Submitted:
04 October 2023
Posted:
09 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We propose a simple framework exploiting contrastive learning to MIM to learn rich and holistic representation. The model learns discriminative representation by contrasting two augmented views, while reconstructing original signals from the corrupted ones.
- A high masking ratio works as strong augmentation. Without additional augmentation like color distortion, blur, etc., our model shows better performance than previous CL-based methods by only using masking and random crop.
- Experimental results prove that our work is effective, outperforming previous MIM methods in ImageNet-1K classification, linear probing and other downstream tasks like object detection and instance segmentation.
2. Related Work
2.1. Contrastive Learning
2.2. Masked Language Modeling and Masked Image Modeling
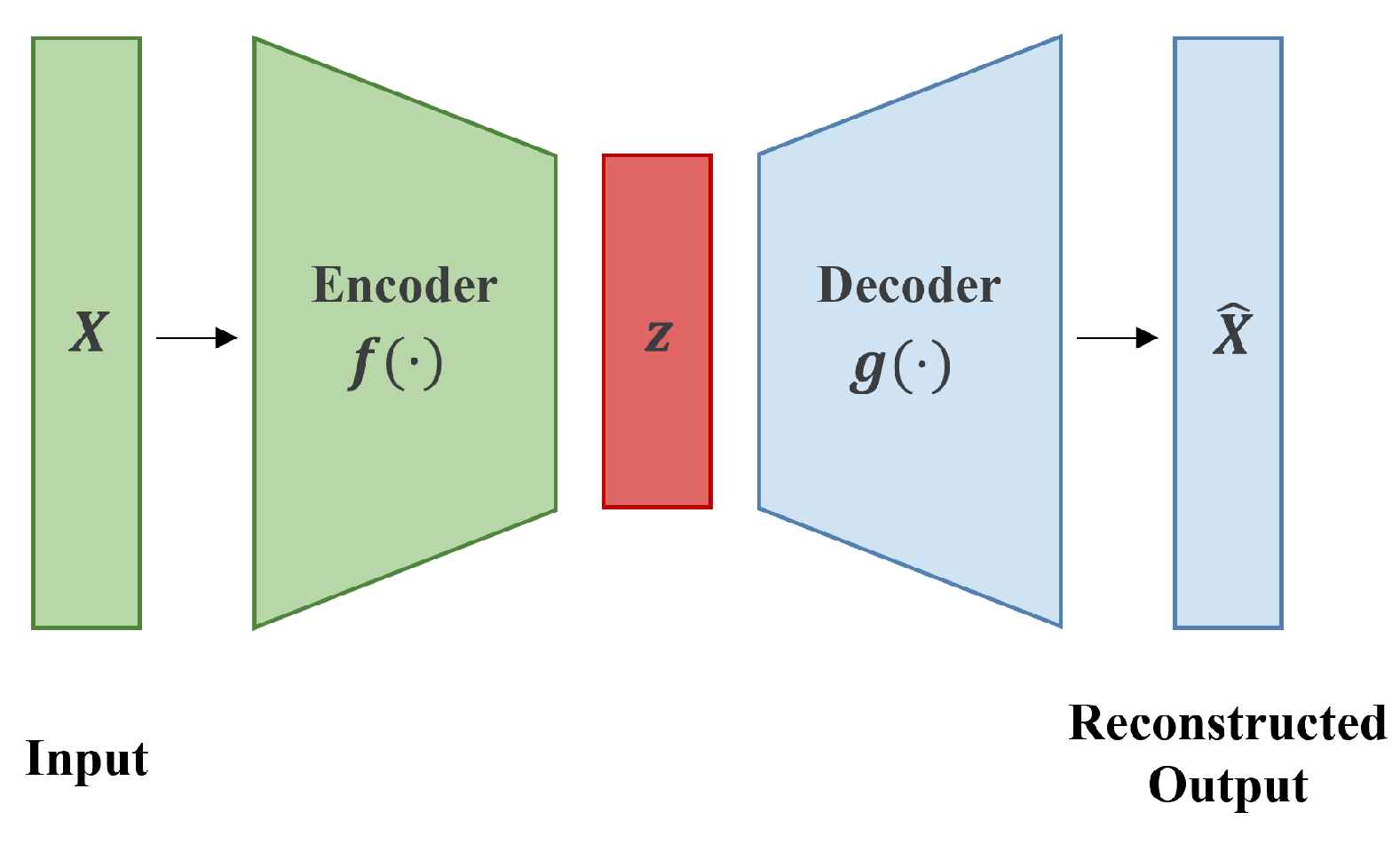
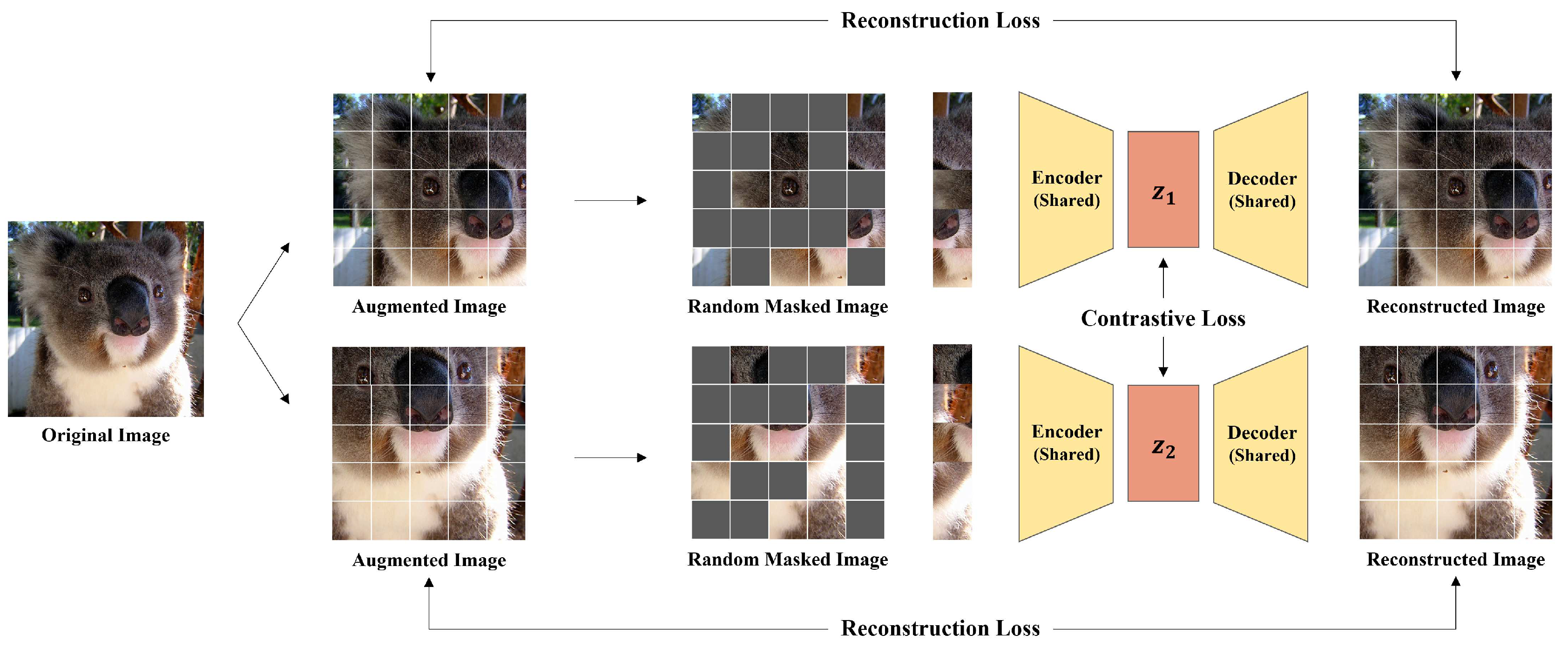
3. Method
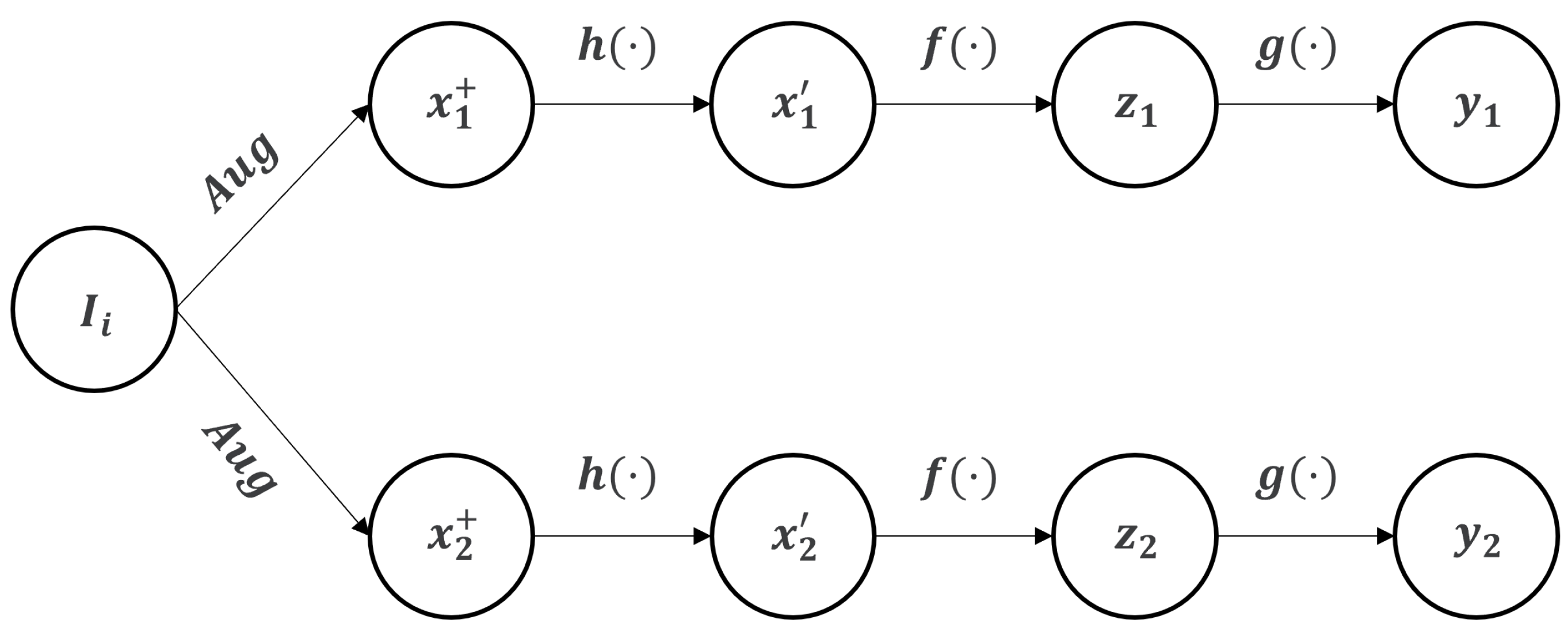
3.1. Framework
3.1.1. Input and Target Views
3.1.2. Patchify and Masking Strategy
3.1.3. Encoder
3.1.4. Decoder
3.2. Training Objectives
3.2.1. Reconstruction loss
3.2.2. Contrastive loss
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation details
4.1.1. Pre-training
4.1.2. Fine-tuning
4.1.3. Linear Probing
4.2. Experimental Results
| Method | AP | AP |
|---|---|---|
| MoCo-v3 [32] | 47.9 | 42.7 |
| BeiT [2] | 49.8 | 44.4 |
| CAE [36] | 50.0 | 44.0 |
| SimMIM [35] | 52.3 | - |
| MAE [23] | 50.3 | 44.9 |
| Ours | 51.3 | 45.6 |
| Method | mIOU |
|---|---|
| MoCo-v3 [32] | 47.3 |
| BeiT [2] | 47.1 |
| CAE [36] | 50.2 |
| SimMIM [35] | 52.8 |
| MAE [23] | 48.1 |
| Ours | 50.2 |
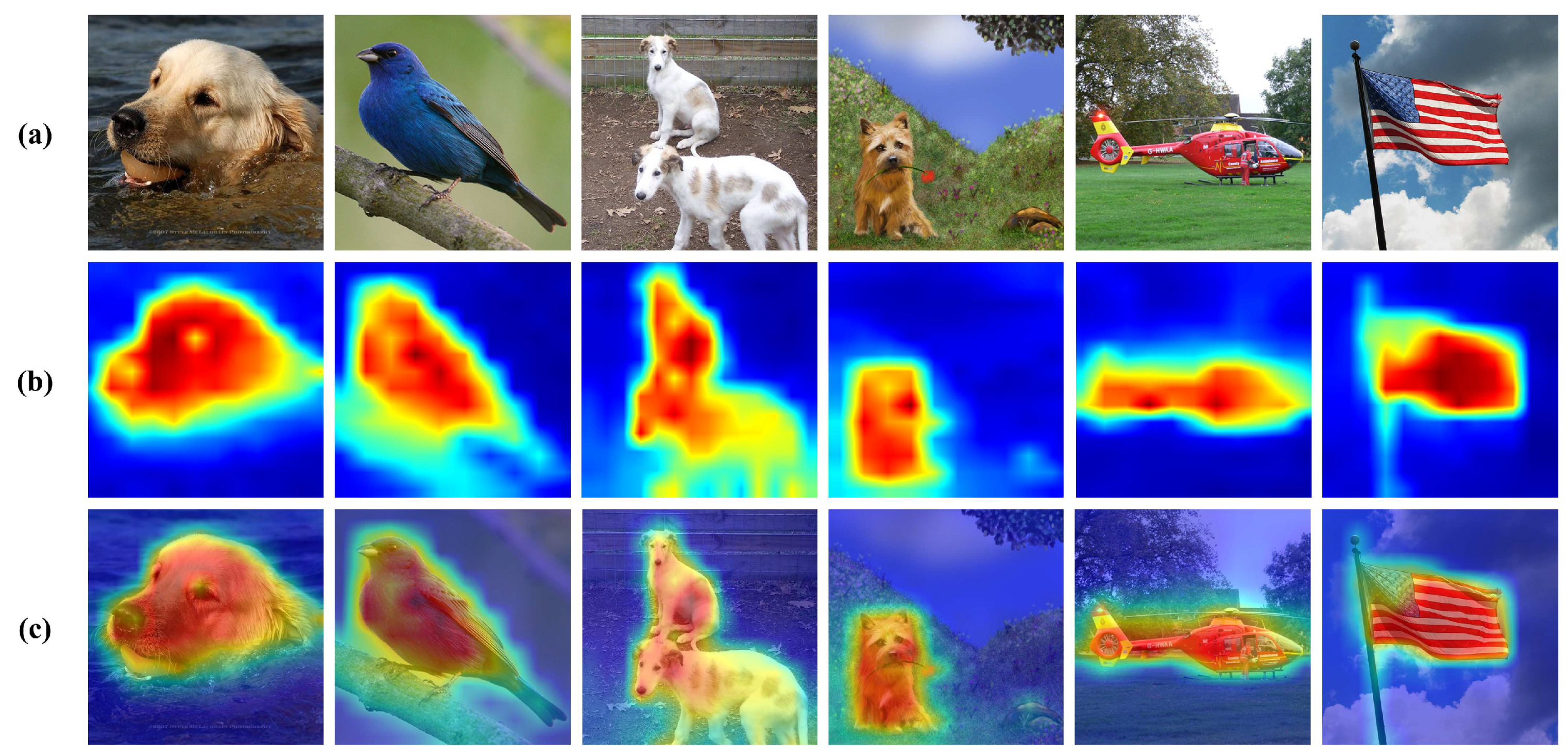
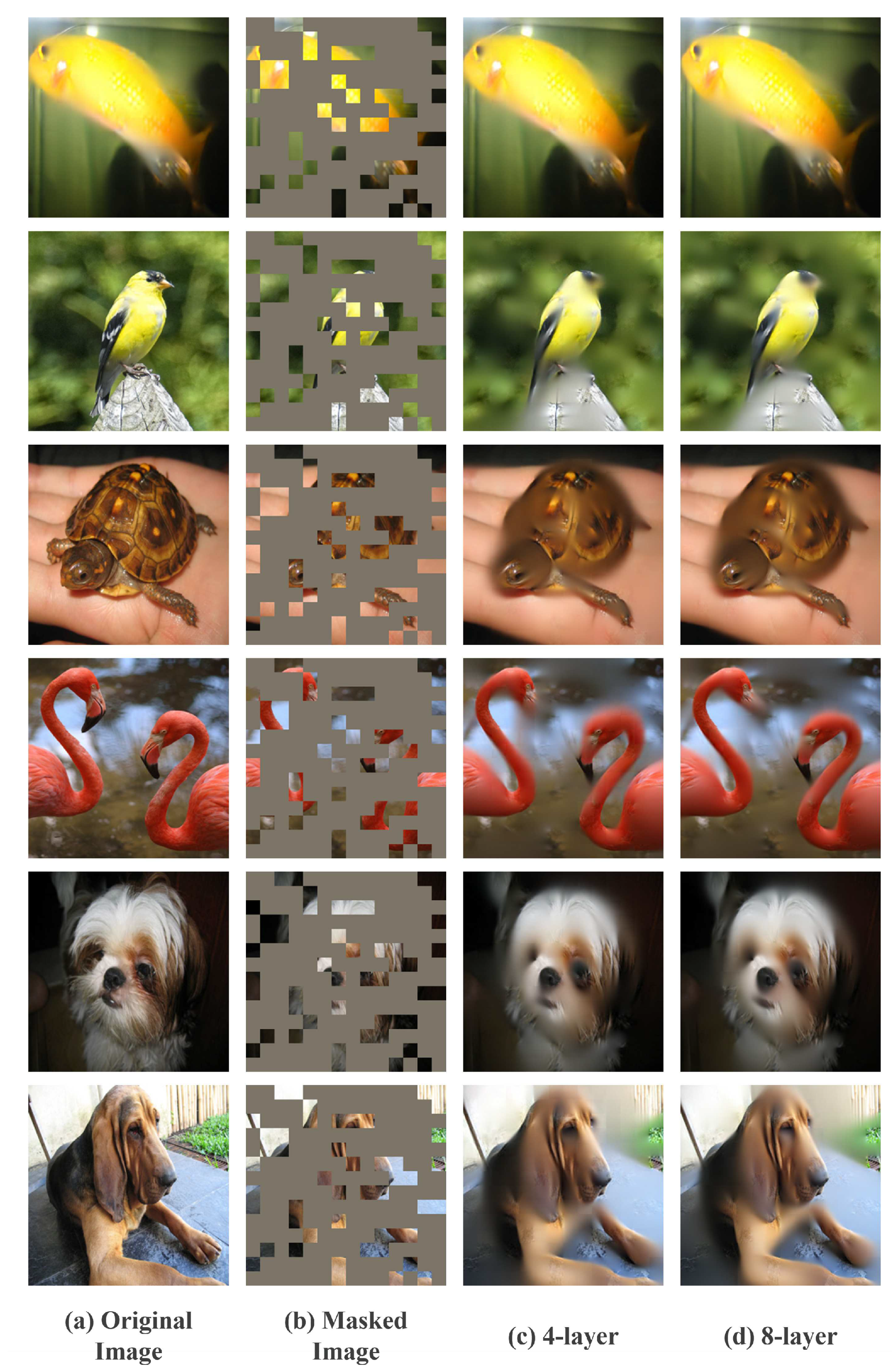
4.2.1. Architecture Analysis
| Mask Ratio | Accuracy | Loss Weight | Accuracy | Decoder Depth | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 79.22 | 0.1 | 78.10 | 1 | 74.89 |
| 75% | 79.09 | 0.5 | 78.09 | 2 | 78.56 |
| 80% | 79.25 | 1 | 78.09 | 4 | 80.03 |
| 90% | 79.23 | 1.5 | 79.31 | 8 | 80.03 |
| 95% | 78.30 | 2.0 | 79.64 | 12 | 79.11 |
4.3. Ablation Studies
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. Beit: Bert pre-training of image transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.08254 2021.
- Liu, Y.; Sangineto, E.; Bi, W.; Sebe, N.; Lepri, B.; Nadai, M. Efficient training of visual transformers with small datasets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2021, 34, 23818–23830. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, A.; Babu, A.R.; Zadeh, M.Z.; Banerjee, D.; Makedon, F. A survey on contrastive self-supervised learning. Technologies 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, F.; Hou, Z.; Mian, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J. Self-supervised learning: Generative or contrastive. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering 2021, 35, 857–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrycks, D.; Mazeika, M.; Kadavath, S.; Song, D. Using self-supervised learning can improve model robustness and uncertainty. Advances in neural information processing systems 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Oliver, A.; Kolesnikov, A.; Beyer, L. S4l: Self-supervised semi-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2019, pp.; pp. 1476–1485.
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Song, J.; Yi, J.S.K.; Zhang, K.; Kweon, I.S. A survey on masked autoencoder for self-supervised learning in vision and beyond. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.00173 2022. arXiv:2208.00173 2022.
- Ng, A.; et al. Sparse autoencoder. CS294A Lecture notes 2011, 72, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bank, D.; Koenigstein, N.; Giryes, R. Autoencoders. Machine Learning for Data Science Handbook: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, 2023; 353–374. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Lajoie, I.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A.; Bottou, L. Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. Journal of machine learning research 2010, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A. Extracting and composing robust features with denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning, 2008, pp.; pp. 1096–1103.
- Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; Hinton, G. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR; 2020; pp. 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Caron, M.; Touvron, H.; Misra, I.; Jégou, H.; Mairal, J.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Emerging properties in self-supervised vision transformers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2021, pp.; pp. 9650–9660.
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2020, pp.; pp. 9729–9738.
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I.; et al. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training 2018.
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 2018. arXiv:1810.04805 2018.
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. Roberta: A robustly optimized bert pretraining approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692 2019. arXiv:1907.11692 2019.
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp.; pp. 770–778.
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30.
- Battaglia, P.W.; Hamrick, J.B.; Bapst, V.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, A.; Zambaldi, V.; Malinowski, M.; Tacchetti, A.; Raposo, D.; Santoro, A.; Faulkner, R.; et al. Relational inductive biases, deep learning, and graph networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.01261 2018. arXiv:1806.01261 2018.
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 2020. arXiv:2010.11929 2020.
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2022, pp.; pp. 16000–16009.
- Chen, X.; Ding, M.; Wang, X.; Xin, Y.; Mo, S.; Wang, Y.; Han, S.; Luo, P.; Zeng, G.; Wang, J. Context autoencoder for self-supervised representation learning. International Journal of Computer Vision 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, M.; Misra, I.; Mairal, J.; Goyal, P.; Bojanowski, P.; Joulin, A. Unsupervised learning of visual features by contrasting cluster assignments. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 9912–9924. [Google Scholar]
- Park, N.; Kim, W.; Heo, B.; Kim, T.; Yun, S. What Do Self-Supervised Vision Transformers Learn? arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.00729 2023. arXiv:2305.00729 2023.
- Abnar, S.; Zuidema, W. Quantifying attention flow in transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00928 2020. arXiv:2005.00928 2020.
- Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Girshick, R.; He, K. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.04297 2020. arXiv:2003.04297 2020.
- Grill, J.B.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; Tallec, C.; Richemond, P.; Buchatskaya, E.; Doersch, C.; Avila Pires, B.; Guo, Z.; Gheshlaghi Azar, M.; et al. Bootstrap your own latent-a new approach to self-supervised learning. Advances in neural information processing systems 2020, 33, 21271–21284. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Krishnan, D.; Isola, P. Contrastive multiview coding. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28; Proceedings, Part XI 16. Springer, 2020; pp. 776–794. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, C.; Pham, T.X.; Yoo, C.D.; Kweon, I.S. How does simsiam avoid collapse without negative samples? a unified understanding with self-supervised contrastive learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.16262 2022. arXiv:2203.16262 2022.
- Chen, X.; Xie, S.; He, K. An Empirical Study of Training Self-Supervised Vision Transformers. arXiv e-prints 2021, p. arXiv:2104.02057, [arXiv:cs.CV/2104.02057]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2104.02057. arXiv:cs.CV/2104.02057. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Radford, A.; Child, R.; Wu, J.; Jun, H.; Luan, D.; Sutskever, I. Generative pretraining from pixels. In Proceedings of the International conference on machine learning. PMLR; 2020; pp. 1691–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Ramesh, A.; Pavlov, M.; Goh, G.; Gray, S.; Voss, C.; Radford, A.; Chen, M.; Sutskever, I. Zero-shot text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR; 2021; pp. 8821–8831. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Bao, J.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Q.; Hu, H. Simmim: A simple framework for masked image modeling. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp.; pp. 9653–9663.
- Fang, Y.; Dong, L.; Bao, H.; Wang, X.; Wei, F. Corrupted image modeling for self-supervised visual pre-training. arXiv preprint, 2022; arXiv:2202.03382 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wettig, A.; Gao, T.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, D. Should you mask 15% in masked language modeling? arXiv preprint, 2022; arXiv:2202.08005. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Ieee; 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6-12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, H.; Puig, X.; Fidler, S.; Barriuso, A.; Torralba, A. Scene parsing through ade20k dataset. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2017; pp. 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1710.09412.
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops, 2020, pp.; pp. 702–703.
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV); 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2017; pp. 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, S.; Chen, X.; Dollár, P.; He, K.; Girshick, R.B. Benchmarking Detection Transfer Learning with Vision Transformers. arXiv, 2021; arXiv: abs/2111.11429. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. Unified perceptual parsing for scene understanding. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV); 2018; pp. 418–434. [Google Scholar]
- Kornblith, S.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Do better imagenet models transfer better? In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2019; pp. 2661–2671. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Li, Y.; Vinyals, O. Representation learning with contrastive predictive coding. arXiv preprint, 2018; arXiv:1807.03748. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikov, A.; Zhai, X.; Beyer, L. Revisiting self-supervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2019, pp.; pp. 1920–1929.
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2019, pp.; pp. 6023–6032.
| Model | Approach | Training Epochs | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| SimCLR [13] | CL | 1000 | 80.4 |
| MoCo-v3 [32] | CL | 300 | 83.2 |
| DINO [14] | CL | 300 | 82.8 |
| CIM [36] | MIM | 300 | 83.3 |
| BEiT [2] | MIM | 800 | 83.2 |
| SimMIM [35] | MIM | 800 | 83.8 |
| CAE [24] | MIM | 1600 | 83.9 |
| MAE [23] | MIM | 1600 | 83.6 |
| Ours | MIM+CL | 800 | 83.2 |
| Ours | MIM+CL | 1600 | 84.3 |
| Method | Approach | Pre-training Epochs | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| SimCLR [13] | CL | 1000 | 76.5 |
| MoCo-v3 [32] | CL | 300 | 76.7 |
| DINO [14] | CL | 300 | 78.2 |
| BEiT [2] | MIM | 800 | 56.7 |
| SimMIM [35] | MIM | 800 | 56.7 |
| CAE [24] | MIM | 1600 | 71.4 |
| MAE [23] | MIM | 1600 | 68.0 |
| Ours | MIM+CL | 1600 | 76.7 |
| Methods | Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Ours | 79.09 |
| Ours w/o two different targets | 77.86 |
| Ours w/o contrastive loss | 74.33 |
| baseline [23] | 76.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





