1. Introduction
Arsenic (As) is a naturally occurring metalloid that is highly toxic and carcinogenic. The International Center for Research on Cancer (IARC) classifies As in group I (sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in humans)[
1], while for The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) is a group A human carcinogen[
2]. Its inorganic forms represent the most significant toxicity for people due to prolonged exposure linked to consumption habits. It is usually incorporated mainly through ingesting contaminated drinking water and contaminated food, either by the water used in its preparation or the irrigation of crops[
3]. In humans, the symptoms are lesions and spots on the skin, especially on the extremities. If exposure continues, cancerous and non-cancerous systemic changes appear. In addition, as a consequence of said exposure, cardiovascular, nervous, hepatic and renal diseases, diabetes mellitus, and different types of lung, bladder, liver and prostate cancer can appear[
4].
Use and Pollution
As is an element widely distributed in the biosphere, its abundant and ubiquitous characteristic is related to the natural degradation of rocks and volcanic emissions. However, there is also a contribution from anthropogenic activities, such as industrial products and processes (mining, metal smelting, pesticides and wood preservatives)[
5]. Today, As is widely used in the electronics industry as gallium arsenide. For example, more than 90% of the domestic consumption of arsenic trioxide in the year 2003 (USA) was used to manufacture the compound copper chromate arsenate (CCA), essential for wood preservatives[
6], consists of a combination of copper salts, chromium oxide and copper arsenate. CCA protects wood from degradation caused by fungi, insects, and other organisms. However, the use of CCA has declined in many countries due to its adverse effects on human health and the environment. According to the USEPA and the Environmental Health Perspectives magazine: "Arsenic is a toxic element, and CCA releases it into the environment contributing to the total Arsenic burden in the population, especially in areas close to wood treatment sites"[
6],[
7]. The As levels are variable since it has high mobility and the ability to be absorbed or desorbed from particles or change their oxidation state by reacting with oxygen, water or soil molecules or by the action of microorganisms. It can occur in organic and inorganic forms, being the speciation of interest in environmental issues due to the different levels of toxicity exhibited by the different species[
8]. It is an endemic problem. As contamination of drinking water is a global concern. So is the interest in efficient and economical methods to detect and eliminate it.
Arsenic as a regional problem
The primary public health problem referred to this contaminant in Argentina, produced by the intake of variable and constant doses over time, is Chronic Regional Endemic Hydroarsenicism (HACRE)[
9]. Previous studies in our country revealed that the population exposed to water consumption with an As content higher than the acceptable level was 4,000,000 habitants[
10]. The most affected region includes the provinces of Salta, La Pampa, Córdoba, San Luis, Santa Fe, Buenos Aires, Santiago del Estero, Chaco, Tucumán, San Juan, Mendoza and[
11]. Concerning drinking water, the maximum limit of As in water recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) is 0.01 mg L
-1 [
12]. In contrast, the tolerated limit in the Province of Santa Fe is 0.05 mg L
-1. The primary treatment for these waters contaminated with As is
Reverse Osmosis[
13], a water treatment process used to desalinate and purify water, removing contaminants and dissolved salts, based on forcing the passage of water through an impermeable membrane for contaminants. Although this technique has several advantages, it also has some disadvantages. One is the generation of large volumes of rejected water, which contains high concentrations of salts and dissolved contaminants, posing environmental and waste disposal challenges. In particular cases, these rejected waters are often returned to the original groundwater or used for irrigation, both options being counterproductive for health and skipping the real solution to the problem. A challenge associated with reverse osmosis is the proper management of rejected water since its discharge without treatment can negatively impact the receiving aquatic environment[
14]. The ability of the chitosan biopolymer to remove As increases when it is part of hybrid sorbents such as chitosan/nanoFe[
15]. This synergy compensates for the competition in the sorption of other ions present in groundwater of high salinity. Chitosan/magnetite hybrid sorbents are stable, have good As removal capacity, and can be more easily separated after use.
2. Results
2.1. FT-IR and XRD spectroscopy
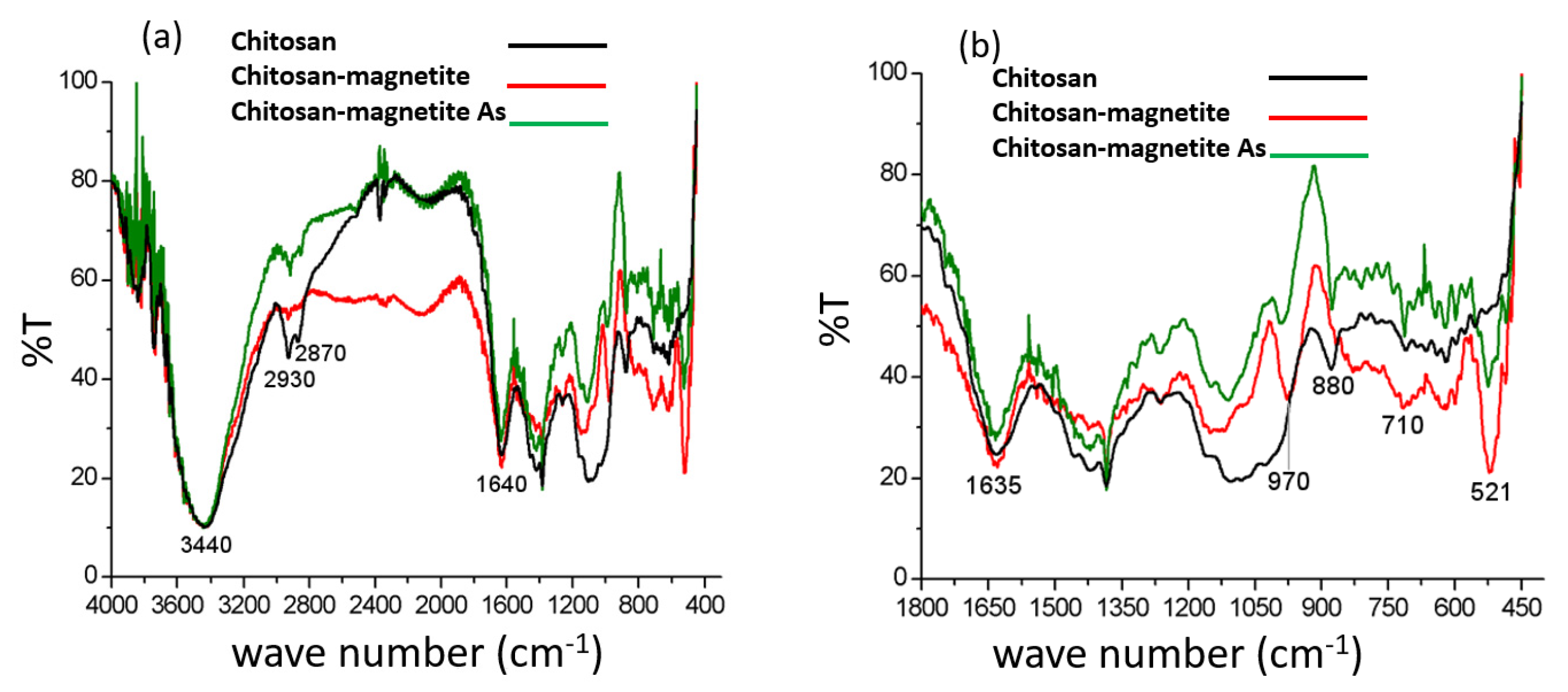
The Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy technique (FT-IR) spectra shown in
Figure 1a correspond to untreated chitosan-magnetite spheres (blank spheres) and treated with As(V) solutions. The chitosan polymer's spectrum is also included to compare the spectral signals. The characteristic signals of the materials are observed: chitosan, chitosan bound to Fe and chitosan-arsenate ions. The figure shows the characteristic signals of the chitosan polymer between (3500 - 3400) cm
-1, where the bands that correspond to the vibration (due to elongation and tension) of the OH and NH groups are visualized. The signals at 2930 and 2870 cm
-1 correspond to the stretching vibrations of the CH
2 groups of the pyranose ring and the vibrations of the C–H bonds of chitosan[
16]. At 1640 cm
-1, the band due to the C=O bond stands out of the carbonyl group of the N-acetyl amide groups[
17]. In order to appreciate it in more detail and deepen the analysis, an extension of the spectrum was carried out in the range of (1800 – 400) cm
-1, as shown in
Figure 1b. In this magnification, two bands are observed in the spectrum of chitosan with magnetite at 970 and 900 cm
-1, corresponding to the vibration of the Fe-O bond of magnetite[
18]. The 970 cm
-1 band is more intense, narrow, and displaced at 990 cm
-1 when As(V) was incorporated; said observation can be attributed to incorporating As(V) into the Fe-O group. It should be noted that the 880 cm
-1 band of the chitosan spectrum presents a deformation in the chitosan spectrum with magnetite in the presence of As(V). A narrow band present in this zone is attributed to the vibration of the sorbed As-O bond in metal oxides[
19].
In addition, an intense band is observed at 521 cm
-1 present in the spectrum of the sorbent with magnetite, absent in the spectrum of chitosan. This band is attributed to the vibration of the Fe-O bond of the metal oxides[
20]. Comparing this band of the sorbent with magnetite before and after treatment with As(V), a decrease in its intensity is observed, so it can be assumed that the incorporation of As(V) into the sorbent occurs in said functional groups associated with magnetite[
17].
Figure 1.
(a) Assignment of FT-IR signals of chitosan (black), chitosan-magnetite (red) and chitosan-magnetite-As (green); (b) Magnified FT-IR spectra and assignment of the signals of chitosan (black), chitosan-magnetite (red), and chitosan-magnetite-As (green).
Figure 1.
(a) Assignment of FT-IR signals of chitosan (black), chitosan-magnetite (red) and chitosan-magnetite-As (green); (b) Magnified FT-IR spectra and assignment of the signals of chitosan (black), chitosan-magnetite (red), and chitosan-magnetite-As (green).
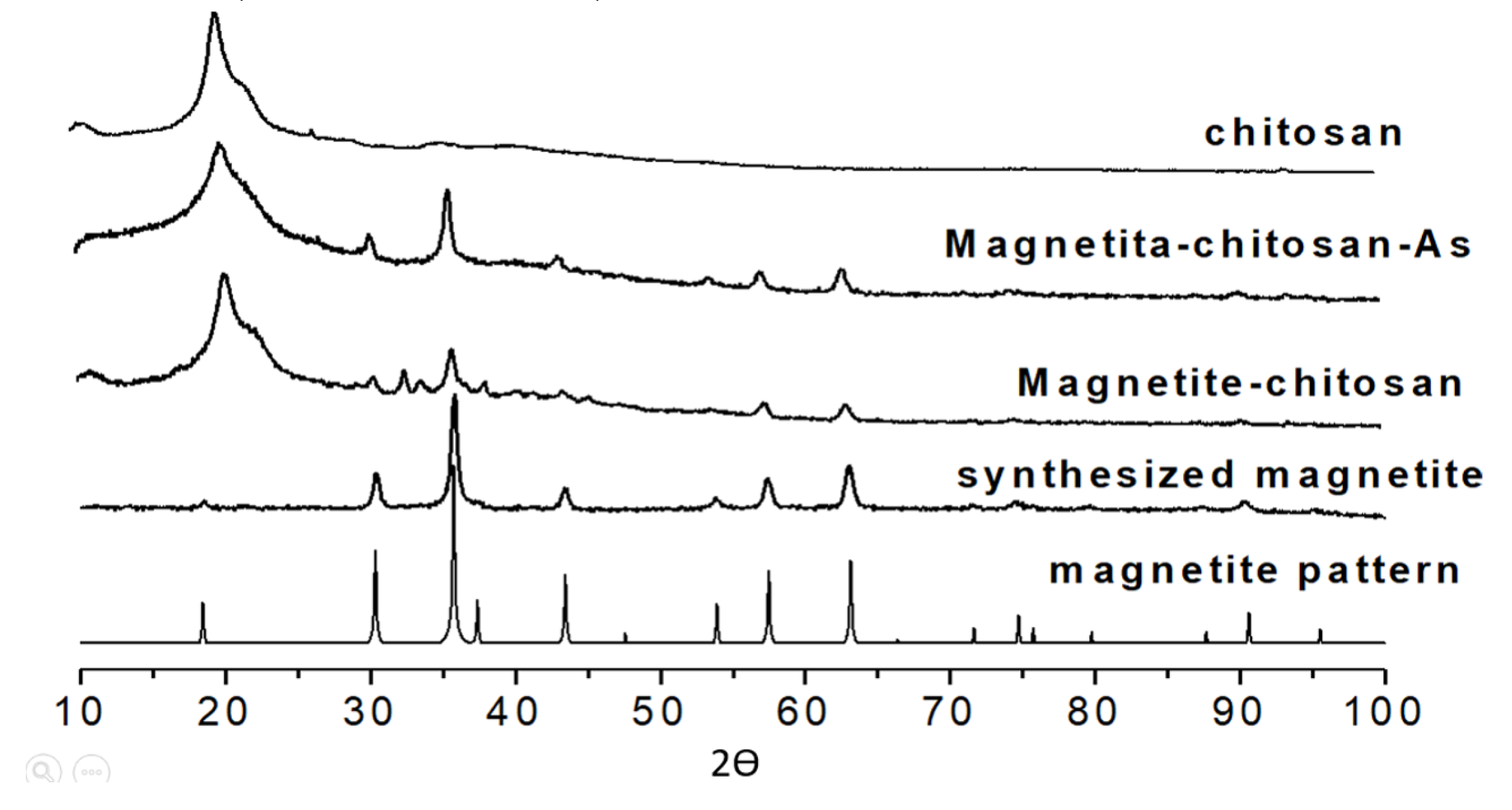
characteristic peaks for magnetite, Fe
3O
4, were observed in X-ray diffraction (XRD),
Figure 2. The figure compares the XRD spectra of a pure magnetite pattern[
21] with that synthesized in this work. The slight broadening of the XRD lines can be interpreted as poor crystallinity of the synthesized magnetite and the small size of the crystals. The presence of chitosan and As further broadens the signals of the synthesized magnetite[
22].
Figure 2.
X-ray powder diffractogram of pure synthesized magnetite, magnetite-chitosan, magnetite-chitosan-As(V) and chitosan.
Figure 2.
X-ray powder diffractogram of pure synthesized magnetite, magnetite-chitosan, magnetite-chitosan-As(V) and chitosan.
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
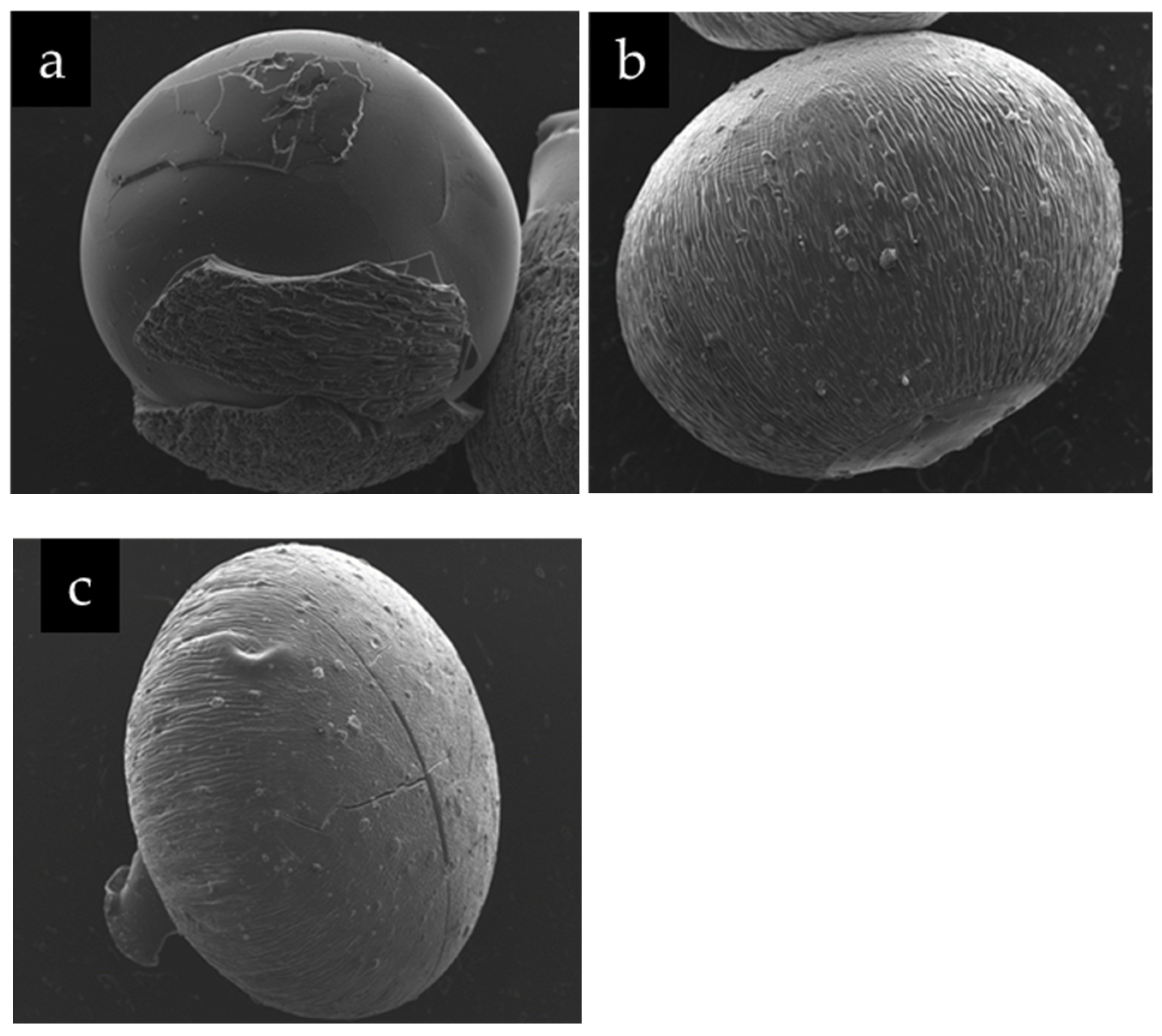
Figure 3 shows the heterogeneity of the chitosan-magnetite spheres and the presence of micro aggregates on their surfaces. It can be seen the chitosan sphere has portions with layers of different roughness irregularly distributed
Figure 3a. On the other hand, the chitosan spheres with magnetite present striations that give them a homogeneous roughness with microaggregates of particles, while the chitosan-magnetite spheres with As(V) present striations, microaggregates and an apparent crystallinity,
Figure 3c. The latter could indicate that incorporating this element gives it structural rigidity. It is notorious, in both spheres, the portion that corresponds to the zone of detachment or cutting during its synthesis. In order to develop a more detailed description of the surface of each sphere, different magnifications were applied in different areas (data not shown). These images are consistent with what is reported in the literature for the different materials: chitosan[
22] and chitosan-magnetite at the concentration used in this work[
23],[
24],[
25].
Figure 3.
SEM images of: (a) chitosan, (b) chitosan-magnetite and (c) chitosan-magnetite-As(V). ETD detector, 240 x magnification.
Figure 3.
SEM images of: (a) chitosan, (b) chitosan-magnetite and (c) chitosan-magnetite-As(V). ETD detector, 240 x magnification.
2.3. pH value at zero charge point (pHpzc)
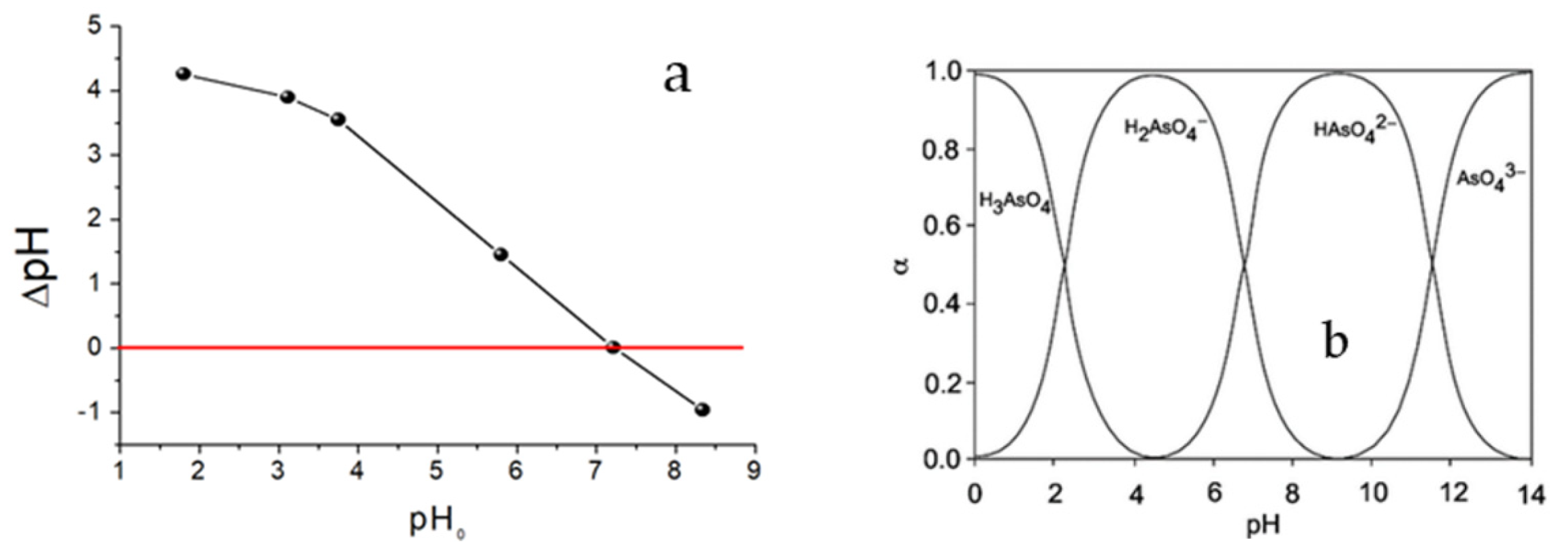
The experimentally determined pHpzc value of the material was 7.21 (Figure 4a); therefore, at a working pH of 6.30, the surface of the sorbent is positively charged. Considering the diagram of As(V) species as a function of pH (Figure 4b), at this pH value the negative H2AsO4- species predominates, which is electrostatically attracted to the surface of the sorbent.
Figure 4.
(a) The pHpzc chitosan polymer. Sorbent dose 28 g L−1, NaNO3 0.01 mol L–1, T = 25 ºC, 24 h equilibrium time and (b) distribution diagram of arsenate species as a function of pH.
Figure 4.
(a) The pHpzc chitosan polymer. Sorbent dose 28 g L−1, NaNO3 0.01 mol L–1, T = 25 ºC, 24 h equilibrium time and (b) distribution diagram of arsenate species as a function of pH.
2.4. As(V) detection and quantification
The concentration of As(V) in solution was spectrophotometrically determined using the molar absorptivity coefficient determined from the calibration curves performed with the molybdenum blue method, as described in section 4.3. The value of ε averaged in triplicate was (223000 ± 100) M-1 cm-1.
The detection limit (LD) is the lowest concentration reliably detectable by the technique. In the modern definition, the detection limit is calculated based on the standard deviation of the predicted concentration for a blank sample[
26],
eq. 1.
Where s(x
inc) is the deviation of a x
inc concentration measurement; s
y/x the standard deviation of the regression residuals; n is the number of repetitions of the experiment; m is the of measured residues; x
m is the arithmetic mean; A is the slope of linearization. The calculation for Q
xx is shown in
eq. 2:
If a sample without analyte is analyzed in triplicate (x
inc = 0),
eq. 1 reduces to
eq. 3:
The LD obtained was 5.27 x 10
-8 M (0.0039 mg L
-1 of As(V)). The limit of quantification (LQ) was calculated as indicated by
eq. 4 and its value was 1.60 x 10
-7 M (0.012 mg L
-1).
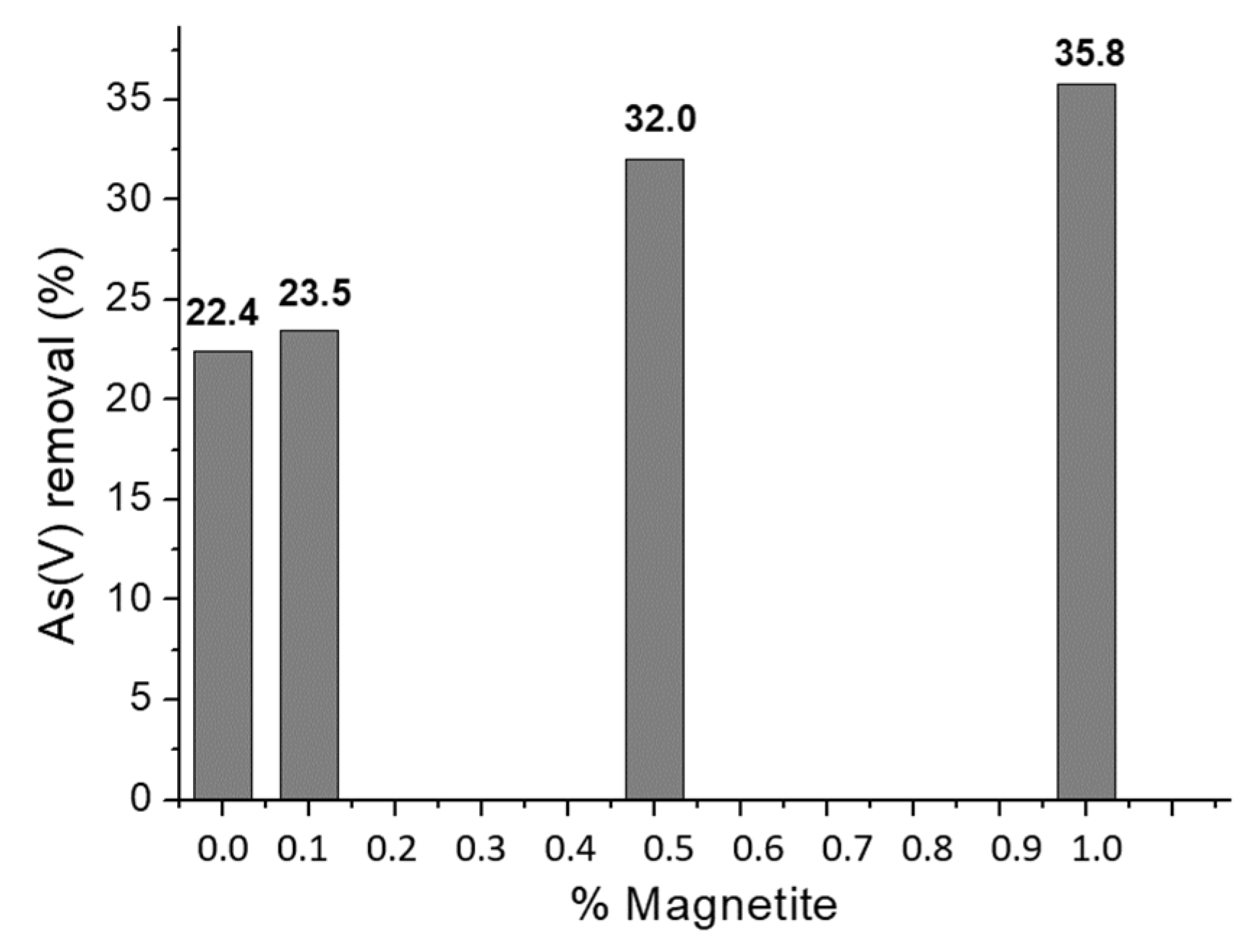
2.5. Effect of the amount of magnetite on As(V) sorption
The percentages of As(V) removal using different amounts of magnetite were compared under the same experimental conditions. Figure 5 shows an increase in sorption related to adding magnetite to chitosan. It was decided to use 0.5% P/V of magnetite for this work since an increase in the percentage of As(V) removal was observed concerning the sorbent without magnetite (10%). In contrast, doubling the amount of magnetite increases the removal yield by 3.8%. In addition, a decrease in the mechanical stability of the chitosan-magnetite spheres with 1% magnetite could be observed.
Figure 5.
Effect of magnetite addition on As(V) sorption.
Figure 5.
Effect of magnetite addition on As(V) sorption.
2.6. Experimental design and optimization of the sorption process
Table 1 summarizes the values for each factor generated by the Central Composite Design (CCD) and the response obtained experimentally (As(V) removal, R%). Table 2 shows the Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) analysis for the quadratic model, which best fits the selected response's experimental data.
Table 1.
Factors calculated by the CCD and the response obtained for each experiment.
Table 1.
Factors calculated by the CCD and the response obtained for each experiment.
| Run |
pH |
Mass (g) |
R (%) |
| 1 |
5.40 |
0.30 |
32.00 |
| 2 |
5.40 |
0.30 |
30.79 |
| 3 |
2.60 |
0.30 |
2.47 |
| 4 |
3.40 |
0.10 |
0.01 |
| 5 |
5.40 |
0,58 |
33.18 |
| 6 |
7.40 |
0.50 |
29.31 |
| 7 |
5.40 |
0.02 |
7.80 |
| 8 |
8.20 |
0.30 |
15.50 |
| 9 |
3.40 |
0.50 |
11.00 |
| 10 |
5.40 |
0.30 |
29.86 |
| 11 |
7.40 |
0.10 |
16.43 |
Table 2.
ANOVA for Reduced Quadratic model. Response %R.
Table 2.
ANOVA for Reduced Quadratic model. Response %R.
| Source |
Sum of Squares |
df |
Mean Square |
F Value |
p-value Prob > F |
|
| Reduced quadratic model |
1509.95 |
4 |
377.49 |
34.55 |
0.0003 |
significant |
| A-pH |
1034.32 |
1 |
1034.32 |
94.67 |
< 0.0001 |
|
| B-masa |
365.46 |
1 |
365.46 |
33.45 |
0.0012 |
|
| A2
|
669.07 |
1 |
669.07 |
61.24 |
0.0002 |
|
| B2
|
169.64 |
1 |
169.64 |
15.53 |
0.0076 |
|
| Residual |
65.55 |
6 |
10.93 |
|
|
|
| Lack of Fit |
63.25 |
4 |
15.81 |
13.73 |
0.0690 |
not significant |
| Pure Error |
2.30 |
2 |
1.15 |
|
|
|
| Cor Total |
1575.51 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
From the ANOVA, it is observed that the quadratic model is significant. The factors pH and mass are significant. The first-order interaction between mass and pH does not significantly influence the response, so it was removed from the model. On the other hand, the lack of fit is not significant, indicating the model has a good correlation with the experimental values. The statistical parameters of the model prediction are shown in Table 3. It is observed that the values of R2-predicted and R2-adjusted did not show a significant difference, which rules out a possible block effect or the presence of outliers within the data set. Adequate precision is related to the signal-to-noise ratio; it is considered correct if its value exceeds 4.
Table 3.
Statistical parameters of the model prediction.
Table 3.
Statistical parameters of the model prediction.
| Std. Dev. |
3,31 |
R² |
0,9584 |
| Mean |
18,94 |
Adjusted R² |
0,9307 |
| C.V. % |
17,45 |
Predicted R² |
0,7988 |
| |
|
Adeq Precision |
14,543 |
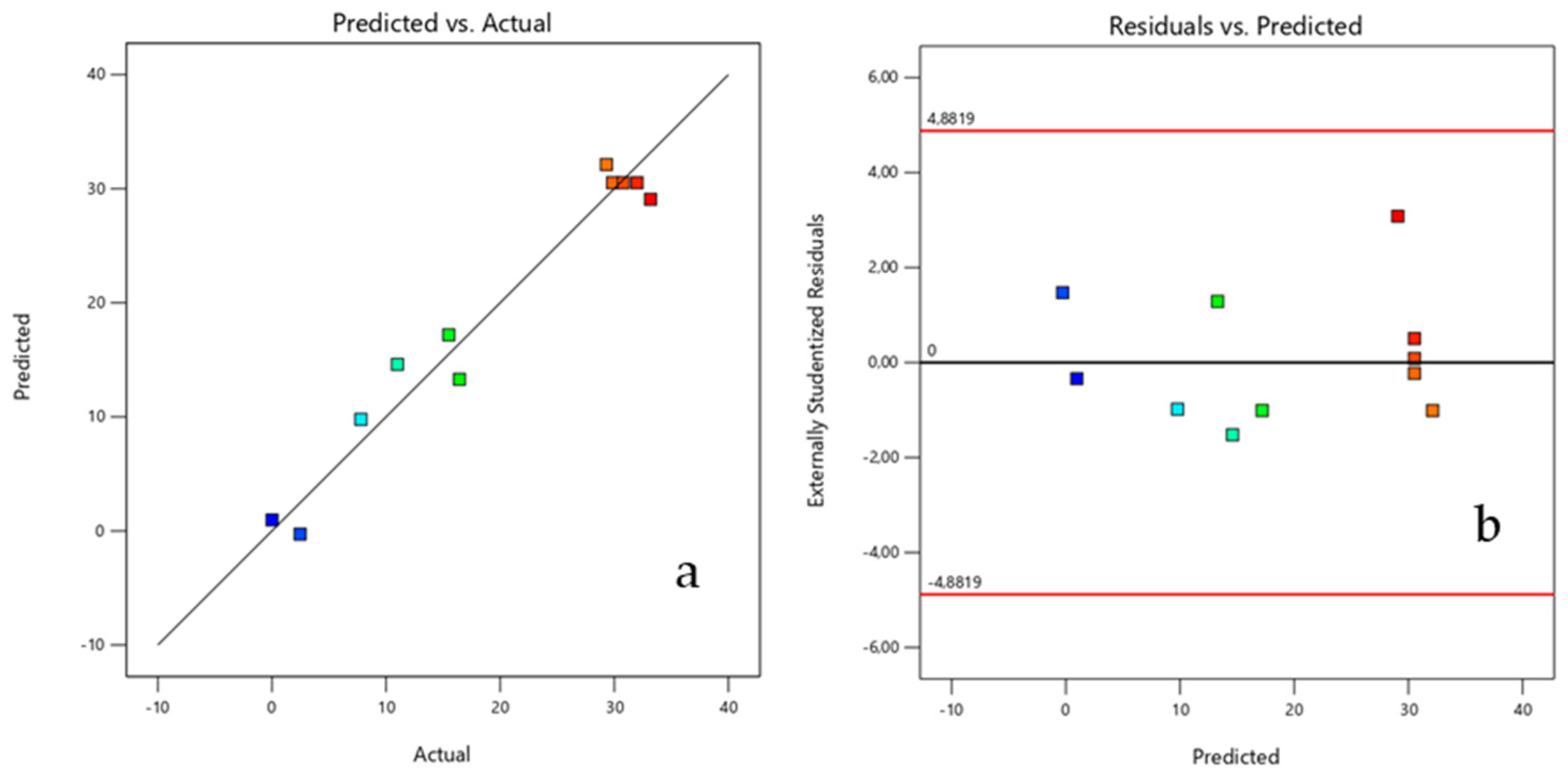
Figure 6. shows the diagnostic plots of the reduced model. These graphs check the assumptions of the model, validating its analysis.
Figure 6.
Normal probability graphs of studentized (a) residuals and (b) outliers.
Figure 6.
Normal probability graphs of studentized (a) residuals and (b) outliers.
Due to the above, the response (%R) can be expressed through the following mathematical
eq. 5 using the encoded coefficients of the model.
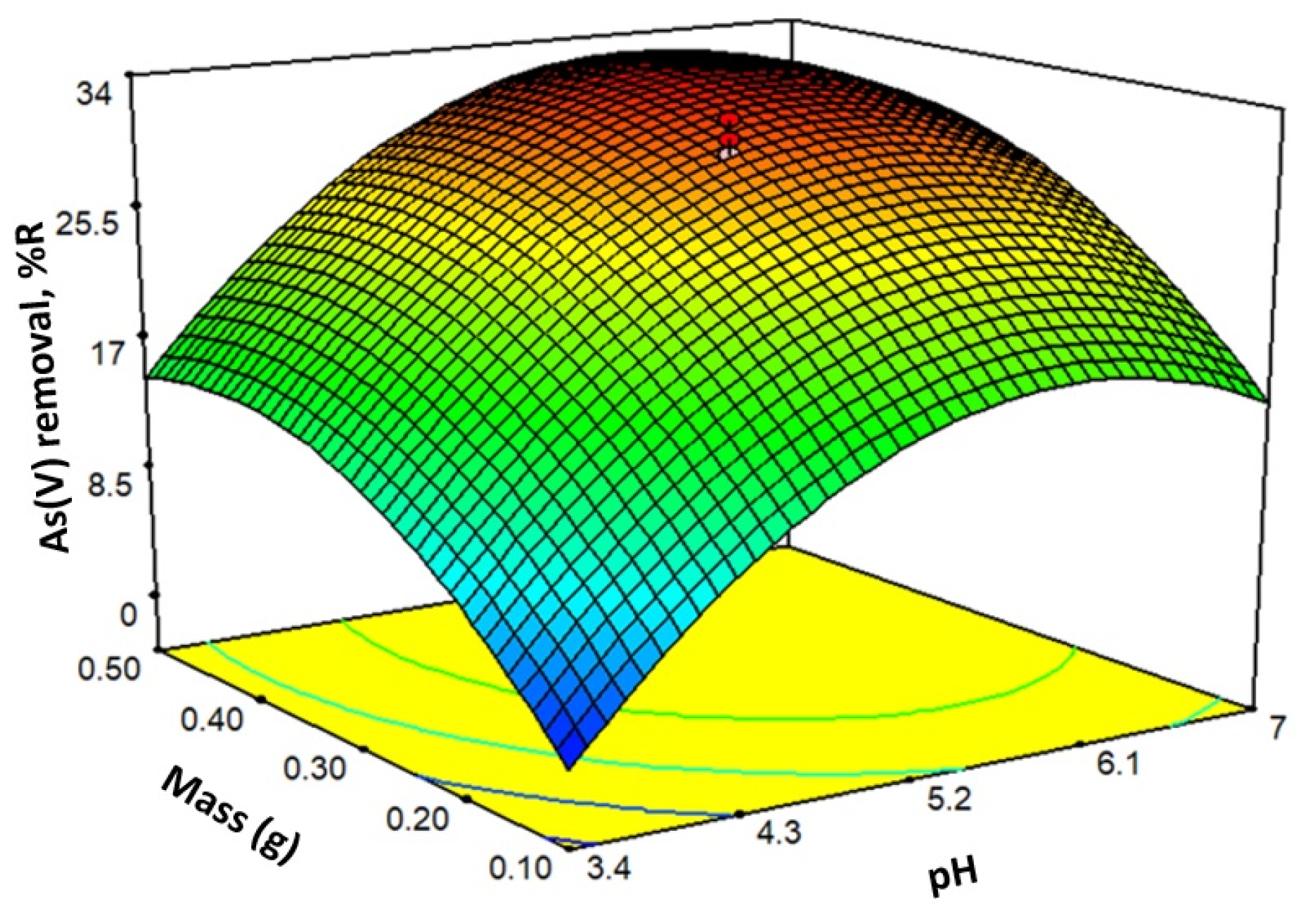
Positive values of the coefficients imply that an increase in the factor increases the response, and negative values indicate a decrease in the response. In the case of eq. 5, it is observed that the factor with the most significant weight in the %R is the pH. Eq. 5 provides the response surface shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7.
Response surface for generated by eq. 5.
Figure 7.
Response surface for generated by eq. 5.
When the pH increases from 2 to 7, the negatively charged As(V) species increases, Figure 4b. At the same time, the positive charge on the sorbent decreases in that same range (at pH 7.2, the charge is zero), Figure 4a. At pH close to 6, the combination of factors is optimal to retain As(V). Increasing the mass to a value of approximately 0.20 g increases the sorption sites and, therefore, the removal of As(V). Above 0.20 g, there is no significant increase in As(V) sorption. This effect may occur because the increase in mass makes it difficult for the contaminant to access.
Optimization of the process under study using the response surface consists of achieving maximum sorption using the minimum amount of sorbent mass, with a pH established in the design range. With these considerations, the model estimated a %R value 27.61 working at pH 6.00 and 0.22 g of sorbent. Three batch experiments were carried out considering the pH and mass values estimated by the model, preserving the initial conditions with which the complete design experiments were carried out: [As(V)] 2 mg L-1, final volume 25.0 mL, temperature 20°C and gentle stirring. The following values were obtained for %R: 26.80 – 27.55 – 27.70.
2.7. Kinetic studies
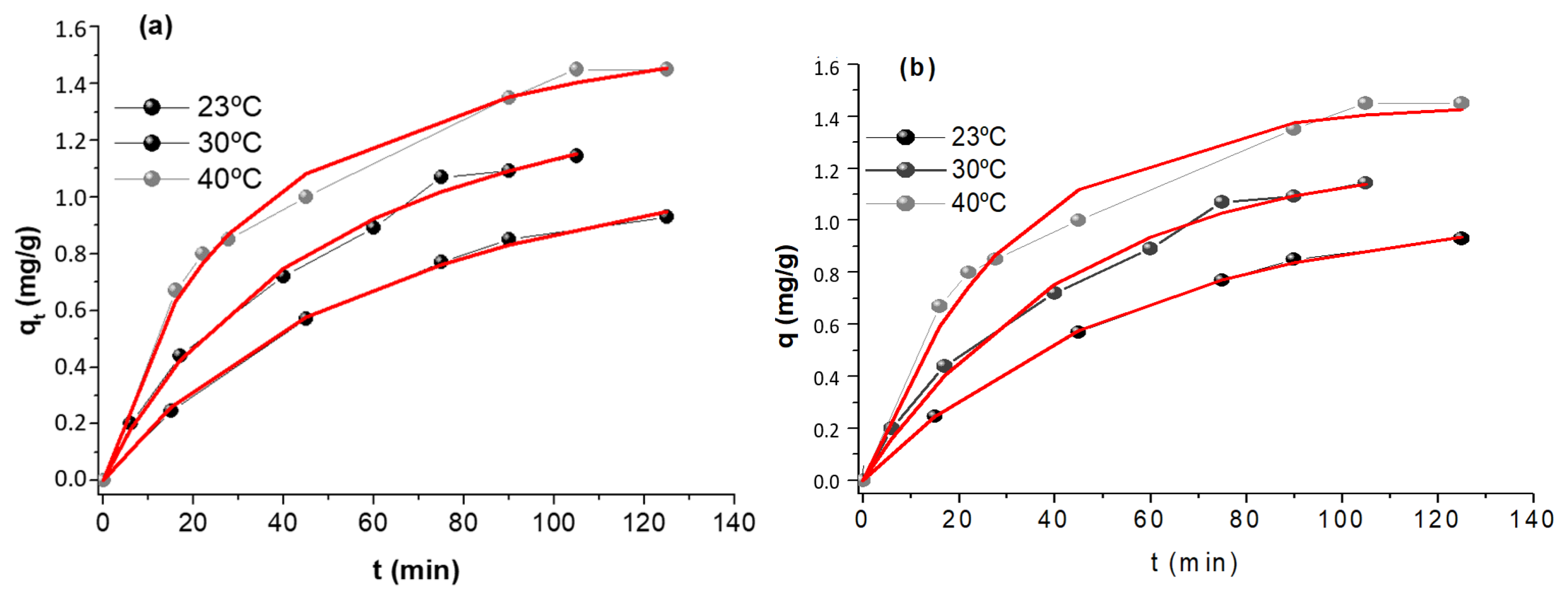
Kinetics experiments were carried out at three temperatures: 23°C, 30°C and 40°C and evaluate using pseudo-first and pseudo-second-order models; for each temperature the amount of contaminant sorbed per gram of sorbent, qt (mg g-1) was represented as a function of time(min). These results are shown in Figure 8 and Table 4.
Figure 8.
Kinetic data and fit employing (a) pseudo-first order and (b) pseudo-second order kinetic model. Initial [As(V)] = 5 mg L-1, sorbent dose = 0.4 g L-1 and pH = 6.00.
Figure 8.
Kinetic data and fit employing (a) pseudo-first order and (b) pseudo-second order kinetic model. Initial [As(V)] = 5 mg L-1, sorbent dose = 0.4 g L-1 and pH = 6.00.
Table 4.
Kinetic parameters of the pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order models at 23°C, 30°C and 40°C.
Table 4.
Kinetic parameters of the pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order models at 23°C, 30°C and 40°C.
| Model |
Parameters |
23ºC |
30ºC |
40ºC |
| pseudo-first order |
k1
|
0.0176±0.0026 |
0.0228±0.0025 |
0.0327±0.0033 |
| |
%E |
14.7 |
11.0 |
10.1 |
| |
qt
%E |
1.05±0.026
2,6% |
1.25±0.055
4.4% |
1.45±0.055
3.8% |
| |
Chi2
|
0.00006 |
0.00127 |
0.00445 |
| |
R2
|
0.9996 |
0.9943 |
0.98408 |
| pseudo-second order |
k2
|
0.0093±0.0013 |
0.0120±0.0016 |
0.0186±0.0020 |
| |
%E |
14,0 |
14.4 |
10.7 |
| |
qt
%E |
1.50±0.066
8.4% |
1.73±0.093
5.4% |
1.82±0.060
3.3% |
| |
Chi2
|
0.00023 |
0.0009 |
0.00207 |
| |
R2
|
0.9986 |
0.9960 |
0.9926 |
The experimental data fits using the applied kinetic models are both reasonably good. From the statistical parameters and the errors of the constants, Table 4, it cannot be decided whether the model that best describes the process is the pseudo-first order or the second order. Using the Arrhenius equation, the values of Activation Energy (Ea) were 28.1 and 31.4 kJ/mol using the pseudo-first order or pseudo-second order constants, respectively.
2.8. Thermodynamic Study
qt (mg g-1) was represented for each temperature as a function of [As(V)] at equilibrium. The Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin-Radushkevich models were used. The results obtained are shown below in Table 5.
Table 5.
Thermodynamic parameters for Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin-Radushkevich models.
Table 5.
Thermodynamic parameters for Langmuir, Freundlich and Dubinin-Radushkevich models.
| Model |
23°C |
30°C |
40°C |
| Langmuir |
|
|
|
| qmax(mg g-1) |
12.2±1,3 |
14.0±1,1 |
15.7±0.6 |
| KLM |
3012±275 |
3593 ± 690 |
4570±424 |
| R2
|
0.9957 |
0.9897 |
0.9972 |
| Χ2
|
0.0558 |
0.1785 |
0.0577 |
| Freundlich |
|
|
|
| KF |
1.0±0.2 |
1.0±0.2 |
0,8±0,2 |
| n |
2.1±0.2 |
2.0±0.2 |
1.8±0.2 |
| R2 |
0.9629 |
0.9785 |
0.9722 |
| Χ2
|
0.4631 |
0.3462 |
0.5342 |
| Dubinin-Radushkevich |
|
|
|
| qmax(mg g-1) |
32.2±3.7 |
36.2±5.2 |
46.7±6.7 |
| β(mol2J-2)x10-9
|
5.16±0.50 |
5.20±0.5 |
5.40±0.46 |
| E(kJ mol-1) |
9.77±0.08 |
8.80±0.05 |
9.60±0.05 |
| R2
|
0.9795 |
0.9854 |
0.9839 |
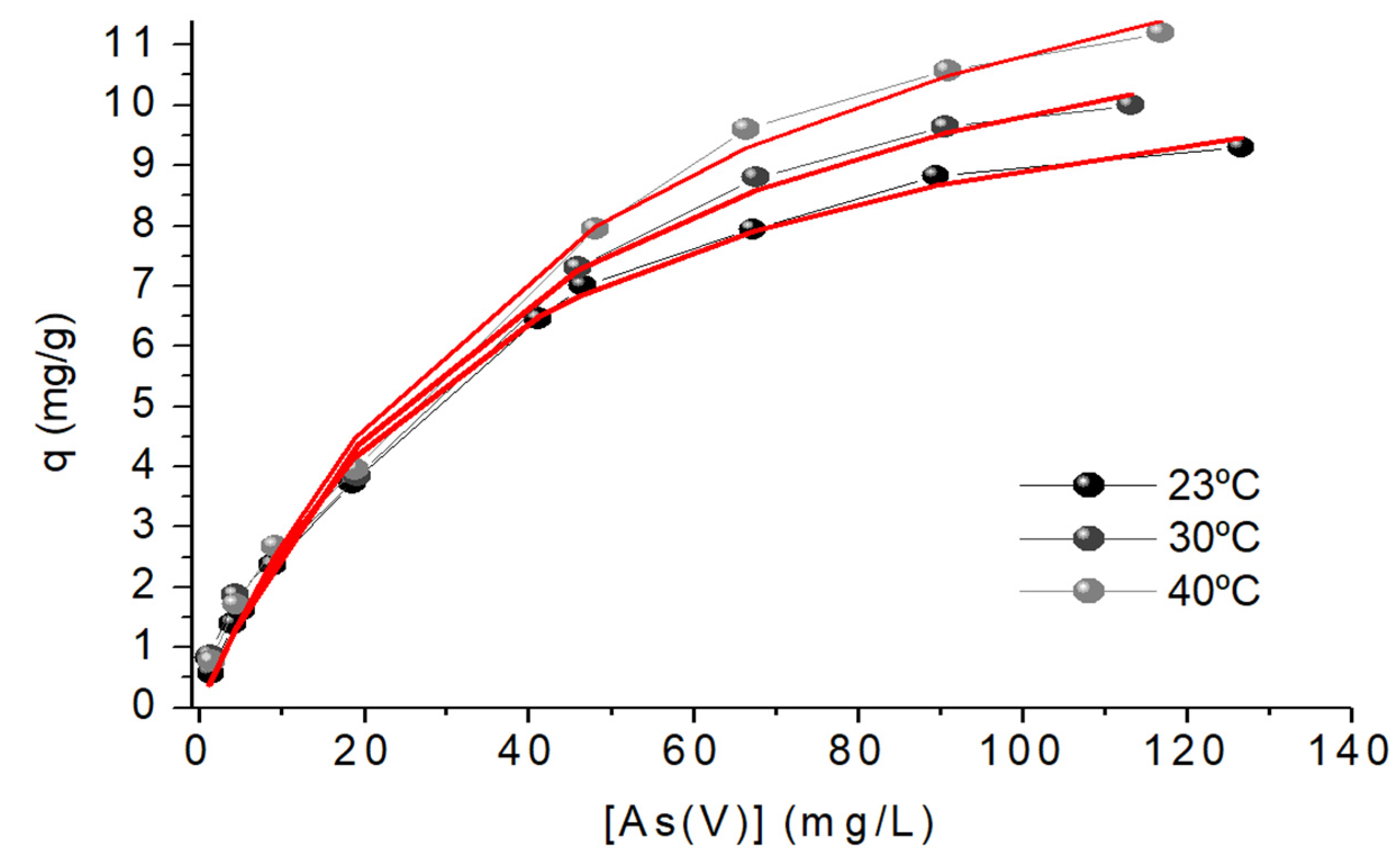
The coefficients R2 and Χ2 suggest that the Langmuir model better fits the experimental data at the studied temperatures, Figure 9. It is also evident that increasing the temperature increases KLM and the maximum sorption capacity, qmax. This increase may be explained because the sorbent has not a rigid structure, so the increase in temperature can increase accessibility to the As(V) binding sites. The maximum sorption capacity is located between the values reported in the literature for the sorption of As(V) with similar sorbents, Table 6.
Figure 9.
Sorption isotherm, Langmuir Model, of As(V) ions onto chitosan-magnetite. Sorbent doses =0.4 g L-1; pH = 6.0; [As(V)]0 = 5-125 mg L-1.
Figure 9.
Sorption isotherm, Langmuir Model, of As(V) ions onto chitosan-magnetite. Sorbent doses =0.4 g L-1; pH = 6.0; [As(V)]0 = 5-125 mg L-1.
Table 6.
Comparison of the maximum sorption capacity for sorbents with similar characteristics.
Table 6.
Comparison of the maximum sorption capacity for sorbents with similar characteristics.
| sorbent |
qmax (mg g-1) |
T (ºC) |
pH |
Reference |
| Chitosan-magnetite spheres |
12,2 |
23 |
6,00 |
[This work] |
| Magnetite- nanoparticles |
16,56 |
20 |
5,8 |
[27] |
| Chitosan-clay-magnetite spheres |
6,5 |
25 |
5,0 |
[28] |
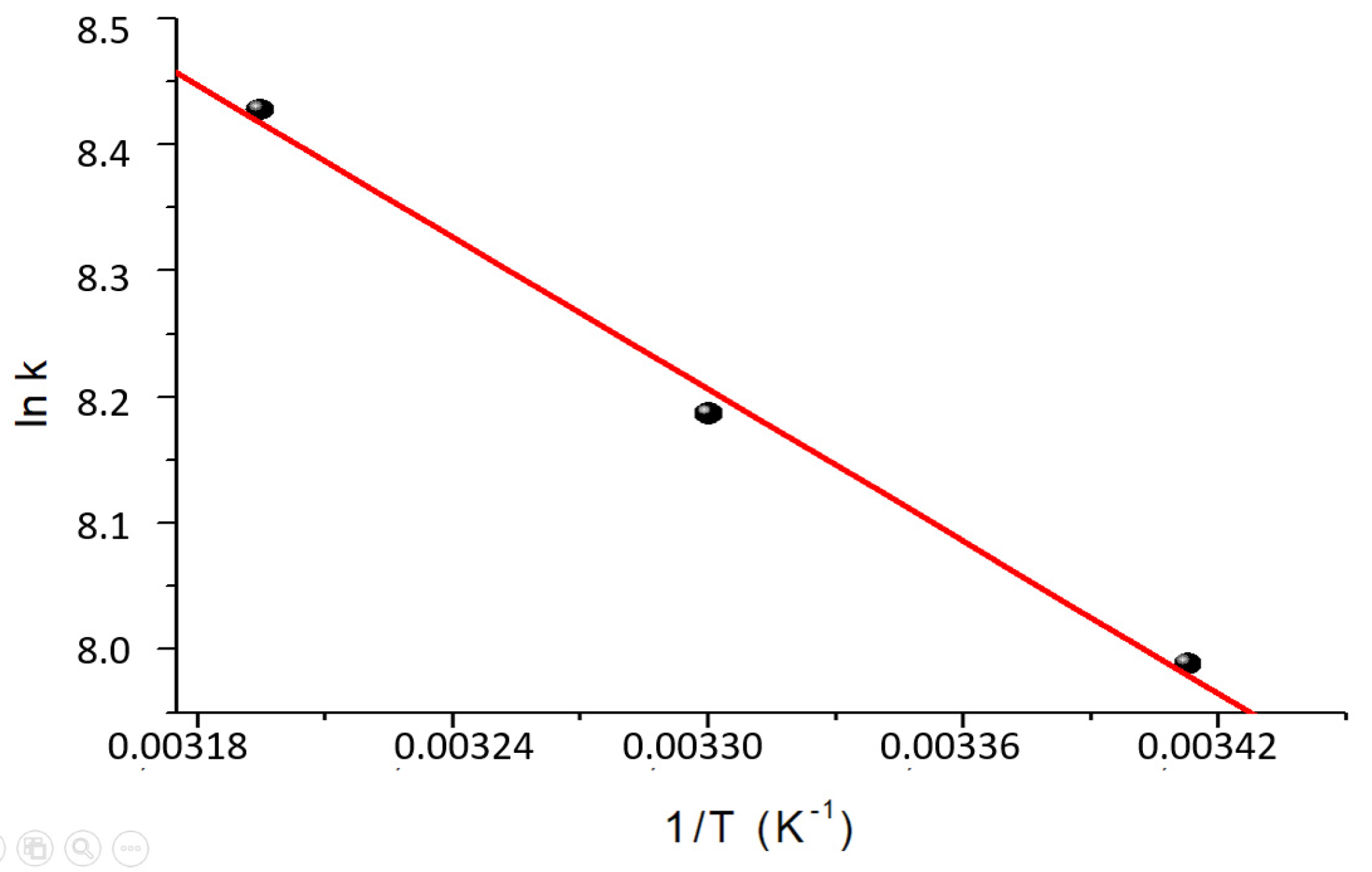
The dimensionless constants of the Langmuir model were used to calculate the thermodynamic parameters (∆H0 and ∆S0) using Van't Hoff's law. The results are shown in Figure 10 and Table 7.
Figure 10.
Van’t Hoff graph for the determination of the thermodynamic parameters ∆H° and ∆S° of the sorption process.
Figure 10.
Van’t Hoff graph for the determination of the thermodynamic parameters ∆H° and ∆S° of the sorption process.
Table 7.
Thermodynamic parameters calculated.
Table 7.
Thermodynamic parameters calculated.
| T(K) |
KLM
(dimensionless) |
ΔG°
(kJ mol-1) |
ΔH°
(kJ mol-1) |
ΔS°
(J mol-1 K-1) |
| 296 |
3012 |
-19.7 |
16.7 |
123.3 |
| 303 |
3593 |
-20.5 |
|
|
| 313 |
4570 |
-21.9 |
|
|
For values of E in the (8-16) kJ mol
-1 and E
a (24-409 kJ mol
-1 ranges, the sorption process is ion exchange. On the other hand, when E is < 8 kJ mol
-1 and E
a is < 40 kJ mol
-1, the process is physical. The process is chemical to E > 16 kJ mol
-1 and E
a > 40 kJ mol
-1 [
29]. This work's E values were (9.8-8.89 kJ mol
-1, indicating that the sorption process follows chemical ion exchange. This result agrees with the conclusion obtained in the Arrhenius equation (28.1-31.4) kJ mol
-1. The ∆H
0 value of 16.7 kJ mol
-1 indicates the endothermic nature of the As(V) sorption process, and the diffusion from bulk solution to sorbent boundary may involve energy to overcome the interaction of water molecules with As(V) ions. The positive enthalpic change coincides with the increase in the value of the K
LM constant with increasing temperature. It is important to note that as the temperature increases, so does the sorption capacity (q
max), which is consistent with the positive value of ∆H
0. The ∆S
0 value of 123.3 J mol
-1 K
-1 is positive and is associated with the increase in the system's disorder during the sorption progression. The ordering produced when the contaminant binds to the sorbent generates a solvent disorder. Finally, the negative ∆G
0 values confirm the spontaneity of the sorption process under the working conditions used. The process is entropically driven because the T∆S° term is greater than the ∆H° term.
2.9. Desorption studies
In order to verify if the sorbent under study can be reused, desorption tests were carried out. Table 8 details the results of calculating the efficiency of the desorption process, %D, for each desorbent used.
Table 8.
The efficiency of the desorption process using different desorbents.
Table 8.
The efficiency of the desorption process using different desorbents.
| Desorbent |
Desorbent concentration (M) |
contact time (h) |
Sorbent dose (g L-1) |
As(V) sorbed (mg) |
As(V) removed (mg)) |
%D (%) |
| Na2SO4
|
1 |
4 |
0,4 |
1.60 |
0.11 |
6.68 |
| NaCl |
0.5 |
4 |
0.4 |
1.40 |
0.10 |
7.14 |
| NaOH |
1 |
4 |
0.4 |
4.56 |
2.30 |
50.44 |
| NaOH |
1 |
20 |
0.4 |
1.50 |
1.10 |
84.62 |
It can be seen that with the use of 1 M NaOH, better results are obtained than with the other desorbents at the same contact time (4 h). In the case of increasing this time to 20 h, removing As(V) is more efficient, although it has a higher operating cost.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Obtaining organic-inorganic hybrid sorbents
The sorbent was prepared as 3.0 mm diameter average size spheres of chitosan-magnetite, as detailed below.
3.1.1. Synthesis of Magnetite
Magnetite Synthesis: 7.84 g of Fe(NH4)(SO4)2·6H2O and 10.80 g of FeCl3·6H2O were weighed to prepare 100 mL of 0.2 M and 0.4 M solution in Fe(II) and Fe(III). To this solu-tion, ammonium hydroxide (20%) was added, with stirring and under a hood, up to pH 9.0, observing the formation of a black suspension that was incubated (80°C, 30 min), fil-tered and washed until neutral pH. Work was carried out in an inert nitrogen atmosphere. The solid obtained was dried (60°C) until constant weight, homogenized with the help of a mortar and stored in a desiccator. The mass of M obtained was 4.549 g.
Reaction:
Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2 + 2FeCl3 + 8NH4OH → Fe3O4 + 4H2O +2(NH4)2SO4 + 6NH4Cl
Theoretical mass = 4.64 g; Mass obtained = 4.55 g Yield = 98.1%.
3.1.2. Synthesis of Magnetite-Chitosan Spheres
Spheres containing various amounts of magnetite were prepared in the 0.1 and 1% W/W range. For this, 4.0 g of chitosan dissolved in 100.0 mL of acetic acid (4.0% W/V at 50°C). The solution was mixed with the desired amounts of magnetite, stirred and homogenized in a sonicator for one hour. The different mixtures were slowly dripped onto a 2.5 M sodium hydroxide solution with gentle stirring, observing the gelling of the drops as they fell. The obtained spheres were incubated for 24 h in the 2.5 M sodium hydroxide solution, washed with enough distilled water to neutral pH, and kept in a refrigerator (4°C).
3.2. Sorbent characterization
3.2.1. FT-IR and XRD spectroscopy
The FT-IR was used to identify the functional chemical groups in the immobilized magnetite-chitosan polymer involved in As(V) sorption. The chitosan-magnetite samples were put in contact with a solution of As(V) 120.0 mg L-1 for 4 h, washed and dried under vacuum for 48 h. A sample of dry spheres without As treatment and chitosan spheres without added magnetite were also used. The samples were prepared according to the KBr 1.5% P/P dilution technique, and spectral scanning was performed in the 400 to 4000 cm-1 range.
The XRD analyses were performed using a Cu Kα (1.5418 A˚) source (30 kV, 10 mA) from Bruker D2 Phaser 2nd Generation Diffractometer (Karlsruhe, Germany), with a graphite secondary monochromator and a scintillation counter detector. The powdered sample was placed on a flat plastic plate rotated at 30 rpm. The scans were performed at 25°C. Time/Step: 1.00 s, Increment: 0.04°; 2 Theta range: 5-100°.
3.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscope
For the observation and morphological characterization of the sorbent, chitosan, chitosan-magnetite and chitosan-magnetite-As(V), images were taken. For this, an FEI Quanta 200F scanning electron microscope with EDS (Energy Dispersive Spectrometer), ETD (Everhart-Thornley Detector) and BSED (Electron Back Scatter Diffraction) detectors were used, which allowed a semi-quantitative elemental analysis to be carried out, achieving textural details and high-resolution topological data, as well as the location of the leading chemical elements of interest. A 15 kV voltage was used with different magnification levels: 240, 800, 3000 and 6000 x.
3.2.3. Determination of the pHpzc
To determine the pH
pzc value, 0.28 g of spheres were placed in 10.0 mL in 0.10 M NaNO
3 solutions adjusted to different pHs, in the range of 1.80 to 8.34. The system was kept under stirring for 24 h, and subsequently, the pH of the solution was measured again. The difference in pH (∆pH) was calculated by subtracting the initial value from the end[
30].
3.3. As(V) detection and quantification
As(V) was quantitatively determined using a variant of the classical molybdenum blue method developed in the working group[
31]. Different As concentrations were prepared by appropriate dilution from a stock solution of 0.66 mM, using 3.50 mL of 1.0 M HCl and enough distilled water to bring the final volume to 25.00 mL. Finally, the following reagents were added: 0.50 mL of tetrahydrate ammonium heptamolybdate ((NH
4)
6Mo
7O
24.4H
2O, 3.0% P/V); 1.25 mL of sulfuric acid (H
2SO
4, 14.0% P/V); 0.25 mL of potassium antimony tartrate (C
8H
4K
2O
12Sb
2.3H
2O, 0.25% P/V); 0.50 mL of ascorbic acid (C
6H
6O
6, 11% P/V). Reagents were added in the order indicated. Except for the sulfuric acid solution, the above reagents are unstable over time, so they must be prepared on the same day. The final volume of the reaction mixture was 27.50 mL, and the final As(V) concentrations ranged from 6.2 x 10
-8 M to 4.4 x 10
-6 M. Significant redox occurs after adding ascorbic acid, which reduces the molybdate to "molybdenum blue." The resulting mixture was allowed to react for 40 minutes, and then absorption spectra measurements were performed in the of 550 - 950 nm range. A glass cuvette with an optical path length of 10.0 cm was used for each measurement to increase the method's sensitivity. The absorbance value of a blank solution was subtracted from each absorbance value for the concentrations under study. The absorbance values at 890 nm were considered for constructing the calibration curves.
3.4. Effect of the amount of magnetite on the sorption of As(V)
The batch was carried out at a fixed pH using spheres with different amounts of magnetite: 0, 0.1, 0.5, and 1% W/V of magnetite, in a final volume of 25.0 mL. The total sorbent mass, the As concentration, and the pH were 0.43 g, 2.0 mg L-1, and 6.3, respectively.
3.5. Sorption process optimization
A CCD optimized the As sorption. The CCD was raised with two factors, sorbent dose and pH, studied at five levels each. The total number of experiments, 11, was obtained from the design's composition arrangement. For the optimization of the As(V) sorption process in batch, the As(V) removal percentage, defined by
eq. 6, was considered as a response.
C0 is the initial, and Cf is the final concentration of As(V), expressed in mg L-1.
To correlate the experimental data and identify the most relevant terms of the model, the second-order polynomial equation was used, taking into account the choice of two factors.
Where y is the response, x1 and x2 are the factors, β0 the constant coefficient, β1 and β11 the linear and quadratic coefficient, respectively, for one of the factors. β2 and β22 are the linear and quadratic coefficients of the second factor. β12 is the linear coefficient of the interaction between the factors, and ϵ is the model error.
The study of the adjustment of the experimental data to the mathematical model was carried out through the ANOVA. Variance measures the variability, or spread, of a probability distribution. In order to carry out the optimization, we worked experimentally in a batch, with a volume of 25.0 mL, [As(V)] of 2 mg L-1, temperature 20°C, with gentle mechanical agitation for 4 h. The values of pH and sorbent ranges dose were taken as proposed by the design. The ranges of the factors studied (calculated by the CCD) were: (2.60 – 8.20) for pH and (0.02 – 0.58) g for sorbent mass. The experimental conditions were kept constant in all the experiments: Volume 25.0 mL; T 20°C, [As(V)] 2 mg L-1 and mechanical gentle stirring (for 4 h).
3.6. Sorption Kinetic Studies
The kinetic studies were carried out in batches at a controlled temperature of 23°C, 30°C and 40°C. A sorbent mass of 0.86 g was used in a final volume of 50.0 mL of solution. Work was carried out at pH 6.3 with an As(V) concentration of 5.0 mg L
-1. Sorption kinetics were analyzed with the pseudo-first order or Lagergren model[
32] and the pseudo-second order or Ho and McKay model[
33].
The pseudo-first order model is commonly used to describe solutes sorption from a solution by a solid sorbent. It can be expressed correctly in nonlinear form by
eq. 7:
and the pseudo-second order equation is defined by
eq. 8:
where q
e (mg g
−1) and q
t (mg g
−1) are the sorption capacity at equilibrium and at any time t, respectively. k
1 and k
2 are the pseudo-first order (min
−1) and the pseudo second order rate constants (g mg
−1 min
−1), respectively. The kinetic data were adjusted using the Sigma Plot 12.0 software. As removal at different contact times (q
t) was calculated using
eq. 9:
Where C0 and Cf are the initial and final As(V) concentrations, respectively, expressed in mg L-1, and V is the volume of the solution in L. The sorbent mass was expressed in g.
3.7. Determination of Activation Energy
The E
a is related to the kinetic constants[
34] as observed in
eq. 10:
Where k is the rate constant of the reaction, A
0 is a temperature-independent factor associated with the frequency of molecular collisions or frequency factor (g mg
-1 min
-1), E
a is the activation energy required for sorption to occur (kJ mol
-1), R the gas constant (8,314.10
–3 kJ mol
-1 K
-1) and T the absolute temperature (K). The linear form of eq. 11 is the most used.
The value of the activation energy was determined graphically from the slope of the curve ln k as a function of 1/T[
34].
3.8. Sorption Isotherms
To thermodynamically describe the process, As(V) sorption isotherms were performed at three temperatures: 23°C, 30°C and 40°C. The experiments were carried out at pH 6.3 and a sorbent mass of 0.86 g, under constant agitation for 4 h, with arsenic concentrations in the range of 5.0 to 125.0 mg L
-1 and a volume of 50 mL. Metal removal at different contact times (qt) was calculated using eq. 9. The data obtained were fitted to the Langmuir [
35], Freundlich [
36] and Dubinin-Radushkevich[
37] sorption isotherm models using the Sigma Plot 12.0 software. From the data obtained, the thermodynamic parameters of the process were calculated.
Modified Langmuir Model
Recently published works accounted for the abuse and misuse of the Langmuir Model, not only to describe the thermodynamics of the adsorption process in aqueous solutions but also on the deduction of the chemical equilibrium constant of the system from the constant of this model[
38] which must be dimensionless.
Eq. 12 shows the modified Langmuir equation:
It is clearly observed that regardless of the unit that the adsorbate concentration has, the constant of this model, KLM, is dimensionless and is proposed to use it directly without any additional transformation for calculating the thermodynamic variables.
Freundlich Model
The Freundlich equation is one of the first empirical equations used to describe sorption phenomena on heterogeneous surfaces. The model equation is as follows:
eq. 13:
Where q
e (mg g
-1) is the amount of sorbate removed at equilibrium, C
e (mg L
-1) is the equilibrium sorbate concentration, K
F (mg g
-1)/(mg L
-1) is the constant of Freundlich, used as an indicator of sorption capacity, and n (dimensionless) is the Freundlich intensity parameter, indicating the magnitude of the driving force of sorption or surface heterogeneity. When n takes values between 1 and 10, the process is said to be favourable[
39]. The Freundlich equation is consistent with the thermodynamics of a heterogeneous sorption[
40]. The units of K
F depend on the units used for the concentration of the liquid phase (C) and the solid phase (q). The most frequently used units for sorption in aqueous solutions are mg L
-1, mmol L
-1 (concentrations) or mg g
-1, mmol g
-1 (q).
Dubinin-Radushkevich model
The Dubinin-Radushkevich equation is expressed as follows,
eq. 14:
where
Where q
DR (mg g
-1) is the adsorption capacity, K
DR (mol
2 kJ
-2) is a constant related to the adsorption energy, ε is Polanyi Potential, R is the gas constant (8,314 J mol
-1), T is the temperature (K), and q
e is the equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg g
-1) for each value of equilibrium adsorbate concentration C
e (mg L
-1). It is further defined as shown in
eq. 16:
E corresponds to the mean energy of adsorption in units (J mol
-1). This isotherm model is often used since the E values can provide information about the adsorption, physical, chemical or ion exchange process. Several authors propose a modification in calculating the Polanyi coefficient contemplating the saturated sorbate concentration in the system (C
s) through
eq. 15 and 16[
41],[
42]
The value of
will depend on the units in which the concentration Ce is expressed. In addition, working with concentrations close to or far from the saturation of the sorbate under study is different. Because the fit of this model presents changes in its curvature as the sorbate concentrations approach saturation. Both considerations significantly affect the value of the KDR parameter related to the sorption mechanism, generating an incorrect interpretation[
43].
Eq. 17 is used in this work to calculate the Polanyi coefficient as it is considered more appropriate regarding the abovementioned considerations.
3.9. Desorption Studies
In order to determine if the sorbent can be reused, batch desorption studies were carried out using solutions of different desorbents: 1 M NaOH, 1 M Na2SO4 and 0.5 M NaCl. When using 1 M NaOH, we worked with different contact times, 4 and 20 h, to evaluate the desorption efficiency concerning time.
For the evaluation of the efficiency of the desorption process (%D),
eq.18 was applied.
Where mdes corresponds to the amount of contaminant desorbed (g), msorb is the amount of contaminant contained in the sorbent (g), calculated by the difference between the initial and remaining contaminant in the solution.
The test consisted of loading As(V) on the sorbent, for which a sorbent mass of 20 mg was used, pH 6.00, T 20°C, initial [As(V)] 50.2 mg L-1 and final volume 67.00 mL, gentle mechanical agitation for 7 h. After this stage, the spheres were separated from the supernatant and washed with distilled water. The second stage corresponds to desorption under the following experimental conditions: sorbent mass 20 mg (spheres washed from the previous stage), 20°C, final volume 50.00 mL, adequate volumes of each desorbent, and gentle mechanical agitation for 4 h. All assays were performed in duplicate.
4. Conclusions
In this work, the main conclusions are the following:
A chitosan magnetite hybrid sorbent has been synthesized for the remediation of As and characterized by DRX, FT-IR and SEM spectroscopies.
The XRD and FT-IR spectroscopy showed the characteristic bands of the components of the hybrid sorbent: magnetite and chitosan. The presence of As on the sorbent is observed in the FT-IR spectrum (521 cm-1) and in the broadening of the bands in XRD.
The hybrid sorbent has sufficient stability to be used in batches and an adequate retention capacity comparable with similar materials: 12.2-15.7 mg of As per gram of sorbent at 23-40°C and pH 6.00. The pH and mass of magnetite were optimized through experimental designs.
The qmax value (12.2-15.7 mg g−1) obtained using equilibrium studies, suggests that the sorption process is favourable, in agreement with the thermodynamics parameters.
The sorption energy (9.8-8.8) kJ mol-1 and Ea (28.3-31.4) kJ mol-1, both indicate that the sorption mechanism is chemical ion exchange.
qmax increases with increasing temperature according to the endothermic nature of the sorption process.
From an environmental point of view, we highlight the use of environmentally friendly sorbents for As(V) sorption and an inexpensive and simple spectrophotometric method, with an appropriate sensitivity, limit detection and quantification.
This work can be described as a starting point for removing arsenic, combining the elimination process of the contaminant with a simple analytical methodology for As determination, that can be applied to assist the country's most deprived areas is the primary purpose of this research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Juan C. González; methodology; validation, María Inés Frascaroli, María F. Mangiameli, and Juan C. González; formal analysis, Juan C. González; investigation, María F. Mangiameli, María Inés Frascaroli, Marianela Batistelli, Julián Bultri, Mayra Trespalacios, Lina Gribaudo; resources, María F. Mangiameli and Sebastián Bellú; data curation, Marianela Batistelli; writing—original draft preparation, Juan C. González; writing—review and editing, María F. Mangiameli; visualization, María F. Mangiameli, María Inés Frascaroli; supervision, Juan C. González; project administration, María F. Mangiameli; funding acquisition, Juan C. González and Sebastián Bellú.
Funding
“This research was funded by National Agency of Scientific and Technological Promotion (ANPCyT) PICT-2020-SERIEA-02610, Santa Fe Province Agency of Science, Technology and Innovation ASACTEI PEICA-2022-039 and National University of Rosario (UNR) 80020180300124UR”.
Data Availability Statement
No data supporting reported results were realized for this manuscript publication.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the contribution of Foundation for the Scientific and Technological Promotion of Rosario and its Region (Foundation RosCyTec), Rosario Chemistry Institute - National Research Council Scientific and Technical (IQUIR-CONICET) and National University of Rosario (UNR). Also, we thanks to Dr. Gustavo Terrestre, for his XDR data acquisition and interpretation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- “International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), 2004. Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans 84. World Health Organization, Lyon, France http:// monograp,” IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum., vol. 84, pp. 1–477, 2004.
- U. Epa and I. Risk Information System Division, “United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). 1998. Arsenic, Inorganic (CASRN 7440-38-2). Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Chemical, Assessment Summary, National Center for Environmental Assessment. h.”.
- M. Argos et al., “A prospective study of arsenic exposure from drinking water and incidence of skin lesions in Bangladesh,” Am. J. Epidemiol., vol. 174, no. 2, pp. 185–194, 2011. [CrossRef]
- G. Marshall et al., “Fifty-Year study of lung and bladder cancer mortality in Chile related to arsenic in drinking water,” J. Natl. Cancer Inst., vol. 99, no. 12, pp. 920–928, 2007. [CrossRef]
- P. Bhattacharya et al., “Distribution and mobility of arsenic in the Río Dulce alluvial aquifers in Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 358, no. 1–3, pp. 97–120, 2006. [CrossRef]
- B. Dubey, H. M. Solo-Gabriele, and T. G. Townsend, “Quantities of arsenic-treated wood in demolition debris generated by Hurricane Katrina,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 41, no. 5, pp. 1533–1536, 2007. [CrossRef]
- A. Navas-Acien et al., “Urine arsenic concentrations and species excretion patterns in American Indian communities over a 10-year period: The strong heart study,” Environ. Health Perspect., vol. 117, no. 9, pp. 1428–1433, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (ATSDR), “Toxicological Profile for Arsenic U.S. Department of Health and Humans Services, Public Health Humans Services, Centers for Diseases Control.,” no. August, 2007.
- M. I. Litter, “Actualización. La problemática del arsénico en la Argentina : el HACRE,” Rev. Soc. Argent. Endocrinol. Ginecol. Reprod.(SAEGRE), vol. XVII, no. 2, pp. 5–10, 2010.
- F. Cirelli, E. Holzapfel, I. De Callejo, M. Billib, A. P. Carrera, and A. F. Cirelli, “Tecnologías económicas para el abatimiento de arsénico en aguas View project,” no. January 2010, 2010.
- A. E. Bardach et al., “Epidemiology of chronic disease related to arsenic in Argentina: A systematic review,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 538, no. 2015, pp. 802–816, 2015. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, “Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality,” no. FOURTH EDITION, p. 564, 2011.
- R. Y. Ning, “Arsenic removal by reverse osmosis,” Desalination, vol. 143, no. 3, pp. 237–241, 2002. [CrossRef]
- L. Madhura, S. Kanchi, M. I. Sabela, S. Singh, K. Bisetty, and Inamuddin, “Membrane technology for water purification,” Environ. Chem. Lett., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 343–365, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Batistelli et al., “A continuous method for arsenic removal from groundwater using hybrid biopolymer-iron-nanoaggregates: improvement through factorial designs,” J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., vol. 96, no. 4, pp. 923–929, 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. Lugo-Lugo, C. Barrera-Díaz, F. Ureña-Núñez, B. Bilyeu, and I. Linares-Hernández, “Biosorption of Cr(III) and Fe(III) in single and binary systems onto pretreated orange peel,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 112, pp. 120–127, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Yasmeen, M. Kabiraz, B. Saha, M. Qadir, M. Gafur, and S. Masum, “Chromium (VI) Ions Removal from Tannery Effluent using Chitosan-Microcrystalline Cellulose Composite as Adsorbent,” Int. Res. J. Pure Appl. Chem., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 1–14, 2016. [CrossRef]
- U. Schwertmann and R. M. Cornell, Iron Oxides in the Laboratory (Second Edition). 2003.
- P. Castaldi, M. Silvetti, S. Enzo, and P. Melis, “Study of sorption processes and FT-IR analysis of arsenate sorbed onto red muds (a bauxite ore processing waste),” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 175, no. 1–3, pp. 172–178, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Raz, F. Moztarzadeh, A. A. Hamedani, M. Ashuri, and M. Tahriri, “Controlled Synthesis, Characterization and Magnetic Properties of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles without Surfactant under N 2 Gas at Room Temperature,” Key Eng. Mater., vol. 493–494, pp. 746–751, 2012. [CrossRef]
- “JCPDS file, PDF No. 65-310”.
- M. Agostini de Moraes, D. S. Cocenza, F. da Cruz Vasconcellos, L. F. Fraceto, and M. M. Beppu, “Chitosan and alginate biopolymer membranes for remediation of contaminated water with herbicides,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 131, pp. 222–227, 2013. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Kloster, O. Moscoso Londoño, K. R. Pirota, M. A. Mosiewicki, and N. E. Marcovich, “Design of super-paramagnetic bilayer films based on chitosan and sodium alginate,” Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl., vol. 2, no. January, p. 100083, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Singh, M. Srivastava, J. Dutta, and P. K. Dutta, “Preparation and properties of hybrid monodispersed magnetic α-Fe2O3 based chitosan nanocomposite film for industrial and biomedical applications,” Int. J. Biol. Macromol., vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 170–176, 2011. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Kloster, D. Muraca, O. Moscoso Londoño, M. Knobel, N. E. Marcovich, and M. A. Mosiewicki, “Structural analysis of magnetic nanocomposites based on chitosan,” Polym. Test., vol. 72, pp. 202–213, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. A. Currie, “Detection and quantification limits: origins and historical overview,” Anal. Chim. Acta, vol. 391, no. 2, pp. 127–134, 1999. [CrossRef]
- L. Feng, M. Cao, X. Ma, Y. Zhu, and C. Hu, “Superparamagnetic high-surface-area Fe 3O 4 nanoparticles as adsorbents for arsenic removal,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 217–218, pp. 439–446, 2012. [CrossRef]
- D. W. Cho et al., “A novel chitosan/clay/magnetite composite for adsorption of Cu(II) and As(V),” Chem. Eng. J., vol. 200–202, pp. 654–662, 2012. [CrossRef]
- V. J. Inglezakis and A. A. Zorpas, “Heat of adsorption, adsorption energy and activation energy in adsorption and ion exchange systems,” Desalin. Water Treat., vol. 39, no. 1–3, pp. 149–157, 2012. [CrossRef]
- F. A. Bertoni, A. C. Medeot, J. C. González, L. F. Sala, and S. E. Bellú, “Application of green seaweed biomass for MoVI sorption from contaminated waters. Kinetic, thermodynamic and continuous sorption studies,” J. Colloid Interface Sci., vol. 446, pp. 122–132, 2015. [CrossRef]
- B. E. Pérez Mora, S. E. Bellú, M. F. Mangiameli, S. I. García, and J. C. González, “Optimization of continuous arsenic biosorption present in natural contaminated groundwater,” J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 547–555, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Zur Lagergren, “Theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar, 24, 1-39,” Handlingar, vol. 24, pp. 1–39, 1898.
- G. M. Y.S. Ho, “Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes,” Process Biochem., vol. 34, pp. 451–465, 1999. [CrossRef]
- G. W. Castellan, Fisicoquímica. 1998.
- I. Langmuir, “The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum.,” J. Am. Chem. Soc., vol. 40, no. 9, pp. 1361–1403, 1918. [CrossRef]
- Freundlich HMF. Uber die, “adsorption in losungen.,” Z. Phys. Chem., vol. 57, pp. 385–470, 1906. [CrossRef]
- R. L. Dubinin MM, “Equation of the Characteristic Curve of Activated Charcoal.,” Proc. Acad. Sci. U.S.S.R. Phys. Chem. Sect., vol. 55, pp. 331–333, 1947.
- S. Azizian, S. Eris, and L. D. Wilson, “Re-evaluation of the century-old Langmuir isotherm for modeling adsorption phenomena in solution,” Chem. Phys., vol. 513, no. May, pp. 99–104, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. N. Tran, S. J. You, A. Hosseini-Bandegharaei, and H. P. Chao, “Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review,” Water Res., vol. 120, pp. 88–116, 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Crittenden, R. R. Trussell, D. W. Hand, K. J. Howe, and G. Tchobanoglous, “Introduction to Adsorption Phenomena,” Adsorpt. MWH’s Water Treat. Princ. Des., 2012.
- M. Abe, K. Kawashima, K. Kozawa, H. Sakai, and K. Kaneko, “Amination of activated carbon and adsorption characteristics of its aminated surface,” Langmuir, vol. 16, no. 11, pp. 5059–5063, 2000. [CrossRef]
- K. Yang, L. Zhu, and B. Xing, “Adsorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by carbon nanomaterials,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 40, no. 6, pp. 1855–1861, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Q. Hu and Z. Zhang, “Application of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: A theoretical analysis,” J. Mol. Liq., vol. 277, pp. 646–648, 2019. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).