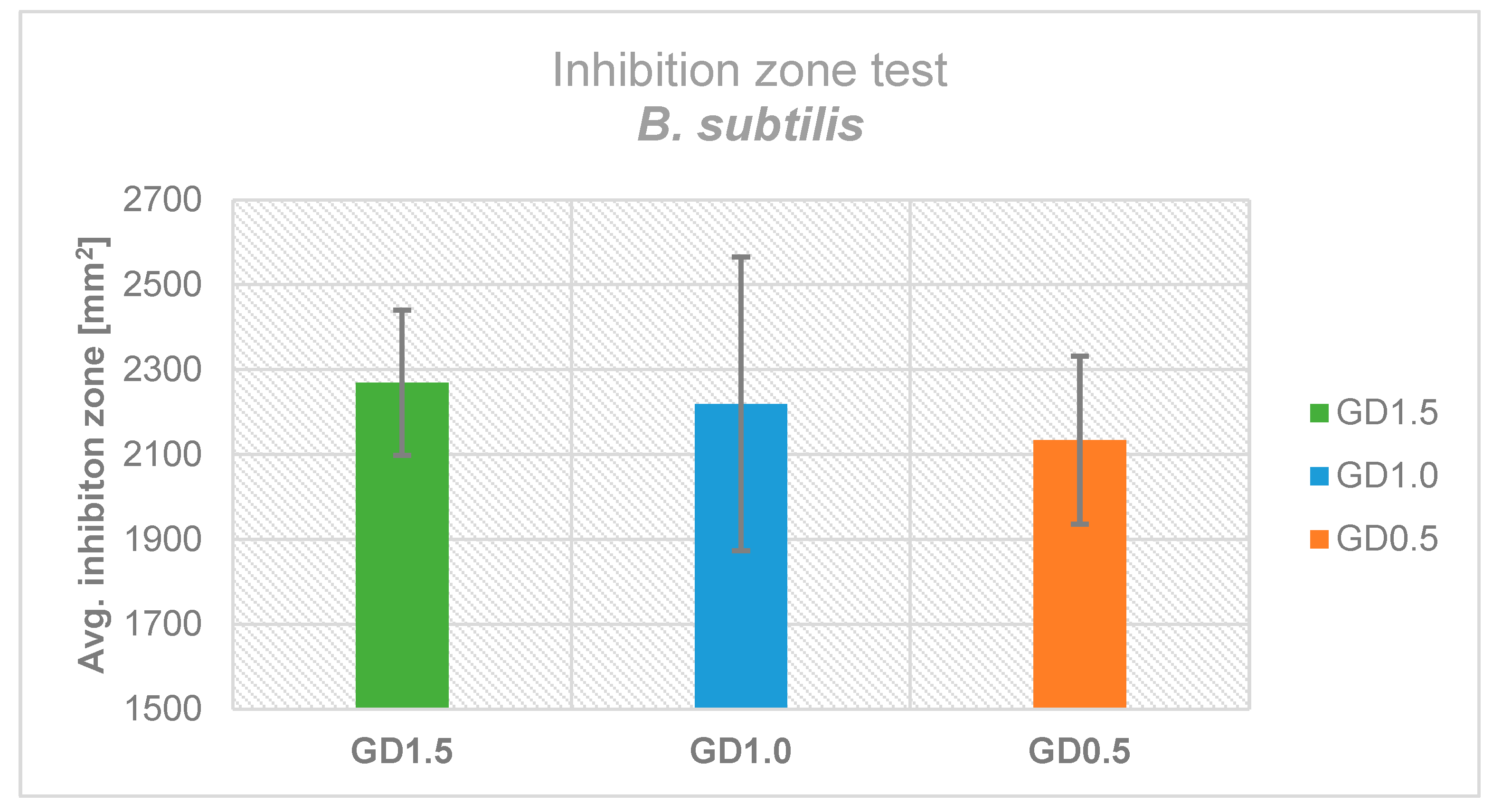
2.2. Antimicrobial Effectiveness based on Inhibition Zone Test
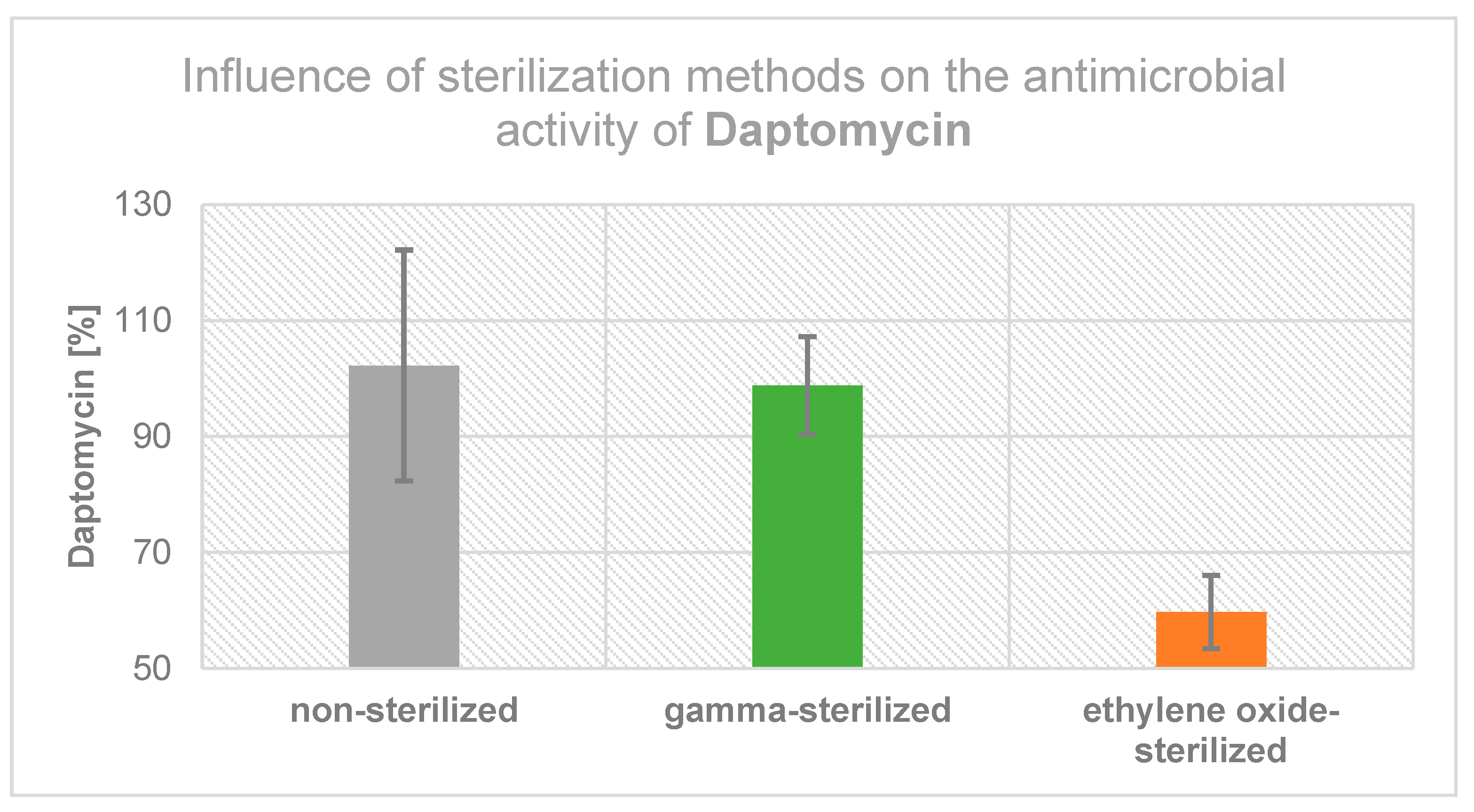
2.3. Influence of Sterilization Method
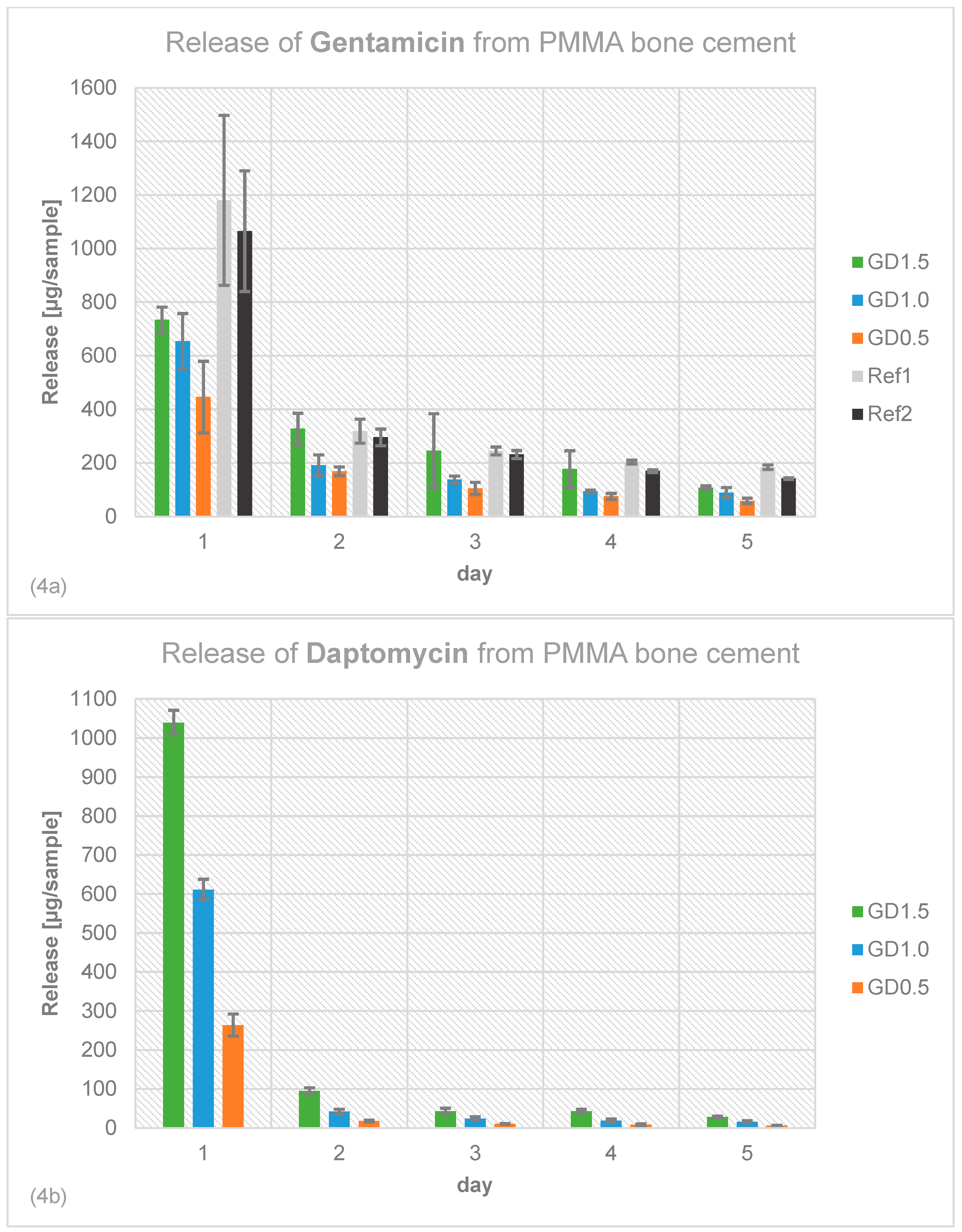
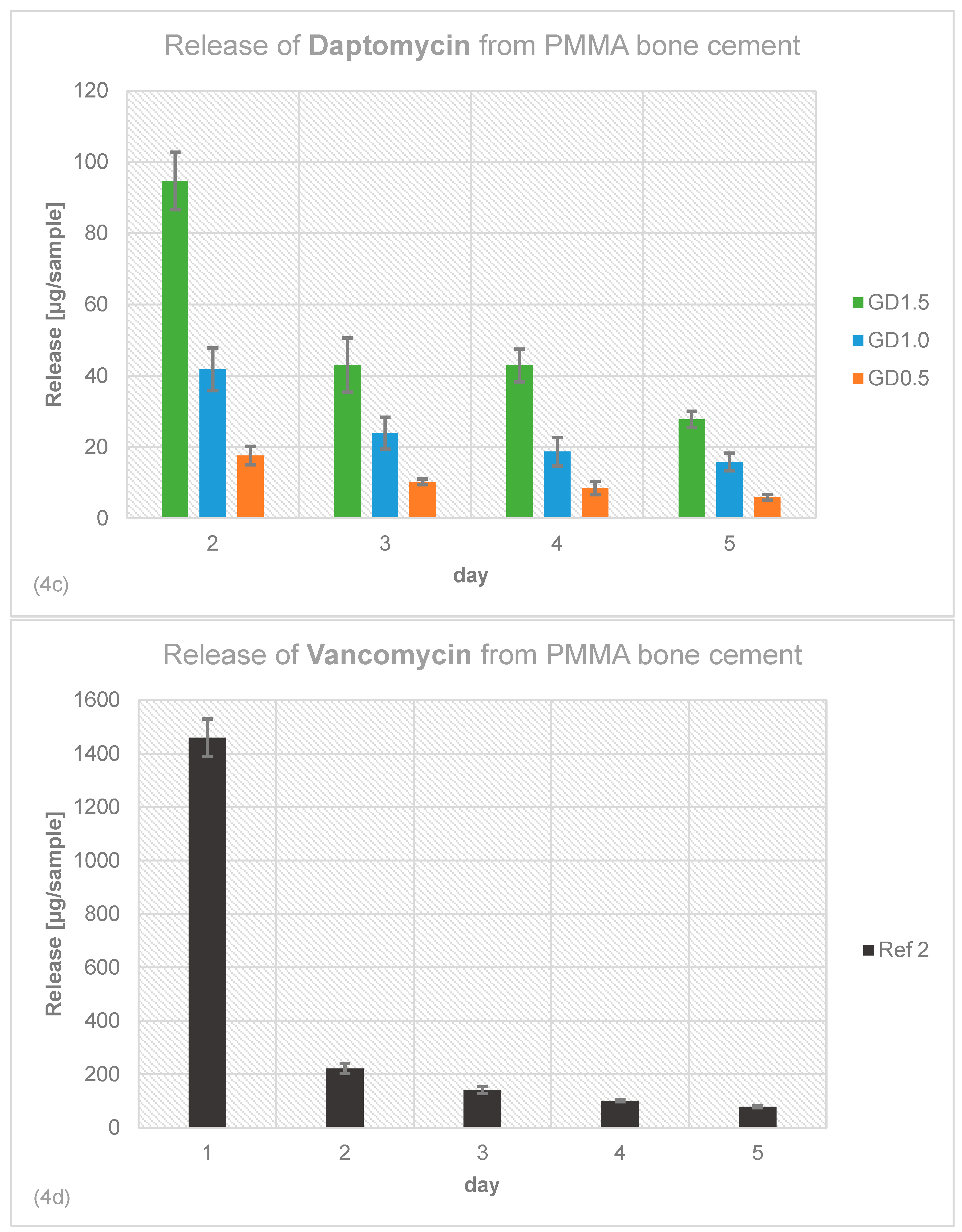
2.4. Antibiotic Release Profile of Gentamicin, Daptomycin and Vancomycin
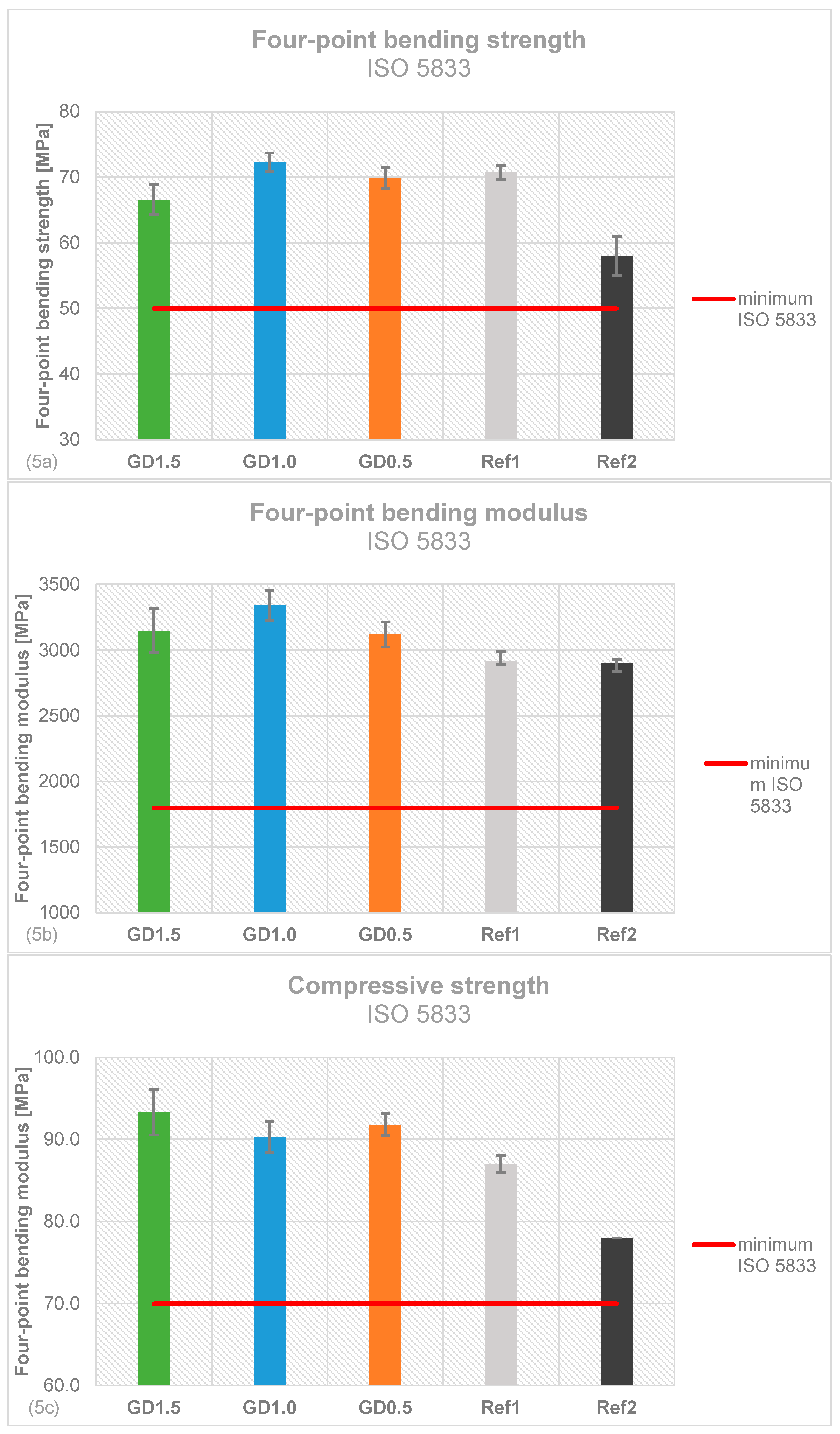
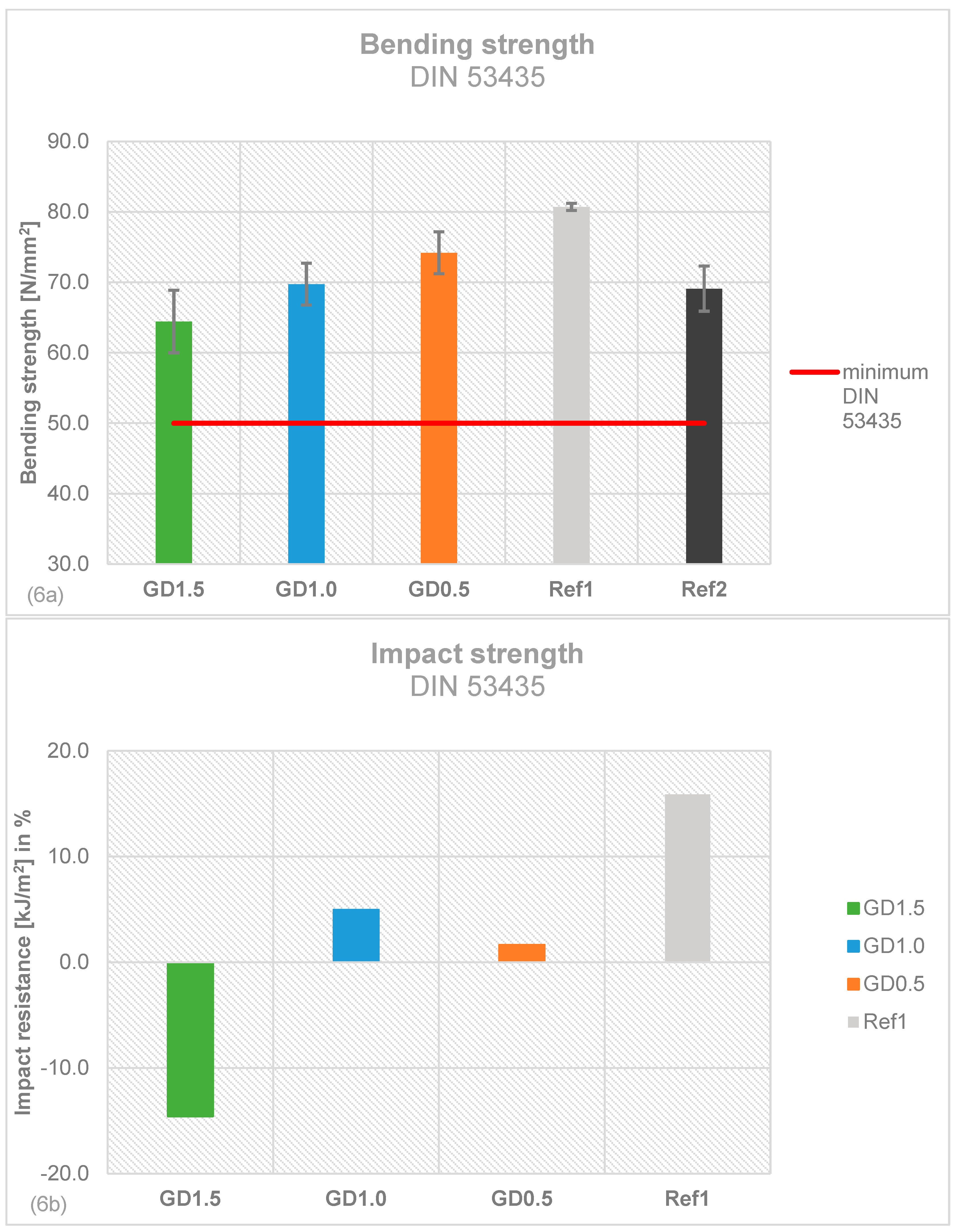
2.5. Mechanical Stability of Daptomycin-loaded Bone Cement
2.6. Handling Properties of Daptomycin-loaded Bone Cement
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
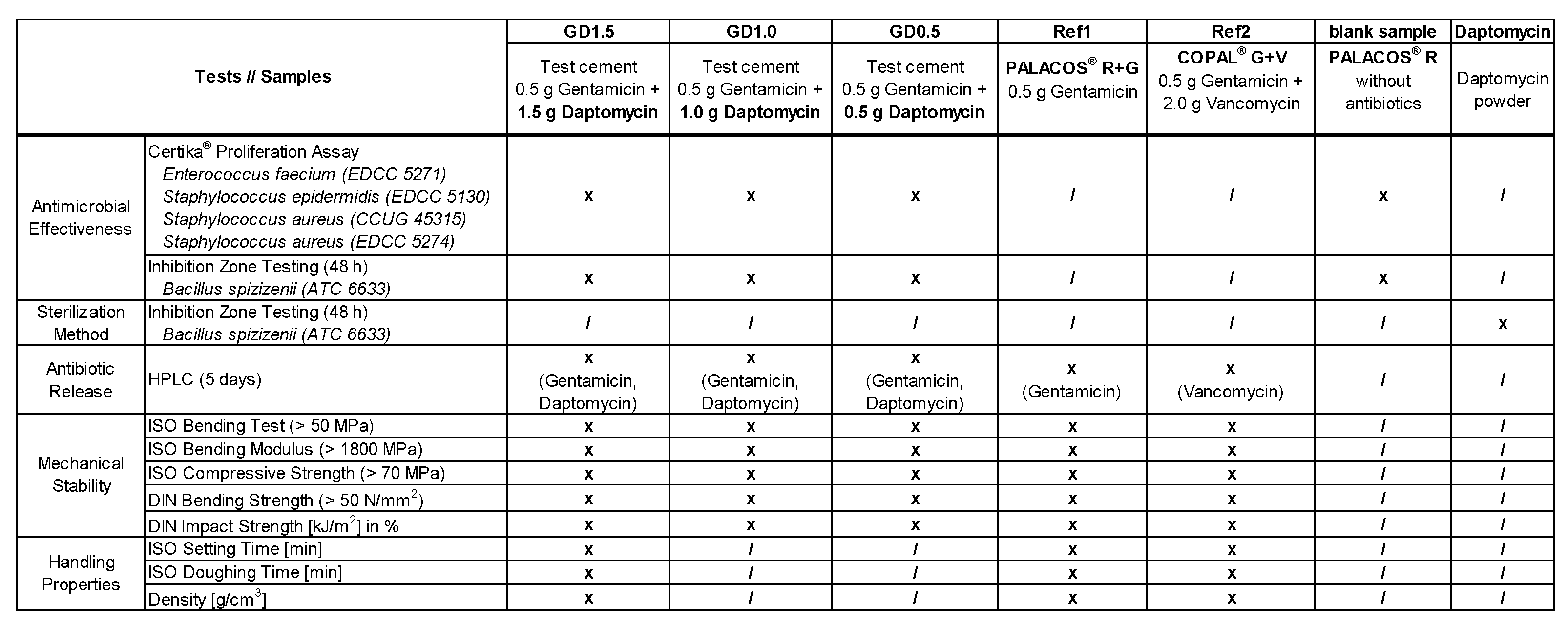
4.1. PMMA Cements and Bacteria
4.2. Certika® Proliferation Assay
4.3. Inhibition Zone Testing
4.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.5. Mechanical stability testing according to ISO 5833 and DIN 53435
4.6. Handling Properties of PMMA Cement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgenstern, M.; Erichsen, C.; Militz, M.; Xie, Z.; Peng, J.; Stannard, J.; Metsemakers, W.-J.; Schaefer, D.; Alt, V.; Søballe, K.; et al. The AO trauma CPP bone infection registry: Epidemiology and outcomes of Staphylococcus aureus bone infection. J. Orthop. Res. 2021, 39, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberich, C.; Josse, J.; Ruiz, P.S. Patients at a high risk of PJI: Can we reduce the incidence of infection using dual antibiotic-loaded bone cement? Arthroplasty 2022, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R. Periprosthetic Joint Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sax, F.H.S.; Fink, B. Total Knee Arthroplasty in Unrecognized Septic Arthritis—A Descriptive Case Series Study. antibiotics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Mihalko, W.M.; Shields, J.S.; Ries, M.; Saleh, K.J. Antibiotic-impregnated cement spacers for the treatment of infection associated with total hip or knee arthroplasty. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2007, 89, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasandoost, L.; Rodriguez, O.; Alhalawani, A.; Zalzal, P.; Schemitsch, E.H.; Waldman, S.D.; Papini, M.; Towler, M.R. The Role of Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) in Management of Bone Loss and Infection in Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Review. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blersch, B.P.; Barthels, M.; Schuster, P.; Fink, B. A Low Rate of Periprosthetic Infections after Aseptic Knee Prosthesis Revision Using Dual-Antibiotic-Impregnated Bone Cement. antibiotics 2023, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leta, T.H.; Fenstad, A.M.; Lygre, S.H.L.; Lie, S.A.; Lindberg-Larsen, M.; Pedersen, A.B.; W-Dahl, A.; Rolfson, O.; Bülow, E.; Ashforth, J.A.; et al. The use of antibiotic-loaded bone cement and systemic antibiotic prophylactic use in 2,97,357 primary total knee arthroplasties from 2010 to 2020: an international register-based observational study among countries in Africa, Europe, North America, and Oceania. Acta Orthopaedica 2023, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Dadashi, M.; Moghadam, M.T.; van Belkum, A.; Yaslianifard, S.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Global prevalence and distribution of vancomycin resistant, vancomycin intermediate and heterogeneously vancomycin intermediate Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwart, R.; Willrich, N.; Haller, S.; Noll, I.; Koppe, U.; Werner, G.; Eckmanns, T.; Reuss, A. The rise in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium in Germany: data from the German Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (ARS). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel, M.P.; Barreira, P.; Battenberg, A.; Berry, D.J.; Blevins, K.; Font-Vizcarra, L.; Frommelt, L.; Goswami, K.; Greiner, J.; Janz, V.; et al. Hip and Knee Section, Treatment, Two-Stage Exchange Spacer-Related: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplasty 2019, 34, S427–S438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaPlante, K.; Rybak Michael. Daptomycin a novel antibiotic against gram positive pathogens. Expert Opoin. Pharmacother. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.A.; Wenzel, M. More Than a Pore: A Current Perspective on the In Vivo Mode of Action of the Lipopeptide Antibiotic Daptomycin. antibiotics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, K.-D. PMMA Cements Are we aware what we are using? Springer-Verlag, p. 58-59; 88-89; 96-109; 157-158: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014, ISBN 13 978-3-642-41535-7.
- PRO-IMPLANT Foundation. Pocket Guide to Diagnosis & Treatment of the Periprosthetic Joint Infection 2023.
- Steadman, W.; Chapman, P.R.; Schuetz, M.; Schmutz, B.; Trampuz, A.; Tetsworth, K. Local Antibiotic Delivery Options in Prosthetic Joint Infection. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréa Cara; Mathilde Ballet; Claire Hemery; Tristan Ferry; Fédéric Laurent; Jérôme Josse. Antibiotics in Bone Cements Used for Prosthesis Fixation: An Efficient Way to Prevent Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Prosthetic Joint Infection. frontiers in Medicine, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Lunz, A.; Schonhoff, M.; Omlor, G.W.; Knappe, K.; Bangert, Y.; Lehner, B.; Renkawitz, T.; Jaeger, S. Enhanced antibiotic release from bone cement spacers utilizing dual antibiotic loading with elevated vancomycin concentrations in two-stage revision for periprosthetic joint infection. Int. Orthop. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, R.M.; Canetti, D.; Riccardi, N. Daptomycin synergistic properties from in vitro and in vivo studies: a systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 78, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.; Kühn, K.-D. Essentials of Cemented Knee Arthroplasty; Springer Berlin Heidelberg, p. 542-548; p. 686-700, 2022, ISBN 978-3-662-63112-6.
- Rouse, M.S.; Piper, K.E.; Jacobson, M.; Jacofsky, D.J.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Daptomycin treatment of Staphylococcus aureus experimental chronic osteomyelitis. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2006, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, N.J.; Lloyd, J.M.; Koziol, L.; O’Hara, L. Successful clinical use of daptomycin-impregnated bone cement in two-stage revision hip surgery for prosthetic joint infection. Ann. Pharmacother. 2013, 47, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eick, S.; Hofpeter, K.; Sculean, A.; Ender, C.; Klimas, S.; Vogt, S.; Nietzsche, S. Activity of Fosfomycin- and Daptomycin-Containing Bone Cement on Selected Bacterial Species Being Associated with Orthopaedic Infections. BioMed Research International 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, D.G.; Cooper, K.B.; Renard, R.L.; Mears, S.C.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Barnes, C.L. Comparative Study of Antibiotic Elution Profiles From Alternative Formulations of Polymethylmethacrylate Bone Cement. J. Arthroplasty 2019, 34, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, M.K.; Arvanitis, M.; Mylonakis, E.; LaPlante, K. Activity of Daptomycin or Lenezolid in Combination with Rifampin or Gentamicin against Biofilm-Forming Enterococcus faecalis or E. faecium in an In Vitro Parmacondynamic Model Using Simulated Endocardial Vegetations and an In Vivo Survival Assay Using Galleria melonella Larvae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 4612–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, N.D.; McCanless, J.D.; Courtney, H.S.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Haggard, W.O. Daptomycin eluted from calcium sulfate appears effective against Staphylococcus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, N.J.; Hill, J.; McAfee, P.; Kirkpatrick, R.; Patrick, S.; Tunney, M. Incorporation of large amounts of gentamicin sulphate into acrylic bone cement: effect on handling and mechanical properties, antibiotic release, and biofilm formation. Proceedings of the I MECH E Part H Journal of Engineering in Medicine 2008, 222, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunz, A.; Knappe, K.; Omlor, G.W.; Schonhoff, M.; Renkawitz, T.; Jaeger, S. Mechanical strength of antibiotic-loaded PMMA spacers in two-stage revision surgery. BMC Muscoskeletal Disorders 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzberg-Boelch, S.P. von; Luedemann, M.; Rudert, M.; Steinert, A.F. PMMA Bone Cement: Antibiotic Elution and Mechanical Properties in the Context of Clinical Use. biomedicines 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SO 5833:2002. Implants for surgery - Acrylic resin cements. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
- MSD SHARP & DOHME GMBH. Cubicin. Instruction for Use. (In German).
- Alt, V.; Bechert, T.; Steinrücke, P.; Wagener, M.; Seidel, P.; Dingeldein, E.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R. An in vitro assessment of the antibacterial properties and cytotoxicity of nanoparticulate silver bone cement. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4383–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alt, V.; Bechert, T.; Steinrücke, P.; Wagener, M.; Seidel, P.; Dingeldein, E.; Domann, E.; Schnettler, R. In vitro testing of antimicrobial activity of bone cement. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4084–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechert, T.; Steinrücke, P.; Guggenbichler, J.P. A new method for screening anti-infective biomaterials. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025:2017. General requirements for the competence of testing and calibration laboratories. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Fuchs, P.; Barry, A.; Brown, S. Evaluation of daptomycin susceptibility testing by Etest and the effect of different batches of media. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2001, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, S.S.; Cooper, J.J.; Florance, H.; Robinson, M.T.; Michell, S. Local release of antibiotics for surgical site infection management using high-purity calcium sulfate: an in vitro elution study. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2015, 16, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, T.J.; Lamping, J.W.; Hendricks, K.J.; McIff, T.E. Increasing the elution of vancomycin from high-dose antibiotic-loaded bone cement: a novel preparation technique. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2012, 94, 1946–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DIN 53435:2018. Testing of plastics - bending test and impact test on dynstat test specimens. GlobalSpec: Albany, NY, USA, 2018.
| Handling Properties | GD1.5 | PALACOS® R+G Ref1 |
COPAL® G+V Ref2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISO Setting Time [min] | 06:45 ± 00:00 | 09:30 ± 00:10 | 08:15 ± 00:18 |
| ISO Doughing Time [min] | 01:30 ± 00:00 | 00:55 ± 00:05 | 01:00 ± 00:05 |
| Density [g/cm3] | 1.13 ± 0.01 | 1.15 ± 0.00 | 1.12 ± 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





