Submitted:
15 November 2023
Posted:
16 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
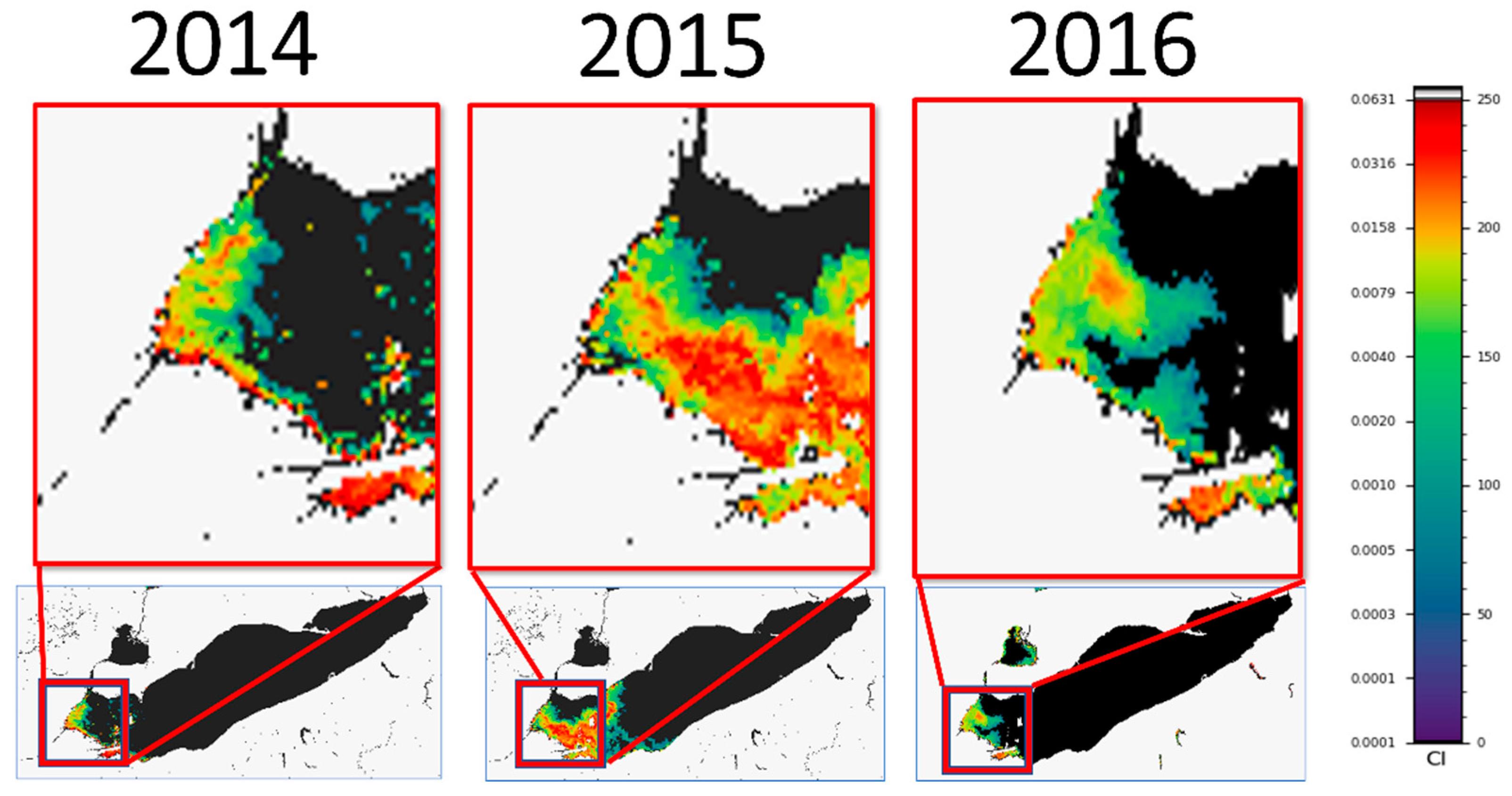
2.1. Case 1
2.2. Case 2
2.3. Case 3
| Patient | Reference Range | Case #1 | Case #2 | Case #3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) | 16 | 14 | 7 | |
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | |
| CyanoHAB Exposure | Summer 2016 | Summer 2015 | Summer 2014 | |
| PMHx | No significant PMHx | MRSA and depression | Asthma | |
| Means of Exposure | Swimming (Maumee river) | Swimming (Maumee Bay) | Swimming (Maumee Bay) | |
| Menstruation | Yes (with tampon) | Yes (with tampon) | No | |
| Primary Symptoms on admission |
Generalized macular rash, fever, headache, genital ulcers | Generalized macular rash, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration | Listless, tachycardia, diminished breath sounds and severe respiratory distress | |
| WBC (x1000 per µL) | 5.5-15×109 L-1 | 3.6 | 22.5 | 15 |
| Band (%) | N/A | 26% | 20% | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.9-14.4 g/dL | 13.2 | 13.3 | 12.2 |
| Platelets (x1000 per µL) | 150-450 | 94 | 247 | 467 |
| AST (U/L) | 0-41 U/L | 192 | 32 | 24 |
| ALT (U/L) | 0-40 U/L | 211 | 15 | 18 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.3-1 mg/dL | 0.84 | 1.29 | 0.39 |
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malcolm, A. Barnard, J.D.C., Haley E. Plaas, Gregory L. Boyer, Bofan Wei, Steven W. Wilhelm, Karen L. Rossignol, Jeremy S. Braddy, George S. Bullerjahn, Thomas B. Bridgeman, Timothy W. Davis, Jin Wei, Minsheng Bu, and Hans W. Paerl. Roles of Nutrient Limitation on Western Lake Erie CyanoHAB Toxin Production. Toxins 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya Yadav, R.P.S. , Shashank Rana, Diksha Joshi, Dharmendra Kumar, Nikunj Bhardwaj, Rajan Kumar Gupta, and Ajay Kumar. Mechanisms of Stress Tolerance in Cyanobacteria under Extreme Conditions. Stresses 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jef Huisman, G.A.C. , Hans W. Paerl, Bas W. Ibelings, Jolanda M. H. Verspagen, & Petra M. Visser Cyanobacterial blooms. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael WW, B.G. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjali Singh, P.K.B. Chapter 20 - Dynamics of harmful cyanobacterial blooms and their toxins: environmental and human health perspectives and management strategies; Academic Press: ScienceDirect, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Apurva Lad, J.D.B. , Robin C. Su, Jordan Murray, Rebecca Kuang, Alison Mascarenhas, John Najjar, Shivani Patel, Prajwal Hegde, Mirella Youssef, Jason Breuler, Andrew L. Kleinhenz, Andrew P. Ault, Judy A. Westrick, Nikolai N. Modyanov, David J. Kennedy, and Steven T. Haller. As We Drink and Breathe: Adverse Health Effects of Microcystins and Other Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins in the Liver, Gut, Lungs and Beyond. Life 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Baliu-Rodriguez, N.J.P. , Sanduni H. Premathilaka, Johnna A. Birbeck, Tomás Baliu-Rodriguez, Judy A. Westrick, and Dragan Isailovic. Identification of Novel Microcystins Using High-Resolution MS and MSn with Python Code. Environmental Science & Technology 2022, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena Ufelmann, T.K. , Bernd Luckas, Dieter Schrenk. Human and rat hepatocyte toxicity and protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitory activity of naturally occurring desmethyl-microcystins and nodularins. Toxicology 293. [CrossRef]
- Xing, N.W.a.Y. PP2A as a master regulator of the cell cycle. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2016, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrine Cestèle, W.A.C. Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxin action on voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayler, K.D.C.a.G.S. An Overview on the Marine Neurotoxin, Saxitoxin: Genetics, Molecular Targets, Methods of Detection and Ecological Functions. Marine Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisabete Valério, S.C. , Rogério Tenreiro. Diversity and Impact of Prokaryotic Toxins on Aquatic Environments: A Review. Toxins 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole, E. Olson, M. E.C., Jia H. Shi, Johnna A. Birbeck, Judy A. Westrick, and Andrew P. Ault. Harmful Algal Bloom Toxins in Aerosol Generated from Inland Lake Water. 2020, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, D. Breidenbach, B.W.F., Tamiya T. Gordon, Andrew L. Kleinhenz, Fatimah K. Khalaf, James C. Willey, Jeffrey R. Hammersley, R. Mark Wooten, Erin L. Crawford, Nikolai N. Modyanov, Deepak Malhotra, Justin G. Teeguarden, Steven T. Haller, David J. Kennedy. Microcystin-LR aerosol induces inflammatory responses in healthy human primary airway epithelium. Environment International 2022, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damjana Drobac Backović, N.T. , Borislava Nikolin, Zorica Svirčev. Cyanobacteria – insidious foe of the skin? Water & Health 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marisa Chattman Nielsen, S.C.J. Can cyanotoxins penetrate human skin during water recreation to cause negative health effects? Harmful Algae 2020, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi Xiao, S.A. , Yaoru Pan, Yan Yu, Ke Li, Jiaping Wu, and Carlos M. Duarte. Warming Amplifies the Frequency of Harmful Algal Blooms with Eutrophication in Chinese Coastal Waters. Environmental Science & Technology 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shideh Pouria, A.d.A. , J Barbosa, RL Cavalcanti, VTS Barreto, CJ Ward, W Preiser, Grace K Poon, GH Neild, GA Codd. Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. The Lancet 1998, 352, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timothy, W. Davis, R.S., George S. Bullerjahn, Robert Michael L. McKay, Justin D. Chaffin, Thomas B. Bridgeman, Christopher Winslow. Science meets policy: A framework for determining impairment designation criteria for large waterbodies affected by cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2019, 81, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justin, D. Chaffin, T.W.D., Derek J. Smith, Mikayla M. Baer, Gregory J. Dick. Interactions between nitrogen form, loading rate, and light intensity on Microcystis and Planktothrix growth and microcystin production. Harmful Algae 2018, 73, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, P. Stumpf, L.T.J., Timoty T. Wayne, David B. Baker. Forecasting annual cyanobacterial bloom biomass to inform management decisions in Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research 2016, 42, 1174–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leticia Díez-Quijada, A.I.P. , Remedios Guzmán-Guillén, Angeles Jos, Ana M. Cameán. Occurrence and toxicity of microcystin congeners other than MC-LR and MC-RR: A review. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2019, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muwaffak Alosman, L.C. , Isaac Yaw Massey, & Fei Yang. The lethal effects and determinants of microcystin-LR on heart: a mini review. Toxin Reviews 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadine Saul, S.C. , Stephen R. Stürzenbaum, Ralph Menzel, Christian E.W. Steinberg. Neurotoxic action of microcystin-LR is reflected in the transcriptional stress response of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chemico-Biologic Interactions 2014, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David Baliu-Rodriguez, D.K. , Dilrukshika S. W. Palagama, Apurva Lad, Grace M. O’Neill, Johnna A. Birbeck, David J. Kennedy, Steven T. Haller, Judy A. Westrick, and Dragan Isailovic. Development and Application of Extraction Methods for LC-MS Quantification of Microcystins in Liver Tissue. Toxins 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilrukshika, S.W. Palagama, D.B.-R., Apurva Lad, Bruce S. Levison, David J. Kennedy, Steven T. Haller, Judy Westrick, Kenneth Hensley, Dragan Isailovic. Development and applications of solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry methods for quantification of microcystins in urine, plasma, and serum. Journal of Chromatography A 2018, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daria Kucheriavaia, D.V. , Nicholas Peraino, Apurva Lad, David J. Kennedy, Steven T. Haller, Judy A. Westrick, and Dragan Isailovic. Toward Revealing Microcystin Distribution in Mouse Liver Tissue Using MALDI-MS Imaging. Toxins 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin C Su, A.L. , Joshua D Breidenbach, Andrew L Kleinhenz, Nikolai Modyanov, Deepak Malhotra, Steven T Haller, David J Kennedy. Assessment of diagnostic biomarkers of liver injury in the setting of microcystin-LR (MC-LR) hepatotoxicity. Chemosphere 2020, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apurva Lad, R.C.S. , Joshua D. Breidenbach, Paul M. Stemmer, Nicholas J. Carruthers, Nayeli K. Sanchez, Fatimah K. Khalaf, Shungang Zhang, Andrew L. Kleinhenz, Prabhatchandra Dube, Chrysan J. Mohammed, Judy A. Westrick, Erin L. Crawford, Dilrukshika Palagama, David Baliu-Rodriguez, Dragan Isailovic, Bruce Levison, Nikolai Modyanov, Amira F. Gohara, Deepak Malhotra, Steven T. Haller, and David J. Kennedy. Chronic Low Dose Oral Exposure to Microcystin-LR Exacerbates Hepatic Injury in a Murine Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Toxins 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, C. Su, T.M.B., Andrew L. Kleinhenz, Fatimah K. Khalaf, Prabhatchandra Dube, Apurva Lad, Joshua D. Breidenbach, Chrysan J. Mohammed, Shungang Zhang, Caitlin E. Baum, Deepak Malhotra, David J. Kennedy, and Steven T. Haller. Exposure to the Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB) Toxin Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) Prolongs and Increases Severity of Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Colitis. Toxins 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Agency | Resource & Description |
|---|---|
| World Health Organization (WHO) International Classification of Diseases (ICD) |
ICD-10-CM codes recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) for use in diagnosing and recording CyanoHAB-related exposure and illnesses: Z77.121: Contact with and (suspected) exposure to harmful algae and algae toxins T65.82: Toxic effect harmful algae & algae toxins WHO guidelines: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/toxic-cyanobacteria-in-water---second-edition |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | |
| Harmful Algal Bloom-Associated Illness Fact Sheets and Reference Cards (Physician Reference, Cyanobacteria FAQ, Facts about Cyanobacterial Blooms for Poison Center Professionals) https://www.cdc.gov/habs/materials/factsheets.html | |
| One Health Harmful Algal Bloom Reporting System (OHHABS) | Infosheet on OHHABS Reporting, including summary information on CyanoHABs and those who may be affected and helping https://www.cdc.gov/habs/pdf/ohhabs-reporting-flow-diagram-508.pdf |
|
Factsheet on CyanoHABs from OHHABS, providing digestible information on CyanoHABs, reporting, surveillance, and current systems in place. https://www.cdc.gov/habs/pdf/ohhabs-fact-sheet.pdf User Resources for the: One Health Harmful Algal Bloom System (OHHABS) and National Outbreak Reporting System (NORS) https://www.cdc.gov/habs/pdf/ohhabs-fact-sheet.pdf | |
| Great Lakes HABs Collaborative | Information on Harmful Algal Blooms and Human Health Effects https://www.glc.org/wp-content/uploads/HABS-FactSheet-Chronic-Health-202205.pdf Easily digestible text and graphics for the inhalation risks of CyanoHAB toxins https://www.glc.org/wp-content/uploads/HABS-FactSheet-Toxins-in-Air-202205.pdf |
| Ohio Department of Health2 | Reporting Human Illness from Recreational CyanoHAB Exposure https://odh.ohio.gov/know-our-programs/harmful-algal-blooms/forms/habs-illness-form-recreation Reporting Human Illness from Ingestion of CyanoHAB Contaminated Waters https://odh.ohio.gov/know-our-programs/harmful-algal-blooms/forms/habs-human-illness-form-drinking |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





