1. Introduction
Thymoquinone (TQ) 2-Methyl-5-(propan-2-yl) cyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione is the main bioactive component found in the volatile oil of
Nigella sativa seeds [
1]. It has been used in conventional medicine for centuries as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and anticancer agent [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6]. In skin, for example, TQ has shown potential for treating acne vulgaris, pigmentation, vitiligo, hypersensitivity reactions, psoriasis, and even early stages of skin tumorigenesis [
7,
8,
9]. Most of these beneficial health effects can be attributed to the free radical scavenging effects of TQ and the induction of antioxidant enzymes [
10,
11]. However, the clinical utilization of TQ has been limited by its high hydrophobicity and chemical instability which in turn leads to poor bioavailability. This is especially evident in dermal applications where these specific physicochemical characteristics limit TQ ability to effectively penetrate the stratum corneum to reach the affected layers of the skin [
12,
13]. Therefore, there is a significant need to develop effective delivery approaches that can enhance solubility, drug stability, and facilitate the penetration and retention of TQ in the skin [
14].
Vesicular systems such as ethosomes and transethosomes could prove to be an effective delivery system for TQ due to their ability to improve drug solubility and enhance therapeutic concentration at the target site. Ethosomal formulations, relatively novel vesicular systems, are composed of phospholipids, ethanol, and water [
15,
16,
17]. They have many advantages over traditional liposomes providing enhanced drug solubility, higher loading capacity, and high deformability which facilitates penetration through the stratum corneum into the deeper skin layers [
18]. Ethosomes have demonstrated enhanced drug entrapment, skin penetration, and deposition for various drugs [
19,
20,
21]. Transethosomes are essentially an advanced version of ethosomes due to the addition of edge activators in comparison to the original ethosomes [
22].
Edge activators are nonionic, ionic, or cationic surfactants. Nonionic surfactants, such as Tween 20, contribute to steric stabilization by forming a protective layer on the particle surface, which prevents interactions between the vesicles [
23]. Ionic surfactants, such as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), provide electrostatic stabilization by creating a charged layer around the nanoparticles, reducing aggregation [
24,
25]. Sodium lauroyl glutamate (SLG) is an ionic surfactant derived from the amino acid glutamic acid and lauric acid [
26]. Addition of nonionic surfactants to ionic surfactants can improve biocompatibility and reduce potential cytotoxicity compared to ionic surfactants [
27]. As a result, we proposed to combine a nonionic surfactant with an ionic surfactant. Tween 20 in combination with sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) or with sodium lauryl glutamate (SLG).
To optimize the composition of these formulations, we employed the Langmuir monolayer technique, which is helpful in understanding the interfacial properties and behavior of phospholipids in ethosome and transethosome formulations [
28,
29]. This kind of study provides valuable insights into the film-forming characteristics and enables optimizing the formulation parameters for improved drug delivery through the skin [
30].
Skin penetration studies usually utilize a fluorescent molecule that can be easily detected by a fluorescence microscope. One such molecule is rhodamine B which has similar properties as TQ and can be easily detected in skin layers. These markers of skin penetration can give important information on the mechanisms of formulation skin penetration. Additionally, to better understand the mechanism of skin penetration of the formulation with or without different permeation enhancers, we utilized Rhodamine B as a model lipophilic compound. This allowed us to verify the mechanisms related to the penetration of such a lipophilic model active into the skin.
The aim of this research was to explore the application of transethosomes as a promising carrier system for facilitating the transdermal administration of thymoquinone. Specifically, we aimed to examine the effect of combining ionic and nonionic surfactants on the performance of the transethosomal formulation using the Langmuir method to achieve the most effective transdermal delivery system while ensuring an acceptable safety profile. To assess the efficiency of transdermal delivery, we performed comparative evaluations with ethosomes and drug-only application. To gain insight into the penetration mechanism, we also used a fluorescent marker, rhodamine B, which allowed us to closely track the accumulation patterns of transethosomes in the skin.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Phospholipon 90G generously provided by LIPOID LLC, located in Newark, NJ, USA. Tween 20 from Sigma-Aldrich, Sodium Lauroyl glutamate from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Ethanol was acquired from Sigma-Aldrich, located in St. Louis, Missouri, USA.. The study utilized HPLC grade water from Sigma-Aldrich and acetonitrile from Midland Scientific, located in Omaha, NE, USA. Dermatomed human cadaver skin was procured from The New York Firefighters Skin Bank, with the donor being a 74-year-old male weighing 118 lbs., NY, USA. The remaining chemicals utilized in the research were of reagent quality and were procured from VWR International in Radnor, Pennsylvania, USA.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Monolayer Study
The experiment was performed using Langmuir trough (Biolin Scientific, Stockholm, Stockholms Lan, Sweden) of the surface area 98 cm
2 equipped with platinum Wilhelmy plate. Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) was used as a subphase. The lipid was dissolved in chloroform and carefully spread on a subphase using a syringe. Following the solvent evaporation, the monolayer was compressed by two movable, symmetrical barriers. Simultaneously the mean molecular area (
A) and surface pressure (
π) were recorded. For the investigation of lipid-surfactant interactions, the soluble surfactants (Tween 20, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sodium lauroyl glutamate (SLG), Tween 20 + SLS, or Tween 20 + SLG) were dissolved in PBS to the concentration of 0.84 µg/mL and 10 µL of the solution was introduced to the subphase before spreading the lipid. The data from the
π-
A isotherms were used to calculate the compression modulus (C
s-1) according to Equation 1:
The lower the value of Cs-1 is, the more compressible a monolayer is. The dilational (rheology experiment was performed using oscillating barrier method. After the monolayer was compressed to π=30 mN/m a sinusoidal area deformation was applied using the frequency (ω) of 10 mHz and the amplitude of 1-20%. Based on the surface pressure response on area deformation the dilational modulus (G) was obtained which is the complex quantity composed of the real component (G’) and the imaginary component (G’’) representing the elastic and viscous behavior respectively. For a perfectly elastic response, the imaginary part equals zero and for a perfectly viscous film, the real part equals zero. Most films of biological relevance are viscoelastic meaning intermediate properties between purely elastic and purely viscous. All monolayer experiments were performed at 20°C.
2.2.2. Preparation of Ethosomes and Transethosomes Formulations with Thymoquinone
Phospholipon 90G was dissolved along with TQ (200 mg) in ethanol, with or without an edge activator, in a sealed glass bottle. The mixture was stirred using a magnetic stirrer at 700 rpm at room temperature. PBS was slowly added at a constant rate of 200 μL/min until reaching the final volume 100% (w/w) (as shown in
Table 1). After the addition of PBS, stirring continued for an additional 5 minutes [
31]. The mixed solution was then placed in an ultrasonic apparatus and subjected to ultrasonic treatment for 2 cycles with total 10 minutes.
2.2.3. Preparation of Ethosomes and Transethosomes Formulations with Rhodamine B
The preparation of Rhodamine B-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes was conducted following the methods described by Yang
et al., [
32] and as described in section 2.2.2. Rhodamine B (0.02% w/v) was loaded in the formulations instead of TQ. To separate the Rhodamine B that was not entrapped within the formulation, centrifugation was performed. In particular, the ethosomes and transethosomes were placed in an ultrafiltration tube (Centrisart 10 kDa MWCO filtration units) and centrifuged at a speed of 40,000 rpm for 20 minutes. The filtrate, which contained the non-entrapped Rhodamine B, was discarded, while the remaining tube containing the entrapped ethosomes was inverted into a new collection tube. Consequently, the collection tube was centrifuged at 40,000 rpm for 10 minutes to obtain the Rhodamine B-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes. These preparations were promptly utilized in the subsequent experiments involving skin penetration using the fluorescence microscope studies.
2.2.4. Characterization of ethosomes and transethosomes
Vesicle Size and Size Distribution
Ethosome and transethosomes vesicle size, size distribution (Polydispersity Index, PDI), and ZetaPotential were determined through Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) using a Zetasizer. (Malvern Zetasizer Nano ZS90). The measurement was performed at wavelength of 632.8 nm He-Ne laser light source (4 mW). Prior to the experiment, each sample was loaded into a single-use, low-volume polystyrene cuvette ( ZEN0118), and allowed to stabilize for 3 minutes. The measurements (N=3) were carried out at a temperature of 25.0°C, utilizing the non-invasive backscatter mode (NIBS) at an angle of 173°.
Entrapment Efficiency (EE)
EE was determined by ultrafiltration of a sample through Centrisart 10 kDa MWCO filtration units and subsequent analysis of the supernatant using the HPLC method described in section 3.6. below. Drug entrapment percentage was calculated using Equation 2:
where Dt is the total amount of drug added and Ds is the amount of drug obtained in the supernatant [
33,
34].
2.2.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
A high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method used an Agilent 1100 series HPLC (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was utilized. The instrument was coupled with UV diode array detector (DAD) and operated using HP Chemstation software V. 32. The composition of the mobile phase was 80% acetonitrile and 20% water. To assess the quantity of TQ, a mobile phase was pumped at the flow rate of 1.0 mL/min through an Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18 column 250 mm length x 4.6 mm internal diameter, 5.0 µm particle sizes as the stationary phase at 25
0C. The sample injection size was 20 μL. The column temperature was maintained at 23 °C, and UV detection of TQ was performed at a wavelength of 250 nm, and the retention time of TQ was 3.4 min [
35]. The linearity of the peak area versus concentration was evaluated using a standard concentration range from 0.39 µg/mL to 100 µg/mL, yielding a coefficient of regression (R²) of 0.99. The method demonstrated precision, with a % RSD (relative standard deviation) of 0.13% for intra-day measurements and 0.86% for inter-day measurements. Tthe limit of detection (LOD) was determined to be 0.54 µg/mL, while the limit of quantification (LOQ) was 1.64 µg/mL.
2.2.6. In Vitro Skin Permeation Study
To assess the release of TQ, full thickness dermatomed human cadaver skin obtained from the posterior torso was obtained from the New York Firefighters Skin Bank, USA. Upon arrival, the skin was immediately frozen at a temperature of -80 °C. On the day of the study, the skin was thawed in filtered PBS (pH 7.4) at room temperature for a duration of 10 minutes. A suitable portion of the skin was then cut and positioned between the donor and receptor chambers of a vertical Franz Diffusion Cells (FDC), with the stratum corneum facing the donor chamber and lower part of the skin was in contact with receptor compartment. The receptor chamber was filled with a known volume of pH 7.4 PBS buffer and continuously stirred using a small PTFE-coated magnetic bar rotating at a speed of 600 rpm. The skin surface temperature was maintained at 32 °C by placing the FDC in a dry block heater (Logan Instruments, Somerset, NJ, USA) set at a precise temperature of 37 ± 0.5 °C. The number of Franz cells per experimental group was n=5.
After allowing the assembled FDCs to equilibrate for a minimum of 30 minutes, 500 μL of each formulation was applied to the skin in the donor compartment as described by Virani
et al. [
36]. At specific time intervals, a sample of the receptor medium was withdrawn 300 ul, and an equivalent volume of fresh buffer solution was added to the receptor chamber. The corrected concentration of TQ in the withdrawn sample was then analyzed using the HPLC methods described in section 2.2.5.
The impact of the formulation on skin integrity was investigated by conducting TEWL measurements before applying the formulation to the donor side and at the conclusion of the study, following established protocols [
37].
The cumulative amount of TQ permeated per unit area was calculated according to Equation (3)
where Q
n is the cumulative amount of the drug permeated per unit area (µg/cm
2) at different sampling times, C
n is the drug concentration in the receiving medium at different sampling times (µg/mL), C
i is the drug concentration in the receiving medium at the i (n−1) sampling time (µg/mL), V
r is the volume of the receptor solution (mL), V
s is the volume of the sample withdrawn (mL), and A is the effective permeation area of the diffusion cell (cm
2). The Qn values were plotted over time, and subsequently, the steady-state flux (Jss) was determined by analyzing the slope of the linear segment within the plot.
The permeability coefficient (K
p) was calculated with Equation (4)
where 𝐽
𝑠𝑠 - steady state flux (μg cm
−2h
−1), and 𝐶
0 - concentration of TQ in the donor compartment (µg mL
−1 ).
The enhancement ratio was calculated by dividing the flux of the test formulation by that of the control formulation (TQ C) with equation (5) below:
2.2.7. Skin Disposition Study
Upon completion of the permeation study, the skin samples were extracted from the Franz Diffusion Cells. They were then carefully cut around the diffusional area, allowed to air-dry, precisely weighed, and subsequently transferred into bead bug tubes. . To isolate the drug, the skin samples were cut into small pieces using a pair of scissors. Subsequently, 1 mL of ethanol was introduced into each sample tube to facilitate the extraction of TQ from the skin.[
38]. Then, skin samples were homogenized using a BeadBug
TM Microtube homogenizer, D1030 (Benchmark Scientific, Sayreville, NJ, USA). Finally, samples were centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 5 min, and filtered through a 0.45 µm polypropylene filter to remove skin debris. Filtered samples were analyzed using validated HPLC. The amount of TQ in the skin was represented as TQ (µg) per skin weight (mg).
2.2.8. In Vitro Permeation Testing of Rhodamine B Loaded Formulation
The time-dependent permeation behavior of Rhodamine B from the ethosomal and transethosomal system in human cadaver skin was measured by an ECHO Revolve 4 microscope (Echo Revolve microscope, R4, Echo Laboratories, U.S.A). A Franz diffusion cell with a donor area of 0.64 sq. cm was used as explained in section 2.2.6. Different formulations loaded with Rhodamine B (500 μL) were added to the skin in the donor compartment. The treated skin samples were removed at 4 and 8 h after Rhodamine B loaded formulation application. The residual formulation was removed from the donor compartment, the skin surface was then washed and cleaned and finally dried with cotton swab and cut only around the permeation area of 0.64 sq. cm. The skin tissue samples were embedded in Optimal Cutting Temperature compound (OCT), left in the freezer at -80 degrees, then sectioned at 10 μm thickness, with a cryo-ultramicrotome (Leica Biosciences, Nussloch, Germany) and observed with the ECHO Revolve 4 microscope, with an excitation wavelength of 556 nm. All procedures were carried out in the dark to prevent the influence of incident light [
31,
39].
2.2.9. Antimicrobial Assay
We used disc diffusion method to test the antimicrobial activity of TQ-loaded films against S. aureus (ATCC, Stock # 49230). Briefly, Muller Hinton agar (MHA) plates were prepared by pouring molten media into sterile Petri dishes. Then, 100 µL of overnight cultured bacteria adjusted to OD concentration of 0.542 (OD 1 = 1 × 109/mL of bacteria) in sterile TSB (Tryptic Soy Broth) was spread on the surface of MHA agar plates with the help of a sterile spreader. Subsequently, a disc-shaped polymer films measuring 0.64 cm2 and 100 µL of 40 µg TQ formulations were placed on the agar surface. The plates were then incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours. As positive controls, azithromycin (Sigma Aldrich, expiration date 31/12/24) at a concentration of 15 µg/ 100ul was employed, while the blank formulation served as a negative control. Following the incubation period, the inhibition zones surrounding the polymer discs were examined.
2.2.10. Cytotoxicity Assay
The cytocompatibility of TQ-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes was assessed on HaCaT cell line (Human Keratinocytes, AddexBio) using AlamarBlue® assay. The cells were seeded into 96 flat bottom well plate at a density of 10,000 cells per well in 80 µL 1 % FBS DMEM dispersion overnight. Then 20 µL of the respective TQ solutions were added and incubated for 24 h. Cells treated with formulation-free media were included as a negative control. Then, 10 µL of AlamarBlue® was added and incubated for 3 hours after which fluorescence was measured using microplate reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland).
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
All results are reported as mean ± SD (n=5). The statistical analysis of the data was evaluated using one-way Anova and Dunnet’s multiple comparison test. Results with p-values <0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results and Discussion
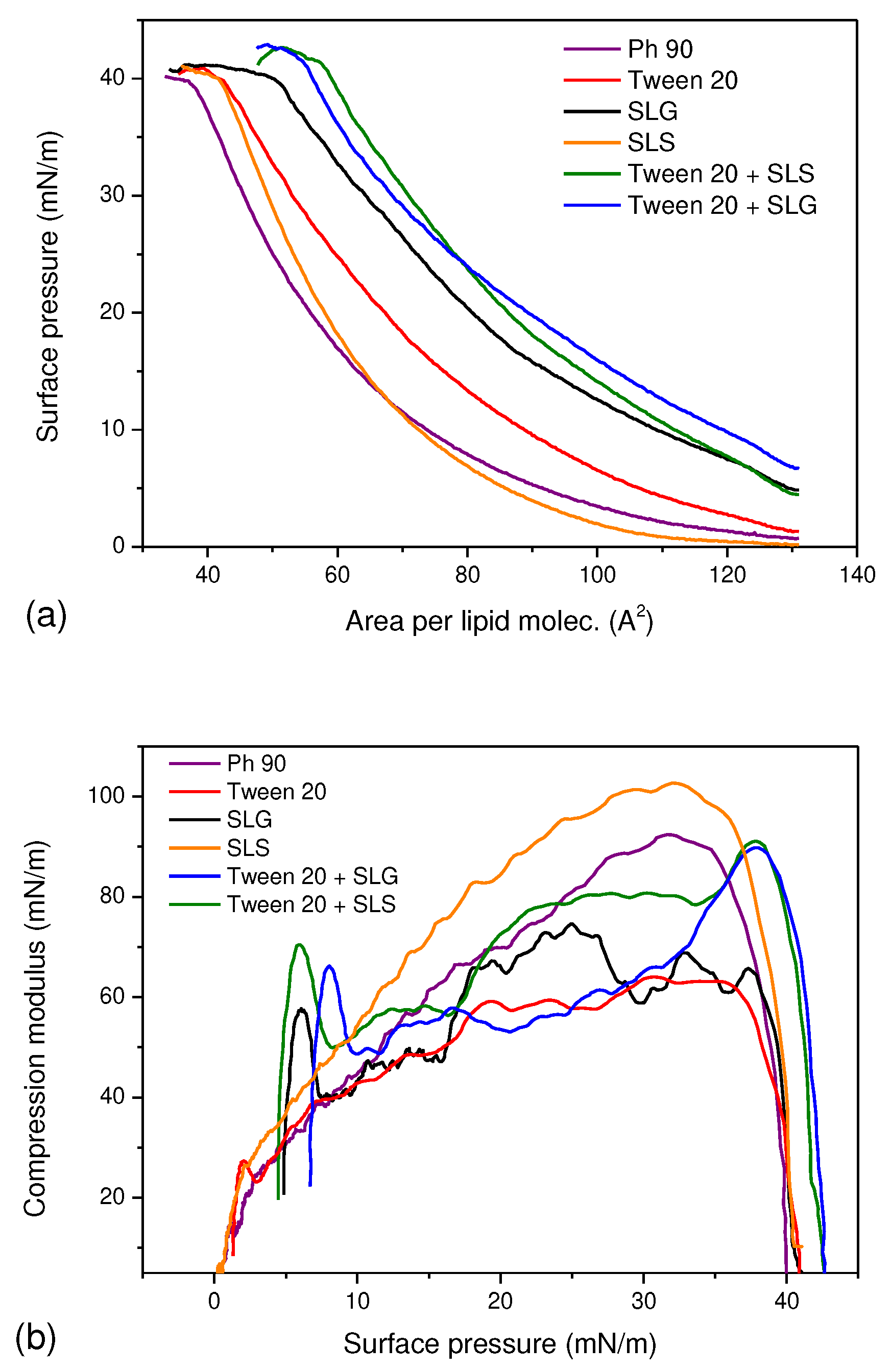
3.1. A Monolayer Study
The
π-
A isotherms for Ph 90 in the presence of various surfactants were shown in
Figure 1a. Except for SLS, the surfactants caused a significant shift of the curves towards higher molecular areas which indicate their insertion into the lipid monolayer. This finding demonstrates the potential of surfactants to act as edge activators in pharmaceutical formulation based on Phospholipon 90. Furthermore, the elevated initial surface pressure at
A≈130 Å
2/mole confirmed the surface activity of the surfactants and synergistic effect of Tween 20 + SLG and Tween 20 + SLS which increased surface pressure more efficiently than the single surfactants alone at the same total concentration. This implies that the functionalization of lipid vesicles might be achieved using smaller total amount of edge activators if Tween 20 is mixed with anionic surfactant in comparison to the single surfactant. The monolayer of Ph 90 was also slightly more stable in the presence of Tween 20 + SLG and Tween 20 + SLS as the monolayer collapsed at higher surface pressure than other films. This result means that addition of these surfactants might have slightly positive impact on the stability of transethosomes. The compression modulus curves shown in
Figure 1b reflect the packing and ordering in the film. The plot indicated the fluidizing effect of Tween 20 and SLG on the lipid monolayer as the maximum values of C
s-1 are lower than for Ph 90. It means that the monolayer is more compressible in the presence of these compounds which might be perceived as beneficial for the lipid vesicle that should more easily undergo deformation during transdermal drug delivery. In contrast to that, SLS caused the increase of compression modulus which suggests the monolayer became more compact. The combination of surfactants caused the fluidization of the monolayer only for π<35 mN/m however the maximum C
s-1 value was reached at 39 mN/m and it was close to the value obtained for the monolayer of Ph90. This result suggests that the vesicles modified with combined surfactants may be more tightly packed, hence smaller in size and less susceptible to drug leakage.
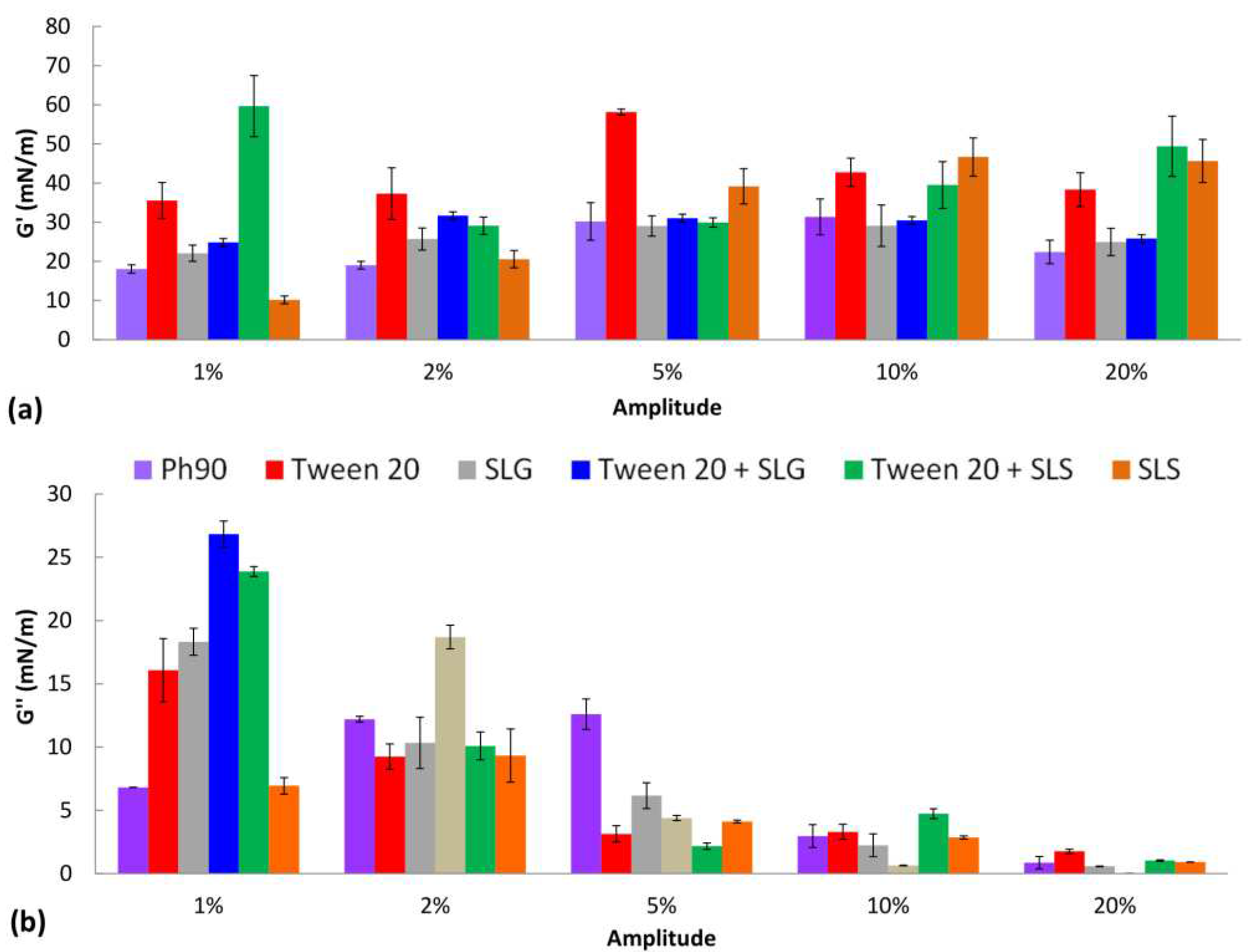
The results of interfacial dilational rheology studies are shown in
Figure 2. The domination of elastic properties over the viscous behavior was observed when comparing the G’ (
Figure 2a) and G’’ (
Figure 2b) values for the same amplitude. Most of the surfactants caused the increase of G’ in comparison to the monolayer of pure Ph 90. The largest effect was observed for Tween 20, SLS, and their combination which may suggest their considerable potential to modify the deformability of lipid nanocarrier in the formulation and enhance the permeation of the drug through the skin. For SLG and Tween 20 + SLG the elastic modulus was close to the G’ for pure Ph 90 regardless of the amplitude applied. The contribution of the viscous component to the interfacial viscoelasticity was the most significant for small amplitudes and it decreased with the growth of amplitude. Considering the capability of transethosomes to significantly decrease their radius when permeating the skin barrier, the results of dilational rheology experiment are the most relevant to the drug permeation through the skin for the largest amplitude of deformation. Therefore, analyzing the values of G’ for the amplitude 20% one can observe the positive impact of Tween 20, SLS and their combination on the elastic response of the lipid layer on area deformation. It means the vesicles modified with these edge activators might be capable of restoring their original size and shape after the force causing deformation is removed. In other words, these vesicles might be more flexible and stable than other formulations.
Overall, the results of the monolayer study indicate the role of edge activators in transethosomes is complex and include several mechanisms which may lead to the increase of stability, changes of size and improvement of deformability. Therefore, all surfactants used may improve the properties of vesicles, however the mechanism of their activity might be slightly different. The combinations of Tween 20 with SLS and SLG may easily incorporate into the lipid vesicle however only Tween 20+SLS efficiently modifies its rheological behavior at high amplitudes which is why this combination might be the most promising for enhancing the transport of the drug through the skin.
3.2. Characterization of TQ-Loaded Ethosomes and Transethosomes and the Effect of Different Edge Activators
Characterizing the prepared TQ-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes is crucial for understanding their permeability, considering factors such as size, zeta potential and encapsulated drug content. Hence, it is imperative to assess the particle size, polydispersity index (PDI), zeta potential, and %EE (
Table 2) of the TQ-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes.
The results revealed that the type of surfactant played a significant role (p < 0.05) in determining the particle size.
Generally, the addition of the edge activator led to a decrease in particle size. Transethosomes prepared with the combination of Tween 20 and SLS exhibited the smallest vesicle sizes (115.4 nm), followed by those prepared with Tween 20 alone (133.7 nm), and finally, the combination of Tween 20 and SLG-based transethosomes (154.3 nm).
Furthermore, the combination of nonionic and ionic surfactants has been shown to increase the entrapment efficiency. The entrapment efficiency is influenced by the phase transition temperature (Tc) of the surfactant, with higher Tc values generally resulting in higher entrapment efficiency. Additionally, the use of an embedded edge activator (surfactant) such as SLS, SLG, and Tween 20 can solubilize the drug in the lipid bilayer, contributing to a significant increase in the entrapment efficiency of the encapsulated drugs [
40].
Anionic surfactants possess a negative charge, which allows them to interact with positively charged drug molecules through electrostatic interactions. This interaction promotes the entrapment of the drug within the vesicles, leading to an increased entrapment efficiency. The anionic surfactant SLS enhances the repulsive force between the lipid bilayers, increasing membrane elasticity and enabling vesicles to accommodate higher amounts of the drug, this finding was confirmed by several publications [
40]. Anionic transethosomes have been reported to exhibit higher %EE compared to cationic ones, which is reflected in their higher EE values [
41].
Transethosomes have also demonstrated significantly higher %EE for TQ compared to ethosomes. This can be attributed to the solubilizing properties of the surfactant and the interactions among the surfactants, thymoquinone, and the lipid bilayer.
3.3. Ex Vivo Skin Disposition and Permeation Study
Ethosomes are a unique type of deformable lipid vesicles characterized by fluid lipid bilayers. They have been reported to enhance the delivery of various molecules into deep skin layers. The precise mechanism of skin drug delivery by ethosomes is not fully understood [
42]. High concentrations of ethanol in the formulation contribute to the flexibility of the vesicles, which evaporates from the formulation upon application to the skin surface under non-occlusive conditions [
33]. However, the impact of the overall composition of ethosomes on the structure of the SC bilayer is not yet completely elucidated. Nevertheless, their simple composition, the solubility-enhancing properties of ethanol for numerous drugs, and their ease of preparation make them promising candidates for the topical delivery of various drugs, particularly lipophilic ones [
43].
The presence of an embedded edge activator, in combination with ethanol, enhances the solubility of the drug and facilitates the formation of deformable lipid structures. These deformable ethosomes can easily traverse through the skin's corneocytes, thereby improving the retention and permeation of the drug in the skin [
40].
When developing a topical formulation, permeation and penetration studies play a crucial role as they provide insights into how the formulation behaves when it meets the skin, ultimately predicting its therapeutic effectiveness in vivo [
44]. The skin barrier creates a hydrophobic environment that is vital for preventing and controlling drug delivery [
45].
To assess skin integrity, TEWL measurements were conducted. The TEWL measurements, ranging from 1.4 to 12.4 g·m−2·h−1 before application, were considered acceptable. Moreover, there was no observed increase in TEWL measurements after 24 hours of application. This suggests that applying ethosomal and transethosomal formulation did not compromise the integrity of the skin barrier.
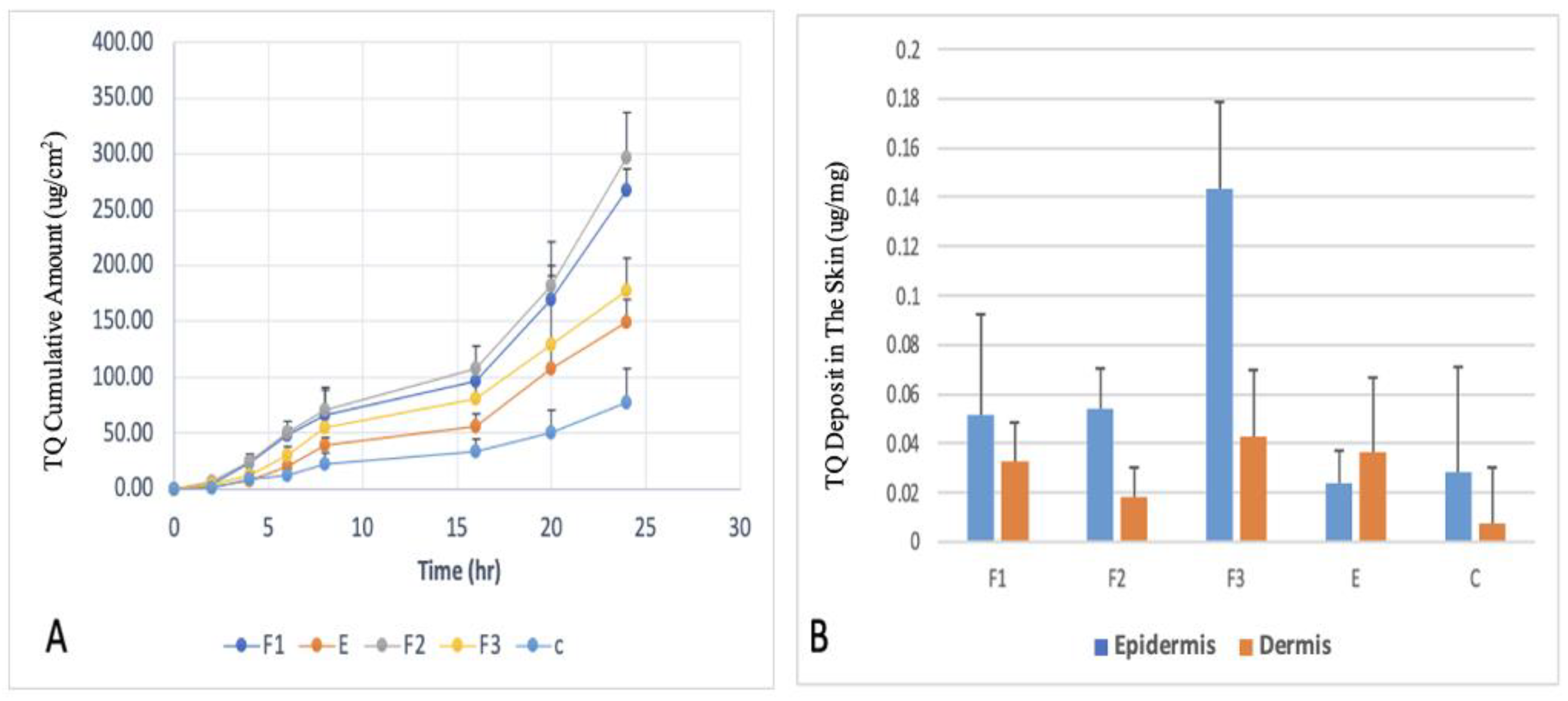
The Ex vivo skin permeation experiments on human cadaver skin were carried out utilizing Franz diffusion cells to evaluate the potential of TQ delivery through the skin using these formulations. The drug permeation profiles of TQ, the cumulative amount of TQ permeated through the epidermal and dermal layers over the 24 hours of the skin permeation study, and the amount of TQ deposited in the epidermal and dermal layers at 24 hours after the completion of skin permeation study, are shown in
Figure 3.
F2 formulation showed the highest permeation after 24h (267.13 ug/cm2), F1 (149.42 ug/cm2), F3 (177.00 ug/cm2) while the value for the control was 60 ug/cm2. The addition of Tween 20 or a combination of Tween 20 and SLS demonstrated a significant difference in flux compared to the formulation without any surfactant. However, the combination of GLS and SLS did not improve the flux when compared to the formulation without a surfactant. The enhanced permeation and deposition of TQ can be attributed to the presence of Tween 20 as an edge activator, along with SLS and GLS. In this study, the selection of Tween 20 was based on its favorable physicochemical characteristics determined through LB studies. The incorporation of Tween 20 and SLS as edge activators in TQ deformable ethosomes resulted in higher entrapment efficiency and smaller particle size. These factors collectively contribute to improved delivery of drugs to the skin.
The values of steady-state fluxes (J
ss), permeability coefficients (Kp), enhancement ratio, and lag time are presented in
Table 3.
3.4. Fluorescent Microscopy
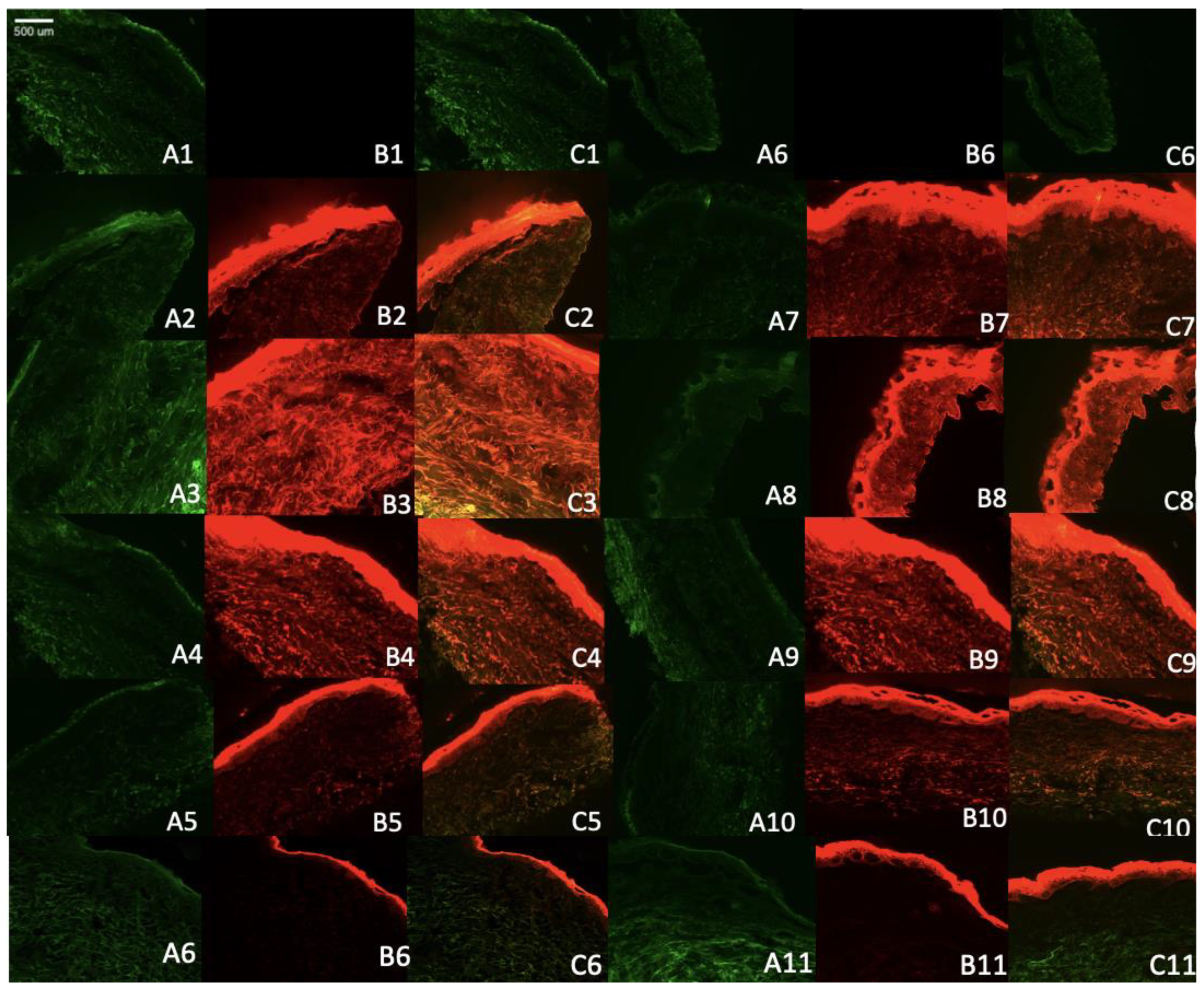
To better understand the mechanism of skin penetration of the formulation with or without different permeation enhancers, we utilized Rhodamine B as a model lipophilic dye. This allowed us to verify the mechanisms related to the penetration of lipophilic drug into the skin.
The results obtained from confocal microscopy demonstrated that the control solution of rhodamine remained restricted to the superficial layer of the stratum corneum. In contrast, the formulation containing Rhodamine B-loaded ethosomes exhibited deeper penetration and a higher release rate over time, as depicted in
Figure 4. This study highlights the improved ability of the ethosomes and transethosomes loaded with Rhodamine B to penetrate and distribute throughout various layers of the skin, including the epidermis and to some extent, the dermis. The fluorescence intensity of the Rhodamine B probe dye served as an indicator of the level of penetration and topical effectiveness of the optimized ethosomes system, as assessed in this study. These permeation findings align with the results reported by Kausar
et al. [
46].
Regarding the transethosomal formulation containing SLS, it demonstrated lesser disposition within the skin, as confirmed by the IVPT results. On the other hand, the SLG formulation exhibited the highest disposition in all layers of the skin, with a greater release rate over time, which was consistent with the IVPT results.
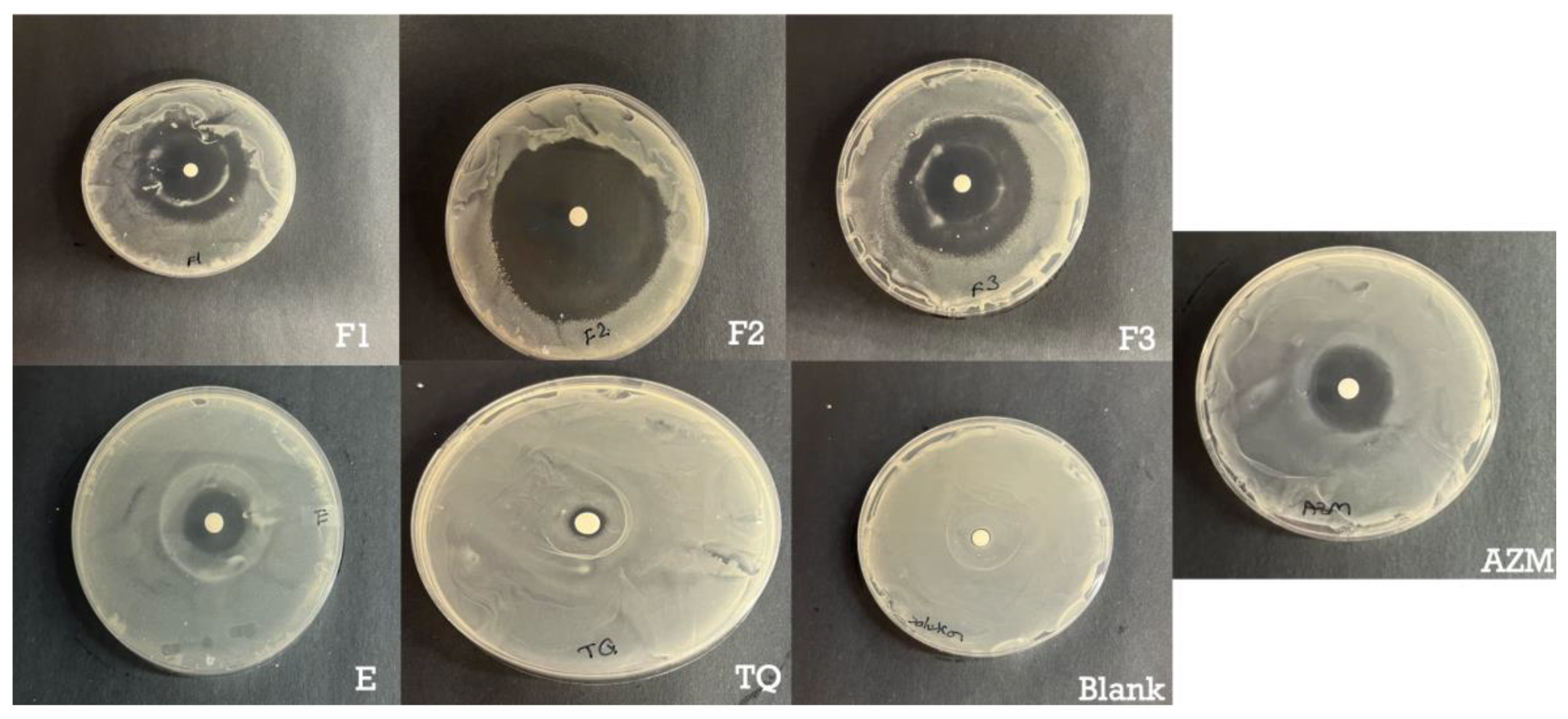
3.5. Antimicrobial Assay
S. aureus is responsible for a significant proportion of skin and soft tissue infections in humans. The emergence of antibiotic resistance in
S. aureus underscores the critical need for novel approaches to address these infections[
47]. Hence, the antimicrobial effectiveness of the ethosomes and transethosomes formulations containing TQ was evaluated by determining the zones of inhibition of S. aureus after 24 h in bacteria culture. The results and zones of inhibition are presented in
Table 4 and
Figure 5. Formulations loaded with TQ showed higher antibacterial activities compared to free TQ.
The enhanced antimicrobial effect of TQ when delivered in transethosomes can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the smaller size of transethosomes compared to ethosomes allows for better penetration of the drug through the bacterial cell membrane, increasing its ability to disrupt the membrane and induce cell death. Secondly, transethosomes can protect the drug from degradation by enzymes, allowing for a higher concentration of active drug to be delivered to the site of action. Both anionic and nonionic surfactants can have some effect on S. aureus, although their specific mechanisms and effectiveness may differ.
Anionic surfactants, such as SLS have antimicrobial activity against S. aureus. As reported by Sonestine
et al., SLS 0.002% in growth medium showed 96% to 100% decrease in the ability of bacteria to produce penicillinase which is a source of resistance [
48]. These surfactants disrupt the bacterial cell membrane by interacting with the lipids, leading to membrane damage and cell lysis. They can disrupt the integrity and function of the bacterial cell, ultimately inhibiting its growth.
Nonionic surfactants, such as Tween 20, generally have less direct antimicrobial activity compared to anionic surfactants. Nonionic surfactants typically do not interact strongly with bacterial cell membranes. However, they can aid in the dispersal and removal of bacteria by reducing surface tension and promoting the wetting and spreading of water. That’s why the combination in the formulation of ionic and nonionic surfactant showed a superior result as F2 showed the highest permeation in the skin and the highest antimicrobial effect, followed by F3 as it composed of Tween 20 and SLG the amino acid derived surfactant. Several studies showed it has an antimicrobial effect as these surfactants’ perturbation of bacterial membrane [
49].
3.6. Cytotoxicity Study
To evaluate the safety of the transethosomal formulations, we performed a series of tests on the human keratinocyte cell line HaCat. The study included the evaluation of three transethosomal formulations (F1-3), one blank formulation, and the single component TQ. Various concentrations of the formulations were examined, ranging from 3.125 to 50 µM TQ in the formulation or an equivalent amount of transethosomes in the blank formulation. The results indicate that the TQ formulations have a significantly improved safety profile compared to TQ alone. Additionally, no discernible changes between the three transethosomal formulations were found. These results highlight the potential of transethosomal delivery systems to improve the safety of TQ-based formulations for future applications.
Figure 6.
Viability of Keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT) as measured by AlamarBlue assay. After 24 hr incubation with hydroethanolic TQ solution or TQ loaded in ethosomes or transethosomes. Data represent average values ± SD (n >3). Statistically significant differences: * (p <0.05), ** (p <0.01), *** (p <0.001) and **** (p <0.0001).
Figure 6.
Viability of Keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT) as measured by AlamarBlue assay. After 24 hr incubation with hydroethanolic TQ solution or TQ loaded in ethosomes or transethosomes. Data represent average values ± SD (n >3). Statistically significant differences: * (p <0.05), ** (p <0.01), *** (p <0.001) and **** (p <0.0001).
4. Conclusions
Transethosomes serve as a more effective skin delivery system compared to ethosomes, particularly when composed of a combination of edge activators. Monolayer studies have revealed that this combination of edge activators enhances the elasticity of these surfactants when interacting with lipids. Specifically, the combination of Tween 20 with either SLS or SLG has been found to significantly enhance permeation, flux, EE, and the antimicrobial effects of TQ.
Funding
This study was funded by the Center for Dermal Research CDR, Rutgers-The State University of New Jersey, 145, Bevier Road, Piscataway NJ 08854, and the European Union's Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No. 778051 (ORBIS project). Scientific work published within the international project was co-founded by the Ministry of Science and Education of Poland “PMW” in years 2019-2022 no. 5014/H2020 – MSCA-RISE/2019/2 dated 2019-12-30. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the European Union’s or the respective institution’s position on the subject.
Abbreviations
Thymoquinone (TQ); Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS); Sodium Lauroyl Glutamate (SLG); Optimal Cutting Temperature compound (OCT); Phospholipon 90G (Ph 90).
References
- Qureshi, K.A.; et al. Antiprotozoal Activity of Thymoquinone (2-Isopropyl-5-methyl-1,4-benzoquinone) for the Treatment of Leishmania major-Induced Leishmaniasis: In Silico and In Vitro Studies. Antibiotics 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Husain, A.; Mujeeb, M.; Alam Khan, S.; Najmi, A.K.; Siddique, N.A.; Damanhouri, Z.A.; Anwar, F. A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Jrah, H.; Mahdouani, K.; Bakhrouf, A. Antibacterial activity of Thymoquinone, an active principle of Nigella sativa and its potency to prevent bacterial biofilm formation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohandel, Z.; Farkhondeh, T.; Aschner, M.; Samarghandian, S. Anti-inflammatory effects of thymoquinone and its protective effects against several diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaev, N.K.; Genrikhs, E.E.; Stelmashook, E.V. Antioxidant Thymoquinone and Its Potential in the Treatment of Neurological Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, B.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Alghamdi, K.S.; Al-Amer, O.; Hassan, K.E.; Elhefny, M.A.; Albarakati, A.J.A.; Alharthi, F.; Althagafi, H.A.; Al Sberi, H.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles Enhance Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Liver and Kidney Tissues: Potential Protective Role of Thymoquinone. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2022, 201, 2942–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanibirgani, A.; Khalili, A.; Rokhafrooz, D. Comparing Nigella sativa Oil and Fish Oil in Treatment of Vitiligo. Iran. Red Crescent Med J. 2014, 16, e4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.R.; Cartron, A.M.; Khachemoune, A. A review of Nigella sativa plant-based therapy in dermatology. Int. J. Dermatol. 2021, 60, e493–e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, R.; Caruso, F.; Aktar, S.; Belli, S.; Kaur, S.; Hernandez, M.; Rossi, M. Antioxidant Properties of Thymoquinone, Thymohydroquinone and Black Cumin (Nigella sativa L.) Seed Oil: Scavenging of Superoxide Radical Studied Using Cyclic Voltammetry, DFT and Single Crystal X-ray Diffraction. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badary, O.A.; Taha, R.A.; El-Din, A.M.G.; Abdel-Wahab, M.H. Thymoquinone Is a Potent Superoxide Anion Scavenger. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 26, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.A.; Nagi, M.N.; El-Khatib, A.S.; Al-Bekairi, A.M. Effects of thymoquinone on antioxidant enzyme activities, lipid peroxidation and DT-diaphorase in different tissues of mice: a possible mechanism of action. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2002, 20, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algahtani, M.S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Shaikh, I.A.; Abdel-Wahab, B.A.; Nourein, I.H.; Ahmad, J. Thymoquinone Loaded Topical Nanoemulgel for Wound Healing: Formulation Design and In-Vivo Evaluation. Molecules 2021, 26, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Ahir, M.; Patra, P.; Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Mazumdar, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Das, T.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Adhikary, A. PEGylated-thymoquinone-nanoparticle mediated retardation of breast cancer cell migration by deregulation of cytoskeletal actin polymerization through miR-34a. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, B.; Ali, M.H.; Wilkhu, J.; Kirby, D.J.; Mohammed, A.R.; Zheng, Q.; Perrie, Y. The application of monolayer studies in the understanding of liposomal formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 417, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, P.; Sharma, I.; Hemrajani, C.; Rathore, C.; Bisht, A.; Raza, K.; Katare, O.P. Thymoquinone-loaded lipid vesicles: a promising nanomedicine for psoriasis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sguizzato, M.; Ferrara, F.; Hallan, S.S.; Baldisserotto, A.; Drechsler, M.; Malatesta, M.; Costanzo, M.; Cortesi, R.; Puglia, C.; Valacchi, G.; et al. Ethosomes and Transethosomes for Mangiferin Transdermal Delivery. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matharoo, N.; Mohd, H.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Transferosomes as a transdermal drug delivery system: Dermal kinetics and recent developments. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnology 2023, e1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtikar, M.; Nagarsekar, K.; Fahr, A. Transdermal delivery from liposomal formulations – Evolution of the technology over the last three decades. J. Control. Release 2016, 242, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Pathak, K. Therapeutic and cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: An overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2010, 1, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, A. Transfersomes: The Ultra-Deformable Carrier System for Non-Invasive Delivery of Drug. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, L.N.; Braz, W.R.; da Silva, N.P.; Cazarim, E.L.C.C.; Palmieri, M.G.S.; Tavares, G.D.; Pittella, F. Ethosomes as delivery system for treatment of melanoma: a mini-review. Oncologie 2023, 25, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Roy, C.; Rajabalaya, R.; Mohaimin, A.W.; Khanam, J.; Nanda, A.; David, S.R. Ethosomes as Novel Vesicular Carrier: An Overview of the Principle, Preparation and its Applications. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 795–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazaridis, N.; Alexopoulos, A.; Chatzi, E.; Kiparissides, C. Steric stabilization in emulsion polymerization using oligomeric nonionic surfactants. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 3251–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.M.; Abdallah, O.Y.; Naggar, V.F.; Khalafallah, N.M. Deformable liposomes and ethosomes: Mechanism of enhanced skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 322, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Dua, K.; Nair, R.S.; Chandran, C.S.; Alex, A.T. Transethosome: An ultra-deformable ethanolic vesicle for enhanced transdermal drug delivery. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2023, 255, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q. Mixed micellization of cationic/anionic amino acid surfactants: Synergistic effect of sodium lauroyl glutamate and alkyl tri-methyl ammonium chloride. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 43, 2227–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, X.; Garamus, V.M.; Handge, U.A.; Bérengère, L.; Zhao, L.; Salamon, G.; Willumeit, R.; Zou, A.; Fan, S. Mixture of Nonionic/Ionic Surfactants for the Formulation of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Effects on Physical Properties. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6920–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanparast, H.; Shahabi, F.; Bahramian, A.; Javadi, A.; Miller, R. The Role of Electrostatic Repulsion on Increasing Surface Activity of Anionic Surfactants in the Presence of Hydrophilic Silica Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojewska, M.; Smułek, W.; Grzywaczyk, A.; Kaczorek, E.; Prochaska, K. Study of Interactions between Saponin Biosurfactant and Model Biological Membranes: Phospholipid Monolayers and Liposomes. Molecules 2023, 28, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczes, A.; Jurak, M.; Chibowski, E. Stability of binary model membranes-Prediction of the liposome stability by the Langmuir monolayer study (vol 372, pg 212, 2012). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2014, 435, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, D.; Shi, D.; Wang, T.; Zhu, X. Mechanism of transdermal permeation promotion of lipophilic drugs by ethosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Wu, D.; Shi, D.; Wang, T.; Zhu, X. Mechanism of transdermal permeation promotion of lipophilic drugs by ethosomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangjit, S.; Obata, Y.; Sano, H.; Onuki, Y.; Opanasopit, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Miyoshi, T.; Kato, S.; Takayama, K. Comparative Study of Novel Ultradeformable Liposomes: Menthosomes, Transfersomes and Liposomes for Enhancing Skin Permeation of Meloxicam. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatif, M.M.; Khalil, I.A.; Khalil, M.A. Sertaconazole nitrate loaded nanovesicular systems for targeting skin fungal infection: In-vitro, ex-vivo and in-vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 527, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Effects of solvents and penetration enhancers on transdermal delivery of thymoquinone: permeability and skin deposition study. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, A.; Puri, V.; Mohd, H.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Effect of Penetration Enhancers on Transdermal Delivery of Oxcarbazepine, an Antiepileptic Drug Using Microemulsions. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořáková, K.; Štěpánek, P.; Kroupová, J.; Zbytovská, J. N-Alkylmorpholines: Potent Dermal and Transdermal Skin Permeation Enhancers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, A.; Dholaria, N.; Matharoo, N.; Michniak-Kohn, B. A Study of Microemulsion Systems for Transdermal Delivery of Risperidone Using Penetration Enhancers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 3109–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Román, R.; Naik, A.; Kalia, Y.; Fessi, H.; Guy, R. Visualization of skin penetration using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balata, G.F.; Faisal, M.M.; Elghamry, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Preparation and Characterization of Ivabradine HCl Transfersomes for Enhanced Transdermal Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Arroyo, C.M.; Cózar-Bernal, M.J.; González-R, P.L.; León, J.M.; Calle, M.; Canca, D.; Rabasco, A.M. Deformability properties of timolol-loaded transfersomes based on the extrusion mechanism. Statistical optimization of the process. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2016, 42, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Osmałek, T.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Deformable Liposomal Hydrogel for Dermal and Transdermal Delivery of Meloxicam. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9319–9335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, E.; Park, M.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, T.; Kim, E.-H.; Jung, K.; Kim, A. Poloxamer-Based Thermoreversible Gel for Topical Delivery of Emodin: Influence of P407 and P188 on Solubility of Emodin and Its Application in Cellular Activity Screening. Molecules 2017, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.K.; et al. A novel vesicular carrier, transethosome, for enhanced skin delivery of voriconazole: Characterization and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces 2012, 92, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Zaafarany, G.M.; Awad, G.A.S.; Holayel, S.M.; Mortada, N.D. Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 397, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kausar, H.; Mujeeb, M.; Ahad, A.; Moolakkadath, T.; Aqil, M.; Ahmad, A.; Akhter, M.H. Optimization of ethosomes for topical thymoquinone delivery for the treatment of skin acne. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, P.; Mudgil, P. The Cell Wall, Cell Membrane and Virulence Factors of Staphylococcus aureus and Their Role in Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonstein, S.A.; Baldwin, J.N. Loss of the Penicillinase Plasmid After Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. J. Bacteriol. 1972, 109, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinazo, A.; Manresa, M.; Marques, A.; Bustelo, M.; Espuny, M.; Pérez, L. Amino acid–based surfactants: New antimicrobial agents. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 228, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The π-A isotherms (a) and compression modulus curves calculated using Equation 1 (b) for Ph 90 in the presence of various edge activators and their combinations in the subphase.
Figure 1.
The π-A isotherms (a) and compression modulus curves calculated using Equation 1 (b) for Ph 90 in the presence of various edge activators and their combinations in the subphase.
Figure 2.
The elastic (G’) and viscous (G’’) dilational moduli of the lipid film in the presence of surfactants determined for various amplitudes of oscillations.
Figure 2.
The elastic (G’) and viscous (G’’) dilational moduli of the lipid film in the presence of surfactants determined for various amplitudes of oscillations.
Figure 3.
(A) Ex vivo drug permeation profiles of thymoquinone (TQ)-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes formulations over 24 hours; (B) TQ deposited in the different layers of skin after 24-hour skin permeation study from formulations tested (n=5.) Data are presented as means with SD.
Figure 3.
(A) Ex vivo drug permeation profiles of thymoquinone (TQ)-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes formulations over 24 hours; (B) TQ deposited in the different layers of skin after 24-hour skin permeation study from formulations tested (n=5.) Data are presented as means with SD.
Figure 4.
Microscopy images of human cadaver skin samples from the skin penetration study of Rhodamine B-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes (A) the skin autofluorescence (B), Rhodamine B florescence (C) Overlap of A and B images. Skin only after 4 hours (A1, B1, C1), Skin only after 8 hours (A6, B6, C6), E after 4 hours (A2, B2, C2), E after 8 hours (A7, B7, C7). F3 after 4 hours (A3, B3, C3). F3 after 8 hours (A8, B8, c8). F1 after 4 hours (A4, B4, C4). F1 after 8 hours (A9, B9, C9). F2 after 4 hours (A5, B5, B6), F2 after 8 hours (A10, B10, C10). Rhodamine B in hydroethanolic solution after 4 hours (A6, B6, C6), after 8 hours (A11,B11,C11).
Figure 4.
Microscopy images of human cadaver skin samples from the skin penetration study of Rhodamine B-loaded ethosomes and transethosomes (A) the skin autofluorescence (B), Rhodamine B florescence (C) Overlap of A and B images. Skin only after 4 hours (A1, B1, C1), Skin only after 8 hours (A6, B6, C6), E after 4 hours (A2, B2, C2), E after 8 hours (A7, B7, C7). F3 after 4 hours (A3, B3, C3). F3 after 8 hours (A8, B8, c8). F1 after 4 hours (A4, B4, C4). F1 after 8 hours (A9, B9, C9). F2 after 4 hours (A5, B5, B6), F2 after 8 hours (A10, B10, C10). Rhodamine B in hydroethanolic solution after 4 hours (A6, B6, C6), after 8 hours (A11,B11,C11).
Figure 5.
Bacterial inhibition study. Inhibition of S. aureus growth on agar plates by control negative; azithromycin 15 µg positive control; F1, F2, F3, E and TQ 40 µg.
Figure 5.
Bacterial inhibition study. Inhibition of S. aureus growth on agar plates by control negative; azithromycin 15 µg positive control; F1, F2, F3, E and TQ 40 µg.
Table 1.
The Composition of the Formulations Investigated in the Study.
Table 1.
The Composition of the Formulations Investigated in the Study.
| Formula |
TQ |
Tween 20 |
SLS |
SLG |
Ethanol (w/w) % |
Ph 90 |
| F1 |
200mg |
500mg |
- |
- |
50% |
3g |
| F2 |
200mg |
400mg |
100mg |
- |
50% |
3g |
| F3 |
200mg |
400mg |
- |
100mg |
50% |
3g |
| E |
200mg |
- |
- |
- |
50% |
3g |
Table 2.
Physiochemical properties of the obtained vesicles. data are presented as means ± SD (n=3).
Table 2.
Physiochemical properties of the obtained vesicles. data are presented as means ± SD (n=3).
| Formula |
Zeta Average (nm) |
PDI |
EE% |
Zeta Potential (mV) |
| F1 |
133.76 ± 1.26 |
0.20 ± 0.03 |
87% ± 0.34 |
-20 ± 0.3 |
| F2 |
115.49 ± 0.72 |
0.19 ± 0.01 |
94% ± 0.26 |
-62 ± 0.4 |
| F3 |
154.67 ± 2.68 |
0.22 ± 0.02 |
92% ± 0.35 |
-32 ± 0.6 |
| E |
164.14 ± 5.05 |
0.12 ± 0.02 |
81% ± 0.41 |
-38 ± 0.2 |
Table 3.
Permeation parameters obtained for the investigated formulations. Data are presented as means ± SD (n=5), * p<0.01 vs. control # p< 0.01 vs E.
Table 3.
Permeation parameters obtained for the investigated formulations. Data are presented as means ± SD (n=5), * p<0.01 vs. control # p< 0.01 vs E.
| Formulation |
Jss (μg cm−2 h −1 ) |
Kp (cm h−1 ) |
Enhancement Ratio |
Lag Time (hr) |
| Control |
3.34 ± 0.90 |
0.003 |
- |
- |
| F1 |
21.37 ± 0.01 *#
|
0.021 |
6.4 |
12.3 ± 0.88 |
| F2 |
23.71 ± 2.5 *#
|
0.037 |
9.8 |
12.72 ± 0.58 |
| F3 |
12.13 ± 1.8 * |
0.013 |
3.63 |
14.19 ± 0.61 |
| E |
11.71 ± 1.0 * |
0.012 |
3.51 |
10.42 ± 0.62 |
Table 4.
Zone of inhibitions of tested formulation against S. aureus n=3.
Table 4.
Zone of inhibitions of tested formulation against S. aureus n=3.
| Formulation |
Zone of Inhibition (mm) |
| Azithromycin |
7.82 ± 0.01 |
| F1 |
10.0 ± 0.9 |
| F2 |
26.4 ± 0.3 |
| F3 |
18.1 ± 0.8 |
| E |
6.55 ± 0.9 |
| TQ |
1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Blank formulation |
0 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).