2. Materials and Methods
Study Registration
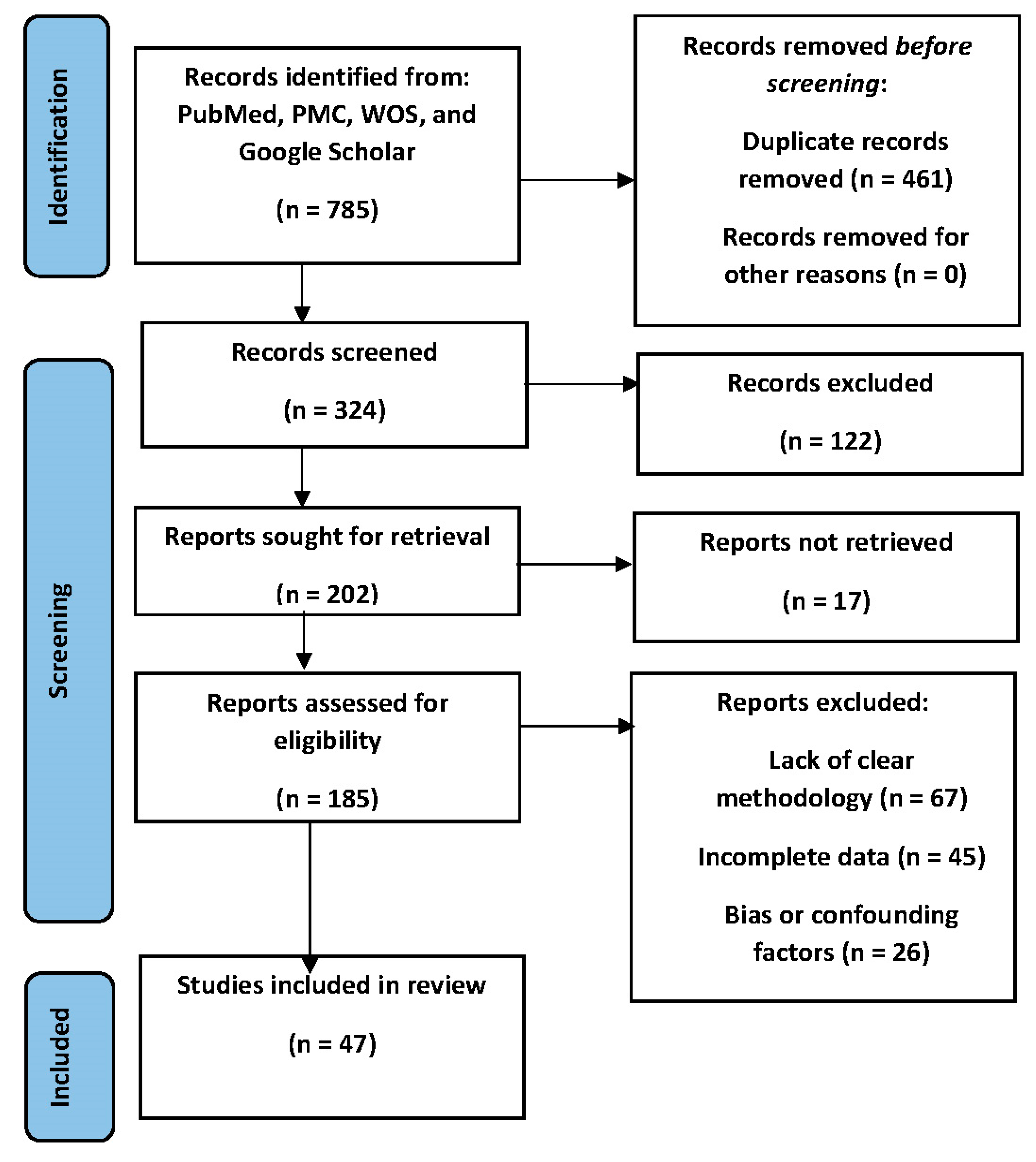
The research study was conducted following 2020 protocols and guidelines of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) for systematic reviews [
12] . The study was prospectively registered with the recognized research registry (Prospero International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews) with the I.D 471034 to ensure transparency and adherence to best practices.
Definition Criteria
Clear and predefined criteria were established to guide the selection of relevant studies for inclusion in this systematic review. The criteria encompassed aspects such as study design, population, interventions, and outcomes of interest. These criteria were developed to ensure the relevance and consistency of the selected studies in addressing the research objectives.
Computer Retrieval of Articles
A comprehensive search strategy was devised to retrieve relevant articles from electronic databases, including PubMed, PMC, and other relevant sources. The search strategy included appropriate keywords, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms, and Boolean operators to ensure the thorough identification of pertinent literature. The PubMed search strategy was designed to comprehensively identify relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. The three search categories used were:
#1: "Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3" OR "SRC-3" OR "Amplified in Breast Cancer 1" OR "AIB1" #2: "Prostate Cancer" OR "Prostatic Neoplasms" OR "Prostate Carcinoma"
#3: "Molecular Mechanisms" OR "Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathways" OR "Cellular Signaling"
These categories were combined using the AND operator as follows:
(#1) AND (#2) AND (#3)
This combined search strategy aimed to retrieve articles that specifically address the molecular mechanisms, biochemical pathways, and cellular signaling involving Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 in the context of Prostate Cancer.
Literature Screening and Data Extraction
Two experienced researchers, denoted as S.Z. and H.Z., independently conducted the initial screening of identified articles based on the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Any discrepancies in their selections were resolved through discussion and consensus or negotiated with a third researcher (O.O.O.). Subsequently, these researchers performed data extraction from the selected studies. The use of three researchers ensured the accuracy and reliability of the extracted data. The following inclusion and exclusion criteria were established to ensure that the selected studies were pertinent to the research objectives and maintained a high level of scientific rigor:
Inclusion Criteria: (1) Studies published in peer-reviewed journals, (2) Studies conducted on human subjects, (3) Studies investigating the role of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 (SRC-3 or AIB1) in Prostate Cancer, (4) Studies examining molecular mechanisms, biochemical pathways, or cellular signaling related to SRC-3 in Prostate Cancer, (5) Studies available in English language.
Exclusion Criteria: (1) Non-peer-reviewed articles, such as conference abstracts and posters, (2) Studies conducted solely on animals or in vitro experiments without relevance to human subjects, (3) Studies not directly related to the molecular mechanisms or cellular signaling of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 in Prostate Cancer. Studies not available in the English language.
Quality Evaluation of the Included Studies
A rigorous quality assessment of the included studies was conducted to evaluate the methodological soundness and risk of bias. The assessment considered various aspects, such as study design, sample size, data collection methods, and statistical analysis. The quality assessment was performed to determine the strength of evidence and potential sources of bias in the selected studies.
Ethical Approval
This systematic review adhered to PRISMA guidelines and other applicable ethical standards. Since this study did not involve human or animal subjects, formal ethical approval was not required. However, ethical considerations related to data usage, citation, and transparency were upheld throughout the research process.
4. Discussion
The discussion section provides a platform for the interpretation of the findings from the selected 47 articles, which collectively shed light on the role of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 (SRC-3) in the context of Prostate Cancer. This section aims to synthesize and analyze the key insights and implications of the reviewed literature.
SRC-3 Protein
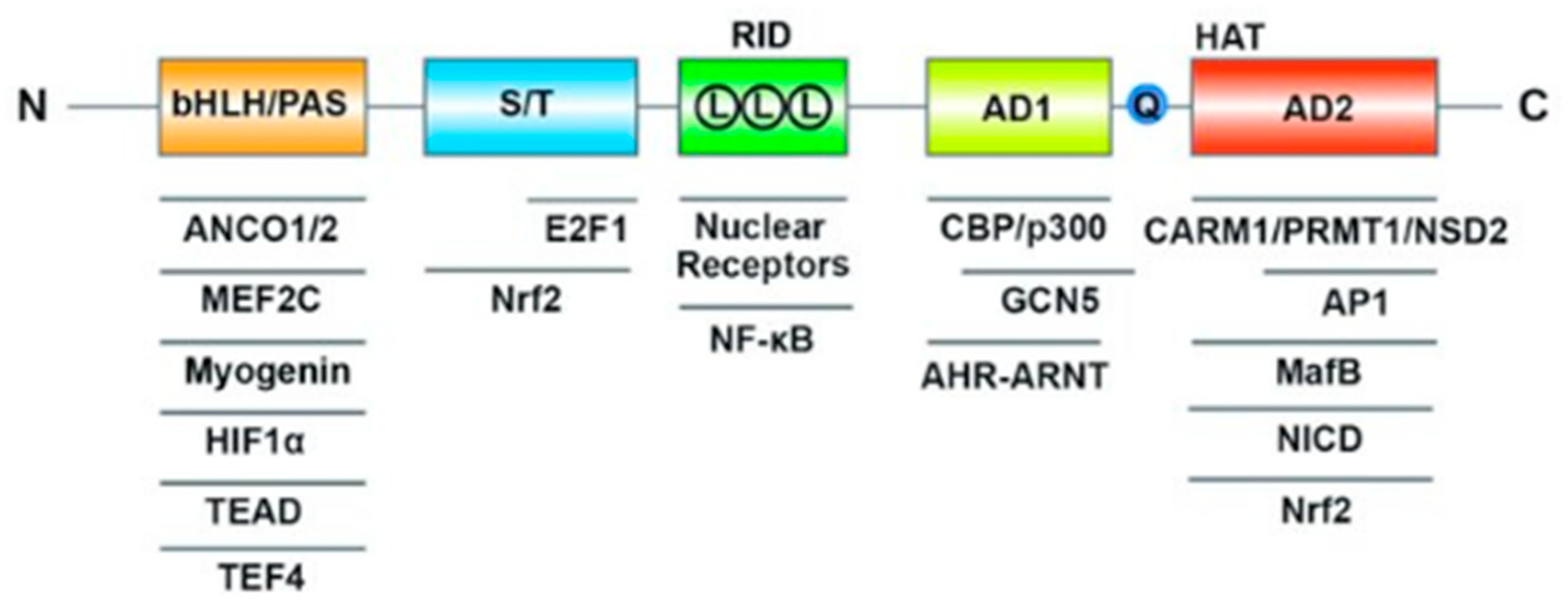
The molecular structure of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 (SRC-3), also known as Amplified in Breast Cancer 1 (AIB1), is a complex and multifunctional protein that plays a crucial role in transcriptional regulation [
11]. SRC-3 consists of several distinct structural and functional domains, each contributing to its diverse functions in gene expression modulation (
Figure 4). In summary, SRC-3's molecular structure is characterized by its bHLH and PAS domains, RID with LXXLL motifs, transcriptional activation domains with a polyglutamate sequence, and HAT activity. These structural features enable SRC-3 to interact with transcription factors and coregulators, facilitating its role as a coactivator in the regulation of gene expression, including genes involved in prostate cancer and other physiological processes.
SRC-3 contains the following domains:
Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) and Per/ARNT/Sim (PAS) Domain: SRC-3 contains a bHLH domain, which is involved in DNA binding and protein-protein interactions. The PAS domain contributes to the regulation of transcription by sensing changes in cellular signals and responding accordingly.
Receptor-Interaction Domain (RID): The RID of SRC-3 is crucial for its role as a coactivator. Within this domain are three LXXLL motifs (L represents leucine and X represents any amino acid), which are responsible for the interaction of SRC-3 with nuclear receptors, including the androgen receptor (AR). These motifs serve as binding sites for nuclear receptors, allowing SRC-3 to coactivate these receptors and enhance their transcriptional activity.
Transcriptional Activation Domains (AD1 and AD2): SRC-3 possesses two transcriptional activation domains, AD1 and AD2. These domains are responsible for activating the transcription of target genes. Additionally, SRC-3 contains a polyglutamate sequence (Q) within these domains, which contributes to its transcriptional activation function.
Histone Acetyltransferase (HAT) Activity: SRC-3 has HAT activity, which enables it to acetylate histone proteins within chromatin. Histone acetylation is a crucial epigenetic modification that relaxes chromatin structure, making it more accessible to transcriptional machinery and promoting gene expression.
Interactions with Transcription Factors and Coregulators: SRC-3 is a versatile coactivator that interacts with multiple transcription factors and coregulators. It forms complexes with nuclear receptors, such as the androgen receptor, estrogen receptor, and others. Additionally, SRC-3 interacts with various other coregulators and proteins involved in transcriptional regulation, creating a network of interactions that modulate gene expression.
SRC-3 as a Key Player in Prostate Cancer Progression
The reviewed studies consistently highlight the pivotal role of SRC-3 in Prostate Cancer progression. SRC-3, also known as Amplified in Breast Cancer 1 (AIB1), or Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 (NCoA3) emerges as a critical coactivator that directly interacts with the Androgen Receptor (AR) and plays a significant role in AR-driven transcriptional activity in Prostate Cancer cells [
13]. SRC-3's role in enhancing the chromatin accessibility at AR-binding sites and recruiting transcriptional machinery to target genes underscores its importance in the regulation of AR-dependent gene expression. The Androgen Receptor (AR) directly interacts with Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 (SRC-3) a member of Steroid Receptor Coactivator family proteins and boosts its transcriptional activity. The SRC family, which comprises SRC-1 (also known as NCOA-1), SRC-2 (NCOA-2), and SRC-3 (NCOA-3), is a group of three evolutionarily conserved coregulators of transcription. These coregulators play a crucial role in mediating the interaction between AR and the transcriptional machinery, ultimately influencing gene regulation.
SRC-1 expression is associated with prostate cancer aggressiveness, and suppressing SRC-1 expression reduced growth and altered AR target gene regulation in prostate cancer cells. However, in a murine prostate cancer model, SRC-1's role differs from that of SRC-3, which is essential for prostate cancer progression and metastasis in mice [
14]. SRC-2, is amplified in both primary and metastatic prostate cancer. Androgen deprivation induces SRC-2, activating PI3K signaling and promoting prostate cancer metastasis and castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) development [
15]. SRC-2 also stimulates reductive carboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate, supporting lipogenesis and metabolic reprogramming, which is strongly increased in metastatic prostate cancers [
16]. Compared with SRC-1 and SRC-2, markedly less is known concerning the individual functional role of SRC-3 in endometrial biology and dysfunction; this knowledge-gap is significant because expression studies indicate that this coregulator may have important roles in both endometrial contexts. SRC-3 expression is elevated in advanced prostate cancer, particularly in CRPC. It negatively correlates with PTEN expression and recurrence-free survival in prostate cancer patients. SRC-3 is essential for CRPC development by enhancing Akt activity and S6K1 expression [
14]. SPOP, a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer, promotes SRC-3 turnover via ubiquitination. Prostate cancer-associated SPOP mutants lose the ability to interact with SRC-3, impairing its ubiquitination [
17].
Androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer cells is augmented by the androgen receptor (AR) coactivator p300, which transactivates and acetylates the AR in the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) [
18]. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein binding protein (CBP) and p300 are other known AR coactivators with oncogenic roles in prostate cancer. Androgen deprivation upregulates CBP/p300 proteins in prostate cancers. Inhibition of the CBP/p300 bromodomain suppresses AR activity at the chromatin level, leading to the downregulation of proliferative gene expression and inhibiting CRPC tumor growth in vitro and in vivo [
19]. SRC-3 acts by enhancing the transcriptional activity of AR, leading to increased expression of genes involved in prostate cancer progression. These coactivator complexes related to AR have the effect of enhancing the accessibility of the chromatin structure at the AR-binding sites. This increased accessibility facilitates the recruitment of the transcriptional machinery required for gene expression. SRC-3 was also found to be a critical regulator of prostate cancer cell proliferation and survival. Studies suggest that it is required for the proliferation of prostate cancer cells, highlighting its role in promoting cancer growth [
20]. SRC-3 is amplified in both primary and metastatic prostate cancer, indicating its importance in the disease progression [
21]. SRC-3 acts as a co-activator, enhancing the activity of the Androgen Receptor (AR) in prostate cancer. This interaction contributes to the androgen signaling pathway, which is pivotal for prostate cancer development and progression [
22]. SRC-3's involvement in prostate cancer highlights its potential as a therapeutic target in the treatment of this disease. Understanding its role in AR signaling and cancer growth may lead to the development of targeted therapies for prostate cancer patients.
Furthermore, our analysis revealed that SRC-3's contribution to Prostate Cancer extends beyond its interaction with AR. The interplay between estrogen signaling and transcriptional coregulator activity has been extensively explored in hormone-dependent models of prostate cancer (PCa). In particular, the upregulated expression and heightened activity of SRC-3 play a pivotal role in driving the initiation and progression of breast cancers. SRC-3 gene amplification is observed in 5% to 10% of breast cancers, and the SRC-3 mRNA or protein is overexpressed by approximately 60% in various cohorts of breast cancer patients [
23]. Notably, SRC-3 overexpression is linked to more aggressive forms of breast cancer and poorer survival rates. Clinical data from breast cancer patients further reveal that high SRC-3 expression is associated with reduced disease-free survival [
24]. Genetic mouse models have demonstrated that the loss of SRC-3 reduces breast tumor incidence and delays tumor growth [
25].
SRC-3 has been shown to coactivate non-nuclear receptor transcription factors (TFs) such as PEA3, leading to the upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) [
26]. This highlights SRC-3's involvement in cancer invasion and metastasis, emphasizing its multifaceted role in disease progression. SRCs play a crucial role in modifying chromatin structure, facilitating transcription. They achieve this by directly or indirectly recruiting other coactivators, leading to chromatin remodeling, de-condensation, and the creation of a transcriptionally favorable environment at gene promoters. Additionally, SRCs possess histone-acetyltransferase activity, enabling them to directly acetylate histones and other chromatin regulators, thus promoting transcriptional activation [
27]. These coactivators participate in a complex gene regulatory network, influenced by various post-translational modifications (PTMs) like phosphorylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, acetylation, and methylation. PTMs on SRCs impact their stability, function, and ability to recruit proteins for transcriptome complex formation. Specific PTM patterns are critical for hormone-dependent tumor growth, proliferation, and metastasis. Phosphorylation of SRC-3, for instance, is associated with prognosis in ER-positive breast cancer and resistance to tamoxifen. Dysregulation of SRCs has been observed in various cancers, emphasizing the significance of coactivators in carcinogenesis [
28]. SRCs notably drive the progression of breast and prostate cancer, and their elevated expression is common in patient samples. Targeting coactivators like SRCs with small molecule inhibitors has shown promise in preclinical models, indicating potential therapeutic benefits. Clinical studies are needed to evaluate their efficacy in treating advanced breast and prostate cancer.
SRC-3 in the Context of Metabolic Reprogramming
Another intriguing aspect illuminated by the reviewed literature is SRC-3's involvement in metabolic reprogramming in Prostate Cancer [
29]. Metabolic reprogramming is a characteristic feature of cancer, describing the alteration of metabolic pathways and gene expression patterns to fuel increased cell proliferation and growth [
30]. This metabolic adaptation is crucial for the survival and spread of aggressive cancers. Even in the presence of oxygen, tumor cells utilize glucose as an energy source through a heightened rate of glycolysis, a phenomenon known as aerobic glycolysis or the Warburg effect [
31]. Although glycolysis is less efficient in terms of ATP production compared to oxidative phosphorylation, it generates additional metabolites that support the synthesis of large molecules required for rapid cell division. Enzymes within the glycolytic pathway, such as glucose-6 phosphate and fructose-6 phosphate, produce glycolytic intermediates that are redirected into the pentose phosphate pathway. This pathway is responsible for synthesizing nucleotides and regenerating dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH), which is essential for supporting tumor growth and metastasis [
32].
In addition to glucose, proliferating tumors exhibit an increased reliance on glutamine consumption, highlighting its critical role in metabolic reprogramming [
33]. Glutamine is converted into glutamate and eventually into α-ketoglutarate, which enters the citric acid cycle via anaplerotic reactions. This process provides energy and supports the synthesis of fatty acids, further fueling the demands of rapidly growing cancer cells. SRC-3 promotes reductive carboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate, facilitating lipogenesis and the reprogramming of glutamine metabolism [
34]. The SRC-3-driven metabolic signature is particularly pronounced in metastatic Prostate Cancers. This metabolic rewiring may play a crucial role in sustaining uncontrolled growth and survival in advanced Prostate Cancer. SRC-3 plays a pivotal role in metabolic reprogramming in castration-resistant prostate cancer, contributing to the altered metabolism observed in CRPC [
35]. Targeting SRC-3 and its associated metabolic pathways holds promise as a potential therapeutic strategy to combat this aggressive form of prostate cancer. SRC-3 is known to stimulate reductive carboxylation of alpha-ketoglutarate, a key metabolic process that promotes lipogenesis [
36]. This process provides cancer cells with the necessary lipids for membrane synthesis and energy storage. Additionally, SRC-3 is involved in the reprogramming of glutamine metabolism, which can provide an alternative source of energy and biosynthetic precursors for rapidly proliferating CRPC cells [
37].
Studies have shown that the metabolic signature associated with SRC-3 is strongly increased in metastatic prostate cancers [
38]. This suggests that SRC-3-dependent transcriptional reprogramming may play a crucial role in resetting the metabolic pathways of tumors to support uncontrolled growth and survival. These metabolic adaptations are essential for CRPC cells to thrive even in the absence of androgen signaling. Given its involvement in metabolic reprogramming, SRC-3 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target in CRPC. Inhibiting SRC-3 activity may disrupt the metabolic adaptations that fuel tumor growth and progression. Researchers are actively exploring the development of SRC-3 inhibitors as a strategy to target the metabolic vulnerabilities of CRPC cells. Understanding the role of SRC-3 in metabolic reprogramming provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying CRPC. It also opens up new avenues for the development of targeted therapies that can complement existing treatments for advanced prostate cancer.
Implications for Therapeutic Strategies
The insights gained from the reviewed literature have significant implications for therapeutic approaches in Prostate Cancer. Dysregulation of Steroid Receptor Coactivator-3 (SRC-3) in prostate cancer (PCa) has significant implications for therapeutic strategies. SRC-3 dysregulation offers a potential target for therapeutic interventions. Developing drugs that specifically inhibit SRC-3 activity or expression can be a promising approach to treat PCa [
39]. Such targeted therapies aim to disrupt the oncogenic functions of SRC-3 and inhibit its contribution to tumor progression. Combining SRC-3-targeted therapies with existing treatments like androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) or chemotherapy could enhance therapeutic outcomes. SRC-3 dysregulation often occurs alongside other molecular changes in PCa, and combination therapies may address multiple pathways driving cancer progression. Targeting SRC-3 and its coactivation mechanisms, particularly in the context of AR-driven transcription, may hold promise as a therapeutic strategy. Strategies to disrupt SRC-3-AR interactions or inhibit SRC-3 expression and activity could be explored to potentially mitigate the progression of Prostate Cancer. In a comparative investigation conducted by Gilad et al., they identified SRC-3 as a unique target within the realm of endocrine therapies [
40]. Apart from its role as a significant regulator of estrogen receptor transcriptional functions, SRC-3 also acts as a coactivator for a diverse array of other transcription factors, indicating that inhibiting SRC-3 could have potential advantages in hormone-independent cancers. The recent unveiling of a potent small molecule inhibitor of SRC-3, known as SI-2, has paved the way for the advancement of related compounds. SI-12 represents an enhanced iteration of SI-2 and, much like its predecessor, exhibits anti-proliferative properties across various cancer types.
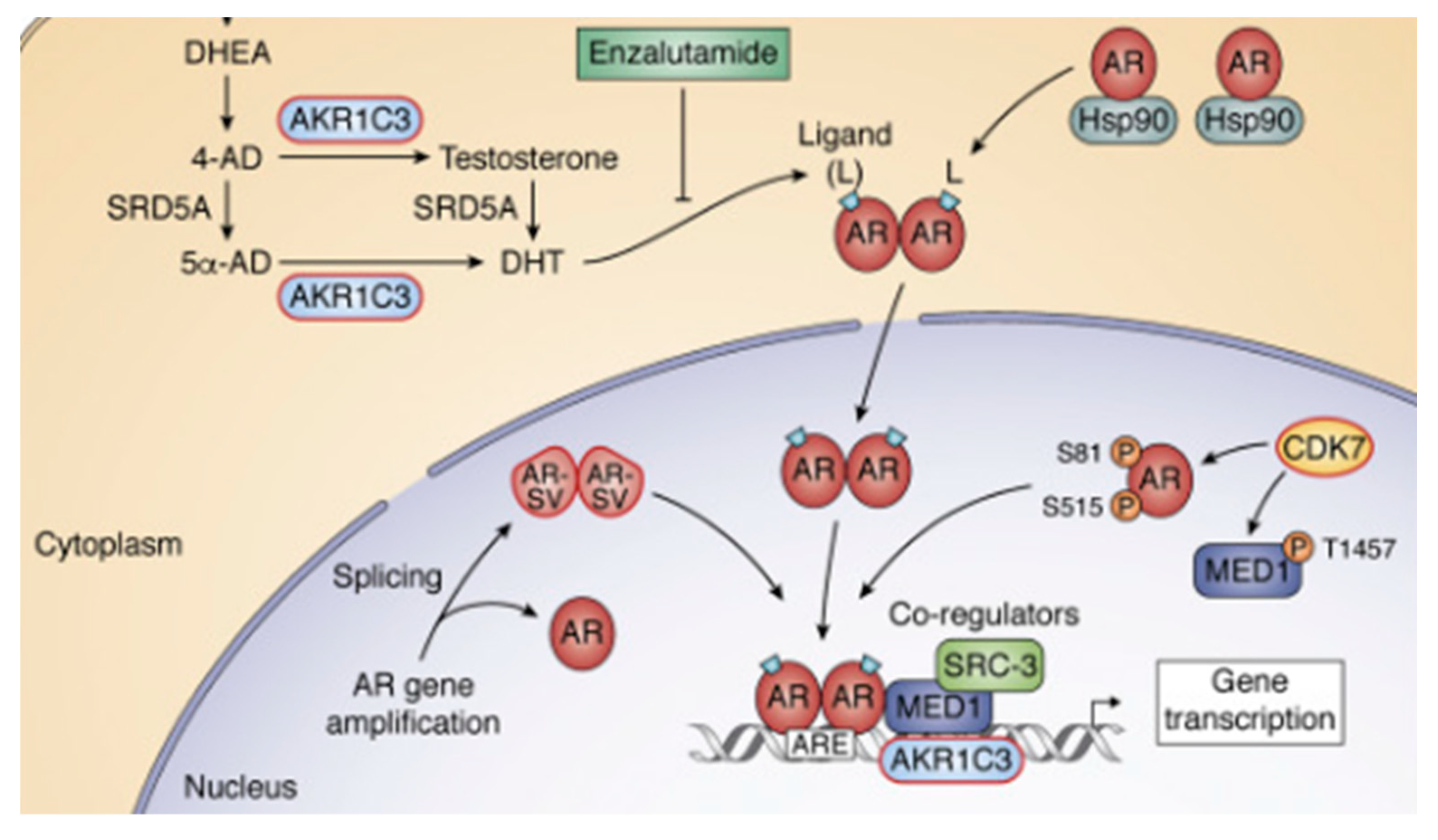
The coactivator role of SRC-3 on AR signaling in prostate cancer and its opportunity for targeting in CRPC (Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer) are pivotal aspects of this review. In CRPC, the activation of the AR signaling pathway initiates with the intratumoral synthesis of testosterone (T) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a process catalyzed by AKR1C3 [
21]. Subsequently, DHT binds to AR, which is initially sequestered by Hsp90 in the cytosol. This binding leads to the translocation of the dimerized AR to the nucleus, where it interacts with androgen response elements (AREs) in the promoters of responsive genes.
Figure 5 illustrates the sites of action for two ARSI (Androgen Receptor Signaling Inhibitor) therapies, abiraterone and enzalutamide. Additionally, it highlights alternative forms of AR, denoted as AR-SV, which are transcriptionally active even in the absence of ligands, and phosphorylated forms of AR [
41]. The recruitment of coregulatory; SRC-3 to the transcriptional complex is also depicted. Notably, within the context of eradicating AR signaling, the review identifies specific protein targets highlighted in red boxes. These targets are crucial in understanding and potentially disrupting the AR signaling pathway in the context of prostate cancer and CRPC.
A study demonstrated that Bufalin effectively targets the SRC-3 protein to reduce the release of MIF (Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor) in chemoresistant cells [
42]. This reduction in MIF plays a crucial role in regulating the polarization of M2 macrophages, which are known to contribute significantly to tumor chemoresistance. Previous research has indicated that Bufalin possesses notable anti-tumor properties, including the ability to decrease the polarization of M2 macrophages in vivo. However, the precise mechanisms underlying this effect have remained unclear. It was observed that Bufalin successfully reduced the polarization of M2 macrophages induced by chemoresistant cells, both in laboratory settings (in vitro) and within living organisms (in vivo). Notably, the study also revealed that Cinobufacini, a medicinal product containing Bufalin as its primary active component, could effectively regulate M2 macrophage polarization. This regulation enhanced the anti-tumor efficacy of oxaliplatin, a chemotherapy agent, both in experimental settings and in clinical applications. This research provides valuable insights into the potential clinical use of Bufalin-containing drugs, particularly in combination with established chemotherapy, for the treatment of colorectal cancer [
42].
In ovarian cancer cell lines, both SRC-3 and TRAF4 exhibited increased expression levels. Investigations unveiled that the interplay between SRC-3 and TRAF4 plays a pivotal role in promoting various aspects of ovarian cancer progression, including cell growth, migration, invasion, and the maintenance of stemness properties [
43]. These effects are primarily mediated through the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. When SRC-3 was silenced, there was a notable reduction in TRAF4 expression. Consequently, the silencing of either SRC-3 or TRAF4 resulted in the inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, invasion, as well as the expression of key stem cell-related factors. Moreover, another study demonstrated that the suppression of SRC-3 or TRAF4, along with the use of LY294002 (an inhibitor of the PI3K/AKT pathway), effectively hindered the phosphorylation of Akt and PI3K. This inhibition subsequently repressed the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ovarian cancer cell lines. The overexpression of TRAF4 counteracted the effects of SRC-3 silencing, thereby reinstating cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and stemness properties. These findings underscore the intricate interplay between SRC-3 and TRAF4 and their significant roles in modulating ovarian cancer progression through the PI3K/AKT pathway [
43].
Additionally, SRC-3 plays a significant role in clinical resistance to tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors [
44]. This resistance is attributed to SRC-3's involvement downstream of growth factor signaling pathways, enabling it to circumvent the inhibition of ER in Breast Cancer cells. Genomic changes have also been identified that contribute to endocrine therapy resistance, including mutations in the ligand-binding domain of the ER gene, allowing receptor activation in the absence of estrogen signaling [
45]. Upstream signaling, including metabolic cues impacting SRC-3, is crucial for inducing hormone-independent activation of target genes. Promisingly, drugs targeting SRC-3, such as phospho-bufalin and SI-2, have shown favorable effects in mouse models of Breast Cancer [
46]. These findings collectively underscore the significance of SRC activity in the context of Breast Cancer and its potential as a therapeutic target. Assessing the status of SRC-3 dysregulation in PCa patients can serve as a valuable biomarker. Identifying patients with elevated SRC-3 expression or activity could help tailor treatment strategies. Patients with SRC-3 dysregulation might benefit more from SRC-3-targeted therapies. SRC-3 dysregulation has been linked to resistance to endocrine therapies like ADT [
47]. Understanding how SRC-3 contributes to treatment resistance can inform the development of strategies to overcome this resistance. This could involve combination therapies or novel approaches to target SRC-3-driven resistance mechanisms. The study of SRC-3 dysregulation in PCa underscores the importance of personalized medicine. Tailoring treatments based on the specific molecular characteristics of a patient's tumor, including SRC-3 status, can improve treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects. Clinical trials evaluating SRC-3-targeted therapies are essential. These trials can provide critical data on the safety and efficacy of novel treatments. The results can guide the development of approved therapies for PCa patients. SRC-3 dysregulation in prostate cancer offers both challenges and opportunities for therapeutic strategies. Targeting SRC-3 and understanding its role in treatment resistance can potentially lead to more effective and personalized treatments for PCa patients. However, rigorous clinical testing and ongoing research are necessary to translate these findings into improved clinical outcomes.
Limitations and Future Directions
While the reviewed literature provides valuable insights, it is essential to acknowledge certain limitations. The heterogeneity in study designs, patient cohorts, and methodologies across the selected articles can pose challenges in synthesizing results. Future research efforts should focus on standardized approaches and larger, more diverse patient cohorts to validate and extend the findings.